The Formation of Knowledge Flow Networks in the Yangtze River Delta, China: Knowledge Implicitness and Proximity Effect
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Theoretical Background
2.1. Knowledge and Knowledge Flow
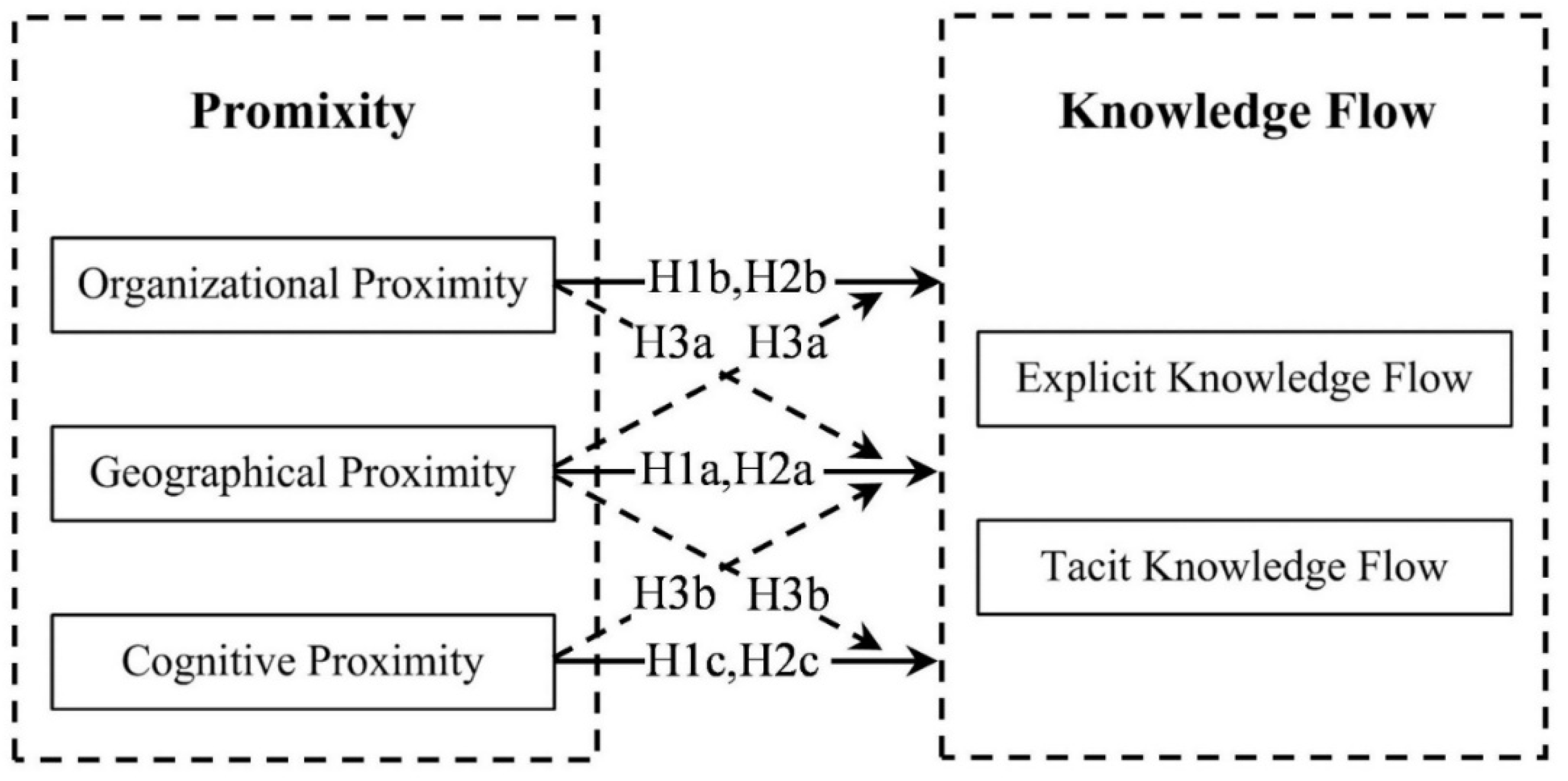
2.2. Knowledge Flow and Its Proximity Mechanism
3. Materials and Methods
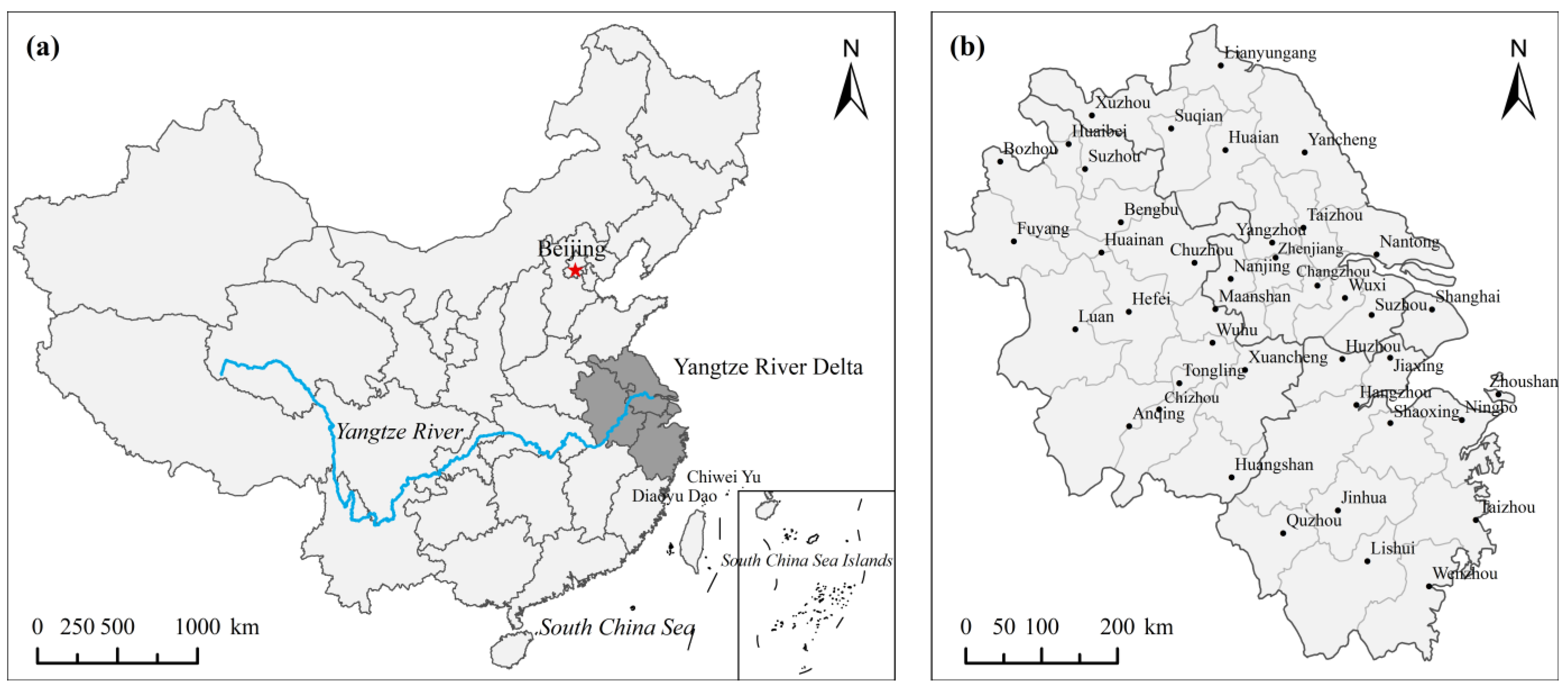
3.1. Study Area
3.2. Data
3.3. Analytical Methods
4. Results
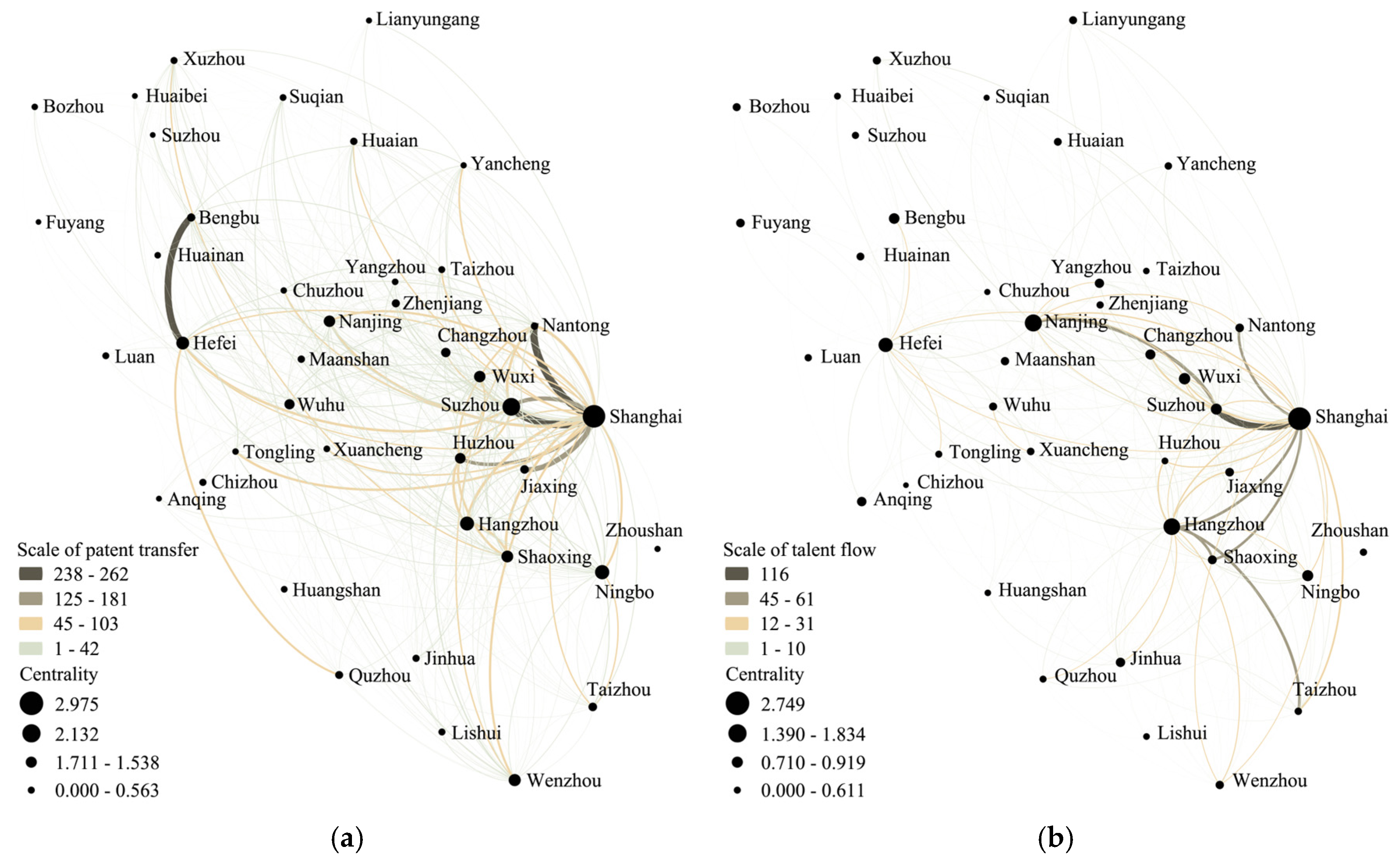
4.1. Knowledge Flow Networks in the Yangtze River Delta
4.2. The Effect of Proximities on Knowledge Flow
5. Discussion
5.1. Proximity Mechanisms of Knowledge Flow
5.2. Policy Implications
6. Conclusions
6.1. Main Conclusions
6.2. Limitations and Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sun, Y.; Wang, T.; Gu, X. A Sustainable Development Perspective on Cooperative Culture, Knowledge Flow, and Innovation Network Governance Performance. Sustainability 2019, 11, 6126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bathelt, H.; Malmberg, A.; Maskell, P. Clusters and knowledge: Local buzz, global pipelines and the process of knowledge creation. Prog. Hum. Geogr. 2004, 28, 31–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Du, D. Determinants of industrial innovation in China: Evidence from its recent economic census. Technovation 2010, 30, 540–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asheim, B. The Changing Role of Learning Regions in the Globalizing Knowledge Economy: A Theoretical Re-examination. Reg. Stud. 2012, 46, 993–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, L.C. The Geography of Innovation; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Rowley, J. The wisdom hierarchy: Representations of the DIKW hierarchy. J. Inf. Sci. 2007, 33, 163–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, K.; Xu, H.Y.; Cui, B. A review of knowledge flow research. J. China Soc. Sci. Tech. Inf. 2020, 39, 1120–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argote, L.; Mcevily, B.; Reagans, R. Managing knowledge in organizations: An integrative framework and review of emerging themes. Manag. Sci. 2003, 49, 571–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amidon, D.M. Dialogue with Customers: Secret to Innovation Strategy. Int. J. Innov. Manag. 1997, 1, 73–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spender, J.C. Making knowledge the basis of a dynamic theory of the firm. Strat. Manag. J. 1996, 17, 45–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nonaka, I.; Takeuchi, H. The Knowledge-Creating Company: How Japanese Companies Create the Dynamics of Innovation; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.L.; Niu, C.C. Spatial evolution and factors of interurban technology transfer network in Northeast China from national to local perspectives. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2019, 74, 2092–2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, S.E.; Fallah, M.H.; Reilly, R.R. Localized sources of knowledge and the effect of knowledge spillovers: An empirical study of inventors in the telecommunications industry. J. Econ. Geogr. 2008, 9, 405–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Latora, V. The evolution of knowledge within and across fields in modern physics. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 12097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behrend, F.D.; Erwee, R. Mapping knowledge flows in virtual teams with SNA. Prog. Hum. Geogr. 2009, 13, 99–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Zhai, W.; Yan, Y.; Wang, X. The Influence of Proximity on the Evolution of Urban Innovation Networks in Nanjing Metropolitan Area, China: A Comparative Analysis of Knowledge and Technological Innovations. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2024, 13, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szulanski, G. Exploring internal stickiness: Impediments to the transfer of best practice within the firm. Strat. Manag. J. 1996, 17, 27–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, X.; Liu, D. Transmission mechanism of knowledge diffusion path to knowledge evolution in agricultural enterprises: Based on intermediary role of knowledge sharing and regulating role of knowledge. Sci. Technol. Manag. Res. 2018, 38, 184–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teece, D.J. Technology transfer by multinational firms: The resource cost of transferring technological know-how. Econ. J. 1977, 87, 242–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartol, K.M.; Srivastava, A. Encouraging knowledge sharing: The role of organizational reward systems. J. Leadersh. Organ. Stud. 2002, 9, 64–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.W.; Zeng, G.; Cao, X.Z.; Si, Y.F. Research progress of innovation network and knowledge flow. World Reg. Stud. 2017, 26, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Fang, C.; Pang, B.; Wang, S. Structure of Chinese city network as driven by technological knowledge flows. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2015, 25, 498–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, D.; Du, D.; Chen, Y.; Zhai, Q. Spatial-temporal complexity and growth mechanism of city innovation network in China. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2018, 38, 1759–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, C.S.; Leal, C.; Marques, C.P.; Cardoso, A.R. Strategic knowledge management, innovation and performance: A qualitative study of the footwear industry. J. Knowl. Econ. 2016, 7, 659–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Cao, Z.; Du, A.; Tu, Q. Where does it matter? Revisiting the role of proximity in knowledge spillovers. Am. J. Econ. Sociol. 2024, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capello, R.; Caragliu, A. Proximities and the intensity of scientific relations: Synergies and nonlinearities. Int. Reg. Sci. Rev. 2016, 41, 7–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malerba, F.; Mancusi, M.L.; Montobbio, F. Innovation, international R&D spillovers and the sectoral heterogeneity of knowledge flows. Rev. World Econ. 2013, 149, 697–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhi, Z.; Liu, J.; Liu, J.; Ai, L. Geospatial Structure and Evolution Analysis of National Terrestrial Adjacency Network Based on Complex Network. J. Geovis. Spat. Anal. 2024, 8, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.O.; Gu, R.X.; Ma, S. Spatial characteristics and proximity mechanism of technology transfer among cities in China. Prog. Geogr. 2019, 38, 370–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polanyi, M. The Tacit Dimension; The University of Chicago Press: Chicago, IL, USA, 1966. [Google Scholar]
- Howells, J.R.L. Tacit knowledge, innovation and economic geography. Urban. Stud. 2002, 39, 871–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gertler, M.S. Tacit knowledge and the economic geography of context, or the undefinable tacitness of being (there). J. Econ. Geogr. 2003, 3, 75–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boschma, R. Proximity and innovation: A critical assessment. Reg. Stud. 2005, 39, 61–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capello, R. Spatial spillovers and regional growth: A cognitive approach. Eur. Plan. Stud. 2009, 17, 639–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crescenzi, R.; Nathan, M.; Rodríguez-Pose, A. Do inventors talk to strangers? On proximity and collaborative knowledge creation. Res. Policy 2016, 45, 177–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, A.T.; Gilly, J. On the analytical dimension of proximity dynamics. Reg. Stud. 2000, 34, 169–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oerlemans, L.; Meeus, M. Do organizational and spatial proximity impact on firm performance? Reg. Stud. 2005, 39, 89–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torre, A.; Rallet, A. Proximity and localization. Reg. Stud. 2005, 39, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breschi, S.; Lissoni, F. Mobility of skilled workers and co-invention networks: An anatomy of localized knowledge flows. J. Econ. Geogr. 2009, 9, 439–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tödtling, F.; Trippl, M. One size fits all? Towards a differentiated regional innovation policy approach. Res. Policy 2005, 34, 1203–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caragliu, A.; Nijkamp, P. Space and knowledge spillovers in European regions: The impact of different forms of proximity on spatial knowledge diffusion. J. Econ. Geogr. 2015, 16, 749–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granovetter, M. Economic Action and Social Structure: The Problem of Embeddedness. Am. J. Sociol. 1985, 91, 481–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miörner, J.; Zukauskaite, E.; Trippl, M.; Moodysson, J. Creating institutional preconditions for knowledge flows in cross-border regions. Environ. Plan. C Polit. Space 2017, 36, 201–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasin, S.M.; Gamidullaeva, L.A.; Wise, N.; Korolev, K.Y. Knowledge Exchange and the Trust Institution: A New Look at the Problem. J. Knowl. Econ. 2020, 11, 1026–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, J.S.; Paul, D. Organizational learning and communities-of-practice: Toward a unified view of working, learning, and innovation. Organ. Sci. 1991, 2, 40–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiiski, S.; Pohjola, M. Cross-country diffusion of the Internet. Inf. Econ. Policy 2002, 14, 297–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancusi, M.L. International spillovers and absorptive capacity: A cross-country cross-sector analysis based on patents and citations. J. Int. Econ. 2008, 76, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castells, M. The Information City; Oxford: Basil Blackwell, UK, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Maggioni, M.A.; Uberti, T.E.; Nosvelli, M. Does intentional mean hierarchical? Knowledge flows and innovative performance of European regions. Ann. Reg. Sci. 2014, 53, 453–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxenian, A. The New Argonauts: Regional Advantage in a Global Economy Cambridge; Harvard University Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Dekker, D.; Krackhardt, D.; Snijders, T.A.B. Sensitivity of MRQAP tests to collinearity and autocorrelation conditions. Psychometrika 2007, 72, 563–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Si, Y.F.; Sun, K.; Zhu, Y.W.; Cao, X.Z. Spatial structure and influencing factors of knowledge network of highly cited Chinese scientists. Geogr. Res. 2020, 39, 2731–2742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegde, D.; Tumlinson, J. Does Social Proximity Enhance Business Partnerships? Theory and Evidence from Ethnicity’s Role in U.S. Venture Capital. Manag. Sci. 2014, 60, 2355–2380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaffe, A.B. Technological opportunity and spillovers of R&D: Evidence from firms’ patents, profits, and market value. Am. Econ. Rev. 1986, 76, 984–1001. [Google Scholar]
- Limtanakool, N.; Dijst, M.; Schwanen, T. A theoretical framework and methodology for characterising national urban systems on the basis of flows of people: Empirical evidence for France and Germany. Urban Stud. 2007, 44, 2123–2145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Q.; Wu, L.; Li, F.; Cheng, S.K.; Zhang, D.; Cheng, X.P. A social-network-based study on geo-relations in Southeast Asia. Acta Geogr. Sinica. 2018, 73, 2014–2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, K.; Cai, D.; Hao, M. Dynamic Innovation Collaboration Based on Complex Network Analysis: Evidence from the “Belt and Road” Initiative. J. Knowl. Econ. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faggian, A.; McCann, P. Human capital, graduate migration and innovation in British regions. Cambr. J. Econ. 2008, 33, 317–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossman, E.B.; Yli-Renko, H.; Janakiraman, R. Resource search, interpersonal similarity, and network tie valuation in nascent entrepreneurs’ emerging networks. J. Manag. 2012, 38, 1760–1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, C.C. Personal and business networks within Chilean biotech. Ind. Innov. 2018, 25, 841–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balland, P.A. Proximity and the evolution of collaboration networks: Evidence from research and development projects within the global navigation satellite system (GNSS) industry. Reg. Stud. 2012, 46, 741–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
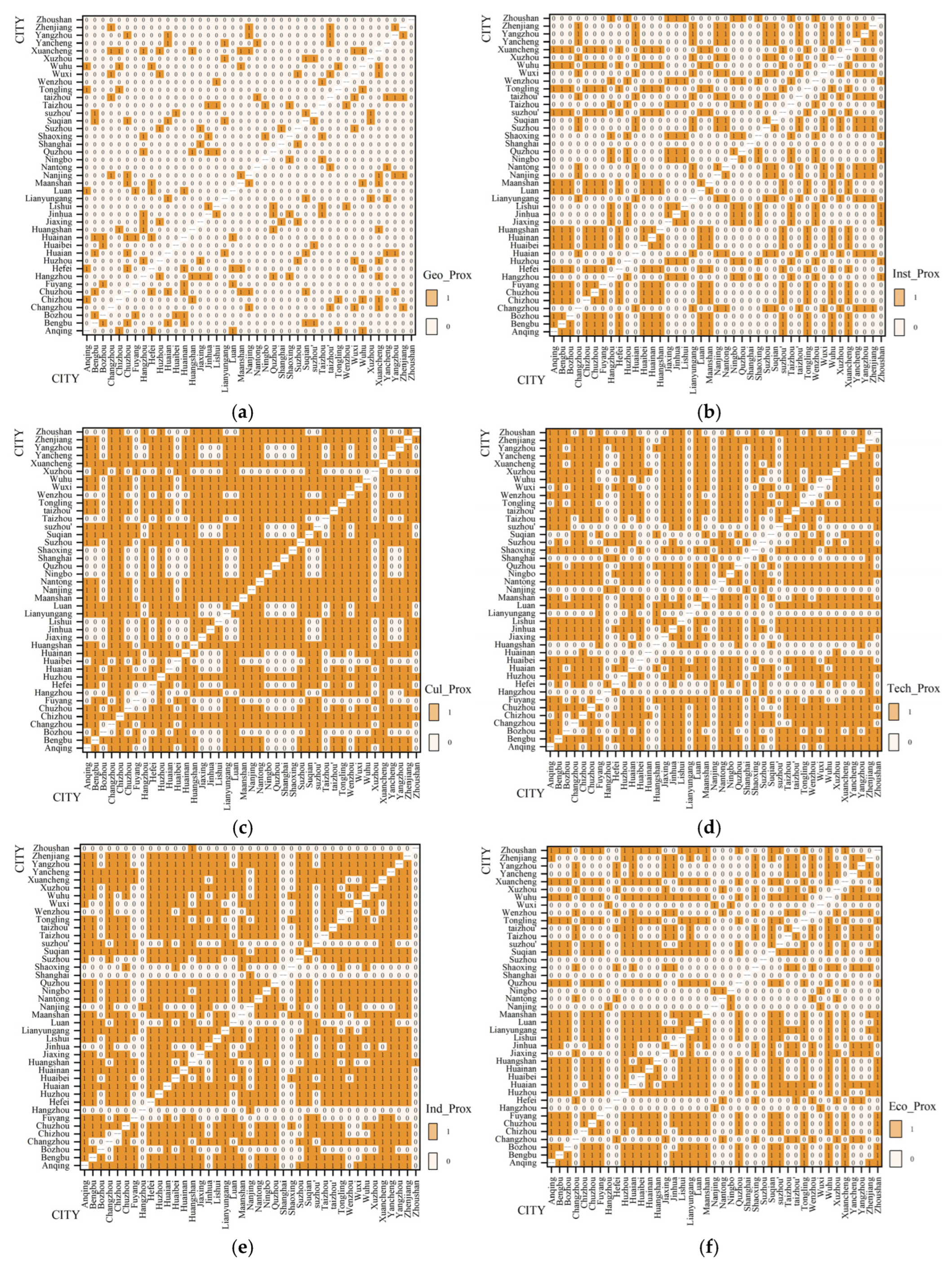
| Variables | Geographical Proximity | Institutional Proximity | Cultural Proximity | Industrial Proximity | Technological Proximity | Economic Proximity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Geographical proximity | 1.000 *** | |||||
| Institutional proximity | 0.357 *** | 1.000 *** | ||||
| Cultural proximity | 0.232 *** | 0.256 *** | 1.000 *** | |||
| Industrial proximity | 0.095 *** | 0.171 *** | 0.220 *** | 1.000 *** | ||
| Technological proximity | −0.033 | 0.044 | −0.002 | 0.277 *** | 1.000 *** | |
| Economic proximity | 0.090 *** | 0.256 *** | 0.037 *** | 0.245 *** | 0.096 * | 1.000 *** |
| Variables | Model 1 | Model 2 | Model 3 | Model 4 | Model 5 | Model 6 | Model 7 | Model 8 | Model 9 | Model 10 | Model 11 | Model 12 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Geo_Prox | 0.083 *** | 0.083 *** | 0.084 *** | 0.086 *** | 0.083 *** | 0.083 *** | 0.083 *** | 0.083 *** | 0.083 *** | 0.083 *** | 0.083 *** | 0.083 *** |
| Inst_Prox | 0.069 ** | 0.068 ** | 0.074 ** | 0.069 ** | 0.069 ** | 0.070 ** | 0.066 ** | 0.075 ** | 0.068 ** | 0.068 ** | 0.068 ** | 0.072 ** |
| Cul_Prox | 0.056 | 0.056 | 0.057 | 0.038 | 0.056 | 0.055 | 0.052 | 0.058 | 0.058 | 0.058 | 0.056 | 0.058 |
| Ind_Prox | 0.074 | 0.075 | 0.074 | 0.074 | 0.074 | 0.072 | 0.082 | 0.071 | 0.073 | 0.078 | 0.073 | 0.060 |
| Tech_Prox | 0.031 | 0.031 | 0.030 | 0.037 | 0.031 | 0.024 | 0.039 | 0.031 | 0.031 | 0.034 | 0.035 | 0.045 |
| Eco_Prox | −0.265 *** | −0.265 *** | −0.263 *** | −0.263 *** | −0.265 *** | −0.266 *** | −0.203 *** | −0.261 *** | −0.264 *** | −0.262 *** | −0.263 *** | −0.215 *** |
| Geo_Prox squared | 0.014 | |||||||||||
| Inst_Prox squared | −0.044 * | |||||||||||
| Cul_Prox squared | 0.060 | |||||||||||
| Ind_Prox squared | 0.000 | |||||||||||
| Tech_Prox squared | −0.023 | |||||||||||
| Eco_Prox squared | −0.191 *** | |||||||||||
| Geo_Prox × Inst_Prox | −0.049 * | |||||||||||
| Geo_Prox × Cul_Prox | −0.008 | |||||||||||
| Geo_Prox × Ind_Prox | −0.029 | |||||||||||
| Geo_Prox × Tech_Prox | −0.015 | |||||||||||
| Geo_Prox × Eco_Prox | −0.161 *** | |||||||||||
| Sample size | 1640 | 1640 | 1640 | 1640 | 1640 | 1640 | 1640 | 1640 | 1640 | 1640 | 1640 | 1640 |
| Adjusted R−square | 0.329 *** | 0.328 *** | 0.335 *** | 0.340 *** | 0.329 *** | 0.328 *** | 0.417 *** | 0.335 *** | 0.327 *** | 0.334 *** | 0.328 *** | 0.393 *** |
| Variables | Model 1 | Model 2 | Model 3 | Model 4 | Model 5 | Model 6 | Model 7 | Model 8 | Model 9 | Model 10 | Model 11 | Model 12 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Geo_Prox | 0.070 ** | 0.071 ** | 0.071 ** | 0.073 ** | 0.071 ** | 0.071 ** | 0.070 ** | 0.069 ** | 0.068 ** | 0.070 ** | 0.070 ** | 0.070 ** |
| Inst_Prox | 0.220 *** | 0.221 *** | 0.227 *** | 0.220 *** | 0.219 *** | 0.218 *** | 0.217 *** | 0.232 *** | 0.218 *** | 0.216 *** | 0.216 *** | 0.223 *** |
| Cul_Prox | 0.119 ** | 0.120 ** | 0.120 ** | 0.105 ** | 0.121 ** | 0.120 ** | 0.115 *** | 0.123 ** | 0.133 *** | 0.123 ** | 0.118 ** | 0.120 ** |
| Ind_Prox | −0.096 * | −0.097 * | −0.095 * | −0.095 * | −0.089 * | −0.094 * | −0.088 * | −0.101 * | −0.101 * | −0.084 * | −0.100 * | −0.111 ** |
| Tech_Prox | −0.097 * | −0.098 * | −0.099 * | −0.092 * | −0.097 * | −0.090 * | −0.090 * | −0.096 * | −0.098 * | −0.090 ** | −0.074 | −0.081 * |
| Eco_Prox | −0.196 *** | −0.195 *** | −0.194 *** | −0.195 *** | −0.195 *** | −0.194 *** | −0.140 *** | −0.190 *** | −0.189 *** | −0.188 *** | −0.188 *** | −0.141 *** |
| Geo_Prox squared | −0.024 | |||||||||||
| Inst_Prox squared | −0.063 ** | |||||||||||
| Cul_Prox squared | 0.046 | |||||||||||
| Ind_Prox squared | −0.027 | |||||||||||
| Tech_Prox squared | −0.024 | |||||||||||
| Eco_Prox squared | −0.173 *** | |||||||||||
| Geo_Prox × Inst_Prox | −0.097 *** | |||||||||||
| Geo_Prox × Cul_Prox | −0.058 | |||||||||||
| Geo_Prox × Ind_Prox | −0.081 ** | |||||||||||
| Geo_Prox × Tech_Prox | −0.078 ** | |||||||||||
| Geo_Prox × Eco_Prox | −0.179 *** | |||||||||||
| Sample size | 1640 | 1640 | 1640 | 1640 | 1640 | 1640 | 1640 | 1640 | 1640 | 1640 | 1640 | 1640 |
| Adjusted R−square | 0.413 *** | 0.413 *** | 0.430 *** | 0.431 *** | 0.412 *** | 0.413 *** | 0.519 *** | 0.440 *** | 0.425 *** | 0.437 *** | 0.430 *** | 0.518 *** |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, P.; Chen, J.; Yuan, F.; Liu, W. The Formation of Knowledge Flow Networks in the Yangtze River Delta, China: Knowledge Implicitness and Proximity Effect. Sustainability 2025, 17, 740. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17020740
Zhu P, Chen J, Yuan F, Liu W. The Formation of Knowledge Flow Networks in the Yangtze River Delta, China: Knowledge Implicitness and Proximity Effect. Sustainability. 2025; 17(2):740. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17020740
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Pengcheng, Jianglong Chen, Feng Yuan, and Weichen Liu. 2025. "The Formation of Knowledge Flow Networks in the Yangtze River Delta, China: Knowledge Implicitness and Proximity Effect" Sustainability 17, no. 2: 740. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17020740
APA StyleZhu, P., Chen, J., Yuan, F., & Liu, W. (2025). The Formation of Knowledge Flow Networks in the Yangtze River Delta, China: Knowledge Implicitness and Proximity Effect. Sustainability, 17(2), 740. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17020740






