Identification of Peanut Cultivars with Low Cadmium Contents and Their Rhizosphere Microbial Characteristics in Alkaline and Acidic Cadmium-Contaminated Fields
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Setup and Sample Collection
2.2. Sample Preparation and Analytical Methods
2.3. Statistical and Bioinformatic Analyses
3. Results
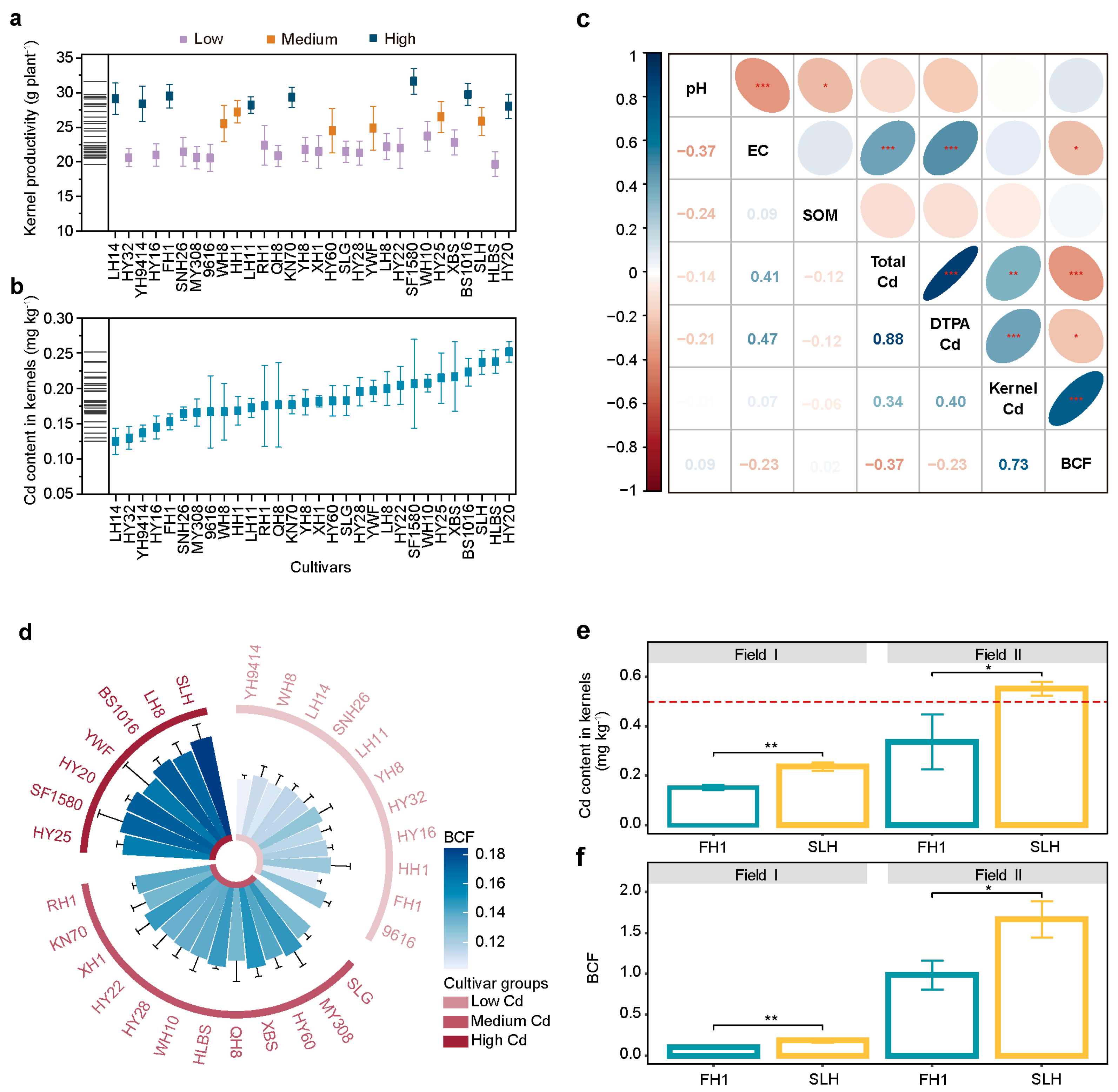
3.1. Identification of High- and Low-Cadmium-Accumulating Peanut Cultivars Based on Bioconcentration Factors
3.2. Differences in Rhizosphere Bacterial Communities Between Peanut Cultivars
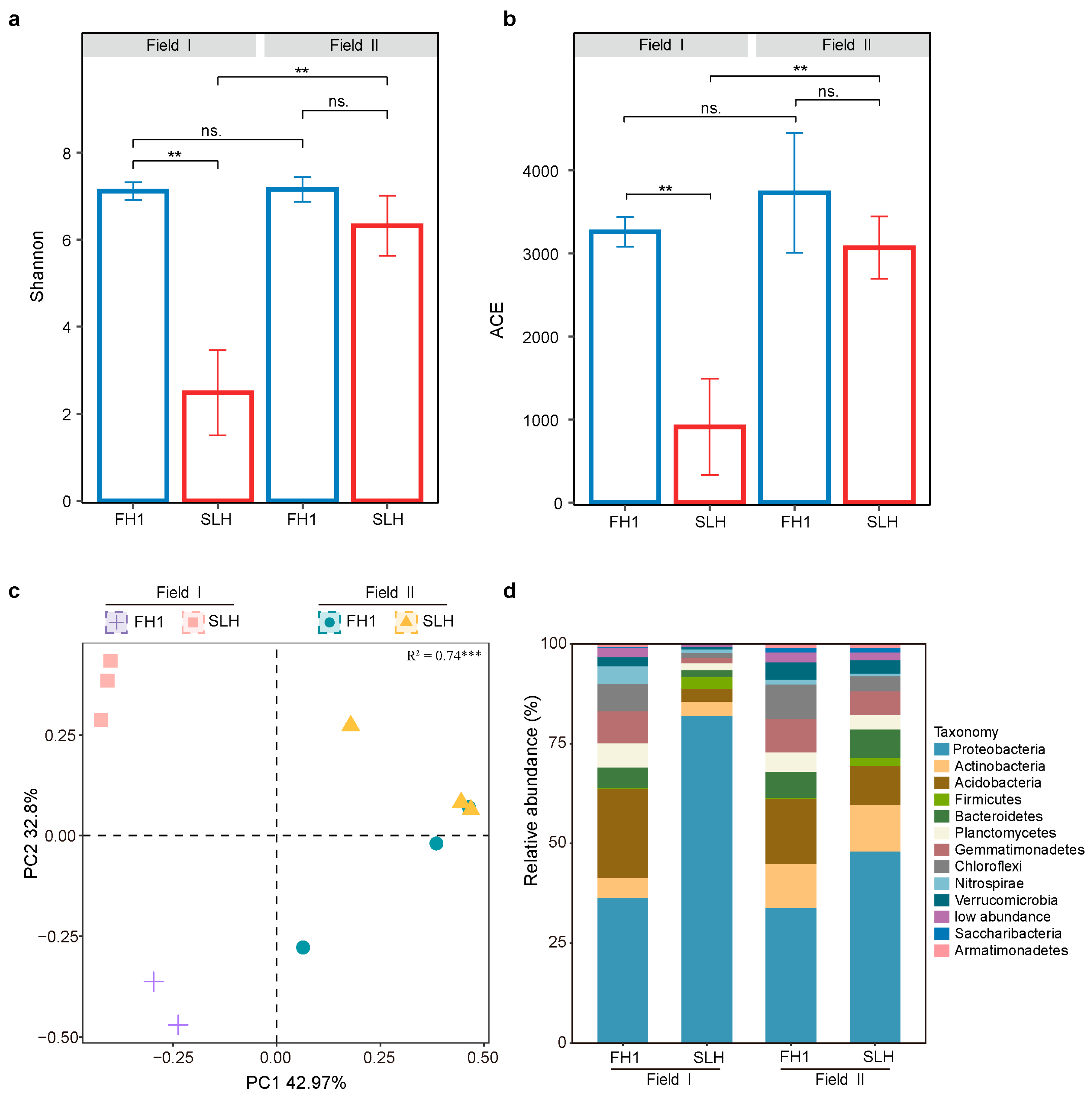
3.2.1. Bacterial Diversity and Composition Differences
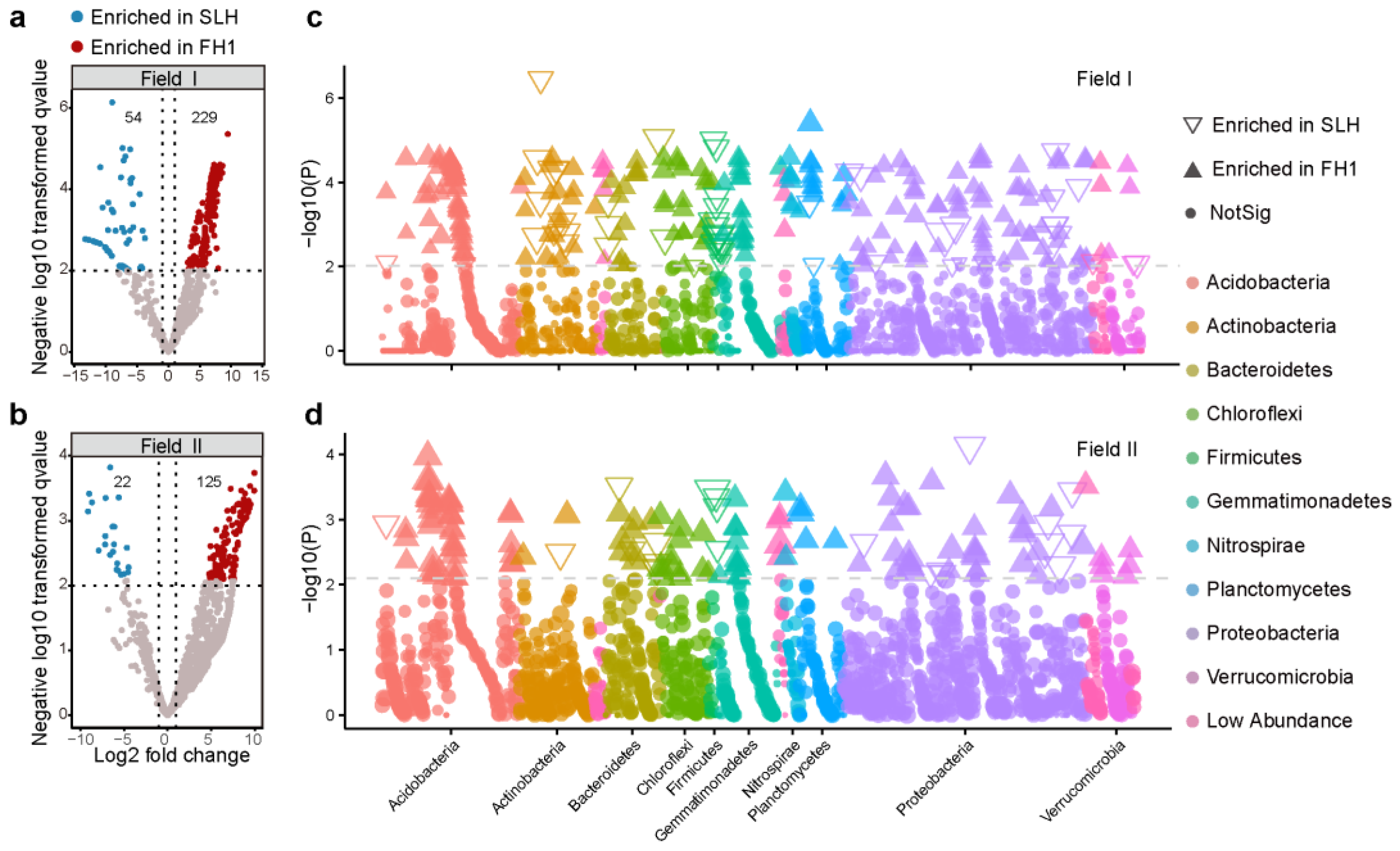
3.2.2. Bacterial Composition Differences at the ASV Level
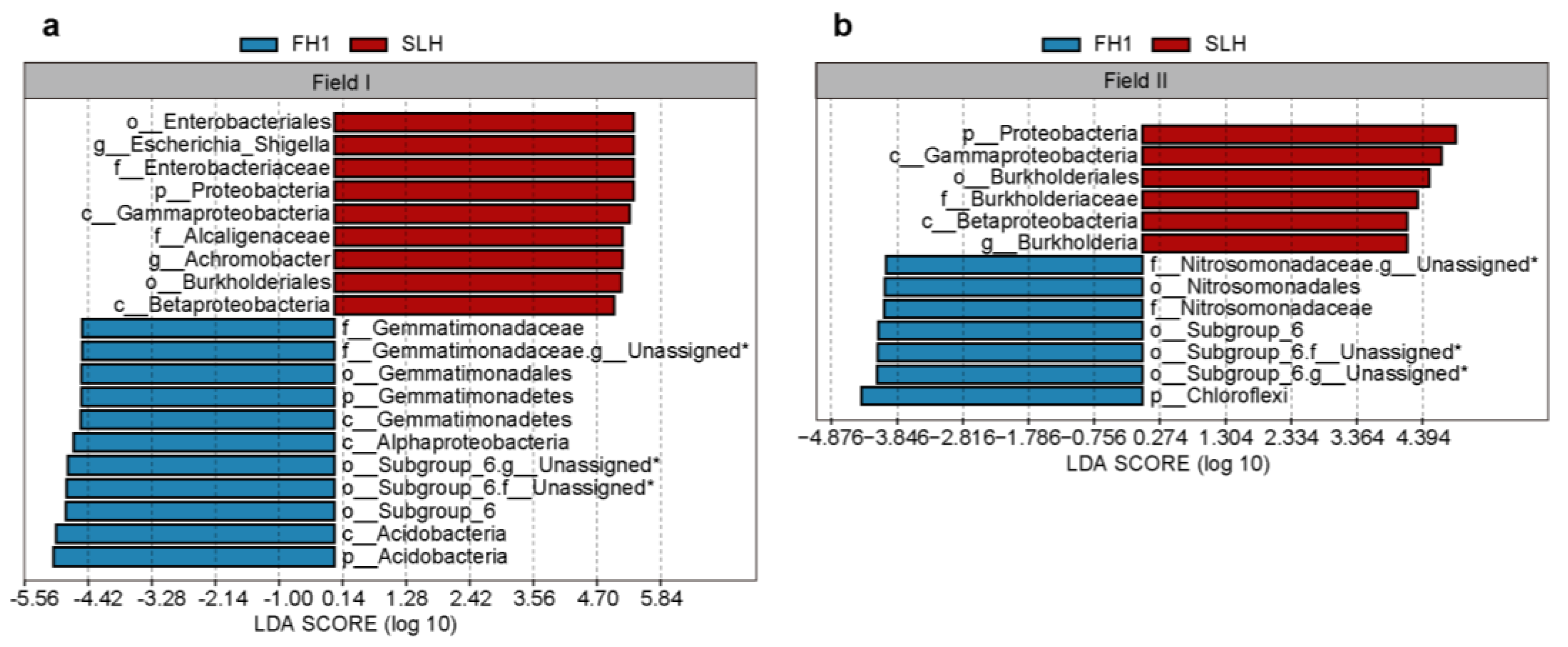
3.3. Biomarkers Among Different Cultivars
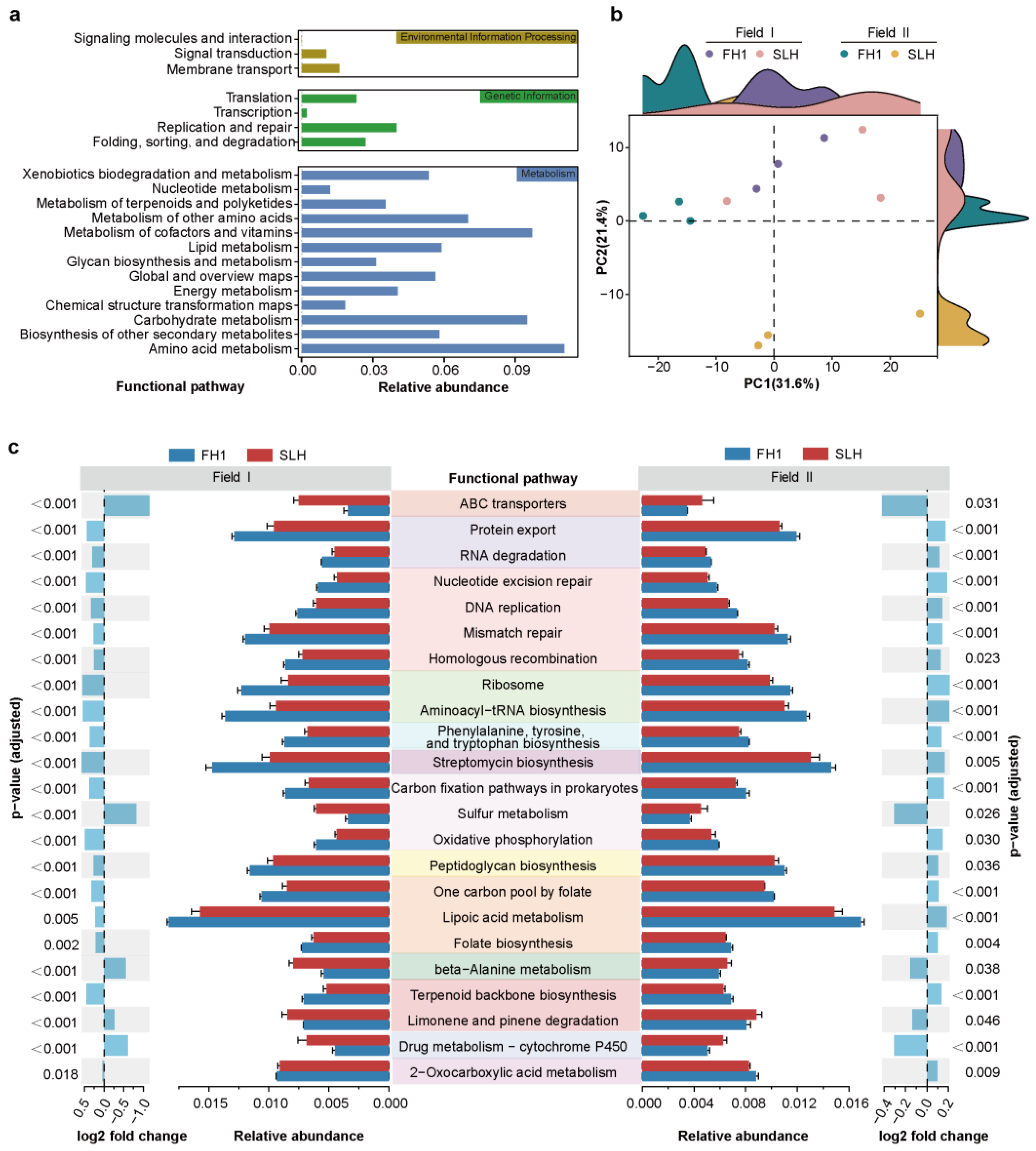
3.4. Functional Prediction Among Different Cultivars
4. Discussion
4.1. Identification and Application of Low-Cadmium Cultivars for Safe Agriculture on Cd-Polluted Farmland
4.2. Differences in Bacterial Diversity and Composition Between Peanut Cultivars
4.3. Predicted Functional Characteristics of the Bacterial Community in the Rhizosphere of the Low-Cd Cultivar FH1
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, P.; Chen, H.P.; Kopittke, P.M.; Zhao, F.J. Cadmium contamination in agricultural soils of China and the impact on food safety. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 249, 1038–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, Y.J.; Li, K.; Xiao, L.; Li, M.Y.; Tian, Y.; Wu, F. Assessment of anthropogenic sources of potentially toxic elements in soil from arable land using multivariate statistical analysis and random forest analysis. Sustainability 2020, 12, 8538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haider, F.U.; Liqun, C.; Coulter, J.A.; Cheema, S.A.; Wu, J.; Zhang, R.; Wenjun, M.; Farooq, M. Cadmium toxicity in plants: Impacts and remediation strategies. Ecotox. Environ. Saf. 2021, 211, 111887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, S.Y.; Liu, H.E.; Nie, Z.J.; Rengel, Z.; Gao, W.; Li, C.; Zhao, P. Toxicity of cadmium and its competition with mineral nutrients for uptake by plants: A review. Pedosphere 2020, 30, 168–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.H.; Chen, G.L.; Xu, K.; Wang, J. Cadmium in cereal crops: Uptake and transport mechanisms and minimizing strategies. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 5961–5974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.M.; Liu, H.Y.; Gao, M.; Zhou, J.; Zhou, J. Effects of soil amendments, foliar sprayings of silicon and selenium and their combinations on the reduction of cadmium accumulation in rice. Pedosphere 2022, 32, 649–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Liang, X.F.; Xu, Y.M.; Qin, X.; Huang, Q.Q.; Wang, L.; Sun, Y.B. Remediation of heavy metal-polluted agricultural soils using clay minerals: A review. Pedosphere 2017, 27, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, Q.Y.; Liao, X.Y.; Li, X.H.; Zheng, S.N.; Zhao, F.H. Phytoexclusion of heavy metals using low heavy metal accumulating cultivars: A green technology. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 413, 125427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, L.Y.; Ding, S.; Li, X.L.; Ning, C.L.; Liu, H.; Sun, M.; Liu, D.M.; Zhang, K.; Li, S.S.; Yu, X.J.; et al. Low-cadmium wheat cultivars limit the enrichment, transport and accumulation of cadmium. Agronomy 2024, 14, 1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, J.; Twardowska, I.; Wang, S.Q.; Wei, S.H.; Chen, Y.Q.; Ljupco, M. Prospective sustainable production of safe food for growing population based on the soybean (Glycine max L. Merr.) crops under Cd soil contamination stress. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 212, 22–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, K.X.; Li, J.X.; Yang, Y.C.; Li, Z.; Wu, W.G. Cadmium absorption in various genotypes of rice under cadmium stress. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 8019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.X.; Wang, O.; Cai, S.B.; Zhao, L.; Zhao, L. Composition, functional properties, health benefits and applications of oilseed proteins: A systematic review. Food Res. Int. 2023, 171, 113061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, B.L.; Zhang, C.X.; Zhang, X.J.; Wang, G.; Li, L.; Geng, H.R.; Liu, Y.; Nie, C.R. Survey of aflatoxin B1 and heavy metal contamination in peanut and peanut soil in China during 2017–2018. Food Control 2020, 118, 107372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.J.; Wang, L.; Cai, D.; Zhang, C.S.; Zhao, S.C. Risk assessment on dietary exposure to aflatoxin B1, heavy metals and phthalates in peanuts, a case study of Shandong province, China. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2023, 120, 105359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, X.L.; Li, B.; Cui, J.H.; Li, G.C.; Wang, Y.H. Assessment of heavy metal pollution and risk of farmland soil and agricultural products around a smelter in Liaoning. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2020, 39, 2249–2258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Yang, Z.F.; Zhang, Q.Z.; Ji, W.B.; Guan, D.X.; Liu, X.; Yu, T.; Wang, L.; Zhuo, X.X.; Ji, J.F. Transferability of heavy metal(loid)s from karstic soils with high geochemical background to peanut seeds. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 299, 118819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Wang, J.G.; Liu, D.W.; Li, L.; Wan, S.B.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, L.Q.; Zou, D.S. Cadmium concentration and translocation in paddy fields with different peanut varieties. Chin. J. Oil Crop Sci. 2019, 41, 568–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Song, S.X.; Li, S.S.; Bai, L.Y.; Liu, H.; Sun, M.; Yu, X.J.; Dai, J.L. Evaluation of cadmium phytoextraction potential of peanut and the rhizospheric properties of specific cultivars. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 452, 142228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Cao, Z.H.; Ma, X.L.; Cao, D.; Zhao, K.K.; Zhao, K.; Ma, Q.; Gong, F.P.; Li, Z.F.; Qiu, D.; et al. Natural resistance-associated macrophage proteins are involved in tolerance to heavy metal Cd2+ toxicity and resistance to bacterial wilt of peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.). Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2024, 207, 108411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; Ding, S.; Yan, Y.; Huang, X.M.; Li, S.S.; Zhao, W.N.; Chen, X.G.; Dai, J.L. Screening of peanut cultivars with low-cadmium accumulation assisted by cadmium resistance: Promoting safe utilization of cadmium contaminated soils. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2024, 193, 105109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, G.R.; Su, G.Q.; Lu, Z.W.; Liu, C.F.; Wang, X.M. Relationship between biomass, seed components and seed Cd concentration in various peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.) cultivars grown on Cd-contaminated soils. Ecotox. Environ. Saf. 2014, 110, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, G.Q.; Li, F.; Lin, J.S.; Liu, C.F.; Shi, G.R. Peanut as a potential crop for bioenergy production via Cd-phytoextraction: A life-cycle pot experiment. Plant Soil 2013, 365, 337–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.H.; Wu, X.Y.; Deng, X.Y.; Lin, Z.; Liu, C.G.; Zhang, J.X.; He, T.; Yi, Y.Q.; Liu, H.; Wang, Y.F.; et al. Mechanisms of low cadmium accumulation in crops: A comprehensive overview from rhizosphere soil to edible parts. Environ. Res. 2024, 245, 118054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.Y.; Rengel, Z.; Zhang, K.; Jin, K.M.; Lyu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Cheng, L.Y.; Zhang, F.S.; Shen, J.B. Ensuring future food security and resource sustainability: Insights into the rhizosphere. iScience 2022, 25, 104168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, X.; Wang, Y.R.; Ding, C.F.; Yin, Y.P.; Zhou, Z.G.; Zhang, T.L.; Wang, X.X. Cadmium found in peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.) kernels mainly originates from root uptake rather than shell absorption from soil. Pedosphere 2024, 34, 726–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.F.; Okoye, C.O.; Chen, X.F.; Zhang, F.S.; Jiang, J.X. High-throughput 16S rRNA gene-based amplicon sequencing reveals the functional divergence of halophilic bacterial communities in the Suaeda salsa root compartments on the eastern coast of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 942, 173775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.B.; Zhang, Q.Q.; Du, W.C.; Ai, F.X.; Yin, Y.; Ji, R.; Guo, H.Y. Microbial communities in the rhizosphere of different willow genotypes affect phytoremediation potential in Cd contaminated soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 769, 145224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.W.; Wu, K.J.; Shi, L.B.; Sun, X.C.; Tan, Q.L.; Hu, C.X. Recruitment of specific microbes through exudates affects cadmium activation and accumulation in Brassica napus. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 442, 130066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 15618-2018; Soil Environmental Quality-Risk Control Standard for Soil Contamination of Agricultural Land. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2018.
- NY/T 1121.6-2006; Technical Rules for Monitroing of Environmental Quality of Farmland Soil. China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 2006.
- Mo, X.H.; Wang, M.K.; Zeng, H.; Wang, J.J. Rhizosheath: Distinct features and environmental functions. Geoderma 2023, 435, 116500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 5009.15-2014; National Food Safety Standard-Determination of Cadmium in Foods. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2014.
- HJ 962-2018; Soil-Determination of pH-Potentiometry. National Environmental Protection Standard of the People’s Republic: Beijing, China, 2018.
- Bao, S.D. Soil and Agricultural Chemistry Analysis, 3rd ed.; China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 2000.
- NY/T 1121.6-2006; Soil Testing Part 6: Method for Determination of Soil Organic Matter. China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 2006.
- Bai, L.Y.; Ding, S.; Huang, X.M.; Chen, X.G.; Chen, Y.H.; Cao, X.Y.; Wang, X.R.; Yu, X.J.; Dai, J.L. Prediction of the cadmium content in grains of low-accumulating wheat cultivars and soil cadmium threshold for safe production. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 417, 138081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 17141-1997; Soil Quality-Determination of Lead, Cadmium-Graphitefurnace Atomic Absorption Spectrophotometry. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 1997.
- Cheng, Z.Y.; Zheng, Q.; Shi, J.C.; He, Y.; Yang, X.L.; Huang, X.W.; Wu, L.S.; Xu, J.M. Metagenomic and machine learning-aided identification of biomarkers driving distinctive Cd accumulation features in the root-associated microbiome of two rice cultivars. ISME Communications 2023, 3, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.X.; Chen, L.; Ma, T.F.; Li, X.F.; Zheng, M.S.; Zhou, X.; Chen, L.; Qian, X.B.; Xi, J.; Lu, H.Y.; et al. EasyAmplicon: An easy-to-use, open-source, reproducible, and community-based pipeline for amplicon data analysis in microbiome research. iMeta 2023, 2, e83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rognes, T.; Flouri, T.; Nichols, B.; Quince, C.; Mahé, F. VSEARCH: A versatile open source tool for metagenomics. PeerJ 2016, 4, e2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edgar, R.C. Search and clustering orders of magnitude faster than BLAST. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 2460–2461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yilmaz, P.; Parfrey, L.W.; Yarza, P.; Gerken, J.; Pruesse, E.; Quast, C.; Schweer, T.; Peplies, J.; Ludwig, W.; Glöckner, F.O. The SILVA and “All-species Living Tree Project (LTP)” taxonomic frameworks. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, D643–D648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F.O. The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: Improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D590–D596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dixon, P. VEGAN, a package of R functions for community ecology. J. Veg. Sci. 2003, 14, 927–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Liu, Y.X.; Huang, L.Q. ImageGP: An easy-to-use data visualization web server for scientific researchers. iMeta 2022, 1, e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.Y.; Zhang, G.X.; Jiang, S.Y.; Liu, Y.X. Wekemo Bioincloud: A user-friendly platform for meta-omics data analyses. iMeta 2024, 3, e175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.; Mai, J.H.; Cao, X.; Burberry, A.; Cominelli, F.; Zhang, L.L.; Elofsson, A. ggpicrust2: An R package for PICRUSt2 predicted functional profile analysis and visualization. Bioinformatics 2023, 39, btad470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GB 2762-2022; National Standards for Food Safety-Limits of Contaminants in Food. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2022.
- Douglas, G.M.; Maffei, V.J.; Zaneveld, J.R.; Yurgel, S.N.; Brown, J.R.; Taylor, C.M.; Huttenhower, C.; Langille, M.G.I. PICRUSt2 for prediction of metagenome functions. Nat. Biotechnol. 2020, 38, 685–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Z.Q.; Ren, B.Z.; Xie, Q.; Deng, X.P.; Yin, W.; Chen, L.Y. Assessment of health risks posed by toxicological elements of the food chain in a typical high geologic background. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 161, 111981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, L.Y.; Huang, X.M.; Li, Z.L.; Li, S.S.; Lv, C.; Zhang, K.; Dai, J.L. Stability and adaptability of wheat cultivars with low cadmium accumulation based on farmland trials. Eur. J. Agron. 2023, 144, 126764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.S.; Huang, X.M.; Liu, N.; Chen, Y.H.; He, H.; Cao, X.Y.; Dai, J.L. Selection of low-cadmium and high-micronutrient wheat cultivars and exploration of the relationship between agronomic traits and grain cadmium. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 42884–42898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, N.; Huang, X.M.; Sun, L.M.; Li, S.S.; Chen, Y.H.; Cao, X.Y.; Wang, W.X.; Dai, J.L.; Rinnan, R. Screening stably low cadmium and moderately high micronutrients wheat cultivars under three different agricultural environments of China. Chemosphere 2020, 241, 125065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.X.; Zhang, Z.; Shi, G.R. Genome-wide identification and expression profiling of heavy metal ATPase (HMA) genes in peanut: Potential roles in heavy metal transport. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, R.G.; Ma, Y.Y.; Li, Y.; Li, X.; Liu, C.F.; Du, X.L.; Shi, G.R. Comparative transcriptome analysis revealed key factors for differential cadmium transport and retention in roots of two contrasting peanut cultivars. BMC Genom. 2018, 19, 938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, R.G.; Jiang, Q.; Xv, C.; Li, L.E.; Bu, S.J.; Shi, G.R. Comparative proteomics analysis of peanut roots reveals differential mechanisms of cadmium detoxification and translocation between two cultivars differing in cadmium accumulation. BMC Plant Biol. 2019, 19, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, K.; Lv, J.L.; He, W.X.; Zhang, H.; Cao, Y.F.; Dai, Y.C. Major factors influencing cadmium uptake from the soil into wheat plants. Ecotox. Environ. Saf. 2015, 113, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bali, A.S.; Sidhu, G.P.S.; Kumar, V. Root exudates ameliorate cadmium tolerance in plants: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2020, 18, 1243–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, K.N.; Williams, D.V.; Zeng, M.; Ahmed, I.M.; Dai, H.X.; Cao, F.B.; Wu, F.B. Identification of low grain cadmium accumulation genotypes and its physiological mechanism in maize (Zea mays L.). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 29, 20721–20730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Z.W.; Zhang, Z.; Su, Y.; Liu, C.F.; Shi, G.R. Cultivar variation in morphological response of peanut roots to cadmium stress and its relation to cadmium accumulation. Ecotox. Environ. Saf. 2013, 91, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, Y.; Liu, J.L.; Lu, Z.W.; Wang, X.M.; Zhang, Z.; Shi, G.R. Effects of iron deficiency on subcellular distribution and chemical forms of cadmium in peanut roots in relation to its translocation. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2014, 97, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.F.; Yu, R.G.; Shi, G.R. Effects of drought on the accumulation and redistribution of cadmium in peanuts at different developmental stages. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2016, 63, 1049–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandran, H.; Meena, M.; Swapnil, P. Plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria as a green alternative for sustainable agriculture. Sustainability 2021, 13, 10986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.; Huang, L.K.; Wang, Q.; Cao, X.R.; Lin, Q.; He, Z.L.; Feng, Y.; Yang, X.E. Soil properties drive the bacterial community to cadmium contamination in the rhizosphere of two contrasting wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) genotypes. J. Environ. Sci. 2023, 128, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.Q.; Zhou, R.X.; Teng, L.D.; Chen, H.B.; Li, M.; Wang, L.; Zhran, M.; Cao, F.B. Genotypic variation in grain cadmium concentration in wheat: Insights into soil pollution, agronomic characteristics, and rhizosphere microbial communities. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 340, 122792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, N.; Liu, Q.; Min, J.M.; Zhang, S.J.; Li, S.S.; Chen, Y.H.; Dai, J.L. Specific bacterial communities in the rhizosphere of low-cadmium and high-zinc wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 838, 156484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.M.; Zhang, Y.X.; Wang, L.; Liu, C.G.; Sun, W.M.; Wang, Y.F.; Long, S.X.; He, X.T.; Lin, Z.; Liang, J.L.; et al. Rhizobacteria communities reshaped by red mud based passivators is vital for reducing soil Cd accumulation in edible amaranth. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 826, 154002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, D.D.; Wang, R.Z.; Gao, X.Y.; Wang, K.; Lin, Z.; Ge, J.; Liu, T.; Wei, S.; Chen, W.K.; Xie, R.H.; et al. Cultivar-specific response of bacterial community to cadmium contamination in the rhizosphere of rice (Oryza sativa L.). Environ. Pollut. 2018, 241, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kou, B.; He, Y.; Wang, Y.; Qu, C.T.; Tang, J.; Wu, Y.M.; Tan, W.B.; Yuan, Y.; Yu, T.Q. The relationships between heavy metals and bacterial communities in a coal gangue site. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 322, 121136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Chi, Y.; Su, X.Y.; Ye, Z.H.; Ren, X.X. Rhizobium soaking promoted maize growth by altering rhizosphere microbiomes and associated functional genes. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Li, C.; Lin, Y.; Chen, Y.J.; Zhang, Z.J.; Wei, K.H.; Lei, M. Biochar and organic fertilizer drive the bacterial community to improve the productivity and quality of Sophora tonkinensis in cadmium-contaminated soil. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 14, 1334338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; He, Y.L.; Lin, D.S.; Yao, Y.P.; Song, N.N.; Wang, F.L. Co-application of biochar and nitrogen fertilizer promotes rice performance, decreases cadmium availability, and shapes rhizosphere bacterial community in paddy soil. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 308, 119624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Li, X.F.; Li, Y.Y.; Dai, X.Z.; Zhang, Q.Z.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, Z.Q.; Tao, Y.; Chen, W.C.; Zhang, M.X.; et al. Improved immobilization of soil cadmium by regulating soil characteristics and microbial community through reductive soil disinfestation. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 778, 146222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.X.; Xiong, Y.; Zhang, J.E.; Lu, X.N.; Wei, G.C. Naturally selected dominant weeds as heavy metal accumulators and excluders assisted by rhizosphere bacteria in a mining area. Chemosphere 2020, 243, 125365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.J.; Song, K.; Shi, L.Z.; Duan, D.C.; Zhang, H.; Sun, Y.F.; Qin, Q.; Xue, Y. Influence of elemental sulfur on cadmium bioavailability, microbial community in paddy soil and Cd accumulation in rice plants. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 11468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.R.; Huang, Y.C.; Yang, X.R.; Xue, W.J.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.H.; Pang, J.; Liu, Y.M.; Liu, Z.Q. Burkholderia sp. Y4 inhibits cadmium accumulation in rice by increasing essential nutrient uptake and preferentially absorbing cadmium. Chemosphere 2020, 252, 126603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, Y.; Wang, X.M.; Liu, C.F.; Shi, G.R. Variation in cadmium accumulation and translocation among peanut cultivars as affected by iron deficiency. Plant Soil 2013, 363, 201–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.F.; Tan, X.Y.; Lu, L.L.; Meng, X.T.; Li, Y.Y.; Yao, H.Y. DNA-SIP delineates unique microbial communities in the rhizosphere of the hyperaccumulator Sedum alfredii which are beneficial to Cd phytoextraction. Ecotox. Environ. Saf. 2024, 272, 116016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.J.; Sheng, X.F.; He, L.Y.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, W.H. Effects of root inoculation with bacteria on the growth, Cd uptake and bacterial communities associated with rape grown in Cd-contaminated soil. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 244–245, 709–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.K.; Huang, H.Y.; Xie, Y.L.; Liu, Y.K.; Shangguan, Y.X.; Xu, H. Integrated biochemical and transcriptomic analysis reveals the effects of Burkholderia sp. SRB-1 on cadmium accumulating in Chrysopogon zizanioides L. under Cd stress. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 337, 117723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.J.; Deng, J.M.; Shao, L.; Jiang, S.M.; Xiao, T.F.; Sun, W.M.; Xiao, E.Z. The rhizosphere microbiome improves the adaptive capabilities of plants under high soil cadmium conditions. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 914103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Xing, Y.N.; Huang, B.; Chen, X.; Ji, L.; Fu, X.W.; Li, T.Y.; Wang, J.N.; Chen, G.H.; Zhang, Q. Rhizospheric mechanisms of Bacillus subtilis bioaugmentation-assisted phytostabilization of cadmium-contaminated soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 825, 154136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasse, J.; Martinoia, E.; Northen, T. Feed your friends: Do plant exudates shape the root microbiome? Trends Plant Sci. 2018, 23, 25–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.J.; Jiang, L.H.; Guo, Z.W.; Sarkodie, E.K.; Li, K.W.; Shi, J.X.; Peng, Y.L.; Liu, H.W.; Liu, X.D. The Cd immobilization mechanisms in paddy soil through ureolysis-based microbial induced carbonate precipitation: Emphasis on the coexisting cations and metatranscriptome analysis. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 465, 133174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, T.Y.; Lu, Y.Q.; Li, F.; Zeng, W.M.; Shen, L.; Yu, R.L.; Li, J.K. Microbial extracellular polymeric substances alleviate cadmium toxicity in rice (Oryza sativa L.) by regulating cadmium uptake, subcellular distribution and triggering the expression of stress-related genes. Ecotox. Environ. Saf. 2023, 257, 114958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Wang, L.F.; Zhao, S.W.; Li, S.S.; Lei, X.Q.; Qin, L.Y.; Sun, X.Y.; Chen, S.B. Manganese facilitates cadmium stabilization through physicochemical dynamics and amino acid accumulation in rice rhizosphere under flood-associated low pe+pH. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 416, 126079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.M.; Wu, P.X.; Liu, J.; Yang, S.S.; Ruan, B.; Rehman, S.; Liu, L.T.; Zhu, N.W. The regulatory mechanism of Chryseobacterium sp. resistance mediated by montmorillonite upon cadmium stress. Chemosphere 2020, 240, 124851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorelova, V.; Ambach, L.; Rébeillé, F.; Stove, C.; Van Der Straeten, D. Folates in plants: Research advances and progress in crop biofortification. Front. Chem. 2017, 5, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turk, H.; Erdal, S.; Karayel, U.; Dumlupinar, R. Attenuation of lead toxicity by promotion of tolerance mechanism in wheat roots by lipoic acid. Cereal Res. Commun. 2018, 46, 424–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, D.D.; Wang, K.; Liu, T.; Wang, H.X.; Lin, Z.; Qian, J.; Lu, L.L.; Tian, S.K. Unique rhizosphere micro-characteristics facilitate phytoextraction of multiple metals in soil by the hyperaccumulating plant Sedum alfredii. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 5675–5684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahad, A.; Ahmad, N.; Ilyas, M.; Batool, T.S.; Gul, A. The role of ABC transporters in metal transport in plants. In Plant Metal and Metalloid Transporters; Kumar, K., Srivastava, S., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2022; pp. 55–71. [Google Scholar]
- Fajardo, C.; Costa, G.; Nande, M.; Botías, P.; García-Cantalejo, J.; Martín, M. Pb, Cd, and Zn soil contamination: Monitoring functional and structural impacts on the microbiome. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2019, 135, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Chen, D.; Li, B.Q.; Yang, Y.P. Cd accumulation characteristics of Salvia tiliifolia and changes of rhizospheric soil enzyme activities and bacterial communities under a Cd concentration gradient. Plant Soil 2021, 463, 225–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, K.; Du, X.; Li, X.; Li, S.; Liu, H.; Bai, L.; Dai, J. Identification of Peanut Cultivars with Low Cadmium Contents and Their Rhizosphere Microbial Characteristics in Alkaline and Acidic Cadmium-Contaminated Fields. Sustainability 2025, 17, 626. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17020626
Zhang K, Du X, Li X, Li S, Liu H, Bai L, Dai J. Identification of Peanut Cultivars with Low Cadmium Contents and Their Rhizosphere Microbial Characteristics in Alkaline and Acidic Cadmium-Contaminated Fields. Sustainability. 2025; 17(2):626. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17020626
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Ke, Xuefeng Du, Xiaoli Li, Shuangshuang Li, Hui Liu, Liyong Bai, and Jiulan Dai. 2025. "Identification of Peanut Cultivars with Low Cadmium Contents and Their Rhizosphere Microbial Characteristics in Alkaline and Acidic Cadmium-Contaminated Fields" Sustainability 17, no. 2: 626. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17020626
APA StyleZhang, K., Du, X., Li, X., Li, S., Liu, H., Bai, L., & Dai, J. (2025). Identification of Peanut Cultivars with Low Cadmium Contents and Their Rhizosphere Microbial Characteristics in Alkaline and Acidic Cadmium-Contaminated Fields. Sustainability, 17(2), 626. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17020626





