Ecosystem Services in Northeast China’s Cold Region: A Comprehensive Review of Patterns, Drivers, and Policy Responses
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
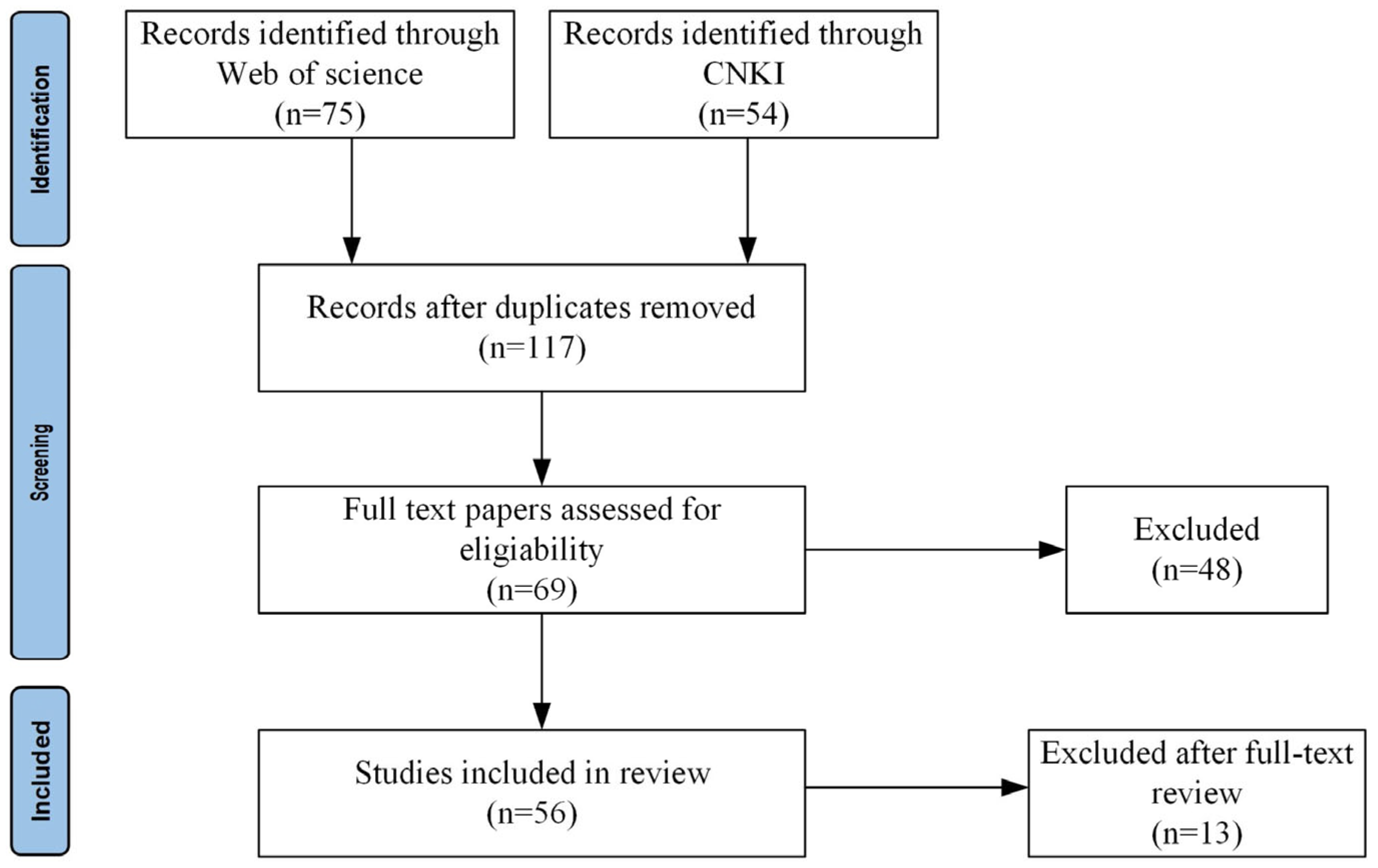
2.1. Literature Acquisition and Data Sources
2.2. Literature Screening and Classification Methods
2.3. Analytical Framework
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Synthesized Patterns and Temporal Evolution of ESs in Northeast China
3.2. Integrated Evidence on Trade-Offs and Synergies Among ESs
3.3. Literature-Based Analysis of Driving Factors Influencing ESs
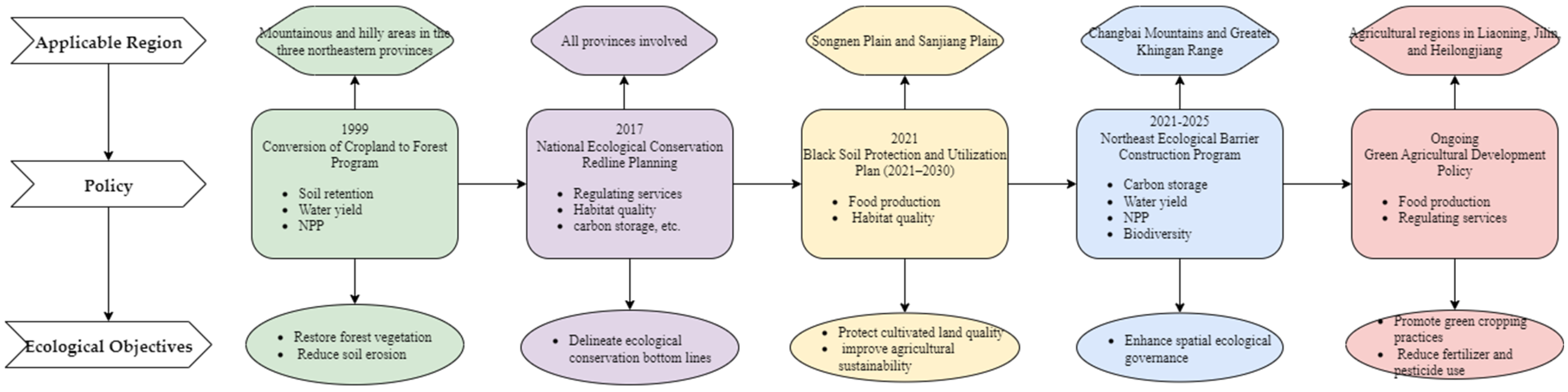
3.4. Review of Regulatory Strategies and Policy Responses in the Context of ESs
3.5. Cross-Regional Comparison of ESs
4. Conclusions and Future Expectations
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Costanza, R.; d’Arge, R.; Rudolf, d.G.; Stephen, F.; Monica, G.; Karin, L.; Shahid, N.; Robert, V.O.; Jose, P.; Robert, G.R.; et al. The value of the world’s ecosystem services and natural capital. Nature 1997, 387, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costanza, R.; de Groot, R.; Braat, L.; Kubiszewski, I.; Fioramonti, L.; Sutton, P.; Farber, S.; Grasso, M. Twenty years of ecosystem services: How far have we come and how far do we still need to go? Ecosyst. Serv. 2017, 28, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MEA, Millennium Ecosystem Assessment. Ecosystems and Human Well-Being: Synthesis; Island Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, B.; Zhang, L. Land-use change and ecosystem services: Concepts, methods and progress. Prog. Geogr. 2014, 33, 441–446. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Yang, J.; Tang, Z.; Xue, L.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, J. Driving mechanisms of ecosystem services and their trade-offs and synergies in the transition zone between the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau and the Loess Plateau. Ecol. Indic. 2025, 171, 113148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi Mirghaed, F.; Mohammadzadeh, M.; Salmanmahiny, A.; Mirkarimi, S.H. Decision scenarios using ecosystem services for land allocation optimization across Gharehsoo watershed in northern Iran. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 117, 106645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, S.; Gupta, S. Provisioning ecosystem services: Multitier bibliometric analysis and visualisation. Environ. Sustain. Indic. 2020, 8, 100081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Xia, J.; Deng, X.; Yan, H. Multilevel modelling of impacts of human and natural factors on ecosystem services change in an oasis, Northwest China. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2021, 169, 105474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Wang, B.; Niu, X.; Gao, P.; Song, Q. Changes in ecosystem services and an analysis of driving factors for China’s Natural Forest Conservation Program. Ecol. Evol. 2019, 9, 3700–3716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Liu, G.; Li, Z.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Z. Processes and driving forces for changing vegetation ecosystem services: Insights from the Shaanxi Province of China. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 112, 106105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Z.; Gong, J.; Teng, W.; Yang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Xu, T.; Jin, T. Climate change and human activities have resulted in substantial alterations to ecosystem quality within the Yarlung Zangbo River basin. Ecol. Front. 2025, 45, 925–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, H.; Zhang, J.; Mao, D.; Wang, Z.; Qiu, Z.; Yan, H. Identifying spatial similarities and mismatches between supply and demand of ecosystem services for sustainable Northeast China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 134, 108501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Bai, Y.; Alatalo, J.M.; Wang, H.; Jiang, B.; Liu, G.; Chen, J. Spatio-temporal changes in water-related ecosystem services provision and trade-offs with food production. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 286, 125316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Huang, C.; Jin, H.; Han, Y.; Kang, S.; Liu, J.; Cai, H.; Hu, T.; Yang, G.; Yu, H.; et al. Spatio-temporal patterns of carbon storage derived using the invest model in Heilongjiang Province, Northeast China. Front. Earth Sci. 2022, 10, 846456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Shi, H.; Xu, X.; Huang, L.; Gu, Q.; Liu, H. County zoning and optimization paths for trade-offs and synergies of ecosystem services in Northeast China. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 164, 112044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, F.; Zhang, S. Ecosystem service decline in response to wetland loss in the Sanjiang Plain, Northeast China. Ecol. Eng. 2019, 130, 117–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, G.; Dong, Y.; Zhang, S.; He, X.; Zheng, H.; Guo, Y.; Shen, G.; Chen, W. Spatiotemporal changes of ecosystem service trade-offs under the influence of forest conservation project in Northeast China. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2022, 10, 978145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Kalantari, M.; Sun, J.; Sun, W.; Guan, G.; Du, G. The spatiotemporal correlation between human activity intensity and the evolution of ecosystem service value in the Songnen Plain, China. Land 2024, 13, 1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Booi, S.; Mishi, S.; Andersen, O. Ecosystem services: A systematic review of provisioning and cultural ecosystem services in Estuaries. Sustainability 2022, 14, 7252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balzan, M.V.; Sadula, R.; Scalvenzi, L. Assessing ecosystem services supplied by agroecosystems in Mediterranean Europe: A literature review. Land 2020, 9, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Chen, J.; Li, Y.; Wu, W. Using the InVEST-PLUS model to predict and analyze the pattern of ecosystem carbon storage in Liaoning Province, China. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 4050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, D.; Cao, A.; Wang, F. Response and multi-scenario prediction of carbon storage and habitat quality to land use in Liaoning Province, China. Sustainability 2023, 15, 4500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wang, W.J.; Liu, Z.; Wang, L.; Zhang, W.; Zou, Y.; Jiang, M. Combined effects of multi-land use decisions and climate change on water-related ecosystem services in Northeast China. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 315, 115131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riao, D.; Zhu, X.; Tong, Z.; Zhang, J.; Wang, A. Study on land use/cover change and ecosystem services in Harbin, China. Sustainability 2020, 12, 6076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, J.; Shi, D.; Zhou, S.; Xia, Z. Spatial and temporal patterns of ecosystem services and trade-off synergistic relationships in Bin County, Heilongjiang Province. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2022, 29, 293–300. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Yu, X.; Jiang, M.; Xue, Z.; Lu, X.; Zou, Y. A consistent ecosystem services valuation method based on total economic value and equivalent value factors: A case study in the Sanjiang Plain, Northeast China. Ecol. Complex. 2017, 29, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Wang, L.; Fu, Q.; Ma, F. Ecological function zoning framework for small watershed ecosystem services based on multivariate analysis from a scale perspective. Land 2024, 13, 1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, K.; Zhou, J.; Ni, H. Effects of temporal and spatial changes in wetlands on regional carbon storage in the Naoli River Basin, Sanjiang Plain, China. Land 2023, 12, 1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, L.; Jiang, R.; Zheng, D.; Liang, L. Impact of climate change and land use/cover change on water yield in the Liaohe River Basin, Northeast China. J. Arid Land 2025, 17, 182–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, W.; Shen, B.; Xin, X.; Gu, Q.; Guo, T. Spatiotemporal variations of grassland ecosystem service value and its influencing factors in Inner Mongolia, China. Agronomy 2022, 12, 2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Xin, X.; Song, J.; Li, X.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, J. Simulation of LUCC dynamics and estimation of carbon stock under different SSP-RCP scenarios in Heilongjiang Province. Land 2023, 12, 1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Fang, H. Modeling the impact of climate change on watershed discharge and sediment yield in the black soil region, northeastern China. Geomorphology 2017, 293, 255–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, X.; Zhan, J.; Li, Z.; Zhang, F.; Qi, W. Assessment on forest carbon sequestration in the Three-North Shelterbelt Program region, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 215, 382–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, H.; Kong, W.; Zhou, G.; Sun, O.J. Impacts of landscape patterns on water-related ecosystem services under natural restoration in Liaohe River Reserve, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 792, 148290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Q.; Tran, L.T.; Wei, W. Understanding synergistic ecosystem services in China’s Northeast Forest Belt: A blueprint for spatially targeted management. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 166, 112434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Cong, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, L.; Fei, L. Ecosystem service trade-offs and synergies in a temperate agricultural region in Northeast China. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wang, W.; Wang, L.; Ma, S.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, W.; Zou, Y.; Jiang, M. Impacts of future climate and land use/cover changes on water-related ecosystem services in Changbai Mountains, Northeast China. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2022, 10, 854497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Wang, W.J.; Wang, L.; Cong, Y.; Wu, H. Impacts of multi-land use decisions on temperate forest habitat quality in the Changbai Mountain Region, Northeast China. Ecol. Evol. 2025, 15, e71123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Wang, L.; Wang, Z.; Fu, Q.; Ma, F. Comparative analysis of dynamic changes and scenario predictions of carbon storage in a small watershed driven by social-natural factors in cold regions. Land Degrad. Dev. 2025, 36, 3134–3149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, H.; Jia, M.; Wang, Z.; Li, L.; Mao, D.; Zhang, D.; Cui, G.; Zhu, W. Impacts of land cover changes on ecosystem carbon stocks over the Transboundary Tumen River Basin in Northeast Asia. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2018, 28, 973–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Li, X.; Lyu, X.; Dang, D.; Cao, W.; Du, Y. Unraveling the complex interconnections between food-energy-water nexus sustainability and the supply-demand of related ecosystem services. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 370, 122532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Li, Y.; Luo, J.; Liu, F.; Wang, Y.; Li, H. Spatio-temporal evolution of habitat quality in the Nenjiang River Basin, Northeast China. Environ. Ecol. 2020, 2, 19–26. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Xiang, H.; Hashimoto, S.; Okuro, T. Observational scale matters for ecosystem services interactions and spatial distributions: A case study of the Ussuri Watershed, China. Sustainability 2021, 13, 10649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Li, Y.; Huang, L.; Lu, Z.; Yu, D.; Zhou, L.; Dai, L. Spatiotemporal variation of water yield and its driving factors in Northeast China. Chin. J. Ecol. 2017, 36, 3216–3223. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, L.; Li, S.; Lewis, B.J.; Wu, J.; Yu, D.; Zhou, W.; Zhou, L.; Wu, S. The influence of land use change on the spatial–temporal variability of habitat quality between 1990 and 2010 in Northeast China. J. For. Res. 2018, 30, 2227–2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Xu, J.; Feng, X.; Guo, M.; Jin, Y.; Gao, X. Effects of land use change on habitat based on InVEST model in Northeast China. Ecol. Sci. 2018, 37, 139–147. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, D.; He, X.; Wang, Z.; Tian, Y.; Xiang, H.; Yu, H.; Man, W.; Jia, M.; Ren, C.; Zheng, H. Diverse policies leading to contrasting impacts on land cover and ecosystem services in Northeast China. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 240, 117961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Dong, L.; Huang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Qin, H.; Qiao, Z. Equilibrium relationship between ecosystem service supply and consumption driven by economic development and ecological restoration. Sustainability 2021, 13, 1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Xing, Y.; Chang, X.; Yang, H. Analysis of spatial distribution of ecosystem services and driving factors in Northeast China. Environ. Sci. 2024, 45, 5386–5394. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Shi, J. Slow recovery of natural ecosystems as an important factor restricting regional coordinated development. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 158, 111435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Jin, X.; Mu, H.; Yang, S.; He, R.; Li, X.; Wang, W.; Huang, S.; Zu, J.; Wang, H.; et al. Impacts of human footprint on habitat quality and permafrost environment in Northeast China. Ecol. Indic. 2025, 175, 113587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Pu, Y.; Gao, W. Spatial correlation analysis and prediction of carbon stock of “Production-living-ecological spaces” in the three northeastern provinces, China. Heliyon 2023, 9, e18923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, Z.; Sun, C.; Hao, S. Matching relationship between supply and demand of ecosystem services from the perspective of water-energy-food nexus in Northeast China. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2024, 44, 4170–4186. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, D.; Liu, J.; Zhao, D. Assessment of carbon storage under different ssp-rcp scenarios in terrestrial ecosystems of Jilin Province, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 3691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, X.; Wang, J.; Liu, D.; Li, S.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, G. Managing the supply–demand mismatches and potential flows of ecosystem services in Jilin Province, China, from a regional integration perspective. Land 2024, 13, 1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Mao, D.; Li, X.; Wang, Z.; Jia, M.; Huang, X.; Xiao, Y.; Xiang, H. Understanding the contrasting effects of policy-driven ecosystem conservation projects in northeastern China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 135, 108578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.Q.; Liu, G.; Yang, Z.H.; Liu, X.Q.; Miao, Q.F.; Fu, H.C. Ecosystem services assessment and multi-scenario prediction in Liaoning Province from 2000 to 2020. Environ. Sci. 2024, 45, 4137–4151. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Wang, L.; Wang, T.; Chen, H.; Du, P. Global versus local? a study on the synergistic relationship of ecosystem service trade-offs from multiple perspectives based on ecological restoration zoning of national land space—A case study of Liaoning Province. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 10421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Qie, R.; Luo, C.; Zhang, W. Assessment and driving factors of wetland ecosystem service function in Northeast China based on InVEST-PLUS model. Water 2024, 16, 2153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, H.; Li, X.; Li, S.; Dang, D.; Li, X.; Lyu, X.; Li, M.; Liu, S. Mapping ecosystem services bundles for analyzing spatial trade-offs in inner Mongolia, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 256, 120444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Liu, C.; Yan, X.; Li, X.; Wang, X. Coupling coordination and matches in ecosystem services supply-demand for ecological zoning management: A case study of Dalian. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2021, 41, 9064–9075. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Y.; Lu, M. Identifying conservation priorities and management strategies based on ecosystem services to improve urban sustainability in Harbin, China. PeerJ 2018, 6, e4597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, Y.; Hu, Y. Spatial-temporal variation and driving forces of water yield in Harbin City. Bull. Soil Water Conserv. 2023, 43, 294–303. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Hu, Y.; Hu, H. Prediction of land use and habitat quality in Harbin city based on the PLUS- InVEST Model. Environ. Sci. 2024, 48, 4709–4721. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; Zhao, C.; Shen, P.; Ren, S.; Hu, Y. Spatiotemporal evolution of soil conservation function value and its driving forces in Harbin city. Bull. Soil Water Conserv. 2024, 44, 357–367. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; Shen, P.; Ren, S.; Chen, T.; Hu, Y. Coupling effect of landscape patterns on the spatial and temporal distribution of ecosystem services: A case study in Harbin City, Northeast China. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 4606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Wu, Y.; Pan, Y.; Meng, D. Spatio-temporal variation evaluation of ecosystem health in Harbin from the perspective of water-energy-food nexus. J. Chin. Urban For. 2025, 23, 84–91. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chang, B.; Chen, B.; Chen, W.; Xu, S.; He, X.; Yao, J.; Huang, Y. Analysis of trade-off and synergy of ecosystem services and driving forces in urban agglomerations in Northern China. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 165, 112210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, S.; Xiao, Y.; Qin, K.; Liu, J.; Xu, J.; Wang, Y.; Niu, Y.; Huang, M.; Xie, G. Analyzing the interrelationships among various ecosystem services from the perspective of ecosystem service bundles in Shenyang, China. Land 2022, 11, 515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, Z.; Li, S.; Li, X. Multi-scenario simulation analysis of land use and carbon storage changes in Changchun city based on flus and invest model. Land 2022, 11, 647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, F.; Tang, H.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, B.; Dai, L. Integrating ecosystem services supply and demand into optimized management at different scales: A case study in Hulunbuir, China. Ecosyst. Serv. 2019, 39, 100984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J. Identification of ecosystem services supply and demand and driving factors in Taihu Lake Basin. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 29735–29745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Xu, G.; Jiang, H. Synergy between ecosystem services and ecosystem health in the forest area of Northeast China. Prog. Geogr. 2015, 34, 761–771. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, Z. Identification of Harbin ecological function degradation areas based on ecological importance assessment and ecological sensitivity. Sustainability 2024, 16, 6763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Liu, L.; Zhang, L.; Zhuang, Y.; Du, J. An optimization model for carbon capture utilization and storage supply chain: A case study in Northeastern China. Appl. Energy 2018, 231, 194–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cord, A.F.; Bartkowski, B.; Beckmann, M.; Dittrich, A.; Hermans-Neumann, K.; Kaim, A.; Lienhoop, N.; Locher-Krause, K.; Priess, J.; Schröter-Schlaack, C.; et al. Towards systematic analyses of ecosystem service trade-offs and synergies: Main concepts, methods and the road ahead. Ecosyst. Serv. 2017, 28, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leong, R.A.T.; Fung, T.K.; Sachidhanandam, U.; Drillet, Z.; Edwards, P.J.; Richards, D.R. Use of structural equation modeling to explore influences on perceptions of ecosystem services and disservices attributed to birds in Singapore. Ecosyst. Serv. 2020, 46, 101211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, B.; David, J.; Campos, F.S.; Cabral, P. Satellite-based machine mearning modelling of ecosystem services indicators: A review and meta-analysis. Appl. Geogr. 2024, 165, 103249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dade, M.C.; Mitchell, M.G.E.; McAlpine, C.A.; Rhodes, J.R. Assessing ecosystem service trade-offs and synergies: The need for a more mechanistic approach. Ambio 2019, 48, 1116–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Wu, J. Spatial and temporal driving mechanisms of ecosystem service trade-off/synergy in national key urban agglomerations: A case study of the Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration in China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 154, 110800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Harms, M.; Balvanera, P. Methods for mapping ecosystem service supply: A review. Int. J. Biodivers. Sci. Ecosyst. Serv. Manag. 2012, 8, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Lautenbach, S. A quantitative review of relationships between ecosystem services. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 66, 340–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.; Zuo, L.; Gao, J.F.; Jiang, Y.; Du, F.; Zhang, Y. Exploring the driving factors of trade-offs and synergies among ecological functional zones based on ecosystem service bundles. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 146, 109827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Yang, G.; Wan, R.; Hamilton, D.P.; Wang, X. Unravelling the spatiotemporal trade-offs and synergies among hydrological ecosystem services in a large floodplain lake. Ecol. Indic. 2025, 172, 113255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Sun, W.; Zhang, S.; Yang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Lan, H.; Yu, T.; Li, X.; Xie, Y. How can ecosystem services trade-offs/synergies help select the optimal cultivated land restoration pattern? A study based on multi-scenario simulations. Appl. Geogr. 2025, 177, 103563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagstad, K.J.; Cohen, E.; Ancona, Z.H.; McNulty, S.G.; Sun, G. The sensitivity of ecosystem service models to choices of input data and spatial resolution. Appl. Geogr. 2018, 93, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, J.D.; Corstanje, R.; Harris, J.A. Bundling ecosystem services at a high resolution in the UK: Trade-offs and synergies in urban landscapes. Landsc. Ecol. 2021, 36, 1817–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Zhao, J.; Li, Y.; Lin, Y. Identifying trade-offs and synergies among land use functions using an XGBoost-SHAP model: A case study of Kunming, China. Ecol. Indic. 2025, 172, 113330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, P.; Huai, H.; Wu, X.; Wang, H.; Liu, W.; Tang, X. Using XGBoost-SHAP for understanding the ecosystem services trade-off effects and driving mechanisms in ecologically fragile areas. Front. Plant Sci. 2025, 16, 1552818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, B.; Su, C.; Wei, Y.; Willett, I.R.; Lü, Y.; Liu, G. Double counting in ecosystem services valuation: Causes and countermeasures. Ecol. Res. 2010, 26, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hang, Y.; Lu, X.; Li, X. Spatiotemporal differentiation characteristics and zoning of cultivated land system resilience in the Songnen Plain. Sustainability 2025, 17, 4314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Du, G.; Teng, H.; Wang, J.; Li, H. Multi-scenario land use change simulation and spatial response of ecosystem service value in Black Soil Region of Northeast China. Land 2023, 12, 962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, G.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, H.; Zhu, S.; Wen, Y.; Sheng, L.; Guo, Y. Disentangling the relative and cumulative impacts of diverse policies on food- and water-related ecosystem services and their trade-offs in ecologically fragile areas. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 447, 141322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanes, R.J.; Gopalakrishnan, V.; Bakshi, B.R. Including nature in the food-energy-water nexus can improve sustainability across multiple ecosystem services. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2018, 137, 214–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhao, X.; Wu, S.; Tong, Z. Developing ecological protection redline policy for land use pattern optimization in the typical black soil region of Northeastern China. Front. Environ. Sci. 2024, 12, 1422077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Lin, N.; Xu, D.; Yu, D.; Zou, C. Research advance on ecological security in China: Assessment models and management measures. J. Ecol. Rural. Environ. 2018, 34, 1057–1063. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, D.; Luo, F.; Bai, J.; Fu, Y. Impact of vegetation restoration on ecosystem services in the Loess plateau, a case study in the Jinghe Watershed, China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 142, 109183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.M.; Gao, J.F.; Fan, X.Y.; Lan, Y.; Zhao, M.S. Response of ecosystem services to socioeconomic development in the Yangtze River Basin, China. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 72, 481–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuur, E.A.G.; McGuire, A.D.; Schädel, C.; Grosse, G.; Harden, J.W.; Hayes, D.J.; Hugelius, G.; Koven, C.D.; Kuhry, P.; Lawrence, D.M.; et al. Climate change and the permafrost carbon feedback. Nature 2015, 520, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Fu, B.; Feng, X.; Zeng, Y.; Liu, Y.; Chang, R.; Sun, G.; Wu, B. A policy-driven large scale ecological restoration: Quantifying ecosystem services changes in the Loess Plateau of China. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e31782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Mao, J.; Peng, Y.; Wu, J.; Wang, X.; Su, L. Exploring the driving forces of ecosystem services in the Yangtze River Basin, China. Land 2025, 14, 411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuur, E.A.G.; Abbott, B.W.; Commane, R.; Ernakovich, J.; Euskirchen, E.; Hugelius, G.; Grosse, G.; Jones, M.; Koven, C.D.; Leshyk, V.; et al. Permafrost and climate change: Carbon cycle feedbacks from the Warming Arctic. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 2022, 47, 343–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, J.; Dong, B. Trade-offs between agricultural production and ecosystem services under different land management scenarios in the Loess Plateau of China. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 21385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.Y.; Wei, P.J.; Wu, T.H.; Wu, Q.B.; Luo, F.D. Effect of permafrost degradation on carbon sequestration of alpine ecosystems. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 899, 165642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
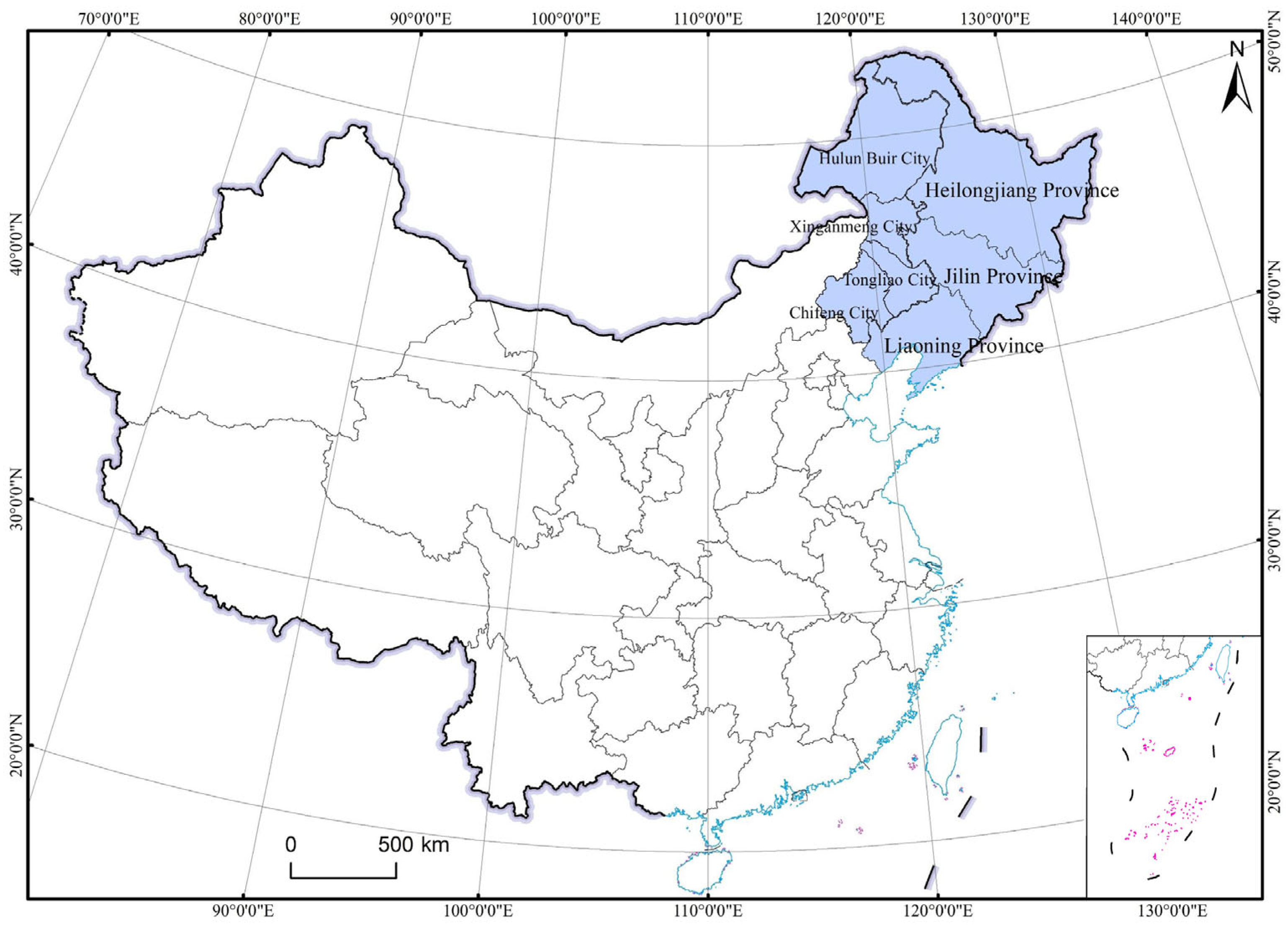
| Study Area | ES Types | Scale | Years | RES | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WY | SR | CS | NPP | FP | PP | MP | OCP | HB | SP | FR | HM | PA | WP | LS | TR | ED | ||||
| Liaohe River Reserve | √ | √ | √ | natural region | 2007, 2011, 2015 | [34] | ||||||||||||||
| Northeast Forest Belt | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | natural region | 2005, 2015 | [35] | ||||||||||||
| Songnen Plain | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | natural region | 2000, 2010, 2020 | [36] | ||||||||||||
| Changbai Mountain region | √ | √ | natural region | 2020, 2050 | [37] | |||||||||||||||
| Changbai Mountain region | √ | natural region | 1990, 2020, 2050 | [38] | ||||||||||||||||
| Ashi River basin | √ | watershed | 1990, 2000, 2010, 2020, 2030 | [39] | ||||||||||||||||
| Tumen River Basin | √ | watershed | 1990, 2015 | [40] | ||||||||||||||||
| Naoli River Basin | √ | √ | √ | watershed | 2005, 2010, 2015 | [41] | ||||||||||||||
| Naoli River Basin | √ | watershed | 1993–2022 | [29] | ||||||||||||||||
| Nenjiang River Basin | √ | watershed | 1980, 2000, 2015 | [42] | ||||||||||||||||
| Naoli River Basin | √ | watershed | 1993, 1998, 2003, 2008, 2013, 2018, 2022 | [28] | ||||||||||||||||
| Songhua River Basin | √ | √ | √ | √ | watershed | 2000, 2015 | [13] | |||||||||||||
| Ussuri Watershed | √ | √ | √ | √ | watershed, grid | 2015 | [43] | |||||||||||||
| Ashi River Basin | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | watershed, town, grid | 1995, 2015 | [27] | |||||||||||
| Northeast China | √ | province | 1990, 2000, 2010 | [44] | ||||||||||||||||
| Northeast China | √ | province | 1990, 2000, 2010 | [45] | ||||||||||||||||
| Northeast China | √ | province | 2005, 2010, 2015 | [46] | ||||||||||||||||
| Northeast China | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | province | 2000, 2015 | [47] | |||||||||||
| Northeast China | √ | √ | √ | province | 1995, 2010, 2018 | [48] | ||||||||||||||
| Northeast China | √ | √ | √ | √ | province | 2015 | [12] | |||||||||||||
| Northeast China | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | province | 2020 | [49] | ||||||||||||
| Northeast China | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | province | 2005, 2010, 2015, 2020 | [50] | ||||||||||||
| Northeast China | √ | province | 2000, 2020 | [51] | ||||||||||||||||
| Northeast China | √ | √ | province | 1990, 2020 | [23] | |||||||||||||||
| Heilongjiang, Jilin, Liaoning Provinces | √ | province | 1990, 2000, 2010, 2020 | [52] | ||||||||||||||||
| Heilongjiang, Jilin, Liaoning Provinces | √ | √ | √ | province | 2000, 2005, 2010, 2015, 2020 | [53] | ||||||||||||||
| Heilongjiang Province | √ | province | 1980, 2015 | [14] | ||||||||||||||||
| Heilongjiang Province | √ | province | 2020, 2030, 2040, 2050 | [31] | ||||||||||||||||
| Jilin Province | √ | province | 2020, 2030, 2040 | [54] | ||||||||||||||||
| Jilin Province | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | province | 2000, 2010, 2020 | [55] | ||||||||||||
| Liaoning Province | √ | √ | √ | √ | province | 2000, 2015 | [56] | |||||||||||||
| Liaoning Province | √ | province | 2000, 2010, 2020 | [21] | ||||||||||||||||
| Liaoning Province | √ | √ | province | 2010, 2020, 2030 | [22] | |||||||||||||||
| Liaoning Province | √ | √ | √ | province | 2000, 2005, 2010, 2015, 2020 | [57] | ||||||||||||||
| Liaoning Province | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | province | 2020 | [58] | ||||||||||||
| Inner Mongolia Province | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | province | 2000–2019 | [30] | |||||||||
| Three-North Shelterbelt Program region | √ | province | 1990, 1995, 2000, 2005, 2010, 2015 | [33] | ||||||||||||||||
| Northeast China | √ | √ | √ | province, city | 2000, 2010, 2020 | [59] | ||||||||||||||
| Inner Mongolia Province | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | province, county | 2010 | [60] | ||||||
| Northeast China | √ | √ | √ | province, county, grid | 2000, 2020 | [15] | ||||||||||||||
| Dalian City | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | city | 2015 | [61] | |||||||||||
| Harbin City | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | city | \ | [62] | |||||||||||
| Harbin City | √ | city | 2000, 2010, 2020 | [63] | ||||||||||||||||
| Harbin City | √ | city | 2000, 2010, 2020 | [64] | ||||||||||||||||
| Harbin City | √ | city | 2000, 2010, 2020 | [65] | ||||||||||||||||
| Harbin City | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | city | 2000, 2010, 2020 | [66] | |||||||||||
| Harbin City | √ | √ | √ | city | 2000, 2010, 2020 | [67] | ||||||||||||||
| Urban Agglomeration in Liaoning Province | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | city | 2000, 2020 | [68] | |||||||||||
| Shenyang City | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | city | 2000, 2019 | [69] | ||||||||
| Changchun City | √ | city | 2010, 2020, 2030 | [70] | ||||||||||||||||
| Hulun Buir City | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | city, county | 2015 | [71] | ||||||||||||
| Binxian, Harbin | √ | √ | √ | county | 2000, 2010, 2020 | [25] | ||||||||||||||
| Arun Banner in Hulun Buir City | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | county | 2005, 2010, 2015, 2018 | [72] | ||||||||||||
| Wangqing, Jiling Province | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | county | \ | [73] | ||||||||||||
| Method Type | Brief Description | Advantages | Limitations | Scale | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Correlation Analysis (Pearson, Spearman) | Assessing the linear or ordinal correlation between two ES variables | Simple and intuitive; easy to compute | Cannot reveal causality; reflects only statistical correlation | Overall | [79,80] |
| Regression Analysis (e.g., multiple linear, nonlinear models) | Building a model that treats a specific service as the dependent variable and the others as independent variables | Strong explanatory power for variables | Assumes linearity; difficult to capture complex nonlinear effects | Overall | [81,82] |
| Principal Component Analysis (PCA)/Factor Analysis | Reducing dimensionality and extracting common variance among services | Suitable for identifying high-dimensional variable structures | Weak interpretability; prone to abstraction | Overall | [82] |
| Cluster Analysis (e.g., K-means) | Identifies “service bundles” or functional groups | Captures spatial heterogeneity of services | Cannot provide strength or direction of service relationships | Spatial | [80,83] |
| Spatial Autocorrelation (Moran’s I) | Measures clustering of services in space | Reveals spatial synergy/conflict patterns | Sensitive to spatial scale, data resolution, and boundary settings | Spatial | [84] |
| Root Mean Square Error (RMSE) | Calculating deviation within service units and overall difference, reflecting strength of mismatch | Intuitive; suitable for identifying pattern mismatch in trade-offs/synergies | Unidirectional; requires normalization, results may depend on scale | Spatial | [17] |
| TSD (Trade-off/Synergy Degree Index) | Using standardized service values to quantify trade-off or synergy levels | Identifies relationship intensity; suitable for spatially explicit trade-off/synergy mapping | Sensitive to standardization; mechanism interpretation may be weak | Spatial | [85] |
| Geographically Weighted Regression (GWR) | Analyzing spatial non-stationarity in service relationships | Suitable for local effect analysis; reveals spatial variation in drivers | Complex model; sensitive to multicollinearity and parameter dependence | Spatial | [36] |
| Coupling Coordination Degree (CCD) | Assessing coordination between multiple service systems over space or time | Reveals interaction strength and synergy balance; suitable for long-term monitoring | Sensitive to parameter settings; cannot explain mechanisms | Overall | [61] |
| Service Pair | Relationship Type | Study Area | Main Driving Factors |
|---|---|---|---|
| Food production vs. Soil retention | Trade-off | Agricultural areas in Heilongjiang | Intensive cultivation, reduced vegetation cover |
| NPP vs. Water yield | Synergy | Binxian, Harbin | High forest coverage, accumulation of soil organic matter |
| Food production vs. NPP | Trade-off | Songnen Plain | Excessive agricultural inputs leading to ecosystem degradation |
| NPP vs. Habitat quality | Synergy | Changbai Mountain region | Vegetation restoration, ecological engineering efforts |
| Water yield vs. Soil retention | Synergy | Northeastern China | Grassland and shrubland protection on sloped land |
| Habitat quality vs. Food production | Trade-off | Western Liaoning | Cropland expansion encroaching on ecologically suitable land |
| Method Name | Advantages | Limitations | Applicable Scale |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pearson/Correlation Analysis | Simple and easy to implement; suitable for preliminary exploration | Unable to reveal spatial or nonlinear relationships | Regional/Provincial |
| Principal Component Analysis (PCA)/Cluster Analysis | Identify service bundles and functional regions | Not suitable for analyzing dynamic evolution processes | Watershed/Municipal level |
| Geodetector | Reveals spatial heterogeneity and driving factors | Lacks capability for temporal dynamic analysis | County/Grid level |
| GWR/GTWR/MGWR | Considers spatial variation and reveals local differences | Computationally complex; requires high-quality input data | County/Township level |
| Machine Learning (RF/XGBoost) | Strong in capturing nonlinear relationships; robust variable interpretability | Requires large training datasets; model has black-box characteristics | Applicable across multiple spatial scales |
| Category of Driving Factors | Representative Variables | Major Impact Pathways |
|---|---|---|
| Natural Factors | Elevation, slope, aspect, NDVI, soil type, soil texture, topographic relief, etc. | Determine the fundamental ecological pattern; affect water conservation, soil retention, and NPP distribution |
| Climatic Factors | Precipitation, temperature, evapotranspiration, wind speed, humidity, etc. | Govern the rate of ecological processes; influence water cycling and vegetation growth |
| Land Use/Land Cover Factors | Cropland ratio, forest coverage, impervious surface area, land use intensity, landscape fragmentation, etc. | Define spatial structure; excessive agricultural expansion may lead to trade-offs in regulating services |
| Socioeconomic Factors | Population density, GDP, urbanization rate, nighttime light index, road density, etc. | Indicate intensity of human disturbance; reflect structural shifts in ES demands |
| Policy and Management Factors | Ecological redlines, land zoning policies, nature reserve designation, reforestation programs | Represent institutional interventions; mediate or constrain trade-offs and synergies among ESs |
| Dimensions | Northeast China | Loess Plateau | Yangtze River Basin | Permafrost Zone |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dominant ES Types | Food production, carbon conservation, etc. | Soil/water conservation, carbon conservation, biodiversity | Hydrological regulation, climate, cultural services | Carbon sequestration, hydrological buffering, climate regulation |
| Assessment Methods | InVEST, statistical models | Remote sensing, ES index models | Hotspot analysis, spatial econometric models | Process-based modeling, remote sensing |
| Trade-off/Synergy Patterns | Provisioning vs. regulating in black soil farmland | Soil conservation, erosion risk | Water yield vs. carbon storage | Carbon release vs. ecosystem resilience |
| Driving Factors | NDVI, elevation, soil type, soil texture, cropping intensity, etc. | Ecological restoration, slope gradient, etc. | Climate, socioeconomic, land use, etc. | Permafrost stability, ground-ice, hydrology, etc. |
| Policy Management | Black soil conservation, ecological redlines, zoning | Grain-for-Green, afforestation-driven ES recovery | ES-based eco-compensation, basin-level planning | Indigenous co-management, permafrost carbon protocols |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, X.; Yang, C.; Wang, Z.; Wang, L. Ecosystem Services in Northeast China’s Cold Region: A Comprehensive Review of Patterns, Drivers, and Policy Responses. Sustainability 2025, 17, 7352. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17167352
Guo X, Yang C, Wang Z, Wang L. Ecosystem Services in Northeast China’s Cold Region: A Comprehensive Review of Patterns, Drivers, and Policy Responses. Sustainability. 2025; 17(16):7352. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17167352
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Xiaomeng, Chuang Yang, Zilong Wang, and Li Wang. 2025. "Ecosystem Services in Northeast China’s Cold Region: A Comprehensive Review of Patterns, Drivers, and Policy Responses" Sustainability 17, no. 16: 7352. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17167352
APA StyleGuo, X., Yang, C., Wang, Z., & Wang, L. (2025). Ecosystem Services in Northeast China’s Cold Region: A Comprehensive Review of Patterns, Drivers, and Policy Responses. Sustainability, 17(16), 7352. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17167352






