Spatial Sustainability of Agricultural Rural Settlements: An Analysis of Rural Spatial Patterns and Influencing Factors in Three Northeastern Provinces of China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
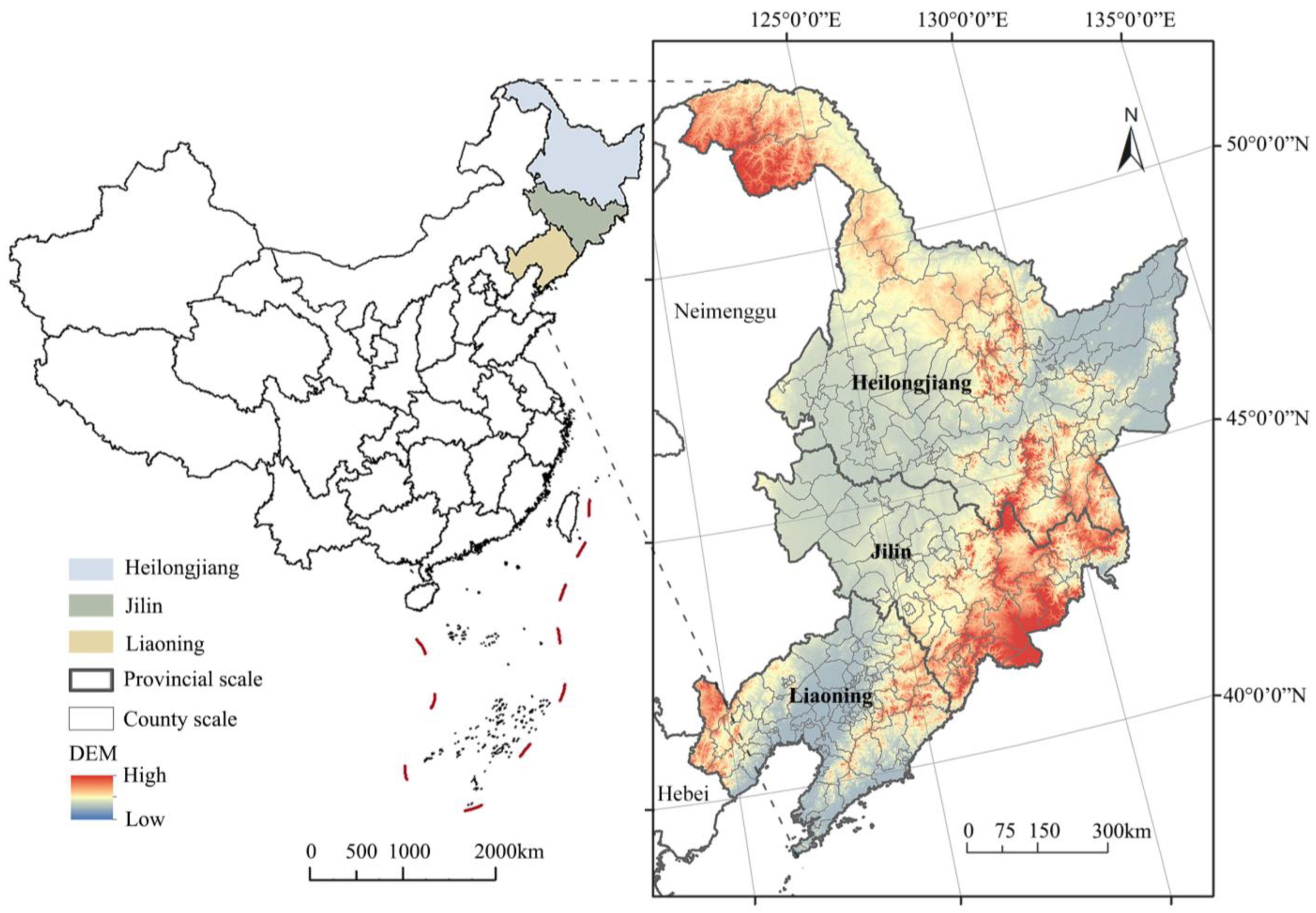
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. Changes in Rural Settlements
2.3.2. Average Nearest Neighbor Analysis and Kernel Density Analysis
- (1)
- Average nearest neighbor index
- (2)
- Kernel density analysis
2.3.3. Spatial Correlation Index
- (1)
- Spatial Autocorrelation Tool (Global Moran’s I)
- (2)
- Hotspot/Coldspot Analysis (Getis–Ord General G)
- (3)
- Hot Spot Analysis
2.3.4. Morphology Characteristics Based on Landscape Pattern Index
2.3.5. Indicator Selection for Driving Factors Research
2.3.6. XGBoost Model and SHAP
- (1)
- Extreme Gradient Boosting Model (XGBoost)
- (2)
- Shapley Additive Explanations (SHAP)
3. Results
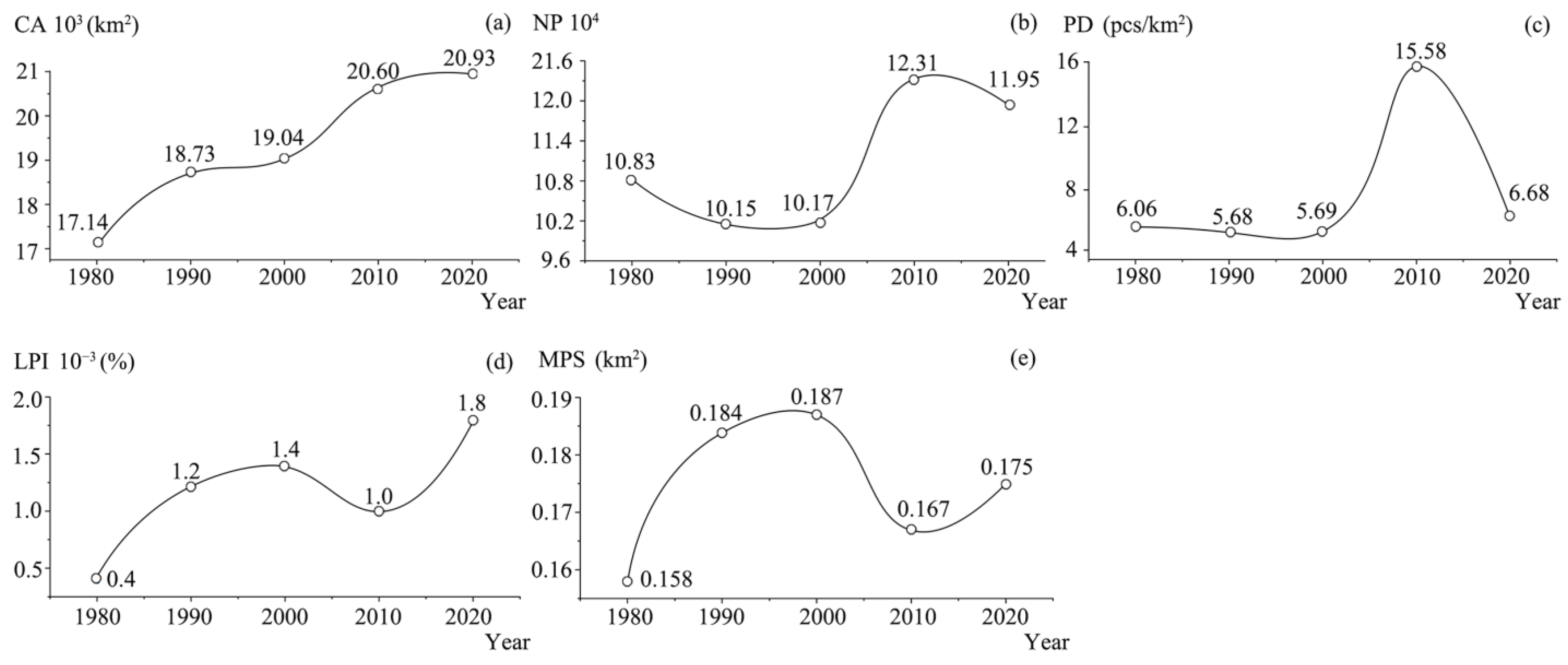
3.1. Characteristics of Land Use Changes in Rural Settlements
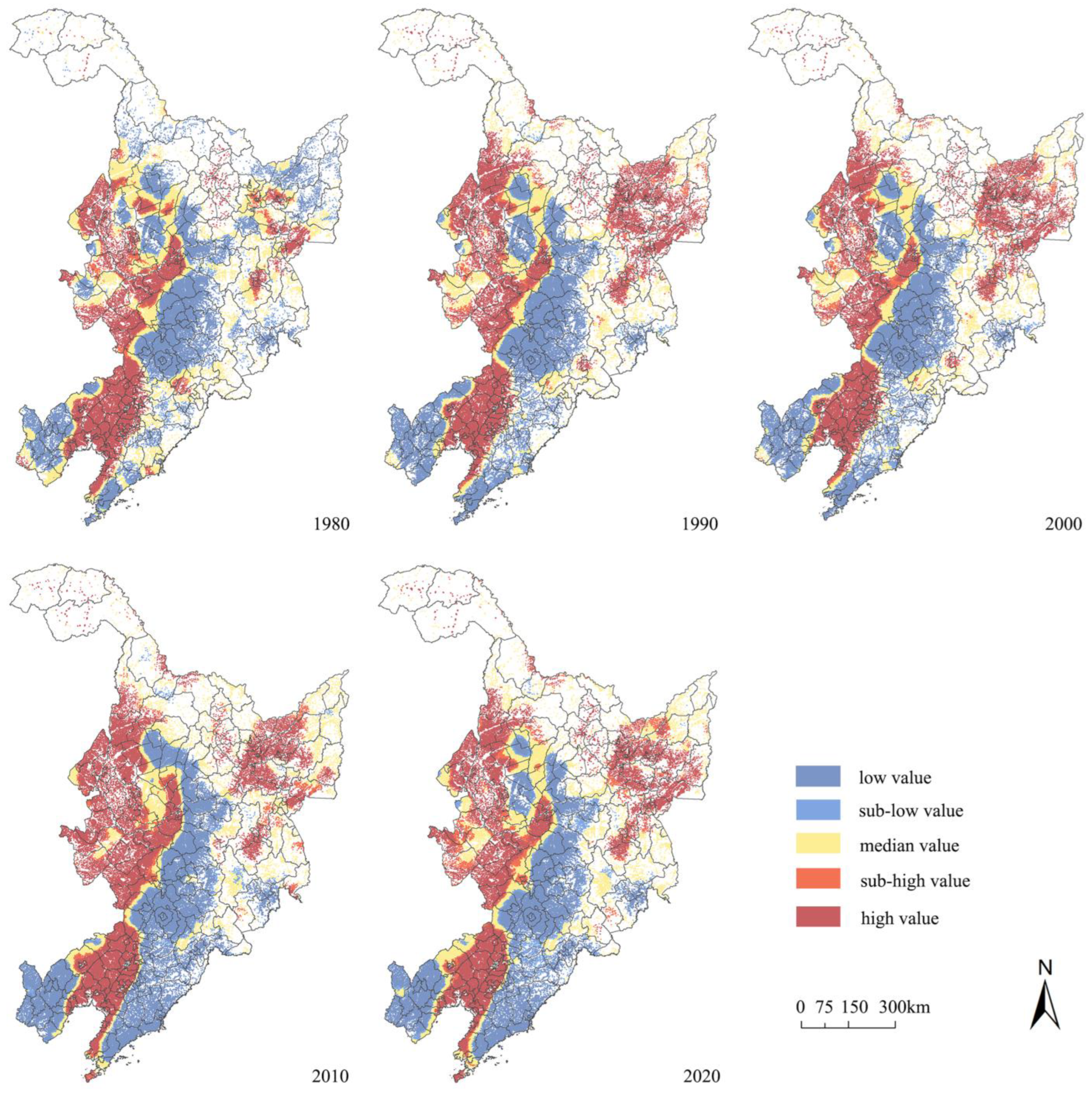
3.2. Analysis of Rural Spatial Evolution Characteristics
3.3. Scale Evolution Characteristics of Rural Settlements
3.3.1. Characteristics of Scale Increase and Decrease
3.3.2. Characteristics of Scale Differentiation
3.4. Analysis of the Morphological Characteristics of Rural Settlements
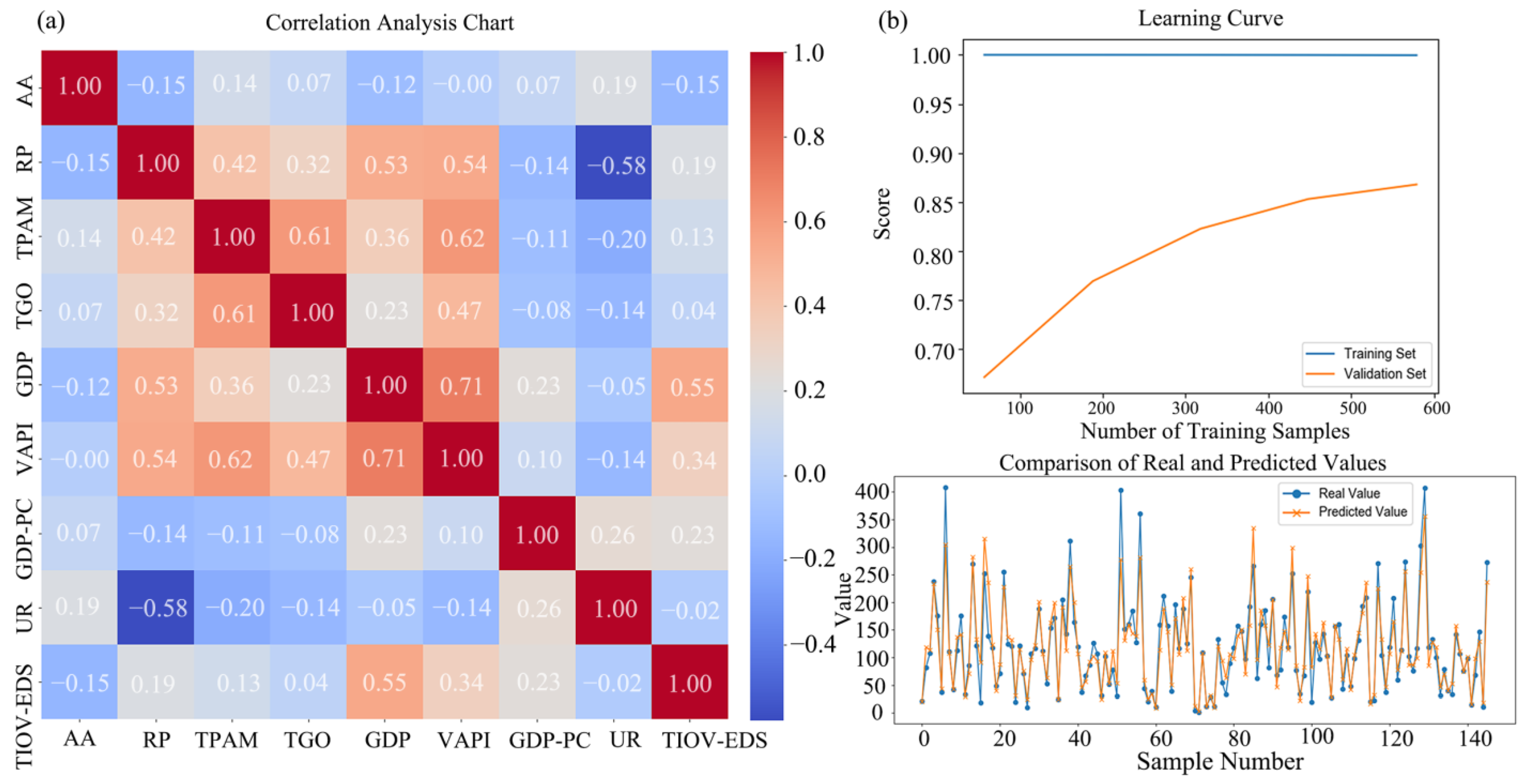
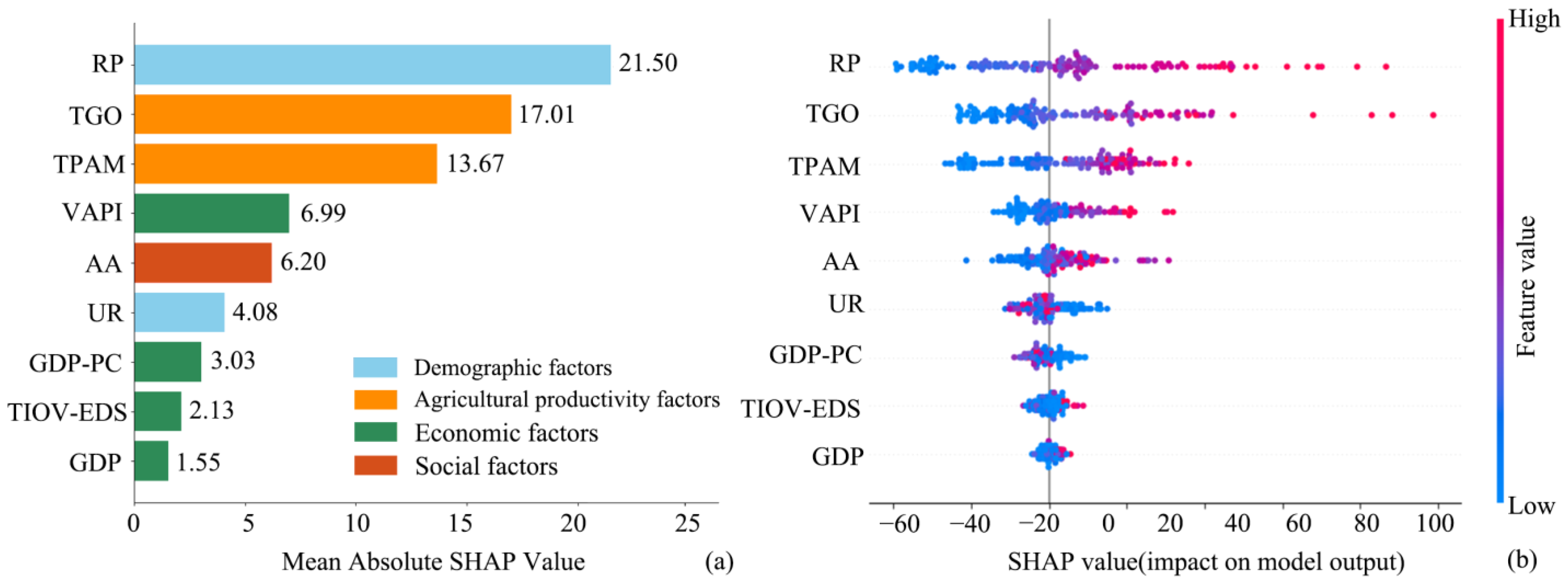
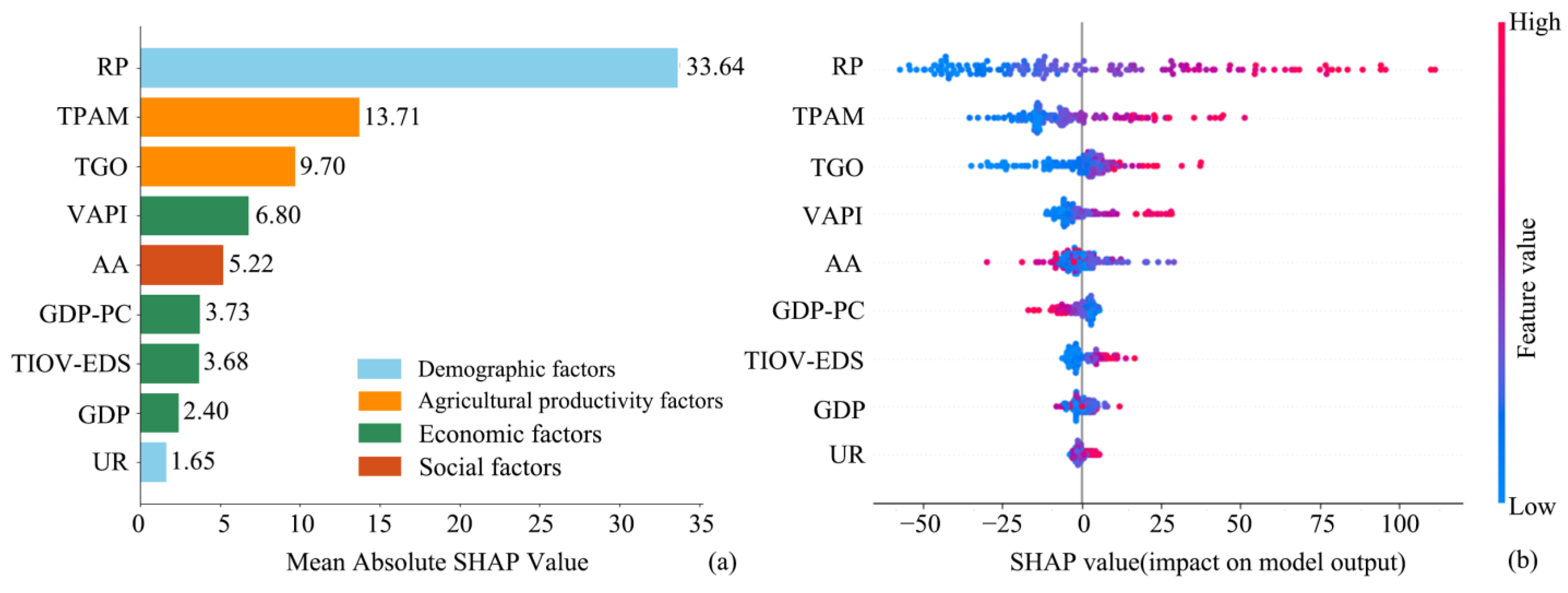
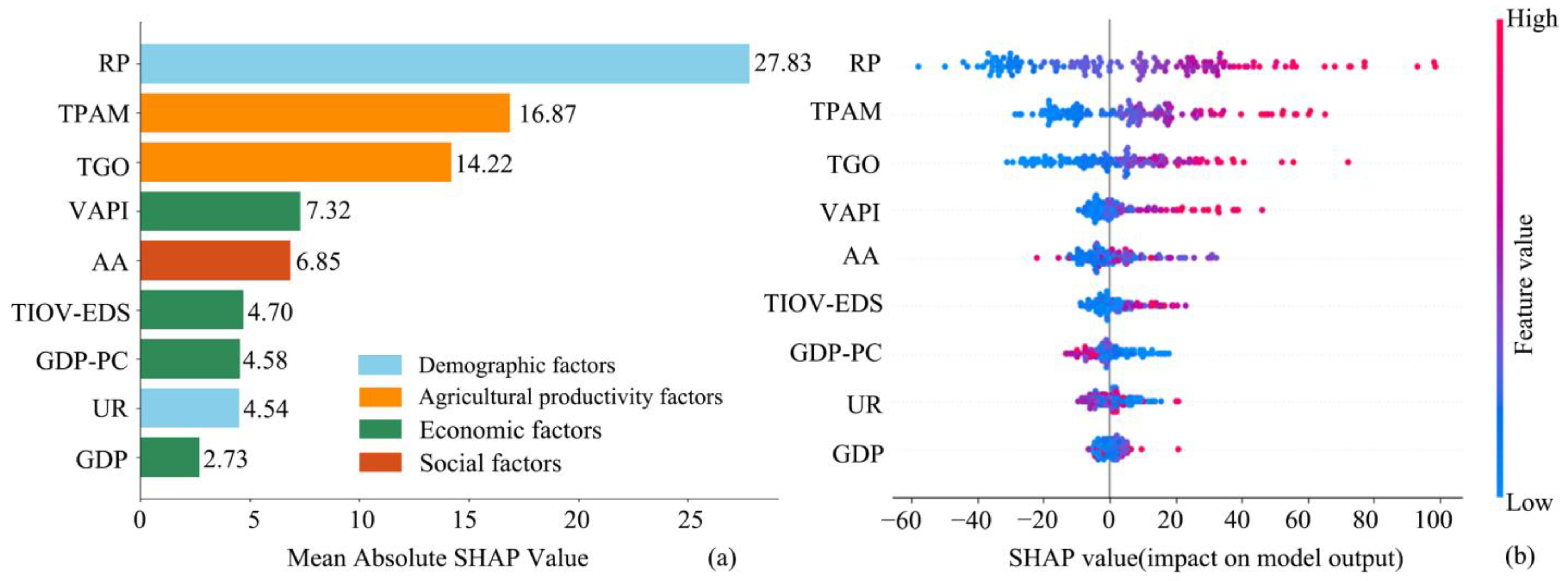
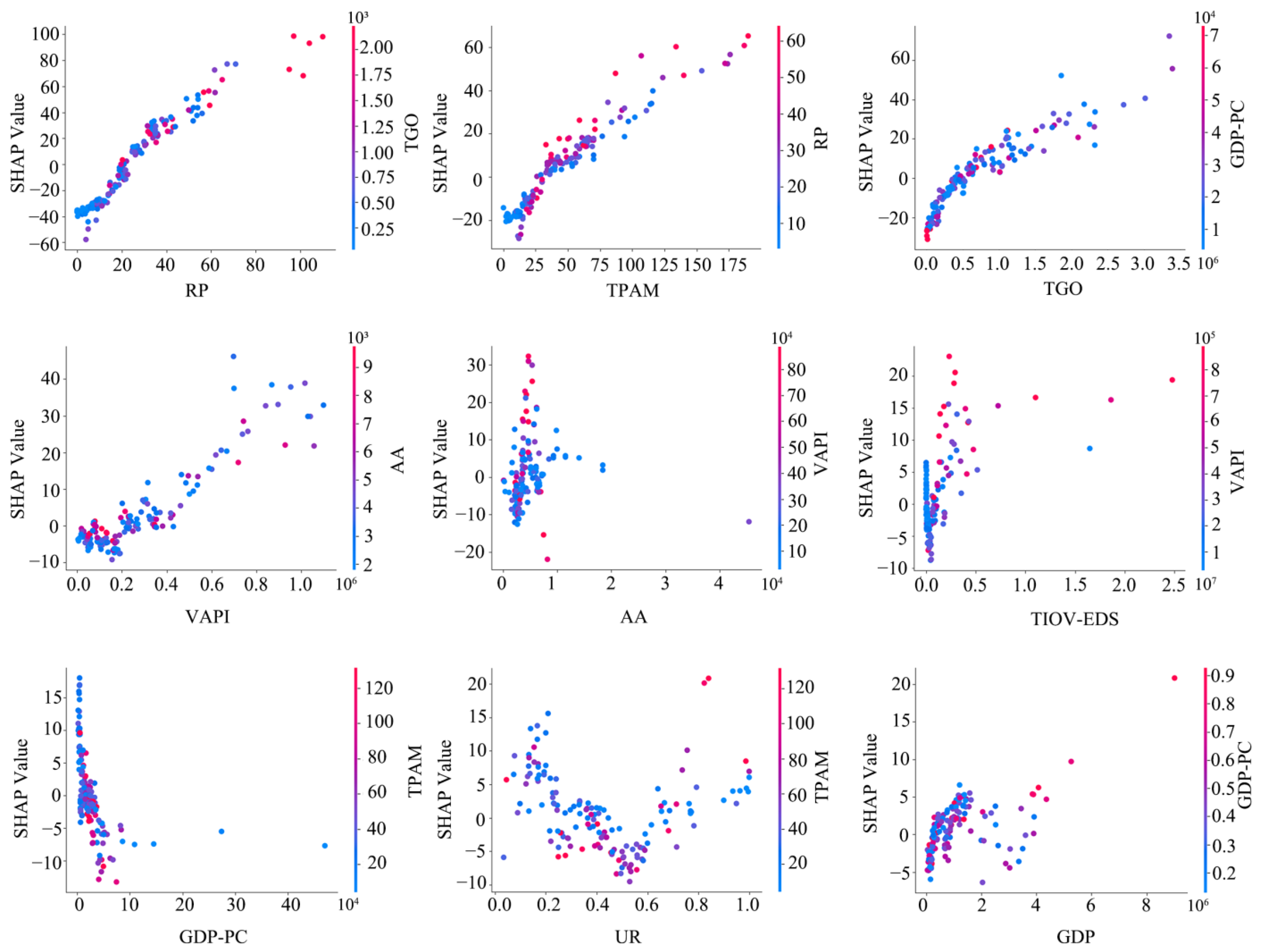
3.5. Analysis of Driving Factors of Rural Settlements
3.5.1. Natural Factors
Elevation
Distance from the Water System
Distance from Road Networks
3.5.2. Socioeconomic Factors
4. Discussion
4.1. A Rational Land Use Structure Is Key to Ensuring Food Security and Sustainable Rural Development
4.2. Multiple Driving Forces Behind Settlement Evolution
4.3. Implications for Rural Planning and Management in Three Northeastern Provinces of China
4.4. Limitations and Future Prospects
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, C.; Gao, J.L.; Cao, H. A literature review of spatial distribution and function of rural settlements and its research prospects: From urbanization to urban-rural integration in China. Geogr. Res. 2023, 42, 1480–1491. [Google Scholar]
- Jian, Y.Q.; Gong, J.Z.; Luo, Y.H.; Li, B.H. Analysis on the land evolution of rural settlement and its main control factors in Guangdong Province. J. Ecol. Rural. Environ. 2021, 37, 155–163. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, M.Q.; Wei, L.Y.; Ge, D.Z.; Sun, D.Q.; Zhang, Z.F.; Lu, Y.Q. Spatial optimization of rural settlements based on the perspective of appropriateness-domination: A case of Xinyi City. Habitat Int. 2020, 98, 102148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bittner, C.; Sofer, M. Land use changes in the rural-urban fringe: An Israeli case study. Land Use Pol. 2013, 33, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, S.S.; Zhou, X.Y.; Long, H.L.; Liang, X.L. Research progress and prospect of spatial evolution and optimization of rural settlements. Econ. Geogr. 2019, 39, 142–149. [Google Scholar]
- Long, H.L.; Liu, Y.S.; Wu, X.Q.; Dong, G.H. Spatio-temporal dynamic patterns of farmland and rural settlements in Su-Xi-Chang region: Implications for building a new countryside in coastal China. Land Use Pol. 2009, 26, 322–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Li, X.J.; Hai, B.B.; Wang, X.F.; Xu, J.W. Evolution of rural settlement in an inland nonmetropolitan region of China at a time of rapid urbanisation: The case of Gongyi. J. Rural Stud. 2020, 79, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, D.Z.; Long, H.L.; Qiao, W.F. The transformation of China’s grain production since reform and opening-up and its prospects. J. Nat. Resour. 2019, 34, 658–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, G.H.; Yang, Q.Y. The spatial production of rural settlements as rural homestays in the context of rural revitalization: Evidence from a rural tourism experiment in a Chinese village. Land Use Policy 2023, 128, 106600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.H.; Jia, L.R.; Wu, W.H.; Yan, J.Y.; Liu, Y.S. Urbanization for rural sustainability—Rethinking China’s urbanization strategy. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 178, 580–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Q.; Zheng, D.Y.; Shi, L.N. Themes evolution of rural revitalization and its research prospect in China from 1949 to 2019. Prog. Geogr. 2019, 38, 1272–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Lo, K.; Zhang, P.Y.; Guo, M. Reclaiming small to fill large: A novel approach to rural residential land consolidation in China. Land Use Policy 2021, 109, 105706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.L.; Ma, X.D.; Shen, Y. Analysis of spatial pattern of rural settlements in northern Jiangsu. Geogr. Res. 2012, 31, 144–154. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.H.; Martens, P. Stakeholder participation for nature-based solutions: Inspiration for rural area’s sustainability in China. Sustainability 2023, 15, 15934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Du, S.S.; Zhang, J.Q.; Chen, J.L. Spatial Evolution and Multi-Scenario Simulation of Rural “Production–Ecological–Living” Space: A Case Study for Beijing, China. Sustainability 2023, 15, 1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Li, H.H. Spatial pattern evolution of rural settlements from 1961 to 2030 in Tongzhou District, China. Land Use Policy 2020, 99, 105044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, W.; Long, Y.; Chen, T.T. Rediscovering Chinese cities through the lens of land-use patterns. Land Use Policy 2018, 79, 362–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.S.; Li, Y.H. Revitalize the world’s countryside. Nature 2017, 548, 275–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohler, F.; Marchand, G.; Negrao, M. Local history and landscape dynamics: A comparative study in rural Brazil and rural France. Land Use Policy 2015, 43, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Lei, G.P. The influence of rural settlements on soil erosion in the typical black soil region of Northeast China. J. Ecol. Rural Environ. 2021, 37, 1011–1021. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, S.K.; Zhang, M.M.; Wang, A.O.; Ni, Q.L. Spatio-temporal evolution and driving factors of rural settlements in low hilly region-a case study of 17 cities in Hubei Province, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 2387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, D.; Sun, Y.Y.; Tang, J.Q.; Luo, Z.Y.; Lu, J.F.; Liu, X. Modeling the interaction of internal and external systems of rural settlements: The case of Guangdong, China. Land Use Policy 2023, 132, 106830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.Y.; Zhang, H. Land use dynamics, built-up land expansion patterns, and driving forces analysis of the fast-growing Hangzhou metropolitan area, eastern China (1978–2008). Appl. Geogr. 2012, 34, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, H.L.; Zhang, Y.N.; Tu, S.S. Rural vitalization in China: A perspective of land consolidation. J. Geogr. Sci. 2019, 29, 517–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, J.Z.; Jian, Y.Q.; Chen, W.L.; Liu, Y.S.; Hu, Y.M. Transitions in rural settlements and implications for rural revitalization in Guangdong Province. J. Rural Stud. 2022, 93, 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.Y.; Li, F.; Chen, C. The spatial evolution characteristics and driving forces of village and town settlements in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Res. Agric. Mod. 2021, 42, 1114–1125. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.B.; Yuan, Y.; Zhang, X.L.; Li, Z.; Wang, Y.H.; Hu, X.L. Evolution and transformation mechanism of the spatial structure of rural settlements from the perspective of long-term economic and social change: A case study of the Sunan region, China. J. Rural Stud. 2022, 93, 234–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuadrado-Ciuraneta, S.; Dura-Guimera, A.; Salvati, L. Not only tourism: Unravelling suburbanization, second-home expansion and “rural” sprawl in Catalonia, Spain. Urban Geogr. 2017, 38, 66–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Recanatesi, F.; Clemente, M.; Grigoriadis, E.; Ranalli, F.; Zitti, M.; Salvati, L. A Fifty-Year Sustainability Assessment of Italian Agro-Forest Districts. Sustainability 2016, 8, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, J. Impulses towards a multifunctional transition in rural Australia: Gaps in the research agenda. J. Rural Stud. 2006, 22, 142–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, L. Spatial morphological traits, influencing factors and implications of typical traditional villages situated along the Jiangsu section of the Grand Canal. J. Nat. Resour. 2024, 39, 1993–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.F.; Liu, Y.S.; Feng, W.L.; Li, Y.R.; Li, L.N. Study on spatial tropism distribution of rural settlements in the Loess Hilly and Gully Region based on natural factors and traffic accessibility. J. Rural Stud. 2022, 93, 441–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.Y.; Sun, Q.; Zou, L.L. Spatial-temporal evolution and driving mechanism of rural production-living-ecological space in Pingtan islands, China. Habitat Int. 2023, 137, 102833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.N.; Zhang, T.Y.; Yang, Y.Y. Unveiling nonlinear effects of transport development on rural settlement transitions along the “southern Jiangsu—Northern shaanxi” transect in China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 159, 111712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, P.Y.; Guo, M. Spatial distribution and optimized reconstructing mode of rural settlement at the village scale of Jilin Province. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2021, 41, 842–850. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.Z.; Fang, Y.A.; Wang, R.R.; Zou, C.M. Rural typology dynamics and drivers in peripheral areas: A case of Northeast China. Land Use Policy 2022, 120, 106260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.G.; Gao, X.D.; Wu, R.H.; Wang, Y.H.; Choi, B.R. How does sustainable rural tourism cause rural community development? Sustainability 2021, 13, 13516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Song, W.; Song, C. Consolidating the layout of rural settlements using system dynamics and the multi-agent system. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 274, 123150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamov, T.; Ciolac, R.; Iancu, T.; Brad, I.; Peț, E.; Popescu, G.; Șmuleac, L. Sustainability of agritourism activity. Initiatives and challenges in Romanian mountain rural regions. Sustainability 2020, 12, 2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gocer, O.; Boyacioglu, D.; Karahan, E.E.; Shrestha, P. Cultural tourism and rural community resilience: A framework and its application. J. Rural Stud. 2024, 107, 103238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stokowski, P.A.; Kuentzel, W.F.; Derrien, M.M.; Jakobcic, Y.L. Social, cultural and spatial imaginaries in rural tourism transitions. J. Rural Stud. 2021, 87, 243–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.Z.; Fang, Y.A.; Qiao, J.J.; Rosenberg, M.W.; Wang, R.R.; Liu, X.Y.; Yu, S.H. Rural transformation and the future of China’s “granary”: A perspective on livelihood trajectories. J. Rural Stud. 2025, 114, 103524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konecny, O.; Sery, O.; Zavadil, T.; Duzí, B.; Kozumplíková, A.; Trojan, J.; Martinát, S.; Novák, R.; Kotek, O.; Lehejcek, J. Adapting rural communities to climate change: The undervalued potential of agricultural land. J. Rural Stud. 2024, 111, 103391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, P.; Hong, B.T.; Zhou, J.M. Research of spatio-temporal pattern and characteristics for the evolution of rural settlements based on spatial autocorrelation model. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Basin 2015, 24, 1993–2002. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, R.; Xu, Q.; Long, H.L. Spatial distribution characteristics and optimized reconstruction analysis of China’s rural settlements during the process of rapid urbanization. J. Rural Stud. 2016, 47, 413–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.P.; Zheng, Y.X. The rural settlement morphological types and spatial system characteristics in the Jianghan Plain. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2021, 41, 121–128. [Google Scholar]
- Conrad, C.; Rudloff, M.; Abdullaev, I.; Thiel, M.; Löw, F.; Lamers, J.P.A. Measuring rural settlement expansion in Uzbekistan using remote sensing to support spatial planning. Appl. Geogr. 2015, 62, 29–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.L.; Ou, L.; Chen, M. Evolution characteristics, drivers and trends of rural residential land in mountainous economic circle: A case study of Chengdu-Chongqing area, China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 154, 110585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.Y.; Gao, J.; Tong, D.; Li, G.C. Spatio-temporal evolution characteristics and influencing factors of rural settlements in Guangdong Province based on GTWR model. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2023, 43, 1249–1258. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Z.J.; Fan, B.L.; Du, X.W.; Liu, X.Q.; Xu, S.H.; Cao, Y.D.; Wang, Y.T.; Zhou, Q.B. Spatial expansion characteristics of rural settlements and its response to determinants in Hangzhou Bay urban agglomeration, China: Geospatial modeling using multiscale geographically weighted regression (MGWR). J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 484, 144339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.P.; He, Y.Q.; Fu, P.; Xiao, J.; Xie, X. A Research on the Dynamics of and the Spatial Responses to the Restructuring Agricultural Rural Settlements. Urban Plan. 2021, 1, 36–43. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, K.; Li, J.L.; Xia, Q.Q. Machine learning evaluation land ecological fitting: A case of the mountain traditional settlement location fitting evaluation. Urban Stud. 2021, 28, 84–92. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, P.; Xiao, J.; Zhao, Z.Q.; Xie, X. The method of “space-dynamic” coupling mechanism of rural settlements based on machine learning: Taking Liyang City, Jiangsu Province as an example. J. Hum. Settl. West China 2022, 37, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Jun, M.J. A comparison of a gradient boosting decision tree, random forests, and artificial neural networks to model urban land use changes: The case of the Seoul metropolitan area. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2021, 35, 2149–2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhou, R.; Rui, J.; Yu, Y. Revealing the impact of urban spatial morphology on land surface temperature in plain and plateau cities using explainable machine learning. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2025, 118, 106046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bansal, P.; Quan, S.J. Examining temporally varying nonlinear effects of urban form on urban heat island using explainable machine learning: A case of Seoul. Build. Environ. 2024, 247, 110957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Kim, Y. Explainable heat-related mortality with random forest and shapley additive explanations (SHAP) models. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2022, 79, 103677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, B.; Tian, Y.G.; Zhang, L.H.; Chen, B. Evolution and its driving forces of rural settlements along the roadsides in the northeast of Jianghan Plain, China. Land Use Policy 2023, 129, 106658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.R.; Qiao, L.Y.; Wang, Q.Y.; Karacsonyi, D. Towards the evaluation of rural livability in China: Theoretical framework and empirical case study. Habitat Int. 2020, 105, 102241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, G.M.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.Q. The spatial pattern and influencing factors of cultivated land fragmentation in typical counties of the northeast black soil region. Res. Agric. Mod. 2023, 44, 858–868. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.C.; Xiao, W.; Ye, Y.M.; He, T.T.; Luo, H. Rural residential land expansion and its impacts on cultivated land in China between 1990 and 2020. Land Use Policy 2023, 132, 106816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uisso, A.M.; Tanrivermis, H. Driving factors and assessment of changes in the use of arable land in Tanzania. Land Use Policy 2021, 104, 105359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.Z.; Shan, L.P.; Guo, Z.; Peng, Y. Cultivated land protection policies in China facing 2030: Dynamic balance system versus basic farmland zoning. Habitat Int. 2017, 69, 126–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.Y.; Kong, X.S.; Jiang, P. Identification of the human-land relationship involved in the urbanization of rural settlements in Wuhan city circle, China. J. Rural Stud. 2020, 77, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Pijanowski, B.C. The effects of China’s cultivated land balance program on potential land productivity at a national scale. Appl. Geogr. 2014, 46, 158–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.J.; Hu, L.L.; Chen, X. Review on the traditional agriculture for the development of intensive rice-fish system. Res. Agric. Mod. 2020, 41, 727–736. [Google Scholar]
- Barinaga-Rementeria, I.; Etxano, I. Weak or strong sustainability in rural land use planning? Assessing two case studies through multi-criteria analysis. Sustainability 2020, 12, 2422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.Y.; Bao, H.X.H.; Yao, S.R. Unpacking the effects of rural homestead development rights reform on rural revitalization in China. J. Rural Stud. 2024, 108, 103265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Cheng, P.; Kong, X.S. Spatially explicit restructuring of rural settlements: A dual-scale coupling approach. J. Rural Stud. 2022, 94, 239–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, D.; Xie, Y.M.; Barbero, S.; Pereno, A. How does systemic design facilitate the sustainability transition of rural communities? A comparative case study between China and Italy. Sustainability 2023, 15, 10202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duvernoy, I.; Zambon, I.; Sateriano, A.; Salvati, L. Pictures from the other side of the fringe: Urban growth and peri-urban agriculture in a post-industrial city (Toulouse, France). J. Rural Stud. 2018, 57, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Jin, X.B.; Xu, W.Y.; Zhou, Y.K. Evolution of cultivated land fragmentation and its driving mechanism in rural development: A case study of Jiangsu Province. J. Rural Stud. 2022, 91, 58–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Dimension | Index Names | Abbreviations | Significance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Scale characteristics | Class area | CA | Overall area of a particular patch type. |
| Number of patches | NP | The total number of patches (NP) for a specific patch type within the landscape | |
| Patch density | PD | The density of specific patch types provides insights into landscape heterogeneity and fragmentation, serving as a key indicator of heterogeneity per unit area. | |
| Largest patch index | LPI | The Largest Patch Index quantifies the percentage of total landscape area occupied by the largest patch of a specific patch type, serving as a crucial indicator of landscape dominance and fragmentation patterns. | |
| Mean patch size | MPS | The Mean Patch Size, calculated as the total area of a specific patch type divided by its number of patches, serves as a fundamental metric for quantifying landscape fragmentation and habitat connectivity | |
| Morphological characteristics | Area–weighted mean shape index | AWMSI | The Area-Weighted Mean Shape Index quantifies the complexity of patch shapes by considering both the geometric form and relative area contribution of individual patches, providing a comprehensive assessment of landscape configuration |
| Area–weighted mean patch fractal dimension | AWMPFD | The Area-Weighted Mean Patch Fractal Dimension quantifies the geometric complexity of landscape patterns by incorporating both the shape irregularity and area contribution of individual patches, providing a robust measure of spatial heterogeneity across multiple scales | |
| Aggregation index | AI | The Aggregation Index examines the connectivity between patches of each landscape type. The smaller the value, the more discrete the landscape |
| Dimension | Factors | Factor Descriptions | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Natural factors | Elevation | The altitude at which the rural settlement is located | |
| Distance from water system | The Euclidean distance of rural settlements from the nearest water system (e.g., rivers, lakes, or reservoirs) | ||
| Distance from road networks | The Euclidean distance of rural settlements from the nearest main roads or transportation networks | ||
| Socioeconomic factors | Demographic factors | Rural population (RP) | The total number of residents living in rural areas within the region |
| Urbanization rate (UR) | The ratio of the urban population to the total population of the region, indicating the level of urbanization | ||
| Agricultural productivity factors | Total power of agricultural machinery (TPAM) | The combined power capacity of all agricultural machinery used in the region for farming and related activities | |
| Total grain output (TGO) | The total yield of grains produced by agricultural producers and operators within the region | ||
| Economic factors | Regional gross domestic product (GDP) | The total monetary value of all goods and services produced within the region in a specific time period | |
| Value added of primary industry (VAPI) | The value added of the primary industry refers to the newly created value during the production process of agriculture, forestry, animal husbandry, and fishery | ||
| GDP per capita (GDP-PC) | The regional GDP divided by the permanent resident population, representing the average economic output per person. | ||
| Total industrial output value of enterprises above designated size (TIOV-EDS) | The total production value of industrial enterprises that meet or exceed a specific size threshold | ||
| Social factors | Administrative area (AA) | The total land area under the jurisdiction of the administrative region. | |
| Area of Other Land Use Types Converted to Rural Settlements | Area of Rural Settlements Converted to Other Land Use Types | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Land Use Types | Area (km2) | Percentage (%) | Land Use Types | Area (km2) | Percentage (%) |
| Arable land | 66,619.95 | 50.32 | Arable land | 28,880.08 | 21.21 |
| Forests | 24,157.23 | 18.24 | Forests | 41,337.38 | 30.36 |
| Grassland | 12,916.32 | 9.75 | Grassland | 35,277.89 | 25.91 |
| Water bodies | 5758.94 | 4.35 | Water bodies | 10,300.23 | 7.56 |
| Urban built–ups | 3725.71 | 2.81 | Urban built-ups | 311.48 | 0.23 |
| Other construction land | 2165.88 | 1.63 | Other construction land | 782.52 | 0.57 |
| Unused land | 17,035.57 | 12.87 | Unused land | 19,272.06 | 14.15 |
| Total | 132,379.63 | 100 | Total | 136,161.64 | 100 |
| Research Year | Area of Rural Settlements (km2) | Changes in Area (km2) | Rural Settlement Dynamics (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1980 | 17,051.37 | - | - |
| 1990 | 18,646.65 | 1595.28 | 0.94 |
| 2000 | 18,957.39 | 310.74 | 0.17 |
| 2010 | 20,507.75 | 1550.36 | 0.82 |
| 2020 | 20,837.04 | 329.29 | 0.16 |
| Research Year | ANN Index | Z-Score | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1980 | 0.528 | −304.522 | 0.000 |
| 1990 | 0.590 | −251.042 | 0.000 |
| 2000 | 0.590 | −250.986 | 0.000 |
| 2010 | 0.613 | −260.713 | 0.000 |
| 2020 | 0.602 | −264.668 | 0.000 |
| Research Year | CA (km2) | NP | PD (pcs/km2) | LPI | MPS (km2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1980 | 17,148.36 | 108,390 | 6.06 | 0.0004 | 0.158 |
| 1990 | 18,738.60 | 101,520 | 5.68 | 0.0012 | 0.184 |
| 2000 | 19,049.71 | 101,784 | 5.69 | 0.0014 | 0.187 |
| 2010 | 20,602.41 | 123,104 | 15.58 | 0.001 | 0.167 |
| 2020 | 20,932.86 | 119,526 | 6.68 | 0.0018 | 0.175 |
| Research Year | Moran’s I | Z-Score | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1980 | 0.098 | 243.599 | 0.000 |
| 1990 | 0.088 | 357.061 | 0.000 |
| 2000 | 0.084 | 342.691 | 0.000 |
| 2010 | 0.090 | 435.936 | 0.000 |
| 2020 | 0.054 | 230.523 | 0.000 |
| Research Year | Z-Score | p |
|---|---|---|
| 1980 | −6.213 | 0.000 |
| 1990 | −19.909 | 0.000 |
| 2000 | −18.491 | 0.000 |
| 2010 | −14.651 | 0.000 |
| 2020 | −13.117 | 0.000 |
| Research Year | AWMSI | AWMPFD | AI (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1980 | 1.558 | 1.069 | 89.958 |
| 1990 | 1.526 | 1.065 | 90.747 |
| 2000 | 1.530 | 1.065 | 90.823 |
| 2010 | 1.569 | 1.070 | 90.033 |
| 2020 | 1.610 | 1.072 | 90.317 |
| Factors | 0–500 m | 500–1000 m | 1000–2000 m | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1980 | 2000 | 2020 | 1980 | 2000 | 2020 | 1980 | 2000 | 2020 | |
| CA (km2) | 16,844.99 | 18,703.40 | 20,458.01 | 316.47 | 362.85 | 490.36 | 0.81 | 1.15 | 1.92 |
| NP | 107,852 | 100,334 | 116,696 | 3366 | 3254 | 5084 | 16 | 11 | 23 |
| PD (pcs/km2) | 6.402 | 5.364 | 5.704 | 10.636 | 8.967 | 10.367 | 19.750 | 9.565 | 11.979 |
| LPI | 0.001 | 0.0039 | 0.0052 | 0.0001 | 0.0028 | 0.0033 | 0 | 0.002 | 0.0021 |
| MPS (km2) | 0.156 | 0.186 | 0.175 | 0.094 | 0.112 | 0.096 | 0.050 | 0.105 | 0.083 |
| AWMSI | 1.626 | 1.608 | 1.684 | 1.656 | 1.657 | 1.697 | 1.571 | 1.531 | 1.528 |
| AWMPFD | 1.076 | 1.073 | 1.079 | 1.081 | 1.079 | 1.084 | 1.082 | 1.073 | 1.075 |
| AI (%) | 86.287 | 87.400 | 86.827 | 83.400 | 84.871 | 83.196 | 80.611 | 86.569 | 84.448 |
| Factors | 0–2 km | 2–4 km | 4–6 km | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1980 | 2000 | 2020 | 1980 | 2000 | 2020 | 1980 | 2000 | 2020 | |
| CA (km2) | 5382.04 | 5875.46 | 6586.21 | 4140.02 | 4535.31 | 4963.89 | 2845.91 | 3120.24 | 3406.84 |
| NP | 38,659 | 36,964 | 43,841 | 33,661 | 32,308 | 37,830 | 22,397 | 21,483 | 25,021 |
| PD (pcs/km2) | 7.182 | 6.291 | 6.656 | 8.130 | 7.123 | 7.621 | 7.869 | 6.885 | 7.346 |
| LPI | 0.0031 | 0.0079 | 0.0074 | 0.0029 | 0.004 | 0.004 | 0.004 | 0.0048 | 0.0089 |
| MPS (km2) | 13.922 | 15.895 | 15.023 | 12.299 | 14.038 | 13.122 | 12.707 | 14.524 | 13.616 |
| AWMSI | 1.533 | 1.515 | 1.585 | 1.520 | 1.499 | 1.560 | 1.523 | 1.496 | 1.547 |
| AWMPFD | 1.067 | 1.065 | 1.071 | 1.067 | 1.064 | 1.070 | 1.067 | 1.064 | 1.069 |
| AI (%) | 89.578 | 90.303 | 89.787 | 89.044 | 89.803 | 89.206 | 89.198 | 89.979 | 89.444 |
| Factors | 0–2 km | 2–4 km | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1980 | 2000 | 2020 | 1980 | 2000 | 2020 | |
| CA (km2) | 8704.31 | 9710.21 | 10,485.80 | 3485.36 | 3792.16 | 4141.78 |
| NP | 54,997 | 51,268 | 57,144 | 29,891 | 28,882 | 33,430 |
| PD (pcs/km2) | 6.318 | 5.279 | 5.449 | 8.577 | 7.616 | 8.072 |
| LPI | 0.0026 | 0.003 | 0.0077 | 0.002 | 0.0022 | 0.0054 |
| MPS (km2) | 0.158 | 0.189 | 0.183 | 0.116 | 0.131 | 0.123 |
| AWMSI | 1.579 | 1.552 | 1.642 | 1.488 | 1.464 | 1.519 |
| AWMPFD | 1.07 | 1.066 | 1.073 | 1.065 | 1.062 | 1.067 |
| AI (%) | 90.164 | 91.071 | 90.761 | 88.735 | 89.424 | 88.887 |
| Model | R2 | RMSE (km2) | MAE (km2) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Extreme Gradient Boosting (XGBoost) | 0.88 | 33.09 | 25.26 |
| Random Forest (RF) | 0.82 | 36.14 | 25.64 |
| Support Vector Machine (SVM) | 0.75 | 42.20 | 30.80 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Duan, S.; Dong, L.; Ding, X. Spatial Sustainability of Agricultural Rural Settlements: An Analysis of Rural Spatial Patterns and Influencing Factors in Three Northeastern Provinces of China. Sustainability 2025, 17, 5597. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17125597
Zhang Y, Duan S, Dong L, Ding X. Spatial Sustainability of Agricultural Rural Settlements: An Analysis of Rural Spatial Patterns and Influencing Factors in Three Northeastern Provinces of China. Sustainability. 2025; 17(12):5597. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17125597
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yu, Siang Duan, Li Dong, and Xiaoming Ding. 2025. "Spatial Sustainability of Agricultural Rural Settlements: An Analysis of Rural Spatial Patterns and Influencing Factors in Three Northeastern Provinces of China" Sustainability 17, no. 12: 5597. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17125597
APA StyleZhang, Y., Duan, S., Dong, L., & Ding, X. (2025). Spatial Sustainability of Agricultural Rural Settlements: An Analysis of Rural Spatial Patterns and Influencing Factors in Three Northeastern Provinces of China. Sustainability, 17(12), 5597. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17125597






