Monitoring and Analysis of Coastal Salt Pans Using Multi-Feature Fusion of Satellite Imagery: A Case Study Along the Laizhou Bay
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
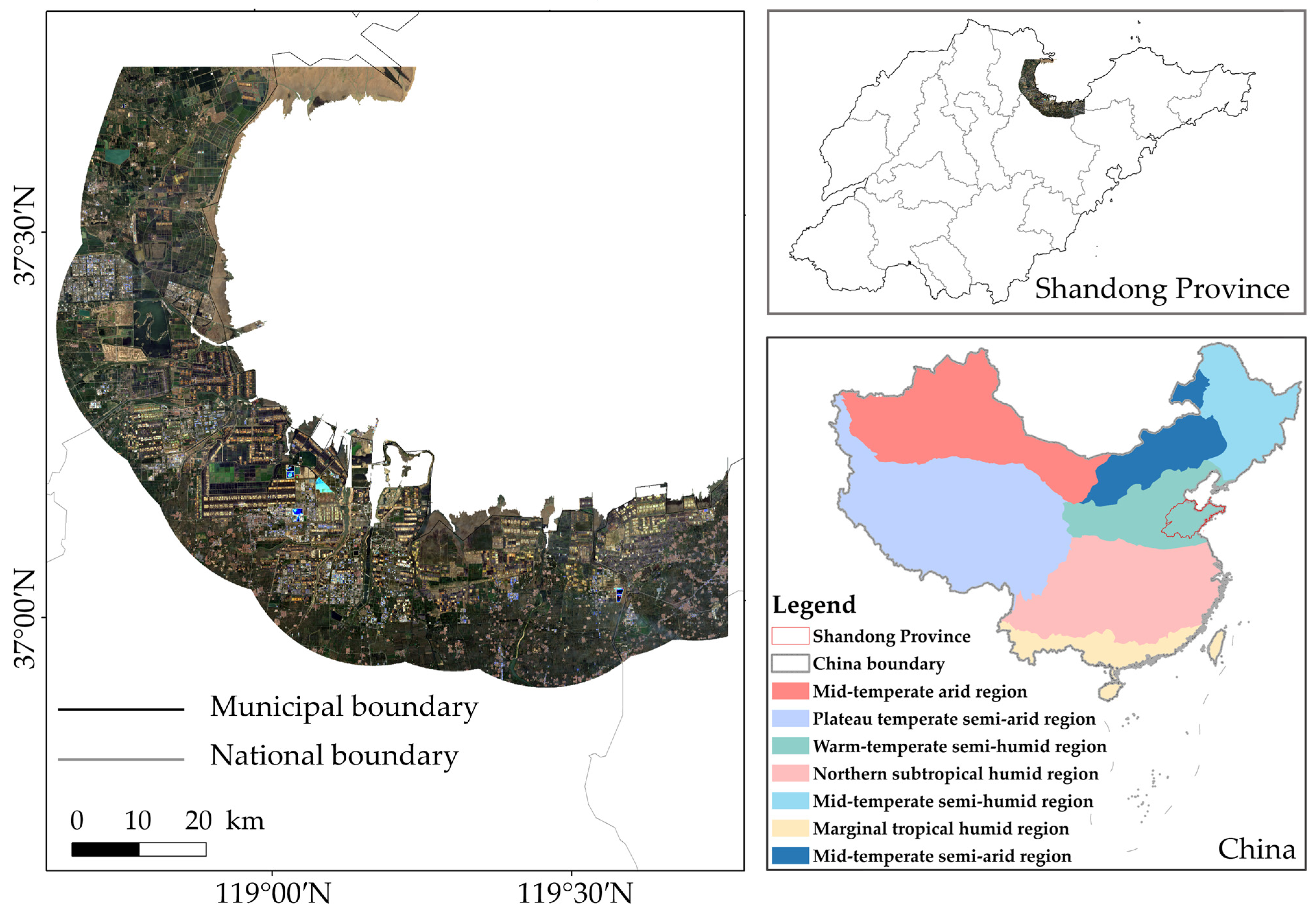
2.1. Study Area Overview
2.2. Dataset
2.3. Methods
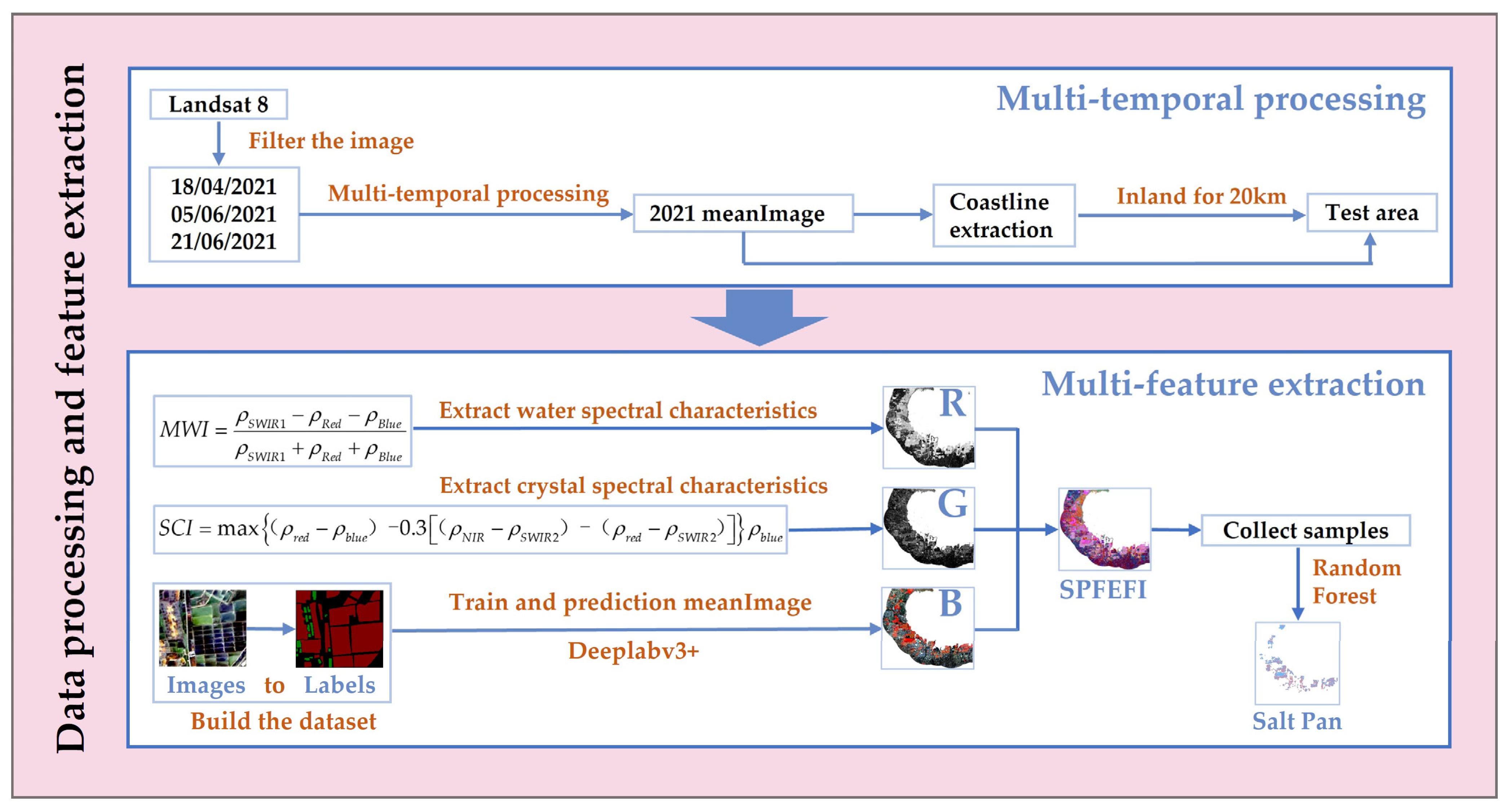
2.3.1. Remote Sensing Indices
- Modified Water Index
- 2.
- Salt Pan Crystallization Index
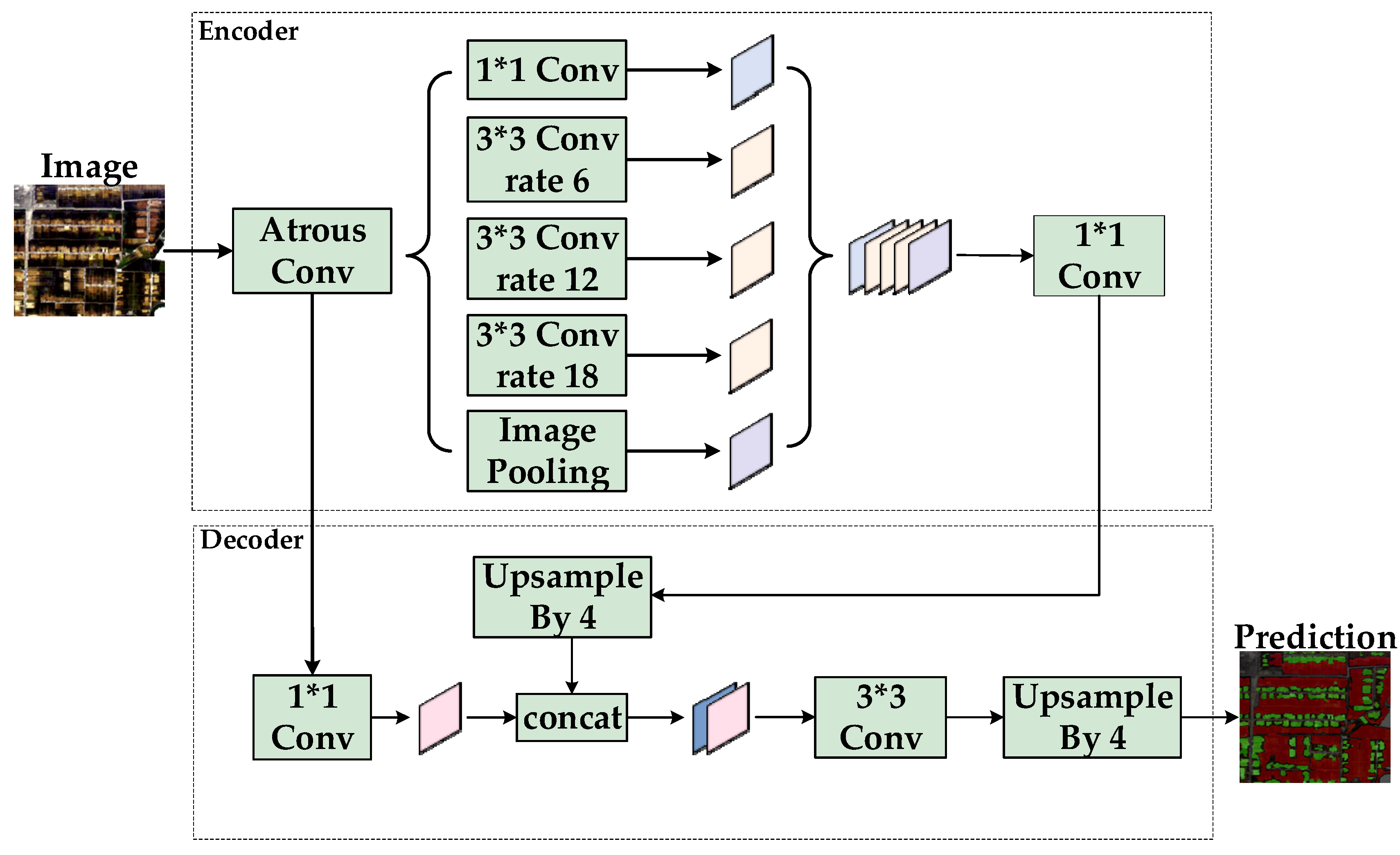
2.3.2. DeepLabv3+
- Network Overview
- 2.
- Dataset Construction
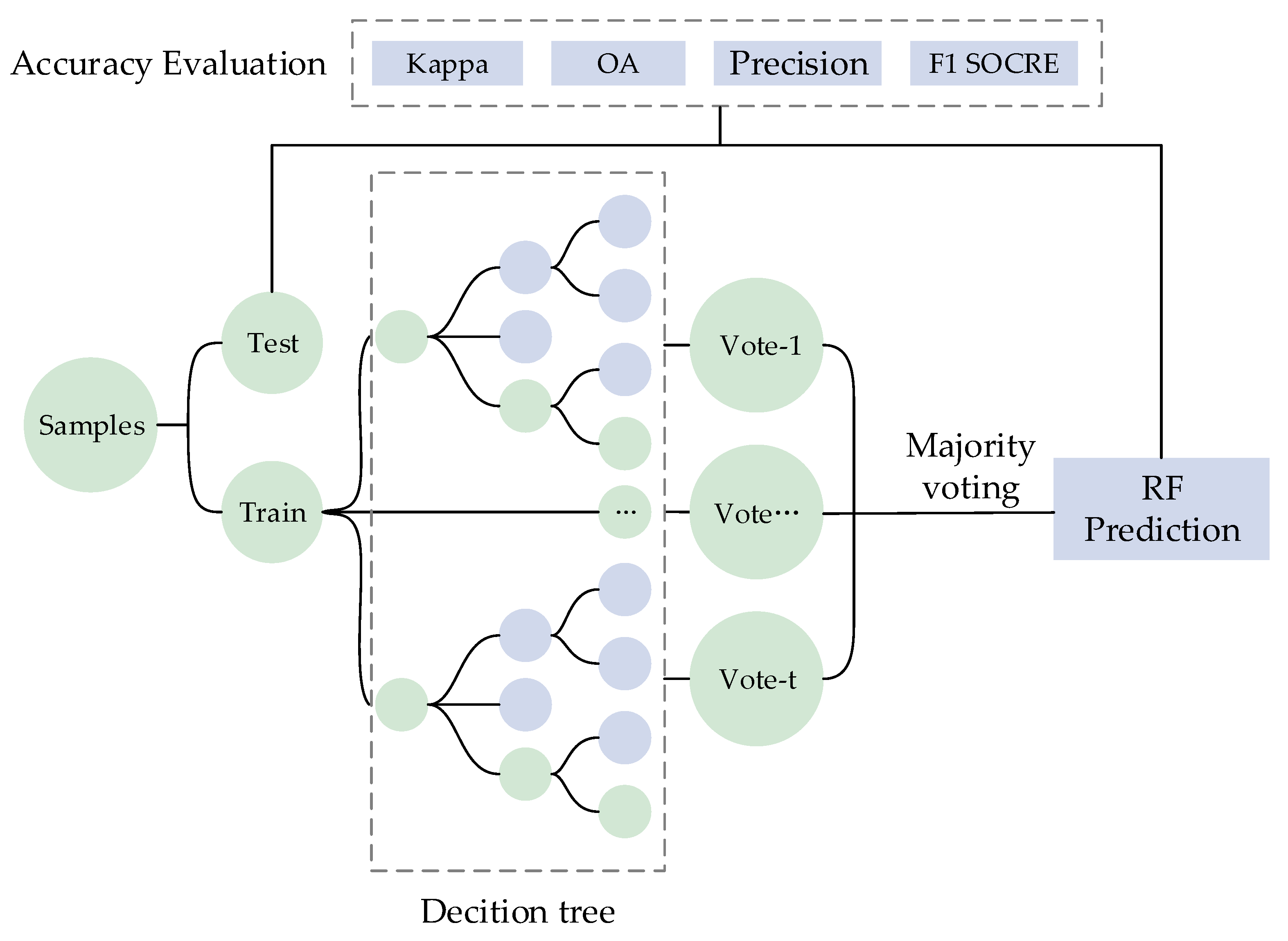
2.3.3. Random Forest (RF)
2.4. Accuracy Assessment Method
3. Results
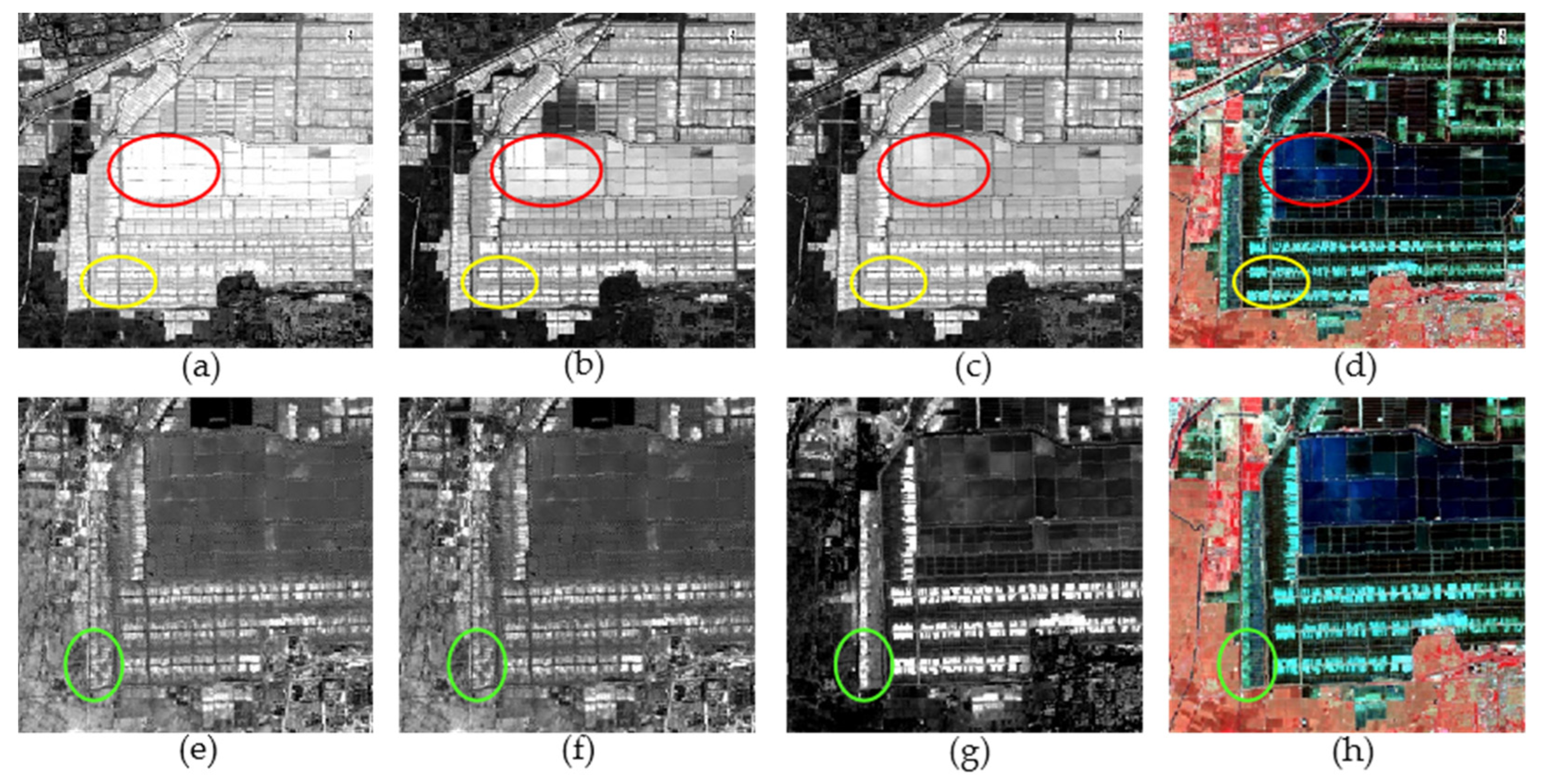
3.1. Multi-Temporal Image Fusion
3.2. Spectral Index Feature Extraction
3.2.1. Modified Water Index (MWI)
3.2.2. Salt Pan Crystallization Index
3.3. Extraction Using DeepLabv3+
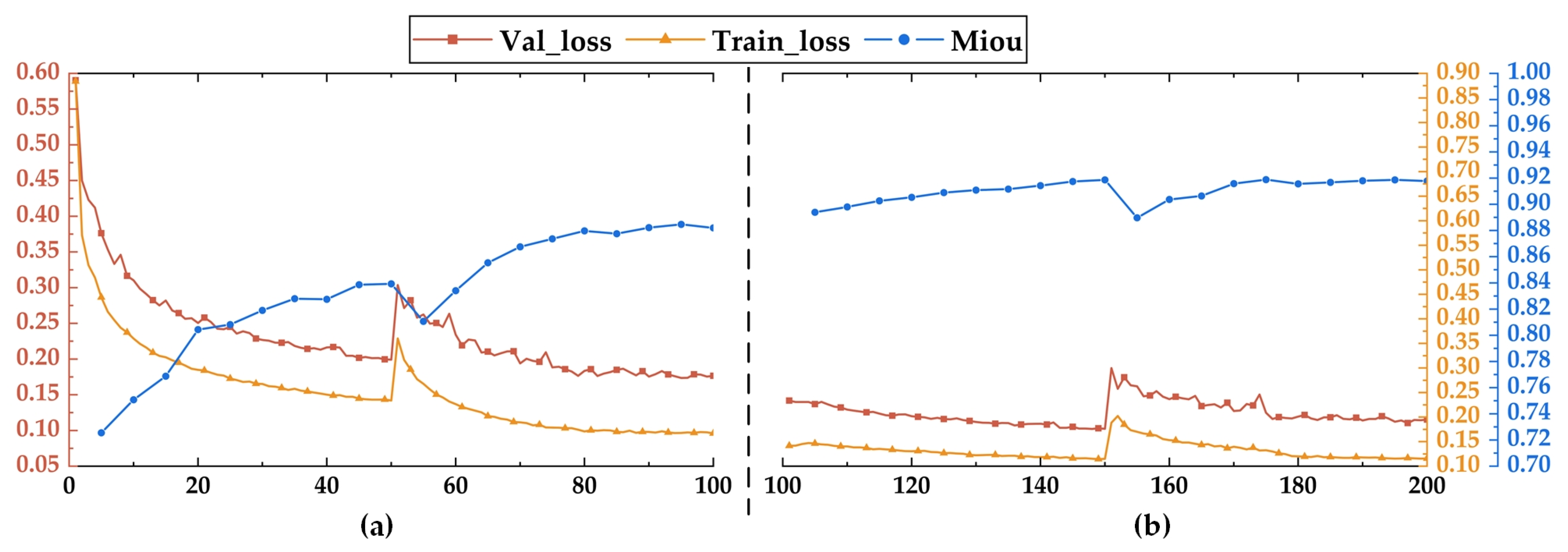
3.3.1. Model Construction
3.3.2. Inference Results of Deeplabv3+
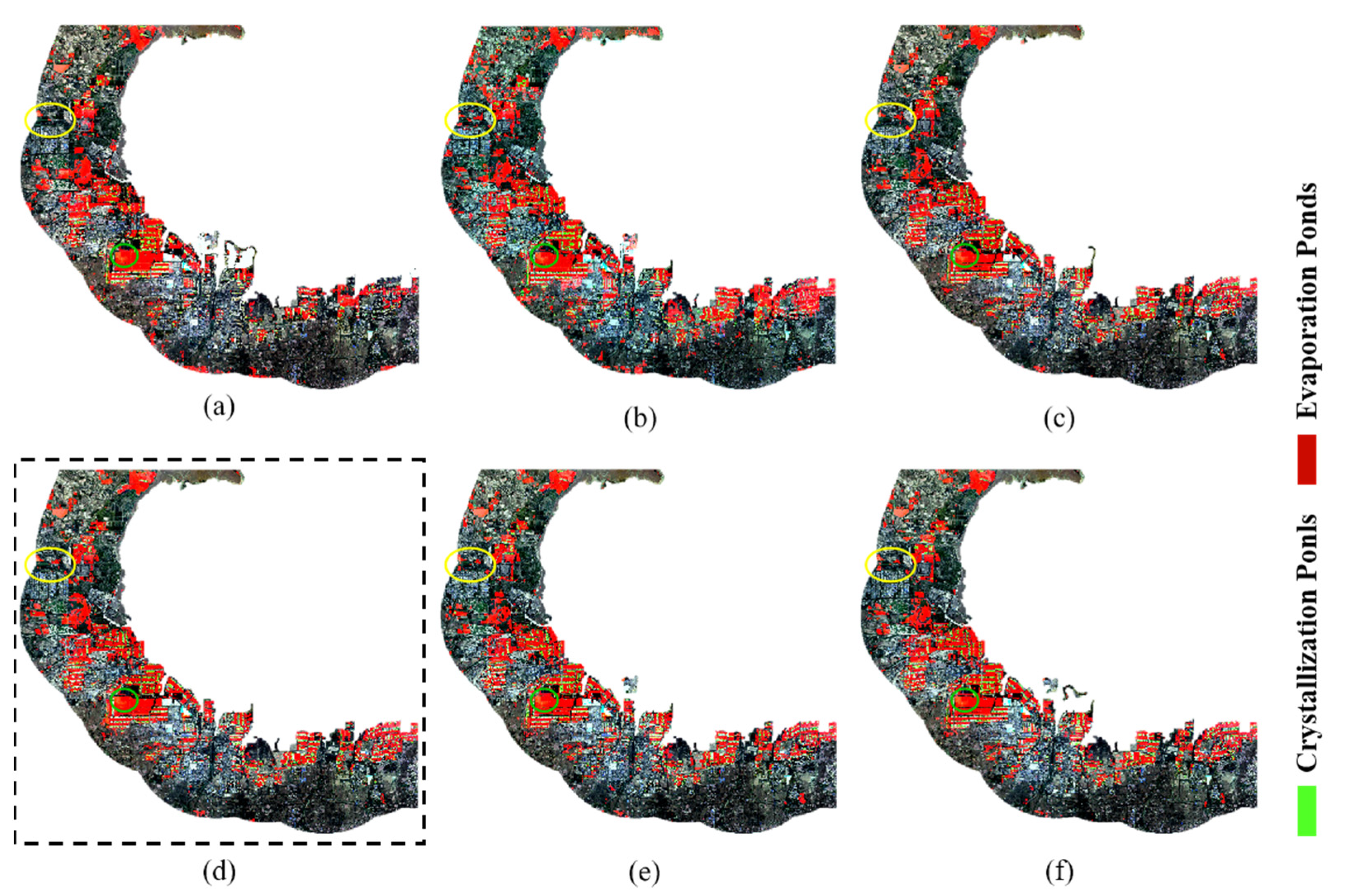
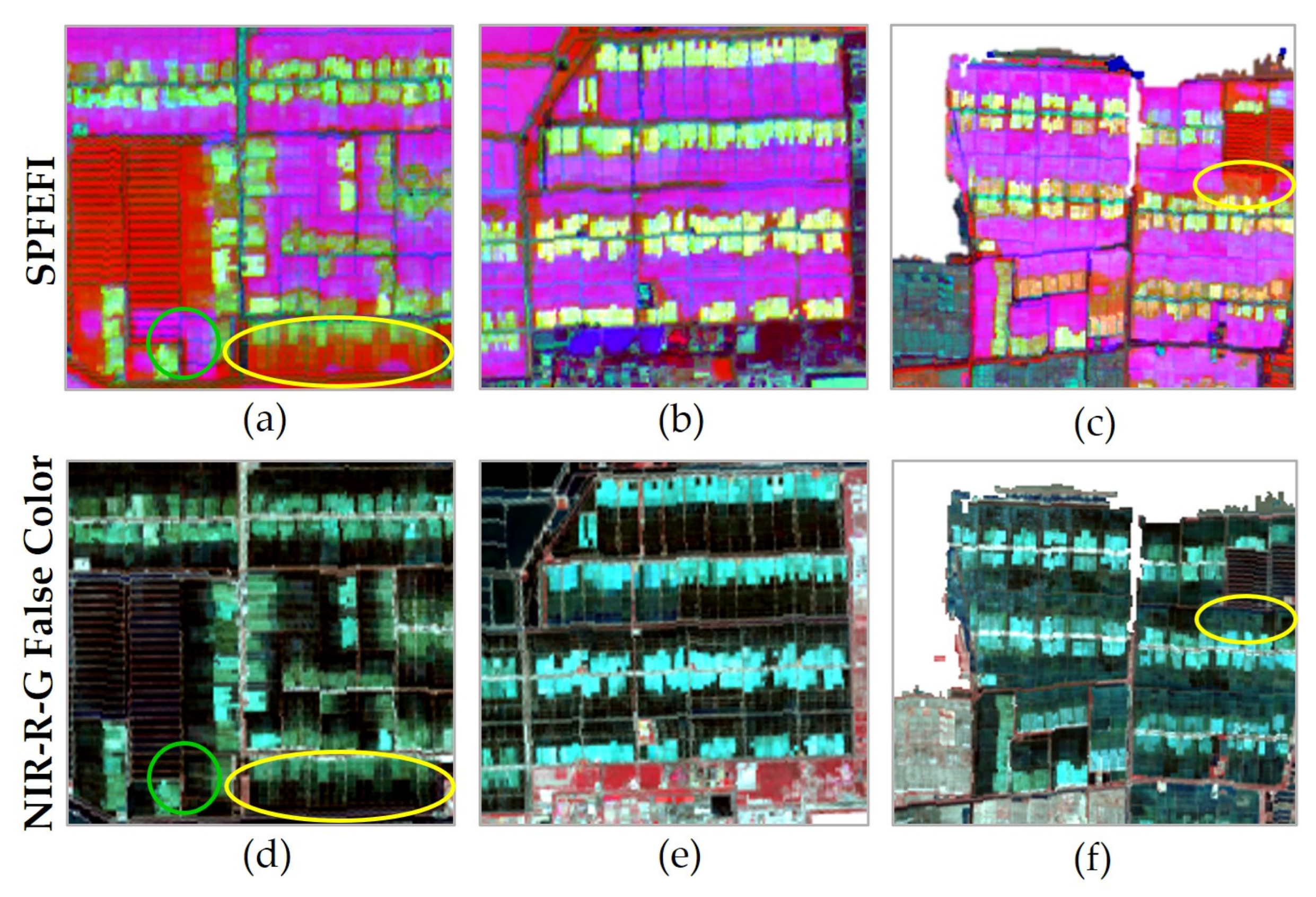
3.4. Result of RGB Strategy Multi-Feature Fusion
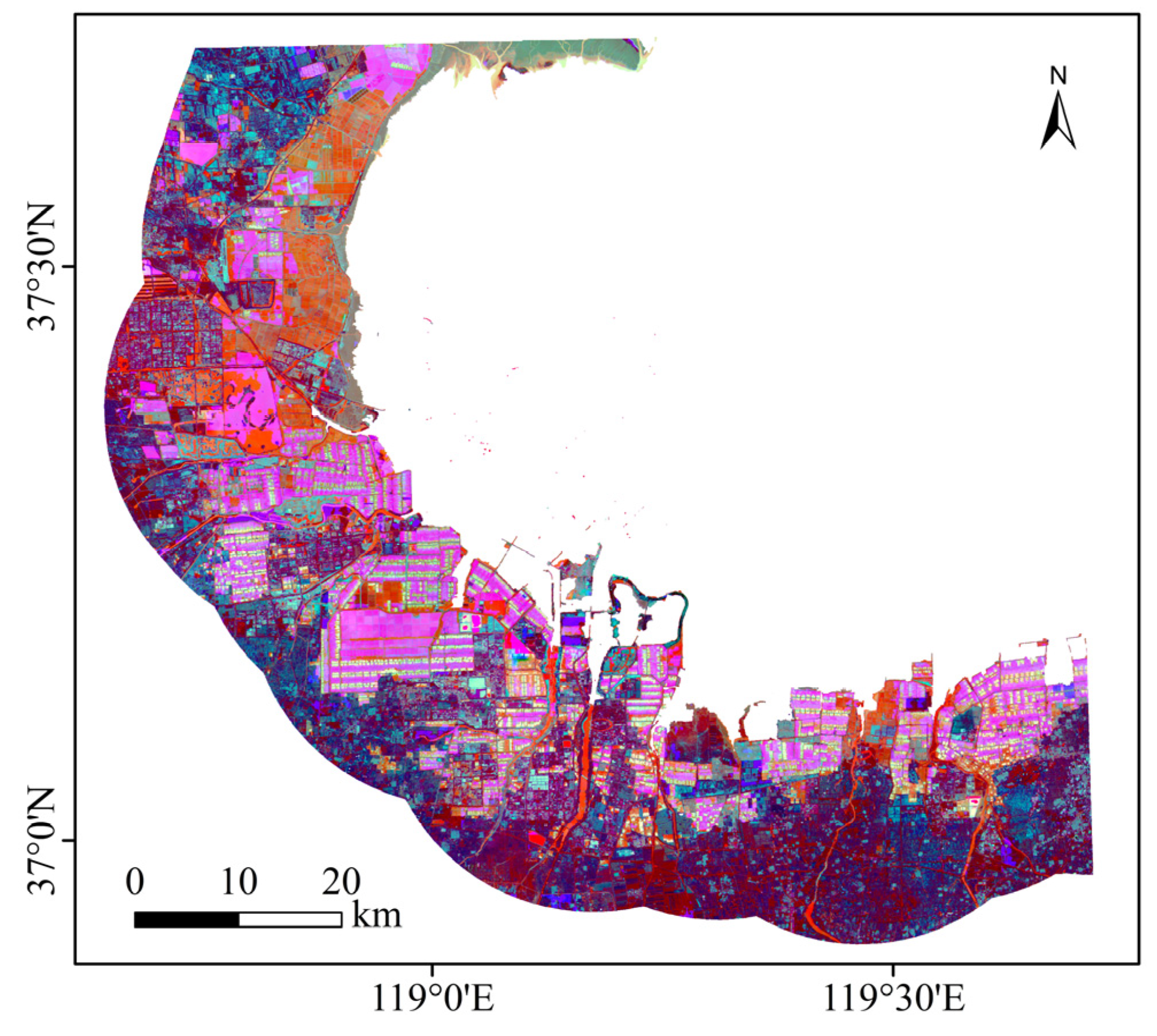
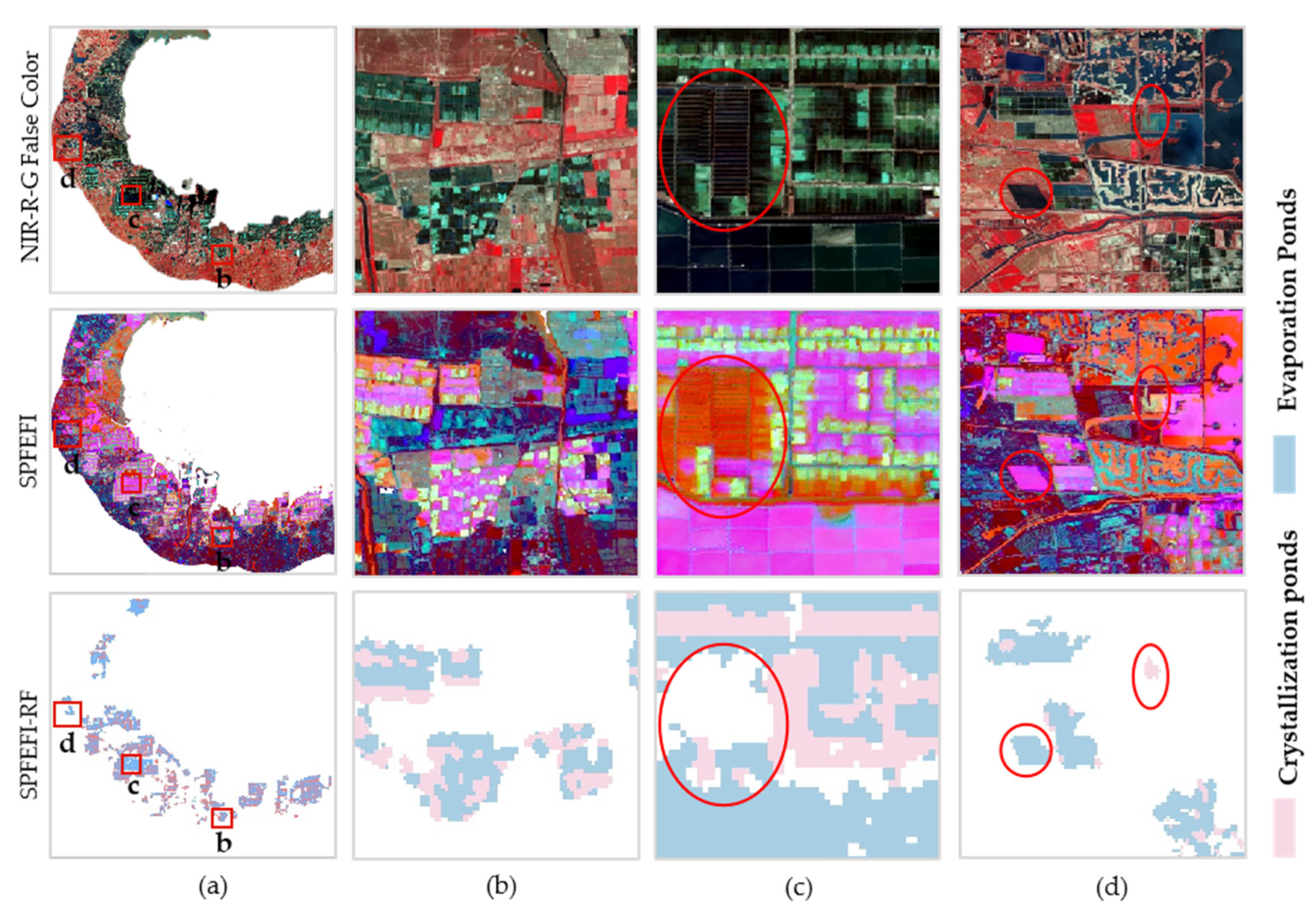
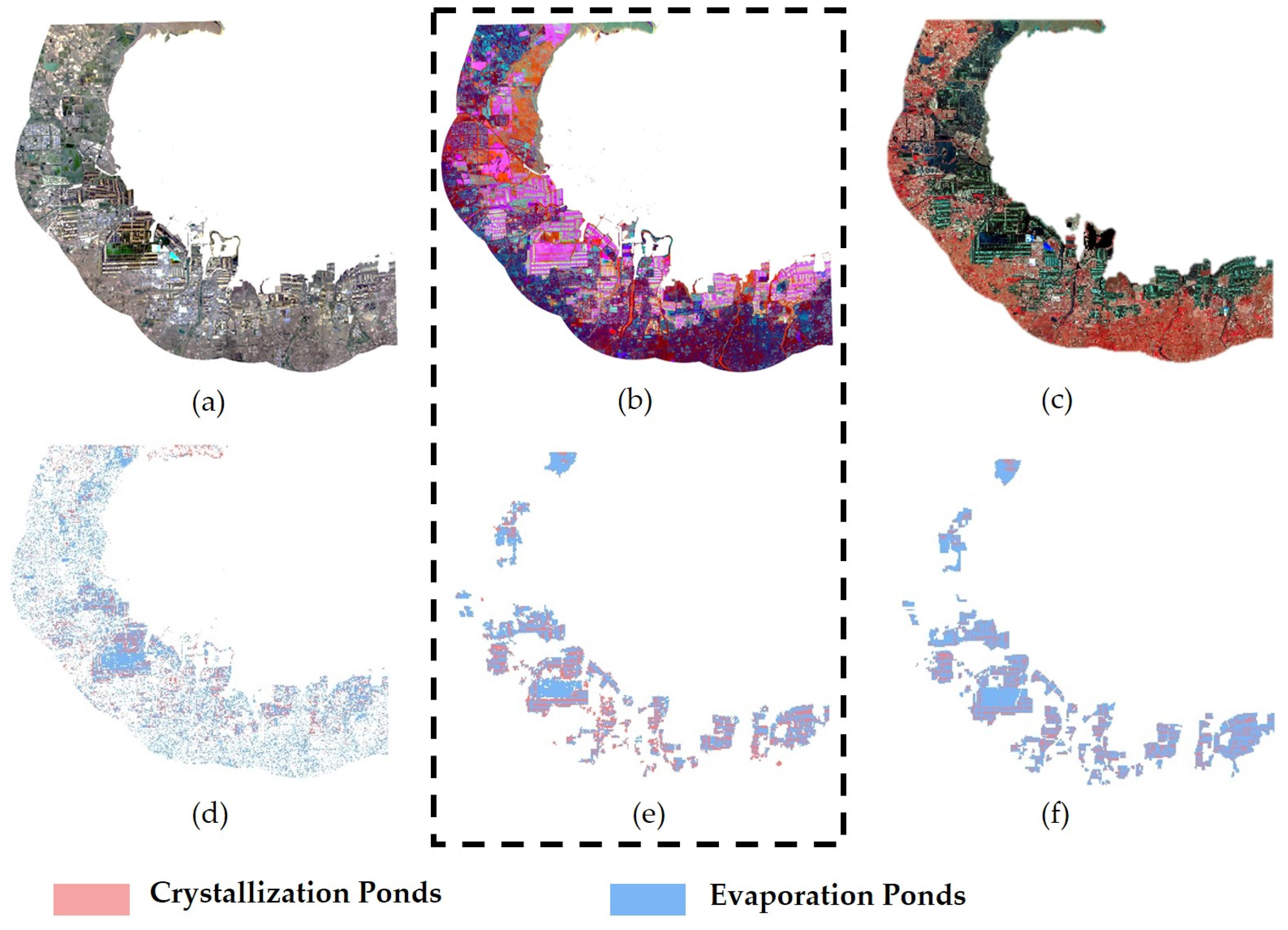
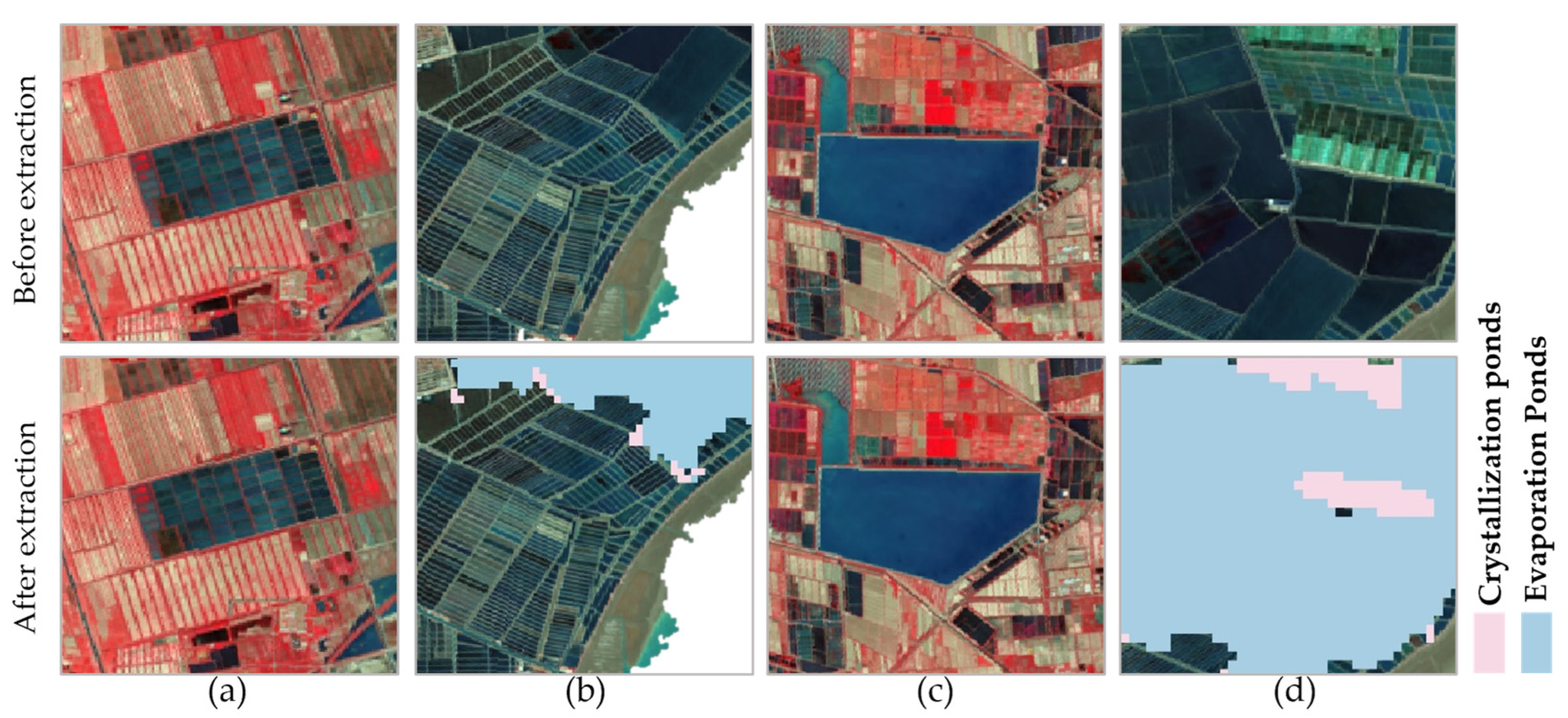
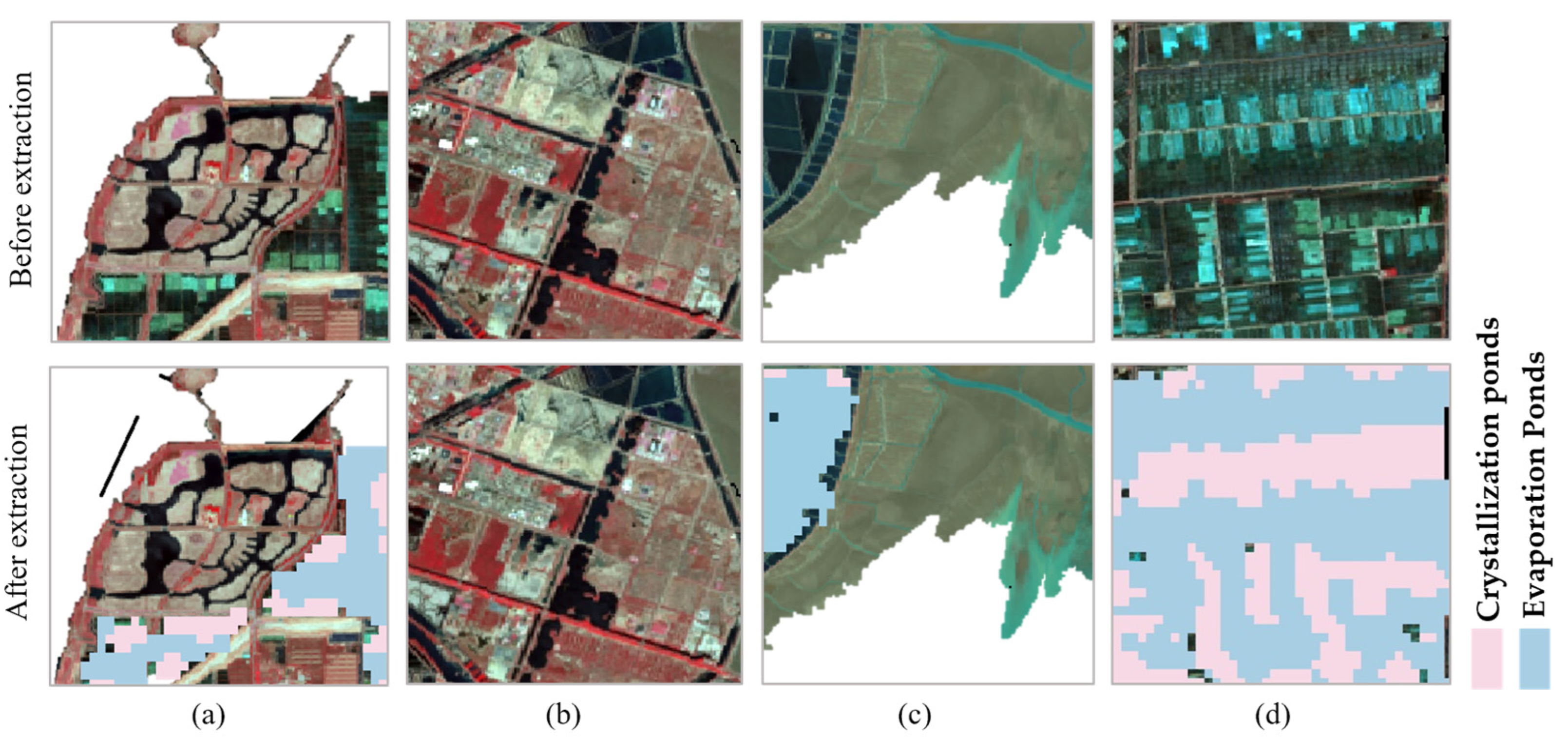
3.5. Extraction of Salt Pan Information
3.6. Accuracy Assessment
4. Discussion
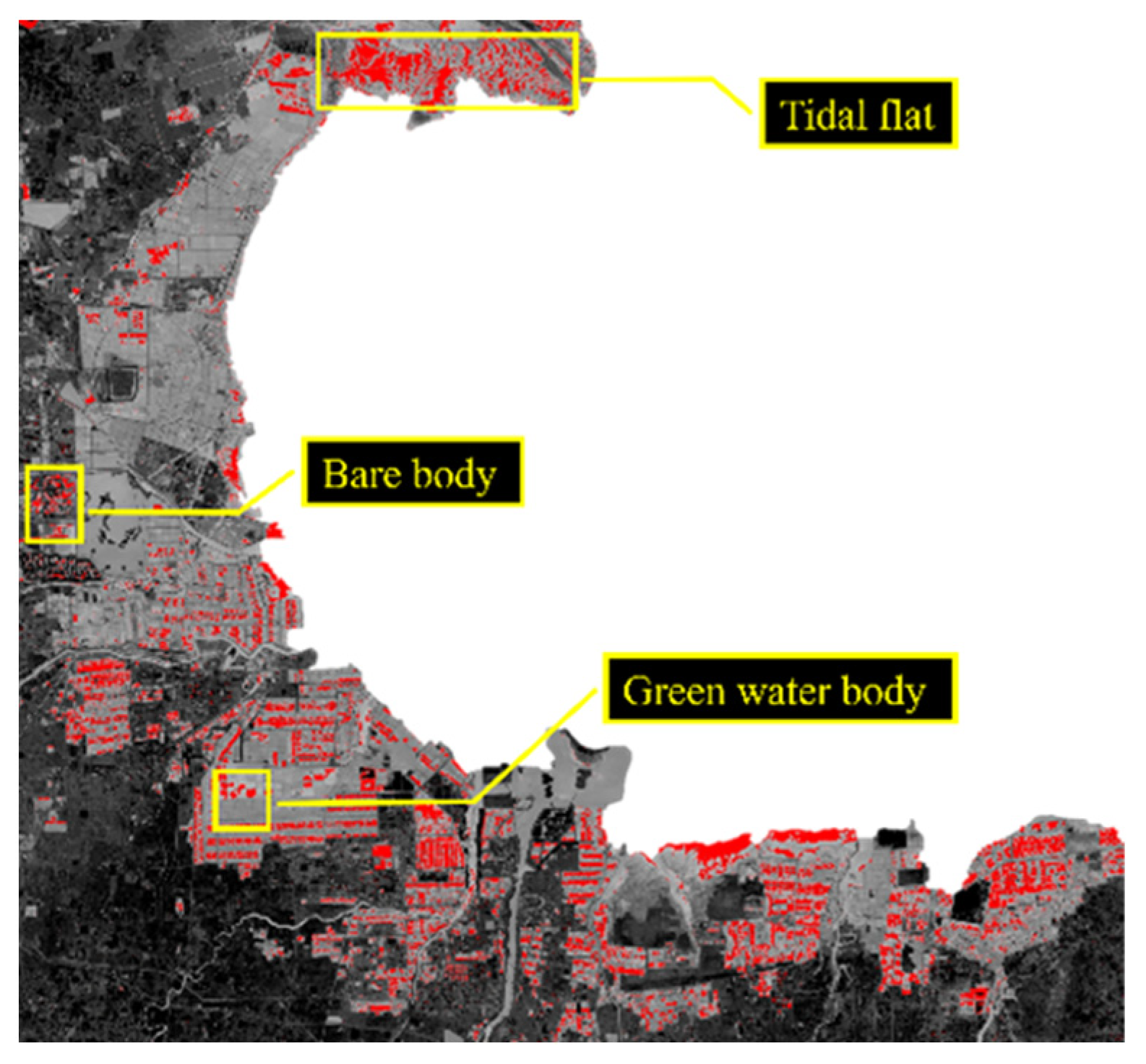
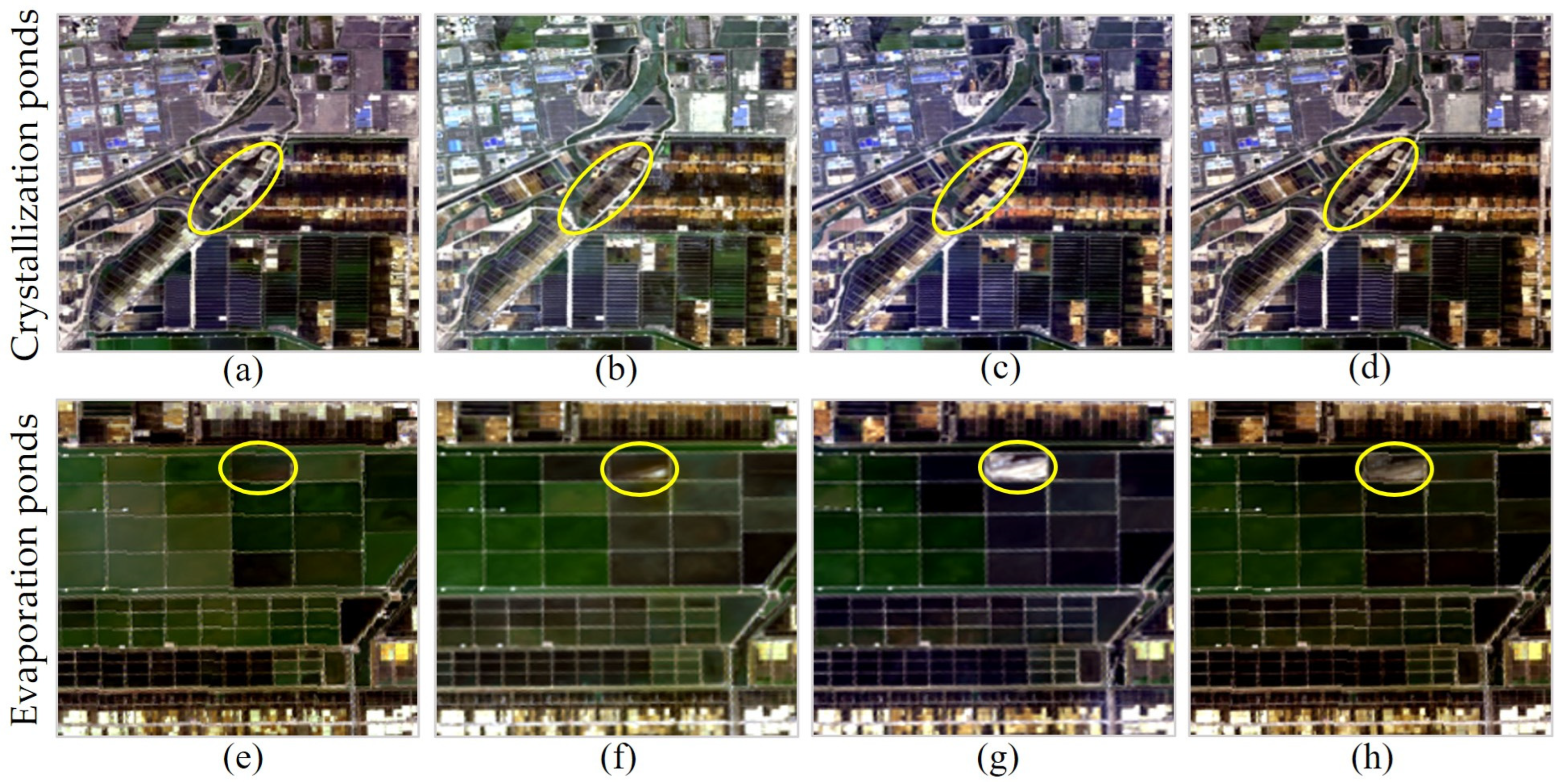
4.1. Factors Affecting the Extraction of Evaporation Ponds
4.2. Factors Affecting the Extraction of Crystallization Ponds
4.3. Advantages and Limitations of the Proposed Method
4.3.1. Advantages
4.3.2. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SPFEFI | Salt Pan Feature-Enhanced Fusion Image |
| MWI | Modified Water Index |
| SCI | Salt Pan Crystallization Index |
| RF | Random Forest |
| DL | DeepLabv3+ |
| SPFEFI-RF | Feature-Enhanced Fusion Image Random Forest |
| NMWI | Normalized Difference Water Index |
| MNDWI | Modified Normalized Difference Water Index |
| SSI | Salinity Sensitivity Index |
| SpI | Salinity Index |
Appendix A
Appendix A.1. MWI
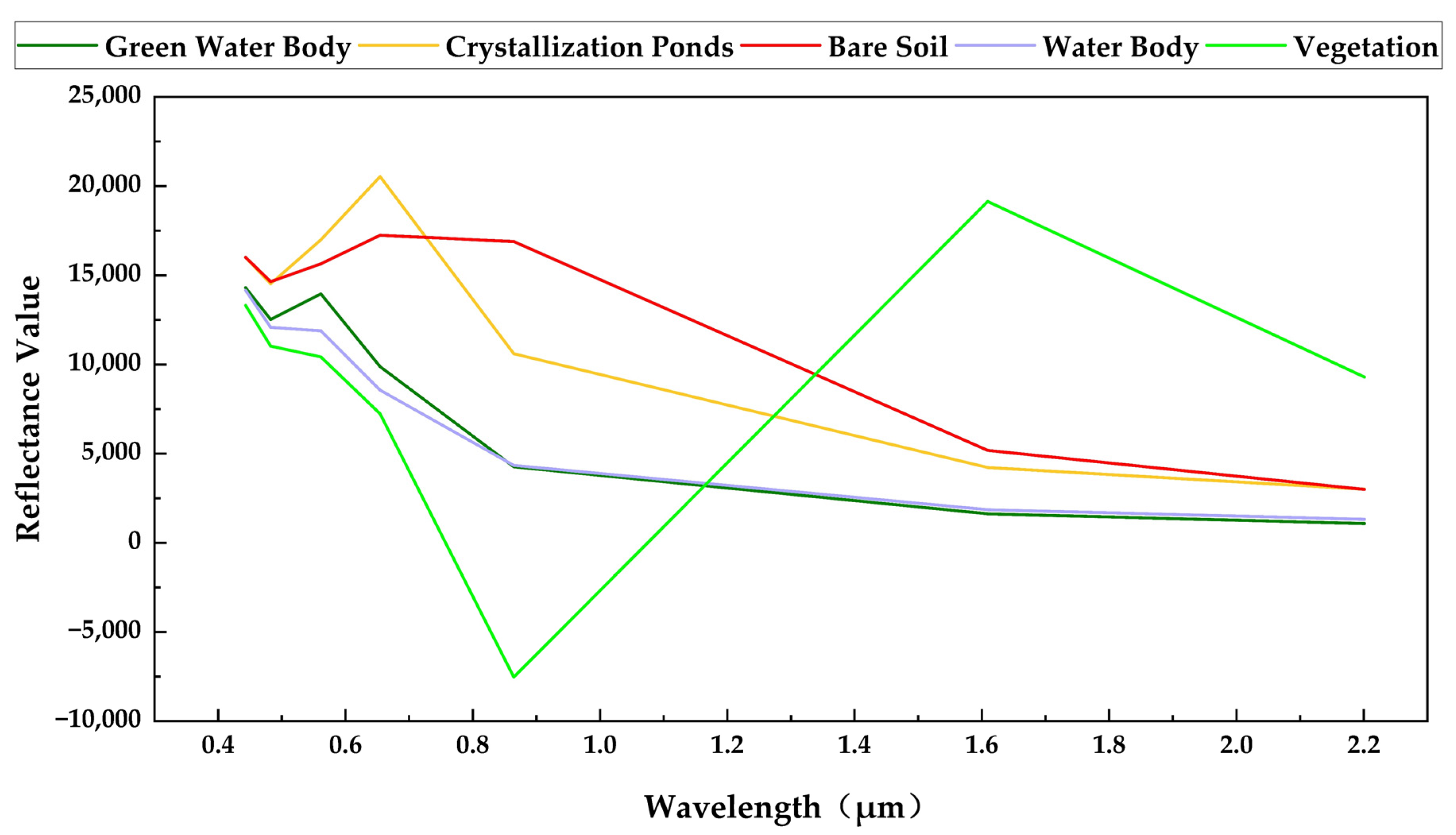
Appendix A.2. SCI
Appendix A.3. Spatial Feature Analysis Methods
- Laplacian operator
- 2.
- Hessian matrix
- 3.
- Local spatial similarity
References
- Zhao, L.; Fan, X.; Xiao, S. Remote-Sensing Indicators and Methods for Coastal-Ecosystem Health Assessment: A Review of Progress, Challenges, and Future Directions. Water 2025, 17, 1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sridhar, P.N.; Surendran, A.; Ramana, I.V. Auto-extraction Technique-based Digital Classification of Saltpans and Aquaculture Plots Using Satellite Data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2008, 29, 313–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, M. Study of Methodology in the Salt Pan Information Extraction Based on High-Resolution Images. Master’s Thesis, China University of Geosciences, Beijing, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, F. Multi-Feature Sequential Extraction Algorithms for Coastal Multi-Type Water Bodies Based on Landsat-8 Imagery. Master’s Thesis, Dalian Maritime University, Dalian, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Ni, K. Extraction Algorithms of Coastal Salt Pans and Aquaculture Ponds Based on Landsat-8 Images. Master’s Thesis, Dalian Maritime University, Dalian, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Jiao, X.; Shi, X.; Shen, Z.; Ni, K.; Deng, Z. Automatic Extraction of Saltpans on an Amendatory Saltpan Index and Local Spatial Parallel Similarity in Landsat-8 Imagery. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 3413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safaee, S.; Wang, J. Towards Global Mapping of Salt Pans and Salt Playas Using Landsat Imagery: A Case Study of Western United States. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2020, 41, 8693–8716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- JI, M.; Jianran, X.U.; Zhang, L.; Wang, C. Large Convolution Kernel Network Algorithm for Extracting Salt Field Farms from High-Resolution Images. Geospat. Inf. 2023, 21, 5–9. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Z.; Sun, H.; Zhang, T.; Xu, H.; Wu, D.; Gao, J. The High Spatial Resolution Drought Response Index (HiDRI): An Integrated Framework for Monitoring Vegetation Drought with Remote Sensing, Deep Learning, and Spatiotemporal Fusion. Remote Sens. Environ. 2024, 312, 114324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, D.; Li, Z.; Gao, X.; Gao, M.; Yu, C.; Zhang, C.; Shi, W. RealFusion: A Reliable Deep Learning-Based Spatiotemporal Fusion Framework for Generating Seamless Fine-Resolution Imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2025, 321, 114689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Zhang, S.; Wang, G.; Ding, J.; Chu, C.; Zhang, J.; Wang, H. Decoding Agricultural Drought Resilience: A Triple-Validated Random Forest Framework Integrating Multi-Source Remote Sensing for High-Resolution Monitoring in the North China Plain. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radford, B.; Puotinen, M.; Sahin, D.; Boutros, N.; Wyatt, M.; Gilmour, J. A Remote Sensing Model for Coral Recruitment Habitat. Remote Sens. Environ. 2024, 311, 114231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Li, L.; Wang, H.; Zhang, W.; Ren, P. Underwater Image Captioning with AquaSketch-Enhanced Cross-Scale Information Fusion. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2025, 63, 4208718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, Q.; Huang, H.; Guan, C.; Li, Y. Utilization of Underground Brine Resources and Phase Diagram Analysis in Laizhou Bay. J. Salt Sci. Chem. Ind. 2023, 52, 42–47. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, B. NDWI—A Normalized Difference Water Index for Remote Sensing of Vegetation Liquid Water from Space. Remote Sens. Environ. 1996, 58, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H. A Study on Information Extraction of Water Body with the Modified Normalized Difference Water Index (MNDWI)c. J. Remote Sens. 2005, 9, 589–595. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, H.; Hu, Q.; Zhao, P.; Wang, S.; Ai, M.; Zheng, D.; Liu, T. FTransDeepLab: Multimodal Fusion Transformer-Based DeepLabv3+ for Remote Sensing Semantic Segmentation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2025, 63, 4406618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Liu, Y.; Georgiou, T.; Lew, M.S. A Review of Semantic Segmentation Using Deep Neural Networks. Int. J. Multimed. Info. Retr. 2018, 7, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunandini, G.; Sivanpillai, R.; Sowmya, V.; Sajith Variyar, V.V. Significance of Atrous Spatial Pyramid Pooling (ASPP) in Deeplabv3+ for Water Body Segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2023 10th International Conference on Signal Processing and Integrated Networks (SPIN), Noida, India, 23 March 2023; pp. 744–749. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, S.; Zhu, C. Cascaded ASPP and Attention Mechanism-Based Deeplabv3+ Semantic Segmentation Model. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE 8th International Conference on Cloud Computing and Intelligent Systems (CCIS), Chengdu, China, 26 November 2022; pp. 315–318. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, J.; Zhou, J.; He, Y.; Jia, H.; Liang, Z. RL-DeepLabv3+: A Lightweight Rice Lodging Semantic Segmentation Model for Unmanned Rice Harvester. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2023, 209, 107823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Cui, Z.; Li, M.; Li, J.; Gao, D.; Ma, F.; Wang, Y. A Grapevine Trunks and Intra-Plant Weeds Segmentation Method Based on Improved Deeplabv3 Plus. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2024, 227, 109568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L. Random Forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, J.; Ghamisi, P.; Yokoya, N.; Iwasaki, A. Random Forest Ensembles and Extended Multiextinction Profiles for Hyperspectral Image Classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 56, 202–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ham, J.; Chen, Y.C.; Crawford, M.M.; Ghosh, J. Investigation of the Random Forest Framework for Classification of Hyperspectral Data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2005, 43, 492–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belgiu, M.; Drăguţ, L. Random Forest in Remote Sensing: A Review of Applications and Future Directions. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2016, 114, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speiser, J.L.; Durkalski, V.L.; Lee, W.M. Random Forest Classification of Etiologies for an Orphan Disease. Stat. Med. 2015, 34, 887–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
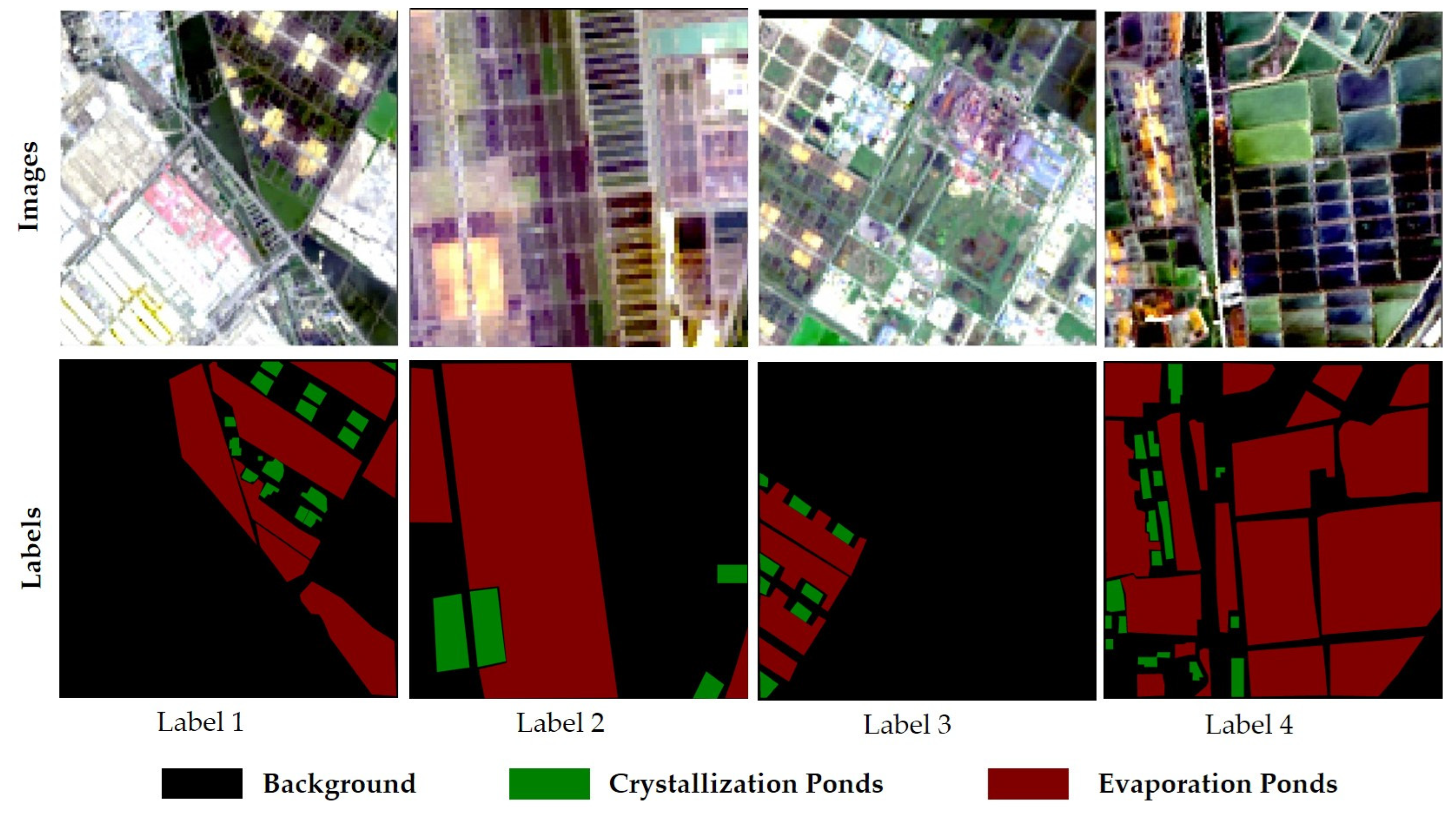

| No. | Date | Path/Row | Cloud Cover | Spatial Resolution (m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 18 April 2021 | 121/034 | 15.00% | 30 |
| 2 | 5 June 2021 | 121/034 | 14.74% | 30 |
| 3 | 21 June 2021 | 121/034 | 26.95% | 30 |
| Cloud Coverage | Sensor | Date |
|---|---|---|
| <30% | LANDSAT 8 LANDSAT 9 | May 2020~July 2020 May 2021~July 2021 May 2022~July 2022 May 2023~July 2023 May 2024~July 2024 |
| Accuracy | Formulation |
|---|---|
| Kappa | |
| Overall Accuracy | |
| Precision | |
| F1 score |
| Accuracy | Crystallization Pond | Evaporation Pond |
|---|---|---|
| Overall Accuracy | 92.29% | 92.29% |
| Kappa | 84.01% | 84.01% |
| Precision | 99.10% | 83.06% |
| F1 score | 90.34% | 93.66% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Y.; Yan, B.; Zhi, P.; Gao, Z.; Zhao, L. Monitoring and Analysis of Coastal Salt Pans Using Multi-Feature Fusion of Satellite Imagery: A Case Study Along the Laizhou Bay. Sustainability 2025, 17, 8436. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17188436
Liu Y, Yan B, Zhi P, Gao Z, Zhao L. Monitoring and Analysis of Coastal Salt Pans Using Multi-Feature Fusion of Satellite Imagery: A Case Study Along the Laizhou Bay. Sustainability. 2025; 17(18):8436. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17188436
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Yilin, Bing Yan, Pengyao Zhi, Zhiyou Gao, and Lihong Zhao. 2025. "Monitoring and Analysis of Coastal Salt Pans Using Multi-Feature Fusion of Satellite Imagery: A Case Study Along the Laizhou Bay" Sustainability 17, no. 18: 8436. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17188436
APA StyleLiu, Y., Yan, B., Zhi, P., Gao, Z., & Zhao, L. (2025). Monitoring and Analysis of Coastal Salt Pans Using Multi-Feature Fusion of Satellite Imagery: A Case Study Along the Laizhou Bay. Sustainability, 17(18), 8436. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17188436






