Abstract
Standardization alliance networks serve as crucial channels for firms to sponsor standards and access external resources, exerting a substantial impact on their standard-setting competitiveness and their ability to foster a sustainable innovation ecosystem. The technology–organization–environment (TOE) framework offers an integrated theoretical perspective for studying the causal recipes of how the technological composition, the network structure, and the environment features of standardization alliance network affect firms’ capabilities to dominate and support technological standardization. Based on the data of 88 vehicle manufacturers with experience in participating in standardization alliances, the results of fuzzy-set Qualitative Comparative Analysis (fsQCA) show that: (1) large-scale networks with low density and high technological diversity can simultaneously explain firms’ high level capabilities to dominate and support standardization; (2) supporting standardization is highly dependent on network scale, as firms embedded in large-scale alliance networks with high technological diversity or proximity both enjoy advantages in supporting standardization; (3) dominating standardization shows relatively low dependence on network scale, a firm can enhance its standardization dominance by maintaining an alliance network with low technological proximity in institutional environment with high government intervention. Overall, this study contributes to the theoretical literature on cooperative standard-setting and provides managerial implications for firms looking to enhance capabilities to dominate and support standardization, thereby shaping sustainable technology trajectories and securing their long-term industrial competitiveness in a rapidly evolving technological environment.
1. Introduction
In technology-intensive industries, firms generally pursue opportunities to influence industrial standard setting for improving their competitiveness and the market acceptance of their products [1,2]. Rapid technological change and complex product designs necessitate cooperation among firms, suppliers, customers, and other organizations to develop technological standards. Such collaboration is crucial to ensure the quality and efficiency of product manufacturing [2]. In order to more fully influence technological standardization, firms also need to engage in standardization alliances to acquire external complementary resources and address technological and market risks [3,4]. Through standardization collaborations, a firm has opportunities to discuss, test, or promote certain technologies with stakeholders, which allows companies to acquire information on new technology developments and evolving standards [5]. The firm also can reduce R&D costs by spreading them over multiple firms and combine the partners’ variety of specialties for the standards they advocated [6]. As such, standardization alliance networks, created by inter-organization linkages, have become important channels for firms to access external resources and to influence standard setting [7,8,9,10].
Prior research on standardization collaboration suggest that alliance network structure and composition help to explain why some firms are capable of influencing standard-setting than other networked actors [2,4,11,12]. As to network structure, research emphasizes the advantage of external resource acquisition deriving from firms’ superior position in alliance network [4,13,14]. Network centrality and structural holes can affect the efficiency of network knowledge transfer and market resources aggregation, thus being associated with firms’ capabilities in setting and promoting technology standards [12,14]. As to network composition, two important aspects have been recognized as a source of value for cooperative standard-setting: network diversity and proximity [15,16,17]. Network diversity determines the range of resources available for standardization [2,18], and network proximity is closely associated with the difficulty of knowledge absorption and utilization among partners [17], therefore affecting a networked firm’s ability to influence standardization. Furthermore, standardization in technology-intensive industries is critically shaped by the external environment. Some scholars argue that higher technological turbulence undermines a firm’s ability to cultivate influence over the industry’s dominant design, as it reduces collaborative willingness among business partners, while simultaneously increasing uncertainty in technological paths [19]. Meanwhile, the government-market relationship, as a key institutional variable, determines the legitimacy and support for different technological paths, thereby directly influencing a firm’s standardization capability [14].
Previous studies have primarily discussed these important alliance network features in isolation, resulting in fragmented findings. Few of them have combined them to examine the role that alliance network plays in affecting firms’ capability of influencing technological standardization. This gap stems from the lack of an integrated theoretical framework to analyze these complex causal mechanisms. However, in practice, a firm’s technological standardization capability is shaped by the complex interplay of multiple alliance network-related variables. Merely examining the ‘net effects’ of individual factors cannot fully clarify the mechanism through which these antecedents interact to foster such capability. Compared to the theoretical limitations of singular perspectives, such as the Resource-Based View and Institutional Theory, the TOE framework provides a comprehensive analytical lens that systematically integrates organizational resources, technical resources, and the external environment [20]. Therefore, this study innovatively introduces the TOE framework into technological standardization research and, from the perspective of alliance networks, systematically examines how the three dimensions of network technological, organizational, and environmental dimensions collectively constitute the key antecedents of a firm’s technological standardization capability.
In addition, most studies predominantly examine capability of influencing standardization as a monolithic construct [12,14], while investigating its origins demands finer conceptual distinctions [21]. Dominating and supporting standardization capabilities are both critical for firms to implement sound standardization strategies yet having different concentrations and requirements for external resource integration [2]. Dominating standardization focuses on designing standards around a firm’s own technology by integrating external resources, while supporting standardization aims to incorporate a firm’s technology into the broader industrial ecosystem by leveraging internal resources to complement external systems [2]. The current study is novel as it examines the effect of alliance network features on specific types of capabilities of influencing standardization: dominating standardization and supporting standardization, to fulfill this research gap.
Therefore, following prior studies, we conceptualize the “T-O-E features of an alliance network” through three dimensions: the Technological composition (i.e., technological diversity and proximity), the Organizational structure (i.e., network size and density), and the Environmental context (i.e., technological turbulence and government-market relations). The purpose of this paper is to investigate how the technology–organization–environment features of a firm’s alliance network influence the firm’s capabilities to dominate and support technological standardization. We aim to address not only the importance of the combined effects of the alliance network’s TOE features on standardization but also their differential impact on different types of standardization. We use fsQCA 4.1 to conduct the empirical analysis based on the data of 88 Chinese vehicle manufacturers with experience in participating in standardization alliances. In doing so, this study extends the literature on standardization collaboration by applying the TOE framework, and it enriches research on the causes and paths of standardization capability development.
2. Theoretical Foundation and Research Framework
2.1. Dominating Standardization vs. Supporting Standardization
Influencing standardization refers to firms’ behaviors that establish and promote industrial standards toward their own preferences [2]. In practice, industrial standards, especially for formal standards which have greater legitimacy than de facto standards, are often set cooperatively [1]. During this cooperative standard-setting process, firms can secure private gains through two different ways: dominating standardization and supporting standardization.
Dominating standardization stresses designing the industry standards around firms’ own technology system, which requires an “integrating external resources to support internal technology system” exercise [2]. Firms firstly need abundant access to external technology or market resources to improve their chances of achieving technological dominance [4,19]. In addition, they further require a strong ability in integrating and coordinating the resources and appeals of different stakeholders within an industrial segment, promoting consensus formation about the standard content to more fully dominate standardization processes. An example of a dominator is Tesla, which aimed to establish its proprietary charging interface as the industry benchmark for electric vehicles in North America. By opening its patents and actively forging strategic alliances with industry giants such as Ford and General Motors, Tesla integrated these key external competitors into its own ecosystem. This strategy successfully propelled the North American Charging Standard (NACS) to become a de facto dominant design, pulling the entire industry into its technological orbit.
By contrast, supporting standardization aims to make firms own technology become a part of the ecosystem of the industrial standard, which can be achieved through supporting and assisting standard-setting leaders to develop and improve standard solutions as module experts. Supporting standardization requires an “integrating internal resources to support external technology systems” excise [2]. Firms who want to enhance their capability to support standardization, need a timely scan of the technology and market environment to seek synergy opportunities and a strong ability to cooperate with external stakeholders. An example of a supporter is Bosch, a leading global automotive supplier, which has supported standards bodies such as ISO and AUTOSAR, as well as major automakers including Volkswagen and Toyota, in setting standards for advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS), electronic stability control, and anti-lock braking systems. By supporting leading firms and consortia in formal standardization, Bosch has successfully promoted its specialized modules and components as indispensable elements within the broader automotive ecosystem.
2.2. Research Framework
The Technology–Organization–Environment (TOE) framework was initially proposed by Tornatzky and Fleischer in 1900, with the aim of explaining and predicting the likelihood of technology and innovation adoption [22]. It consists of three main components that may influence the adoption or implementation of innovations, including technology, organization and environment. The TOE theory is a highly generalized model of innovation adoption with strong flexibility in practice and theoretical application, which does not prescribe specific variables within technology, organization and environment, allowing researchers to extend boundaries based on specific research contexts [23]. Scholars have gradually extended its applications from a single specific micro-organization level to a complex and dynamic macro-level, such as e-commerce system [24,25], public sector [26,27] and smart cities governance [28]. In technology-intensive industries such as automobiles, technical standard activities are essentially a complex process of proactive technology absorption, integration and promotion. This process is usually carried out in the form of alliance cooperation, which not only involves diverse stakeholders and collaboration models, but is also often restricted by technological fluctuations and policy environments. Therefore, based on the TOE framework, the technical resources embedded in the alliance network, the structural characteristics of the network, and the external environment together constitute the key network influencing factors for the adoption and promotion of new technology standards. The research model is shown in Figure 1.
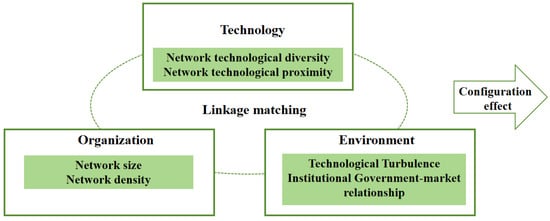
Figure 1.
Research Framework.
2.2.1. Technology: Technological Composition of Alliance Networks
The network technological composition refers to the types of technologies within a network, characterized by their stable attributes or functional capabilities [29]. Its features usually focus on the variety of technological types present (diversity) and the similarity of their core attributes across nodal pairs (proximity) [18,29,30]. The former affects the integration potential and value-capture capacity of external technological resources [18], while the latter decides the efficiency of external knowledge absorption and coordination in the standardization process [31].
Network technological diversity shapes firms’ standardization capabilities through the heterogeneous distribution of knowledge and technological resources among network members. Its core value derives from the synergistic effects of heterogeneous knowledge integration [32,33]. Alliance network with high technological diversity can provide firms heterogeneous resource pools, bringing together valuable information and knowledge of product technology and production [34]. Such information advantage is helpful to enhance the standards’ quality and compatibility [7,35], and offers inter-organizational learning opportunities for novel and unmatched knowledge and technology [36], thus enabling firms to be more influential in dominating the specifications development of a product system and supporting the technology of standard-setting leaders. However, some studies also suggest that diverse alliance network brings absorptive capacity problems and coordination difficulties [37,38], reducing the firms’ bargaining power and resource integration efficiency in the standard-setting processes.
Network technological proximity refers to the similarity in technology base between focal firms and their partners in egocentric alliance networks [30,39]. Proximity offers benefits such as higher absorption efficiency and combinable market resources [40,41]. Firstly, similar knowledge bases can facilitate tacit knowledge sharing and absorption, which reduces collaborative standardization costs and accelerates the compatible integration of technological modules [30], thereby improving the competitiveness of the standard proposals. Secondly, high technological proximity ensures network partners to quickly and accurately assess each other’s technological competencies and avoid potential opportunistic behaviors. As a result, it acquires their support, which is an excellent way to gather market power for a specific technology solution [42]. Thirdly, a high level of network technological proximity can enhance the professional depth and market credibility of proposals, which directly affects the government institutions’ review and the proposals’ adoption rate. However, high technological proximity also suggests low complementarity of network technological resources for the focal firms [43]. This may bring problems of innovation path dependence, weakening firms’ differentiated competitiveness in standard-setting and forming innovation traps during technological iterations [39].
2.2.2. Organization: Alliance Network Structure
The network organization structure refers to the structural attributes of an “alliance network” as a virtual integrated organization, addressing how the number of actors and the relationships between them affect resource flows and actors’ conduct [20,44]. In the context of cooperative standard-setting, the network size and network density are the important organizational factors of alliance network that will affect a firm’s access to network knowledge, network actors’ willingness to share knowledge, and the efficiency of knowledge exchange [29,45].
Network size indicates the scale of a firm’s external resource pool and the number of potential supporters for its technical solution [46]. It affects a firm’s capability to influence standardization mainly through the following two ways: First, firms embedded in large-scale alliance networks can possess information advantage, which helps firm capture the latest technology trends and promising niche market [14,42], and then discover standardization opportunities to support standard-setting leaders. Second, firms within larger alliance networks also have more channels to advertise their expertise and technologies to partners and drum up more support in standardization negotiations [4], thus improve the competitiveness of their standard proposals through the scale effect. However, some scholars also suggest that expanding alliance network size also increase relationship coordination costs and decrease the level of network trust, hindering firms from coordinating and integrating network resources to form superior technical proposals [47,48].
Network density, which refers to the connectivity among network actors, is closely associated with the depth of cooperation and level of network trust [42,49]. Dense networks can facilitate the knowledge exchange and reduce standardization uncertainty, thereby enabling firms to be more capable of coordinating network resources to dominate standard setting [50]. Moreover, at higher levels of network density, frequent cooperation and communication between partners can accelerate consensus formation about the standard content through facilitating the establishment of trust and reciprocal relationships, reducing information asymmetry and opportunistic behaviors among firms [14]. However, as partners become more interconnected, firms may face the information redundancy and homogenization of perspectives [14,51], which will lower their ability to identify standardization opportunities and to exploit late-mover advantages in standard-setting process. In addition, high levels of density will also reduce the amount of power and control a firm can exert over its network [29,52], constraining the firm’s ability to dominate standardization.
2.2.3. Environment: Technological and Institutional Contexts
The environmental context places greater emphasis on how the macro-environment, as a key set of contextual factors (e.g., technology, policy, market, society), affects organizations’ behavior and development [53]. This study focuses on two critical environmental dimensions—the technological and institutional environments—because ongoing technological evolution drives changes in technical standards from both supply-side and market-demand perspectives [54], while institutional reforms in China’s standardization system are systematically reshaping the behavioral logic and strategic choices of firms engaged in standard-setting at the regulatory level [55].
Technological turbulence refers to the rate of technological changes within an industry [19]. It reflects the dynamic, complex, and unpredictable nature of the technological environment. On the one hand, high technological turbulence will accelerate product iterations and demand diversification, eroding the advantages of dominating and supporting standardization that a firm established [54,56]. On the other hand, such pressure forces firms to develop learning and adaptation capabilities, thereby contributing to the external resource integration and breakthrough innovation [57]. This not only can help firms to strengthen their standard proposals’ competitiveness and to improve their dominance in standardization processes but also enables firms to develop market-sensing capabilities and to be more efficient in identifying new standardization potentials to complement and support the technology of standard-setting leaders [19].
Institutions, as the rules of the game in a society, shape and constrain the behaviors of all organizations operating in the environment [58]. Firms need to adjust their behaviors and strategies to fit the rules, regulation and norms of regions in which they operate [59]. Following these insights, we examine a specific institutional environment feature (i.e., government-market relations, GMR) that is particularly salient for our phenomenon of standardization. GMR indicates the relative influence of the government and the market on resource allocation in a region [14,60]. High GMR suggests greater dominance of market mechanisms in economic coordination, with correspondingly reduced governmental influence [14]. In this context, firms enjoy more flexibility to dominate participants’ behaviors or to choose the standard-setting leaders they want to support. Moreover, higher GMR regions are often associated with greater information transparency. Firms can acquire abundant knowledge and industrial information through collaboration. These joint efforts enable firms to possess greater decision-making flexibility and autonomy, and to enhance the effectiveness of external knowledge integration in the standardization process [14]. However, high GMR may also cause monopolies and inefficiency. Government intervention, through antitrust policies and subsidies, stimulates R&D while helping firms build industry authority to boost standard competitiveness [61].
3. Data and Method
3.1. Sample and Data
The research setting is standardization alliance networks in the Chinese automobile industry. We focus on automobile industry for two reasons. First, the global automotive industry is undergoing significant technological changes and industrial upgrading. Participating or dominating the formulation of industrial technology standards plays a vital role in firm performance and market competition [2,7]. Especially in the fields of new energy and intelligent connected vehicles, the new standard system and dominant designs are not yet fully established. There is an urgent need for unified technical standards and a stable development environment to regulate industry competition and growth [62]. Second, the automotive industry is technology-intensive, with complex product systems and diverse technological categories. Alliance cooperation has become the preferred approach for automotive firms to engage in standard setting. Thus, alliance activities are frequent in this industry, with over half of formal standards being developed collaboratively.
The data used in this study were collected from authoritative sources to ensure comprehensiveness and reliability. Formal standard data were obtained from the China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI) China Standards Database, which provides extensive coverage of standards issued by Chinese standardization bodies since the 1970s. We downloaded all formal standards classified under “T (Vehicles)” from 2018 to 2021. The data included standard numbers, drafting organizations, and publication dates, as part of a large-scale nationally funded research project on standardization in the Chinese automotive sector (see also, e.g., Dai et al., 2018; Xu & Zeng, 2021; Feng et al., 2024 who use different cross-sections and time periods from similar data sources) [19,63,64]; Patent data were retrieved from the National Intellectual Property Information Service System, which consolidates patent information from multiple official channels, including the China National Intellectual Property Administration. We collected all patent types except design patents for the sample firms and their alliance network partners from 2013 to 2019; The GMR index was sourced from the Chinese provincial marketization index database, a widely used and academically recognized resource for measuring regional institutional development in China [14].
Data processing involved the following steps: we first identified standardization alliances by considering firms that co-drafted and submitted the same standard proposal. Based on expert input and industry practice indicating that the inter-firm cooperation on formal standards usually lasts 2–3 years (Authors’ interview with the vice-president of China National Institutes of Standardization, conducted on 28 May 2014). Therefore, we used a three-year time window of the joint drafting data from 2018 to 2020 to construct the 2019 alliance network [2]. In addition, to mitigate endogeneity concerns related to reverse causality, we lagged the dependent variable by one period (t + 1) in regression models. Accordingly, standardization capability was measured using the number of standards developed in 2020. Then, we extracted the list of vehicle manufacturers from the annual “Road Motor Vehicle Manufacturing Enterprises and Product Announcements” published by China’s Ministry of Industry and Information Technology (MIIT). A total of 88 vehicle manufacturers were embedded in the 2019 standardization alliance network. In addition, we downloaded patent data from the National Intellectual Property Information Service System. This included all patents except design patents, spanning 2013 to 2019, for these 88 manufacturers and the actors in their egocentric alliance networks.
3.2. Measures
3.2.1. Outcome Variables
Firms who are drafters for a formal standard are more capable of affecting other firms and organizations’ decisions about the preferences and technical alternatives involved in standards, and getting its technical proposal accepted [4]. Therefore, the count of published standards drafted by each firm is a relatively good proxy to measure a company’s ability to influence formal standardization [4].
Dominating standardization (DS) and supporting standardization (SS) are two important types of firms’ capability to influence technological standardization. There are also two types of drafters (chief-drafters and ordinary participants) whose influence is different for formal standard development. A chief drafter for a standard dominates the standard drafting process, coordinating and integrating all participants’ resources and efforts to draft the standard [4]. Ordinary participants typically undertake part of the standard drafting work (such as sub-module technology solution, testing, and technical review), supporting chief-drafters to develop and promote the standards [2]. Based on the different roles of firms in standards development, we assume that setting standards as chief drafters/participants can better exhibit a firm’s dominating/supporting capability in technological standardization. Therefore, we use the count of published standards drafted by each firm as a chief-drafter/participant to measure a firm’s capability to dominate/support standardization (DS/SS). Additionally, to reduce potential endogeneity from reverse causality, we lag the dependent variables by one period (t + 1) in our analysis.
3.2.2. Condition Variables
Network Technological Diversity (NTD). When embedded in a network with high technological diversity, a firm can integrate more heterogeneous technologies and knowledge, thereby improving the quality and compatibility of its technical standard proposals [34]. Consistent with prior research [65], we use the entropy index to measure the extent of technological diversification of alliance network, which can reflect the breadth of knowledge distribution across different technological domains accurately [66]. The first three-digit IPC number of patents is used to define technological classes. The entropy measure of NDT is defined as follows:
where N denotes the number of patent classes applied by the focal firm’s partners over a seven-year period (2013–2019), denotes the proportion of patents in category j relative to the total patents filed by partners.
Network Technological Proximity (NTP). A high degree of technological similarity enhances knowledge absorption efficiency, thereby reducing collaboration costs and improving the professional depth and market competitiveness of standard proposals [39]. We use the technological distance measurement proposed by Jaffe (1989) [67]. This method is widely used to calculate technological structure similarity based on patent. Following this approach, we define network technological proximity as the average patent structure similarity between the focal firm and its ego network members. This metric reflects the technological proximity within the focal firm’s ego network. The formula is as follows:
where N denotes the total number of partner firms j in the egocentric alliance network of focal firm i. (or ) represents the proportion of patents that focal firm i (or partner firm j) has applied for in technological class k over the past seven years, relative to the total number of patents applied for by the focal firm (or partner firm) during the observation period; indicates the technological proximity between focal firm i and partner firm j, while denotes the network technological proximity of the focal firm i.
Network size (NS). Firms in large alliance networks gain greater access to information and influence, thereby enhancing their standardization capability [46]. We measure network size by counting the total number of members in a focal firm’s ego network [68].
Network density (ND). Stronger inter-node ties enhance trust and consensus-building, thereby improving a firm’s capacity to orchestrate network resources for dominating standard setting [49]. It reflects the closeness of relationships among nodes in the focal firm’s ego network. We calculate network density as the ratio of the actual number of connections to the maximum possible number of connections in the ego network [69].
Technological Turbulence (TT). While technological turbulence can undermine established standard-based advantages, it primarily enhances standardization capability by pressuring firms to learn and innovate, thereby boosting the competitiveness of their proposals and market sensing abilities [57]. We follow Dess et al.’s approach for measuring technological environmental turbulence [70]. Specifically, we use the total number of patents in the focal firm’s ego network for each of the past seven years (from year t − 7 to t) as the dependent variable, and the numbers 1 to 7 as the independent variable in a regression. We then divide the standard deviation of the regression coefficients by the mean of the annual patent counts over the seven-year period. This value approximates the level of technological environment turbulence for the focal firm in year t.
Government-market relationship (GMR). Following Wang et al. (2024), The GMR score is a weighted synthesis of three indicators: the proportion of economic resources allocated by the market, the reduction in government intervention in firms, and the shrinking size of government [14]. A higher score indicates less government intervention and stronger market influence, which enhances technological standardization capability primarily by empowering firms with greater decision-making autonomy and more effective knowledge integration through market mechanisms.
3.3. Method
This study adopts fuzzy-set Qualitative Comparative Analysis (fsQCA). fsQCA is well-suited to handle the ambiguity and complexity in causal relationships [71]. It effectively examines how multiple conditions combine to influence technology standardization [72]. Compared to crisp-set QCA (csQCA), fsQCA allows variables to have continuous membership scores, better capturing fuzzy boundaries and gradual changes in reality [73]. Moreover, unlike traditional quantitative methods, fsQCA excels at identifying multiple causal pathways and heterogeneous causal mechanisms. Therefore, fsQCA is an appropriate approach for investigating the complex causality between standardization alliance networks and firm standardization capabilities.
4. Results
4.1. Calibration
Calibration is the first step in fsQCA analysis. It converts raw variables into values of fuzzy set membership ranging from 0 to 1. Compared to indirect calibration, direct calibration is more straightforward and transparent. It also better reflects the actual distribution of the data’s membership scores. Therefore, this study uses direct calibration to process the sample data [74]. Given the absence of established calibration criteria for this research question and the highly skewed distribution of the sample, the 95th, 50th, and 5th percentiles of each variable are selected as calibration anchors [75], representing full membership, crossover point, and full non-membership, respectively. Furthermore, because many cases had membership scores exactly at 0.5, we adjusted these scores by subtracting 0.001 to avoid ambiguity in case classification [74]. The specific calibration anchors for conditions and outcome variables are shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Calibration of condition and outcome variables.
4.2. Analysis of Necessary Conditions
Before conducting the analysis of sufficient conditions, it is important to test whether each single causal condition is necessary for firms to achieve a high level of technological standardization capability [75]. The academic consensus is that a condition with consistency above 0.9 can be considered necessary. As shown in Table 2, the consistency and coverage of all conditions are below the recommended threshold of 0.9 [73,76], indicating that no single condition fully explains the outcome variables. In summary, there is no necessary condition for the cultivation of dominating or supporting standardization capability.

Table 2.
Necessity of the conditions relative to the high-tech standardization capability.
4.3. Analysis of Sufficient Conditions
Sufficiency analysis is based on data calibration and necessity analysis, aiming to identify whether certain conditions or combinations of conditions are sufficient to produce the outcome. In this study, we distinguish technological standardization capability into dominating and supporting capabilities and analyze the configurations that lead to high levels of each separately. Based on existing research, we set the raw consistency threshold at 0.8, the PRI consistency threshold at 0.75 [77], and the case frequency value at 1 or 2 [73,74]. Compared with the number of standards that firms participate in supporting, the number of standards where firms act as leaders is relatively small; indeed, many firms do not dominate any standard-setting outcomes in the short term. Therefore, to better reflect the configurations, and while meeting the requirement of at least 75% of cases [77,78], we set the case frequency value to 2 for dominating capability and 1 for supporting capability. The results of fsQCA 4.1 show three types of solutions: complex, parsimonious, and intermediate solutions. We selected the intermediate solution to interpret the final configurations because it maintains explanatory power while offering a more concise and interpretable set of configurations, which helps to highlight the core causal conditions.
4.3.1. Sufficient Conditions Analysis of Dominating Standardization
The key to sufficiency analysis is assessing the consistency and coverage between conditions and the outcome. As shown in Table 3, there are two driving paths (S1 and S2) for high level dominating standardization, with an overall consistency of 0.932, indicating a high level of reliability. Further, the overall coverage of this study (0.657) indicates that 65.7% of cases with high level capability of dominating standardization exhibit these two configurations of causal conditions. Therefore, these two configurations were sufficient for achieving a high level of dominating standardization capability.

Table 3.
Configurations of high-level dominating standardization.
Configuration S1 shows that when external technological pressure is low, firms embedded in standardization alliance networks with large-scale, non-redundant, and highly technological diversity features, can effectively foster their capability to dominate standardization. Network size (network organization feature) is the core condition in this configuration. Although network technological diversity, ~network density and ~technological turbulence act as peripheral conditions, they also play a supporting role in fostering high-level capability of dominating standardization within large-scale alliance networks. Therefore, we named this configuration “network organization-driven with network technology and environment support”.
Under this configuration, firms gain access to abundant external resources from diverse fields and organizations. By maintaining extensive alliance partnerships, firms can integrate and coordinate heterogeneous and complementary resources within the network. This enables them to develop more comprehensive and efficient technological standard solutions. The process not only strengthens the internal completeness of the advocated standard but also significantly improves the standards’ compatibility, facilitating effective alignment and interoperability with other technological systems. As a result, firms can enjoy an advantage in dominating standardization. This pathway explains about 54.8% of the cases with high-level capability of dominating standardization, with approximately 36.2% of cases explained exclusively by this pathway.
Configuration S2 shows that when the regional government intervention is strong and the technological environment is turbulent, embedded in small-scale networks with high network density, low technological proximity and diversity is also beneficial for dominating standardization. In this configuration, “~network technological proximity” and “~GMR” (institutional environment feature) are the core driven conditions. Network density and technological turbulence are the peripheral conditions. Low technological similarity between a firm and its network partners is more conducive to acquiring complementary external knowledge resources for dominating standardization. In low GMR regions characterized by strong government intervention, the benefits of low network technological proximity for firms dominating standardization are enhanced. Because government institutions, considering long-term industrial development, tend to favor and recommend firms capable of integrating and balancing the technologies and interests of diverse industry stakeholders to serve as lead editors of formal standards. Network density (network organization feature) acts as a supporting condition, which plays an important role in dominating standardization through affecting the network resource integration and knowledge exchange efficiency. This configuration is named “network technology and institutional environment co-driven with network organization support”.
4.3.2. Sufficient Conditions Analysis of Supporting Standardization
As shown in Table 4, there are three configurations that can cultivate high-level supporting standardization capability. Among them, configurations H1a and H1b share the same core condition, forming a second-order equivalent configuration [74]. Consequently, these three configurations can be grouped into two distinct cultivation pathways (H1 and H2). All three configurations demonstrate consistency scores exceeding 0.8. The overall consistency is 0.951, and the overall coverage is 0.672, indicating strong consistency and robust explanatory power in fostering high levels of supporting standardization capability.

Table 4.
Configurations of high-level supporting standardization.
Configuration H1 consists of two sub-configurations, H1a and H1b. As shown in Table 4, these two configurations share the same core conditions but differ in the technological and institutional environments. This suggests that regardless of whether the environment has strong government intervention or a relatively stable technological change, firms can effectively enhance their capability to support standardization by collaborating broadly with technology-proximate partners and building large-scale, non-redundant networks. Network technological proximity (network technology feature) and network size (network organization feature) are the core driving factors for cultivating high levels of supporting standardization capability. Hence, these configurations are referred to as the “network technology and network organization co-driven with environment support”.
Under this configuration, firms engaging in large-scale and technologically proximate alliance networks, can effectively enhance their capability to support and refine standard proposal advocated by other standard-setting leaders through in-depth development and optimization of technical solutions in their existing domains. Configuration H1a and H1b explain approximately 53.5% and 46.6% of the cases with high supporting standardization, respectively. Among them, about 0.6% of the cases are explained only by H1a, while about 1.7% are explained only by H1b.
Configuration H2 is similar to S1, which indicates that in a stable technological environment, firms maintaining numerous alliance partnerships with diverse technology and occupying structural holes can gain advantages in supporting standardization. The only difference between them is that “~network density” and “~technological turbulence” are the core conditions of H2, but peripheral conditions in S1. But whether in S1 and H2, network size serves as a core condition and network technological diversity’s role is peripheral. Large-scale alliance networks with high network technological diversity can accelerate knowledge convergence and constitute innovation synergies, offering more standardization opportunities to integrate their technologies into mainstream innovation ecosystems. Therefore, configuration H2 is named “network organization and technological environment co-driven with network technology-supported”. This configuration explains about 63.2% of cases with high level of supporting standardization, with approximately 12% explained exclusively by this pathway.
4.4. Robustness Test
We analyzed the robustness of our fsQCA results by independently adjusting the consistency threshold, the PRI threshold and the calibration anchor [79,80]. First, we raised the consistency threshold from 0.80 to 0.95. The results showed no change in the configurations of the two types of technological standardization capabilities. Second, we adjusted the PRI threshold. For the dominating standardization, the PRI threshold was increased from 0.75 to 0.85. The resulting configuration of dominating standardization was a subset of the original configuration. For the supporting capability, the PRI threshold was lowered from 0.75 to 0.70. The new configuration included the original one. Although even small changes in parameters can sometimes cause noticeable differences in the final solutions [81], our tests revealed no significant deviations from the initial results. Finally, we recalibrated the thresholds to (0.9, 0.5, 0.1); the results are presented in Table 5 and Table 6. The core conditions for both dominating and supporting standardization remain unchanged. However, a second-order equivalent configuration (H2b) emerges within the original path H2. This not only confirms the stability of the core causal relationships under different calibration schemes but also enriches the set of alternative pathways, thereby strengthening the robustness of the original findings. Therefore, we concluded that our findings were robust.

Table 5.
Configurations of high-level dominating standardization after changing calibration threshold.

Table 6.
Configurations of high-level supporting standardization after changing calibration threshold.
5. Conclusions and Implications
5.1. Conclusions
Using data from 88 vehicle manufacturers involved in standardization alliances, this study applies fsQCA to explore how TOE-based alliance network features shape firms’ capabilities to dominate and support standardization. The research results are as follows:
First, no single condition variable is necessary for cultivating high-level technological standardization capabilities. The development of both dominating and supporting standardization results from the interplay of the Technological, Organizational, and Environmental (TOE) factors in an alliance network. The two configurations (S1, S2) for dominating standardization, and the two configurations (H1, H2) for supporting standardization, all draw on factors from the three TOE dimensions. Although factors in each configuration can play either a core or peripheral role, the effective pathway for firms to enhance standardization capability lies in the synergistic interaction of all three aspects.
Second, the cultivation paths for dominating and supporting capabilities share commonalities. There are similar configurations (S1 and H2) of alliance network TOE features that can help firms to improve both dominating and supporting standardization capabilities. In a stable technological environment, large-scale alliance networks, combined with low density and high technological diversity, can offer firms abundant and diverse resource sources, efficient and exclusive resource acquisition ways, as well as strong resource control and coordination capabilities. These advantages not only can benefit dominating standardization by facilitating complementary resource integration and value chain coordination but also contribute to supporting standardization through efficiently identifying standardization opportunities and cooperating with external stakeholders.
Third, the configurations of alliance networks for developing dominating and supporting capabilities also exhibits significant distinctions. Supporting standardization is highly dependent on network scale, firms embedded in large-scale alliance networks with high technological diversity or proximity both enjoy advantages in supporting standardization (see H1 and H2 in Table 4). Dominating standardization shows relatively low dependence on network scale. As the technical environment transitions from stable to turbulent, often accompanied by strong government intervention, market rules and technical directions tend to become uncertain. Firms can enhance standardization dominance by shifting its strategic focus from extensive exploration to focused collaboration. Maintaining small-scale trust networks with low technological proximity (see S2 in Table 3) can foster the pooling of complementary resources to improve the solution’s compatibility and completeness. It also can prevent firms within the same field from collusive monopoly, thereby increasing the government’s approval rate for the standards firm advocates.
Finally, the cultivation of firms’ technological standardization capabilities is influenced by multiple factors, with an asymmetric impact of these factors on the two types of capabilities—dominating and supporting. Under specific conditions, the functional substitution of technological, organizational, and environmental elements enables the enhancement of standardization capabilities through different configurations. Specifically: first, the technological and institutional environments can act as functional substitutes within a specific network structure (~ND-NTP-NS), leading to an equivalent improvement in supporting standardization (H1a and H1b). Second, markedly different configurations of antecedent conditions (S1 and S2) demonstrate equifinality, both contributing to high-level dominating standardization. Third, nearly identical configurations may yield asymmetric outcomes—enhancing either dominating or supporting standardization—depending on the variation in a few core conditions (S1 and H2). These findings confirm that the pathways to strengthening standardization capabilities are multiple and asymmetrical, rather than simple mirror opposites.
5.2. Theoretical and Practical Implications
This study has two important implications for theory. First, this study contributes to an understanding of the role of alliance network in the standard-setting process, by proposing a TOE-based alliance network management framework for developing firm capability to influence technological standardization. Prior research on standardization collaboration mainly explores the effects of alliance network structure and composition features on firm standardization capability separately, overlooking the interactions among these features on the results. This study takes a integrated perspective and innovatively introduces the TOE framework to examine how alliance network affects a firm’s ability to influence technological standardization. Specifically, our study shows that a single-dimensional network features cannot always promote standardization; a firm’s standardization advantage is the combined result of three-dimensional TOE network features. The findings expand and refine the research on the causes of firm standardization competitiveness and represent a significant contribution in this direction.
Second, this study contributes to the literature of standardization by highlighting the importance of distinguishing between two types of capabilities of influencing technological standardization. Previous studies emphasize that firms differ in their capability to influence standardization and assume that firms that participated in standardization strive to be dominators [7,19,82]. However, it is complicated and unnecessary for firms to dominate all standards related to their technology and products in practice, firms also can gain significant private benefits from standard development by supporting and assisting their preferred technologies proposed by others. The current study argues that firms also differ in the type of capabilities to influence standardization and distinguishing between dominating standardization and supporting standardization is essential because the network configurations for fostering them share both similarities and significant differences. Thus, the findings will hopefully help scholars to further advance our understanding of the firm’s standardization capability.
In addition, the results of this study also have three implications for practice. For managers, the findings provide theoretical support in making decisions about the inter-firm alliance networking strategy to promote dominating standardization and supporting standardization. When firms strive to develop strong capabilities of dominating standardization and supporting standardization simultaneously, they should implement a “network organization and technological environment co-driven with network technology-supported” strategy. Firms in a relatively stable technological environment are encouraged to broadly build and maintain partnerships with organizations across different industries and technological domains. Taking the traditional automobile industry as an example, its internal combustion engine manufacturing, motor and battery technology and other fields have entered a mature stage of development. In this context, traditional manufacturers should focus their alliance strategies on consolidating existing competitive advantages. Large-scale networks with high technological diversity are helpful for firms to participate in or dominate the formulation of universal technical specifications and interface standards, thereby strengthening their technical support role and system influence in standardization of these fields.
When the prioritized objective is to dominate standard-setting, they should implement a “network technology and institutional environment co-driven with network organization support” strategy. In an institutional environment with strong government intervention, firms can also connect with a small number of high-quality partners who have low technological overlap. Electric vehicle manufacturers serve as a typical case where core technological pathways remain unconsolidated—with fierce competition persisting in areas like solid-state/semi-solid-state batteries and intelligent driving solutions—combined with strong government intervention, including subsidies, carbon emission quotas, and mandatory charging infrastructure standards. Accordingly, EV producers may concentrate on forming a dense, small-scale alliance with a select group of core partners who are technologically complementary and share a strategic vision. Such a structure enables the integration of key complementary resources and facilitates agile adaptation to policy directions, thereby enhancing the compatibility and competitiveness of their proposed standards and securing a stronger positioning in standardization activities. However, strong government intervention may restrict firms’ autonomy in standard-setting, cause inefficient industrial coordination, and result in reduced innovation [83]. Therefore, firms should focus on integrating network resources to enhance their standard proposals’ quality and competitiveness, rather than engaging in tick-the-box collaborations merely to pass government reviews. To ensure the industry’s sustainable development, the government should act as a supportive service provider, not a strict controller.
Alternatively, if firms only want to achieve a high level of supporting standardization capability, managers then also can pay attention to “network technology and network organization co-driven with environment support” strategy. Firms are encouraged to construct large-scale alliance networks with high technological proximity and low density. This network structure is suitable for both electric vehicle manufacturers and traditional automobile manufacturers. Maintaining a large number of non-redundant alliance ties with partners who have similar technological trajectories and standardization objectives, can strengthen firms’ core technologies and leverage their role as module “experts” to better support and follow dominant firms in refining their standard solutions.
5.3. Limitations and Future Research
Although this paper fills some research gaps, there are still limitations that require further investigation. First, we only analyzed a few important features within the TOE framework that influence technological standardization capabilities. However, other antecedent conditions, such as tie strength, network heterogeneity, institutional/organization proximity and so on., may also impact the cultivation of technological standardization capabilities. Future research could consider using different condition variables for a more comprehensive analysis.
Second, our sample was based solely on Chinese automobile manufacturers, which may affect the generalizability of the findings. In China, the unique social “relationship” culture will affect the operating model of alliances activities. This informal trust relationship is often more important than formal contracts. In addition, China’s institutional environment presents a typical collaborative governance mechanism between the government and the market. It is normal for the government to carry out macro-control through industrial policies and other means in China. These unique cultural and institutional factors may result in the low applicability of our research results to different industries in other countries, making it difficult to promote our empirical conclusions. Cross-cultural and cross-industry comparative research can be conducted in the future, which will not only verify the boundaries of this theory but also help to construct a more general theory of technology standardization strategies.
Finally, the fsQCA method employed in this study only allows for a static analysis of the various paths to achieving high levels of dominating and supporting standardization. However, the cultivation of technological standardization capabilities is a dynamic process. The characteristics of alliance networks (e.g., technological diversity, network size) and their effective configurations are not static but continually evolve alongside changes in the technological environment and institutional setting. Subsequent research can collect panel data and utilize a qualitative comparative analysis (QCA) approach suitable for multiple periods to explore how the trajectory changes in multiple key factors influence the development trajectory of technological standardization capabilities over time.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.W.; methodology, J.W.; software, D.T. and H.W.; validation, D.T., H.W. and Y.G.; formal analysis, J.W. and D.T.; investigation, D.T.; resources, J.W. and H.W.; data curation, D.T.; writing—original draft preparation, J.W.; writing—review and editing, J.W.; visualization, H.W. and D.T. and Y.G.; supervision, Y.G. and H.W.; project administration, J.W.; funding acquisition, J.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 72002070; 71932005; 72102236); the National Social Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 22BGL037) and the Excellent Young Scientists Fund of the Education Department of Hunan Province, China (Grant No. 23B0606).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data supporting this study’s findings are available upon request from the corresponding author, upon reasonable request.
Acknowledgments
During the preparation of this manuscript, the authors used DeepSeek-R1-0528 for the purposes of polishing the language and improving the readability. The authors have reviewed and edited the output and take full responsibility for the content of this publication.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| TOE | Technology–Organization–Environment |
| fsQCA | Fuzzy-Set Qualitative Comparative Analysis |
| GMR | government-market relations |
References
- Blind, K.; Mangelsdorf, A. Motives to standardize, empirical evidence from Germany. Technovation 2016, 48–49, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, J.; Li, J.; Zhou, Q.; Zeng, D.; Harms, R. How firms support formal standardization: The role of alliance portfolio and internal technological diversity. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2023, 196, 122854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, J.; Venkatraman, N. Joint venture formations and stock market reactions, an assessment in the information technology sector. Acad. Manag. J. 1991, 34, 869–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, J.; Qualls, W.J.; Zeng, D. Standardization Alliance Networks, Standard-setting Influence, and New Product Outcomes. J. Prod. Innov. Manag. 2020, 37, 138–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nambisan, S. Industry technical committees, technological distance, and innovation performance. Res. Policy 2013, 42, 928–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Axelrod, R.; Mitchell, W.; Thomas, R.E.; Bennett, D.S.; Bruderer, E. Coalition formation in standard-setting alliances. Manag. Sci. 1995, 41, 1493–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leiponen, A.E. Competing through cooperation, the organization of standard setting in wireless telecommunications. Manag. Sci. 2008, 54, 1904–1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakke, P.; Blind, K.; Ramel, F. The impact of participation within formal standardization on firm performance. J. Product. Anal. 2016, 45, 317–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delcamp, H.; Leiponen, A. Innovating standards through informal consortia, The case of wireless telecommunications. Int. J. Ind. Organ. 2014, 36, 36–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gawer, A.; Cusumano, M.A. Industry platforms and ecosystem innovation. J. Prod. Innov. Manag. 2014, 31, 417–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; de Vries, H.J. Effects of participation in standardization on firm performance from a network perspective: Evidence from China. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2022, 175, 121376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Gong, X. Superior position equal to greater influence? The moderating role of technological complexity. J. Manuf. Technol. Manag. 2020, 31, 1457–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dokko, G.; Rosenkopf, L. Social capital for hire? Mobility of technical professionals and firm influence in wireless standards committees. Organ. Sci. 2010, 21, 677–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zeng, D.; Li, J.; Wen, J. Does engagement in international alliances affect a firm’s influence on domestic standard-setting? The moderating role of government–market relations. Technol. Anal. Strateg. Manag. 2024, 36, 4657–4671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Li, S.; Shan, J.; Xu, Q. Can standard cooperation enhance enterprises’ standardization capability: The moderating role of technological capability. J. Eng. Technol. Manag. 2024, 73, 101828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodan, S.; Galunic, C. More than network structure: How knowledge heterogeneity influences managerial performance and innovativeness. Strateg. Manag. J. 2004, 25, 541–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Runge, S.; Schwens, C.; Schulz, M. The invention performance implications of coopetition: How technological, geographical, and product market overlaps shape learning and competitive tension in R&D alliances. Strateg. Manag. J. 2022, 43, 266–294. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, J.; Qualls, W.J.; Zeng, D. To explore or exploit: The influence of inter-firm R&D network diversity and structural holes on innovation outcomes. Technovation 2021, 100, 102178. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, H.; Zeng, D.; Qualls, W.J.; Li, J. Do social ties matter for the emergence of dominant design? The moderating roles of technological turbulence and IRP enforcement. J. Eng. Technol. Manag. 2018, 47, 96–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.; Peng, Y.; Shi, C.; Liu, S.; Liu, H. Research on the driving paths and evolution of digital innovation in intelligent connected vehicle enterprises—A configurational analysis based on dynamic fsqca. Sustainability 2024, 16, 10545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carnabuci, G.; Operti, E. Where do firms’ recombinant capabilities come from? Intraorganizational networks, knowledge, and firms’ ability to innovate through technological recombination. Strateg. Manag. J. 2013, 34, 1591–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tornatzky, L.G.; Fleischer, M. The Processes of Technological Innovation; Lexington Book: Lanham, MD, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Li, X. Digitization policy combination analysis based on technology-organization-environment framework. Sci. Res. 2022, 40, 841–851. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamin, M.; Abdul Adis, A.A. The impact of TOE framework on E-commerce advantage among small medium enterprise (SME’s) digital channel in Malaysia. J. Distrib. Sci. 2022, 20, 33–46. [Google Scholar]
- Religia, Y.; Ekhsan, M.; Huda, M.; Fitriyanto, A.D. TOE framework for e-commerce adoption by MSMEs during the Covid-19 pandemic: Can trust moderate? Appl. Inf. Syst. Manag. 2023, 6, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basloom, R.S.; Mohamad, M.H.S.; Auzair, S.M. Applicability of public sector reform initiatives of the Yemeni government from the integrated TOE-DOI framework. Int. J. Innov. Stud. 2022, 6, 286–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jais, R.; Ngah, A.H.; Rahi, S.; Rashid, A.; Ahmad, S.Z.; Mokhlis, S. Chatbots adoption intention in public sector in Malaysia from the perspective of TOE framework. The moderated and mediation model. J. Sci. Technol. Policy Manag. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Liu, X.; Yang, J. TOE Configuration analysis of smart city construction in China under the concept of sustainable Development. Sustainability 2024, 16, 10708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phelps, C.C. A longitudinal study of the influence of alliance network structure and composition on firm exploratory innovation. Acad. Manag. J. 2010, 53, 890–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Wang, W. Does technological proximity accelerate innovation speed in R&D collaboration? The evidence of rapid vaccine R&D for fighting the COVID-19 pandemic. Int. J. Technol. Manag. 2024, 94, 295–318. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Xiong, W.; Hu, X. The geography of intercity technological proximity: Evidence from China. Int. J. Urban Sci. 2023, 27, 355–370. [Google Scholar]
- Kobarg, S.; Stumpf-Wollersheim, J.; Welpe, I.M. More is not always better: Effects of collaboration breadth and depth on radical and incremental innovation performance at the project level. Res. Policy 2019, 48, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, B.; Ye, J.; Feng, Y.; Cai, Z. Explicit and tacit synergies between alliance firms and radical innovation: The moderating roles of interfirm technological diversity and environmental technological dynamism. RD Manag. 2020, 50, 432–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penney, C.R.; Combs, J.G. A transaction cost perspective of alliance portfolio diversity. J. Manag. Stud. 2020, 57, 1073–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranganathan, R.; Ghosh, A.; Rosenkopf, L. Competition–cooperation interplay during multifirm technology coordination: The effect of firm heterogeneity on conflict and consensus in a technology standards organization. Strateg. Manag. J. 2018, 39, 3193–3221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardito, L.; Peruffo, E.; Natalicchio, A. The relationships between the internationalization of alliance portfolio diversity, individual incentives, and innovation ambidexterity: A microfoundational approach. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2019, 148, 119714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.; Kirkpatrick-Husk, K.; Madhavan, R. Diversity in alliance portfolios and performance outcomes: A meta-analysis. J. Manag. 2017, 43, 1472–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Noya, A.; García-Canal, E. Innovation performance feedback and technological alliance portfolio diversity: The moderating role of firms’ R&D intensity. Res. Policy 2021, 50, 104321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, J.C.; Yan, Y. Technological proximity and recombinative innovation in the alternative energy field. Res. Policy 2016, 45, 1460–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knoben, J.; Oerlemans, L.A. Proximity and inter-organizational collaboration: A literature review. Int. J. Manag. Rev. 2006, 8, 71–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buffa, F.; Beritelli, P.; Martini, U. Project networks and the reputation network in a community destination: Proof of the missing link. J. Destin. Mark. Manag. 2019, 11, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schildt, H.; Keil, T.; Maula, M. The temporal effects of relative and firm-level absorptive capacity on interorganizational learning. Strateg. Manag. J. 2012, 33, 1154–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nooteboom, B.; Van Haverbeke, W.; Duysters, G.; Gilsing, V.; Van den Oord, A. Optimal cognitive distance and absorptive capacity. Res. Policy 2007, 36, 1016–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afuah, A. Are network effects really all about size? The role of structure and conduct. Strateg. Manag. J. 2013, 34, 257–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Sun, S.; Xu, H.; Zhao, S.; Chen, Y. Enterprises’ network structure and their technology standardization capability in Industry 4.0. Syst. Res. Behav. Sci. 2020, 37, 749–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.H. The effects of innovation alliance on network structure and density of cluster. Expert Syst. Appl. 2011, 38, 299–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koka, B.R.; Prescott, J.E. Designing alliance networks: The influence of network position, environmental change, and strategy on firm performance. Strateg. Manag. J. 2008, 29, 639–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzola, E.; Perrone, G.; Handfield, R. Change is good, but not too much: Dynamic positioning in the interfirm network and new product development. J. Prod. Innov. Manag. 2018, 35, 960–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.Z. The Relationship Between Multi-Dimension Propinquity, Network Structure and Technology Standardization; Hunan University: Changsha, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, J.L.; Fang, S.C.; Fang, S.R.; Tsai, F.S. Network embeddedness and technology transfer performance in R&D consortia in Taiwan. Technovation 2009, 29, 763–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Chen, Y.; Wang, H. Overseas Resource Integration, Global Network Embeddedness Path and Knowledge Spillover. Stud. Sci. Sci. 2019, 37, 679–688. [Google Scholar]
- Burt, R.S. Structural Holes: The Social Structure of Competition; Harvard University Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Ng, P.M.; Lit, K.K.; Cheung, C.T. Remote work as a new normal? The technology-organization-environment (TOE) context. Technol. Soc. 2022, 70, 102022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huo, B.; Wang, B.; Li, Z. How to deal with technological turbulence for improving innovation performance. Technol. Anal. Strateg. Manag. 2024, 36, 549–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Development and Reform Commission; State Administration for Market Regulation. Outline for National Standardization Development. 2021. Available online: http://www.gov.cn/zhengce/2021-10/10/content_5641727.htm (accessed on 20 October 2025).
- De Leeuw, T.; Gilsing, V.; Duysters, G. Greater adaptivity or greater control? Adaptation of IOR portfolios in response to technological change. Res. Policy 2019, 48, 1586–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efrat, K.; Shoham, A. Born global firms: The differences between their short-and long-term performance drivers. J. World Bus. 2012, 47, 675–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- North, D.C. Institutions, Institutional Change and Economic Performance; Cambridge University: Cambridge, UK, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Krammer, S.M.S. Human resource policies and firm innovation: The moderating effects of economic and institutional context. Technovation 2022, 110, 102366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, G.; Wang, X.L.; Ma, G.R. Contribution of Marketization to China’s Economic Growth. Econ. Res. J. 2011, 46, 4–16. [Google Scholar]
- Colonnelli, E.; Li, B.; Liu, E. Investing with the government: A field experiment in China. J. Political Econ. 2024, 132, 248–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Zeng, D.; Zhang, J.; Dai, H. How tie strength in alliance network affects the emergence of dominant design: The mediating effects of exploration and exploitation innovation. Technol. Anal. Strateg. Manag. 2022, 34, 112–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Zeng, D. When does the diverse partnership of R&D alliances promote new product development? The contingent effect of the knowledge base. Technol. Soc. 2021, 65, 101590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, K.; Karreman, B.; Zeng, D.; Pennings, E. R&D collaboration, social coordination, and standardization: Evidence from the Chinese automotive industry. J. Technol. Transf. 2024, 49, 158–190. [Google Scholar]
- Bolli, T.; Seliger, F.; Woerter, M. Technological diversity, uncertainty and innovation performance. Appl. Econ. 2020, 52, 1831–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eagle, N.; Macy, M.; Claxton, R. Network diversity and economic development. Science 2010, 328, 1029–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaffe, A.B. Characterizing the “technological position” of firms, with application to quantifying technological opportunity and research spillovers. Res. Policy 1989, 18, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borgatti, S.P.; Everett, M.G.; Johnson, J.C. Centrality. In Analyzing Social Networks; SAGE Publications Ltd.: London, UK, 2013; pp. 189–208. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, S.; Zeng, D.; Zhang, L.; Chen, W. A study of network relationship, technology diversity and technology standardization capability of enterprises. Sci. Res. Manag. 2017, 38, 12–20. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Dess, G.G.; Beard, D.W. Dimensions of organizational task environments. Adm. Sci. Q. 1984, 29, 52–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Sahoo, S.; Ali, F.; Cobanoglu, C. Rise of fsQCA in tourism and hospitality research: A systematic literature review. Int. J. Contemp. Hosp. Manag. 2024, 36, 2165–2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urueña, A.; EArenas, Á.; Hidalgo, A. Understanding workers’ adoption of productivity mobile applications: A fuzzy set qualitative comparative analysis (fsQCA). Econ. Res. -Ekon. Istraživanja 2018, 31, 967–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragin, C.C. Redesigning Social Inquiry: Fuzzy Sets and Beyond; University of Chicago Press: Chicago, IL, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Fiss, P.C. Building better causal theories: A fuzzy set approach to typologies in organization research. Acad. Manag. J. 2011, 54, 393–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, S.; Yao, C.; Zhang, D. How to promote green innovation of high-pollution firms? A fuzzy-set QCA approach based on the TOE framework. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2025, 27, 4911–4935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, M.R.; Schulze-Bentrop, C.; Paunescu, M. Mapping the institutional capital of high-tech firms: A fuzzy-set analysis of capitalist variety and export performance. J. Int. Bus. Stud. 2010, 41, 246–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Kim, P.H. One size does not fit all: Strategy configurations, complex environments, and new venture performance in emerging economies. J. Bus. Res. 2021, 124, 272–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greckhamer, T.; Furnari, S.; Fiss, P.C.; Aguilera, R.V. Studying configurations with qualitative comparative analysis: Best practices in strategy and organization research. Strateg. Organ. 2018, 16, 482–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomann, E.; Maggetti, M. Designing research with qualitative comparative analysis (QCA): Approaches, challenges, and tools. Sociol. Methods Res. 2020, 49, 356–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gligor, D.M.; Golgeci, I.; Rego, C.; Russo, I.; Bozkurt, S.; Pohlen, T.; Hiatt, B.; Garg, V. Examining the use of fsQCA in B2B marketing research: Benefits, current state and agenda for future research. J. Bus. Ind. Mark. 2022, 37, 1542–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, G.H.; Ferreira, L.T.; Miranda, S.G. Green buying behavior and the theory of consumption values: A fuzzy-set approach. J. Bus. Res. 2016, 69, 1484–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van de Kaa, G.; Janssen, M.; Rezaei, J. Standards battles for business-to-government data exchange: Identifying success factors for standard dominance using the Best Worst Method. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2018, 137, 182–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howell, S.T. Government intervention in innovation. Annu. Rev. Financ. Econ. 2024, 16, 367–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).