Primary Particulate Matter and Aerosol Emissions from Biodiesel Engines During Idling in Plateau Environments of China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Diesel Engine and Fuel
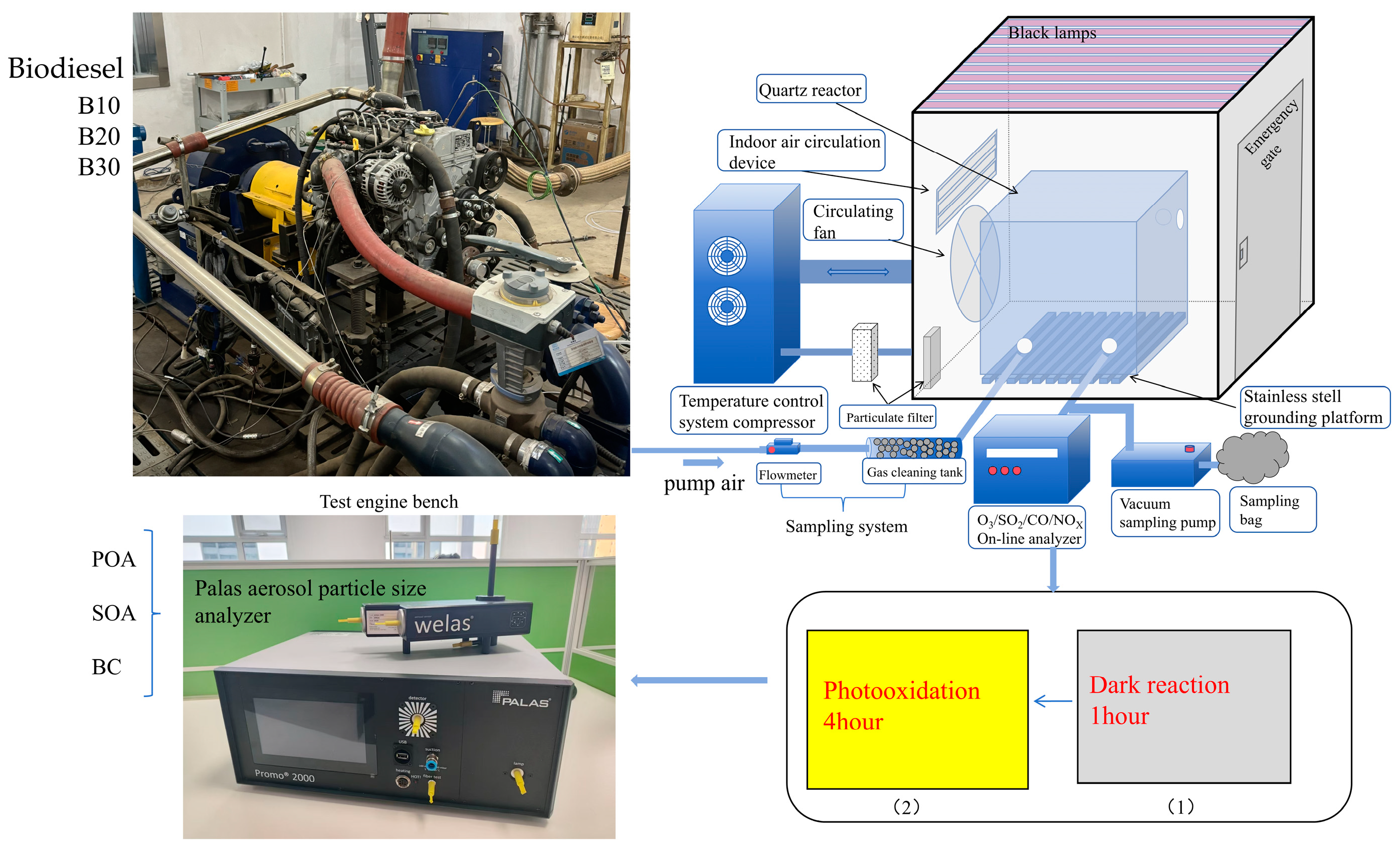
2.2. Experimental Setup
2.3. Instruments
2.4. Smog Chamber Reactor Operation Process
2.5. Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
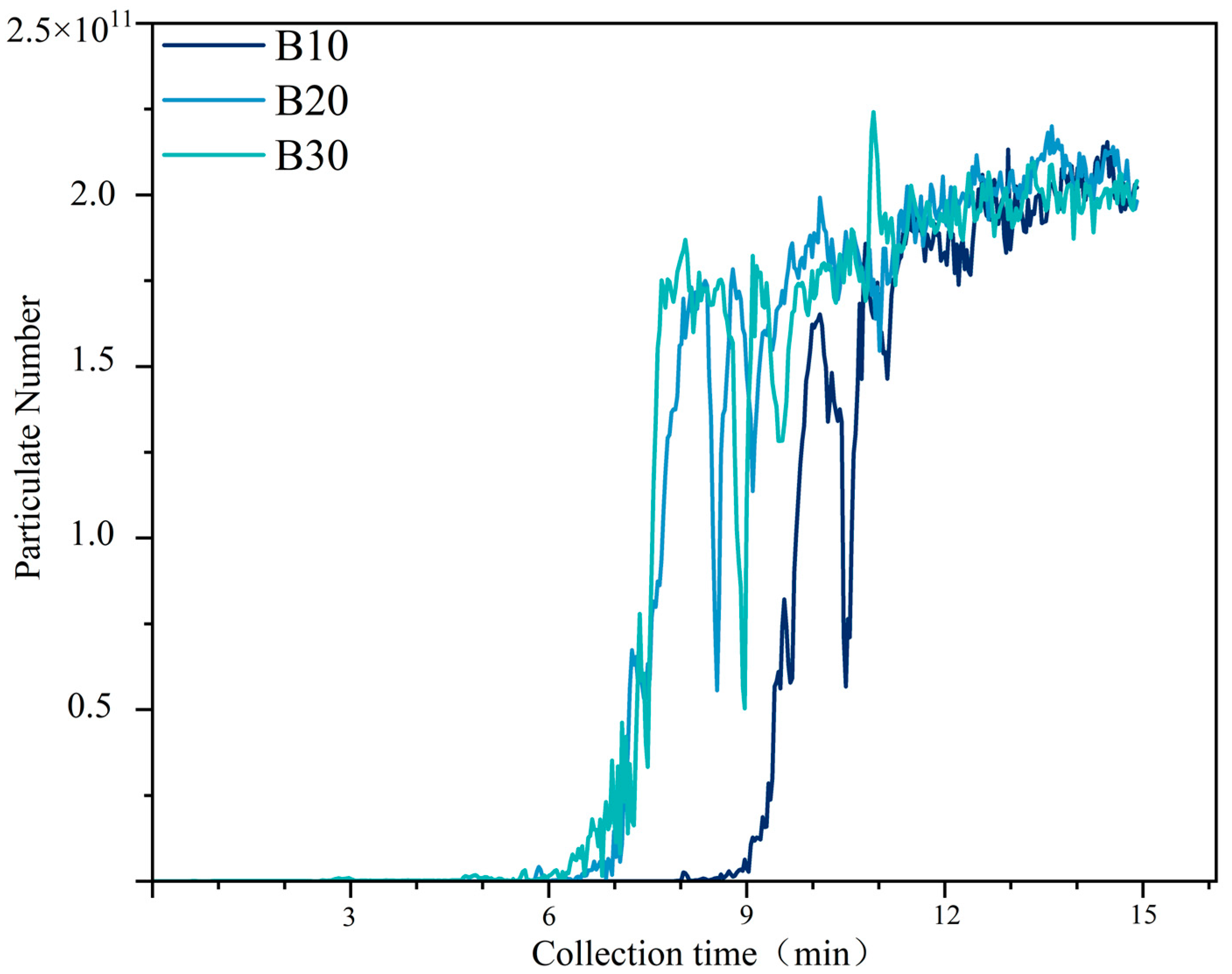
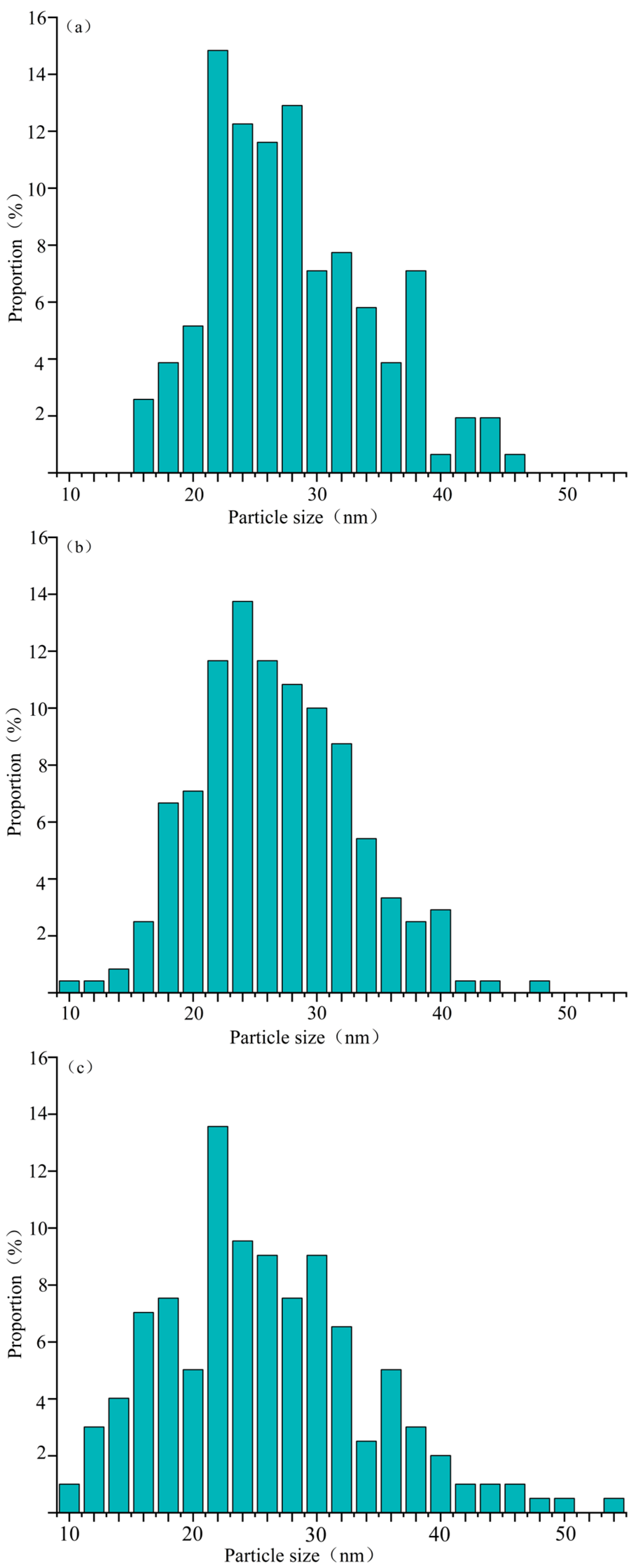
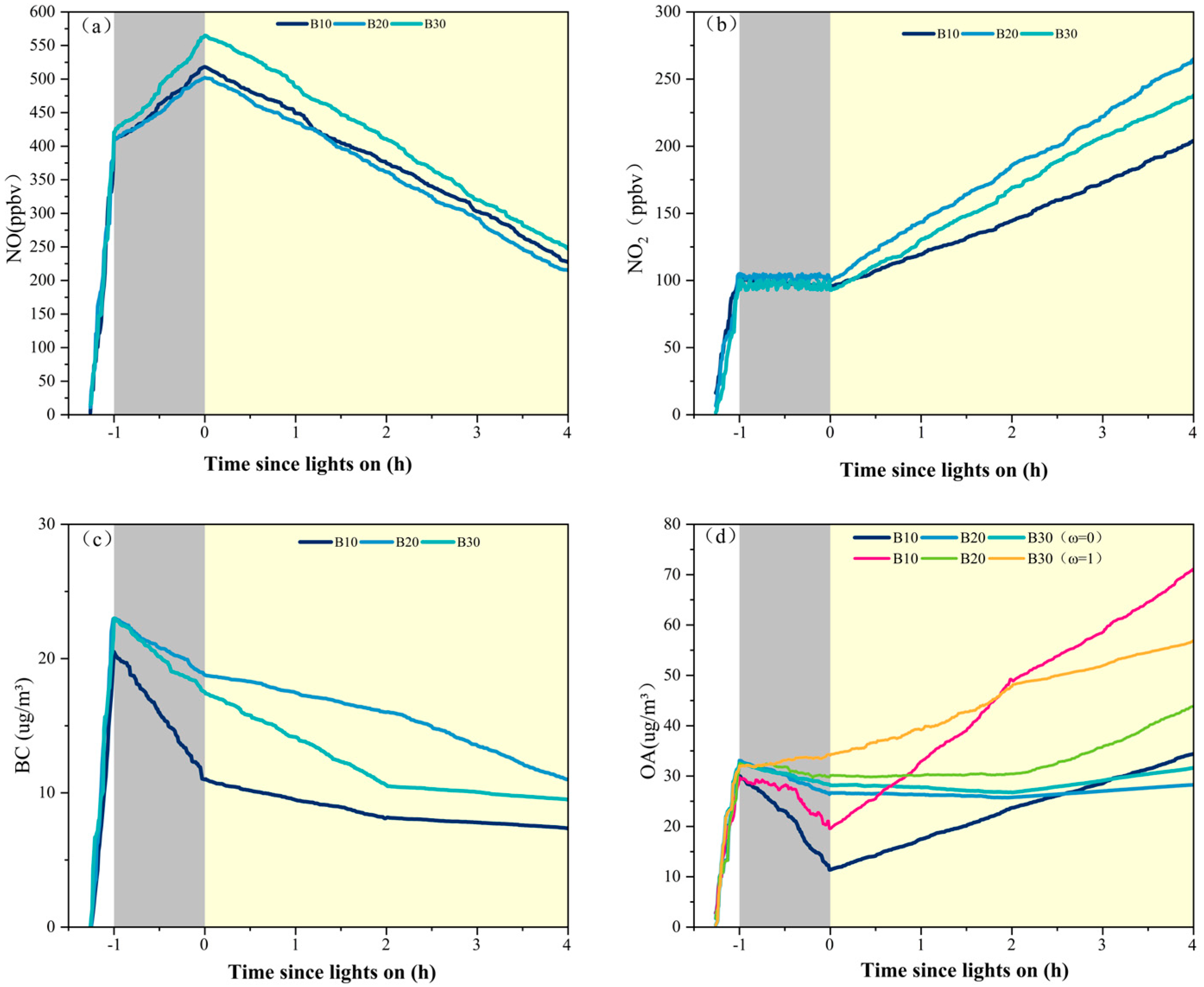
3.1. Primary Emissions of Particulate Matter
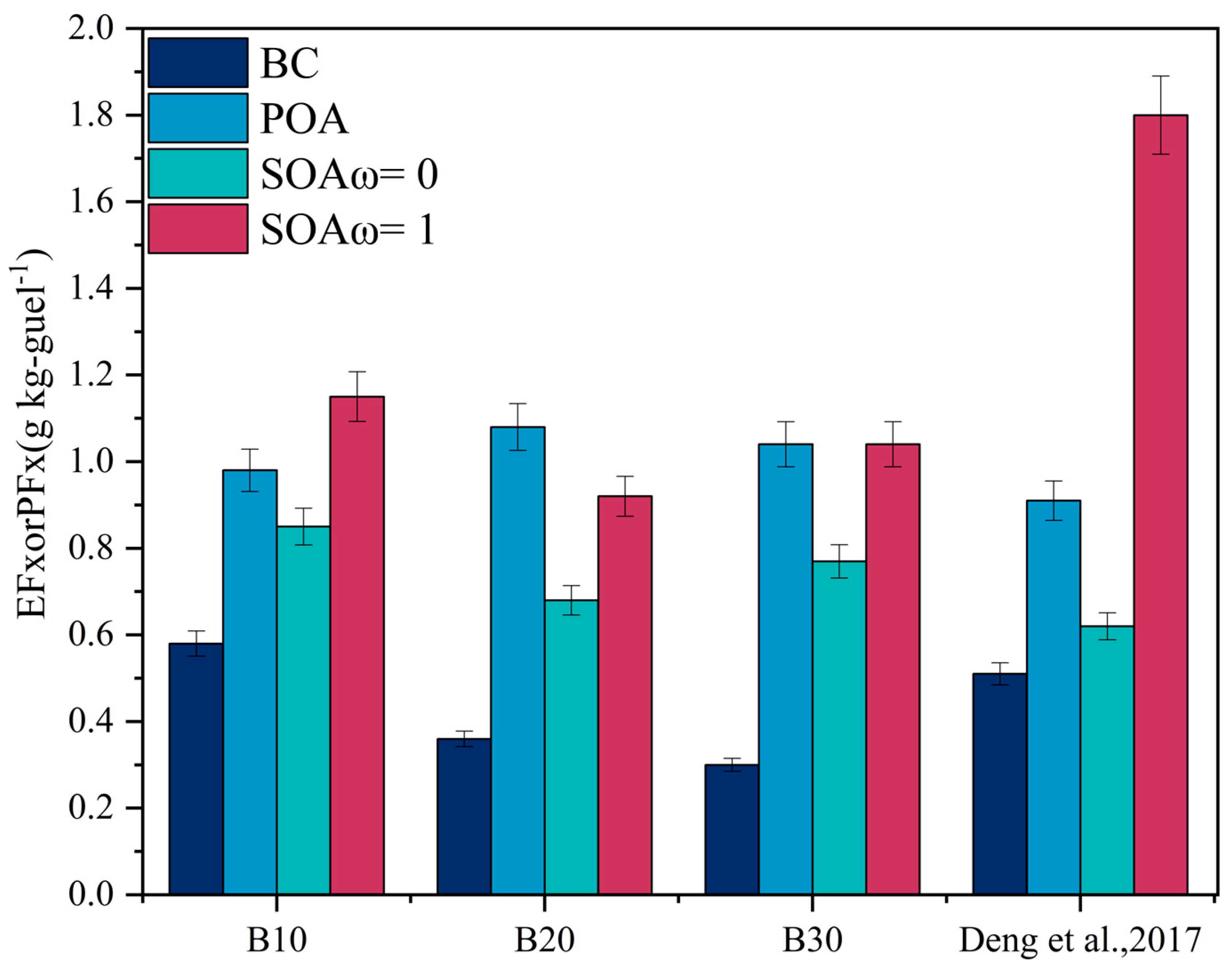
3.2. SOA Formation from Biodiesel Exhaust
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Reff, A.; Bhave, P.V.; Simon, H.; Pace, T.G.; Pouliot, G.A.; Mobley, J.D.; Houyoux, M. Emissions Inventory of PM2.5 Trace Elements across the United States. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 5790–5796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordon, T.D.; Presto, A.A.; May, A.A.; Nguyen, N.T.; Lipsky, E.M.; Donahue, N.M.; Gutierrez, A.; Zhang, M.; Maddox, C.; Rieger, P.; et al. Secondary Organic Aerosol Formation Exceeds Primary Particulate Matter Emissions for Light-Duty Gasoline Vehicles. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 4661–4678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentner, D.R.; Jathar, S.H.; Gordon, T.D.; Bahreini, R.; Day, D.A.; El Haddad, I.; Hayes, P.L.; Pieber, S.M.; Platt, S.M.; de Gouw, J.; et al. Review of Urban Secondary Organic Aerosol Formation from Gasoline and Diesel Motor Vehicle Emissions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 1074–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Lei, G.; Liu, C.; Wu, Y.; Hu, K.; Zhu, J.; Bao, J.; Lin, W.; Jin, J. Characteristics of Particulate-Bound n-Alkanes Indicating Sources of PM2.5 in Beijing, China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2023, 23, 3015–3029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, B.; Liu, Y.; Yu, P.; Zhang, B.; Bai, Y. Characterizations of PM2.5 Pollution Pathways and Sources Analysis in Four Large Cities in China. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2015, 15, 1836–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Zhou, M.; Qiao, L.; Huang, D.D.; Wang, Q.; Wang, S.; Gao, Y.; Jing, S.; Wang, Q.; Wang, H.; et al. Evolution and Chemical Characteristics of Organic Aerosols during Wintertime PM2.5 Episodes in Shanghai, China: Insights Gained from Online Measurements of Organic Molecular Markers. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2023, 23, 7551–7568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Rawi, Y.A.; Imlus, M.H.; Yusup, Y.; Yahya, S.B. Factors Affecting Vehicle Exhaust Emissions, Driver Motivations as a Mediator. Environ. Econ. Policy Stud. 2021, 23, 361–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Z.; Li, X.; Hao, Y.; Deng, S. Potential of Diesel Emissions Reduction Strategies in Xi’an, China. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2016, 18, 2717–2724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chacon-Madrid, H.J.; Murphy, B.N.; Pandis, S.N.; Donahue, N.M. Simulations of Smog-Chamber Experiments Using the Two-Dimensional Volatility Basis Set: Linear Oxygenated Precursors. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 11179–11186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lelieveld, J.; Evans, J.S.; Fnais, M.; Giannadaki, D.; Pozzer, A. The Contribution of Outdoor Air Pollution Sources to Premature Mortality on a Global Scale. Nature 2015, 525, 367–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brook, R.D.; Rajagopalan, S.; Pope, C.A.; Brook, J.R.; Bhatnagar, A.; Diez-Roux, A.V.; Holguin, F.; Hong, Y.; Luepker, R.V.; Mittleman, M.A.; et al. Particulate Matter Air Pollution and Cardiovascular Disease. Circulation 2010, 121, 2331–2378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, G.; Ge, J.C.; Choi, N.J. A Comprehensive Review of the Application Characteristics of Biodiesel Blends in Diesel Engines. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 8015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Živković, S.; Veljković, M. Environmental Impacts the of Production and Use of Biodiesel. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.-F.; Yu, J.Z.; He, L.-Y.; Hu, M. Size Distribution Characteristics of Elemental Carbon Emitted from Chinese Vehicles: Results of a Tunnel Study and Atmospheric Implications. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 5355–5360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Wen, S.; Herrmann, H.; Yang, W.; Huang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, Z.; He, Q.; George, C. On-Road Vehicle Emissions of Glyoxal and Methylglyoxal from Tunnel Tests in Urban Guangzhou, China. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 127, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Z.; Shen, X.; Ye, Y.; Cao, X.; Jiang, X.; Zhang, Y.; He, K. On-Road Emission Characteristics of VOCs from Diesel Trucks in Beijing, China. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 103, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Shen, X.; Cao, X.; Zhang, W.; Wu, H.; Yao, Z. Carbonaceous Composition of PM2.5 Emitted from on-Road China III Diesel Trucks in Beijing, China. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 116, 216–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Li, G.; Yang, W.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, X.; Deng, W.; Liu, T.; Huang, Z.; et al. Emission Factors of Fine Particles, Carbonaceous Aerosols and Traces Gases from Road Vehicles: Recent Tests in an Urban Tunnel in the Pearl River Delta, China. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 122, 876–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, W.; Liu, X.; Chen, Y.; Yang, T.; Qiao, M. The Study on Emission Characteristics of Biodiesel Fuels in Agricultural Tractors. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2021, 40, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veeraraghavan, S.M.; Kaliyaperumal, G.; Dillikannan, D.; Poures, M.V.D. Influence of Hydrogen Induction on Performance and Emission Characteristics of an Agricultural Diesel Engine Fuelled with Cultured Scenedesmus Obliquus from Industrial Waste. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2024, 187, 1576–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weitkamp, E.A.; Sage, A.M.; Pierce, J.R.; Donahue, N.M.; Robinson, A.L. Organic Aerosol Formation from Photochemical Oxidation of Diesel Exhaust in a Smog Chamber. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 6969–6975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, W.; Hu, Q.; Liu, T.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Song, W.; Sun, Y.; Bi, X.; Yu, J.; Yang, W.; et al. Primary Particulate Emissions and Secondary Organic Aerosol (SOA) Formation from Idling Diesel Vehicle Exhaust in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 593–594, 462–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, W.; Fang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, M.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, M.; Song, W.; Lowther, S.; Huang, Z.; Jones, K.; et al. Primary Emissions and Secondary Organic Aerosol Formation from In-Use Diesel Vehicle Exhaust: Comparison between Idling and Cruise Mode. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 699, 134357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunmore, R.E.; Hopkins, J.R.; Lidster, R.T.; Lee, J.D.; Evans, M.J.; Rickard, A.R.; Lewis, A.C.; Hamilton, J.F. Diesel-Related Hydrocarbons Can Dominate Gas Phase Reactive Carbon in Megacities. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 9983–9996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, A.L.; Donahue, N.M.; Shrivastava, M.K.; Weitkamp, E.A.; Sage, A.M.; Grieshop, A.P.; Lane, T.E.; Pierce, J.R.; Pandis, S.N. Rethinking Organic Aerosols: Semivolatile Emissions and Photochemical Aging. Science 2007, 315, 1259–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chirico, R.; DeCarlo, P.F.; Heringa, M.F.; Tritscher, T.; Richter, R.; Prévôt, A.S.H.; Dommen, J.; Weingartner, E.; Wehrle, G.; Gysel, M.; et al. Impact of Aftertreatment Devices on Primary Emissions and Secondary Organic Aerosol Formation Potential from In-Use Diesel Vehicles: Results from Smog Chamber Experiments. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 11545–11563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 20828-2014; Biodiesel (BD100) for diesel engine fuel blending. Standardization Administration of China: Beijing, China, 2014.
- Demirbas, A. Progress and Recent Trends in Biodiesel Fuels. Energy Convers. Manag. 2009, 50, 14–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 19147-2016; Automotive diesel. Standardization Administration of China: Beijing, China, 2016.
- Xu, D.; Yu, H.; Yu, H.; Xu, J.; Wang, Z.; Li, J. Design and Characterization of a New Quartz Smog Chamber System for Studying the Atmospheric Effects of Vehicle Emissions on Plateaus. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2024, 16, 102361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, J.; Ma, Y.; Zhou, M.; Tan, Z.; Zeng, L.; Lu, K.; Zhang, Y. A Review of Gas-Phase Chemical Mechanisms Commonly Used in Atmospheric Chemistry Modelling. J. Environ. Sci. 2023, 123, 522–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Presto, A.A.; Gordon, T.D.; Robinson, A.L. Primary to Secondary Organic Aerosol: Evolution of Organic Emissions from Mobile Combustion Sources. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 5015–5036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Ling, Z.H.; Cheung, K.; Jiang, F.; Wang, D.W.; Simpson, I.J.; Barletta, B.; Meinardi, S.; Wang, T.J.; Wang, X.M.; et al. Characterization of Photochemical Pollution at Different Elevations in Mountainous Areas in Hong Kong. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 3881–3898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odum, J.R.; Hoffmann, T.; Bowman, F.; Collins, D.; Flagan, R.C.; Seinfeld, J.H. Gas/Particle Partitioning and Secondary Organic Aerosol Yields. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1996, 30, 2580–2585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- III, D.R.C.; Mader, B.T.; Kalberer, M.; Flagan, R.C.; Seinfeld, J.H. The Effect of Water on Gas–Particle Partitioning of Secondary Organic Aerosol: II. m-Xylene and 1,3,5-Trimethylbenzene Photooxidation Systems. Atmos. Environ. 2001, 35, 6073–6085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinfeld, J.I. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics: From Air Pollution to Climate Change. Environ. Sci. Policy Sustain. Dev. 1998, 40, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epping, R.; Koch, M. On-Site Detection of Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs). Molecules 2023, 28, 1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, P.R. Recent Applications of Fourier Transform Infrared Spectrometry in Chemical and Environmental Analysis. Appl. Spectrosc. 1977, 31, 497–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Väkevä, M.; Hämeri, K.; Puhakka, T.; Nilsson, E.D.; Hohti, H.; Mäkelä, J.M. Effects of Meteorological Processes on Aerosol Particle Size Distribution in an Urban Background Area. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2000, 105, 9807–9821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Tsou, C.-H.; Yu, Y.; Wu, C.-S.; Zhang, X.; Chen, Z.; Yang, T.; Ge, F.; Liu, P.; Guzman, M.R.D. Conductivity and Mechanical Properties of Carbon Black-Reinforced Poly(Lactic Acid) (PLA/CB) Composites. Iran. Polym. J. 2021, 30, 1251–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Wu, Y.; Jiang, J.; Zhang, S.; Liu, H.; Song, S.; Li, Z.; Fan, X.; Fu, L.; Hao, J. Characteristics of On-Road Diesel Vehicles: Black Carbon Emissions in Chinese Cities Based on Portable Emissions Measurement. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 13492–13500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knothe, G. Dependence of Biodiesel Fuel Properties on the Structure of Fatty Acid Alkyl Esters. Fuel Process. Technol. 2005, 86, 1059–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanowitz, J.; McCormick, R.L.; Graboski, M.S. In-Use Emissions from Heavy-Duty Diesel Vehicles. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2000, 34, 729–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul-Khalek, I.; Kittelson, D.; Brear, F. The Influence of Dilution Conditions on Diesel Exhaust Particle Size Distribution Easurements. SAE Trans. 1999, 108, 563–571. [Google Scholar]
- Jeffries, H.; Fox, D.; Kamens, R. Outdoor Smog Chamber Studies: Light Effects Relative to Indoor Chambers. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1976, 10, 1006–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, P.; Ding, X.; Hakala, J.; Hofbauer, V.; Robinson, E.S.; Donahue, N.M. Vapor Wall Loss of Semi-Volatile Organic Compounds in a Teflon Chamber. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 822–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirjola, L.; Dittrich, A.; Niemi, J.V.; Saarikoski, S.; Timonen, H.; Kuuluvainen, H.; Järvinen, A.; Kousa, A.; Rönkkö, T.; Hillamo, R. Physical and Chemical Characterization of Real-World Particle Number and Mass Emissions from City Buses in Finland. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 294–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rönkkö, T.; Lähde, T.; Heikkilä, J.; Pirjola, L.; Bauschke, U.; Arnold, F.; Schlager, H.; Rothe, D.; Yli-Ojanperä, J.; Keskinen, J. Effects of Gaseous Sulphuric Acid on Diesel Exhaust Nanoparticle Formation and Characteristics. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 11882–11889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, F.; Pirjola, L.; Rönkkö, T.; Reichl, U.; Schlager, H.; Lähde, T.; Heikkilä, J.; Keskinen, J. First Online Measurements of Sulfuric Acid Gas in Modern Heavy-Duty Diesel Engine Exhaust: Implications for Nanoparticle Formation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 11227–11234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, X.; Zhang, X.; Chang, S. Scenario Analysis on Alternative Fuel/Vehicle for China’s Future Road Transport: Life-Cycle Energy Demand and GHG Emissions. Energy Policy 2010, 38, 3943–3956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Wang, X.; Deng, W.; Hu, Q.; Ding, X.; Zhang, Y.; He, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Lü, S.; Bi, X.; et al. Secondary Organic Aerosol Formation from Photochemical Aging of Light-Duty Gasoline Vehicle Exhausts in a Smog Chamber. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 9049–9062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Lai, M.-C.; Harrington, D.L. Automotive Spark-Ignited Direct-Injection Gasoline Engines. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 1999, 25, 437–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Item | Parameter |
|---|---|
| Engine Model | D19TCI |
| Engine Type | High-Pressure Common Rail Diesel Engine |
| Inner Diameter of the Hole | 80 mm |
| Stroke | 92 mm |
| Rated Power (kW)/Speed (r/min) | 85/3600 |
| Maximum Torque (N·M)/Speed (r/min) | 225/2300 |
| Compression Ratio | 18.5:1 |
| Post-Processing Device | None |
| Fuel Name | B00 | B10 | B20 | B30 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Physical or Chemical Property | |||||
| Cetane Number | 50 | 50.54 | 50.83 | 51.6 | |
| Oxygen Content (%) | 0 | 1.64 | 2.24 | 3.68 | |
| Density (g/mL) | 0.83 | 0.835 | 0.84 | 0.845 | |
| Low Calorific Value (MJ/kg) | 42.68 | 41.87 | 41.59 | 41.06 | |
| Flash Point | 60 | 67 | 74 | 83 | |
| Viscosity (mm2/s) | 2-4 | 3.15 | 3.26 | 3.41 | |
| Expt. No | T (°C) | RH (%) | NO (ppbv) | NO2 (ppbv) | BC (μg/m3) | POA (μg/m3) | SOAt=4 (μg/m3) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ω = 0 | ω = 1 | |||||||
| 1. (B10) | 25.3 | 25.1 | 518.276 | 95.763 | 7 | 10.5 | 32.232 | 29.835 |
| 2. (B20) | 25.1 | 24.3 | 502.135 | 99.521 | 23 | 24.6 | 26.544 | 43.91 |
| 3. (B30) | 25.7 | 24.8 | 564.821 | 92.876 | 17.509 | 26 | 29.704 | 56.87 |
| Expt. No. | EFBC (g kg−1 Fuel) | EFPOA (g kg−1 Fuel) | PFSOA (g kg−1 Fuel) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ω = 0 | ω = 1 | |||
| 1. (B10) | 0.58 | 0.99 | 0.85 | 1.15 |
| 2. (B20) | 0.36 | 1.06 | 0.68 | 0.92 |
| 3. (B30) | 0.31 | 1.05 | 0.77 | 1.04 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, D.; Yu, H.; Cai, W.; Xu, J.; Li, J. Primary Particulate Matter and Aerosol Emissions from Biodiesel Engines During Idling in Plateau Environments of China. Sustainability 2025, 17, 976. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17030976
Xu D, Yu H, Cai W, Xu J, Li J. Primary Particulate Matter and Aerosol Emissions from Biodiesel Engines During Idling in Plateau Environments of China. Sustainability. 2025; 17(3):976. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17030976
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Dingmin, Hongyang Yu, Wenjie Cai, Jiacheng Xu, and Jiaqiang Li. 2025. "Primary Particulate Matter and Aerosol Emissions from Biodiesel Engines During Idling in Plateau Environments of China" Sustainability 17, no. 3: 976. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17030976
APA StyleXu, D., Yu, H., Cai, W., Xu, J., & Li, J. (2025). Primary Particulate Matter and Aerosol Emissions from Biodiesel Engines During Idling in Plateau Environments of China. Sustainability, 17(3), 976. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17030976




