The Persistent Innovation Effect of Platform Ecosystem Embeddedness
Abstract
1. Introduction
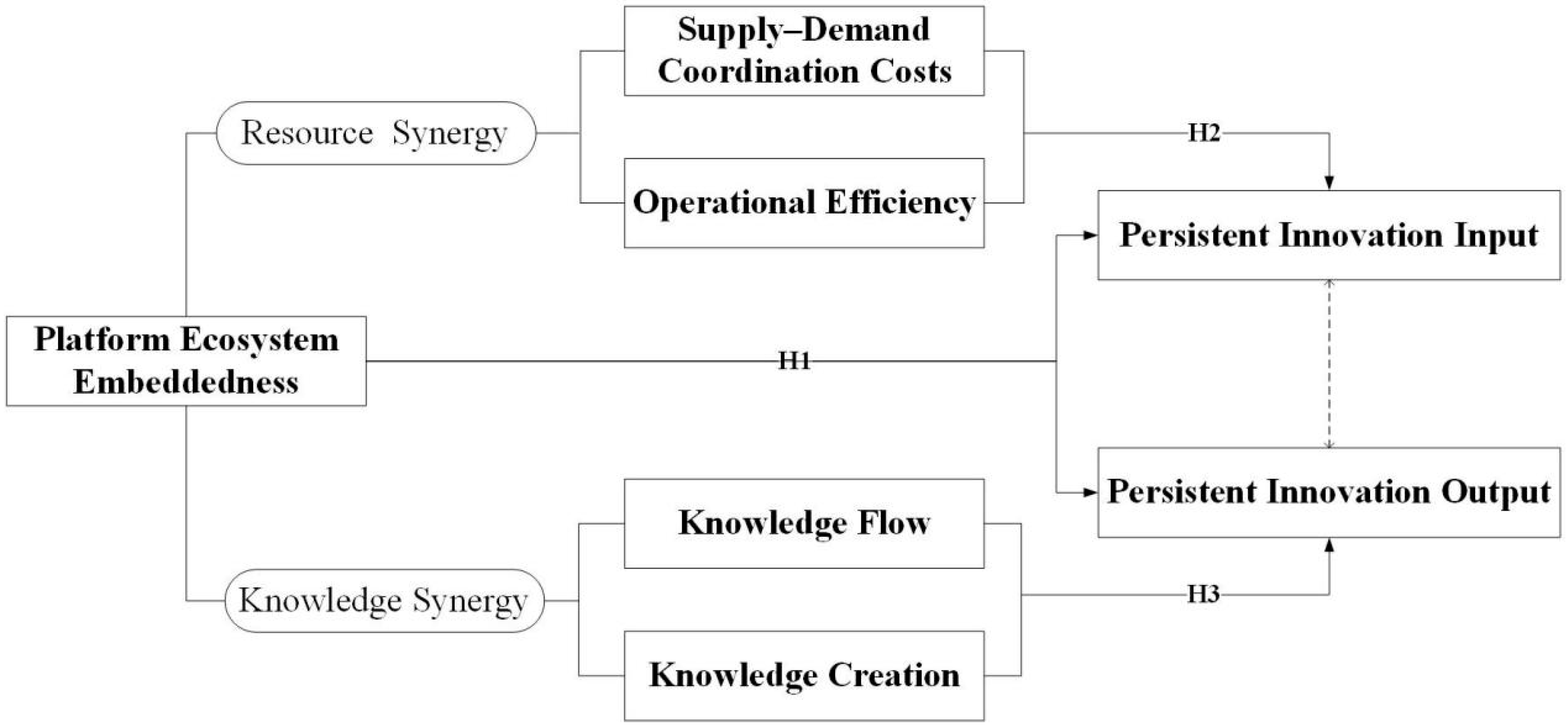
2. Theoretical Analysis and Research Hypotheses
2.1. Platform Ecosystem Embeddedness and Persistent Innovation
2.2. The Impact of Platform Ecosystem Embeddedness on Persistent Innovation Input
2.3. The Impact of Platform Ecosystem Embeddedness on Persistent Innovation Output
3. Research Design
3.1. Data Sources
3.2. Variable Construction
- Independent Variable
- Dependent Variables
- Control Variables
3.3. Model Specification
4. Empirical Analysis
4.1. Descriptive Statistics
4.2. Multicollinearity Test
4.3. Baseline Regression
4.4. Endogeneity Test
4.5. Robustness Test
4.6. Heterogeneity Analysis
4.6.1. External Environment of Companies
4.6.2. Internal Company Characteristics
5. Further Analysis
5.1. Mechanism Analysis of Persistent Innovation Input
5.1.1. Supply–Demand Coordination Costs
5.1.2. Operational Efficiency
5.2. Mechanism Analysis of Persistent Innovation Output
5.2.1. Knowledge Flow
5.2.2. Knowledge Creation
6. Discussion
7. Conclusions and Implications
7.1. Research Conclusions
7.2. Managerial Implications and Policy Recommendations
- Managerial Implications for Companies
- Policy Recommendations for Governments
7.3. Research Limitations and Directions for Future Research
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Adner, R. Match Your Innovation Strategy to Your Innovation Ecosystem. Harv. Bus. Rev. 2006, 84, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bertani, F.; Ponta, L.; Raberto, M.; Teglio, A.; Cincotti, S. The Complexity of the Intangible Digital Economy: An Agent-Based Model. J. Bus. Res. 2021, 129, 527–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Li, J.; Zhang, J. Digitalisation, Data-Driven Dynamic Capabilities and Responsible Innovation: An Empirical Study of SMEs in China. Asia Pac. J. Manag. 2024, 41, 1211–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gawer, A.; Cusumano, M.A. Industry Platforms and Ecosystem Innovation. J. Prod. Innov. Manag. 2014, 31, 417–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nambisan, S.; Lyytinen, K.; Majchrzak, A.; Song, M. Digital Innovation Management: Reinventing Innovation Management Research in a Digital World. MIS Q. 2017, 41, 223–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Yang, M. Research on the Sustained Innovation Effect of Digital Transformation. J. Quant. Technol. Econ. 2025, 42, 109–129. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cenamor, J.; Frishammar, J. Openness in Platform Ecosystems: Innovation Strategies for Complementary Products. Res. Policy 2021, 50, 104148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hein, A.; Weking, J.; Schreieck, M.; Wiesche, M.; Böhm, M.; Krcmar, H. Value Co-Creation Practices in Business-to-Business Platform Ecosystems. Electron. Mark 2019, 29, 503–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; Chen, J. The Impact of Industrial Internet Platform on Green Innovation: Evidence from a Quasi-Natural Experiment. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 414, 137645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirmon, D.G.; Hitt, M.A.; Ireland, R.D. Managing Firm Resources in Dynamic Environments to Create Value: Looking Inside the Black Box. Acad. Manag. Rev. 2007, 32, 273–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, P.; Wilson, V.H. Circular Innovation Ecosystem: A Multi-Actor, Multi-Peripheral and Multi-Platform Perspective. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2023, 26, 14327–14350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kretschmer, T.; Leiponen, A.; Schilling, M.; Vasudeva, G. Platform Ecosystems as Meta-Organizations: Implications for Platform Strategies. Strateg. Manag. J. 2022, 43, 405–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, A.; Bieck, C.; Dencik, J.; Goehring, B.C.; Warrick, R. How Generative AI Will Drive Enterprise Innovation. Strat. Leadersh. 2024, 52, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, G.; Van Alstyne, M.; Jiang, X. Platform Ecosystems: How Developers Invert the Firm. MIS Q. 2017, 41, 255–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, B. Persistence of Innovation: Stylised Facts and Panel Data Evidence. J. Technol. Transf. 2009, 34, 226–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suárez, D. Persistence of Innovation in Unstable Environments: Continuity and Change in the Firm’s Innovative Behavior. Res. Policy 2014, 43, 726–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Qi, N.; Li, L.; Li, Z.; Han, X.; Xuan, L. How Do Knowledge Diversity and Ego-Network Structures Affect Firms’ Sustainable Innovation: Evidence from Alliance Innovation Networks of China’s New Energy Industries. J. Knowl. Manag. 2023, 27, 178–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malerba, F.; Orsenigo, L. Technological Entry, Exit and Survival: An Empirical Analysis of Patent Data. Res. Policy 1999, 28, 643–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonelli, C.; Crespi, F.; Scellato, G. Inside Innovation Persistence: New Evidence from Italian Micro-Data. Struct. Chang. Econ. Dyn. 2012, 23, 341–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, W.; Nasir, M.H.; Yousaf, Z.; Khattak, A.; Yasir, M.; Javed, A.; Shirazi, S.H. Innovation Performance in Digital Economy: Does Digital Platform Capability, Improvisation Capability and Organizational Readiness Really Matter? Eur. J. Innov. Manag. 2021, 25, 1309–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F.; Liu, Q. Competing with Complementors: An Empirical Look at Amazon.Com. Strateg. Manag. J. 2018, 39, 2618–2642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granovetter, M. Economic Action and Social Structure: The Problem of Embeddedness. In The Sociology of Economic Life; Routledge: London, UK, 1985; ISBN 978-0-429-49433-8. [Google Scholar]
- Jacobides, M.G.; Cennamo, C.; Gawer, A. Towards a Theory of Ecosystems. Strateg. Manag. J. 2018, 39, 2255–2276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teece, D.J. Profiting from Innovation in the Digital Economy: Enabling Technologies, Standards, and Licensing Models in the Wireless World. Res. Policy 2018, 47, 1367–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winter, S.G.; Nelson, R.R. An Evolutionary Theory of Economic Change; Harvard University Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- McIntyre, D.P.; Srinivasan, A. Networks, Platforms, and Strategy: Emerging Views and next Steps. Strateg. Manag. J. 2017, 38, 141–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gawer, A. (Ed.) Platforms, Markets and Innovation; Edward Elgar Publishing: Cheltenham, UK, 2009; ISBN 978-1-84980-331-1. [Google Scholar]
- Cennamo, C. Building the Value of Next-Generation Platforms: The Paradox of Diminishing Returns. J. Manag. 2018, 44, 3038–3069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudary, S.P.; Van Alstyne, M.W.; Parker, G.G. Platform Revolution: How Networked Markets Are Transforming the Economy—And How to Make Them Work for You, 1st ed.; W. W. Norton & Company: New York, NY, USA, 2016; ISBN 978-0-393-24913-2. [Google Scholar]
- Bresnahan, T.; Greenstein, S. Mobile Computing: The Next Platform Rivalry. Am. Econ. Rev. 2014, 104, 475–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catalini, C.; Gans, J.S. Some Simple Economics of the Blockchain. Commun. ACM 2020, 63, 80–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.; Li, M.; Diao, Y.; Han, D. Assessing the Effect of Digital Platforms on Innovation Quality: Mechanism Identification and Threshold Characteristics. Humanit. Soc. Sci. Commun. 2024, 11, 951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wulfert, T. Boundary Resource Management in Innovation Ecosystems: The Case of e-Commerce. Electron. Mark. 2023, 33, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwana, A. Platform Synergy: Architectural Origins and Competitive Consequences. Inf. Syst. Res. 2018, 29, 829–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forrester Consulting. The Total Economic ImpactTM of Microsoft Azure AI; Microsoft Corporation: Redmond, WA, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, X.; Chen, J. The Relationship between Platform Choice and Supplier’s Efficiency- Evidence from China’s Online to Offline (O2O)e-Commerce Platforms. Electron. Mark. 2019, 29, 153–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Xu, C.; Zhang, J.; Bao, J.; Zhong, R. A Collaborative Architecture of the Industrial Internet Platform for Manufacturing Systems. Robot. Comput. Integr. Manuf. 2020, 61, 101854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourgeois, L. On the Measurement of Organizational Slack1. Acad. Manag. Rev. 1981, 6, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teece, D.J. Explicating Dynamic Capabilities: The Nature and Microfoundations of (Sustainable) Enterprise Performance. Strateg. Manag. J. 2007, 28, 1319–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, R.M. Toward a Knowledge-Based Theory of the Firm. Strateg. Manag. J. 1996, 17, 109–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nonaka, I. The Knowledge-Creating Company. In The Economic Impact of Knowledge; Routledge: Abingdon, UK, 1998; ISBN 978-0-08-050502-2. [Google Scholar]
- Fleming, L.; Mingo, S.; Chen, D. Collaborative Brokerage, Generative Creativity, and Creative Success. Adm. Sci. Q. 2007, 52, 443–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldwin, C.Y.; Clark, K.B. Design Rules, Volume 1: The Power of Modularity; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2000; ISBN 978-0-262-29185-9. [Google Scholar]
- Saville, B.R.; Berry, S.M. Efficiencies of Platform Clinical Trials: A Vision of the Future. Clin. Trials 2016, 13, 358–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleming, L. Recombinant Uncertainty in Technological Search. Manag. Sci. 2001, 47, 117–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.; Li, Y. Platform Ecosystem Embeddedness and Traditional Enterprises’ Value Chain Upgrading: Empirical Evidence from China’s Manufacturing Listed Companies. J. Manag. 2024, 37, 100–121. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Geroski, P.A.; Van Reenen, J.; Walters, C.F. How Persistently Do Firms Innovate? Res. Policy 1997, 26, 33–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triguero, Á.; Córcoles, D. Understanding Innovation: An Analysis of Persistence for Spanish Manufacturing Firms. Res. Policy 2013, 42, 340–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coad, A.; Segarra, A.; Teruel, M. Innovation and Firm Growth: Does Firm Age Play a Role? Res. Policy 2016, 45, 387–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knott, A.M.; Vieregger, C. Reconciling the Firm Size and Innovation Puzzle. Organ. Sci. 2020, 31, 477–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, L.T.M.; Vo, L.V.; Le, H.T.T.; Le, D.V. Asset Liquidity and Firm Innovation. Int. Rev. Financ. Anal. 2018, 58, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fama, E.F.; French, K.R. The Cross-Section of Expected Stock Returns. J. Financ. 1992, 47, 427–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, N.; Xu, J.F.; Fareed, Z.; Wan, G.; Ma, L. Financial Leverage and Corporate Innovation in Chinese Public-Listed Firms. Eur. J. Innov. Manag. 2022, 25, 299–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beladi, H.; Deng, J.; Hu, M. Cash Flow Uncertainty, Financial Constraints and R&D Investment. Int. Rev. Financ. Anal. 2021, 76, 101785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdogan, M.; Yamaltdinova, A. A Panel Study of the Impact of R&D on Financial Performance: Evidence from an Emerging Market. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2019, 158, 541–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Z.; Hofman, P.S.; Newman, A. Ownership Concentration and Product Innovation in Chinese Private SMEs. Asia Pac. J. Manag. 2013, 30, 717–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, D.N.; Tran, Q.-N.; Truong, Q.-T. The Ownership Concentration − Innovation Nexus: Evidence From SMEs Around The World. Emerg. Mark. Financ. Trade 2022, 58, 1288–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Yang, J. Effects of CEO Duality and Tenure on Innovation. J. Strategy Manag. 2019, 12, 536–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Q.; Yang, Q.; Zhao, R. Trade Network Deepening and Enterprise Capacity Utilization. J. Quant. Technol. Econ. 2024, 41, 111–133. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Wu, Q. Research on Platform Economy Empowering Real Economy Development: Evidence from China’s Provincial Panel Data. J. Ind. Technol. Econ. 2024, 43, 103–112. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.; Zhou, X. Governance Effect or Financing Effect? The Impact of Stock Liquidity on Tax Avoidance Behavior of Listed Companies. Account. Res. 2020, 9, 120–133. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Pan, A.; Liu, X.; Qiu, J. Can Green M&A Under Media Pressure Promote Substantial Transformation of Heavy Polluting Enterprises? China Ind. Econ. 2019, 2, 174–192. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Cachon, G.P.; Randall, T.; Schmidt, G.M. In Search of the Bullwhip Effect. Manuf. Serv. Oper. Manag. 2007, 9, 457–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persico, N.; Postlewaite, A.; Silverman, D. The Effect of Adolescent Experience on Labor Market Outcomes: The Case of Height. J. Political Econ. 2004, 112, 1019–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alesina, A.; Zhuravskaya, E. Segregation and the Quality of Government in a Cross Section of Countries. Am. Econ. Rev. 2011, 101, 1872–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Pan, W.; Yuan, K. Enterprise Digital Transformation and China’s Real Economy Development. J. Quant. Technol. Econ. 2022, 39, 5–25. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Fung, M.K.; Chow, W.W. Measuring the Intensity of Knowledge Flow with Patent Statistics. Econ. Lett. 2002, 74, 353–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghion, P.; Akcigit, U.; Bergeaud, A.; Blundell, R.; Hemous, D. Innovation and Top Income Inequality. Rev. Econ. Stud. 2019, 86, 1–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akcigit, U.; Baslandze, S.; Stantcheva, S. Taxation and the International Mobility of Inventors. Am. Econ. Rev. 2016, 106, 2930–2981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cusumano, M.A.; Yoffie, D.B.; Gawer, A. The Future of Platforms; MIT SMR: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2020; p. 61. [Google Scholar]
| Keyword Statistics | |
|---|---|
| Platform Ecosystem Embeddedness | Internet solutions, Internet thinking, Internet actions, Internet strategy, Internet model, Internet business model, Internet, Internet+, online and offline, from online to offline, online and offline integration, O2O, Cloud computing, stream computing, graph computing, in-memory computing, secure multi-party computation, brain-inspired computing, green computing, cognitive computing, converged architecture, 100-million-level concurrency, EB-level storage, Internet of Things (IoT), cyber-physical systems, big data, data mining, text mining, data visualization, heterogeneous data, credit investigation, augmented reality (AR), mixed reality (MR), virtual reality (VR), Internet platforms, Internet technology, mobile Internet, Internet services, Internet applications, Internet, B2B, C2C, B2C, C2B, industrial Internet, industrial platform, Internet ecosystem |
| Variable Type | Symbol | Variable Name | Definition |
|---|---|---|---|
| Independent Variable | PEE | Platform Ecosystem Embeddedness | See definition in previous section |
| Dependent Variables | Inno_in | Persistent Innovation Input | See definition in previous section |
| Inno_out | Persistent Innovation Output | See definition in previous section | |
| Control Variables | Age | Company Age | ln (Current Year−Year of Establishment + 1) |
| Size | Company Size | Natural logarithm of total assets | |
| FIXED | Proportion of Fixed Assets | Net fixed assets/Total assets | |
| BM | Book-to-Market Ratio | Book value/Market value | |
| Lev | Leverage | Total liabilities at year-end/Total assets at year-end | |
| Cashflow | Cash Flow Ratio | Net cash flow from operating activities/Total assets | |
| ROE | Return on Equity | Net income/Equity | |
| Shrcr1 | Ownership Concentration | Number of shares held by the largest shareholder/Total number of shares | |
| Dual | CEO Duality | Dummy variable: 1 if the Chairman also serves as CEO, 0 otherwise |
| Variable | Obs | Mean | Std. Dev. | Min | Max |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inno_in | 9279 | 19.572 | 1.346 | 12.690 | 25.488 |
| Inno_out | 9279 | 3.202 | 1.379 | 0.077 | 9.460 |
| l.PEE | 9279 | 1.646 | 1.401 | 0.000 | 6.290 |
| Age | 9279 | 3.002 | 0.274 | 1.792 | 4.220 |
| Size | 9279 | 22.499 | 1.250 | 19.857 | 28.636 |
| FIXED | 9279 | 0.206 | 0.133 | 0.001 | 0.876 |
| BM | 9279 | 0.592 | 0.250 | 0.044 | 1.559 |
| Lev | 9279 | 0.417 | 0.184 | 0.014 | 0.979 |
| Cashflow | 9279 | 0.056 | 0.065 | −0.313 | 0.839 |
| ROE | 9279 | 0.067 | 0.147 | −4.320 | 1.442 |
| Shrcr1 | 9279 | 31.894 | 14.206 | 3.003 | 86.347 |
| Dual | 9279 | 0.294 | 0.456 | 0.000 | 1.000 |
| Variable | VIF | 1/VIF |
|---|---|---|
| l.PEE | 1.180 | 0.846 |
| Age | 1.090 | 0.921 |
| Size | 1.820 | 0.550 |
| FIXED | 1.230 | 0.811 |
| BM | 1.530 | 0.652 |
| Lev | 1.540 | 0.649 |
| Cashflow | 1.310 | 0.761 |
| ROE | 1.310 | 0.766 |
| Shrcr1 | 1.070 | 0.936 |
| Dual | 1.040 | 0.966 |
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | |
| Inno_in | Inno_in | Inno_in | Inno_out | Inno_out | Inno_out | |
| l.PEE | 0.185 *** | 0.094 *** | 0.038 *** | 0.168 *** | 0.125 *** | 0.105 *** |
| (18.92) | (14.93) | (5.81) | (16.72) | (12.62) | (8.83) | |
| Age | 0.064 ** | –0.067 ** | –0.182 *** | 0.064 | ||
| (2.08) | –2.36) | (–3.76) | (1.25) | |||
| Size | 0.920 *** | 0.992 *** | 0.504 *** | 0.561 *** | ||
| (104.59) | (124.63) | (36.57) | (38.93) | |||
| FIXED | –0.804 *** | –0.328 *** | –0.366 *** | –0.282 ** | ||
| (–11.82) | (–4.92) | (–3.44) | (–2.34) | |||
| BM | –0.593 *** | –0.668 *** | –0.568 *** | –0.658 *** | ||
| (–14.67) | (–17.58) | (–8.95) | (–9.58) | |||
| Lev | –0.082 | –0.115 ** | 0.113 | –0.050 | ||
| (–1.49) | (–2.40) | (1.31) | (–0.58) | |||
| Cashflow | 0.305 ** | 0.380 *** | –0.346 | –0.206 | ||
| (2.12) | (3.13) | (–1.53) | (–0.94) | |||
| ROE | 0.184 *** | 0.212 *** | 0.254 ** | 0.223 ** | ||
| (2.90) | (3.97) | (2.55) | (2.32) | |||
| Shrcr1 | –0.005 *** | –0.001 ** | –0.000 | 0.001 | ||
| (–9.14) | (–2.32) | (–0.07) | (0.65) | |||
| Dual | 0.071 *** | 0.004 | 0.056 * | 0.054 * | ||
| (3.88) | (0.29) | (1.95) | (1.96) | |||
| _cons | 19.267 *** | –0.802 *** | –2.095 *** | 2.925 *** | –7.450 *** | –9.343 *** |
| (910.57) | (–4.21) | (–11.83) | (134.44) | (–24.97) | (–29.18) | |
| Year | NO | NO | YES | NO | NO | YES |
| Industry | NO | NO | YES | NO | NO | YES |
| N | 9279 | 9279 | 9276 | 9279 | 9279 | 9276 |
| R2 | 0.037 | 0.660 | 0.772 | 0.029 | 0.203 | 0.290 |
| Adj. R2 | 0.037 | 0.660 | 0.770 | 0.029 | 0.203 | 0.284 |
| F | 358.140 | 1798.833 | 2420.434 | 279.601 | 236.592 | 247.883 |
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | |
| l.PEE | Inno_in | Inno_out | Inno_in | Inno_out | |
| Avg_PEE_City | 0.506 *** | ||||
| (30.71) | |||||
| l.PEE | 0.222 *** | 0.109 *** | 0.0395 *** | 0.114 *** | |
| (9.95) | (2.82) | (5.02) | (7.47) | ||
| Controls | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| Year | NO | NO | NO | YES | YES |
| Industry | NO | NO | NO | YES | YES |
| N | 9279 | 9279 | 9279 | 6196 | 5755 |
| R2 | 0.517 | 0.753 | 0.290 | 0.783 | 0.324 |
| Adj. R2 | 0.513 | 0.745 | 0.274 | 0.781 | 0.315 |
| F | 124.95 | 364.88 | 46.67 | 1703.000 | 177.000 |
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | |
| Inno_in | Inno_out | Inno_in | Inno_out | Inno_in | Inno_out | |
| l.Platform | 0.090 *** | 0.155 *** | ||||
| (5.50) | (5.24) | |||||
| l.Plat_number | 0.118 *** | 0.075 *** | ||||
| (12.00) | (4.20) | |||||
| l.Plat_trade | 0.106 *** | 0.041 *** | ||||
| (12.45) | (2.65) | |||||
| Controls | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| N | 9276 | 9276 | 7861 | 7861 | 7861 | 7861 |
| R2 | 0.772 | 0.286 | 0.771 | 0.285 | 0.771 | 0.284 |
| Adj. R2 | 0.770 | 0.280 | 0.769 | 0.278 | 0.769 | 0.277 |
| F | 2419.163 | 241.522 | 2011.963 | 203.891 | 2015.855 | 202.552 |
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | |
| persistence | Inno_in | Inno_out | Inno_in | Inno_out | |
| l.PEE | 0.820 *** | 0.037 *** | 0.097 *** | 0.033 *** | 0.110 *** |
| (37.07) | (3.55) | (5.42) | (2.92) | (6.28) | |
| Controls | YES | YES | YES | −0.025 | 0.026 |
| Year | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| Year | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| N | 9276 | 4317 | 4317 | 9248 | 9248 |
| R2 | 0.592 | 0.741 | 0.294 | 0.818 | 0.376 |
| Adj. R2 | 0.588 | 0.737 | 0.283 | 0.811 | 0.352 |
| F | 266.066 | 893.567 | 112.300 | 576.575 | 64.104 |
| Inno_in | Inno_out | Inno_in | Inno_out | |||||||
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | (7) | (8) | (9) | (10) | |
| H_C | L_C | H_C | L_C | E | C | W | E | C | W | |
| l.PEE | 0.070 *** | 0.014 | 0.120 *** | 0.088 *** | 0.043 *** | 0.039 ** | 0.030 | 0.135 *** | 0.031 | 0.073 * |
| (7.22) | (1.55) | (6.81) | (5.47) | (6.63) | (2.01) | (0.90) | (10.18) | (0.94) | (1.77) | |
| Controls | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| Year | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| Industry | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| N | 4634 | 4641 | 4634 | 4641 | 6908 | 1419 | 940 | 6908 | 1419 | 940 |
| R2 | 0.785 | 0.768 | 0.312 | 0.272 | 0.823 | 0.751 | 0.673 | 0.308 | 0.372 | 0.384 |
| Adj. R2 | 0.782 | 0.765 | 0.302 | 0.262 | 0.822 | 0.741 | 0.654 | 0.300 | 0.346 | 0.349 |
| F | 1247.854 | 1218.056 | 144.295 | 104.857 | 2463.195 | 258.247 | 111.002 | 209.024 | 32.683 | 25.230 |
| Inno_in | Inno_out | Inno_in | Inno_out | |||||
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | (7) | (8) | |
| H_T | N_H_T | H_T | N_H_T | H_P | N_H_P | H_P | N_H_P | |
| l.PEE | 0.043 *** | 0.014 | 0.113 *** | 0.071 *** | –0.015 | 0.049 *** | 0.101 *** | 0.109 *** |
| (6.65) | (0.77) | (8.35) | (2.90) | (–0.77) | (7.37) | (3.72) | (8.23) | |
| Controls | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| Year | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| Industry | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| N | 6874 | 2402 | 6874 | 2402 | 2013 | 7263 | 2013 | 7263 |
| R2 | 0.809 | 0.713 | 0.290 | 0.323 | 0.716 | 0.796 | 0.340 | 0.281 |
| Adj. R2 | 0.808 | 0.705 | 0.287 | 0.306 | 0.712 | 0.795 | 0.329 | 0.275 |
| F | 2529.093 | 319.838 | 221.752 | 40.464 | 281.165 | 2362.744 | 39.129 | 213.580 |
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | |
| Inno_in | l.DSDD | Inno_in | Inno_in | |
| l2.PEE | 0.037 *** | –0.004 *** | 0.037 *** | |
| (5.09) | (–2.73) | (5.03) | ||
| l.DSDD | –0.180 *** | –0.175 *** | ||
| (–3.57) | (–3.16) | |||
| Controls | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| Year | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| Industry | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| N | 7152 | 7120 | 9269 | 7120 |
| R2 | 0.785 | 0.074 | 0.772 | 0.785 |
| Adj. R2 | 0.782 | 0.064 | 0.770 | 0.783 |
| F | 2005.210 | 5.393 | 2406.956 | 1815.627 |
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | |
| Inno_in | l.asset_turn | Inno_in | Inno_in | |
| l2.PEE | 0.037 *** | 0.012 *** | 0.031 *** | |
| (5.09) | (4.07) | (4.29) | ||
| l.asset_turn | 0.620 *** | 0.589 *** | ||
| (24.36) | (20.59) | |||
| Controls | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| Year | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| Industry | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| N | 7152 | 7125 | 9276 | 7125 |
| R2 | 0.785 | 0.386 | 0.785 | 0.797 |
| Adj. R2 | 0.782 | 0.380 | 0.784 | 0.795 |
| F | 2005.210 | 107.741 | 2622.973 | 1965.149 |
| (5) | (6) | (7) | (8) | |
| Inno_out | l.Kflow | Inno_out | Inno_out | |
| l2.PEE | 0.098 *** | 0.008 *** | 0.094 *** | |
| (7.16) | (4.73) | (6.86) | ||
| l.Kflow | 0.415 *** | 0.409 *** | ||
| (5.26) | (4.24) | |||
| Controls | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| Year | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| Industry | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| N | 7152 | 7122 | 9251 | 7122 |
| R2 | 0.308 | 0.709 | 0.286 | 0.310 |
| Adj. R2 | 0.301 | 0.706 | 0.280 | 0.302 |
| F | 206.080 | 22.940 | 240.211 | 188.062 |
| (5) | (6) | (7) | (8) | |
| Inno_out | l.Kcreat | Inno_out | Inno_out | |
| l2.PEE | 0.098 *** | 0.007 *** | 0.087 *** | |
| (7.16) | (6.68) | (6.39) | ||
| l.Kcreat | 1.497 *** | 1.384 *** | ||
| (12.41) | (9.32) | |||
| Controls | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| Year | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| Industry | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| N | 7152 | 7125 | 9276 | 7125 |
| R2 | 0.308 | 0.145 | 0.295 | 0.316 |
| Adj. R2 | 0.301 | 0.136 | 0.290 | 0.309 |
| F | 206.080 | 63.168 | 257.470 | 196.207 |
| Hypothesis | Hypothesis Statement | Mechanism Type | Empirical Result |
|---|---|---|---|
| H1 | Platform ecosystem embeddedness significantly promotes persistent innovation. | Overall Effect | Supported H1 |
| H2a | Platform ecosystem embeddedness promotes persistent innovation input by reducing coordination costs. | Resource Synergy Mechanism | Supported H2a |
| H2b | Platform ecosystem embeddedness promotes persistent innovation input by improving operational efficiency. | Resource Synergy Mechanism | Supported H2b |
| H3a | Platform ecosystem embeddedness promotes persistent innovation output by enhancing knowledge flow. | Knowledge Synergy Mechanism | Supported H3a |
| H3b | Platform ecosystem embeddedness promotes persistent innovation output by enhancing knowledge creation. | Knowledge Synergy Mechanism | Supported H3b |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Q.; Liu, T.; Wang, H.; Huang, T. The Persistent Innovation Effect of Platform Ecosystem Embeddedness. Sustainability 2025, 17, 5507. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17125507
Wang Q, Liu T, Wang H, Huang T. The Persistent Innovation Effect of Platform Ecosystem Embeddedness. Sustainability. 2025; 17(12):5507. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17125507
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Qianying, Tingli Liu, Haoyu Wang, and Tingyang Huang. 2025. "The Persistent Innovation Effect of Platform Ecosystem Embeddedness" Sustainability 17, no. 12: 5507. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17125507
APA StyleWang, Q., Liu, T., Wang, H., & Huang, T. (2025). The Persistent Innovation Effect of Platform Ecosystem Embeddedness. Sustainability, 17(12), 5507. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17125507





