Innovative Design of PLA Sandbag–Fiber Mesh Composite Wind Fences and Synergistic Windbreak Performance
Abstract
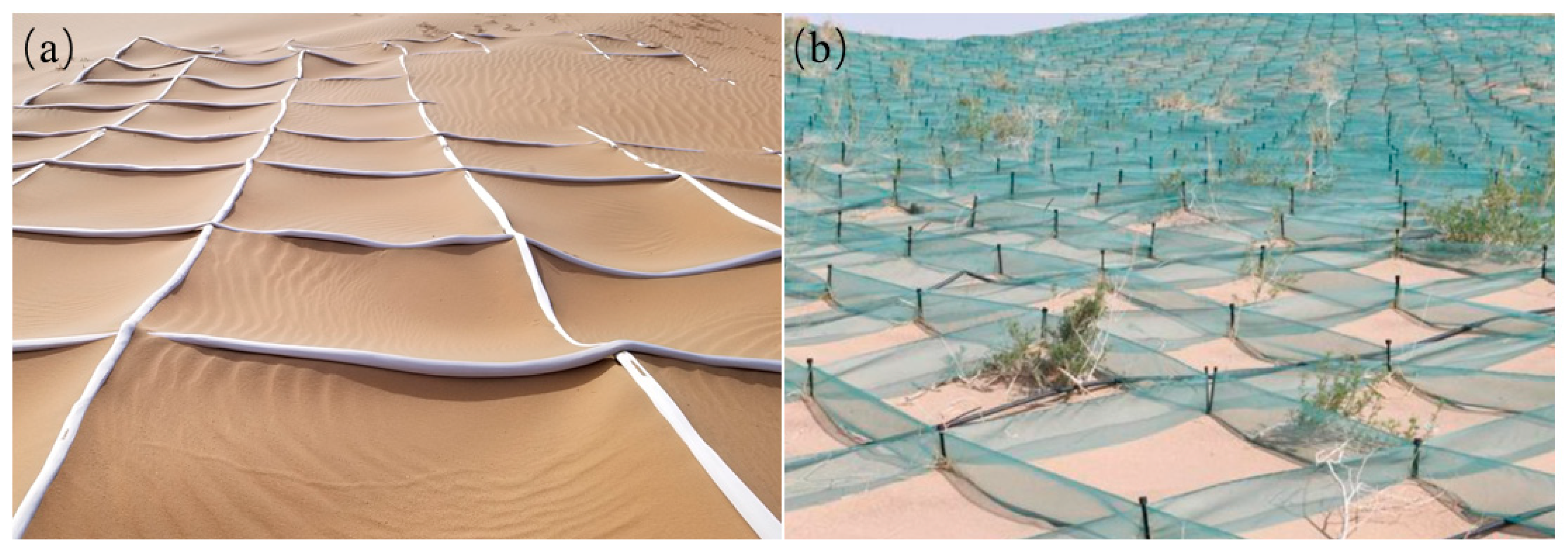
1. Introduction
2. Research Methodology
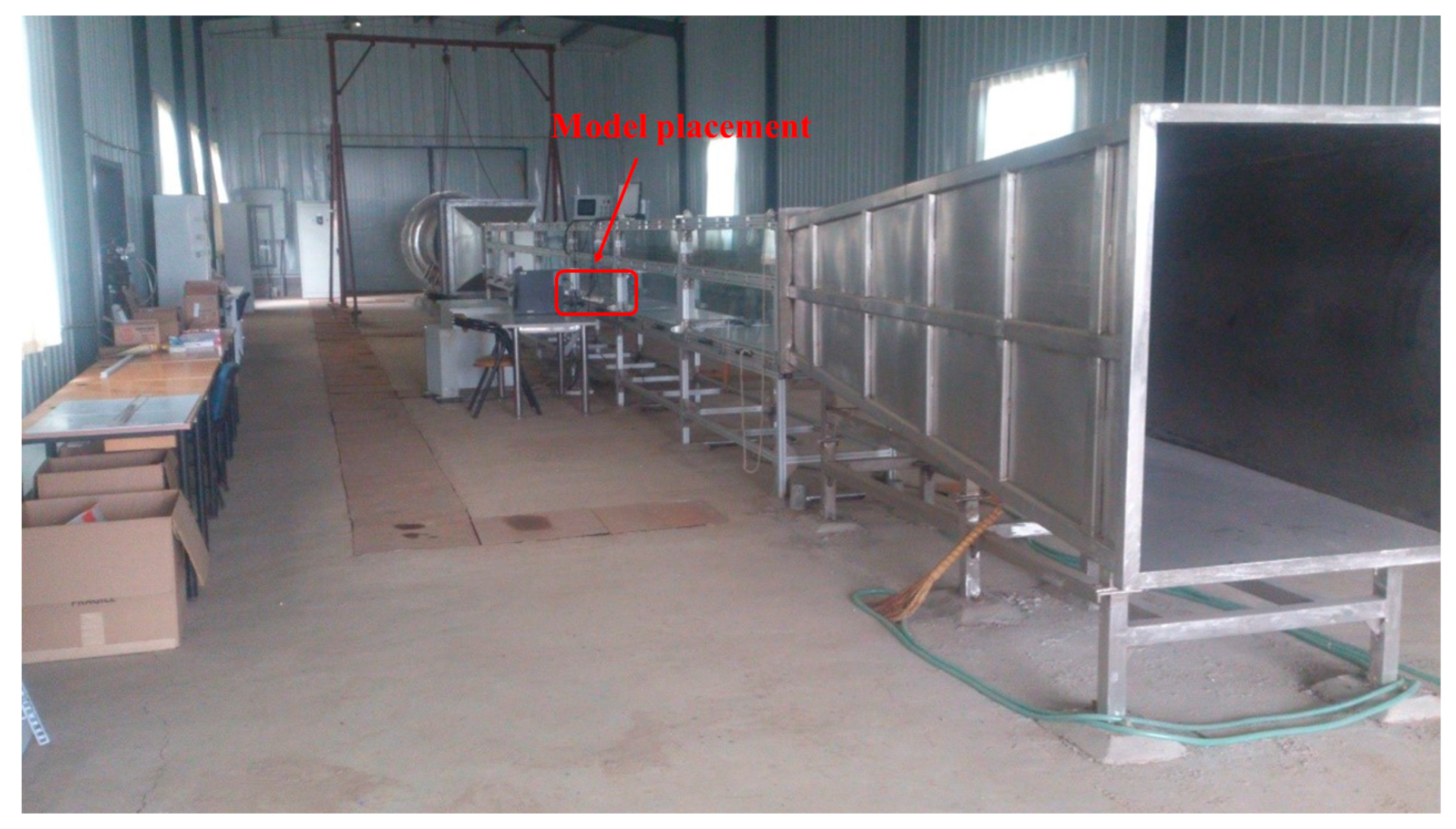
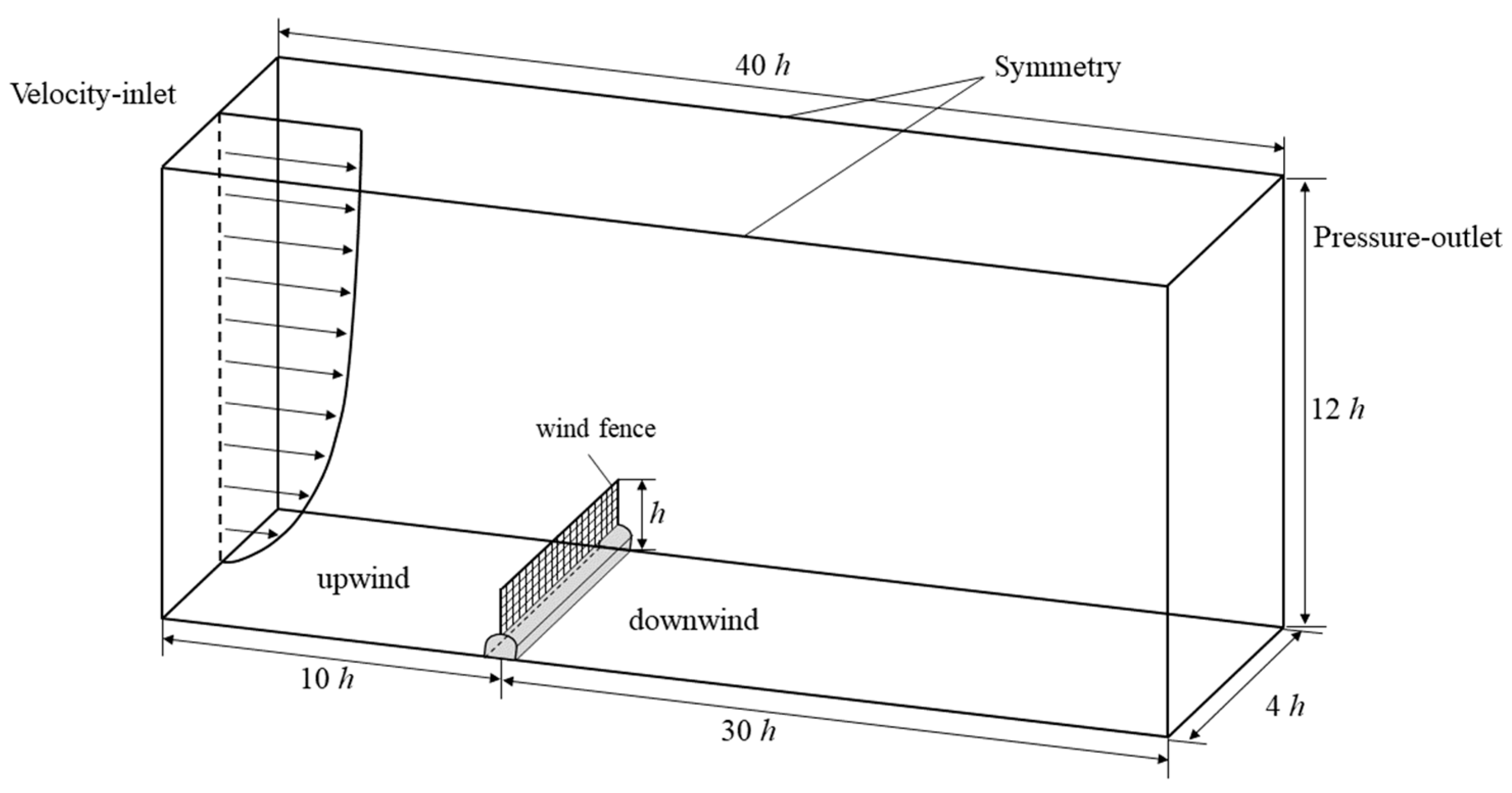
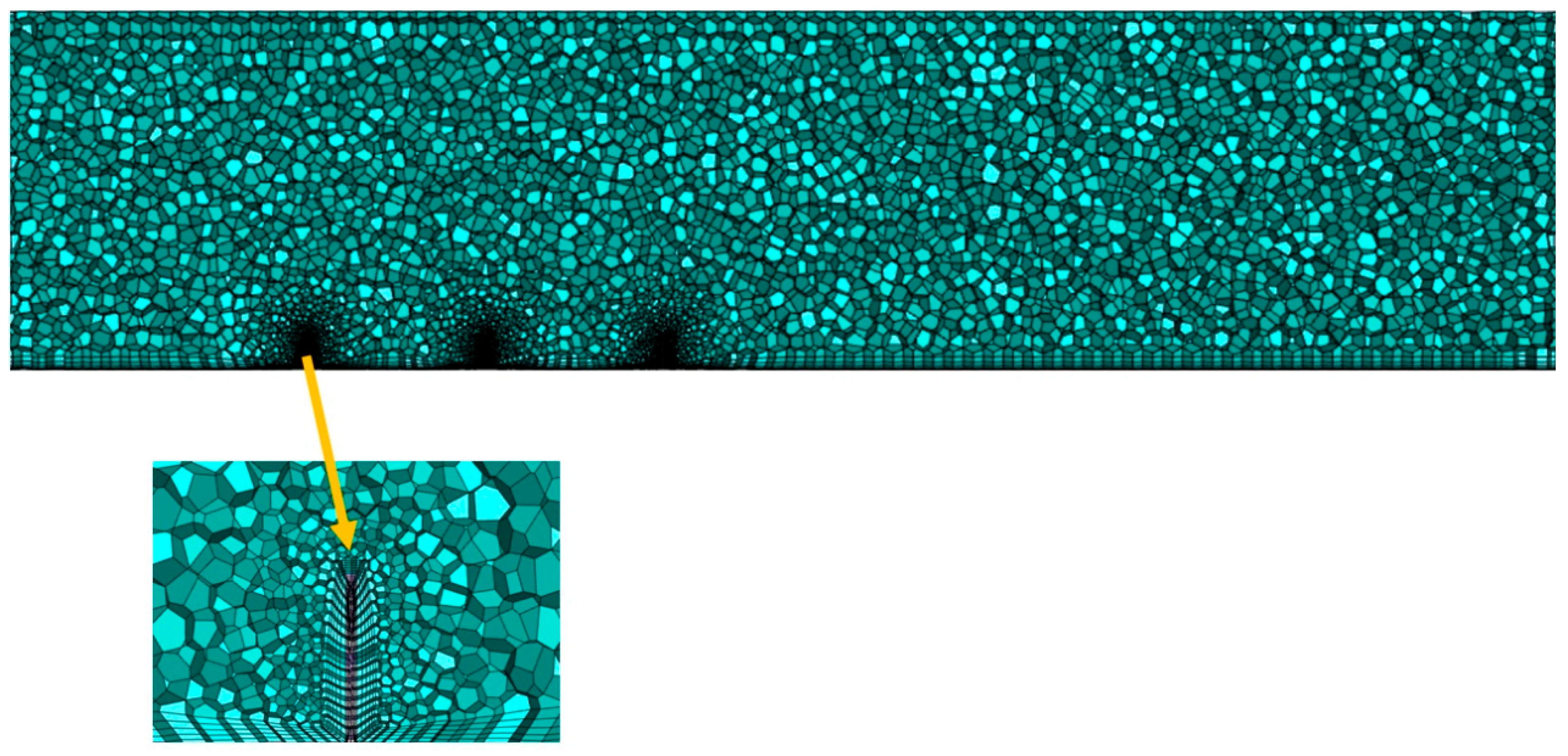
2.1. Boundary Conditions and Computational Domain Setup
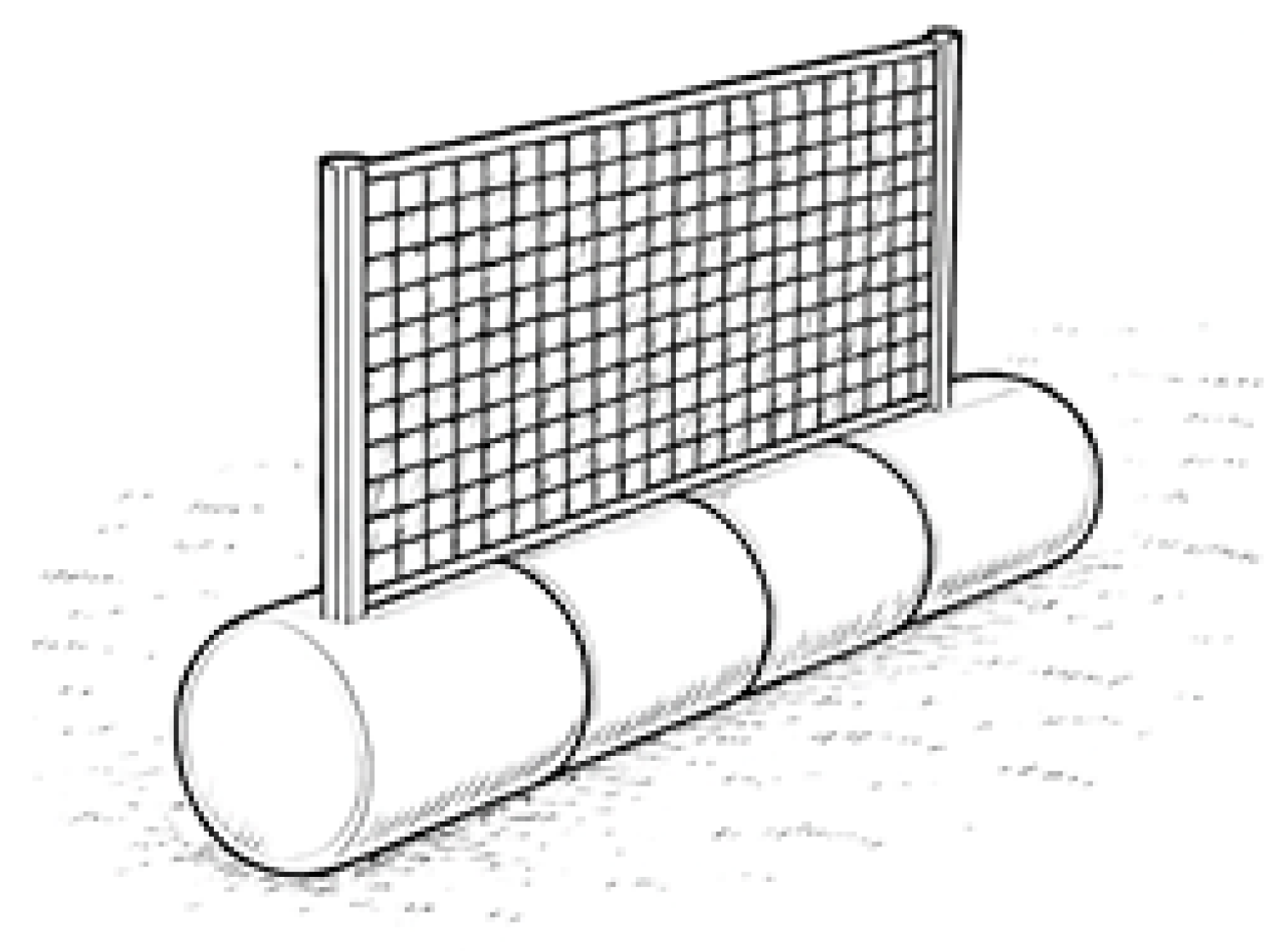
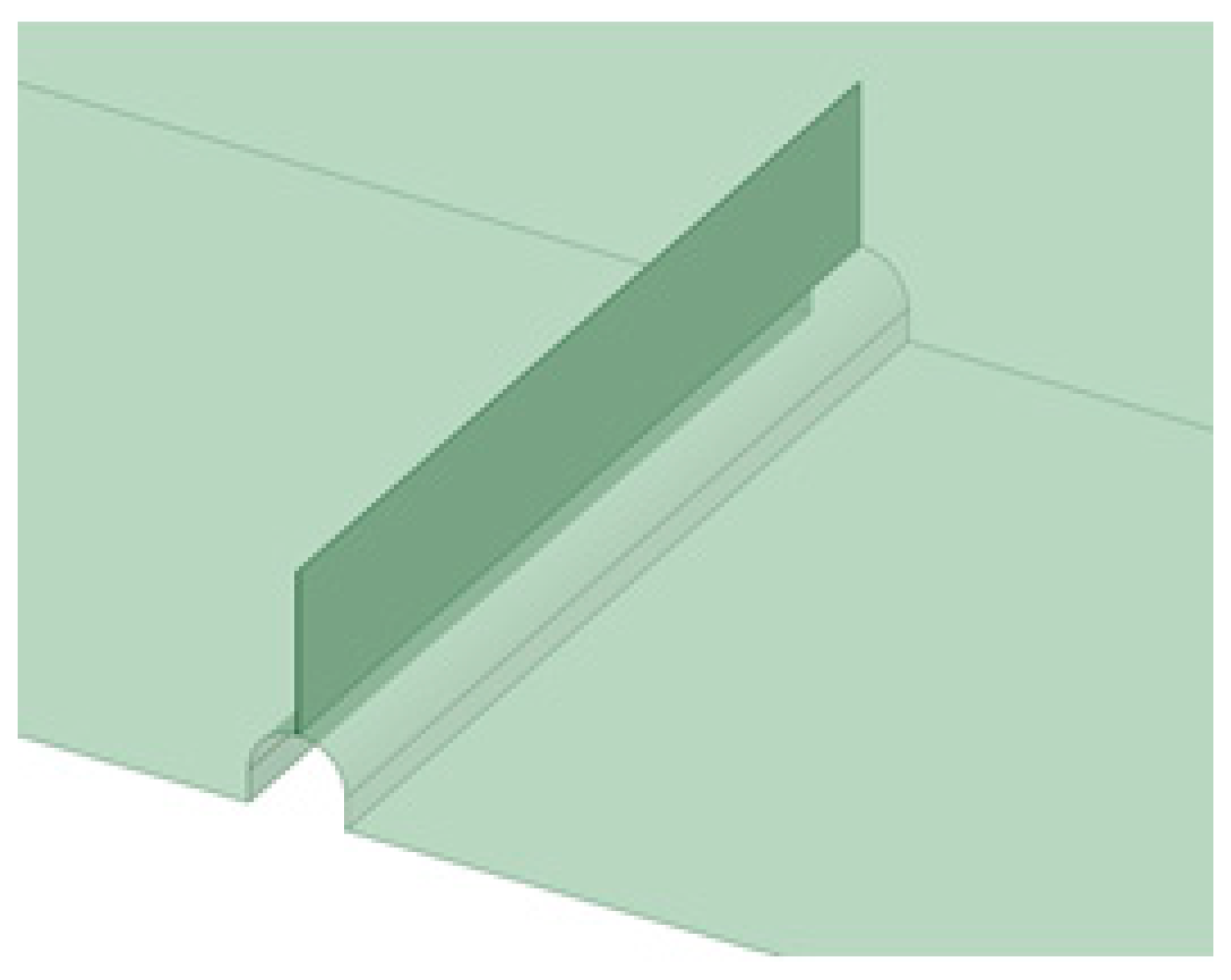
2.2. Model Setup
2.3. The Evaluation Parameters for Windbreak Performance of Wind Fences
2.3.1. Effective Protection Distance
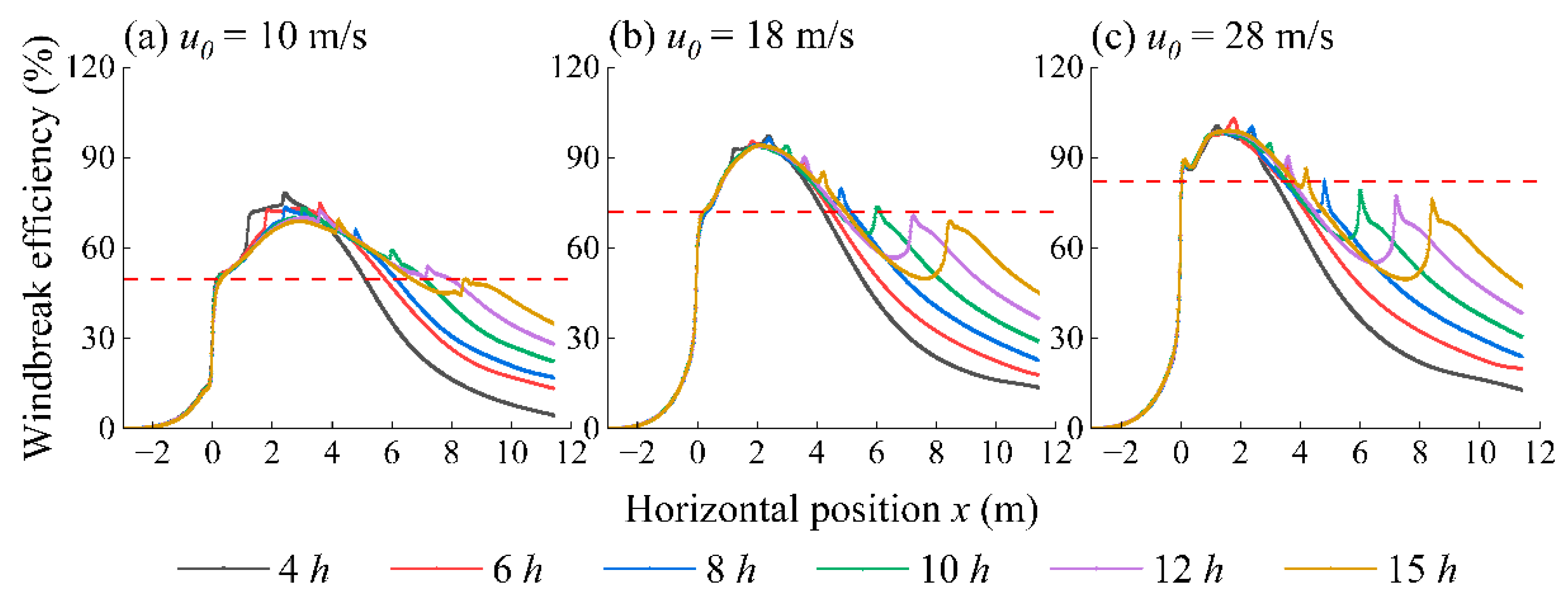
2.3.2. Windbreak Efficiency
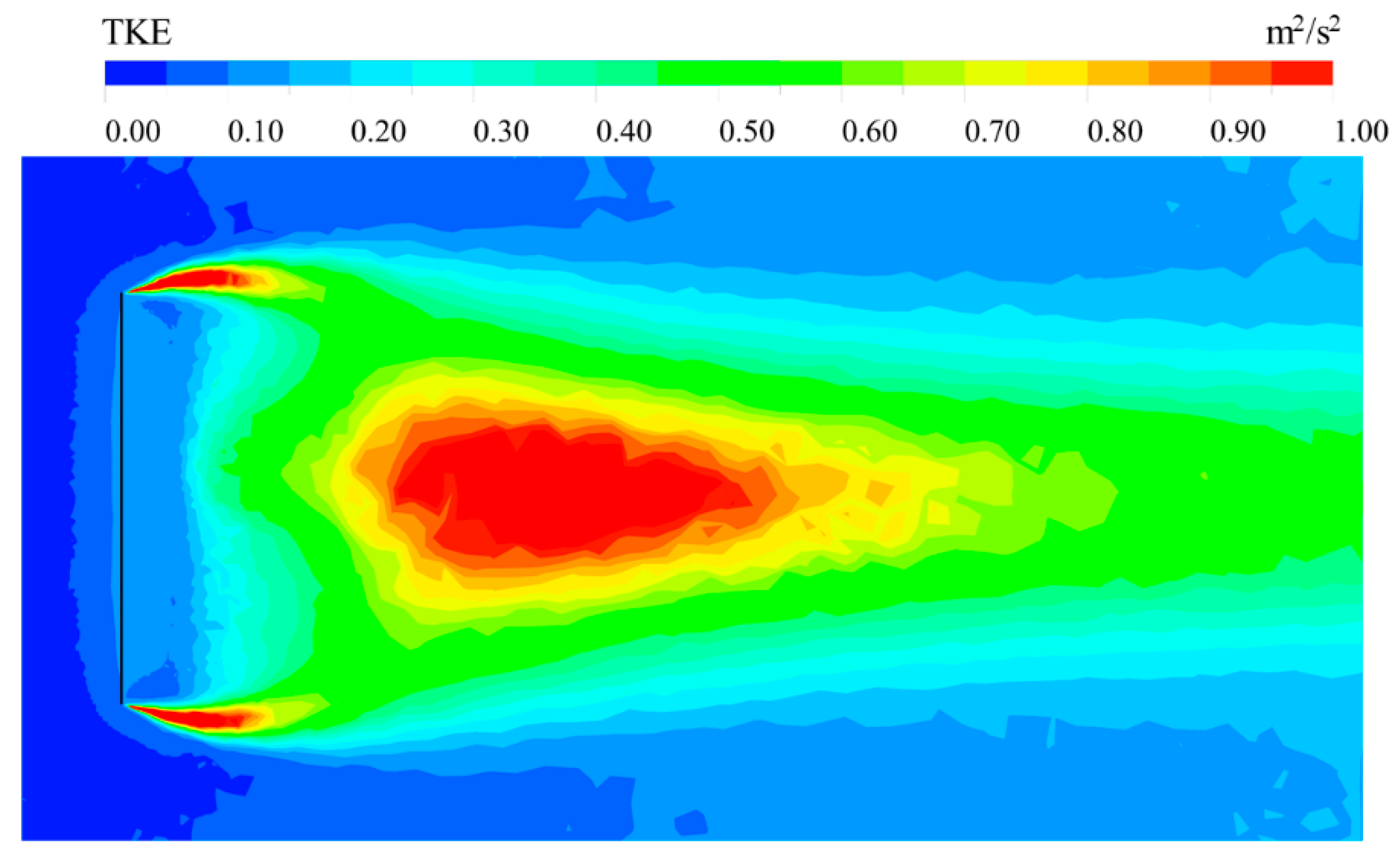
2.3.3. Turbulence Kinetic Energy
2.4. CFD Model Validation
3. Results
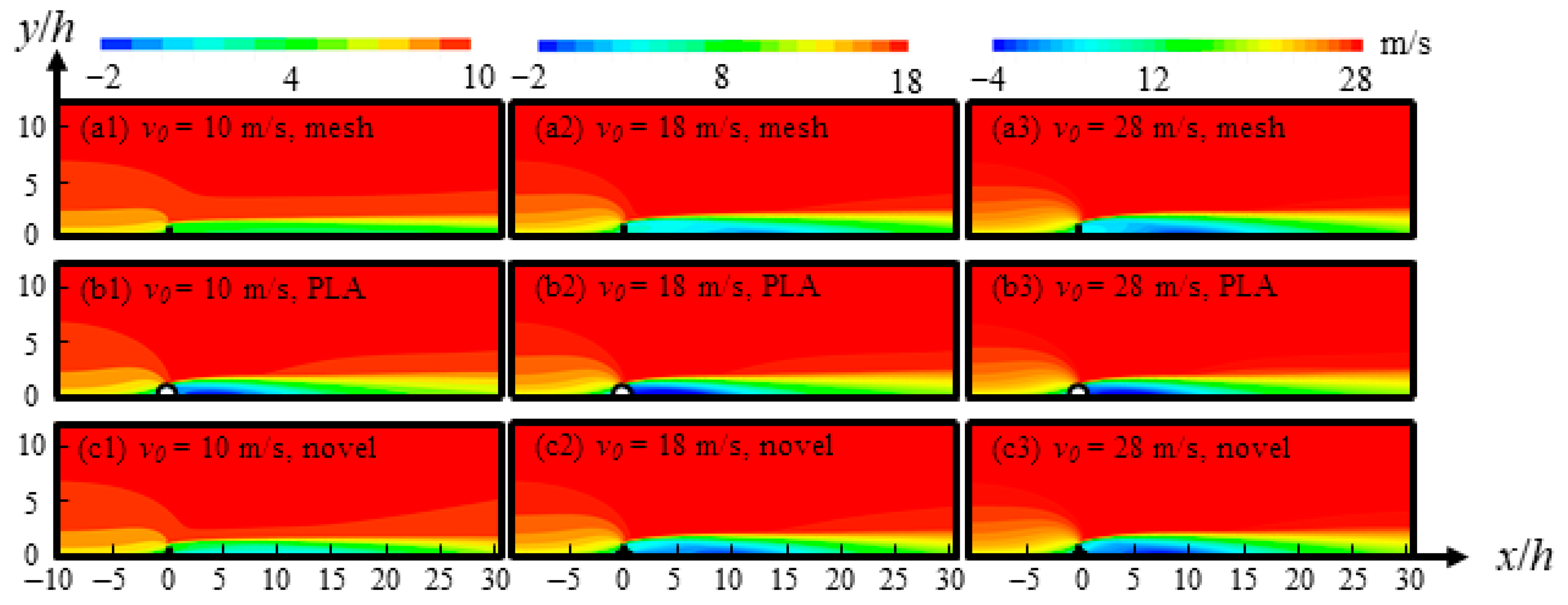
3.1. Analysis of the Dynamic Differences Between Novel Composite Wind Fences and Single–Material Wind Fences
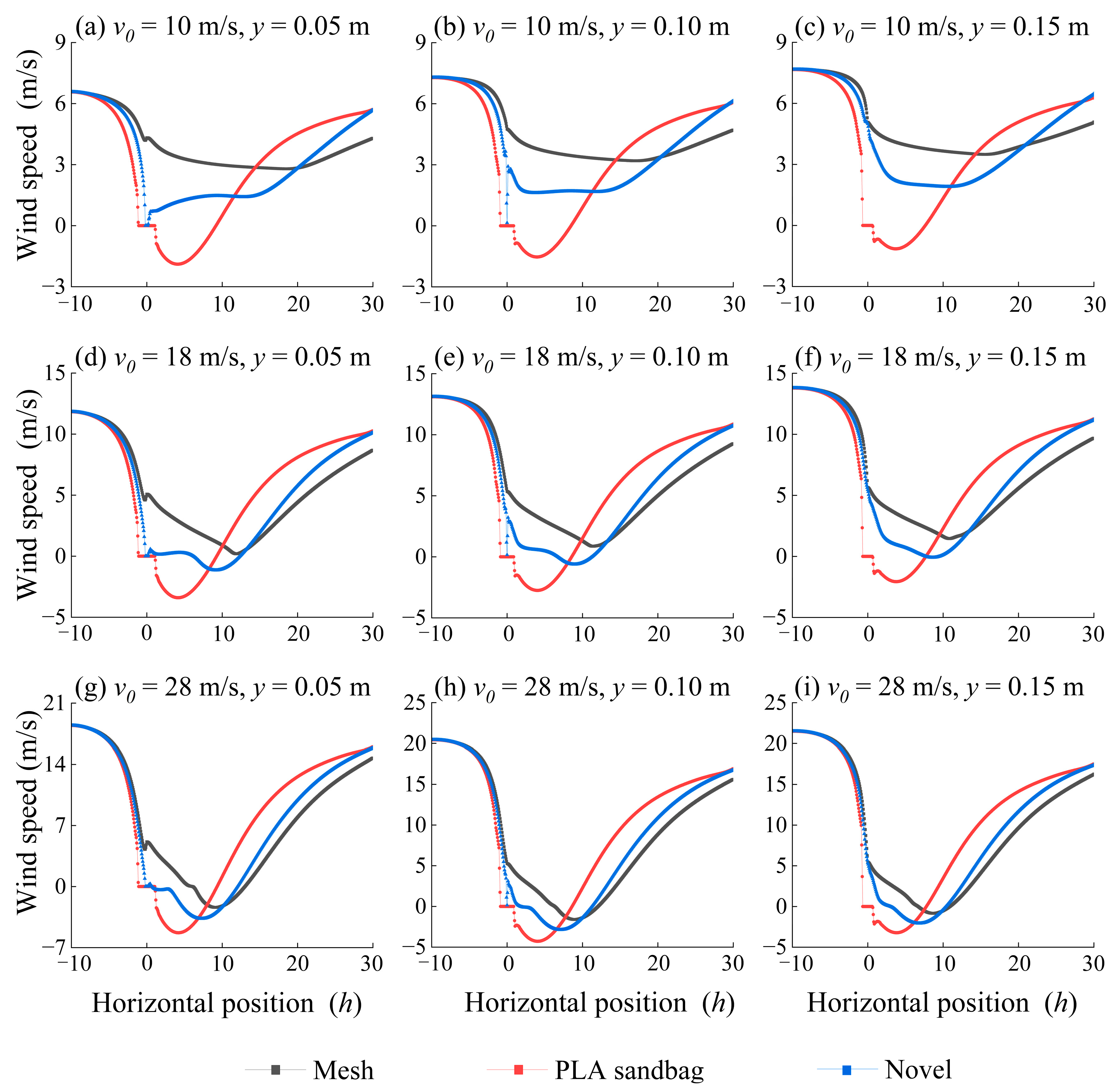
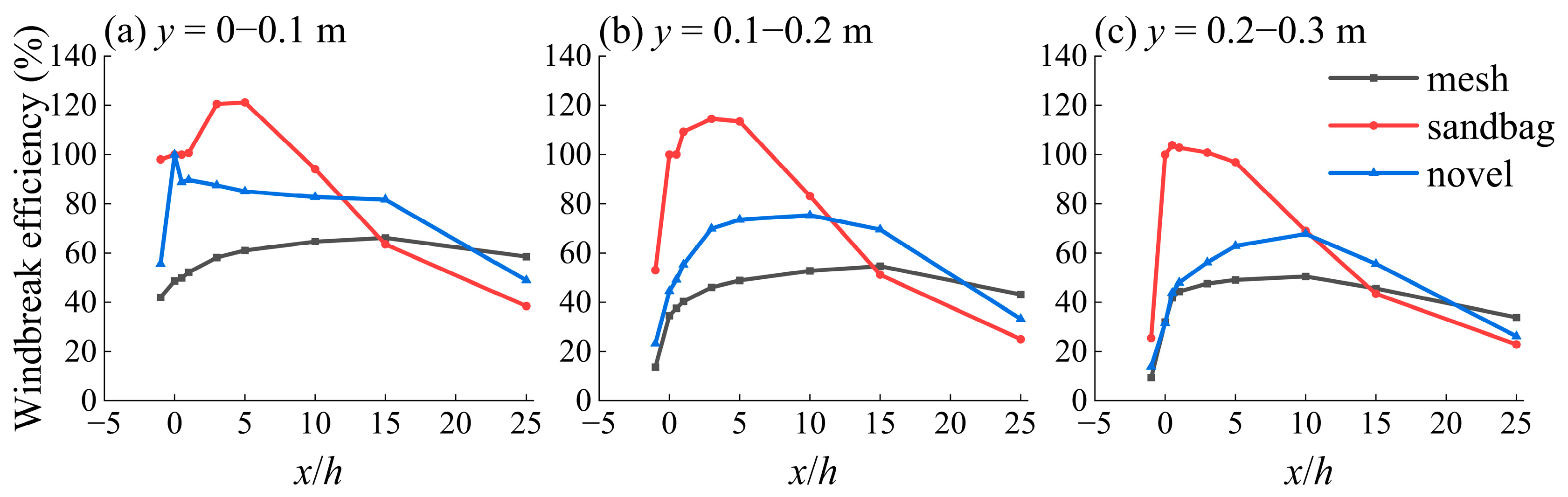
3.2. The Variation Characteristics of Wind Speed and Windbreak Efficiency at Different Horizontal Positions of Three Wind Fence Types
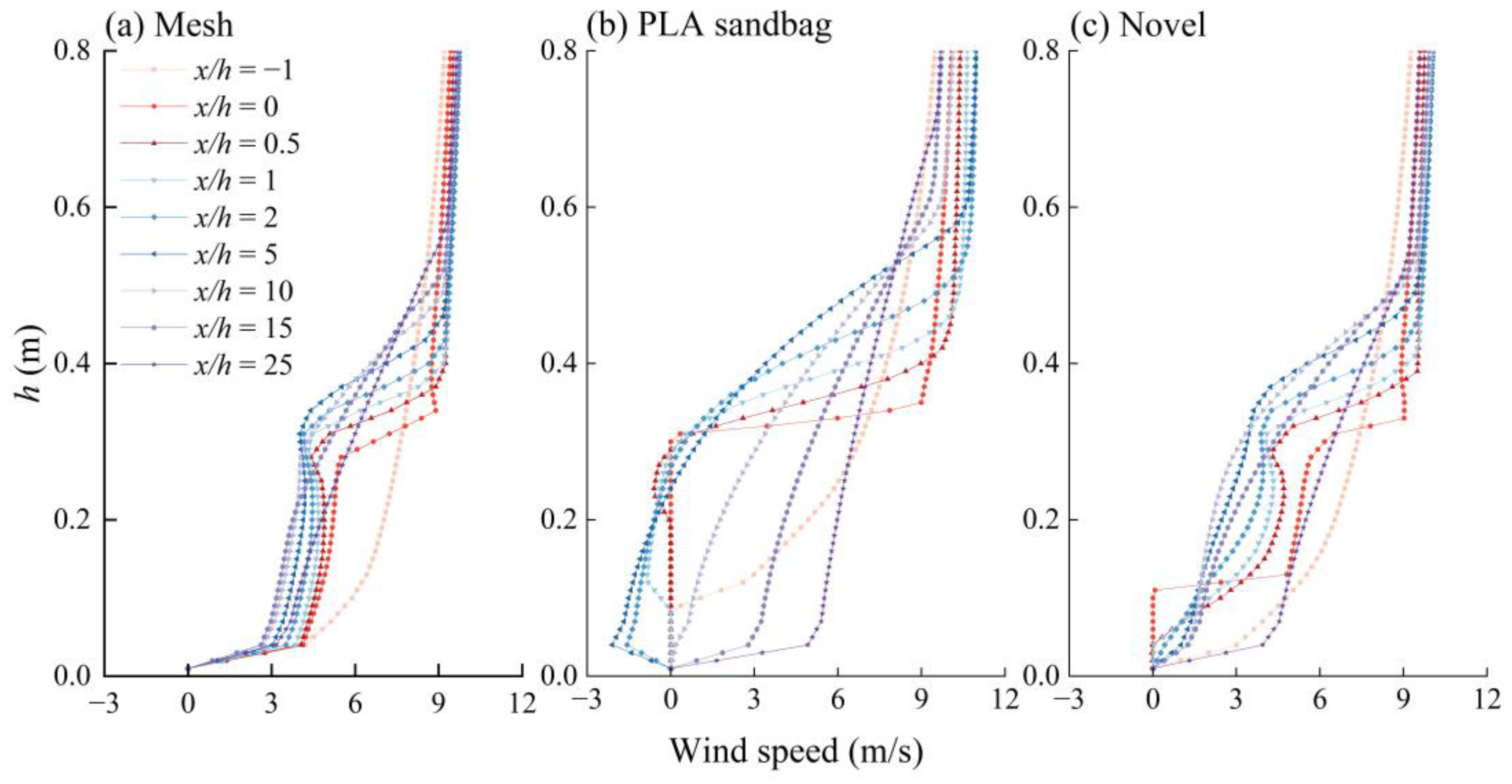
3.3. Variation in Wind Speed Profiles for the Three Types of Wind Fences
3.4. Effective Protection Distance of the Novel Composite Structural Wind Fence
3.5. Variation in Turbulence Characteristics Around the Novel Wind Fence
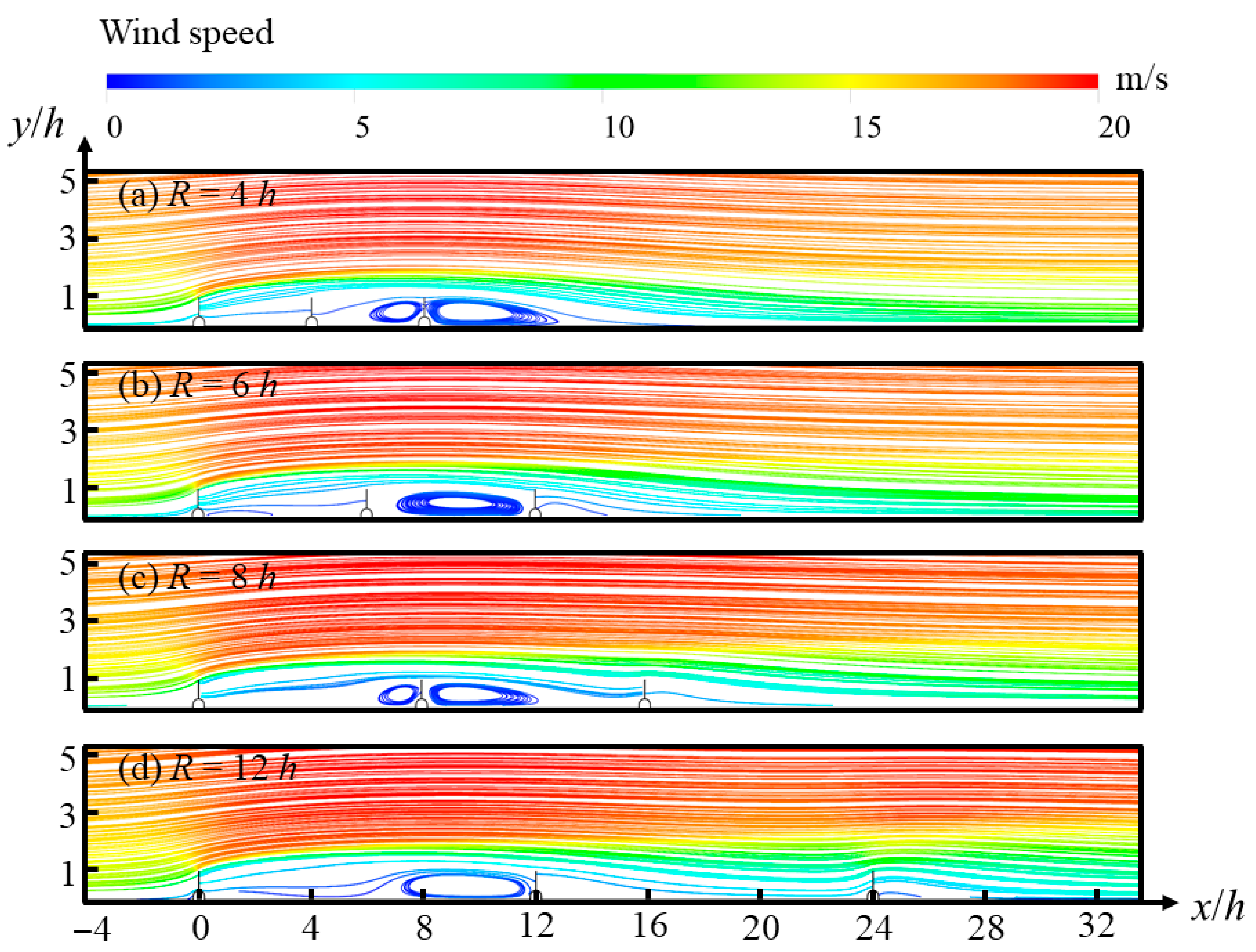
3.6. Windbreak Performance of Multi–Row Novel Wind Fences
4. Discussion
4.1. Airflow Structure and Synergistic Protection Performance of the Composite Wind Fence
4.2. Flow Dynamics and Protective Effectiveness in Multi–Row Configurations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Teng, Y.M.; Zhan, J.Y.; Liu, W.; Sun, Y.X.; Agyemang, F.B.; Liang, L.; Li, Z.H. Spatiotemporal dynamics and drivers of wind erosion on the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau, China. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 123, 107340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordstrom, K.F.; Hotta, S. Wind erosion from cropland in the USA: A review of problems, solutions and prospects. Geoderma 2004, 121, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.G.; Fan, J.Q.; Sun, L.; Zhang, H.F.; Xu, Y.; Yao, Y.F.; Yan, X.D.; Zhou, J.; Jia, Y.S.; Chi, W.F. Wind erosion and its ecological effects on soil in the northern piedmont of the Yinshan Mountains. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 128, 107825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, J.F.; Smith, D.M.S.; Lambin, E.F.; Turner, B.; Mortimore, M.; Batterbury, S.P.; Downing, T.E.; Dowlatabadi, H.; Fernández, R.J.; Herrick, J.E. Global desertification: Building a science for dryland development. Science 2007, 316, 847–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.H.; Cui, M.; Cai, Q.; Liu, Y.G.; Bo, W.J. Spatiotemporal patterns and drivers of trade–offs and synergy in the Beijing–Tianjin sand source control project: A bayesian belief network–based analysis. Sustainability 2024, 16, 1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, G.W.; Huang, N.; Zhang, J.; Dun, H.C. Investigations into the design of sand control fence for Gobi buildings. Aeolian Res. 2021, 49, 100662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Liu, B.; Yin, D.; Li, M.; Hu, C.; Xiao, X.; Duan, Y.; Fang, M.; Hou, P. Study on the shelter and sand control effect of new porous sand barriers from recycled wind turbine blades. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2025, 13, 475–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Wang, S.; Liu, Y.Z.; Meng, J.J.; Hong, J.Z.; Wang, J.; Chang, P.; Liu, H.B.; Zhang, B.Y.; Li, Y. Experimental study on a combined sand barrier: Integration of porous mesh plate and novel porous sand–fixing bricks. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 2024, 251, 105809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, G.P.; Zuo, H.J.; Wang, H.B.; Yan, M.; Yao, Y.F.; Han, X.Y.; Liu, F. Numerical simulation and experiment of wind–sand movement characteristics around high vertical nylon mesh sand barriers. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2020, 36, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Li, H.Y.; Zhao, Y.X.; Ren, Y.Y.; He, J.J.; Yu, F.Q.; Eerdun, H. Benefit evaluation of wind prevention and sand fixation under the combined measures of sand barrier in mobile dunes in Mu Us sandy land. Arid. Zone Res. 2023, 40, 268–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagherpour, M.; Zare, S.; Liu, H.J.; Ekhtesasi, M.R.; Samani, A.A.N. Developing natural based biodegradable sand barriers for mitigation of aeolian sands. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 394, 127525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.L.; Cai, Z.L.; Liu, F.R. Development of biobased materials applications. In Research and Applications of Bio–Based Degradable Materials; Springer: Singapore, 2025; pp. 287–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naser, A.Z.; Deiab, I.; Darras, B.M. Poly (lactic acid)(PLA) and polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs), green alternatives to petroleum–based plastics: A review. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 17151–17196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cislaghi, A.; Sala, P.; Borgonovo, G.; Gandolfi, C.; Bischetti, G.B. Towards more sustainable materials for geo–environmental engineering: The case of geogrids. Sustainability 2021, 13, 2585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.Y. Study on Mechanism and Benefit of Wing Bag Sand Barrier. Ph.D. Thesis, Inner Mongolia Agricultural University, Hohhot, China, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Li, Q.; Hou, J.Y.; Ji, S. Evaluation of protection benefit of sand barrier fence with different heights on desert highway. PLoS ONE 2025, 20, e0324869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, B.Y.; Cheng, J.J.; Xin, L.G.; Wang, R. Effectiveness of hole plate–type sand barriers in reducing aeolian sediment flux: Evaluation of effect of hole size. Aeolian Res. 2019, 38, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, Q.; Wu, X.X. A review of computational fluid dynamics (CFD) methodology and analysis on airflow and sand transport over aeolian landforms. Catena 2024, 241, 108010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, P.P.; Wu, X.X. Flow field simulation and protective effectiveness research on sand barriers by computational fluid dynamics (CFD)—A review. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 2025, 259, 106024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.G.; Cheng, J.J.; Li, Y.P.; Chen, Y.Q.; Zhang, R.Y.; Chen, D.H. Erosion and deposition patterns over a wind-blown sand dune behind a high vertical-type sand fence. Land Degrad. Dev. 2024, 35, 5452–5469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patankar, S.V.; Spalding, D.B. A calculation procedure for heat, mass and momentum transfer in three dimensional parabolic flows. In Numerical Prediction of Flow, Heat Transfer, Turbulence and Combustion; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1983; pp. 54–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, T.H.; Liou, W.W.; Shabbir, A.; Yang, Z.G.; Zhu, J. A new k–epsilon eddy viscosity model for high Reynolds number turbulent flows. Comput. Fluids 1994, 24, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, L.K.; Ding, G.D.; Qu, M.Y. Evaluation of the porosity–wind speed coupling mechanism and wind erosion control efficiency of mesh sand barriers based on numerical simulation. J. Arid Land Resour. Environ. 2025, 39, 104–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.B.; Qian, G.Q.; Luo, W.Y.; Wang, H.T. Threshold velocity for wind erosion: The effects of porous fences. Environ. Geol. 2006, 51, 471–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, G.P. Fluent Numerical Simulation of Protective Effectiveness of Double–Row Nylon Sand–Blocking Net. Master’s Thesis, Inner Mongolia Agricultural University, Hohhot, China, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohanizadegan, M.; Petrone, R.M.; Pomeroy, J.W.; Kosovic, B. Analysis of turbulence and turbulence kinetic energy dynamics in complex terrain. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2025, 130, e2023JD040558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, J.; Nickling, W.G.; Gillies, J.A. Investigations of the law–of–the–wall over sparse roughness elements. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2008, 113, F2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuman, C.M.; Sanderson, R.S.; Sutton, S. Vortex shedding and morphodynamic response of bed surfaces containing non–erodible roughness elements. Geomorphology 2013, 198, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durlofsky, L.; Brady, J.F. Analysis of the Brinkman equation as a model for flow in porous media. Phys. Fluids 1987, 30, 3329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Zhang, H.L.; Deng, Y.H.; Qu, J.J.; Wang, Z.H.; Li, S. Effects of sand sedimentation and wind erosion around sand barrier: Numerical simulation and wind tunnel test studies. J. Mt. Sci. 2023, 20, 962–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Liu, S.X.; Jiang, Y.J.; Duan, W.J. Research on the effect of sand barriers on highways in desert areas on sand control. Sustainability 2023, 15, 13906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornelis, W.M.; Gabriëls, D. Optimal windbreak design for wind–erosion control. J. Arid Environ. 2005, 61, 315–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruno, L.; Fransos, D.; Giudice, A.L. Solid barriers for windblown sand mitigation: Aerodynamic behavior and conceptual design guidelines. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 2018, 173, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X. Evolution of Aeolian Dune Systems Considering Turbulent Fluctuations and Topographic Effects. Ph.D. Thesis, Lanzhou University, Lanzhou, China, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, J.D. Numerical studies of flow through a windbreak. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 1985, 21, 119–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.B.; Huang, N.; Dun, H.C. Analysis of wind–sand movement over sand dune with different railway forms downstream. Chin. J. Theor. Appl. Mech. 2020, 52, 680–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.B.; Luo, W.Y.; Qian, G.Q.; Wang, H.T. Evaluating the optimal porosity of fences for reducing wind erosion. Sci. Cold Arid Reg. 2011, 3, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.G.; Li, H.Y.; Wu, Z.F.; Wang, Z.R.; Yin, J.; Qing, D.M.N.; Eerdun, H. Sand fixation mechanism and effect evaluation of sand barriers in Mu Us sandy land, China. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2023, 68, 1312–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.X.; Wang, H.F.; Li, S.Y.; Kang, X.G.; Sun, N. Comparison of sand–protecting efficiency and terrain adapted of two checkerboard barriers. Bull. Soil Water Conserv. 2015, 35, 344–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, H.; Yang, W.B.; Zhu, B.; Liu, D.Y.; Zhou, M.; Yang, B. Low–coverage desertification control: Theory and practice. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2025, 45, 1070–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdallah, M.N.I.; Qulin, T.; Ramadan, M.; Habumuremyi, P. Mitigation measures for wind erosion and sand deposition in desert railways: A geospatial analysis of sand accumulation risk. Sustainability 2025, 17, 4016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Zhao, P.W.; Zhao, J.C.; Zhang, X.X. Protective effect of multi–row HDPE board sand fences: A wind tunnel study. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2021, 9, 103–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Jin, A.F.; Zhang, S.Z.; Zheng, B. Numerical simulation and parameter optimization of a new reed–nylon net combined sand fence. Sustainability 2023, 15, 13920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.X.; Guo, Z.Y.; Wang, R.D.; Fan, P.P.; Xiang, H.X.; Zou, X.Y.; Yin, J.; Fang, H. Optimal design for wind fence based on 3D numerical simulation. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2022, 323, 109072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.Y.; Cheng, J.J.; Li, S.Y. Reasonable spacing of high–parallel reed sand barriers along the Xinjiang S214 provincial highway. Arid Zone Res. 2020, 37, 782–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Parameter | Value | Parameter | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerodynamic roughness/m | 0.00003 | Turbulent viscosity ratio | 10 |
| Roughness constant | 0.5 | Convergence criterion | <10−4 |
| Air density/(kg·m−3) | 1.225 | Temperature/K | 288.16 |
| Air viscosity | 1.7894 × 10−5 | Turbulence intensity | 0.05 |
| Incoming Wind Speed | Mesh | Sandbag | Novel |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 m/s | 5.20 | 4.66 | 6.36 |
| 18 m/s | 4.38 | 3.62 | 4.86 |
| 28 m/s | 4.14 | 3.24 | 4.18 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qu, M.; Cai, L.; Li, J.; Ding, G.; Guo, X. Innovative Design of PLA Sandbag–Fiber Mesh Composite Wind Fences and Synergistic Windbreak Performance. Sustainability 2025, 17, 9418. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17219418
Qu M, Cai L, Li J, Ding G, Guo X. Innovative Design of PLA Sandbag–Fiber Mesh Composite Wind Fences and Synergistic Windbreak Performance. Sustainability. 2025; 17(21):9418. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17219418
Chicago/Turabian StyleQu, Mengyu, Likun Cai, Jinrong Li, Guodong Ding, and Xiaoping Guo. 2025. "Innovative Design of PLA Sandbag–Fiber Mesh Composite Wind Fences and Synergistic Windbreak Performance" Sustainability 17, no. 21: 9418. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17219418
APA StyleQu, M., Cai, L., Li, J., Ding, G., & Guo, X. (2025). Innovative Design of PLA Sandbag–Fiber Mesh Composite Wind Fences and Synergistic Windbreak Performance. Sustainability, 17(21), 9418. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17219418





