Assessment of Land Resource Utilization Efficiency, Spatiotemporal Pattern, and Network Characteristics in Resource-Based Regions: A Case Study of Shanxi Province
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Data
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Sources
3. Methodology
3.1. Super-Efficiency SBM Model
3.2. Global Moran’s I
3.3. Synergistic Effect Model
3.4. Spatial Network Analysis
4. Results
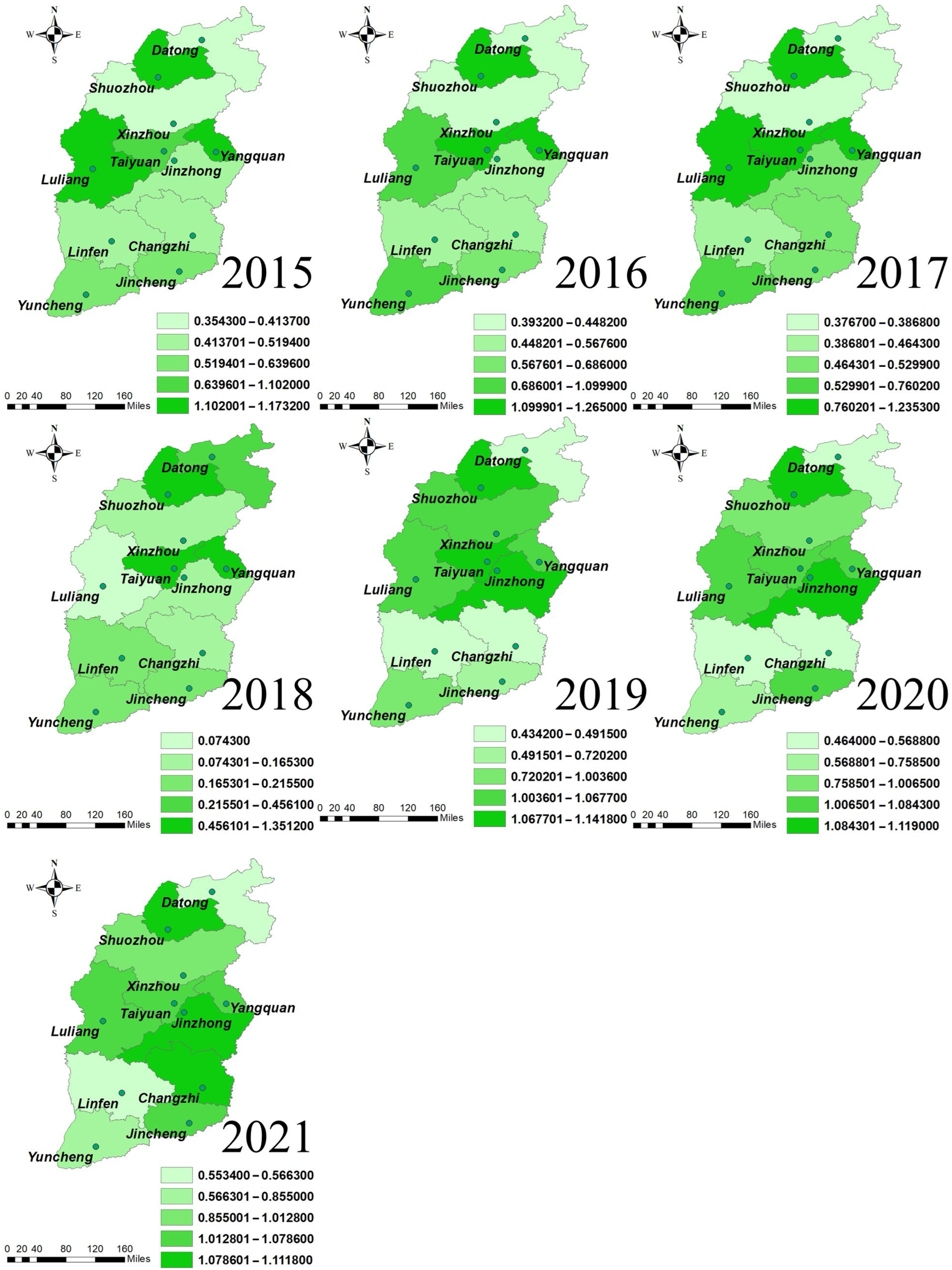
4.1. Temporal and Spatial Differentiation of Land Resource Utilization Efficiency
4.2. Agglomeration Development and the Synergistic Effect of Land Resource Utilization Efficiency
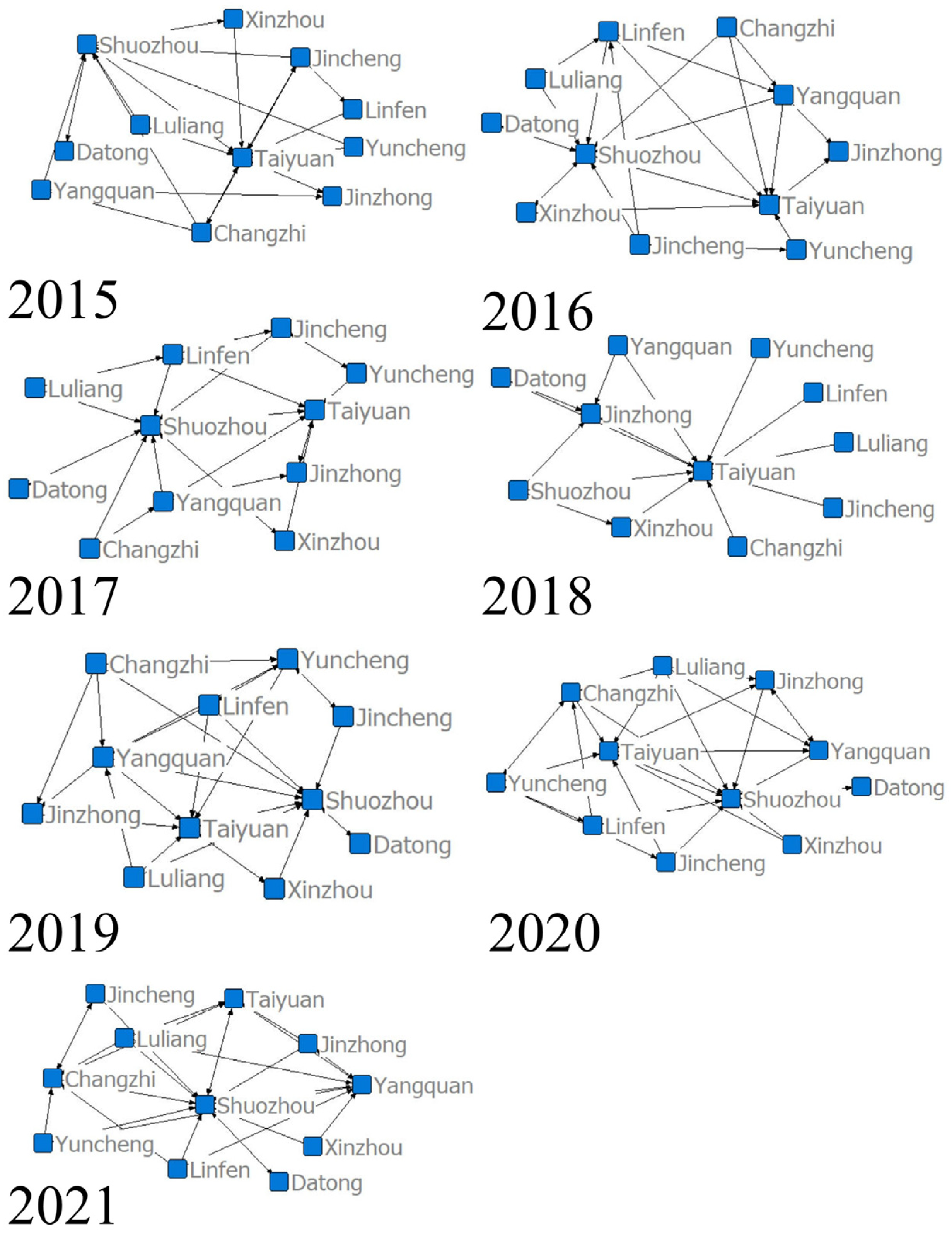
4.3. Network Characteristics of Land Resource Utilization Efficiency
5. Discussion
5.1. Research Findings and Comparative Analysis
5.2. Strategies for Enhancement
5.2.1. Centralized Provincial Land Governance
5.2.2. Coordinated Land Resource Utilization
5.2.3. Strengthen Environmental Regulations
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, J.; Li, W.; Li, B.; Duan, L.; Zhang, T.; Jia, Q. Construction Land Expansion of Resource-Based Cities in China: Spatiotemporal Characteristics and Driving Factors. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 16109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinga, G.D.; Mama, N.; Achuo, E.D. Resource abundance: Blessing or curse? Comparative analyses of point and diffuse resources. Heliyon 2024, 10, e25078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, P.; Du, P.; Ruan, Z. Spatio-temporal pattern evolution of green development efficiency in Northeastern China and its driving factors. Heliyon 2024, 10, e32119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Zhu, M.; Wang, Z.; Hong, J.; Wang, Y. Synergy level of urban resilience and urban land use efficiency in the Yellow River Basin: Spatial-temporal evolution characteristics and driving factors. Heliyon 2024, 10, e31456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Tian, Y. Research on the spatio-temporal coupling relationship between agricultural green development efficiency and food security system in China. Heliyon 2024, 10, e31893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Gong, X.; Ding, J.; Ma, L. Environmental regulation influences urban land green use efficiency: Incentive or disincentive effect? Evidence from China. Heliyon 2024, 10, e30122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, M.; Hu, F. Land urbanization and urban CO2 emissions: Empirical evidence from Chinese prefecture-level cities. Heliyon 2023, 9, e19834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Li, Z. Can the digitalization level of agriculture improve its ecological efficiency under carbon constraints: Evidence from China. Heliyon 2024, 10, e26750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yu, Z. The Multiple Heterogeneity of Low Carbon Technology Progress Driving Carbon Reduction in Resource Based Cities. China Popul. Resour. Environ. 2022, 32, 156–170. [Google Scholar]
- Cen, Z.; Wang, Z. Interprovincial Differences in the Driving Factors of Carbon Reduction Pressure for Local Governments in China: Based on the STIRPAT Model. Resour. Sci. 2012, 34, 718–724. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Du, X.; Lin, C. A Study on the Multiple Heterogeneity of Environmental Regulation Intensity in Resource Based Cities in China. Ecol. Econ. 2022, 38, 88–93+111. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, W.; Zhao, L.; Wang, N.; Zhang, L.; Li, H. A Study on the Driving Factors of Pollution Reduction and Carbon Reduction in the Yangtze River Delta Urban Agglomeration. J. Ecol. Rural. Environ. 2022, 38, 1273–1281. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Wang, J. The spatiotemporal evolution of carbon emission efficiency in resource-based cities in China and the impact of green technology innovation. Geogr. Res. 2023, 42, 878–894. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, H.; Ye, A. The spatial correlation network structure and influencing factors of carbon emissions in urban agglomerations. Chin. Environ. Sci. 2022, 42, 2413–2422. [Google Scholar]
- Psycharis, Y.; Kallioras, D.; Pantazis, P. Economic crisis and regional resilience: Detecting the ‘geographical footprint’of economic crisis in Greece. Reg. Sci. Policy Pract. 2014, 6, 121–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobbinah, P.B.; Erdiaw-Kwasie, M.O.; Amoateng, P. Africa’s urbanisation: Implications for sustainable development. Cities 2015, 47, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobbinah, P.B.; Finn, B.M. Planning and climate change in African cities: Informal urbanization and ‘Just’Urban transformations. J. Plan. Lit. 2023, 38, 361–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florida, R.; Mellander, C.; Stolarick, K. Inside the black box of regional development—Human capital, the creative class and tolerance. J. Econ. Geogr. 2008, 8, 615–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Cao, B.; Hua, Y.; Ding, L. Efficiency measurement of green regional development and its influencing factors: An improved data envelopment analysis framework. Sustainability 2020, 12, 4361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, W.; Wu, D.; Huang, L.; Liu, L. Spatial and temporal variations and significance identification of ecosystem services in the Sanjiangyuan National Park, China. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 6151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; He, X.; Liu, Z.; Sun, W.; Dong, H.; Chu, Y. Analysis of regional economic development based on land use and land cover change information derived from Landsat imagery. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 12721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoekveld, J.J. Understanding Spatial Differentiation in Urban Decline Levels. Eur. Plan. Stud. 2014, 22, 362–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Döringer, S.; Uchiyama, Y.; Penker, M.; Kohsaka, R. A meta-analysis of shrinking cities in Europe and Japan. Towards an integrative research agenda. Eur. Plan. Stud. 2020, 28, 1693–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobbinah, P.B.; Asibey, M.O.; Gyedu-Pensang, Y.A. Urban land use planning in Ghana: Navigating complex coalescence of land ownership and administration. Land Use Policy 2020, 99, 105054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobbinah, P.B.; Aboagye, H.N. A Ghanaian twist to urban sprawl. Land Use Policy 2017, 61, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Long, R.; Chen, H. Economic transition policies in Chinese resource-based cities: An overview of government efforts. Energy Policy 2013, 55, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Chang, J.; Li, Z.; Ming, L.; Li, C.; Li, C. Coupling Coordination and Spatiotemporal Analysis of Urban Compactness and Land-Use Efficiency in Resource-Based Areas: A Case Study of Shanxi Province, China. Land 2023, 12, 1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouratidis, K. Compact city, urban sprawl, and subjective well-being. Cities 2019, 92, 261–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Z.; Jiang, C.; Shan-shan, F. Effects of urban growth boundaries on urban spatial structural and ecological functional optimization in the Jining Metropolitan Area, China. Land Use Policy 2022, 117, 106113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Song, Y.; Zhang, M.; Duan, Y. Land use efficiency and energy transition in Chinese cities: A cluster-frontier super-efficiency SBM-based analytical approach. Energy 2024, 304, 132049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Bai, Y.; Che, L.; Qiao, F.; Xie, L. Incorporating ecological constraints into urban growth boundaries: A case study of ecologically fragile areas in the Upper Yellow River. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 124, 107436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerqueira, P.A.; Martins, R. Measuring the determinants of business cycle synchronization using a panel approach. Econ. Lett. 2009, 102, 106–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, K.; Li, Z. Coupling coordination and spatial network characteristics of carbon emission efficiency and urban green innovation in the Yellow River Basin, China. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 27690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nel, E.; Marais, L.; Mqotyana, Z. The regional implications of just transition in the world’s most coal-dependent economy: The case of Mpumalanga, South Africa. Front. Sustain. Cities 2023, 4, 1059312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Chen, Z.; Xu, G.; Tian, Z. Built-up land efficiency in urban China: Insights from the General Land Use Plan (2006–2020). Habitat Int. 2016, 51, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Zhang, A.; Sun, Z. How regional economic integration influence on urban land use efficiency? A case study of Wuhan metropolitan area, China. Land Use Policy 2020, 90, 104329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.Y.; Lee, J.; Zhou, T.; Wu, D. Shrinking cities and resource-based economy: The economic restructuring in China’s mining cities. Cities 2017, 60, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Huang, C. How does urbanization affect carbon emission efficiency? Evidence from China. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 272, 122828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Han, L.; Liu, M.; Li, L. Spatial differentiation of carbon emissions from energy consumption based on machine learning algorithm: A case study during 2015–2020 in Shaanxi, China. J. Environ. Sci. 2024, 149, 358–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Yang, Y. Spatial-temporal differentiation characteristics and driving factors of China’s energy eco-efficiency based on geographical detector model. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 434, 140153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, X.J.; Liu, X. Urban Land Use Efficiency under Resource-Based Economic Transformation—A Case Study of Shanxi Province. Land 2021, 10, 850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Hu, J.; Kang, J.; Shu, W. Spatio-temporal variation and prediction of land use and carbon storage based on PLUS-InVEST model in Shanxi Province, China. Landsc. Ecol. Eng. 2025, 21, 107–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, L.; Wang, G.; Meng, Y. Multidimensional Measurement and Regulation of Regional Coordinated and Balanced Development Levels: Using the Yangtze River Delta Region in China as an Example. Sustainability 2024, 16, 927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X. The Dilemma of Economic Transformation behind Shanxi’s Coal Maximization. In Proceedings of the 2018 2nd International Conference on Education Science and Economic Management (ICESEM 2018), Xiamen, China, 25–26 August 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Srzentić, M. Strukturne promene u privredama SAD i EU prouzrokovane širenjem klastera. Међунарoднa Пoлитика 2021, 72, 65–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Zhang, Y. Impact of Manufacturing Agglomeration on the Green Innovation Efficiency—Spatial Effect Based on China’s Provincial Panel Data. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 4238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deweerdt, T.; Fabre, A. The role of land use planning in urban Transport to Mitigate climate Change: A literature review. Adv. Environ. Eng. Res. 2022, 3, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Lu, J. Spatial–temporal pattern and convergence characteristics of provincial urban land use efficiency under environmental constraints in China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 10729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheshire, L.; Everingham, J.-A.; Lawrence, G. Governing the impacts of mining and the impacts of mining governance: Challenges for rural and regional local governments in Australia. J. Rural. Stud. 2014, 36, 330–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Houtum, H.; Lagendijk, A. Contextualising regional identity and imagination in the construction of polycentric urban regions: The cases of the Ruhr area and the Basque country. Urban Stud. 2001, 38, 747–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T. Industry cluster’s innovation network structure and competitiveness in Zhejiang Province. In Proceedings of the 2008 4th IEEE International Conference on Management of Innovation and Technology, Bangkok, Thailand, 21–24 September 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Hao, Q.; Chen, X.; Zhu, C.; Zhang, L.; Hong, M.; Wu, J.; Gan, M. Exploring Spatial Network Structure of the Metropolitan Circle Based on Multi-Source Big Data: A Case Study of Hangzhou Metropolitan Circle. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Li, H.; Shang, D.; Ding, L. Evolution of the Industrial Innovation Ecosystem of Resource-Based Cities (RBCs): A Case Study of Shanxi Province, China. Sustainability 2021, 13, 11350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Dong, X.; Wang, X.; Zhao, B.; Wei, H.; Fan, W.; Zhang, C. The Trade-Offs/Synergies and Their Spatial-Temporal Characteristics between Ecosystem Services and Human Well-Being Linked to Land-Use Change in the Capital Region of China. Land 2022, 11, 749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.; Chen, N.; Yao, W.; Meng, M.; Wang, X. Integrating Environmental Impact and Ecosystem Services in the Process of Land Resource Capitalization—A Case Study of Land Transfer in Fuping, Hebei. Sustainability 2021, 13, 2837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Singh, R.K.; Cui, L.; Xu, Z.; Liu, H.; Fava, F.; Kumar, S.; Song, X.; Tang, L.; Wang, Y.; et al. Navigating the landscape of global sustainable livelihood research: Past insights and future trajectory. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 103291–103312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Indicator | Primary Indicator | Secondary Indicator | Data Sources |
|---|---|---|---|
| Input | Land resource input | Urban construction land area | China City Statistical Yearbook |
| Capital input | Total fixed asset investment | China City Statistical Yearbook and National Economic and Social Development Statistical Bulletin | |
| Human resource input | Urban employment population | China City Statistical Yearbook and National Economic and Social Development Statistical Bulletin | |
| Output | Expected output | Regional gross domestic product | China City Statistical Yearbook |
| Unexpected output | Industrial wastewater discharge | China City Statistical Yearbook and National Economic and Social Development Statistical Bulletin | |
| Industrial dust emission | China City Statistical Yearbook and National Economic and Social Development Statistical Bulletin |
| City | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | Mean |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Taiyuan | 1.1020 | 1.2650 | 1.2353 | 1.3512 | 1.1138 | 1.0617 | 1.0786 | 1.1725 |
| Datong | 0.3543 | 0.3932 | 0.3767 | 0.4561 | 0.4342 | 0.4640 | 0.5534 | 0.4331 |
| Yangquan | 1.1424 | 1.1568 | 1.1323 | 1.1074 | 1.0507 | 1.0752 | 1.0701 | 1.1050 |
| Changzhi | 0.5073 | 0.5199 | 0.5293 | 0.1616 | 0.4915 | 0.5688 | 1.0888 | 0.5525 |
| Jincheng | 0.5712 | 0.6860 | 0.5095 | 0.2155 | 0.7202 | 1.0545 | 1.0634 | 0.6886 |
| Shuozhou | 1.1732 | 1.1374 | 1.1466 | 1.1128 | 1.0975 | 1.1034 | 1.1116 | 1.1261 |
| Jinzhong | 0.5148 | 0.5369 | 0.5299 | 0.1653 | 1.1418 | 1.1190 | 1.1118 | 0.7314 |
| Yuncheng | 0.6396 | 1.0084 | 0.7602 | 0.2015 | 1.0036 | 0.7585 | 0.855 | 0.7467 |
| Xinzhou | 0.4137 | 0.4482 | 0.3868 | 0.1431 | 1.0445 | 1.0065 | 1.0128 | 0.6365 |
| Linfen | 0.5194 | 0.5676 | 0.4643 | 0.1899 | 0.4867 | 0.4938 | 0.5663 | 0.4697 |
| Luliang | 1.1533 | 1.0999 | 1.1104 | 0.0743 | 1.0677 | 1.0843 | 1.0531 | 0.9490 |
| Mean | 0.7356 | 0.8018 | 0.7438 | 0.4708 | 0.8775 | 0.8900 | 0.9604 |
| Year | Global Moran’s I | p-Value | z-Score |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2015 | −0.202 | 0.6218 | −0.4932 |
| 2016 | −0.2122 | 0.5897 | −0.5393 |
| 2017 | −0.1681 | −0.3291 | 0.7421 |
| 2018 | 0.0126 | 0.5721 | 0.5673 |
| 2019 | 0.0234 | 0.5442 | 0.6064 |
| 2020 | −0.1085 | 0.9666 | −0.0418 |
| 2021 | −0.1726 | 0.6945 | −0.3927 |
| City | Direction | Distance (km) | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | Mean | Rank |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Datong | Northeast | 281 | 0.6212 | 0.3808 | 0.9944 | −0.7979 | −3.1435 | 0.0040 | −0.0798 | 3 |
| Yangquan | East | 115 | 0.8181 | 0.9771 | −0.8230 | 0.7213 | 0.9508 | 0.9927 | 0.7393 | 1 |
| Changzhi | South | 225 | 0.8799 | 0.6596 | −4.4009 | 0.0071 | −1.7539 | 0.5214 | −0.7697 | 7 |
| Jincheng | South | 304 | 0.6878 | 0.7845 | −4.4263 | −1.1186 | −4.6507 | −1.4753 | −1.4853 | 8 |
| Shuozhou | North | 213 | 0.8964 | 0.9719 | −1.8011 | 0.9531 | 0.9493 | 0.9998 | 0.5569 | 2 |
| Jinzhong | South | 27 | 0.0706 | 0.2380 | −4.9083 | −3.0539 | −3.2730 | −0.9788 | −1.5068 | 10 |
| Yuncheng | Southwest | 39 | 0.7078 | 0.9963 | −4.1712 | −1.0068 | −0.2214 | 0.5391 | −0.3524 | 5 |
| Xinzhou | North | 81 | 0.2102 | −0.3394 | −4.6199 | −3.2709 | −3.3054 | −0.9690 | −1.4904 | 9 |
| Linfen | Southwest | 263 | 0.8100 | 0.9970 | −4.2023 | 0.0653 | −0.6643 | 0.3787 | −0.3495 | 4 |
| Luliang | West | 184 | 0.9603 | 0.7936 | −4.4352 | −0.0642 | −0.8164 | 0.1662 | −0.3949 | 6 |
| Mean | 0.1273 | 0.0526 | −3.4781 | 0.4351 | −0.2343 | 0.0179 | −0.5133 |
| Density | Hierarchy | Efficiency | Connectedness | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2015 | 0.2091 | 0.8810 | 0.8000 | 1.0000 |
| 2016 | 0.2273 | 0.7755 | 0.7778 | 1.0000 |
| 2017 | 0.2182 | 0.7234 | 0.8222 | 1.0000 |
| 2018 | 0.1364 | 0.9500 | 0.9111 | 1.0000 |
| 2019 | 0.2636 | 0.7451 | 0.7111 | 1.0000 |
| 2020 | 0.2909 | 0.6800 | 0.6889 | 1.0000 |
| 2021 | 0.2545 | 0.7660 | 0.7111 | 1.0000 |
| City | Degree | Betweenness | Closeness |
|---|---|---|---|
| Taiyuan | 50.000 | 66.667 | 2.296 |
| Datong | 10.000 | 52.632 | 0.000 |
| Yangquan | 70.000 | 76.923 | 12.222 |
| Changzhi | 60.000 | 71.429 | 8.148 |
| Jincheng | 20.000 | 55.556 | 0.000 |
| Shuozhou | 100.000 | 100.000 | 47.111 |
| Jinzhong | 30.000 | 58.824 | 0.000 |
| Yuncheng | 30.000 | 58.824 | 0.444 |
| Xinzhou | 20.000 | 55.556 | 0.000 |
| Linfen | 30.000 | 58.824 | 0.444 |
| Luliang | 40.000 | 62.500 | 0.444 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, R.; Li, M. Assessment of Land Resource Utilization Efficiency, Spatiotemporal Pattern, and Network Characteristics in Resource-Based Regions: A Case Study of Shanxi Province. Sustainability 2025, 17, 2458. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17062458
Ma R, Li M. Assessment of Land Resource Utilization Efficiency, Spatiotemporal Pattern, and Network Characteristics in Resource-Based Regions: A Case Study of Shanxi Province. Sustainability. 2025; 17(6):2458. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17062458
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Ran, and Muru Li. 2025. "Assessment of Land Resource Utilization Efficiency, Spatiotemporal Pattern, and Network Characteristics in Resource-Based Regions: A Case Study of Shanxi Province" Sustainability 17, no. 6: 2458. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17062458
APA StyleMa, R., & Li, M. (2025). Assessment of Land Resource Utilization Efficiency, Spatiotemporal Pattern, and Network Characteristics in Resource-Based Regions: A Case Study of Shanxi Province. Sustainability, 17(6), 2458. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17062458







