Increasing Selin Co Lake Area in the Tibet Plateau with Its Moisture Cycle
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
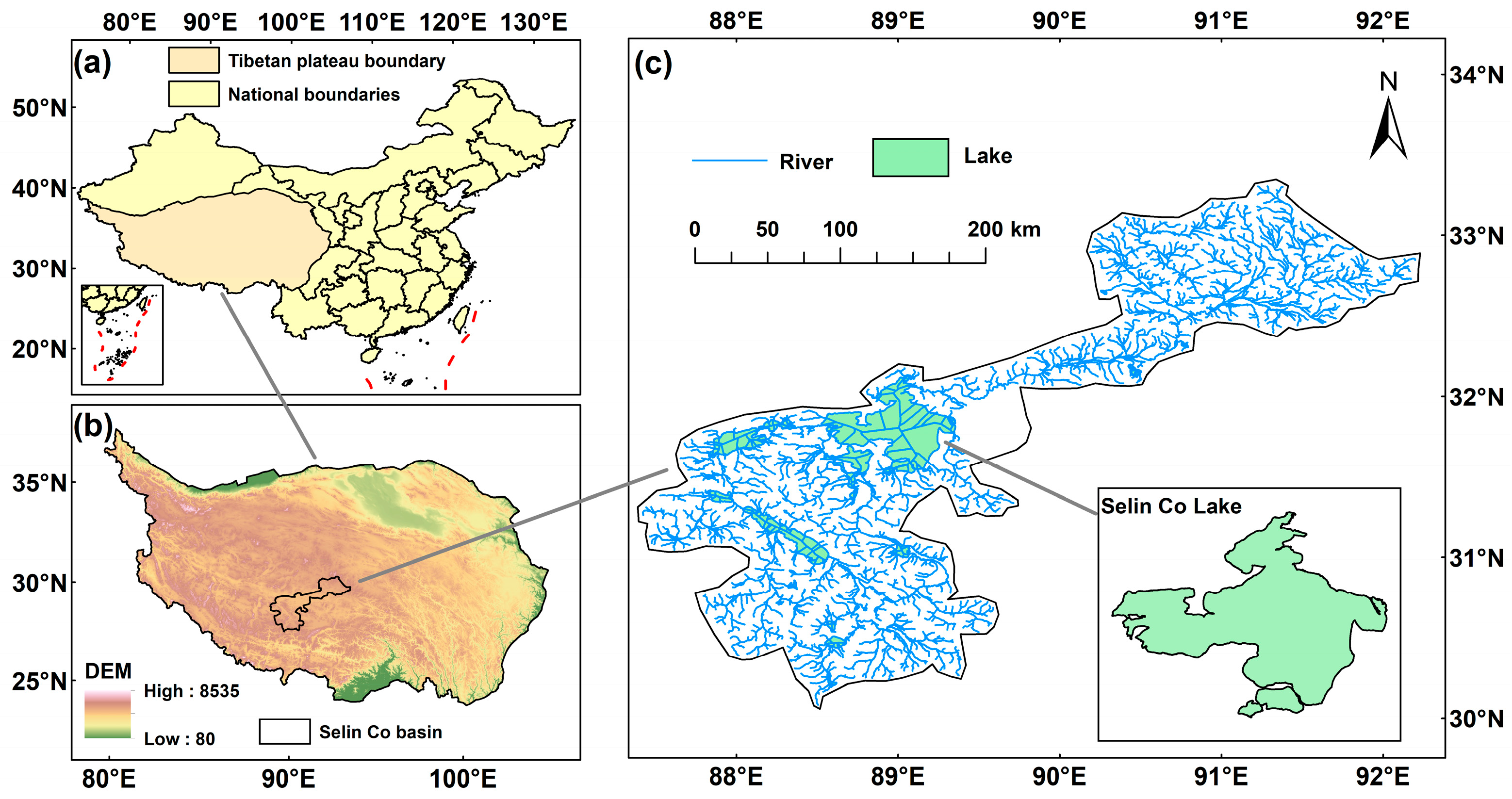
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data
2.2.1. Landsat
2.2.2. Climate Data
2.2.3. ERA5 Dataset
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. Lake Information Extraction
2.3.2. Glacier Information Extraction
2.3.3. Water Accounting Model-2layers Model
3. Results
3.1. Changes in Characteristics of Lake Area in Selin Co
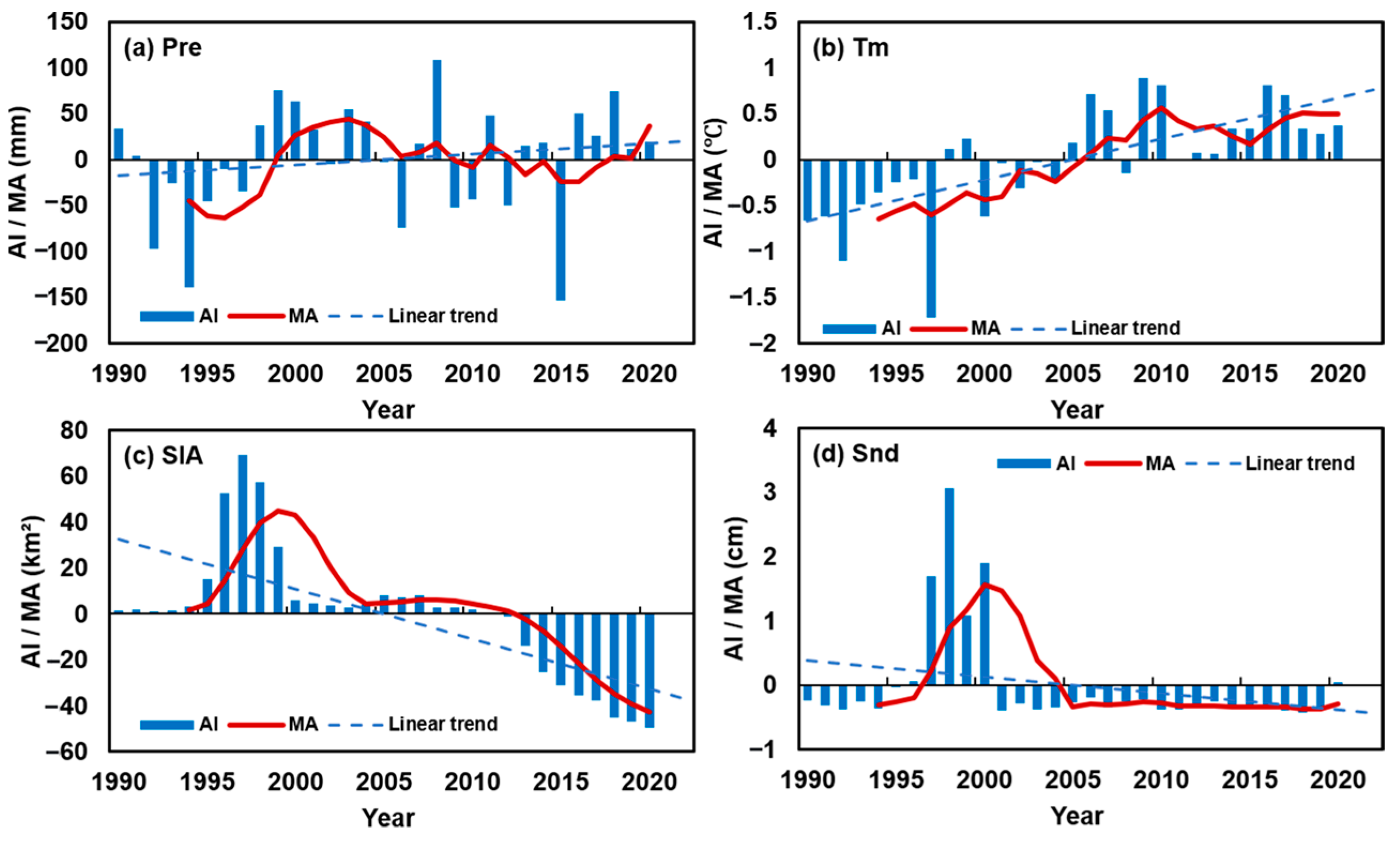
3.2. Climatic Driving Factors of Lake Area Changes in Selin Co
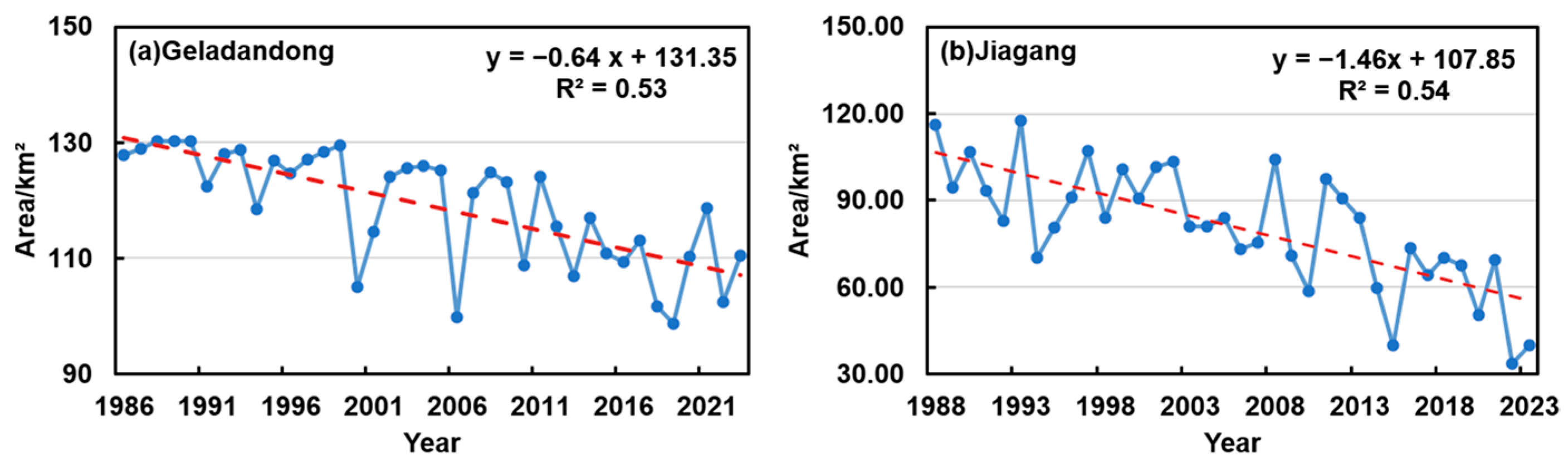
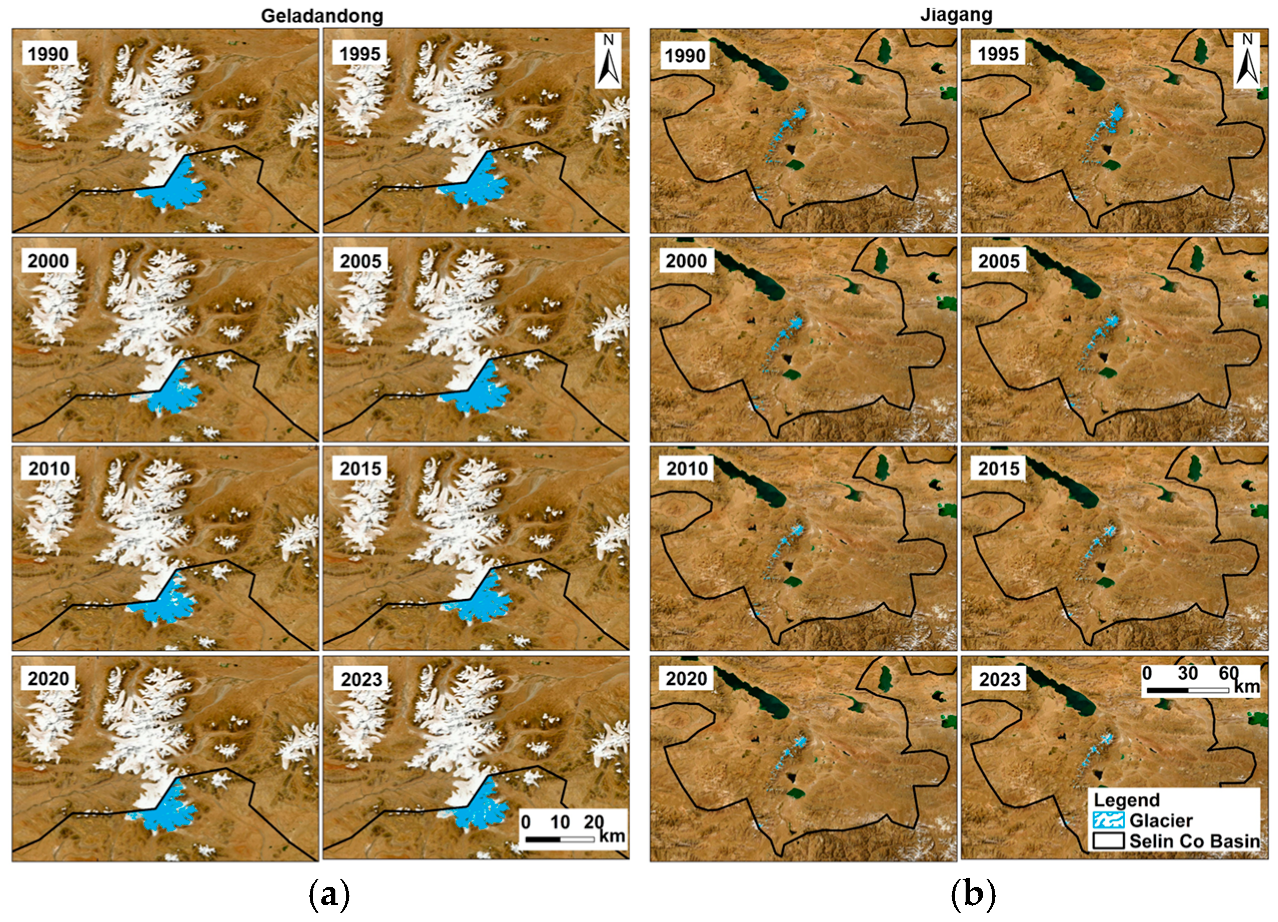
3.3. Changes in Characteristics of Selin Co Glacier Area
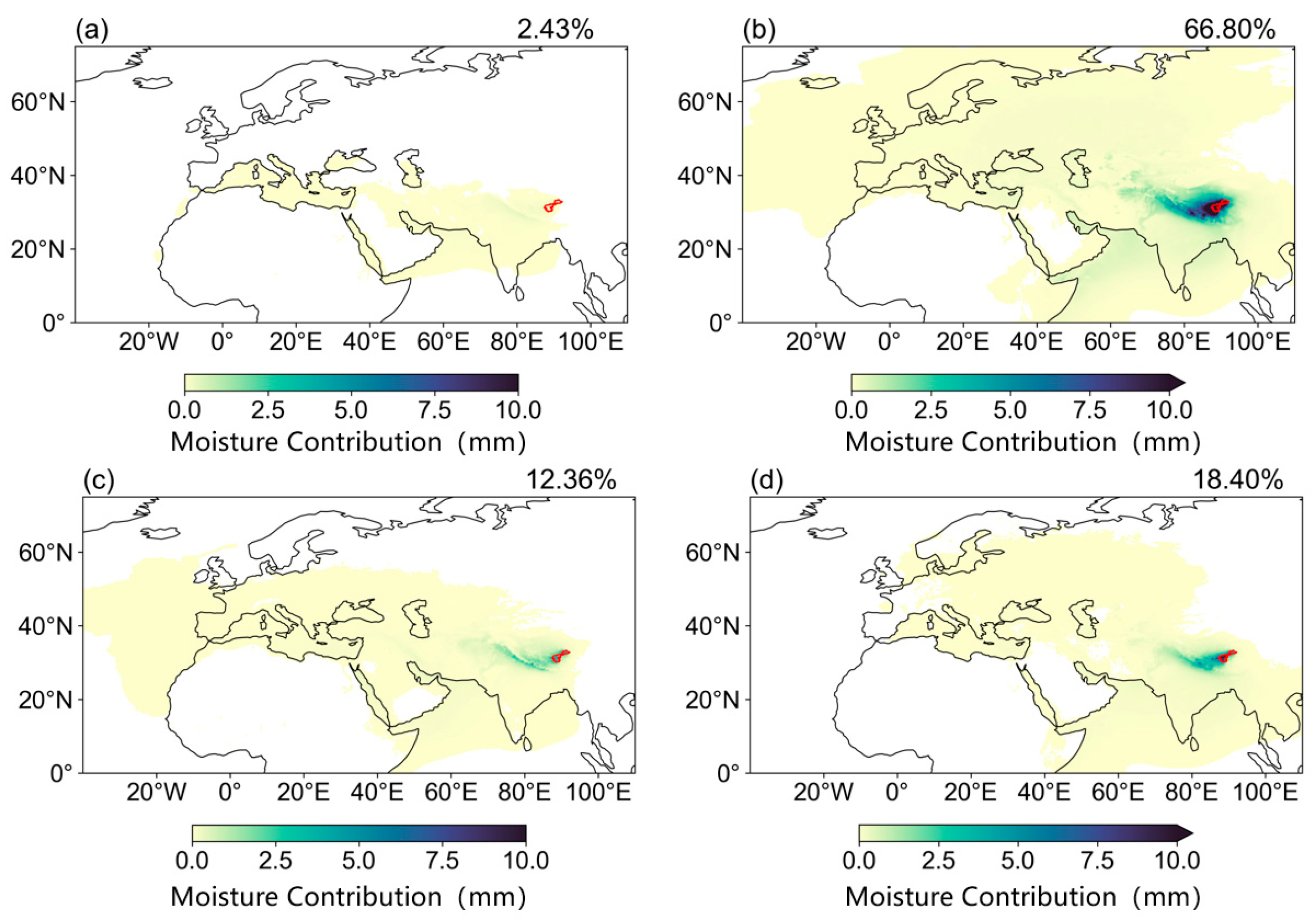
3.4. Water Vapor Transport in the Selin Co Basin
3.4.1. Water Vapor Source in Selin Co Basin
3.4.2. Seasonal Characteristics of Water Vapor Sources
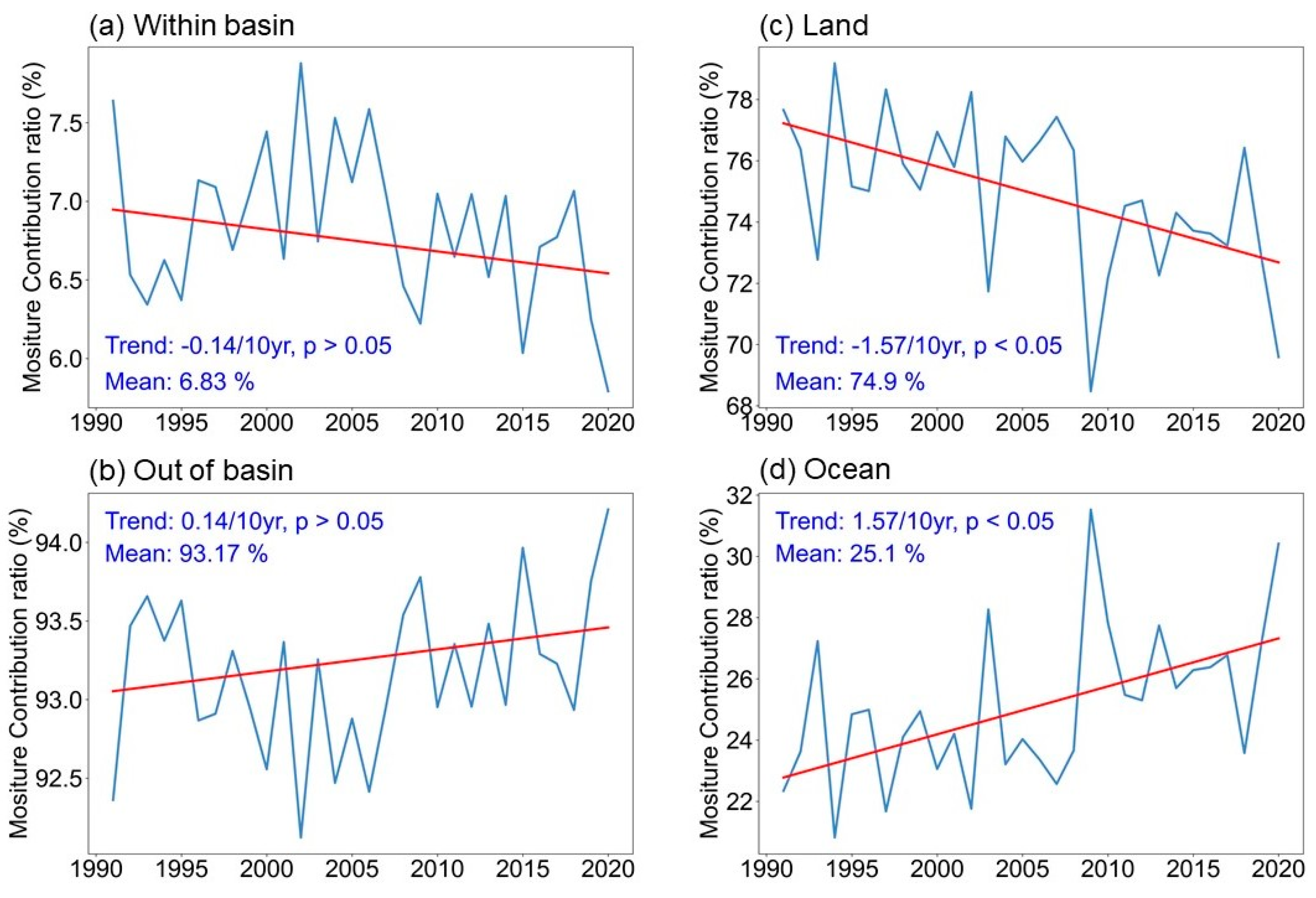
3.4.3. Time Series Changes in Water Vapor Contribution Rates from Different Source Regions
4. Discussion
4.1. Reasons for Lake Expansion
4.2. Reasons for Glacier Retreat
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- In the 36 years from 1988 to 2023, the area of Selin Co has generally continued to increase. The lake area was 1702.43 km2 in 1988, and it reached 2462.59 km2 in 2023, with a total area increase of 760.16 km2. The lake surface grew particularly rapidly from 2001 to 2010, mainly in the northern and southern parts of the lake. The increasing trend in the Selin Co area is affected by a variety of climatic factors, among which changes in temperature, glacier area, and precipitation are the main driving factors.
- (2)
- From 1986 to 2023, the area of glaciers around the Selin Co basin generally showed a decreasing trend. The area of the Geladandong Glacier in the watershed was 127.85 km2 in 1986. By 2023, the glacier area had dropped to 110.46 km2. The glacier area decreased by 17.39 km2, but the change was relatively stable. The area of the Jiagang Glacier in the basin was 116.23 km2 in 1988. By 2023, the glacier had dropped to 39.81 km2. The glacier area had decreased by 76.42 km2 in total, but the changes were relatively volatile. The main reason for the decrease in glacier area in the Selin Co basin may be the increase in temperature caused by climate change, and topographic factors may also have a certain impact on it.
- (3)
- Precipitation in the Selin Co basin showed an increasing trend. The precipitation and moisture in the Selin Co basin are mainly influenced by the westerlies and the Indian monsoon, which originate from the North Atlantic and the Indian Ocean. The closer to the basin itself, the more the water vapor contribution. The watershed outside contributes about 89.12% of the water vapor, with an internal water cycle rate of 10.88%. 30.61% of the water vapor comes from the ocean, while 69.39% comes from land. The water vapor contribution rate in the Selin Co basin during the summer is the largest throughout the year, and the ocean provides the largest proportion of precipitation water vapor. There is a significant trend of increasing water vapor contribution from the ocean in the Selin Co basin, making it more dependent on water vapor provided by the ocean. Rising oceanic water vapor contributions exacerbate climate change impacts, increasing the likelihood of crossing critical thresholds and triggering irreversible climatic shifts.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Immerzeel, W.W.; Lutz, A.F.; Andrade, M.; Bahl, A.; Biemans, H.; Bolch, T.; Hyde, S.; Brumby, S.; Davies, B.J.; Elmore, A.C.; et al. Importance and vulnerability of the world’s water towers. Nature 2020, 577, 364–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Zhang, Q.; Yu, H.; Shen, Z.; Sun, P. Double increase in precipitation extremes across China in a 1.5 °C/2.0 °C warmer climate. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 746, 140807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Zou, D.; Hu, G.; Du, E.; Pang, Q.; Xiao, Y.; Li, R.; Sheng, Y.; Wu, X.; Sun, Z.; et al. Changing climate and the permafrost environment on the Qinghai–Tibet (Xizang) plateau. Permafr. Periglac. Process. 2020, 31, 396–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Zhang, T.; Liu, Y. Permafrost temperatures and thickness on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2010, 72, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ye, A.; Peng, D.; Miao, C.; Di, Z.; Gong, W. Spatiotemporal variations in water conservation function of the Tibetan Plateau under climate change based on InVEST model. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2022, 41, 101064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Deng, G.; Liu, X.; He, Y.; Shen, Q.; Chen, Q. Heatwave magnitude quantization and impact factors analysis over the Tibetan Plateau. Npj Clim. Atmos. Sci. 2025, 8, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Immerzeel, W.W.; van Beek, L.P.H.; Bierkens, M.F.P. Climate Change Will Affect the Asian Water Towers. Science 2010, 328, 1382–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, T.; Bolch, T.; Chen, D.; Gao, J.; Immerzeel, W.; Piao, S.; Su, F.; Thompson, L.; Wada, Y.; Wang, L.; et al. The imbalance of the Asian water tower. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2022, 3, 618–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Zhai, J.; Liu, Y.; Han, S.; Liu, K. Research on the Impact of Climate Change and Human Activities on the NDVI of Arid Areas—A Case Study of the Shiyang River Basin. Land 2024, 13, 533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Liu, H.; Xie, C.; Zhao, J.; Liu, G.; Wang, W.; Zhang, Q.; Zhao, Q. Dynamic changes in lakes and potential drivers within the Selin Co basin, Tibetan Plateau. Environ. Earth Sci. 2022, 81, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.; Yang, G.; Duan, H.; Jiang, J.; Wang, S.; Feng, X.; Li, A.; Kong, F.; Xue, B.; Wu, J.; et al. China’s lakes at present: Number, area and spatial distribution. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2011, 54, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Yao, T.; Xie, H.; Zhang, K.; Zhu, F. Lakes’ state and abundance across the Tibetan Plateau. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2014, 59, 3010–3021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Xie, C.; Zhao, L.; Li, R.; Liu, G.; Wang, W.; Liu, H.; Wu, T.; Yang, G.; Zhang, Y. Rapid expansion of lakes in the endorheic basin on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau since 2000 and its potential drivers. Catena 2021, 197, 104942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Y.; Yang, K.; Wang, B.; Sheng, Y.; Bird, B.W.; Zhang, G.; Tian, L. Response of inland lake dynamics over the Tibetan Plateau to climate change. Clim. Chang. 2014, 125, 281–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Huang, B.; Ke, L. Modeling and analysis of lake water storage changes on the Tibetan Plateau using multi-mission satellite data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 135, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Y.; Yao, T.; Sheng, Y.; Yang, K.; Yang, W.; Li, S.; Zhou, J.; Jiang, Y.; Yu, Y. Unprecedented lake expansion in 2017–2018 on the Tibetan Plateau: Processes and environmental impacts. J. Hydrol. 2023, 619, 129333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Yao, T.; Chen, W.; Zheng, G.; Shum, C.K.; Yang, K.; Piao, S.; Sheng, Y.; Yi, S.; Li, J.; et al. Regional differences of lake evolution across China during 1960s–2015 and its natural and anthropogenic causes. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 221, 386–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Jiang, L.; Zhang, X.; Druce, D.; Kittel, C.M.; Tøttrup, C.; Bauer-Gottwein, P. Impacts of water resources management on land water storage in the North China Plain: Insights from multi-mission earth observations. J. Hydrol. 2021, 603, 126933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, Y.; Li, X.; Liu, W. Exploring the water storage changes in the largest lake (Selin Co) over the Tibetan Plateau during 2003–2012 from a basin-wide hydrological modeling. Water Resour. Res. 2015, 51, 8060–8086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Wang, J.; Ju, J.; Ma, N.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, C.; Han, B.; Liu, L.; Wang, M.; Ma, Q. Climatic and lake environmental changes in the Serling Co region of Tibet over a variety of timescales. Sci. Bull. 2019, 64, 422–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Li, W.; Deng, H.; Fang, G.; Li, Z. Changes in Central Asia’s Water Tower: Past, Present and Future. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 35458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Xu, Z.; Yang, H.; Vaghefi, S.A. Responses of the Glacier Mass Balance to Climate Change in the Tibetan Plateau During 1975–2013. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2021, 126, e2019JD032132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, W.; Feng, L.; Kuang, X.; Zheng, C.; Liu, J.; Chen, D.; Tian, Y.; Yao, Y. Divergent and Changing Importance of Glaciers and Snow as Natural Water Reservoirs in the Eastern and Southern Tibetan Plateau. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2022, 127, e2021JD035888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hugonnet, R.; McNabb, R.; Berthier, E.; Menounos, B.; Nuth, C.; Girod, L.; Farinotti, D.; Huss, M.; Dussaillant, I.; Brun, F.; et al. Accelerated global glacier mass loss in the early twenty-first century. Nature 2021, 592, 726–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Shen, Z.; Pokhrel, Y.; Farinotti, D.; Singh, V.P.; Xu, C.-Y.; Wu, W.; Wang, G. Oceanic climate changes threaten the sustainability of Asia’s water tower. Nature 2023, 615, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, D. Some Characteristics of the Summer Circulation Over the Qinghai-Xizang (Tibet) Plateau and Its Neighborhood. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1981, 62, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Dong, L.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Y. Effect of the Asian Water Tower over the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau and the characteristics of atmospheric water circulation. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2019, 64, 2830–2841. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, K.; Zhong, L.; Ma, Y.; Zou, M.; Huang, Z. A study on the water vapor transport trend and water vapor source of the Tibetan Plateau. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2020, 140, 1031–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Xu, X.-D.; Yang, S.; Zhang, W. On the origin and destination of atmospheric moisture and air mass over the Tibetan Plateau. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2012, 110, 423–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, K.; Su, F.; Xu, B. Quantifying the contribution of glacier meltwater in the expansion of the largest lake in Tibet. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2016, 121, 11,158–11,173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Xie, Y.; Duan, H.; Wang, X.; Bie, Q.; Guo, Z.; He, L.; Qin, W. Spatial quantification method of grassland utilization intensity on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau: A case study on the Selinco basin. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 302, 114073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Xie, Y.; Duan, S.-B.; Qin, W.; Guo, Z.; Xi, G.; Zhang, X.; Bie, Q.; Duan, H.; He, L. Characterization of spatio-temporal patterns of grassland utilization intensity in the Selinco watershed of the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau from 2001 to 2019 based on multisource remote sensing and artificial intelligence algorithms. GIScience Remote Sens. 2022, 59, 2217–2246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, G.; Ma, C.; Ji, F.; Huang, H.; Xie, Y. Characteristics of Changes in Livestock Numbers and Densities in the Selinco Region of the Qinghai–Tibetan Plateau from 1990 to 2020. Land 2024, 13, 1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Chen, H.; Yang, Y. Annual and seasonal changes in means and extreme events of precipitation and their connection to elevation over Yunnan Province, China. Quat. Int. 2015, 374, 46–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De, J.Y.; Ni, M.J.; Qiang, B.O.; Zeng, L.; Luo, S. Lake Area Variation of Selin Tso in 1975~2016 and Its Influential Factors. Plateau Mt. Meteorol. Res. 2018, 38, 35–41, 96. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Zhao, L.; Zhou, H.; Liu, S.; Du, E.; Zou, D.; Liu, G.; Xiao, Y.; Hu, G.; Wang, C. Contribution of ground ice melting to the expansion of Selin Co (lake) on the Tibetan Plateau. Cryosphere 2022, 16, 2745–2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Gao, X.-J. A gridded daily observation dataset over China region and comparison with the other datasets. Chin. J. Geophys. 2013, 56, 1102–1111. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Huang, X. 30 m annual land cover and its dynamics in China from 1990 to 2019. Earth Syst. Sci. Data Discuss. 2021, 13, 3907–3925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, T.; Dai, L.; Li, X. Long-term series of daily snow depth dataset in China (1979-2023). In National Tibetan Plateau; Cryosphere Datasets; National Tibetan Plateau Data Center: Beijing, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Che, T.; Li, X.; Jin, R.; Armstrong, R.; Zhang, T. Snow depth derived from passive microwave remote-sensing data in China. Ann. Glaciol. 2008, 49, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, L.; Che, T.; Ding, Y. Inter-calibrating SMMR, SSM/I and SSMI/S data to improve the consistency of snow-depth products in China. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 7212–7230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, L.; Che, T.; Ding, Y.; Hao, X. Evaluation of snow cover and snow depth on the Qinghai–Tibetan Plateau derived from passive microwave remote sensing. Cryosphere 2017, 11, 1933–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hersbach, H.; Bell, B.; Berrisford, P.; Hirahara, S.; Horányi, A.; Muñoz-Sabater, J.; Nicolas, J.; Peubey, C.; Radu, R.; Schepers, D.; et al. The ERA5 global reanalysis. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2020, 146, 1999–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McFeeters, S.K. The use of the Normalized Difference Water Index (NDWI) in the delineation of open water features. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1996, 17, 1425–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Li, Z.; Zhou, J.M.; Zhang, P. An automatic method for clean glacier and nonseasonal snow area change estimation in High Mountain Asia from 1990 to 2018. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 258, 112376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raup, B.; Kääb, A.; Kargel, J.S.; Bishop, M.P.; Hamilton, G.; Lee, E.; Paul, F.; Rau, F.; Soltesz, D.; Khalsa, S.J. Remote sensing and GIS technology in the Global Land Ice Measurements from Space (GLIMS) project. Comput. Geosci. 2007, 33, 104–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, P.; Nolin, A. Using atmospherically-corrected Landsat imagery to measure glacier area change in the Cordillera Blanca, Peru from 1987 to 2010. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 140, 165–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C. Moisture sources for precipitation in Southwest China in summer and the changes during the extreme droughts of 2006 and 2011. J. Hydrol. 2020, 591, 125333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Ent, R.J.; Savenije, H.H.G.; Schaefli, B.; Steele-Dunne, S.C. Origin and fate of atmospheric moisture over continents. Water Resour. Res. 2010, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, M.; Cui, Y. Source of Evaporation for the Seasonal Precipitation in the Pearl River Delta, China. Water Resour. Res. 2021, 57, e2020WR028564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, L.; Wang, R.; Jiang, H.; Li, J.; Tang, Q.; Yao, Z. Examining moisture contribution for precipitation in response to climate change and anthropogenic factors in Hengduan Mountain Region, China. J. Hydrol. 2023, 620, 129562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhang, X.; Tang, Q.; Chen, D.; Huang, J.; Wu, S.; Liu, Y. Quantifying precipitation moisture contributed by different atmospheric circulations across the Tibetan Plateau. J. Hydrol. 2024, 628, 130517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Chen, D.; Tang, Q.; Huang, J. Fate and Changes in Moisture Evaporated From the Tibetan Plateau (2000–2020). Water Resour. Res. 2023, 59, e2022WR034165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Lu, M.; Zhang, L.; Cheng, T.F. Remote Influence of Southern Tibetan Plateau Heating on North Pacific Atmospheric Rivers. J. Clim. 2025, 38, 101–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Ent, R.J.; Wang-Erlandsson, L.; Keys, P.W.; Savenije, H.H.G. Contrasting roles of interception and transpiration in the hydrological cycle—Part 2: Moisture recycling. Earth Syst. Dynam. 2014, 5, 471–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Yao, T.; Piao, S.; Bolch, T.; Xie, H.; Chen, D.; Gao, Y.; O’Reilly, C.M.; Shum, C.; Yang, K. Extensive and drastically different alpine lake changes on Asia’s high plateaus during the past four decades. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2017, 44, 252–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Weng, B.; Yan, D.; Bi, W.; Wang, H. Variation trends and attribution analysis of lakes in the Qiangtang Plateau, the Endorheic Basin of the Tibetan Plateau. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 837, 155595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liao, J.; Guo, H.; Liu, Z.; Shen, G. Patterns and potential drivers of dramatic changes in Tibetan lakes, 1972–2010. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e111890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Carrivick, J.L.; Emmer, A.; Shugar, D.H.; Veh, G.; Wang, X.; Labedz, C.; Mergili, M.; Mölg, N.; Huss, M. Characteristics and changes of glacial lakes and outburst floods. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2024, 5, 447–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Yao, T.; Zhang, G.; Woolway, R.I.; Yang, W.; Xu, F.; Zhou, T. Glacier surface heatwaves over the Tibetan Plateau. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2023, 50, e2022GL101115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Gong, W.; Bianchini, S.; Yang, Z. Linking glacier retreat with climate change on the Tibetan Plateau through satellite remote sensing. Cryosphere 2024, 18, 5595–5612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Yang, T.; He, Y. Glaciers and lakes changes and climate response in the Selin Co Basin from 1990 to 2011. J. Arid Land Resour. Environ. 2014, 28, 88–93. [Google Scholar]
- Miao, C.; Immerzeel, W.W.; Xu, B.; Yang, K.; Duan, Q.; Li, X. Understanding the Asian water tower requires a redesigned precipitation observation strategy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2024, 121, e2403557121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, F.; Zhang, G.; Woolway, R.I.; Yang, K.; Wada, Y.; Wang, J.; Crétaux, J.-F. Widespread societal and ecological impacts from projected Tibetan Plateau lake expansion. Nat. Geosci. 2024, 17, 516–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Yao, T.; Xie, H.; Yang, K.; Zhu, L.; Shum, C.K.; Bolch, T.; Yi, S.; Allen, S.; Jiang, L.; et al. Response of Tibetan Plateau lakes to climate change: Trends, patterns, and mechanisms. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2020, 208, 103269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, J.J.; Shen, G.Z.; Li, Y.K. Lake variations in response to climate change in the Tibetan Plateau in the past 40 years. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2013, 6, 534–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.-M.; Ma, L.-G.; Li, C.-Z.; Liu, Y.; Ding, J.-L.; Yang, S.-T. Temporal-spatial variations and influencing factors of Lakes in inland arid areas from 2000 to 2017: A case study in Xinjiang. Geomat. Nat. Hazards Risk 2019, 10, 519–543. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, D.; Xu, B.; Yao, T.; Guo, Z.; Cui, P.; Chen, F.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Fan, J. Assessment of past, present and future environmental changes on the Tibetan Plateau. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2015, 60, 3025–3035. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G.; Duan, S. Lakes as sentinels of climate change on the Tibetan Plateau. All Earth 2021, 33, 161–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, K.; Jia, T.; Luo, Y. Influence of natural factors and land use change on changes in the main lake area in China over the past 30 years. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 155, 111005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Gao, T.; Kang, S.; Shangguan, D.; Luo, X. Albedo reduction as an important driver for glacier melting in Tibetan Plateau and its surrounding areas. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2021, 220, 103735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.; Vlug, A.; Piao, S.; Li, F.; Wang, T.; Krinner, G.; Li, L.Z.; Wang, X.; Wu, G.; Li, Y. Regional and tele-connected impacts of the Tibetan Plateau surface darkening. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vassiljev, J. The simulated response of lakes to changes in annual and seasonal precipitation: Implication for Holocene lake-level changes in northern Europe. Clim. Dyn. 1998, 14, 791–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Deji, Y. Variation of Selin Co lake area during 1988-2020 and its response to climate change. Nanjing Xinxi Gongcheng Daxue Xuebao 2023, 15, 24–33. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, Y.; Yao, T.; Bird, B.W.; Yang, K.; Zhai, J.; Sheng, Y. Coherent lake growth on the central Tibetan Plateau since the 1970s: Characterization and attribution. J. Hydrol. 2013, 483, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, E.E.; Liljedahl, A.K. Diminishing lake area across the northern permafrost zone. Nat. Geosci. 2023, 16, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, T.; Zhang, Y.; Kang, S.; Abbott, B.W.; Wang, X.; Zhang, T.; Yi, S.; Gustafsson, Ö. Accelerating permafrost collapse on the eastern Tibetan Plateau. Environ. Res. Lett. 2021, 16, 054023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, T.; Pu, J.; Lu, A.; Wang, Y.; Yu, W. Recent glacial retreat and its impact on hydrological processes on the Tibetan Plateau, China, and surrounding regions. Arct. Antarct. Alp. Res. 2007, 39, 642–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, F.; He, B.; Liu, C.; Zeng, Y. Comparison of Hydrological Patterns between Glacier-Fed and Non-Glacier-Fed Lakes on the Southeastern Tibetan Plateau. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Long, H.; Shen, J.; Gao, L. Holocene lake-level fluctuations of Selin Co on the central Tibetan plateau: Regulated by monsoonal precipitation or meltwater? Quat. Sci. Rev. 2021, 261, 106919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; An, C.-B.; Zheng, L.-Y.; Liu, L.-Y.; Zhang, W.-S.; Lu, C.; Zhang, Y.-Z. Assessment of lake area in response to climate change at varying elevations: A case study of Mt. Tianshan, Central Asia. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 869, 161665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.-L.; Zhou, T.-C.; Yu, H.; Sun, J. Dynamics and Driving Forces of Lake Changes inTibet During the Past 25 Years. J. Yangtze River Sci. Res. Inst. 2018, 35, 145. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, R.-H.; Yu, X.-Z.; Li, Y.-L. The dynamic analysis of remote sensing information for monitoring the expansion of the Selincuo Lake in Tibet. Remote Sens. Land Resour. 2003, 2, 64–67. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, Y.; Yang, K.; Immerzeel, W.W.; Song, P.; Bird, B.W.; He, J.; Zhao, H.; Li, Z. Critical role of groundwater inflow in sustaining lake water balance on the Western Tibetan Plateau. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2022, 49, e2022GL099268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Melack, J.M.; Li, Y. Groundwater dynamics of a lake-floodplain system: Role of groundwater flux in lake water storage subject to seasonal inundation. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 857, 159414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaheddoost, B.; Aksoy, H. Interaction of groundwater with Lake Urmia in Iran. Hydrol. Process. 2018, 32, 3283–3295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Kang, S. Melting glaciers threaten ice core science on the Tibetan Plateau. Nat. Geosci. 2023, 16, 656–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowan, A.V.; Egholm, D.L.; Clark, C.D. Forward modelling of the completeness and preservation of palaeoclimate signals recorded by ice-marginal moraines. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2022, 47, 2198–2208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huybers, K.; Roe, G.H. Spatial patterns of glaciers in response to spatial patterns in regional climate. J. Clim. 2009, 22, 4606–4620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Satellite | Time Range | Variable | Blue Band | Green Band | Red Band | Near-Infrared Band | Shortwave Infrared 1 | Shortwave Infrared 2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Landsat 5 | 1984–2012 | Band name | SR_B1 | SR_B2 | SR_B3 | SR_B4 | SR_B5 | SR_B7 |
| Wavelength / | 0.45~0.52 | 0.52~0.60 | 0.63~0.69 | 0.76~0.90 | 1.55~1.75 | 2.08~2.35 | ||
| Landsat 7 | 1999–2021 | Band name | SR_B1 | SR_B2 | SR_B3 | SR_B4 | SR_B5 | SR_B7 |
| Wavelength / | 0.45–0.52 | 0.52–0.60 | 0.63–0.69 | 0.77–0.90 | 1.55–1.75 | 2.08–2.35 | ||
| Landsat 8 | 2013–Present | Band name | SR_B2 | SR_B3 | SR_B4 | SR_B5 | SR_B6 | SR_B7 |
| Wavelength / | 0.452–0.512 | 0.533–0.590 | 0.636–0.673 | 0.851–0.879 | 1.566–1.651 | 2.107–2.294 |
| Time | Mean/km2 | Range/km2 | CV/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1988–2000 | 1735.53 | 167.08 | 2.49 |
| 2001–2010 | 2170.02 | 409.14 | 7.06 |
| 2011–2023 | 2397.64 | 104.94 | 1.51 |
| 1988–2023 | 2095.32 | 789.56 | 14.38 |
| Glacier | Time | Mean/km2 | Range/km2 | CV/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Geladandong | 1986–2000 | 125.78 | 25.26 | 5.24 |
| 2001–2010 | 119.31 | 26.18 | 7.41 | |
| 2011–2023 | 110.73 | 25.28 | 6.49 | |
| 1988–2023 | 118.91 | 31.48 | 8.21 | |
| Jiagang | 1988–2000 | 95.12 | 47.40 | 14.87 |
| 2001–2010 | 83.31 | 45.57 | 18.36 | |
| 2011–2023 | 69.77 | 63.69 | 30.52 | |
| 1988–2023 | 80.85 | 83.87 | 25.85 |
| Source Region | Annual | Spring | Summer | Autumn | Winter |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Within basin | 6.85 | 5.05 | 7.40 | 6.66 | 2.49 |
| Outside basin | 93.15 | 94.95 | 92.60 | 93.34 | 97.51 |
| Land | 74.94 | 26.25 | 23.82 | 73.38 | 53.49 |
| Ocean | 25.06 | 74.75 | 76.18 | 16.62 | 46.51 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, G.; Feng, A.; Xu, L.; Zhang, Q.; Song, W.; Singh, V.P.; Wu, W.; Zhang, K.; Sun, S. Increasing Selin Co Lake Area in the Tibet Plateau with Its Moisture Cycle. Sustainability 2025, 17, 2024. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17052024
Wang G, Feng A, Xu L, Zhang Q, Song W, Singh VP, Wu W, Zhang K, Sun S. Increasing Selin Co Lake Area in the Tibet Plateau with Its Moisture Cycle. Sustainability. 2025; 17(5):2024. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17052024
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Gang, Anlan Feng, Lei Xu, Qiang Zhang, Wenlong Song, Vijay P. Singh, Wenhuan Wu, Kaiwen Zhang, and Shuai Sun. 2025. "Increasing Selin Co Lake Area in the Tibet Plateau with Its Moisture Cycle" Sustainability 17, no. 5: 2024. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17052024
APA StyleWang, G., Feng, A., Xu, L., Zhang, Q., Song, W., Singh, V. P., Wu, W., Zhang, K., & Sun, S. (2025). Increasing Selin Co Lake Area in the Tibet Plateau with Its Moisture Cycle. Sustainability, 17(5), 2024. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17052024









