Robustness Evaluation and Optimization of China’s Multilayer Coupled Integrated Transportation System from a Complex Network Perspective
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Data and Methodology
2.1. Data Sources and Processing
2.2. Network Topological Properties
- (1)
- Degree and degree distribution
- (2)
- Average path length
- (3)
- Network diameter
- (4)
- Clustering coefficient
2.3. Key Node Identification
2.4. Network Robustness Analysis
- (1)
- The largest connected component ratio
- (2)
- Relative network efficiency
- (3)
- Comprehensive robustness
2.5. Network Robustness Optimization
- Using all prefecture-level administrative regions nationwide as nodes, a candidate edge set covering the entire network was generated, excluding edges that already exist in the original network.
- Node importance values are calculated based on the PLEA model. High-importance nodes are defined as those ranking within the top 30% of importance scores across the entire network; these nodes typically correspond to transportation hubs or nodes connecting core regions, characterized by high degree and strong connectivity. Low-importance nodes are defined as those in the bottom 30% of importance scores, usually located at the network periphery with fewer connections, lower redundancy, and weaker structural embedding.
- The importance of candidate edges is evaluated by the sum of the PLEA values of the node pairs, combined with the geographical distance between nodes to construct a priority score. A weighted ranking principle is applied: “higher importance and shorter distance correspond to higher priority,” ensuring that added edges balance structural benefits with real-world constraints.
- Based on the priority rankings, edges are selected from the candidate set at varying proportions (5%, 10%, and 15%) to conduct two types of edge addition experiments. In the high mode, all added edges connect pairs of high-importance nodes, thereby strengthening the interconnectivity among hubs. In the low mode, added edges connect pairs of low-importance nodes, aiming to improve the connectivity and redundancy of peripheral nodes.
- The effectiveness of different edge addition proportions and strategies in enhancing network robustness under various disturbance scenarios is comparatively analyzed based on three categories of indicators: S, RE, and R.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Network Topology Analysis
3.2. Key Node Ranking
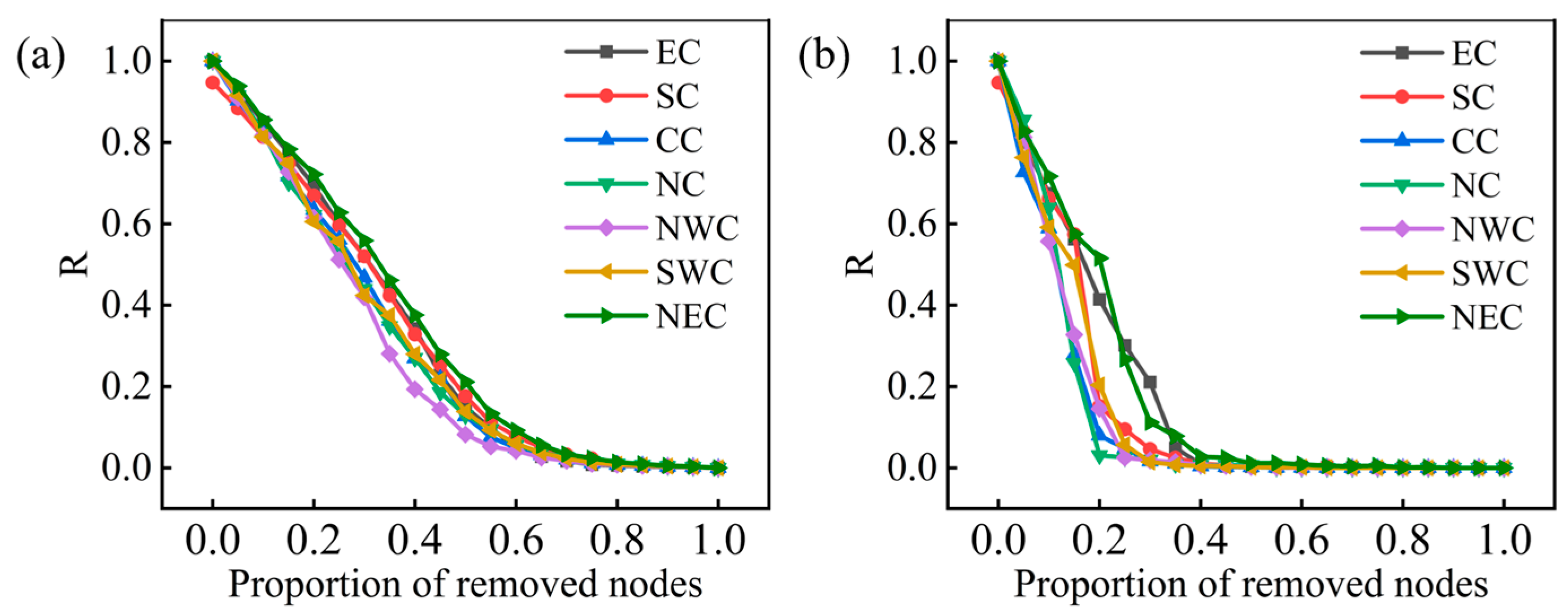
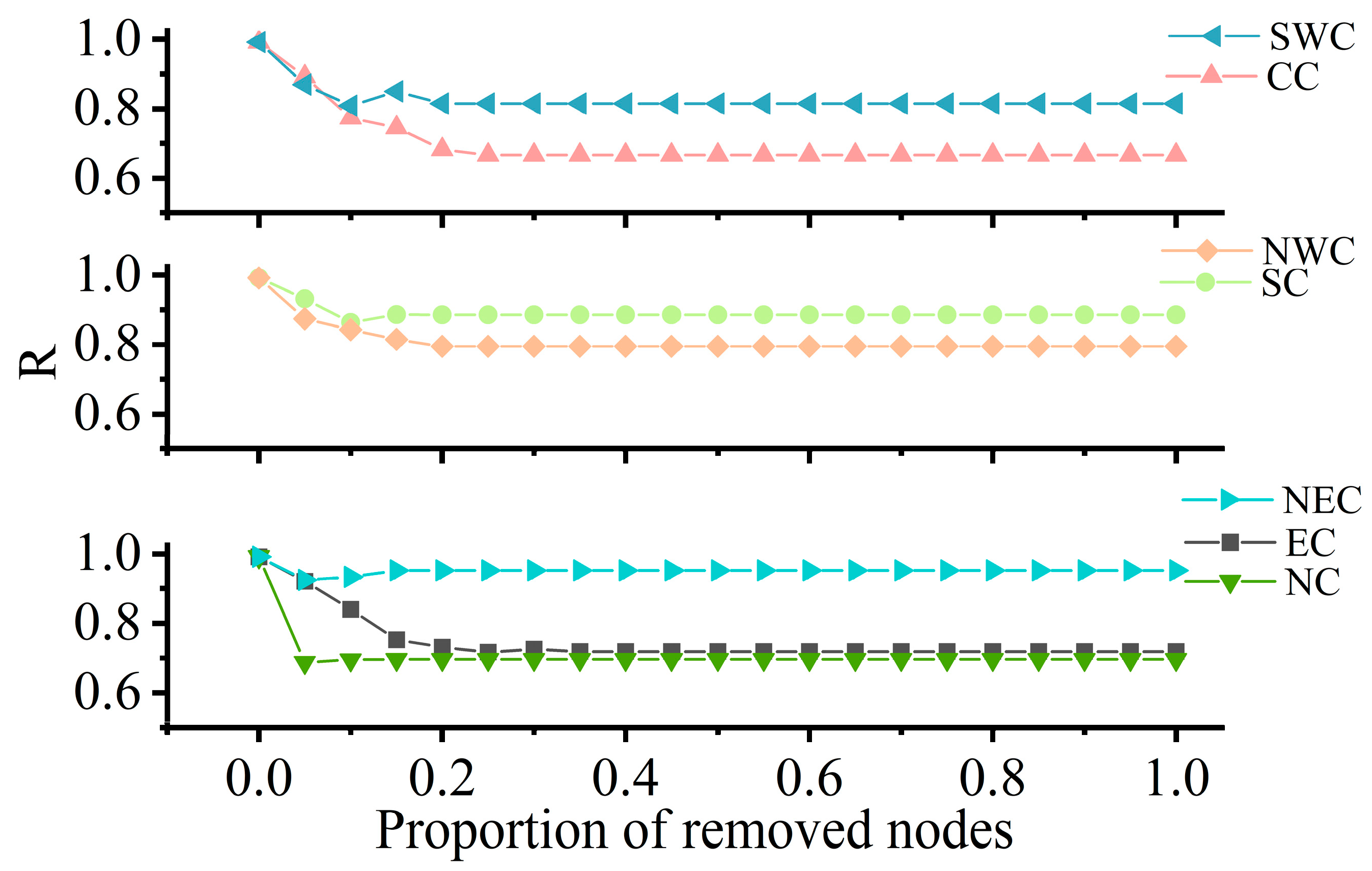
3.3. Robustness Evaluation
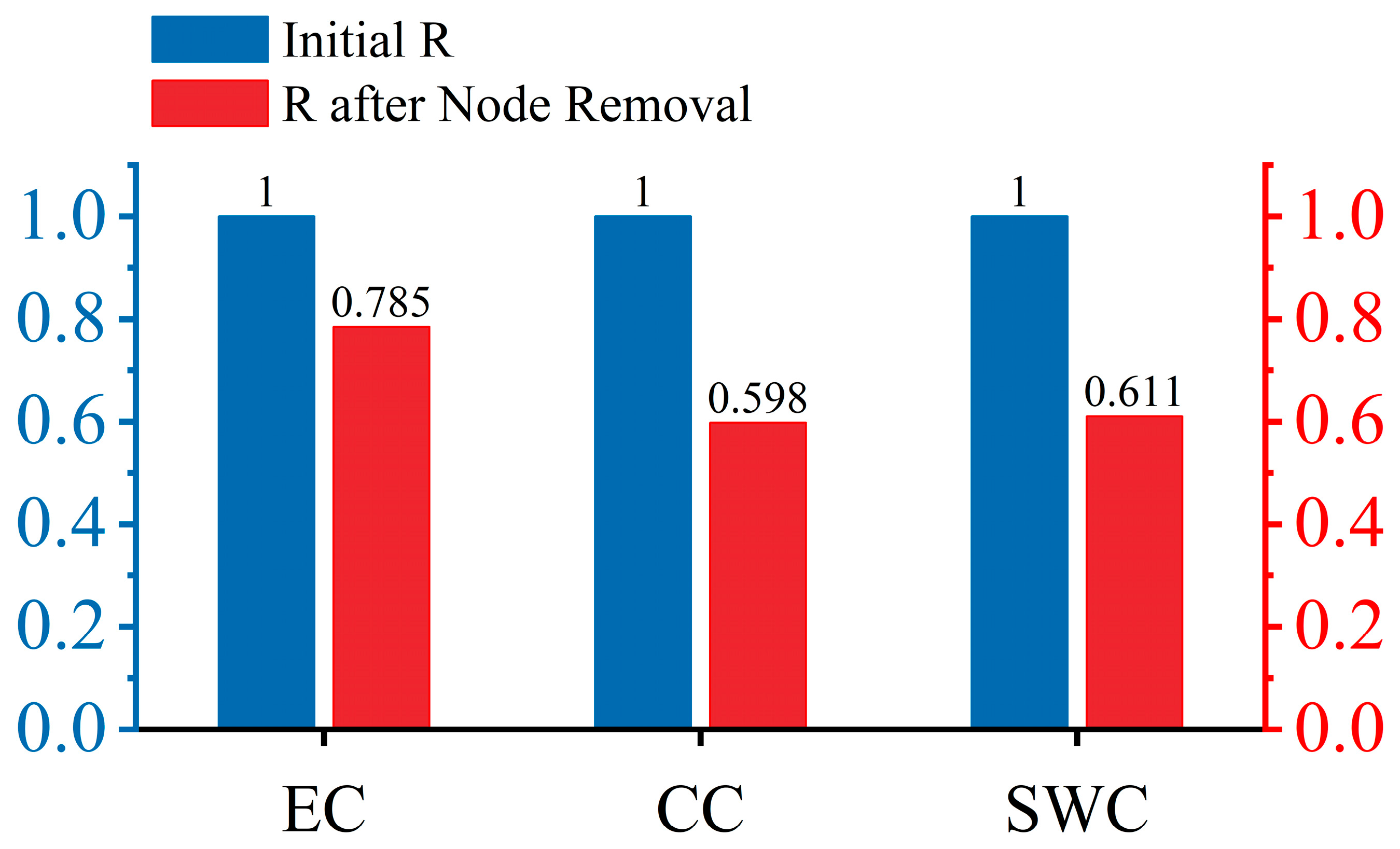
3.4. Robustness Optimization
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, S.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, F. Interdependency in transportation system resilience: Review and discussion. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2025, 140, 104618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Q.; Shen, S.-L.; Zhou, A.; Lyu, H.-M. Inundation risk assessment based on G-DEMATEL-AHP and its application to Zhengzhou flooding disaster. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2022, 86, 104138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, C.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, D.; Yan, X.; Fan, S. Resilience in transportation systems: A systematic review and future directions. Transp. Rev. 2018, 38, 479–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, Y.; Chen, X. The 1998 flood on the Yangtze, China. Nat. Hazards 2000, 22, 165–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, C.; Xu, C.; Huang, Y.; Liu, J.; Shao, X.; Xu, X.; Gao, H.; Ma, J.; Xiao, Z. Advances in the study of natural disasters induced by the “23.7” extreme rainfall event in North China. Nat. Hazards Res. 2025, 5, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Lian, F. Optimization of the Sino-Russian trade transportation network under geopolitical risks such as the Russia-Ukraine conflict. Transp. Res. Part E Logist. Transp. Rev. 2025, 198, 104144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artime, O.; Grassia, M.; De Domenico, M.; Gleeson, J.P.; Makse, H.A.; Mangioni, G.; Perc, M.; Radicchi, F. Robustness and resilience of complex networks. Nat. Rev. Phys. 2024, 6, 114–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Ma, S.; Chen, L.; Yang, L. Resilience measurement and analysis of intercity public transportation network. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2024, 131, 104202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albert, R.; Barabási, A.-L. Statistical mechanics of complex networks. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2002, 74, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Cai, X. Empirical analysis of a scale-free railway network in China. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2007, 382, 693–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Zhong, Z.; Sun, R. Analysis of Topological Properties and Robustness of Urban Public Transport Networks. Sustainability 2024, 16, 6527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Su, B.; Chen, Z. Generalized-Norm-Based Robustness Evaluation Model of Bus Network under Snowy Weather. Sustainability 2024, 16, 5260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Günay, E.E.; Kremer, G.E.O.; Zarindast, A. A multi-objective robust possibilistic programming approach to sustainable public transportation network design. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 2021, 422, 106–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frutos Bernal, E.; Martín del Rey, A. Study of the structural and robustness characteristics of madrid metro network. Sustainability 2019, 11, 3486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bombelli, A.; Santos, B.F.; Tavasszy, L. Analysis of the air cargo transport network using a complex network theory perspective. Transp. Res. Part E Logist. Transp. Rev. 2020, 138, 101959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Wu, L.; Yu, J.; Wang, M.; Kong, H.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, J. Robustness of bilayer railway-aviation transportation network considering discrete cross-layer traffic flow assignment. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2024, 127, 104071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ippolito, N.; Cats, O. Multi-modal and multi-layer robustness analysis of the European rail and air networks. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 26950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, F.; Shi, W.; Yuen, K.F.; Sun, Q.; Xu, X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Z. Exploring the robustness of public transportation for sustainable cities: A double-layered network perspective. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 265, 121747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Du, Q.; Li, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Martinez-Pastor, B. Cascading failure and recovery of metro–bus double-layer network considering recovery propagation. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2023, 122, 103861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, L.C. Centrality in social networks: Conceptual clarification. Soc. Netw. Crit. Concepts Sociol. 2002, 1, 238–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, L.C. A set of measures of centrality based on betweenness. Sociometry 1977, 40, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonacich, P.; Lloyd, P. Eigenvector-like measures of centrality for asymmetric relations. Soc. Netw. 2001, 23, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabidussi, G. The centrality index of a graph. Psychometrika 1966, 31, 581–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitsak, M.; Gallos, L.K.; Havlin, S.; Liljeros, F.; Muchnik, L.; Stanley, H.E.; Makse, H.A. Identification of influential spreaders in complex networks. Nat. Phys. 2010, 6, 888–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agryzkov, T.; Oliver, J.L.; Tortosa, L.; Vicent, J.F. An algorithm for ranking the nodes of an urban network based on the concept of PageRank vector. Appl. Math. Comput. 2012, 219, 2186–2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Wang, S.L.; Chen, G.W.; Yan, G.H. Key node mining in complex network based on improved local structural entropy. J. Comput. Appl. 2023, 43, 1109–1114. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Dunn, S.; Wilkinson, S.M. Increasing the resilience of air traffic networks using a network graph theory approach. Transp. Res. Part E Logist. Transp. Rev. 2016, 90, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.J.; Guan, S. Measuring vulnerability of urban metro network from line operation perspective. Transp. Res. Part A Policy Pract. 2016, 94, 348–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, F.; Ao, Y.; Wang, X.; He, H.; Liu, Q.; Yang, D.; Gou, H. Assessing and enhancing urban road network resilience under rainstorm waterlogging disasters. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2023, 123, 103928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Xu, M.; Ouyang, M. A multi-perspective functionality loss assessment of coupled railway and airline systems under extreme events. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2024, 243, 109831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Rong, L. Impacts of service feature on vulnerability analysis of high-speed rail network. Transp. Policy 2021, 110, 238–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liao, F.; Wu, J.; Sun, H.; Wang, W.; Gao, Z. Measurement of functional resilience of transport network: The case of the Beijing subway network. Transp. Policy 2023, 140, 54–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wandelt, S.; Shi, X.; Sun, X. Estimation and improvement of transportation network robustness by exploiting communities. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2021, 206, 107307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Chopra, S.S.; Lee, H. Resilient urban public transportation infrastructure: A comparison of five flow-weighted metro networks in terms of the resilience cycle framework. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2021, 23, 12688–12699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Deng, W.; Zhu, Y.; Lü, L. Assessing and improving the structural robustness of global liner shipping system: A motif-based network science approach. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2023, 240, 109576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ayyub, B.M.; Saadat, Y.; Zhang, D.; Huang, H. A double-weighted vulnerability assessment model for metrorail transit networks and its application in Shanghai metro. Int. J. Crit. Infrastruct. Prot. 2020, 29, 100358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, M.; Li, F.; Sun, C. Robustness assessment of urban rail transit based on complex network theory: A case study of the Beijing Subway. Saf. Sci. 2015, 79, 149–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.-Y.; Hero, A.O. Assessing and safeguarding network resilience to nodal attacks. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2014, 52, 138–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Xiao, R. Enhancing the global and local robustness of networks: A network motif-based approach. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 2025, 140, 108439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chujyo, M.; Hayashi, Y. A loop enhancement strategy for network robustness. Appl. Netw. Sci. 2021, 6, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.H. eXplainable DEA approach for evaluating performance of public transport origin-destination pairs. Res. Transp. Econ. 2024, 108, 101491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.H.; Lee, E. Iterative DEA for public transport transfer efficiency in a super-aging society. Cities 2025, 162, 105957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaidya, O.S.; Kumar, S. Analytic hierarchy process: An overview of applications. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2006, 169, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mardani, A.; Zavadskas, E.K.; Govindan, K.; Amat Senin, A.; Jusoh, A. VIKOR technique: A systematic review of the state of the art literature on methodologies and applications. Sustainability 2016, 8, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, C.; Zhang, X.; Yuan, J.; Chen, X.; Zhang, X.; Fathollahi-Fard, A.; Wang, C.; Wu, J.; Tian, G. A hybrid approach for low-carbon transportation system analysis: Integrating CRITIC-DEMATEL and deep learning features. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 21, 791–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Liu, J.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, B. A study of highway logistics transportation network structure in China: From the perspective of complex network. J. Data Inf. Manag. 2022, 4, 89–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, K.; Wu, J.; Wang, W.; Lee, D.-H.; Wei, Y. An integrated resilience assessment model of urban transportation network: A case study of 40 cities in China. Transp. Res. Part A Policy Pract. 2023, 173, 103687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Yang, L.; Chen, X.; Zhu, M. Cluster characteristics analysis and critical node identification in ecologically integrated transport networks in urban agglomerations. J. Tsinghua Univ. (Sci. Technol.) 2023, 63, 1770–1780. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, S.J.; Qian, M.; Zeng, W. A Comprehensive GIS Database for China’s Surface Transport Network with Implications for Transport and Socioeconomics Research; National Bureau of Economic Research: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]

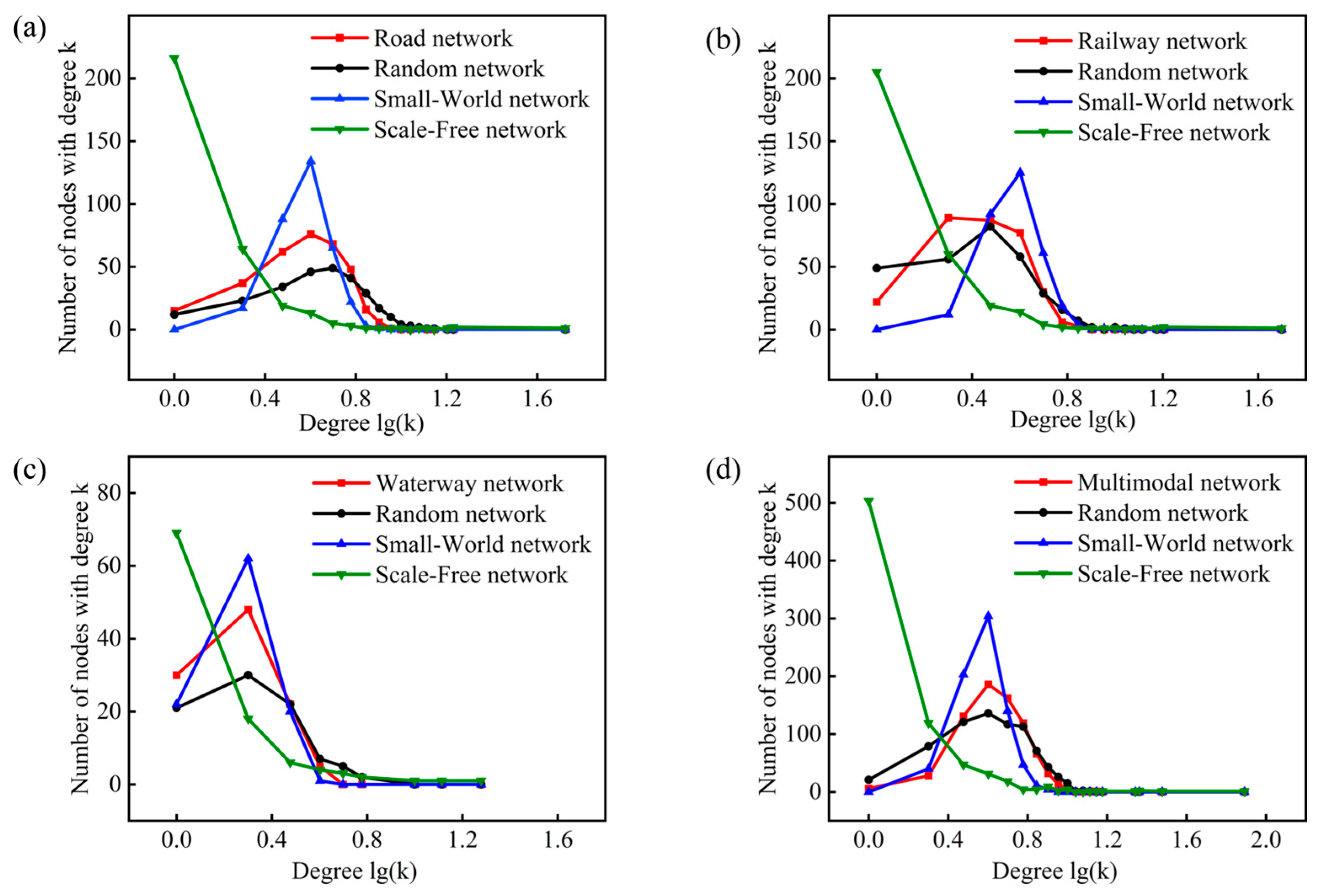
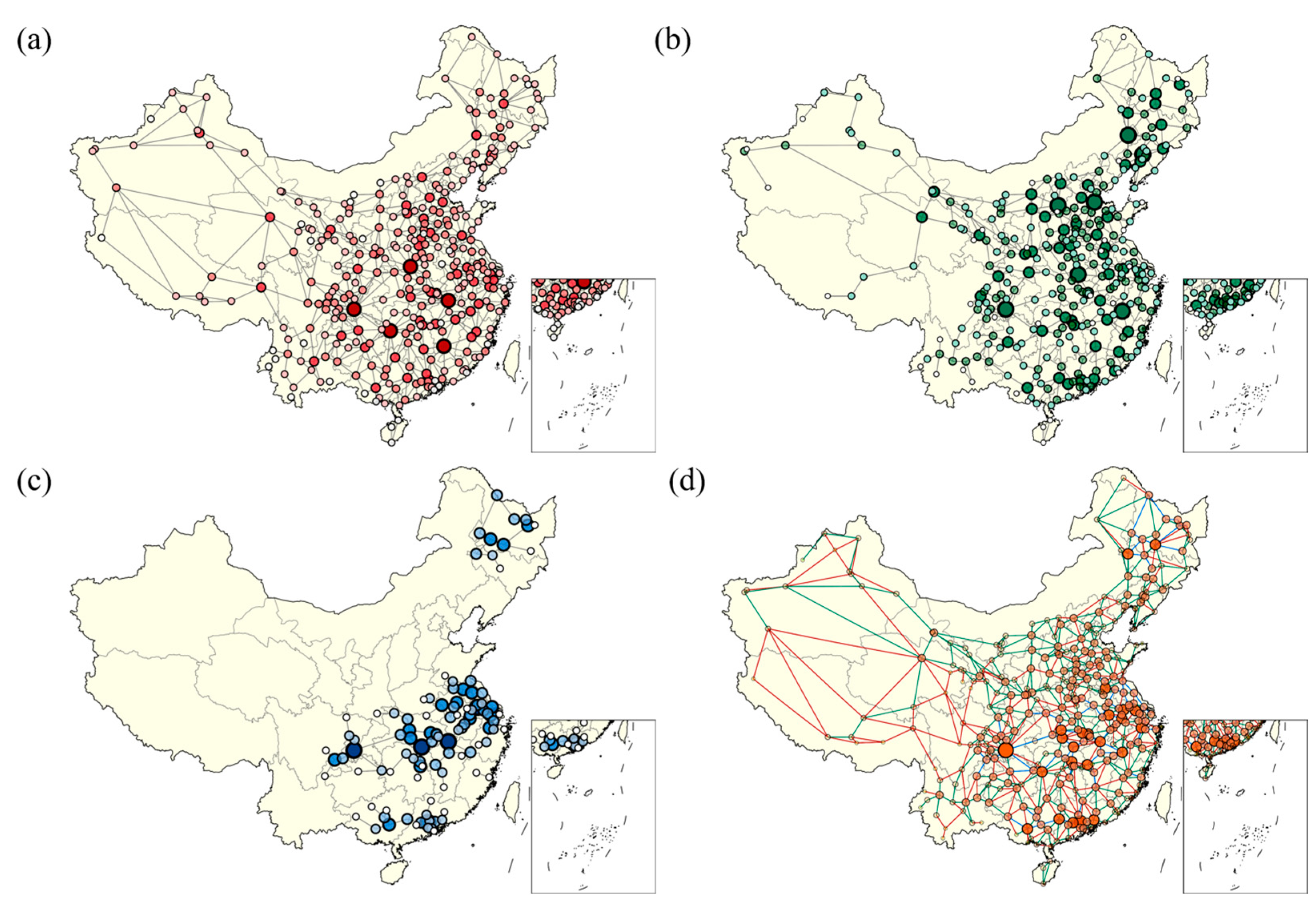

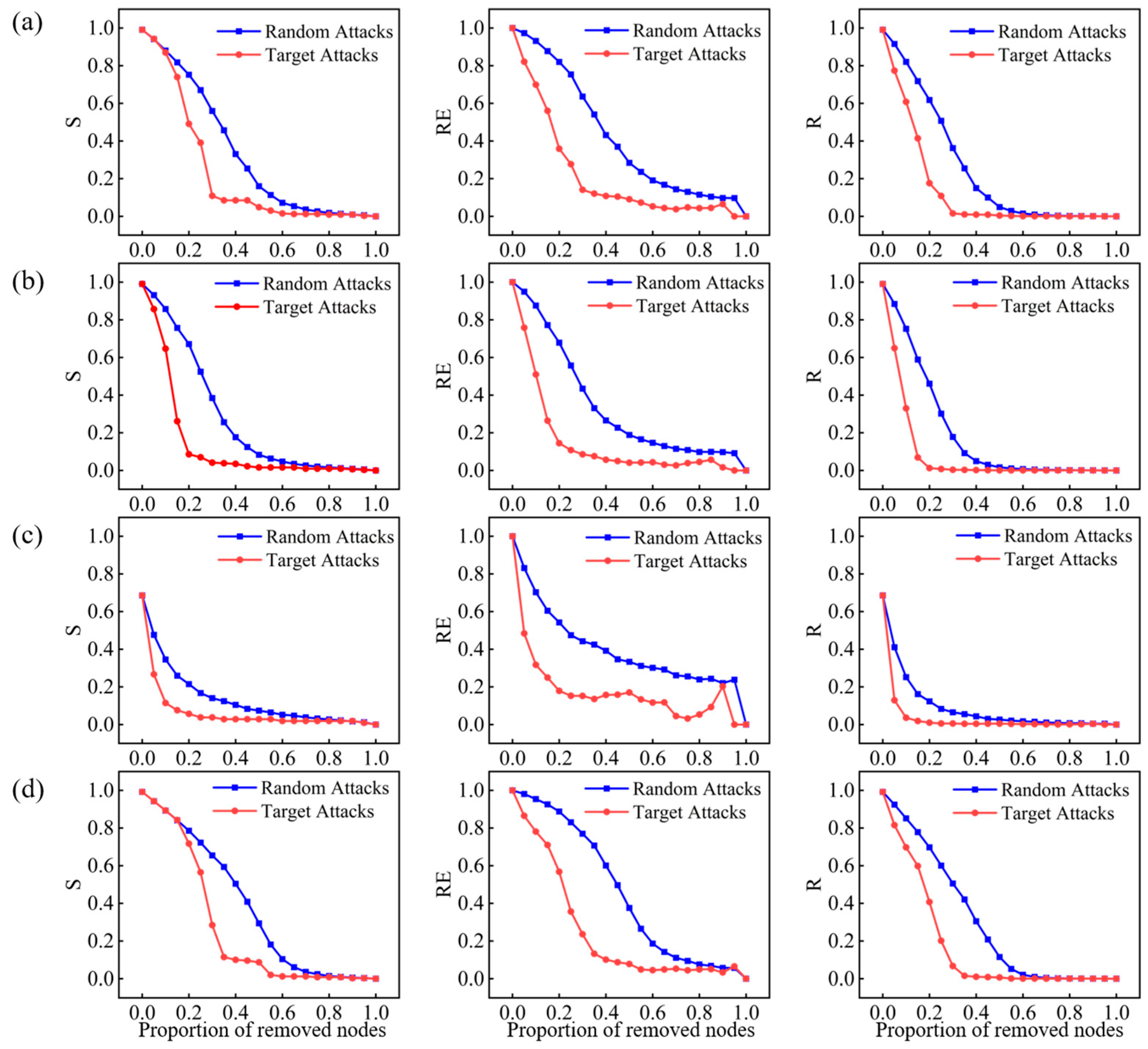
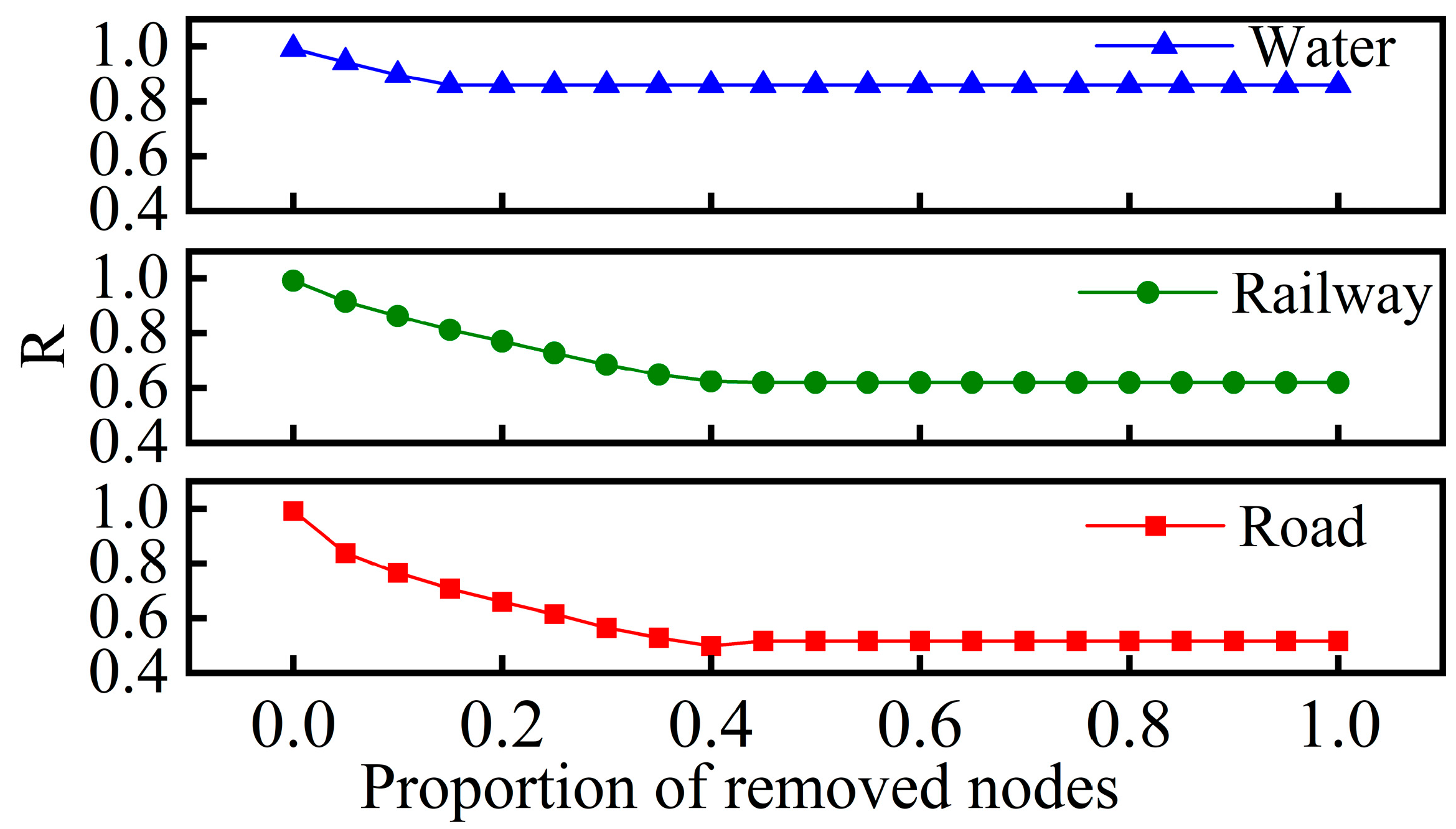


| Network Model | Node | Edge | Degree | Clustering Coefficient | Network Diameter | Average Path Length |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Road sub-network | 330 | 694 | 4.2061 | 0.3196 | 24 | 9.3619 |
| Railway sub-network | 314 | 488 | 3.1083 | 0.1452 | 28 | 11.0293 |
| Waterway sub-network | 105 | 106 | 2.0190 | 0.0222 | 27 | 8.9334 |
| Integrated transportation network | 749 | 1811 | 4.8358 | 0.1555 | 26 | 9.9832 |
| Region Network | Node | Edge | Degree | Clustering Coefficient | Network Diameter | Average Path Length |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NEC | 94 | 207 | 4.4043 | 0.1295 | 10 | 4.3294 |
| NC | 107 | 219 | 4.0935 | 0.1548 | 13 | 5.2957 |
| EC | 229 | 531 | 4.6376 | 0.1482 | 18 | 6.4255 |
| SC | 113 | 250 | 4.4248 | 0.1669 | 12 | 4.5761 |
| CC | 162 | 351 | 4.3333 | 0.1422 | 15 | 5.7301 |
| NWC | 124 | 225 | 3.6290 | 0.0871 | 13 | 5.3345 |
| SWC | 131 | 268 | 4.0916 | 0.1439 | 13 | 5.1617 |
| Road Sub-Network | Railway Sub-Network | Waterway Sub-Network | Integrated Transportation Network | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chongqing | 3.38 | Chongqing | 2.70 | Chongqing | 2.00 | Chongqing | 8.88 |
| Nanyang | 2.92 | Shenyang | 2.61 | Yueyang | 1.97 | Jiujiang | 8.02 |
| Jiujiang | 2.81 | Xinzhou | 2.53 | Foshan | 1.97 | Shangrao | 7.73 |
| Huaihua | 2.81 | Shangrao | 2.44 | Zhenjiang | 1.81 | Haerbin | 7.66 |
| Ganzhou | 2.73 | Tongliao | 2.40 | Jiujiang | 1.80 | Jingzhou | 7.53 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mei, X.; Ye, W.; Li, W.; Chen, C.; Li, A.; Wu, J.; Du, H. Robustness Evaluation and Optimization of China’s Multilayer Coupled Integrated Transportation System from a Complex Network Perspective. Sustainability 2025, 17, 7398. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17167398
Mei X, Ye W, Li W, Chen C, Li A, Wu J, Du H. Robustness Evaluation and Optimization of China’s Multilayer Coupled Integrated Transportation System from a Complex Network Perspective. Sustainability. 2025; 17(16):7398. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17167398
Chicago/Turabian StyleMei, Xuanling, Wenjing Ye, Wenjie Li, Cheng Chen, Ang Li, Jianping Wu, and Hongbo Du. 2025. "Robustness Evaluation and Optimization of China’s Multilayer Coupled Integrated Transportation System from a Complex Network Perspective" Sustainability 17, no. 16: 7398. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17167398
APA StyleMei, X., Ye, W., Li, W., Chen, C., Li, A., Wu, J., & Du, H. (2025). Robustness Evaluation and Optimization of China’s Multilayer Coupled Integrated Transportation System from a Complex Network Perspective. Sustainability, 17(16), 7398. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17167398





