Abstract
Heavy metals in lead refining waste slag pose persistent environmental risks, challenging conventional treatment methods that struggle to balance long-term stabilization with resource recovery potential. To address this issue, we developed a sustainable stabilization strategy. The simultaneous and long-lasting stabilization of Zn, Pb, and As heavy metals in lead refining waste slag was achieved by using an Fe-S(II) stabilizer, and the leaching toxicity of Zn, As and Pb was less than 1 mg/L, which is lower than the concentration limit of the Identification standards for hazardous wastes–Identification for extraction toxicity (GB5085.3-2007). The samples were analyzed by characterization before and after stabilization, and it was found that Fe-S(II) formed a protective layer of sulfide capsule on the surface of the samples. This stabilization mechanism, which has been termed the “nucleation-capture-sulfide encapsulation” process, involves after the oxidation of Fe0 to form a core–shell structure for trapping metal ions, where the external oxide layer undergoes mineralization via S(II) sulfide reduction. This microencapsulation-based passivation not only ensures long-term heavy metal immobilization but also preserves the slag’s potential for secondary resource recovery, aligning with circular economy principles. By minimizing environmental leakage risks while retaining metal reclamation feasibility, this approach offers a green and sustainable solution for heavy-metal-laden industrial waste management.
1. Introduction
The foundation of a country’s economic growth is its non-ferrous metals. Still, their smelting process generates a lot of waste materials, including dust, slag, sewage sludge, combustion leftovers, and more. As smelting wastes are constantly dumped around the smelter, under the action of natural weathering and microbial activities, toxic heavy metals in the wastes will be released and migrate continuously through rainfall and washing, which is one of the main sources of harmful heavy metals in the surrounding ecosystems [1]. It poses a significant obstacle to the sustainable development of the industry and represents a threat to the surrounding environment [1,2]. According to statistics, the world produces about 30 million tons of smelting slag every year [3,4], which usually contains a large number of heavy metal pollutants, such as As, Pb, Cd, Zn, Cr, etc. [2,5]. Therefore, to avoid further irreparable damage to the environment caused by non-ferrous metal smelting slag, it is necessary to carry out reasonable and harmless treatment. However, the contradiction between the potentially huge recovery value of the remaining resources in non-ferrous metal smelting slags and the current lack of efficient and economical means of separation and extraction puts forward higher requirements for the environmentally sound treatment of these slags, i.e., to ensure environmental safety while retaining the enforceability of secondary mining.
Currently, the existing research on the harmless treatment of non-ferrous metal slag is mainly divided into two categories: heavy metal removal and heavy metal stabilization [6,7]. Compared with heavy metal removal technology, heavy metal stabilization has many advantages, such as a good remediation effect, short remediation cycle, and low remediation cost [8]. Passivation/stabilization is a relatively flexible and harmless treatment method that stabilizes heavy metals through the addition of chemicals and has the possibility of meeting the requirement of ensuring environmental safety while retaining the practicability of secondary mining [9,10]. Bradley et al. utilized soluble PO43⁻ to stabilize heavy metals, achieving significant reductions in leachability: 52% for Ca, 14% for Cd, 98% for Cu, 99% for Pb, and 36% for Zn [11]. Wang et al. used CaHPO4 and CaCO3 as stabilizers to reduce Cd, Cu, Pb and Zn leachability by more than 87% [12]. However, the passivation/stabilization method requires the compounding of chemicals according to the leaching characteristics of different heavy metals in the solid waste, which is specific to cationic and anionic heavy metals, and thus it is difficult to achieve the simultaneous stabilization of multi-metals for smelting wastes that often contain both cationic and anionic heavy metals. In addition, the passivation/stabilization approach mainly targets heavy metals with mobility, but the heavy metals in the waste slag will be abundantly endowed with different minerals after smelting, and these carrier minerals are prone to morphological changes such as oxidation–reduction and dissolution under the influence of dynamic environmental conditions during the stockpiling process, which will lead to further release of the endowed heavy metals [13]; moreover, it is still unclear how the mineralogical factors can control the leaching behavior of the heavy metals [14]. Thus, the current passivation/stabilization methods cannot meet the long-term needs of slag stabilization.
Heavy metal surface passivation is a method developed to prevent oxidative weathering of slag, tailings, and other inorganic solid wastes containing toxic heavy metals. The principle involves forming an insoluble, inert, and dense protective film on the surface of sulfide mineral particles. This film acts as a barrier, preventing the intrusion of oxygen, water, and other oxidants into the tailing particles. The method is cost-effective and simple to implement [15,16,17]. Currently, the more-researched microcapsule passivation methods include phosphate passivation, silicate passivation, the hydroxide precipitation encapsulation method, and so on [18,19]. Huminicki et al. used the iron oxyhydroxide coating of pyrite to treat acid mine drainage, taking advantage of the fact that iron oxide precipitates will form on the surface of pyrite under sufficiently alkaline conditions to reduce the rate of oxidation of pyrite as the precipitates progressively become thicker and denser to form microcapsules [10]. Evangelou investigated the feasibility of controlling the oxidation of pyrite by forming precipitates from silicate and metallic iron ions that cover the mineral surface to form a passivated film insulating the mineral from oxygen intrusion. However, this method also reflects several shortcomings in the research process: ① the existing surface passivation method is not ideal in practical application, and the response of different mineral types to the passivation treatment varies significantly; and ② the current surface passivation method is not able to efficiently passivate a variety of heavy metals simultaneously.
Because the current treatment of waste residues is mainly based on in situ risk control, and taking into account the convenience of reuse of the potentially valuable components of waste residues, it is proposed to adopt a stabilization method based on sulfide mineralization to reduce the risk of heavy metal pollution in the process of waste residue stockpiling. The characterization results indicate that the release of Zn, Pb, and As from lead smelting slag is primarily influenced by their free-state content and the dissolution of soluble and sulfur–iron minerals. Therefore, based on the idea of using the sulfide reduction of weathered minerals to form capsule protection and ensure in situ precipitation/capture of free-state heavy metals, the simultaneous stabilization of multiple heavy metals in lead refining waste slag can be achieved through the independent and synergistic effects of Fe0 and S(II), using the commonly used industry stabilizers, sulfurizing agent Na2S and reduced iron powder (Fe0).
2. Experimental
2.1. Experimental Details
2.1.1. Sample Source and Compositional Analysis
Samples were obtained from a slag dump in the city of Gejiu, Yunnan Province, which is the lead smelting slag of the blast furnace. The dump has been stockpiled for nearly 20 years in an open environment without vegetation cover. The area is situated at an altitude of approximately 2000 m above sea level and is classified as part of the humid monsoon subtropical mountain climate zone, characterized by an average annual temperature of 15.9 °C and an average annual rainfall of 1080 mm. Samples were collected from various slag piles to remove impurities such as stones and plant debris. These samples were then mixed and dried naturally in the laboratory at room temperature.
The collected lead smelting slag is a substantial dry slag that exhibits a relatively balanced crystalline structure, accompanied by the presence of certain amorphous vitreous structures. The lead refining waste slag is a complex, non-homogeneous aggregate. As shown in Figure 1a, the background of the XRD pattern is elevated between 20° and 40° 2theta, which corresponds to the amorphous phase formed during the smelting process in the blast furnace. As shown in Figure 1b, the mineral composition of the waste sludge was analyzed using MLA, and the mineralogical composition of the waste slag is dominated by silicate minerals, including yellow feldspar, pyroxene, and olivine, along with sulfide minerals comprising sulfurous iron ore, the carbonate mineral chalcopyrite, and magnetite and gypsum. Refer to the Supporting Information for the comprehensive materials.
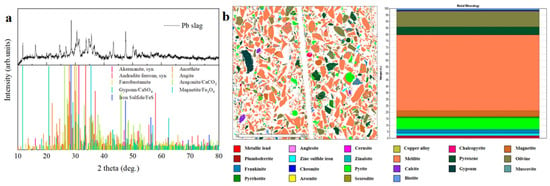
Figure 1.
(a) XRD analysis results of lead smelting slag. (b) Mineral composition and content of lead smelting slag.
2.1.2. Heavy Metal Leaching by Rainfall
Slag leachate is the main source of heavy metal pollution in mining areas. Under the effect of rainwater leaching, the dissolved heavy metal groups will affect the neighboring areas with the continuous diffusion and migration of leachate. Based on this, many scholars have conducted a lot of research on the leaching release of heavy metals [2,3]. The column leaching method was used in this study. The leaching column consisted of filter paper, quartz sand (5 cm), slag (1 kg), quartz sand (5 cm), and filter paper from bottom to top. The collected slag was leached with HNO3 solution at pH = 3.1, pH = 4.6, pH = 5.1, and pH = 6.8, and 400 mL of leaching solution was pumped into the column at a flow rate of 6 mL/min using a peristaltic pump. The leachate was collected every 3 days and measured for the heavy metal concentrations (test equipment: ICP-OES/MS (Agilent 5110 (OES), Santa Clara, CA, USA)). The leaching apparatus is shown in Figure 2.
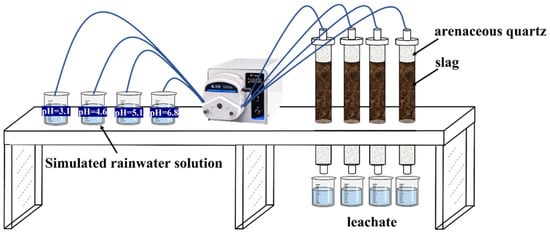
Figure 2.
Experimental setup for rainfall leaching of lead smelting waste slag.
2.1.3. Heavy Metal Stabilization Experiment
Based on the idea of the sulfide reduction of weathered minerals to form capsule protection and ensure in situ precipitation/capture of free-state heavy metals, the industry’s commonly used vulcanizing agent Na2S and reduced iron powder (Fe0) were used as stabilizers to achieve the simultaneous stabilization of a variety of heavy metals in the lead smelting waste slag through the independent and synergistic effects of Fe0 and S(II). The experiments were conducted in a rain-sheltered outdoor environment with a cycle of 24 days, while the appropriate amount of deionized water was sprayed at intervals of 2 days to maintain a water content of about 10% of the sample to simulate the weathering process of the waste slag. The ratio and additional amount of stabilizer are described in the main text, and the stabilizing effect of lead slag was tested and analyzed by the “Solid Waste Leaching Toxicity Leaching Method Sulfuric Acid Nitric Acid Method” (HJ/T299-2007 [20]).
2.2. Test Methods
After the lead slag was crushed to about 0.15 mm and sieved, 5 mL of hydrochloric acid was added to a polytetrafluoroethylene crucible with a pretreatment sample weight of 0.2 to 0.5 g and heated at 120 °C. Next, 15 mL of HNO3 was added and heated until viscous, and then 5 mL of HF and 2 mL of HClO4 were added sequentially. The mixture was heated continuously at 160 °C until the white smoke disappeared. The crucible was rinsed with 2% HNO3 and fixed through a 50 mL volumetric flask, and then the elemental (Pb, Zn, Cu, As, Cd, Cr) concentrations were measured using an inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometer (ICP-OES, Prodigy, Leeman) and an inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometer (ICP-MS, ELAN DRC II, Pe). The secondary spectral line of Fe (239.562 nm) was used as the analytical wavelength, and the internal standard element Sc was added to correct for signal fluctuations and interferences. The relative standard deviation of the soil samples was less than 10%. The detection limits of arsenic, lead, zinc, cadmium, copper, and chromium were 2 mg/kg. To ensure the reliability and quality of the data, the standard reference soils were purchased from the National Center for State Standard Materials. All the test results were corrected with blanks and the relative standard deviations (RSDs) were less than 10%.
3. Results and Discussion
This study first analyzed the basic physicochemical characteristics and heavy metal release pattern of the original ore samples. According to the XRF analysis results of the waste slag shown in Supplementary Table S1, the elements in the waste slag are mainly Fe, Si, and Ca, and the main heavy metal elements are Pb, Zn, and As, as can be seen from Figure S1. The main minerals in the waste slag include silicate minerals such as yellow feldspar, pyroxene, and olivine, sulfide minerals dominated by sulfide iron ore, the carbonate mineral chalcocite, and magnetite and gypsum. Sulfide minerals that are not fully oxidized in the smelting furnace and undergo continuous weathering in the open environment can lead to the geochemical instability of toxic elements such as cadmium, copper, manganese, lead, zinc, etc., which are released and migrate to the surrounding environment by physicochemical and biological processes [4,5]. The authors also further analyzed the leaching characteristics and release characteristics of heavy metals in the lead slag, and the results are shown in Figures S2–S4. The waste slags of five heavy metals with a high content of Zn, Pb, As, Cu and Cr are more likely to be released to the surrounding environment through rainfall leaching, and the average leaching concentrations are 0.32, 0.25 and 0.15 mg/L, respectively. The analysis of the heavy metal accumulation pattern and the risk of environmental pollution showed that Zn, As, and Pb have a higher risk of leaching release and migration, and therefore they are listed as the key elements in this study to further analyze the release of heavy metals and the stabilizing mechanism of sulfide mineralization.
3.1. Individual Stabilization of Heavy Metals in Smelting Slag by Ferrous Sulfur
This study was carried out by adding Fe0 and S(II) to the lead slag, respectively, where the main source of S(II) was Na2S, mixing well and then stacking for 7 days. After 7 days, samples were taken and the leaching toxicities of Zn, Pb and As in the samples were determined by the sulfuric acid–nitric acid method and the results are shown in Figure 3. The leaching toxicity of Zn decreased significantly with the increase of Na2S addition, and the Zn in the waste slag tended to be more stable as the stacking time was increased to 7 days. The leaching toxicity of Pb also decreased with the increase of Na2S addition, but the stabilizing effect was rather weakened with the increase of Na2S addition after 7 days of stacking. According to the release mechanism of Zn, Pb, and As mentioned in the Supporting Information, it can be seen from Figure S8 that the release of Zn is mainly Zn2+ released from the free state or from the dissolution of soluble minerals, which can be easily stabilized by ion-exchange reaction with S(II) to produce water-insoluble ZnS. From Figure S9, it can be seen that the release of Pb is mainly controlled by the weathering dissolution of iron sulfide minerals, and the introduction of S(II) causes the surface of the weathered layer of iron sulfide minerals to reduce to produce FeS, which forms certain protection for the internal iron(hydro)oxides and their endowment of Pb, and thus the leaching toxicity of Pb is reduced, but the excess of S(II) as well as the increase in the sulfidation time, and the increased iron(hydro)oxide reduction, lead to further release of the endowment of Pb. The mechanism of As release can be obtained from Figure S10. The leaching of As is strongly influenced by the pH and increases with a decreasing pH, and As(V) arsenate is converted to As(III) with higher mobility. The stabilizing effect of the added S(II) on As was limited, with the As leaching concentration only decreasing from 3.9 mg/L to 2.3 mg/L at 7.5% addition. After 7 days of stacking, the As in the slag also tends to be more stable, but the effect is still not significant. Free As reacts with S2− to form insoluble As2S3 or As2S5, but because the amorphous form of arsenic sulfide is unstable, it is susceptible to further release in the environment under the influence of the temperature, pH, organic matter, and coexisting cations [6]. For example, some of the arsenic sulfide may undergo surface dissolution to form dissolved As(III), which is further converted to the more soluble As2O3 after dehydration. The dissolution of As2S3 increased significantly when the pH exceeded 9 [7]. The arsenic-containing sulfide tailings waste stabilized with cement increased the arsenic release by more than 10 times under sulfide oxidation [8]. Similar to the release pattern of Pb, the release of As is inhibited by the control of the weathering and dissolution of iron sulfide minerals, but Na2S increases the pH inside the waste slag, which increases the mobility of As.
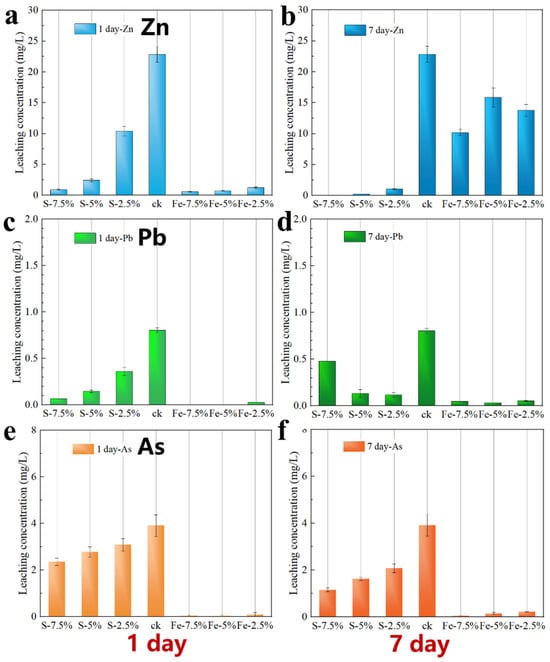
Figure 3.
The effect of adding Fe0 and S (II) separately on heavy metal leaching from lead slag: (a,b) are the stabilization effects on the heavy metal Zn, with (a) being the first day and (b) being the seventh day; (c,d) are the stabilization effects on the heavy metal Pb, with (c) being the first day and (d) being the seventh day; and (e,f) are the stabilization effects on the heavy metal As, with (e) being the first day and (f) being the seventh day. In the figure, ck is a blank sample, with the S content on the left and the Fe content on the right of ck.
The use of the Fe0 agent initially had a good inhibitory effect on the Zn leaching, but after 7 days, the stabilizing effect was significantly reduced. However, the stabilizing effect of Fe on Pb and As was significant, and the effect was still evident after 7 days. It is hypothesized that the Pb2+ and Fe3+ in the waste slag will undergo a redox reaction with Fe0 to produce monomeric Pb, while the surface of the reduced iron powder will be rapidly oxidized to form iron (hydroxide) oxides, which will have a complexing and trapping effect on As, and at the same time, the formation of Fe(II) and Fe(III) oxides/hydroxides by the oxidation of Fe0 stabilizes the As trapping by adsorption and co-precipitation [9]. On the other hand, corrosion of zero-valent iron by oxygen through multiphase iron surface reactions leads to the oxidation of As(II) [10], and the resulting As(V) can be easily captured by ionic oxides. It can be seen that sodium sulfide has a better stabilizing effect on the cationic heavy metals in the waste slag, but the effect on the anionic heavy metals is not obvious, and the effect is opposite after adding reduced iron powder.
3.2. Synergistic Stabilization of Multi-Metals in Smelting Slag by Iron–Sulfur
From the above study, since S(II) and Fe0 have very different passivation effects on the anionic heavy metals in lead slag, we wondered whether it is possible to compound both stabilizers to synchronize the stabilization of two different types of heavy metals in lead slag, which is one of the main challenges facing heavy metal passivation at present. Consequently, experiments were conducted to investigate the synergistic stabilization of iron sulfide with multiple heavy metals. Based on a total agent addition of 10% wt, the ratios of S(II)/Fe, S(II)/Fe(II), and S(II)/Fe(III) were varied by adjusting the additions of the sulfuring agent Na2S to Fe0, FeO, and Fe2O3, respectively, so that the three experimental groups were in the range of 3/1, 1, and 1/3 under three different molar ratio conditions. The three different molar ratios were placed in a rain-sheltered outdoor environment for 24 days, while the samples were sprayed with an appropriate amount of deionized water at intervals of 2 days to maintain the water content of the samples at approximately 10% to simulate the weathering process of the waste residue.
3.2.1. Synergistic Stabilization Experiments on Iron and Sulfur with Various Heavy Metals
The variation of the Zn leaching toxicity during lead slag co-stabilization is shown in Figure 4. From the above study, the leaching toxicity of Zn significantly decreased with increasing addition and stacking time when S(II) is added alone. At this time, the Fe-S(II) system also showed an excellent stabilization effect on Zn, and the leaching toxicity of Zn during the 24-day stacking process was lower than the concentration limit of the Identification standards for hazardous wastes–Identification for extraction toxicity (GB5085.3-2007 [21]). After replacing Fe with Fe(II), the stabilizing effect gradually deteriorated with the decrease of the relative content of S(II) in the stabilizer, and the leaching toxicity was even higher than that of the control lead slag when the S(II)/Fe(II) was 1/3. A similar trend was observed after replacing Fe with Fe(III), but Fe(III) promoted Zn leaching much more than Fe(II).
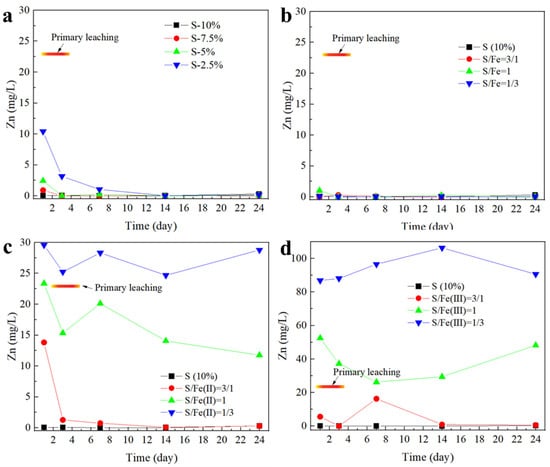
Figure 4.
Synergistic stabilization effect of iron and sulfur on Zn in lead smelting waste residue. In figure (a), sulfur is added separately; in figure (b), S and Fe0 are added proportionally; in figure (c), S and Fe (II) are added proportionally; and in figure (d), S and Fe (III) are added proportionally.
The main functional component of the Fe-S(II) system for the stabilization of Zn is S2−, and from the Supplementary Information, it is known that the lead slag contains a large amount of free Zn, and S2− can quickly react with it to generate insoluble ZnS, reducing the mobility of Zn. Also, the alkaline environment produced by S(II) acts as an inhibitor of the dissolution of alkaline silicate minerals. The stabilization of Zn by Fe0 is mainly attributed to the adsorption of the surface oxide layer, which explains the stabilizing effect of Fe alone in lead slag where a large amount of free-state Zn exists, but the effect is not significant. Fe(II) and Fe(III), on the other hand, accelerate the dissolution of carbonate minerals by double hydrolysis, leading to the release of large amounts of Zn.
The variation of the Pb leaching toxicity during the synergistic stabilization of lead slag iron–sulfur is shown in Figure 5. From the Supporting Information, there is less free Pb in the lead slag, and the leaching toxicity is much lower than that of Zn. When Na2S was added alone, the leaching toxicity of Pb at the initial stage decreased with the increase in the amount of Na2S added, but the opposite trend was observed after 7 days, and the leaching toxicity of Pb increased with the increase in the amount of Na2S added, and the leaching of Pb in the lead slag with the addition of 10% Na2S was even higher than that of the lead slag in the control group by the 24th day. This result further illustrates that the release and stabilization of Pb are mainly affected by the morphological changes in the weathering products of iron sulfide minerals, i.e., the sulfide reduction of the surface iron (hydroxide) oxides provides some protection to the interior, but the iron (hydroxide) oxides are over-reduced to lead to the release of the endowed Pb.
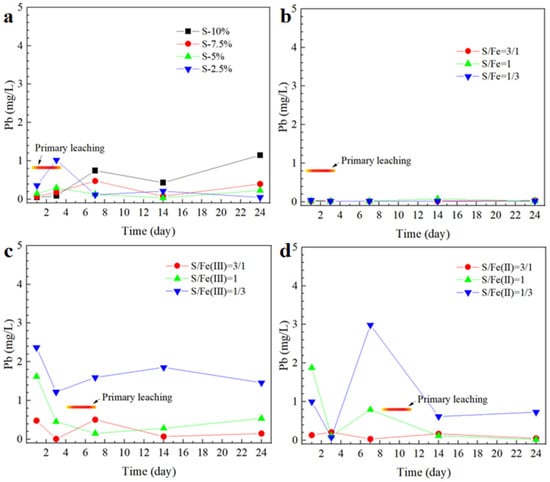
Figure 5.
Synergistic stabilization effect of iron and sulfur on Pb in lead smelting waste residue. In figure (a), sulfur is added separately; in figure (b), S and Fe0 are added proportionally; in figure (c), S and Fe (II) are added proportionally; and in figure (d), S and Fe (III) are added proportionally.
Compared with the stabilizing effect of Na2S alone, the Fe-S(II) system demonstrated an excellent stabilizing effect on Pb, and the leaching toxicity of Pb was lower than the concentration limit of the Identification standards for hazardous wastes–Identification for extraction toxicity (GB5085.3-2007) during all the 24-day stacking process. The stabilization of Pb by Fe0 consists mainly of electrostatic adsorption, complex formation, reduction, and precipitation. First, since the standard reduction potential of Pb2+ (−0.13 V) is greater than that of Fe2+ (−0.44 V), Pb2+ is reduced to insoluble monomeric Pb by Fe0. Secondly, the iron oxides formed on the surface of the Fe particles after oxidation have an adsorption and trapping effect on Pb2+. At the same time the oxidation of Fe0 consumes the oxygen inside the lead slag particles, leaving the iron sulfide minerals in a relatively stable environment and avoiding the release of new Pb due to the oxidative dissolution of the iron sulfide minerals. When Fe was replaced with Fe(II)/Fe(III), the stabilizing effect became progressively worse as the relative amount of S(II) in the stabilizer decreased, especially for Fe(III). The reason may be that the hydrolysis of Fe(II)/Fe(III) produces excess H+ in the interior of the lead slag particles, leading to the dissolution of Pb and PbCO3.
The changes in the As leaching toxicity during lead slag iron–sulfur co-stabilization are shown in Figure 6. According to the results, a small amount of added Na2S has a certain stabilizing effect on the leaching of As from lead slag, but the leaching toxicity is much higher than the concentration limit value of the Identification standards for hazardous wastes–Identification for extraction toxicity (GB5085.3-2007). With the increase of Na2S addition, the leaching of As was promoted. Similar to Pb, the leaching characteristics of As are also mainly influenced by the morphological changes in the weathering products of Fe–sulfur minerals, so that excess Na2S disrupts the iron (hydroxide) oxides porous structure on the surface of Fe–sulfur and Fe-oxidized minerals, leading to the release of As. However, the effect of Na2S on As leaching is much greater than that of Pb, mainly because the free As mainly exists in the form of anions, and these iron (hydrogen) oxide surfaces have a greater ability to capture As than Pb, while the increase in internal pH of the waste residue due to Na2S hydrolysis accelerates the release and dissolution of As.
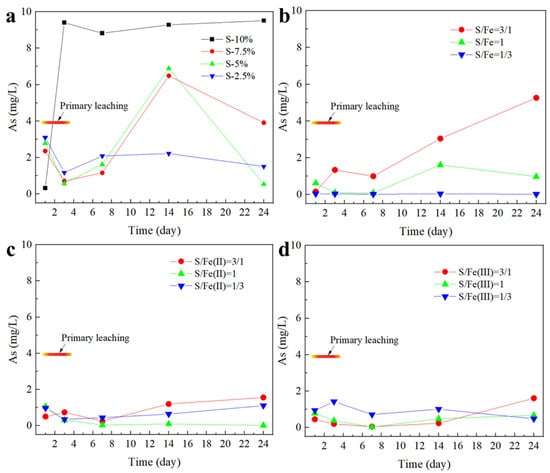
Figure 6.
Synergistic stabilization effect of iron and sulfur on As in lead smelting waste residue. In figure (a), sulfur is added separately; in figure (b), S and Fe0 are added proportionally; in figure (c), S and Fe (II) are added proportionally; and in figure (d), S and Fe (III) are added proportionally.
In the S(II)-Fe(II) and S(II)-Fe(III) ones, the leaching toxicity of As was significantly reduced by replacing part of the S(II) with Fe(II) and Fe(III) and decreased with the increase in the percentage of Fe(II) and Fe(III). The main reason is that Fe(II) and Fe(III) react with free As to form stable iron arsenate minerals. In the S(II)-Fe system, the leaching toxicity of As in the lead slag reached the concentration limit value of the Identification standards for hazardous wastes–Identification for extraction toxicity (GB5085.3-2007) at the S(II)/Fe percentage of 1/3. However, excess Na2S also inhibits the role played by the reduced iron powder. Reduced iron powder forms iron oxide (e.g., γ-FeOOH) and magnetite/magnetite (Fe3O4/γ-Fe2O3) through weathering to stabilize arsenic, while the Fe(II) and Fe(III) produced by Fe0 oxidative dissolution also have a stabilizing effect on As.
Taking the above results together, it can be seen that the Zn, Pb, and As in the lead slag were efficiently and synchronously stabilized under the synergistic effect of S(II) and Fe0 when the S(II)/Fe was 1/3. In the S(II)-Fe stabilization system, there is no direct chemical reaction between S(II) and Fe0, and the soluble S(II) can rapidly sulfurize and mineralize a large number of free heavy metals. The remaining heavy metals are then captured by the oxidation products of Fe0, and after that, the oxidation products of the topmost layer of Fe0 may be reduced to FeS by the remaining S(II) to encapsulate the captured heavy metals. The simultaneous and efficient stabilization of multiple metals in lead slag has been achieved by the S(II) and Fe0 sequential batch and synergistic action.
3.2.2. Pattern of Change in pH
The changes in the internal pH of the samples have an important influence on whether the heavy metals are stabilized or dissolved and migrated, so the study of the pH changes in the samples during the experiments is especially necessary to investigate the mechanism of the simultaneous stabilization of polymetallic metals by the Fe- S(II) system. The pH changes during the co-stabilization of lead refining waste iron–sulfur during the experiment are shown in Figure 7. Oxidative acidification is considered to be the main driving mechanism for heavy metal release from iron sulfide minerals. The pH of the lead slag was 6.97, and oxidation during prolonged stockpiling, buffered by carbonate minerals, did not acidify the slag. The pH increased to about 8 after the addition of Na2S to the lead slag and increased with the amount of addition and stacking time, mainly due to the hydrolysis of S2−. After replacing a portion of Na2S with Fe(II) or Fe(III), the pH under the neutralization of the hydrolysis of Fe(II) and Fe(III) decreased to between 6 and 7. In the system of Fe-S(II), the acidity and alkalinity inside the lead slag are mainly dominated by Na2S, and the main value of the pH is kept in a slightly alkaline environment from 7.5 to 9. Reducing iron powder in this pH environment facilitates the formation of a stable iron oxide surface layer with stabilizing effects on heavy metals through a controlled autoxidation process. The stability of the material following heavy metal passivation under varying pH conditions is detailed in the Supplementary Information.
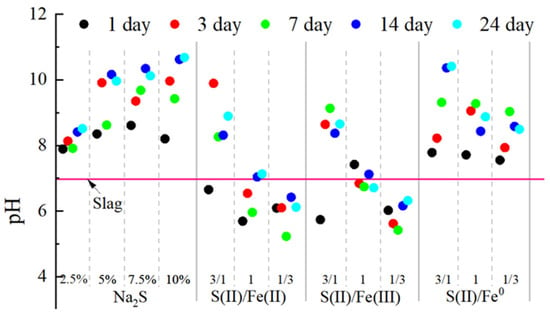
Figure 7.
pH changes during co-stabilization of lead smelting waste slag with iron–sulfur.
3.3. Mechanism of Simultaneous Stabilization of Multiple Metals in Smelting Slag
3.3.1. Analysis of the Encapsulation Process of the Fe-S(II) System Surface Sulfide Layer
It has been reported that the stabilization mechanism of Fe0 against heavy metals has been elucidated, i.e., Fe0 is oxidized to form a core–shell structure with a surface layer of iron (hydrogen) oxides such as iron oxides (e.g., γ-FeOOH) and magnetite/magnetite (Fe3O4/γ-Fe2O3), and free metal ions are captured by a variety of mechanisms such as electrostatic adsorption, complex formation, reduction, and precipitation [11,12]. In the Fe-S(II) stabilization system, we proposed the hypothesis of “nucleation-capture-sulfide encapsulation” based on this mechanism (shown in Figure 8a), i.e., after the oxidation of Fe0 to form a nucleation–shell structure and capture the metal ions, the external oxide layer is mineralized by the S(II) sulfide reduction, which encapsulates the internal Fe(H)oxides and adsorbed heavy metals.
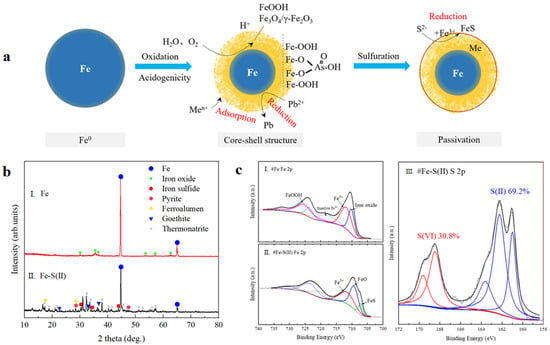
Figure 8.
Nucleation–capture–sulfide encapsulation mechanism in the stabilization of heavy metals in lead slag by the Fe−S(II) system: (a) the schematic diagram of the nucleation–capture–sulfide encapsulation mechanism, (b) XRD patterns of the reduced iron powders Fe and Fe−S(II), and (c) XPS patterns of the reduced iron powders Fe and Fe−S(II).
To prove the theory, the two experimental groups of Fe and Fe-S(II) were placed in a rain-sheltered outdoor environment for 14 days, while spraying appropriate amounts of deionized water at 1-day intervals to maintain a water content of the samples of about 10%, to simulate the process of natural weathering and to clarify the redox process of the reduced iron powders on their own and when coexisting with S(II), as well as the generation and structural changes of the functionalized functional groups in this process.
According to the XRD analysis results shown in Figure 8b, the match after 14 days showed a stronger zero-valent iron (α-Fe), as well as a broad peak with a weaker intensity of iron oxide (FeO), indicating that the Fe0 was partially oxidized under natural conditions, producing amorphous forms of iron oxides. This result is further confirmed in Figure 7, showing the XPS pattern of Fe(a), where 710.31 eV, 718.41 eV, and 723.87 eV in Fe 2p represent Fe 2p3/2, vibrational satellites Fe 2p3/2, and Fe 2p1/2, respectively, suggesting the presence of iron oxides (FeO+Fe2O3) [13,14]. Also, the peaks at 725.75 eV and 712.24 eV indicate the presence of iron (hydro)oxides (FeOOH) with higher relative content than iron oxides [15]. FeOOH is the product of the hydroxylation and subsequent dehydration of Fe when it comes into contact with an aqueous solution. It is noteworthy that the characteristic peaks around 706.4–707 eV, representing zero-valent iron, do not appear in the Fe 2p spectra, probably because XPS is a surface analysis technique with a probing depth of only 2–5 nm, which is not able to penetrate the microcapsule structure to detect Fe0 inside the nucleus. A comparison of the analytical results of the XRD indicates that Fe0 formed a multilayered core–shell structure during the gradual oxidation process, which consists of the Fe0 core from the inside to the outside, the intermediate Fe oxidized iron oxides (FeO, Fe2O3), and the surface layer of FeOOH-dominated iron (hydroxide) oxides mixtures formed by further weathering of the iron oxides. These iron (hydroxide) oxide inclusions have a certain pore structure that captures free heavy metals by adsorption. In particular, for As, a stable inner surface complex of the sphere will be formed in the form of a single-tooth angle-sharing, double-tooth angle-sharing, or double-tooth edge-sharing complex, which reduces the mobility of As [16,17]. However, iron (hydro)oxides are unstable in the environment and can be further dehydrated to form iron oxides, leading to the re-release of heavy metals.
When Fe0 and Na2S coexisted (Fe-S(II)), as can be seen in Figure S12, at first the Na2S and Fe0 existed as separate particles that could be distinguished by the naked eye, and by day 7, the surface showed a yellow color due to the weathering of Fe0, and after 14 days, the post-mixed Fe-S(II) mixture turned black and agglomeration occurred. Zero-valent iron (α-Fe), iron sulfides (FeS, FeS2), ferrous alum (FeSO4), and clinopyroxene (FeOOH) were retrieved through the XRD pattern in Figure 8b. The increase in acicular ferrite compared to weathered and reduced iron powders alone is mainly attributed to the alkaline environment provided by Na2S. According to the Fe 2p of Fe-S(II) (Figure 8c, there is no match to the characteristic peaks of FeOOH in the surface layer, increasing the iron sulfide, while the relative amount of Fe3+ is significantly reduced, combined with the fact that 30.8% of the S(II) is oxidized in the S 2p profile of Fe-S(II) (Figure 8c). It suggests that based on the multilayered core–shell structure formed by the gradual oxidation of the reduced iron powder, the topmost layer of FeOOH is reduced to the water-insoluble FeS, and these iron–sulfur compounds are also responsible for the agglomeration phenomenon of the Fe-S(II) mixtures in the later stage. Meanwhile, FeS is gradually oxidized to Fe3O4 in the presence of oxygen and water in the environment, which provides a relatively stable environment for the unstable FeOOH to act as encapsulation protection.
The results demonstrate the “nucleation-capture-sulfide encapsulation” mechanism in the stabilization of heavy metals in lead slag by the Fe-S(II) system, and indirectly, the directional and sequential batch processes of S(II) and Fe0 for different types of heavy metals. That is, there is no direct chemical reaction between S(II) and Fe0 so that soluble S(II) can rapidly sulfide mineralize a large number of free metal ions, and by the time Fe0 completes the core–shell transformation, sulfide encapsulation will not occur immediately so that the iron-based materials with a core–shell structure have enough time to capture heavy metals.
3.3.2. Stabilization Mechanism of Fe-S(II) on Waste Slag
To further clarify the stabilization mechanism of Fe-S(II) on polymetallic lead slag, four experimental groups of lead slag, lead slag-S(II), lead slag-Fe and lead slag-Fe-S(II) were set up to simulate the weathering environment during the stacking process of lead slag, which were placed in a rain-sheltered outdoor environment for 14 days, while the appropriate amount of deionized water was sprayed at intervals of one day to maintain the moisture content of the samples at about 10%.
Figure 9a shows the XRD patterns of the lead refining waste slag before and after stabilization. According to the results, high-peak-intensity gypsum (CaSO4) was retrieved from the lead slag, which is considered to be a characteristic product of the weathering of hazardous solid wastes such as slag and tailings containing sulfur and iron minerals and carbonate minerals, suggesting that severe oxidization processes occurred within the lead slag after 14 days of weathering simulation experiments. After the addition of S(II) and Fe within the lead slag, respectively, the peak intensity of the gypsum was weakened, indicating that S(II) and Fe inhibited the oxidation process in the waste slag, mainly because the oxidation process of S(II) and Fe with the minerals consumed the oxygen inside the slag, and in the samples synergistically stabilized with Fe-S(II), the peak intensity of the gypsum was significantly reduced, suggesting that the oxidation of the lead slag itself was inhibited by Fe-S(II), probably due to the protective effect of the sulfide reduction encapsulation mentioned above.
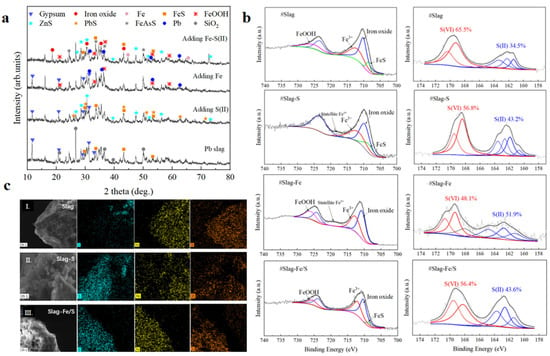
Figure 9.
Stabilization mechanism analysis of Fe-S(II) on waste slag: (a) XRD patterns of slag, slag-S(II), slag-Fe and slag-Fe-S(II), (b) XPS patterns of slag, slag-S(II), slag-Fe and slag-Fe-S(II), and (c) SEM patterns of slag, slag-S(II), slag-Fe and slag-Fe-S(II).
In addition, metal sulfides such as ZnS, PbS, and FeS were retrieved from the samples with Na2S added alone as compared to the blank lead slag, indicating that soluble S(II) indeed stabilized the free heavy metals in the lead slag rapidly by sulfide precipitation. Iron (hydrogen) oxides, iron oxides, and monomeric Pb were retrieved from samples with Fe0 added alone, suggesting that Fe0 forms an oxide layer with adsorption capacity during weathering while reducing free Pb2+ to water-insoluble Pb monomers. In the samples co-stabilized by Fe-S(II), the oxidation products of Fe0, the sulfide precipitation products of heavy metals by S(II), and the sulfide reduction products of Fe3+ (FeS) were simultaneously retrieved, consistent with the “nucleation-capture-sulfide encapsulation” mechanism and the directed and sequential batch stabilization of S(II) and Fe0. The results are summarized in the following figure.
The XPS patterns of the lead refining slag samples before and after stabilization are shown in Figure 9b. The 710.31 eV, 718.41 eV, and 723.87 eV in Fe 2p represent Fe 2p3/2, vibrational satellites Fe 2p3/2 and Fe 2p1/2, respectively, which indicate the presence of iron oxides (FeO + Fe2O3), and the peaks of 725.75 eV, 712.24 eV, and 707.30 eV originated from iron (hydro)oxides (FeOOH), Fe(III) and FeS, respectively. The peaks from 161 to 164 eV in S 2p were attributed to S(II), while the peaks from 168 to 171 eV were identified as S(VI) [18,19], with relative contents of 34.5% and 65.5%, respectively. This result further suggests that the surface of the lead slag particles underwent severe weathering, and that sulfite was oxidized as the main mineral phase and dissolved as sulfate.
When S(II) was added to the waste slag, the overall peak intensity of the Fe 2p was significantly weakened, while the increase in the intensity of the S 2p peak indicated that the added element S covered the surface of the lead slag particles. Compared to the Fe 2p profile of lead slag, FeOOH disappears, the relative amount of Fe(III) decreases, and the relative amount of FeS increases. The main reason is the redox reaction between S(II) and Fe3+ formed by the oxidation of the surface layer of lead slag particles, which generates new FeS minerals and reseals the heavy metals captured in the oxidized layer of the original lead slag particles, which is in line with the result of the weakened intensity of the gypsum peaks in the XRD analysis. It also indirectly proves the stabilization law of S(II) on Pb and As released by the dissolution control of sulfuric iron ore, i.e., the moderate amount of S(II) addition has a better stabilizing effect on Pb and As, but an excessive amount of S(II) will lead to the decomposition of FeOOH and increase the release of Pb and As. When Fe was added to the waste residue, similar to the addition of S(II), the overall peak intensities of the Fe 2p and S 2p were enhanced and weakened, respectively, due to the coverage of Fe elements. Compared to the Fe 2p profile of lead slag, the relative contents of FeOOH and Fe3+ increased, consistent with the results of Fe0 core–shelling.
When Fe-S(II) was added to the waste slag, the lead slag particles were covered by a mixed system of Fe-S(II), and in contrast to the weathered Fe-S(II) alone, FeS, the sulfide reduction product of FeOOH, was also observed in the surface layer, partially FeOOH, but FeOOH was also retained. This is due to the fact that a part of the Na2S is consumed by the original metal ions in the waste slag, generating a refractory metal sulfide precipitate through an ion-exchange process. The S 2p mapping further illustrates this process, with no significant oxidation of S(II) occurring and soluble S(II) reacting primarily with free heavy metals to produce sulfide mineral precipitates.
In order to further verify the surface passivation theory of Fe-S(II) on slag, the lead refining slag particles with obvious weathering traces on the surface were screened by SEM for the EDS analysis, and the results are shown in Figure 9c, where (a) is listed as the original slag samples, (b) is listed as the slag after vulcanization with Na2S, and (c) is listed as the slag after synergistic stabilization with Na2S and Fe. As can be seen from the figure, the relative content of element S in the surface layer of the particles of the original ore samples is low, with Fe and O predominating, and the main weathering products are iron (hydrogen) oxides. After vulcanization by Na2S, it was observed that part of the area was covered by S, while the relative proportions of the Fe and O content remained essentially unchanged, indicating that S2− was not oxidized to SO32−/SO42− but existed mainly in the form of S(II) or monomers. The relative contents of S and Fe on the surface after the synergistic stabilization of Na2S and Fe were increased and higher than that of O. The main reason may be the formation of a layer of FeS on the surface of the slag particles, which serves as an encapsulation of the slag particles. The results corroborate the analytical results of the XRD and XPS, further confirming the surface passivation process of Fe-S(II) on the slag.
To further investigate the microscopic morphology and encapsulation characteristics of iron sulfide, we conducted TEM analysis after meticulous grinding of the material. The images reveal that the reaction between Na2S and Fe0 formed a core–shell structure of S@Fe0. The Fe0 particles were uniformly encapsulated within the sulfide shell. As shown in Figure 10, the encapsulated spherical particles predominantly exhibit diameters of 15–20 nm. The sulfide outer layer achieves complete encapsulation of the particles, enabling effective containment and passivation of heavy metals adsorbed on the Fe0 particles.
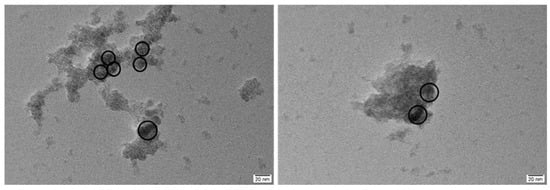
Figure 10.
TEM patterns of slag-Fe-S(II).
To summarize the above analysis, in the Fe-S(II) stabilization system, as shown in Figure 11, there is a stabilization mechanism of “nucleation-capture-sulfide encapsulation” with Fe0 as the core, i.e., after the oxidation of Fe0 to form the nucleation–shell structure and capture metal ions, the external oxidized layer is mineralized by the sulfide reduction of S(II) to encapsulate the internal iron (hydrogen) oxides and adsorb heavy metals. At the same time, S(II)-Fe0 has a directional and sequential batch stabilization process for different kinds of heavy metals, i.e., Fe0 does not react directly between S(II), and soluble S(II) rapidly sulfurizes and mineralizes a large number of free metal ions, and at the same time, sulfurizes and passivates the weathering products of alkaline silicate minerals and iron sulfide minerals, and the sulfuric encapsulation does not occur immediately until the completion of the core–shell transformation of Fe0 so that the core–shell structure of the iron-based materials has enough time to capture heavy metals.
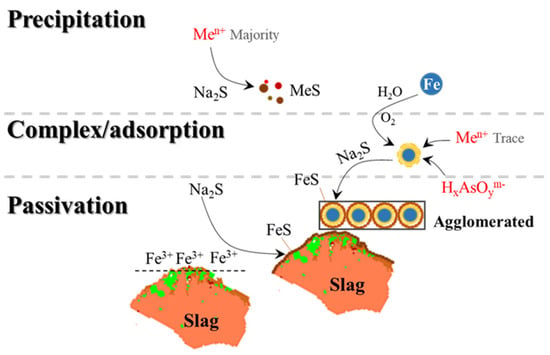
Figure 11.
Mechanism of S(II)−Fe synergistic stabilization of lead smelting waste slag from a blast furnace.
4. Conclusions
How to achieve in situ stabilization of multiple heavy metals in smelting slag is an important challenge in the current treatment of waste slag. In this study, the simultaneous stabilization of multiple heavy metals in lead refining waste slag was achieved through the independent and synergistic effects of Fe0 and S(II), and the leaching toxicities of Zn, As, and Pb were all lower than the concentration limit of the Identification standards for hazardous wastes–Identification for extraction toxicity (GB5085.3-2007). In the Fe-S(II) stabilization system, there exists a stabilization mechanism of “nucleation-capture-sulfide encapsulation” with Fe0 as the core, i.e., after Fe0 is oxidized to form a nucleation–shell structure and captures the metal ions, the external oxide layer is mineralized by S(II) sulfide reduction so that the internal iron (hydrogen) oxides and adsorbed heavy metals are encapsulated. At the same time, S(II)-Fe0 has a directional and sequential batch stabilization process for different kinds of heavy metals, i.e., Fe0 does not react directly between S(II), and soluble S(II) rapidly sulfurizes and mineralizes a large number of free metal ions, and at the same time, sulfurizes and passivates the weathering products of alkaline silicate minerals and iron sulfide minerals, and sulfuric encapsulation does not occur immediately after the completion of core–shell transformation of Fe0 so that the core–shell structure of the iron-based materials has enough time to capture heavy metals. Through the synergistic effect of the above Fe-S(II) composite stabilizers, Zn, As, Pb, and other heavy metals in the lead smelting slag were stabilized in situ, and the researched agents can provide new ideas for the in situ treatment of smelting slag and environmental risk control.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/su17125445/s1, Table S1. Results of the XRF analysis of lead smelting waste slag %. Figure S1. Analysis of the total amount of heavy metals in lead smelting slag. Figure S2. Heavy metal leaching toxicity of lead smelting waste (horizontal shock method). Figure S3. Results of the morphological analysis of heavy metals in lead refining waste (left) and the associated environmental risks (right) (exchangeable (F1), carbonate-bound (F2), iron/manganese oxide-bound (F3), organics/sulfide-bound (F4) and residue (F5)). Figure S4. Mineral grain analysis of yellow feldspar (left), pyroxene (center), and olivine (right). Figure S5. Characteristics of the silicate mineral embedded in lead smelting waste slag. Figure S6. Mineral particle analysis of sulfide (left) and magnetite (right). Figure S7. Characteristics of the sulfurous iron ore and magnetite embedded in lead smelting slag. Figure S8. Single leach release (left) and cumulative release (right) of Zn from lead slag. Figure S9. Single leach release (left) and cumulative release (right) of Pb from lead slag. Figure S10. Single leachate release (left) and cumulative release (right) of As from lead slag. Figure S11. Stabilization of heavy metals by materials under different pH conditions. Figure S12. Changes in the appearance of lead slag during the simultaneous stabilization of Fe0 and Na2S. Figure S13. XPS profiles of lead smelting slag before and after rainfall leaching.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, K.X. and R.X. (Rui Xu); methodology, Z.L.; software, Y.Y.; validation, K.X. and Z.L.; formal analysis, K.X.; data curation, C.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, R.X. (Ruosong Xie) and K.X.; writing—review and editing, Z.L; visualization, Y.Y.; supervision, G.Q.; project administration, R.X. (Ruosong Xie) and G.Q.; funding acquisition, R.X. (Ruosong Xie) and G.Q. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
Financial support for this project was provided by the National Natural Science Foundation of China Youth Science Fund Project (52000094) and the Yunnan Provincial Major Science and Technology Special Program (202302AE090014).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors on request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Peterson, E.K.; Carsella, J.; Varian-Ramos, C.W.; Schiffer, T.; Staples, S.K.; Diawara, M. Effects of Lead (Pb) from Smelter Operations in an Urban Terrestrial Food Chain at a Colorado Superfund Site. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2024, 112, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Liu, J.; Jia, D.; Chen, Y.; Li, L.; Evrendilek, F.; Yang, C.; Yuan, H.; Ninomiya, Y.; Li, W. Migration and transformation pathways of chlorine and sulfur in producing pyrolytic biochar of a Zn/Cd-remediating plant amended with modified kaolin. Fuel 2025, 383, 133856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Huang, Z.; Chen, Z.; Wang, J.; Evrendilek, F.; Liu, J.; He, Y.; Ninomiya, Y.; Xie, W.; Zhuang, G. Simultaneous optimizations of heavy metal immobilizations, products, temperature, and atmosphere dependency by acid pretreatment-assisted pyrolysis and gasification of hyperaccumulator (Pteris vittate L.) biomass. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 450, 142004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.-M.; Fu, R.-B.; Tong, Y.-H.; Shen, D.-L.; Guo, X.-P. The potential environmental risk implications of heavy metals based on their geochemical and mineralogical characteristics in the size-segregated zinc smelting slags. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 315, 128199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.-M.; Zhan, C.-L.; Liu, H.-X.; Lin, H.-Z. A critical review on environmental implications, recycling strategies, and ecological remediation for mine tailings. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 35657–35669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhattacharya, A.; Routh, J.; Jacks, G.; Bhattacharya, P.; Mörth, M. Environmental assessment of abandoned mine tailings in Adak, Västerbotten district (northern Sweden). Appl. Geochem. 2006, 21, 1760–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floroiu, R.M.; Davis, A.P.; Torrents, A. Kinetics and mechanism of As2S3 (am) dissolution under N2. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 1031–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coussy, S.; Benzaazoua, M.; Blanc, D.; Moszkowicz, P.; Bussière, B. Arsenic stability in arsenopyrite-rich cemented paste backfills: A leaching test-based assessment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 185, 1467–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Triszcz, J.M.; Porta, A.; Einschlag, F.S.G. Effect of operating conditions on iron corrosion rates in zero-valent iron systems for arsenic removal. Chem. Eng. J. 2009, 150, 431–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huminicki, D.M.; Rimstidt, J.D. Iron oxyhydroxide coating of pyrite for acid mine drainage control. Appl. Geochem. 2009, 24, 1626–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eighmy, T.T.; Crannell, B.S.; Butler, L.G.; Cartledge, F.K.; Emery, E.F.; Oblas, D.; Krzanowski, J.E.; Eusden, J.D.; Shaw, E.L.; Francis, C.A. Heavy Metal Stabilization in Municipal Solid Waste Combustion Dry Scrubber Residue Using Solu-ble Phosphate. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1997, 31, 3330–3338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, T.C.; Yeh, K.J.; Shue, M.F. Stabilization of an elevated heavy metal contaminated site. J. Hazard. Mater. 2001, 88, 63–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xi, Y.; Mallavarapu, M.; Naidu, R. Reduction and adsorption of Pb2+ in aqueous solution by nano-zero-valent iron—A SEM, TEM and XPS study. Mater. Res. Bull. 2010, 45, 1361–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.-P.; Li, X.-Q.; Cao, J.; Zhang, W.-X.; Wang, H.P. Characterization of zero-valent iron nanoparticles. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 120, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, D.; Wang, L.; Li, Z.; Tang, X.; He, M.; Yang, S.; Liu, X.; Xu, J. Simultaneous adsorption of Cd (II) and As (III) by a novel biochar-supported nanoscale zero-valent iron in aqueous systems. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 708, 134823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherman, D.M.; Randall, S.R. Surface complexation of arsenic (V) to iron (III)(hydr) oxides: Structural mechanism from ab initio molecular geometries and EXAFS spectroscopy. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2003, 67, 4223–4230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beak, D.G.; Basta, N.T.; Scheckel, K.G.; Traina, S.J. Bioaccessibility of arsenic (V) bound to ferrihydrite using a simulated gastrointestinal system. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 1364–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Guo, D.; Qiu, G.; Liu, C.; Ning, Z. Photooxidation of Fe (II) to schwertmannite promotes As (III) oxidation and immobilization on pyrite under acidic conditions. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 317, 115425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.; Zhang, H.; Wang, X.; Yao, D.; Hou, H.; Shi, Y.; Chen, J.; Wang, L.; Ma, M.; Liu, J. The mechanism of microwave-induced mineral transformation and stabilization of arsenic in realgar tailings using ferrous sulfate. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 393, 124732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HJ/T299-2007; Solid Waste. Extraction Procedure for Leaching Toxicity. Sulphuric Acid and Nitric Acid Method. Chinese Standard: Beijing, China, 2007.
- GB5085.3-2007; Identification Standards for Hazardous Wastes—Identification for Extraction Toxicity. Chinese Standard: Beijing, China, 2007.
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).