Sustainable Management of Poly- and Perfluoroalkyl Substances (PFASs)-Contaminated Areas: Tackling a Wicked Environmental Problem
Abstract
1. PFAS: Sources and Human Exposure Pathways
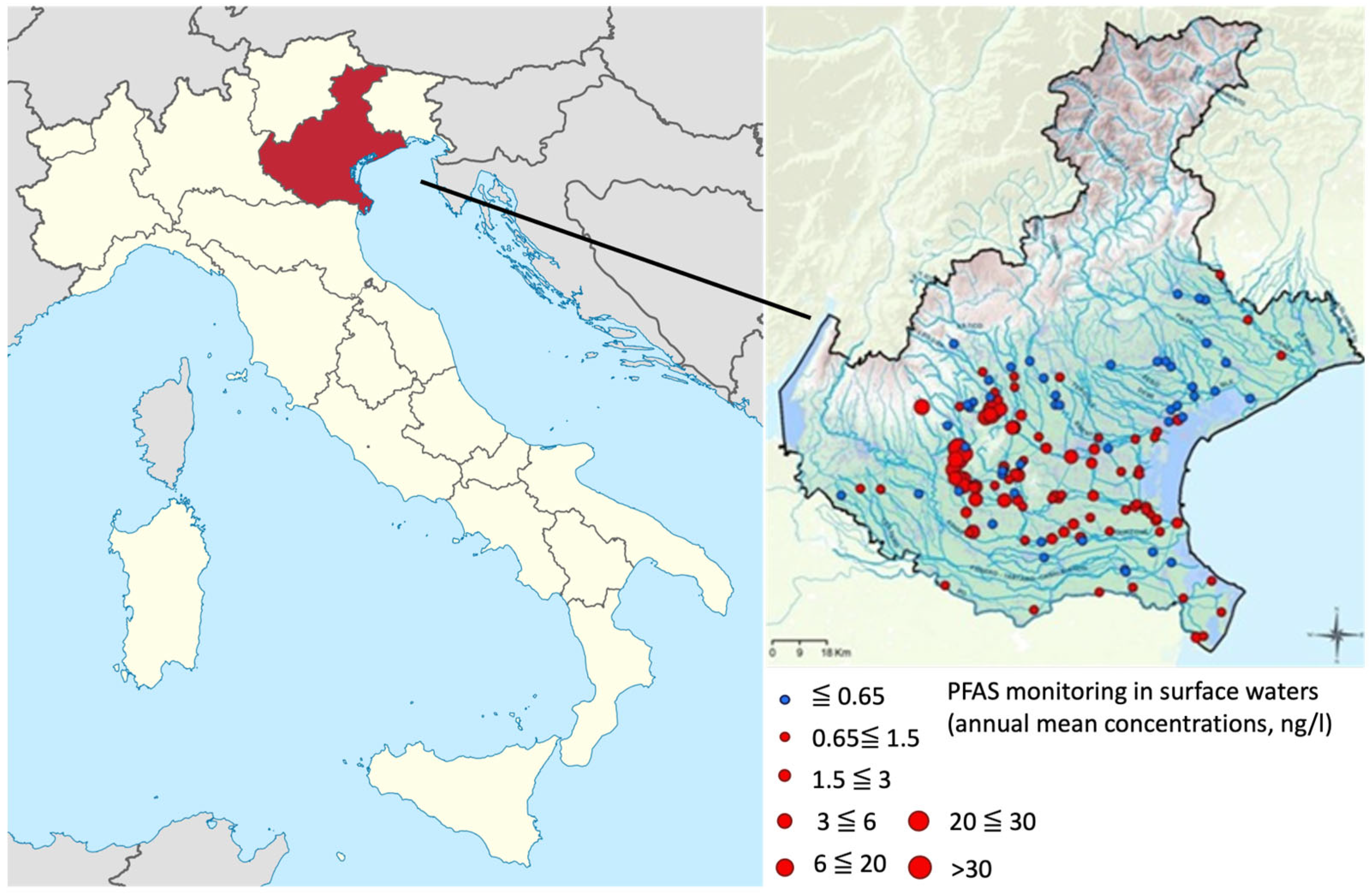
2. PFAS Environmental Pollution: Major Clusters in the European Union
3. Elements of Global and Local Regulatory Trends
| Country | Matrix and Concentrations | References | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Surface and Groundwater | Discharge/Immission Water | Drinking Water | Soil | Biosolids | Food | Other Matrices | ||
| USA | 70 ng/L for PFOA and PFOS and their sum | TBD at Federal level Limits for different States (see references) | PFOA 4.0 ng/L, PFOS, 4.0 ng/L, PFHxS 10 ng/L, PFNA 10 ng/L, HFPO-DA [GenX] 10 ng/L, Mixtures containing two or more of PFHxS, PFNA, HFPO-DA, and PFBS Hazard Index = 1 (see references) | Non legally binding regional Guidance Screening Levels for PFAS | ME PFOS = 5.2[µg/g] PFOA = 2.5[µg/g] PFBS = 1900[µg/g] MI: PFOS = 125[µg/g] | TBD | None | [37,38,39] |
| Canada | TBD at National level Limits for different States | Sum of 30 PFAS ≤ 30 ng/L Determined with the USEPA methods 533 and or 537.19 | PFOS = 10 (µg/g) | TBD | TBD | None | [40,41,42] | |
| European Union | PFOS = 0.65 ng/L annual average for sea water | TBD at Community level Limits for different States and Regions | Total PFAS 0.500 ng/L or 100 ng/L for the sum of 20 C4-C13 carboxyl and sulfonic PFAS | DK: 400 ng/g sum of 12 PFAS; NL: 0.9 ng PFOS, 0.8 ng/g PFOA SE: 3-20 ng/g PFOA+PFOS DE:100 ng PFAS/g < 100 µg/L total PFAS by leaching test for landfilling | 100 µg/kg PFOA+PFOS * | 4.4 ng/kg b.w./week | None For fertilizers (DE) 100 ng/g | [7,43,44,45,46,47] |
| China | TBD at National level | PFOA 80 ng/L, PFOS 40 ng/L for PFOS | None | None | [48] | |||
| Australia and New Zealand | TBD at Federal level Limits for different States (See references) | PFOA 560 ng/L, PFOS and PFHxS 70 ng/L | 1 mg/kg PFOS 10 mg/kg PFOA | ng/g PFOS = 1 PFOS+PFHxS = 2 PFHxS = 3 PFOA = 4 PFBA, PFPeA, PFHxA = 1 Sum C9-C14 PFCA = 10 PFSA = 1 n:2 FTS = 4 | TDI = 160 ng/kg b.w./day for PFOA 20 ng/kg b.w./day for PFOS + PFHxS | None | [4,49,50,51] | |
| World Health Organization | None | PFOS and PFOA 100 ng/L singly | None | None | None | None | [51] | |
4. Chemical Properties Controlling PFAS Environmental Persistence and Mobility in Soil
PFAS Biodegradation: Past and Recent Evidence
5. Management Options of PFAS-Polluted Areas
5.1. Current Approaches to Remediation and Management of PFAS-Polluted Soils
5.2. Circular Economy Can Recirculate PFASs in the Agricultural Environment: The Case of Biosolids
6. Sustainable Management and Mitigation Strategies
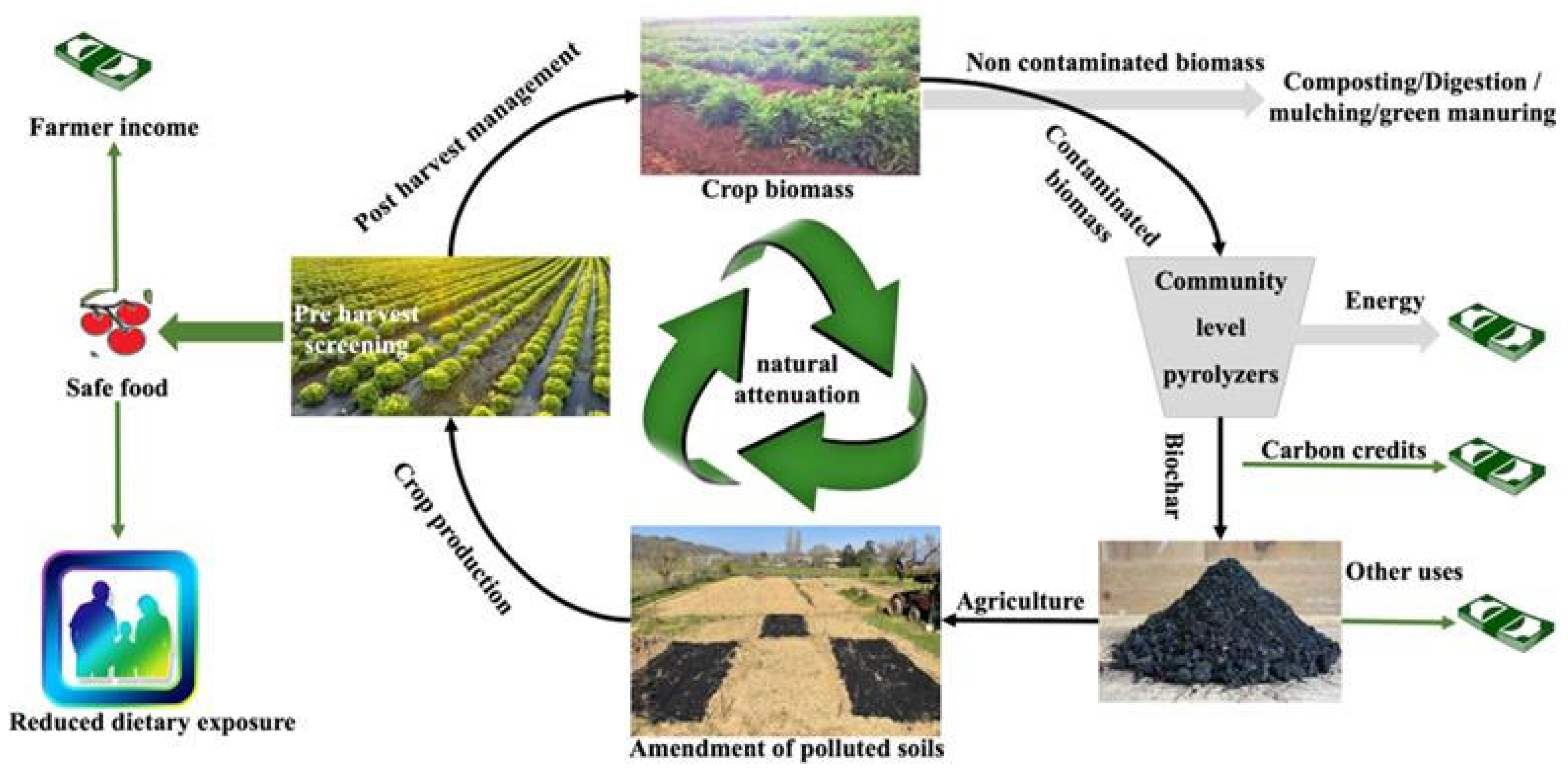
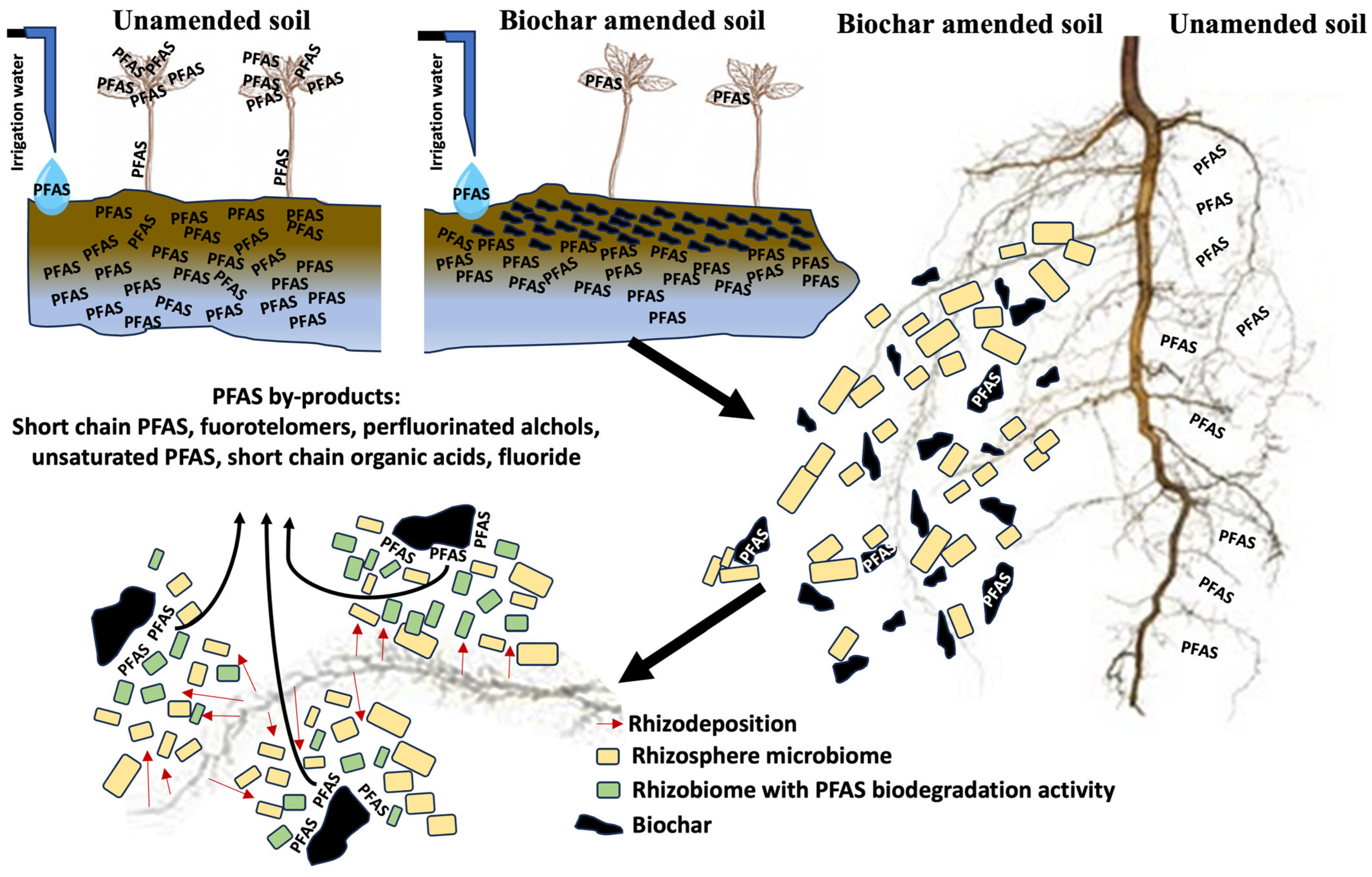
6.1. Pyrolysis of Pre-Screened Harvests and Biochar-Assisted Mitigation
6.2. Phytomanagement
6.3. Irrigation with Rainwater
7. Stakeholders’ Engagement: From a Wicked Problem to Awareness and Consensus Solutions
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gaines, L.G.T.; Sinclair, G.; Williams, A.J. A proposed approach to defining per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) based on molecular structure and formula. Integr. Environ. Assess. Manag. 2023, 19, 1333–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ITRC. Interstate Technology Regulatory Council. History and Use of Per-and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS). 2017. Available online: https://pfas-1.itrcweb.org/wp-content/uploads/2022/09/HistoryandUse_PFAS_Fact-Sheet_090722_508.pdf (accessed on 12 August 2024).
- Fenton, S.E.; Ducatman, A.; Boobis, A.; DeWitt, J.C.; Lau, C.; Ng, C.; Smith, J.S.; Roberts, S.M. Per-and polyfluoroalkyl substance toxicity and human health review: Current state of knowledge and strategies for informing future research. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2021, 40, 606–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- NEMP. PFAS National Environmental Management Plan Version 2.0—National Chemicals Working Group of the Heads of EPAs Australia and New Zealand. 2020. Available online: https://www.dcceew.gov.au/sites/default/files/documents/pfas-nemp-2.pdf (accessed on 5 August 2024).
- Glüge, J.; Scheringer, M.; Cousins, I.T.; DeWitt, J.C.; Goldenman, G.; Herzke, D.; Lohmann, R.; Ng, C.A.; Trier, X.; Wang, Z. An overview of the uses of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS). Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2020, 22, 2345–2373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EFSA. PFAS in Food: EFSA Assesses Risks and Sets Tolerable Intake. 2020. Available online: https://www.efsa.europa.eu/en/news/pfas-food-efsa-assesses-risks-and-sets-tolerable-intake (accessed on 5 August 2024).
- Schrenk, D.; Bignami, M.; Bodin, L.; Chipman, J.K.; Del Mazo, J.; Grasl-Kraupp, B.; Hogstrand, C.; Hoogenboom, L.R.; Leblanc, J.-C.; Nebbia, C.S.; et al. Scientific Opinion on the risk to human health related to the presence of perfluoroalkyl substances in food. EFSA J. 2020, 18, e06223. [Google Scholar]
- Sunderland, E.M.; Hu, X.D.C.; Dassuncao, C.; Tokranov, A.K.; Wagner, C.C.; Allenm, J.G. A review of the pathways of human exposure to poly- and perfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) and present understanding of health effects. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2019, 29, 131–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EC. European Commission, Regulation (EU) 2019/1021 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 20 June 2019 on Persistent Organic Pollutants (recast). 2023. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/PDF/?uri=CELEX:02019R1021-20230828 (accessed on 12 August 2024).
- Ruyle, B.J.; Pickard, H.M.; LeBlanc, D.R.; Tokranov, A.K.; Thackray, C.P.; Hu, X.C.; Vecitis, C.D.; Sunderland, E.M. Isolating the AFFF signature in coastal watersheds using oxidizable PFAS. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 16, 3686–3695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guckert, M.; Scheurer, M.; Schaffer, M.; Reemtsma, T.; Nödler, K. Combining target analysis with sum parameters-a comprehensive approach to determine sediment contamination with PFAS and further fluorinated substances. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 85802–85814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwiatkowski, C.F.; Andrews, D.Q.; Birnbaum, L.S.; Bruton, T.A.; DeWitt, J.C.; Knappe, D.R.U.; Maffini, M.V.; Miller, M.F.; Pelch, K.E.; Reade, A.; et al. Scientific basis for managing PFAS as a chemical class. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2020, 7, 532–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ECHA. PFAS Restriction Proposal ECHA/NR/23/04. 2023. Available online: https://echa.europa.eu/-/echa-publishes-pfas-restriction-proposal (accessed on 5 August 2024).
- Ackerman Grunfeld, D.; Gilbert, D.; Hou, J.; Jones, A.M.; Lee, M.J.; Kibbey, T.C.G.; O’Carroll, D.M. Underestimated burden of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances in global surface waters and groundwaters. Nat. Geosci. 2024, 17, 340–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingelido, A.M.; Abballe, A.; Gemma, S.; Dellatte, E.; Iacovella, N.; De Angelis, G.; Zampaglioni, F.; Marra, V.; Miniero, R.; Valentini, S.; et al. Biomonitoring of perfluorinated compounds in adults exposed to contaminated drinking water in the Veneto Region, Italy. Environ. Int. 2018, 110, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebbink, W.A.; van Leeuwen, S.P.J. Environmental contamination and human exposure to PFASs near a fluorochemical production plant: Review of historic and current PFOA and GenX contamination in the Netherlands. Environ. Int. 2020, 137, 105583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weidemann, E.; Lämmer, R.; Stahl, T.; Göckener, B.; Bücking, M.; Breuer, J.; Kowalczyk, J.; Just, H.; Boeddinghaus, R.S.; Gassmann, M. Leaching and transformation of perfluoroalkyl acids and polyfluoroalkyl phosphate diesters in unsaturated soil column studies. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2022, 41, 2065–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lasters, R.; Groffen, T.; Eens, M.; Bervoets, L. Dynamic spatiotemporal changes of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in soil and eggs of private gardens at different distances from a fluorochemical plant. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 346, 123613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ARPAV. Veneto Regional Environmental Protection Agency. 2024. Available online: https://www.arpa.veneto.it/dati-ambientali/open-data/idrosfera/concentrazione-di-sostanze-perfluoroalchiliche-pfas-nelle-acque-prelevate-da-arpav (accessed on 12 August 2024).
- Pitter, G.; Da Re, F.; Canova, C.; Barbieri, G.; Jeddi, M.Z.; Daprà, F.; Manea, F.; Zolin, R.; Bettega, A.M.; Stopazzolo, G.; et al. Serum levels of perfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in adolescents and young adults exposed to contaminated drinking water in the Veneto Region, Italy: A cross-sectional study based on a health surveillance program. Environ. Health Perspect. 2020, 128, 027007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Washington, J.W.; Rankin, K.; Libelo, E.L.; Lynch, D.G.; Cyterski, M. Determining global background soil PFAS loads and the fluorotelomer-based polymer degradation rates that can account for these loads. Sci. Tot. Environ. 2019, 651, 2444–2449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brusseau, M.L. Estimating the relative magnitudes of adsorption to solid-water and air/oil-water interfaces for per-and poly-fluoroalkyl substances. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 254, 113102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwok, K.Y.; Yamazaki, E.; Yamashita, N.; Taniyasu, S.; Murphy, M.B.; Horii, Y.; Petrick, G.; Kallerborn, R.; Kannan, K.; Murano, K.; et al. Transport of perfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) from an arctic glacier to downstream locations: Implications for sources. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 447, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, J.H.; Salter, M.E.; Acosta Navarro, J.C.; Leck, C.; Nilsson, E.D.; Cousins, I.T. Global transport of perfluoroalkyl acids via sea spray aerosol. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2019, 21, 635–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rankin, K.; Mabury, S.A.; Jenkins, T.M.; Washington, J.W. A North American and global survey of perfluoroalkyl substances in surface soils: Distribution patterns and mode of occurrence. Chemosphere 2016, 161, 333–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, K.C. Persistent Organic Pollutants [POPs] and related chemicals in the global environment: Some personal reflections. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 9400–9412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, P.; Xu, H.; Wang, C.; Chen, Y.; Guo, L.; Wang, X. Persistent organic pollutant cycling in forests. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2021, 2, 182–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Chang, S.; Zhao, Y.; Tang, J.; Sun, H.; Xie, Z. Per- and poly-fluoroalkyl substances (PFASs)in the urban, industrial, and background atmosphere of Northeastern China coast around the Bohai Sea: Occurrence, partitioning, and seasonal variation. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 167, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wegmann, F.; Scheringer, M.; Möller, M.; Hungerbühler, K. Influence of vegetation on the environmental partitioning of DDT in two global multimedia models. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 1505–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moeckel, C.; Nizzetto, L.; Di Guardo, A.; Steinnes, E.; Freppaz, M.; Filippa, G.; Camporini, P.; Benner, J.; Jones, K.C. Persistent organic pollutants in boreal and montane soil profiles: Distribution, evidence of processes and implications for global cycling. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 8374–8380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nizzetto, L.; Macleod, M.; Borgå, K.; Cabrerizo, A.; Dachs, J.; Di Guardo, A.; Ghirardello, D.; Hansen, K.M.; Jarvis, A.; Lindroth, A.; et al. Present, and future controls on levels of persistent organic pollutants in the global environment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 6526–6531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNEP. Listing of Perfluorooctanoic Acid (PFOA), Its Salts and PFOA-Related Compounds (UNEP/POPS/COP.9/SC-9/12). In Proceedings of the 9th Meeting of the Conference of the Parties to the Stockholm Convention on Persistent Organic Pollutants, Geneva, Switzerland, 29 April–10 May 2019; Available online: https://www.unep.org/topics/chemicals-and-pollution-action/pollution-and-health/persistent-organic-pollutants-pops/why (accessed on 12 August 2024).
- Cousins, I.T.; Johansson, J.H.; Salter, M.E.; Sha, B.; Scheringer, M. Outside the safe operating space of a new planetary boundary for per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 11172–11179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 3M. 3M to Exit PFAS Manufacturing by the End of 2025. 3M News Center. 2022. Available online: https://news.3m.com/2022-12-20-3M-to-Exit-PFAS-Manufacturing-by-the-End-of-2025 (accessed on 5 August 2024).
- Karlsruhe Regional Council. 2024. Available online: https://rp.baden-wuerttemberg.de/seite-nicht-gefunden (accessed on 12 August 2024).
- Naidu, R.; Nadebaum, P.; Fang, C.; Cousins, I.; Pennell, K.; Conder, J.; Newell, C.J.; Longpré, D.; Warner, S.; Crosbie, N.D.; et al. Per- and poly-fluoroalkyl substances (PFAS): Current status and research needs. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2020, 19, 1000915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NPDWR. United States of America Environmental Protection Agency. National Primary Drinking Water Regulation (NPDWR). 10 April 2024. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/sdwa/and-polyfluoroalkyl-substances-pfas (accessed on 12 August 2024).
- Maine PFAS Report. Managing PFAS in Maine. 2020. Available online: https://www.maine.gov/pfastaskforce/materials/report/PFAS-Task-Force-Report-FINAL-Jan2020.pdf (accessed on 12 August 2024).
- EGLE. Michigan Department of Environment, Great Lakes, and Energy. Biosolids and PFAS: Quick Facts for Landowners/Farmers. 2022. Available online: https://www.michigan.gov/-/media/Project/Websites/egle/Documents/Programs/WRD/Biosolids/biosolids-pfas-facts-landowners-farmers.pdf?rev=641c693bd1c24188a5a14a83704302cf (accessed on 12 August 2024).
- Health Canada. Federal Government of Canada. Canadian Food Inspection Agency (CFIA) Interim Norm. Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) in Drinking Water. 2023. Available online: https://www.canada.ca/en/health-canada/services/environmental-workplace-health/reports-publications/water-quality/water-talk-per-polyfluoroalkyl-substances-drinking-water.html (accessed on 12 August 2024).
- Health Canada. Federal Government of Canada. Draft Objective for Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances in Canadian Drinking Water: Rationale. 2023. Available online: https://www.canada.ca/en/health-canada/programs/consultation-draft-objective-per-polyfluoroalkyl-substances-canadian-drinking-water/rationale.html (accessed on 12 August 2024).
- CCME. Canadian Soil and Groundwater Quality Guidelines for the Protection of Environmental and Human Health. 2021. Available online: https://ccme.ca/en/res/pfosfactsheeten.pdf (accessed on 12 August 2024).
- EC. European Commission 2020. European Parliament and Council of the European Union. Drinking Water Directive 2020/2814. Off. J. Eur. Union 2020, L 435, 1–62. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/eli/dir/2020/2184/oj (accessed on 12 August 2024).
- NICOLE. Network for Industrially Contaminated Land in Europe. Environmental Fate and Effects of Poly and Perfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS). 2016. Available online: https://www.concawe.eu/wp-content/uploads/2016/06/Rpt_16-8.pdf (accessed on 12 August 2024).
- RIVM. The Dutch National Institute for Public Health and the Environment. Nitrogen and PFAS Suddenly Big Societal Issues in The Netherlands. 2020. Available online: https://www.rivm.nl/en/newsletter/content/2020/issue1/nitrogen-pfas-in-NL (accessed on 12 August 2024).
- Biegel-Engler, A.; Frauenstein, J. PFAS in Soil and Groundwater: Comprehensive Challenges and Progress in Regulation and Management in Germany. In International Yearbook of Soil Law and Policy 2022; Ginzky, H., De Andrade Corrêa, F., Dooley, E., Heuser, I.L., Kameri-Mbote, P., Kibugi, R., Ruppe, O.C.L., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 285–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UBA. German Federal Environment Agency Guidelines for PFAS Assessment. 2022. Available online: https://www.bmuv.de/fileadmin/Daten_BMU/Download_PDF/Bodenschutz/pfas_leitfaden_2022_en_bf.pdf (accessed on 12 August 2024).
- 8GB5749-2022; Standards for Drinking Water Quality. National Standard of the People’s Republic of China. Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2022. Available online: https://openstd.samr.gov.cn/ (accessed on 12 August 2024).
- NHRMC. Australian Drinking Water Guidelines. 2023. Available online: https://www.nhmrc.gov.au/about-us/publications/australian-drinking-water-guidelines (accessed on 12 August 2024).
- ENEW07359617. Department of Environment and Science, State of Queensland 2020. End of Waste Code Biosolids, Waste Reduction and Recycling Act. 2011. Available online: https://www.des.qld.gov.au/policies?a=272936:policy_registry/wr-eowc-approved-biosolids.pdf (accessed on 12 August 2024).
- WHO. World Health Organization. PFOS and PFOA in Drinking-Water: Background Document for Development of WHO Guidelines for Drinking Water Quality. 2022. Available online: https://www.cmbg3.com/library/WHO-Draft-Drinking-Water-Document.pdf (accessed on 12 August 2024).
- Sadtler, V.M.; Giulieri, F.; Krafft, M.P.; Riess, J.G. Micellization and adsorption of fluorinated amphiphiles: Questioning the 1CF2≈1.5 CH2 rule. Chem. Eur. J. 1998, 4, 1952–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, A. Carbon-fluorine bond cleavage mediated by metalloenzymes. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 4906–4925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.X.; Wang, L.; Xu, C.Q.; Zhi, R.; Miao, R.; Liang, T.; Yue, X.L.; Lv, Y.T.; Liu, T.T. Perfluorooctane sulfonate and perfluorobutane sulfonate removal from water by nanofiltration membrane: The roles of solute concentration, ionic strength, and macromolecular organic foulants. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 332, 787–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.M.H.; Bräunig, J.; Thompson, K.; Thompson, J.; Kabiri, S.; Navarro, D.A.; Kookana, R.S.; Grimison, C.; Barnes, C.M.; Higgins, C.P.; et al. Influences of chemical properties, soil properties, and solution pH on soil–water partitioning coefficients of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 15883–15892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burkhardt, J.B.; Cadwallader, A.; Pressman, J.G.; Magnuson, M.L.; Williams, A.J.; Sinclair, G.; Speth, T.F. Polanyi adsorption potential theory for estimating PFAS treatment with granular activated carbon. J. Water Process. Eng. 2023, 53, 103691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Jaffé, P.R. Defluorination of perfluorooctanoic Acid (PFOA) and perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS) by Acidimicrobium sp. strain A6. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 11410–11419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Bentel, M.J.; Yu, Y.; Ren, C.; Gao, J.; Pulikkal, V.F.; Sun, M.; Men, Y.; Liu, J. Near-quantitative defluorination of perfluorinated and fluorotelomer carboxylates and sulfonates with integrated oxidation and reduction. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 7052–7062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldman, P. The enzymatic cleavage of the carbon-fluorine bond in fluoroacetate. J. Biol. Chem. 1965, 240, 3434–3438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexandrino, D.A.M.; Ribeiro, I.; Pinto, L.M.; Cambra, R.; Oliveira, R.S.; Pereira, F.; Carvalho, M.F. Biodegradation of mono-, di- and trifluoroacetate by microbial cultures with different origins. Nat. Biotechnol. 2018, 43, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsons, J.R.; Sáez, M.; Dolfing, J.; de Voogt, P. Biodegradation of perfluorinated compounds. Rev. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2008, 196, 53–71. [Google Scholar]
- Kwon, B.G.; Lim, H.J.; Na, S.H.; Choi, B.I.; Shin, D.S.; Chung, S.Y. Biodegradation of perfluorooctanesulfonate (PFOS) as an emerging contaminant. Chemosphere 2014, 109, 221–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, L.B.; Chai, L.Y.; Xie, Y.; Peng, Q.J.; Peng, Q.Z. Isolation, identification, and degradation performance of a PFOA-degrading strain. Gen. Mol. Res. 2016, 15, 235–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chetverikov, S.P.; Sharipov, D.A.; Korshunova, T.Y.; Loginov, O.N. Degradation of perfluorooctanyl sulfonate by strain Pseudomonas plecoglossicida 2.4-D. Appl. Biochem. Microbiol. 2017, 53, 533–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochoa-Herrera, V.; Field, J.A.; Luna-Velsaco, A.; Sierra-Alvarez, R. Microbial toxicity and biodegradability of perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS) and shorter chain perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs). Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2016, 18, 1236–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Avendaño, S.M. Microbial degradation of polyfluoroalkyl chemicals in the environment: A review. Environ. Int. 2013, 61, 98–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, V.; Miles, Z.D.; Winter, J.M.; Eustáquio, A.S.; El Gamal, A.A.; Moore, B.S. Enzymatic halogenation and dehalogenation reactions: Pervasive and mechanistically diverse. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 5619–5674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, B.G.; Borneman, J.G.; Wackett, L.P.; Lipscomb, J.D. Haloalkene oxidation by the soluble methane monooxygenase from Methylosinus trichosporium OB3b: Mechanistic and environmental implications. Biochemistry 1990, 29, 6419–6427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renganathan, V. Possible involvement of toluene-2,3-dioxygenase in defluorination of 3-fluoro-substituted benzenes by toluene-degrading Pseudomonas sp. strain T-12. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1989, 55, 330–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bygd, M.D.; Aukema, K.G.; Richman, J.E.; Wackett, L.P. Unexpected mechanism of biodegradation and defluorination of 2,2-difluoro-1,3-benzodioxole by Pseudomonas putida F1. mBio 2021, 12, e03001-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondar, V.S.; Boersma, M.G.; Golovlev, E.L.; Vervoort, J.; Van Berkel, W.J.H.; Finkelstein, Z.I.; Solyanikova, I.P.; Golovleva, L.A.; Rietjens, I.M.C.M. 19F NMR study on the biodegradation of fluorophenols by various Rhodococcus species. Biodegradation 1998, 9, 475–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Chen, G.; May, A.L.; Yan, J.; Brown, L.P.; Powers, J.B.; Campagna, S.R.; Löffler, F.E. Pseudomonas sp. strain 273 degrades fluorinated alkanes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 14994–15003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merino, N.; Wang, M.; Ambrocio, R.; Mak, K.; O’Connor, E.; Gao, A.; Hawley, E.L.; Deeb, R.A.; Tseng, L.Y.; Mahendra, S. Fungal biotransformation of 6:2 fluorotelomer alcohol. Remediat. J. 2018, 28, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Buck, R.C.; Szostek, B.; Sulecki, L.M.; Wolstenholme, B.W. 5:3 Polyfluorinated acid aerobic biotransformation in activated sludge via novel “one-carbon removal pathways”. Chemosphere 2012, 87, 527–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Z.; Vogel, T.M.; Wang, Q.; Wei, C.; Ali, M.; Song, X. Microbial defluorination of TFA, PFOA, and HFPO-DA by a native microbial consortium under anoxic conditions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 465, 133217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Black, A.S.; Campbell, A.S. Ionic strength of soil solution and its effect on charge properties of some New Zealand soils. J. Soil Sci. 1982, 33, 249–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolling, P.J.; Ritchie, G.S.P. Estimates of soil solution ionic strength and the determination of pH in West Australian soils. Aus. J. Soil Res. 1985, 23, 309–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raynaud, X.; Jaillard, B.; Leadley, P.W. Plants may alter competition by modifying nutrient bioavailability in rhizosphere: A modeling approach. Am. Nat. 2008, 171, 44–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghisi, R.; Vamerali, T.; Manzetti, S. Accumulation of perfluorinated alkyl substances (PFAS) in agricultural plants: A review. Environ. Res. 2019, 169, 326–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesmeister, L.; Lange, F.T.; Breuer, J.; Biegel-Engler, A.; Giese, E.; Scheurer, M. Extending the knowledge about PFAS bioaccumulation factors for agricultural plants-A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 766, 142640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Sun, J.; Li, P. Exposure routes, bioaccumulation and toxic effects of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) on plants: A critical review. Environ. Int. 2022, 158, 106891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultan, H.; Buckley, J.P.; Kalkwarf, H.J.; Cecil, K.M.; Chen, A.; Lanphear, B.P.; Yolton, K.; Braun, J.M. Dietary per- and polyfluoroalkyl substance [PFAS] exposure in adolescents: The HOME study. Environ. Res. 2023, 231, 115953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casson, R.; Chiang, S.Y. Integrating total oxidizable precursor assay data to evaluate fate and transport of PFASs. Rem. J. 2018, 28, 71–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Röhler, K.; Haluska, A.A.; Susset, B.; Liu, B.; Grathwohl, P. Long-term behavior of PFAS in contaminated agricultural soils in Germany. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2021, 241, 103812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Liu, J. Aerobic biotransformation of polyfluoroalkyl phosphate esters (PAPs) in soil. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 212, 230–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Lu, X.; Wang, N.; Buck, R.C. Biotransformation potential of 6:2 fluorotelomer sulfonate (6:2 FTSA) in aerobic and anaerobic sediment. Chemosphere 2016, 154, 224–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.; Nishimura, F.; Hidaka, T. Effects of microbial activity on perfluorinated carboxylic acids (PFCAs) generation during aerobic biotransformation of fluorotelomer alcohols in activated sludge. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 610–611, 776–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimison, C.; Knight, E.R.; Nguyen, T.M.H.; Nagle, N.; Kabiri, S.; Bräunig, J.; Navarro, D.A.; Kookana, R.S.; Higgins, C.P.; McLaughlin, M.J.; et al. The efficacy of soil washing for the remediation of per- and poly-fluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) in the field. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 445, 130441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, R.A. Soil-washing technology and practice. J. Hazard. Mater. 1995, 40, 175–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolan, N.; Sarkar, B.; Yan, Y.; Li, Q.; Wijesekara, H.; Kannan, K.; Tsang, D.C.W.; Schauerte, M.; Bosch, J.; Noll, H.; et al. Remediation of poly- and perfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) contaminated soils–To mobilize or to immobilize or to degrade? J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 401, 123892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solo-Gabriele, H.M.; Jones, A.S.; Lindstrom, A.B.; Lang, J.R. Waste type, incineration, and aeration are associated with per- and polyfluoroalkyl levels in landfill leachates. Waste Manag. 2020, 107, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, S.; Lee, T.; Sahle-Demessie, E.; Ateia, M.; Nadagouda, M.N. Recent advances on PFAS degradation via thermal and nonthermal methods. Chem. Eng. J. Adv. 2023, 13, 100421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, P.H.; Yamada, T.; Striebich, R.C.; Graham, J.L.; Giraud, R.J. Investigation of waste incineration of fluorotelomer-based polymers as a potential source of PFOA in the environment. Chemosphere 2014, 110, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.Y.; So, S.; da Silva, G. Decomposition kinetics of perfluorinated sulfonic acids. Chemosphere 2020, 238, 124615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Zhang, D.; Liang, Y. Nanotechnology in remediation of water contaminated by poly- and perfluoroalkyl substances: A review. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 247, 266–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Lu, X.; Li, X.; Shih, K. Effectiveness and mechanisms of defluorination of perfluorinated alkyl substances by calcium compounds during waste thermal treatment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 5672–5680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.; Taniyasu, S.; Yamazaki, E.; Wu, R.; Lam, P.K.S.; Eun, H.; Yamashita, N. Fluorine mass balance analysis and per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances in the atmosphere. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 435, 129025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 100421Vecitis, C.D.; Park, H.; Cheng, J.; Mader, B.T.; Hoffmann, M.R. Kinetics and mechanism of the sonolytic conversion of the aqueous perfluorinated surfactants, perfluorooctanoate (PFOA), and perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS) into inorganic products. J. Phys. Chem. A 2008, 112, 4261–4270. [Google Scholar]
- Sirés, I.; Brillas, E.; Oturan, M.A.; Rodrigo, M.A.; Panizza, M. Electrochemical advanced oxidation processes: Today and tomorrow. A review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 8336–8367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrie, B.; Barden, R.; Kasprzyk-Hordern, B. A review on emerging contaminants in wastewaters and the environment: Current knowledge, understudied areas and recommendations for future monitoring. Water Res. 2015, 72, 3–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.; Megharaj, M.; Naidu, R. Electrochemical advanced oxidation processes (EAOP) to degrade poly- and perfluoroalkyl substances [PFASs]. J. Adv. Oxid. Technol. 2017, 20, 20170014. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, Y.-J.; Tian, Y.; Sobhani, Z.; Naidu, R.; Fang, C. Synergistic degradation of PFAS in water and soil by dual-frequency ultrasonic activated persulfate. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 388, 124215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bräunig, J.; Baduel, C.; Barnes, C.M.; Mueller, J.F. Sorbent assisted immobilisation of perfluoroalkyl acids in soils–effect on leaching and bioavailability. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 412, 125171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucharzyk, K.H.; Darlington, R.; Benotti, M.; Deeb, R.; Hawley, E. Novel treatment technologies for PFAS compounds: A critical review. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 204, 757–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Tian, H.; Li, H.; Li, J.; Hong, R.; Sheng, F.; Wang, C.; Gu, C. Application of surfactant modified montmorillonite with different conformation for photo-treatment of perfluorooctanoic acid by hydrated electrons. Chemosphere 2019, 235, 1180–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.; Niu, J.; Liang, S.; Wang, C.; Wang, Y.; Jin, F.; Luo, Q.; Huang, Q. Development of macroporous Magnéli phase Ti4O7 ceramic materials: As an efficient anode for mineralization of poly- and perfluoroalkyl substances. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 354, 1058–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenorio, R.; Liu, J.; Xiao, X.; Maizel, A.C.; Higgins, C.; Schaefer, C.; Strathmann, T. Destruction of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) in aqueous film-forming foam [AFFF] with UV-sulfite photo-reductive treatment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 6957–6967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, U.; Su, Y.; Khor, C.M.; Jung, B.; Ma, S.; Cwiertny, D.M.; Wong, B.M.; Jassby, D. Structural dependence of reductive defluorination of linear PFAS compounds in a UV/electrochemical system. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 10668–10677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Zhang, K.; Li, Z.; Ren, C.; Chen, J.; Lin, Y.H.; Liu, J.; Men, Y. Microbial cleavage of C–F bonds in two C6 per- and polyfluorinated compounds via reductive defluorination. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 14393–14402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, S.; Jin, B.; Liu, Z.; Yu, Y.; Liu, J.; Men, Y. Structure-specific aerobic defluorination of short-chain fluorinated carboxylic acids by activated sludge communities. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2021, 8, 668–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EEA. European Environmental Agency. Bio-Waste in Europe—Turning Challenges into Opportunities EEA Report 2020, No 04/2020. Available online: https://www.eea.europa.eu/publications/bio-waste-in-europe (accessed on 12 August 2024).
- Saliu, T.D.; Sauvé, S. A review of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances in biosolids: Geographical distribution and regulations. Front. Environ. Chem. 2024, 5, 1383185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazcano, R.K.; Choi, Y.J.; Mashtare, M.L.; Lee, L.S. Characterizing and comparing per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances in commercially available biosolid and organic non-biosolid-based products. Environ Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 8640–8648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Li, X.; Liu, H.; Dong, S.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Li, J.; Nghiem, L.D.; Khan, S.J.; Wang, Q. Occurrence, fate, and remediation for per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in sewage sludge: A comprehensive review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 466, 133637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UN. United Nations Habitat Global Atlas of Excreta, Wastewater Sludge, and Biosolids Management: Moving Forward the Sustainable and Welcome Uses of a Global Resource. 2008. Available online: https://unhabitat.org/sites/default/files/download-manager-files/Global%20Atlas%20of%20Excreta%2C%20Wastewater%20Sludge%2C%20and%20Biosolids%20Management.pdf (accessed on 12 August 2024).
- Lenka, S.P.; Kah, M.; Padhye, L.P. A review of the occurrence, transformation, and removal of poly- and perfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in wastewater treatment plants. Rev. Water Res. 2021, 199, 117187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subedi, B.; Codru, N.; Dziewulski, D.M.; Wilson, L.R.; Xue, J.C.; Yun, S.H.; Braun-Howland, E.; Minihane, C.; Kannan, K. A pilot study on the assessment of trace organic contaminants including pharmaceuticals and personal care products from on-site wastewater treatment systems along Skaneateles Lake in New York State, USA. Water Res. 2015, 72, 28–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lakshminarasimman, N.; Gewurtz, S.B.; Parker, W.J.; Smyth, S.A. Removal and formation of perfluoroalkyl substances in Canadian sludge treatment systems—A mass balance approach. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 754, 142431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerra, P.; Kim, M.; Kinsman, L.; Ng, T.; Alaee, M.; Smyth, S.A. Parameters affecting the formation of perfluoroalkyl acids during wastewater treatment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 272, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinclair, E.; Kannan, K. Mass loading and fate of perfluoroalkyl surfactants in wastewater treatment plants. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 1408–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gole, V.L.; Sierra-Alvarez, R.; Peng, H.; Giesy, J.P.; Deymier, P.; Keswani, M. Sono-chemical treatment of per- and poly-fluoroalkyl compounds in aqueous film-forming foams by use of a large-scale multi-transducer dual-frequency based acoustic reactor. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2018, 45, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krahn, K.; Cornelissen, G.; Castro, G.; Arp, H.P.H.; Asimakopoulos, A.G.; Wolf, R.; Holmstad, R.; Zimmerman, A.R.; Sørmo, E. Sewage sludge biochars as effective PFAS-sorbents. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 445, 130449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundu, S.; Patel, S.; Halder, P.; Patelm, T.; Marzbali, M.H.; Pramanik, B.K.; Paz-Ferreiro, J.; de Figueiredo, C.C.; Bergmann, D.; Surapanenim, A. Removal of PFASs from biosolids using a semi-pilot scale pyrolysis reactor and the application of biosolids derived biochar for the removal of PFASs from contaminated water. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2021, 7, 638–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, G.; Smalla, K. Plant species and soil type cooperatively shape the structure and function of microbial communities in the rhizosphere. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2009, 68, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wackett, L.P.; Robinson, S.L. The ever-expanding limits of enzyme catalysis and biodegradation: Polyaromatic, polychlorinated, polyfluorinated, and polymeric compounds. Biochem. J. 2020, 477, 2875–2891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gale, E.F. The Chemical Activities of Bacteria; University Tutorial Press: London, UK, 1947; p. 199. [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell, S.M.; Ahmad, M.; Teel, A.L.; Watts, R.J. Degradation of perfluorooctanoic acid by reactive species generated through catalyzed H2O2 propagation reactions. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2014, 1, 117–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javed, H.; Metz, J.; Eraslan, T.C.; Mathieu, J.; Wang, B.; Wu, G.; Tsai, A.-L.; Wong, M.S.; Alvarez, P.J.J. Discerning the relevance of superoxide in PFOA degradation. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2020, 7, 653–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vangronsveld, J.; Herzig, R.; Weyens, N.; Boulet, J.; Adriaensen, K.; Ruttens, A.; Thewys, T.; Vassilev, A.; Meers, E.; Nehnevajova, E.; et al. Phytoremediation of contaminated soils and groundwater: Lessons from the field. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2009, 16, 765–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, N.; Barion, G.; Shrestha, I.; Ebinezer, L.B.; Trentin, A.R.; Vamerali, T.; Mezzalira, G.; Masi, A.; Ghisi, R. Accumulation and effects of perfluoroalkyl substances in three hydroponically grown Salix L. species. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 191, 110150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nassazzi, W.; Wu, T.-C.; Jass, J.; Lai, F.Y.; Ahrens, L. Phytoextraction of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) and the influence of supplements on the performance of short–rotation crops. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 333, 122038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weyens, N.; van der Lelie, D.; Taghavi, S.; Vangronsveld, J. Phytoremediation: Plant-endophyte partnerships take the challenge. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2009, 20, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDowell, N.G.; Allen, C.D. Darcy’s law predicts widespread forest mortality under climate warming. Nat. Clim. Change 2015, 5, 669–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxton, K.E.; Rawls, W.J. Soil water characteristic estimates by texture and organic Matter for hydrologic solutions. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2006, 70, 1569–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholander, P.F.; Bradstreet, E.D.; Hemmingsen, E.A.; Hammel, H.T. Sap pressure in vascular plants. Science 1965, 148, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maan, C.; ten Veldhuis, M.-C.; van de Wiel, B.J.H. Dynamic root growth in response to depth-varying soil moisture availability: A rhizobox study. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2023, 27, 2341–2355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ENoLL. European Network of Living Labs. 2024. Available online: https://enoll.org/ (accessed on 5 August 2024).



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Renella, G.; Carletti, P.; Masi, A. Sustainable Management of Poly- and Perfluoroalkyl Substances (PFASs)-Contaminated Areas: Tackling a Wicked Environmental Problem. Sustainability 2025, 17, 510. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17020510
Renella G, Carletti P, Masi A. Sustainable Management of Poly- and Perfluoroalkyl Substances (PFASs)-Contaminated Areas: Tackling a Wicked Environmental Problem. Sustainability. 2025; 17(2):510. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17020510
Chicago/Turabian StyleRenella, Giancarlo, Paolo Carletti, and Antonio Masi. 2025. "Sustainable Management of Poly- and Perfluoroalkyl Substances (PFASs)-Contaminated Areas: Tackling a Wicked Environmental Problem" Sustainability 17, no. 2: 510. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17020510
APA StyleRenella, G., Carletti, P., & Masi, A. (2025). Sustainable Management of Poly- and Perfluoroalkyl Substances (PFASs)-Contaminated Areas: Tackling a Wicked Environmental Problem. Sustainability, 17(2), 510. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17020510








