Abstract
Tyre wear particles (TWPs), generated from tyre-road abrasion, are a pervasive and under-regulated environmental pollutant, accounting for a significant share of global microplastic contamination. Recent estimates indicate that 1.3 million metric tons of TWPs are released annually in Europe, dispersing via atmospheric transport, stormwater runoff, and sedimentation to contaminate air, water, and soil. TWPs are composed of synthetic rubber polymers, reinforcing fillers, and chemical additives, including heavy metals such as zinc (Zn) and copper (Cu) and organic compounds like polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) and N-(1,3-dimethylbutyl)-N′-phenyl-p-phenylenediamine (6PPD). These constituents confer persistence and bioaccumulative potential. While TWP toxicity in aquatic systems is well-documented, its ecological impacts on terrestrial environments, particularly in agricultural soils, remain less understood despite global soil loading rates exceeding 6.1 million metric tons annually. This review synthesizes global research on TWP sources, environmental fate, and ecotoxicological effects, with a focus on soil–plant systems. TWPs have been shown to alter key soil properties, including a 25% reduction in porosity and a 20–35% decrease in organic matter decomposition, disrupt microbial communities (with a 40–60% reduction in nitrogen-fixing bacteria), and induce phytotoxicity through both physical blockage of roots and Zn-induced oxidative stress. Human exposure occurs through inhalation (estimated at 3200 particles per day in urban areas), ingestion, and dermal contact, with epidemiological evidence linking TWPs to increased risks of respiratory, cardiovascular, and developmental disorders. Emerging remediation strategies are critically evaluated across three tiers: (1) source reduction using advanced tyre materials (up to 40% wear reduction in laboratory tests); (2) environmental interception through bioengineered filtration systems (60–80% capture efficiency in pilot trials); and (3) contaminant degradation via novel bioremediation techniques (up to 85% removal in recent studies). Key research gaps remain, including the need for long-term field studies, standardized mitigation protocols, and integrated risk assessments. This review emphasizes the importance of interdisciplinary collaboration in addressing TWP pollution and offers guidance on sustainable solutions to protect ecosystems and public health through science-driven policy recommendations.
1. Introduction
The accelerating pace of global urbanization and transportation infrastructure development has led to an exponential increase in vehicle ownership and usage worldwide [1,2]. This expansion has significantly elevated the demand for tyre manufacturing, accompanied by a parallel rise in tyre abrasion and degradation during routine vehicular operations [3]. Among the by-products of this process, tyre wear particles (TWPs) are a class of non-exhaust particulate matter generated primarily through the mechanical abrasion of tyre treads against road surfaces [2]. TWPs typically range in size from a few microns to several millimetres, with a substantial proportion falling within the PM10 (≤10 µm) and PM2.5 (≤2.5 µm) fractions, which are especially relevant to air quality and human health [1]. This size range distinguishes TWPs from other non-exhaust emissions such as brake wear particles, road surface abrasion, or suspension component debris, which often differ in both particle size distribution and chemical composition [3]. The physicochemical complexity of TWPs, including synthetic and natural rubber, fillers, and various additives, further differentiates them from other particulate pollutants [4]. TWPs are microscopic to millimetric particles, with diameters typically ranging from about 500 µm up to a few millimetres, although many studies report particles smaller than 300 µm formed through the mechanical abrasion of tyre treads [5]. Composed of a complex mixture of synthetic and natural rubber polymers, fillers, plasticizers, vulcanizing agents, and various chemical additives, including heavy metals and persistent organic compounds, TWPs represent a diverse class of environmental pollutants. They possess high environmental persistence, physicochemical stability, and a marked resistance to biodegradation [6,7,8].
These particles have been identified in multiple environmental matrices, including air, freshwater, marine systems, and terrestrial soils, due to their mobility via atmospheric transport, runoff from impervious surfaces, and incorporation into wastewater streams [9,10]. Current estimates suggest that approximately 1.3 million metric tons of TWPs are discharged into the environment annually in Europe alone, and globally, TWPs account for up to 30% of microplastic pollution found in aquatic systems [3,4,5]. Notably, the magnitude and distribution of TWP emissions can vary substantially by region, influenced by differences in climate, vehicle fleet composition, and road infrastructure [1]. For example, regions with hotter climates or a higher proportion of heavy-duty vehicles may experience accelerated tyre wear and greater TWP emissions compared to cooler or passenger-car-dominated areas [6,7]. However, while much of the existing literature has focused on aquatic systems, soil environments, particularly those used for agriculture, are emerging as increasingly vulnerable sinks for TWP accumulation [11,12]. TWPs can enter agricultural soils through several pathways, including atmospheric fallout, stormwater infiltration, sewage sludge application, and irrigation with contaminated water, leading to their widespread presence even in remote agroecosystems [13,14]. Unlike many conventional microplastics, the ecotoxicological significance of TWPs lies in their particulate nature, chemical complexity, and reactivity [15]. The leaching of toxic additives, such as polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs), aniline derivatives, and heavy metals, including zinc (Zn), copper (Cu), and lead (Pb), poses substantial risks to both biotic and abiotic components of the soil [8,9,10,11,12]. Of particular concern is the elevated concentration of Zn, which, while essential in trace amounts, becomes phytotoxic at elevated levels and can suppress beneficial microbial communities [16]. These contaminants can disrupt soil pH, alter cation exchange capacity, reduce enzymatic activities, and interfere with nutrient cycling, ultimately compromising soil fertility and sustainability [17,18,19].
Recent experimental evidence has shown that TWPs can significantly alter the physical structure and functional characteristics of agricultural soils [19,20]. Their deposition has been associated with reduced soil porosity, increased compaction, and diminished water infiltration and retention capacities [3,21]. These alterations impair aeration and root penetration, directly affecting plant root growth and microbial colonization in the rhizosphere [22]. Furthermore, TWPs have been shown to negatively influence soil microbial diversity, suppressing key functional groups such as nitrogen-fixing bacteria and decomposers, thereby disrupting critical nutrient transformation processes [17,23]. These changes collectively destabilize the soil–plant–microbe continuum that underpins agricultural productivity [24].
The effects of TWPs on crops are both direct and indirect [11,12]. Nanoplastics derived from tyre particles have demonstrated the ability to penetrate root cell walls, translocate via vascular tissues, and accumulate in leaves and other above-ground plant organs [18,24]. These processes can interfere with photosynthetic efficiency, impair chlorophyll biosynthesis, reduce nutrient uptake, and trigger oxidative stress responses such as the overproduction of reactive oxygen species (ROS) [25,26]. Furthermore, TWPs have been implicated in reducing seed germination rates, inhibiting plant biomass accumulation, and disrupting hormonal signalling pathways, thereby contributing to yield losses and compromised crop health [11,12,25,26]. These impacts are compounded by disruptions in soil microbial communities, which further affect nutrient availability, pathogen suppression, and overall plant resilience [27]. Beyond ecological implications, TWPs pose substantial risks to human health, particularly through their capacity to bioaccumulate in food chains [28,29]. Exposure can occur through the inhalation of airborne particles (notably PM2.5 and PM10), ingestion of contaminated water and food, or dermal contact [30]. Health outcomes linked to TWP exposure include respiratory diseases, cardiovascular dysfunction, developmental abnormalities, and carcinogenic effects, raising serious concerns about long-term food safety and public health in agricultural regions exposed to high vehicular traffic or irrigation from polluted sources [31,32,33].
Although significant progress has been made in understanding the toxicological effects of TWPs in aquatic systems [4,7,15,28], research on their behaviour, transformation, and ecological impacts in agricultural soils remains limited. Existing studies often focus on isolated endpoints or individual media, lacking an integrated perspective on soil–plant–microbe interactions. The long-term fate of TWPs in soils, their translocation within plants, and their implications for food quality and security are poorly understood. Moreover, remediation approaches specifically designed for agricultural soils remain underdeveloped. Hence, this review addresses these knowledge gaps by synthesizing current literature on the sources, environmental pathways, and toxic effects of TWPs in agroecosystems. It examines their physicochemical properties, dispersion mechanisms, and impacts on soil structure, microbial diversity, nutrient cycling, and crop performance. Potential risks to terrestrial animals and the transmission of food chain contamination are also considered. Additionally, the review assesses recent advancements and challenges in remediation technologies applicable to agricultural soils. By highlighting research gaps and proposing integrative management strategies, this work aims to support evidence-based policies and sustainable agricultural practices that mitigate the long-term risks of TWPs to ecosystem and human health.
2. Review Methodology
A systematic review was conducted to comprehensively assess the scientific literature on TWPs in terrestrial and agricultural environments. Publications from January 2000 to April 2025 were identified through structured searches of the Web of Science (WOS) Core Collection, Scopus, and China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI) databases. Boolean keyword combinations included: (“tyre wear particle” OR “tyre wear particle” OR “tyre-derived microplastic” OR “TWP” OR “tyre microparticles” OR “tyre and road wear particles”) AND (“soil” OR “terrestrial” OR “agriculture” OR “plant” OR “remediation”). For CNKI, additional terms such as “tyre microplastics” and “tyre road wear particles” were used to maximize retrieval in Chinese literature. This search yielded 1284 English-language and 312 Chinese-language records. After duplicate removal, titles and abstracts were screened for relevance to TWP sources, environmental fate, toxicity, or remediation in terrestrial or agricultural contexts. Studies were included if they (1) were published in peer-reviewed journals between January 2000 and April 2025; (2) focused on TWPs in terrestrial or agricultural environments; and (3) provided original data or substantive reviews on TWP sources, distribution, environmental fate, toxicity, or remediation. Exclusion criteria were the following: (1) studies not focused on TWPs; (2) studies exclusively examining aquatic environments; (3) conference abstracts, editorials, or non-peer-reviewed literature; and (4) articles lacking sufficient methodological detail or quantitative results. This process resulted in 214 English and 57 Chinese articles for full-text review, of which 136 English and 38 Chinese articles met all criteria and were included in the synthesis.
Both English- and Chinese-language sources were subjected to identical inclusion and exclusion criteria, screening procedures, and data extraction protocols to ensure consistency and minimize bias. Screening and data extraction were conducted independently by two reviewers, with discrepancies resolved by consensus. Data from the included studies were compiled into a standardized table, capturing publication year, study location, environmental matrix, analytical methods, and key findings. Descriptive statistics summarized publication trends, research focus areas, and the frequency of analytical techniques. Keyword co-occurrence analysis was performed using CiteSpace software version 6.1.R3 to visualize research hotspots and thematic evolution. The bibliometric analysis revealed a marked increase in annual publications on TWPs in terrestrial and agricultural environments after 2005, with more than 30 articles per year published after 2020. The most frequently occurring keywords included “particulate matter”, “source apportionment”, “environment”, “emissions”, “air pollution”, and “toxicity”, reflecting a strong research emphasis on environmental pathways, pollutant characterization, and ecotoxicological impacts. Recent studies increasingly address remediation strategies and human health risks, highlighting the growing interdisciplinary focus in this field.
3. Analytical Techniques for the Detection of Tyre Wear Particles
The detection and quantification of TWPs in environmental samples pose significant analytical challenges due to their complex composition and the presence of similar microplastics [2]. Several methodologies have been developed to enable specific and selective identification of TWPs in field-collected matrices [5]. Pyrolysis-gas chromatography/mass spectrometry (Py-GC/MS) is widely used for its ability to detect characteristic tyre-derived polymers and additives, such as styrene-butadiene rubber, and specific chemical markers (e.g., benzothiazoles and N-(1,3-dimethylbutyl)-N′-phenyl-p-phenylenediamine (6PPD)) [17,28,31]. Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) and Raman spectroscopy are also employed to distinguish TWPs based on their unique spectral fingerprints, although these techniques may be limited by particle size and matrix interference [30,32]. Additionally, scanning electron microscopy coupled with energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (SEM-EDS) provides morphological and elemental analysis to support TWP identification [12,23]. The combination of these analytical techniques enhances the reliability of TWP detection in complex environmental samples and is critical for advancing field-based research on TWP distribution and impacts [17,19].
4. Sources of TWPs
TWPs are small particulate matter generated by friction between tyres and road surfaces during vehicle operation [34]. These particles, also known as tyre fragment mixtures, are a significant source of non-exhaust emissions and are increasingly recognized as contributors to environmental pollution [35]. The generation of TWPs is closely tied to the inherent properties of tyres, including material composition, wear resistance, load-bearing capacity, and lifespan [36]. For instance, tyres made from harder materials with lower wear resistance experience greater mechanical and internal friction during vehicle operation [37]. This intensifies shear stress between the tyre and the road surface, accelerating the production of TWPs. While these intrinsic tyre properties fundamentally determine the baseline generation rate of TWPs, their influence is further modulated by a range of external or extrinsic factors encountered during real-world vehicle operation [34,35,36]. External factors also play a critical role in determining the quantity of TWPs produced. Vehicle type, road type, environmental conditions, and maintenance practices have a significant influence on TWP generation [38]. Research indicates that heavy-duty trucks produce 5 to 10 times more TWPs than small passenger cars when travelling at the same speed on identical roads [19]. Similarly, rural roads contribute to 1.5 to 2 times higher TWP emissions than urban roads for vehicles of the same type [39]. Furthermore, prolonged exposure of tyres to sunlight or immersion in oil stains and corrosive liquids accelerates their degradation, increasing TWP production [40]. Driving behaviours such as emergency braking or aggressive cornering also exacerbate tyre wear [41]. For example, laboratory simulation studies have shown that a single emergency braking maneuver can increase tyre wear by approximately 6% compared to steady-state driving conditions in small passenger cars [40]. Additionally, a 1 °C rise in tyre surface temperature has been observed to result in a 2% increase in tyre wear under controlled experimental conditions, with this relationship being approximately linear over the temperature range of 20–60 °C [20]. These values may vary depending on vehicle type, tyre composition, and specific driving scenarios [41]. To enhance clarity and accessibility, Table 1 summarizes the key internal and external factors influencing the generation of TWPs, their respective effects, and representative references.

Table 1.
Key internal and external factors influencing the generation of tyre wear particles (TWPs) and their effects.
While the factors influencing TWP generation are broadly similar worldwide, significant regional differences exist. For instance, studies have shown that TWP emissions are typically higher in hotter climates, such as southern Europe and parts of Asia, where elevated temperatures accelerate tyre degradation [6,21]. In the United States, regions with a higher proportion of heavy-duty vehicles, such as the Midwest and industrial corridors, report substantially greater TWP emissions compared to areas dominated by passenger vehicles [42]. Comparative assessments indicate that annual TWP emissions per capita are highest in the EU (up to 0.9 kg person−1 year−1), followed by the US and China, reflecting differences in vehicle density, road infrastructure, and maintenance practices [7]. Urban centres in rapidly developing Asian countries also exhibit elevated TWP concentrations due to dense traffic and limited emission controls [43]. These regional disparities highlight the need for tailored mitigation strategies.
The widespread use of vehicles has led to a significant rise in tyre usage and frequency, resulting in massive TWP production [20]. These particles are released into various environmental media, i.e., air, soil, and water, causing severe ecological pollution. Studies reveal that only 1–10% of TWPs become airborne particulate matter, while the majority settle as sedimentary particles on road surfaces or nearby areas [36,37,38]. Airborne TWPs can travel long distances through atmospheric transport mechanisms, which are processes like wind dispersion or turbulent mixing that carry particles through the air, contributing to particulate pollution even in remote areas [39]. In water bodies, TWPs enter via runoff from rainfall or urban drainage systems, further exacerbating aquatic pollution [15,28]. TWPs are complex mixtures that include tyre tread fragments and road surface elements such as minerals and dust. Their chemical composition often contains harmful substances like Zn-oxides and PAHs, which pose significant risks to ecosystems and human health [24,34]. PAHs released under high-temperature conditions are known for their mutagenic and carcinogenic properties, while Zn accumulation can disrupt microbial communities in soil and aquatic environments [44]. These toxic components degrade environmental quality and infiltrate food chains via soil or water contamination [37].
TWPs represent a growing environmental challenge due to their diverse sources and widespread distribution [45]. Intrinsic tyre properties, such as material hardness, and external factors, like driving habits and road conditions, influence their generation [46]. As vehicle ownership rises globally, addressing TWP emissions will require interdisciplinary research into their generation mechanisms, environmental behaviour, and mitigation strategies, such as developing more durable and eco-friendly tyre materials, implementing stricter maintenance practices, or improving driving habits [47,48]. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for developing effective policies to reduce their ecological footprint while safeguarding public health. Ultimately, the interplay between TWP generation and environmental dispersion determines the extent to which these particles contaminate air, soil, and water systems, underscoring the urgent need for integrated mitigation strategies.
5. Environmental Distribution and Migration of TWPs
TWPs represent one of the most pervasive and environmentally mobile classes of microplastics, exhibiting complex transport dynamics across atmospheric, aquatic, and terrestrial systems [49,50,51]. Their environmental behaviour is governed by an intricate interplay of physical, chemical, and biological processes that collectively determine their spatial distribution, persistence, and ultimate ecological impacts [52,53] (Figure 1). Understanding these multifaceted migration pathways is crucial for developing accurate environmental risk assessments and formulating effective mitigation strategies in response to the growing global demand for vehicles.
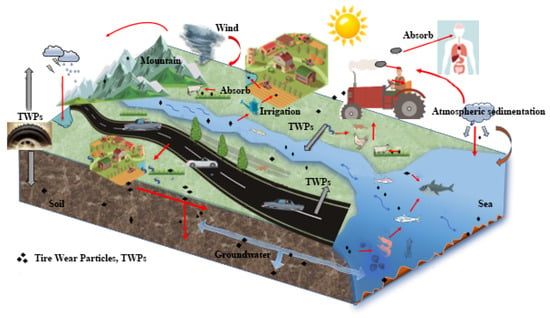
Figure 1.
Pathways of tyre wear particles (TWPs) in the environment. The figure illustrates how TWPs are transported by wind and water (e.g., irrigation, runoff), deposited in soil, absorbed into groundwater, and ultimately carried to the sea. This highlights the widespread environmental dispersion of microplastics from tyre wear.
5.1. Atmospheric Transport: From Urban Emissions to Global Dispersion
The atmospheric transport of TWPs represents a significant yet often overlooked contributor to particulate air pollution, with far-reaching implications for environmental quality, human health, and climate dynamics [54]. Recent studies have quantified the staggering rates at which TWPs are generated, approximately 1300 times greater than regulated exhaust emissions per vehicle kilometre, establishing them as a dominant particulate pollutant from road transport [55]. Once released, approximately 10% of freshly generated TWPs become aerosolized, entering the atmosphere as suspended particulate matter with complex aerodynamic properties [56]. Notably, both particle diameter and shape significantly influence atmospheric residence time and travel distance. Recent research has demonstrated that cylindrical TWP fibres can be transported over considerably greater distances than spherical particles due to their aerodynamic properties [57]. These airborne particles exhibit a bimodal size distribution: the coarse fraction (PM10–2.5), comprising 85–90% of atmospheric TWPs, dominates near-source deposition within 100–500 m of roadways [58]; in contrast, the fine fraction (PM2.5), representing 10–15% of emissions, remains suspended for extended periods with atmospheric residence times ranging from 5 to 15 days [59]. Globally, TWPs contribute significantly to urban particulate matter pollution, accounting for approximately 11% of PM10 loads and 0.27% of PM2.5 concentrations under typical conditions [60]. However, the contribution of TWPs to PM2.5 varies considerably by region. For example, in London, TWP-derived PM2.5 has been estimated at 0.8–1.3% of total PM2.5 [61], while studies in Beijing report values ranging from 0.15% to 0.5% [59]. In high-traffic corridors or tunnel environments, these contributions can spike dramatically, reaching up to 28% for PM10 and 1.3% for PM2.5 [60]. The long-range transport potential of TWPs has been unequivocally demonstrated through their detection in remote environments far from their emission sources [56,57,58]. For instance, TWPs have been identified in Alpine snowpacks in the Swiss Alps at concentrations ranging from 1200 to 3400 particles per litre, in Arctic ice cores showing a three-fold increase since 1990, and in marine boundary layer aerosols in the North Pacific Gyre at approximately 17 ± 6 particles per cubic metre [59,60,61]. These findings underscore the global dispersion capabilities of TWPs via atmospheric circulation [56,57,58].
The environmental and climatic interactions of atmospheric TWPs are particularly concerning due to their unique physical and chemical properties [62]. Their high light absorption efficiency (MAC~0.5 m2 g−1 at 550 nm) enables them to act as potent radiative forcing agents, contributing to regional atmospheric warming estimated at +0.1–0.3 °C per decade in urban areas [59,60,61]. Furthermore, TWPs can serve as cloud condensation nuclei (CCN), altering cloud microphysical properties and precipitation patterns by influencing droplet formation processes [63]. This role in cloud dynamics may exacerbate regional hydrological imbalances and intensify extreme weather events [64]. TWPs also contribute to cryospheric degradation by reducing surface albedo when deposited onto snow and ice surfaces [65]. This phenomenon accelerates melting rates in sensitive regions, such as the Arctic and Alpine zones, further amplifying the effects of global warming and threatening ecosystems that rely on stable cryospheric conditions [66]. The deposition of TWPs onto vegetation and agricultural lands near urban areas adds another layer of complexity; their chemical composition, including PAHs and heavy metals, can adversely affect plant health and soil quality [67,68]. In short, the atmospheric transport of TWPs is a multifaceted process with profound implications for air quality, climate systems, and ecological integrity on both regional and global scales. Addressing these impacts requires interdisciplinary research into their emission rates, aerodynamic behaviour, chemical interactions within the atmosphere, and long-term environmental consequences. Such efforts are essential for developing effective mitigation strategies that balance public health needs with sustainable environmental management.
5.2. Aquatic Pathways: The Hydrological Conveyor of TWP Pollution
Aquatic systems serve as major sinks for TWPs, which are transported through multiple interconnected pathways, facilitating their widespread distribution across freshwater and marine environments [69]. The hydrological pathway begins with the initial mobilization of TWPs from road surfaces, where they accumulate at densities ranging from 2 to 15 g m−2, depending on traffic intensity [70]. These particles are then introduced into aquatic ecosystems via three primary mechanisms: stormwater runoff, wastewater systems, and direct atmospheric deposition [2,3,4,5]. Stormwater runoff represents a critical pathway for TWP ingress into aquatic environments, particularly during precipitation events [19]. The “first flush” effect during moderate rainfall (10–20 mm h−1) mobilizes 60–80% of road-deposited TWPs within the initial 30 min of rainfall [38]. For example, monitoring in the Thames catchment revealed TWP fluxes of 4.7–18.2 kg day−1 km−1 during wet weather conditions, underscoring the significant contribution of urban runoff to aquatic pollution [19]. Wastewater systems also play a substantial role in TWP transport, with approximately 35% of TWPs bypassing conventional treatment due to their small effective diameter (<50 µm) and variable buoyancy [71]. While many TWPs exhibit near-neutral densities of around 1.2 g cm−3, tyre-derived particles can range up to 2.7 g cm−3 depending on their material composition and additives [72]. This broad density spectrum influences their fate during treatment: denser particles are more likely to settle and be removed, whereas less dense TWPs tend to remain suspended and escape into effluent streams [71,72]. This results in continuous point-source emissions from treatment plant outfalls into the receiving water bodies. Additionally, direct atmospheric deposition contributes 8–12% of total TWPs to water surfaces, with higher contributions observed in coastal zones (15–22%), where proximity to urban centres, increased port and shipping traffic, and wind-driven resuspension of road dust collectively exacerbate contamination [69].
Once introduced into aquatic systems, TWPs undergo complex fate processes that differ significantly between freshwater and marine environments [5]. In freshwater systems, fluvial transport carries TWPs downstream; however, hydrodynamic conditions and the type of waterbody strongly influence their retention and subsequent sedimentation [73]. In high-energy rivers, rapid flow and turbulence keep most TWPs in suspension, resulting in less than 1% being retained in sediments. In contrast, lentic systems, such as lakes and wetlands, characterized by low flow and longer settling times, can exhibit sedimentation rates exceeding 40% [15]. For instance, studies conducted in Australian urban wetlands have revealed that TWPs comprise 15–38% of sediment samples, highlighting the potential for significant accumulation in low-energy aquatic environments [5]. In marine environments, TWPs account for approximately 28% of total microplastic pollution, with notable accumulation in coastal sediments at concentrations ranging from 300 to 5600 particles kg−1 and in surface waters at densities between 1 and 25 particles m−3 [74]. The ecotoxicological consequences of TWP contamination in aquatic systems are severe and multifaceted. Chemical leaching from TWPs releases harmful substances such as Zn at rates of up to 2.1 µg g-TWP−1 day−1 in seawater, exceeding toxicity thresholds for sensitive marine organisms [75]. Furthermore, TWPs serve as substrates for biofilm colonization by pathogenic bacteria such as Vibrio spp., thereby increasing disease transmission risks within aquatic ecosystems [76]. Trophic transfer is another critical concern; field studies have demonstrated the presence of TWPs in the gastrointestinal tracts of approximately 12% of commercial fish species, leading to gut blockage and metabolic disruption [77]. These impacts not only threaten biodiversity but also pose risks to human health through the consumption of contaminated seafood [74,75,76]. In summary, the hydrological pathways of TWPs pollution highlight their pervasive impact on aquatic environments, driven by stormwater runoff, wastewater emissions, and atmospheric deposition. The complex fate processes and ecotoxicological effects underscore the urgent need for targeted research into mitigation strategies that address both point-source and diffuse emissions while safeguarding aquatic ecosystems and human health.
5.3. Soil Contamination: The Silent Accumulation of TWPs in Terrestrial Ecosystems
Soil systems represent the ultimate long-term repository for TWPs, with complex infiltration dynamics leading to persistent contamination at multiple scales [78]. Global estimates indicate that the annual TWP loading to soils exceeds 6.1 million metric tons, resulting in distinct spatial patterns of contamination [1,2,3,4]. The lateral distribution of TWPs follows a power-law decay from roadsides, where concentrations are highest [10,11,12,13,14]. Specifically, TWP concentrations start at approximately 4200 mg kg−1 within 0–5 m of the immediate roadside, decline to less than 800 mg kg−1 at 30 m, and stabilize at 50–150 mg kg−1 beyond 100 m [79]. This pattern highlights the significant impact of proximity to roadways on soil contamination levels [80]. Vertical migration of TWPs occurs through multiple mechanisms, including macropore flow, tillage incorporation, and bioturbation [81]. Macropore flow, facilitated by earthworm burrows and root channels, enables TWPs to penetrate depths of up to 1.5 m within two years [82]. Conventional agricultural practices, such as tillage, redistribute TWPs from the surface to depths of 15–30 cm at rates of 12–25 kg ha−1 yr−1 [28]. Additionally, soil fauna, such as earthworms, enhance downward movement through gut passage and casting activities, further contributing to the vertical distribution of TWPs [33].
The ecological impacts of TWPs in soil are profound and multifaceted. Microbial communities are significantly affected, with a 40–60% reduction in nitrogen-fixing Rhizobia populations observed in contaminated soils [83]. Mesofauna, such as earthworms, also experience decreased survival rates of 15–30% at TWP concentrations exceeding 1000 mg kg−1 [84]. Plant interactions are also altered, with root morphological changes, including a 25–40% reduction in fine root density [85]. Chemical leaching from soil-resident TWPs releases harmful substances like Zn at rates of 0.8–3.2 mg kg-TWP−1 year−1, PAHs, particularly benzo[a]pyrene, at 5–15 µg kg-TWP−1 year−1, and vulcanization accelerators such as MBT at 0.2–1.1 mg kg-TWP−1 year−1 [10,11,12,13,14,15]. These contaminants alter fundamental soil processes, leading to a 20–35% reduction in organic matter decomposition rates, a 15–25% decrease in water holding capacity, and significant changes in cation exchange capacity (ΔCEC = −2 to −5 cmol(+) kg−1) [51,52,53,54,55]. The long-term implications for ecosystem services are particularly concerning in agricultural systems, where TWP accumulation may compromise soil health and crop productivity over decadal timescales [7]. Emerging evidence suggests that TWPs can persist in soils for more than 50 years, creating a legacy contamination issue that warrants immediate policy attention [86]. Addressing this challenge requires interdisciplinary research into the fate and effects of TWPs in soil, as well as the development of effective strategies for mitigating their impacts on terrestrial ecosystems.
6. Hazardous Effects of TWPs
The widespread distribution of TWPs across environmental compartments poses significant risks to soil health, agricultural productivity, and human health [5,6,7,8]. Their complex chemical composition, including heavy metals, organic additives, and persistent polymers, enables multifaceted toxicity mechanisms that threaten ecosystem integrity and public health [66,67,68,69,70,71].
6.1. Impact of TWPs on Soil and Microbes
TWPs have emerged as an insidious and increasingly prevalent source of soil contamination in agroecosystems, driven by their continuous release through vehicular abrasion [87]. These particles exhibit distinctive physicochemical properties and are rich in synthetic polymers, heavy metals, and organic additives, which set them apart from conventional microplastics and confer a unique capacity to alter soil environments in multifaceted ways [88]. Their presence in agricultural soils not only degrades the physical and chemical structure of these systems but also exerts profound disruptions on microbial communities and the vital ecosystem services they mediate [89]. The structural integrity of soil is one of the first casualties in TWP-contaminated environments. When TWPs accumulate in agricultural soils, they significantly compromise soil architecture by decreasing porosity and increasing bulk density [90]. Quantitative assessments reveal a porosity decline of up to 25%, accompanied by an increase in bulk density from baseline values of approximately 1.32 g cm−3 to as high as 1.48 g cm−3 [61]. These alterations restrict the movement of air and water, resulting in a 35–60% reduction in infiltration rates and a diminished moisture retention capacity [91]. Such changes are not merely physical in consequence; they reshape the soil microhabitat, particularly disadvantaging moisture-dependent microbial taxa and root systems that rely on adequate pore networks for growth and respiration [92]. For instance, filamentous bacteria such as Streptomyces spp., known for their role in antibiotic production and organic matter turnover, are severely impeded in their growth due to the restriction of hyphal extension in compacted soils [93].
Beyond structural degradation, TWPs function as vectors for a diverse suite of chemical contaminants, including high concentrations of heavy metals, most notably Zn, and persistent organic pollutants such as PAHs [24]. In agricultural soils adjacent to roadways, Zn levels derived from TWPs have been reported in the range of 120–450 mg kg−1, exceeding safety thresholds and posing phytotoxic risks [94]. These metals readily leach into the soil solution, disrupting microbial enzymatic activities and triggering oxidative stress responses [37]. TWPs also exert dual and sometimes opposing effects on soil pH. Their carbonate components may buffer acidic soils, raising pH by up to 0.8 units, while sulphide oxidation can acidify neutral or alkaline soils by as much as 1.2 units [95]. These shifts in pH profoundly influence nutrient solubility and metal mobility, indirectly altering microbial nutrient acquisition and population dynamics [96]. The chemical stress imposed by TWPs disproportionately affects specific microbial taxa and functional groups. Ammonia-oxidizing bacteria, such as Nitrosomonas europaea L. and Nitrobacter winogradskyi L., which are integral to the nitrification process, exhibit reductions in population densities exceeding 70% under elevated Zn concentrations [97]. Simultaneously, acidophilic and heavy metal-resistant taxa such as Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans L. and Cupriavidus metallidurans L. become enriched, signalling a transition in community composition toward stress-adapted assemblages [77,78,79]. Such shifts not only diminish microbial biodiversity but also disrupt key nitrogen cycling processes [8,9,10]. Functional gene analyses reveal a significant reduction in the abundance of nitrogen fixation genes, such as nifH spp., with activity losses ranging from 55% to 70% [51,52,53,54,55]. These functional impairments carry significant implications for soil fertility and agricultural productivity, particularly in low-input systems that rely heavily on biological nitrogen fixation [20,41,42,43].
Fungal communities are similarly affected, albeit with species-specific responses. Beneficial fungi such as Trichoderma harzianum L., which play a critical role in plant pathogen suppression, exhibit growth inhibition of up to 50% at relatively low TWP concentrations (≥500 mg kg−1) [80,81,82]. In contrast, resilient fungi such as Aspergillus niger L. and Rhizophagus irregularis L. may persist or even proliferate under contamination stress, potentially altering symbiotic relationships with plants and soil carbon dynamics [35,36,37]. Mycorrhizal colonization, particularly by Glomus mosseae L., declines by approximately 40% in contaminated soils, indicating a weakening of mutualistic interactions critical for phosphorus uptake in crops [15]. The microbial responses to TWPs extend beyond taxonomic shifts to functional reconfigurations of entire soil ecosystems [6,7,8]. For example, the decline of decomposer communities like Cellulomonas flavigena L. and Saccharomonospora spp. leads to significant reductions in cellulose degradation rates, impairing carbon cycling and organic matter turnover [51,52,53]. Similarly, predatory bacteria such as Myxococcus xanthus L., key regulators of microbial population balance, experience constrained mobility in compacted soils, disrupting trophic interactions and microbial succession patterns [57,58]. Anaerobic niches created by poor aeration conditions favour the proliferation of obligate anaerobes like Clostridium pasteurianum L., further altering soil redox dynamics and metabolic pathways [7,84,85].
Mechanistically, TWP toxicity operates through both direct and indirect pathways (Table 2; Figure 2). The leaching of Zn2+ ions has been implicated in the disruption of microbial electron transport chains, impairing adenosine triphosphate (ATP) production and inducing cell membrane instability [98]. Organic additives, such as 6PPD, a known oxidative stressor, selectively inhibit Gram-positive bacteria, including Bacillus subtilis L. and Staphylococcus aureus L., through enhanced cell wall penetration and uncoupling of oxidative phosphorylation [99]. These chemical effects are compounded by the stress matrix created by altered soil structure, which restricts microbial dispersal, limits access to resources, and amplifies sensitivity to toxicants [100]. An emerging concern in TWP-contaminated soils is the rise in pathogenic and antibiotic-resistant microbes [29]. The enrichment of opportunistic pathogens such as Pseudomonas aeruginosa L., Enterobacteriaceae spp., and multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii L. has been consistently observed, suggesting a potential link between environmental pollution and public health risk [20,42,43,44]. Simultaneously, declines in beneficial taxa such as Pseudomonas fluorescens L. and Bradyrhizobium japonicum L. weaken biocontrol functions and symbiotic nitrogen fixation, respectively, compromising crop resilience and yield potential [5,72].

Table 2.
Toxic effects of tyre wear particles on soil environment.
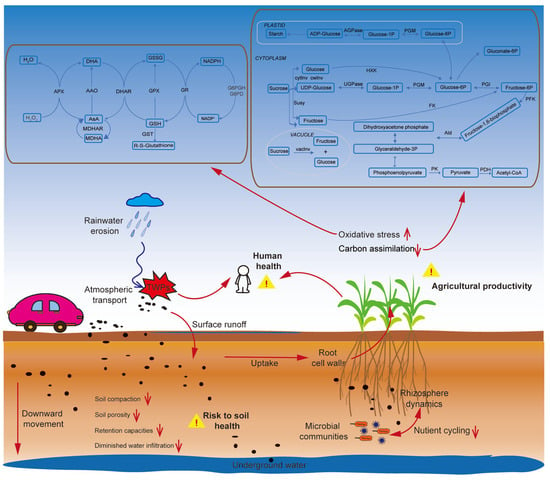
Figure 2.
Schematic illustration of the adverse effects of tyre wear particles (TWPs) on plant health, soil ecosystems, and human wellbeing. TWPs are introduced into the environment through atmospheric transport, surface runoff, and rainwater erosion. Upon entering the soil, they cause soil compaction, reduce porosity, and impair water retention and infiltration, ultimately disrupting soil structure. These particles negatively impact microbial communities and rhizosphere dynamics, thereby impairing nutrient cycling. TWPs are taken up by plant roots, where they induce oxidative stress and disrupt carbon assimilation and metabolic pathways (e.g., antioxidant and carbohydrate metabolism), leading to compromised agricultural productivity. Furthermore, the accumulation and transport of TWPs pose significant risks to human health via food chain contamination and environmental exposure.
The cumulative effects of TWP contamination on agricultural soils represent a confluence of structural degradation, chemical toxicity, and microbial dysbiosis [28]. These stressors do not act independently but interact synergistically, producing nonlinear and often unpredictable outcomes that undermine soil health and ecosystem functionality [101]. The current understanding highlights the need to adopt integrative research frameworks that simultaneously assess both physical and chemical perturbations [102]. Standardized methods for quantifying TWP concentrations across various soil types and biogeographic regions will be crucial for accurate risk assessment [95]. Moreover, targeted strategies must be developed to mitigate their impact, ranging from improved material engineering of tyres to bioremediation approaches that restore microbial equilibrium and soil productivity [42,43,44]. In conclusion, the intrusion of TWPs into agricultural landscapes constitutes a pressing ecological challenge with far-reaching implications for soil function, microbial ecology, and food security. As vehicular traffic continues to intensify globally, the need for robust scientific inquiry and proactive policy responses becomes increasingly urgent.
6.2. Impact of TWPs on Agricultural Plants
TWPs, generated from the abrasion of tyre tread during vehicular movement, represent a growing class of environmental pollutants with significant implications for terrestrial ecosystems, particularly plant health [20,21,22,23]. TWPs are composed of a heterogeneous mixture of synthetic polymers, inorganic fillers, and a broad spectrum of chemical additives, and their deposition into agricultural soils via road runoff, atmospheric transport, and irrigation systems is becoming increasingly widespread [104]. A growing body of evidence indicates that TWPs can directly interact with plant systems and modify critical soil properties, including structure and hydrodynamics [105]. These modifications not only affect water retention and aeration but also influence nutrient bioavailability and root–soil interactions, thereby disrupting the edaphic environment essential for plant growth [75,106,107]. Initial toxicological assessments have revealed that TWPs may suppress plant development at both morphological and physiological levels. For instance, experimental observations by Wik and Dave [20] demonstrated significant inhibition of soybean (Glycine max L.) growth following TWP exposure, highlighting the phytotoxic potential of these particles. However, the specific pathways through which TWPs exert growth-inhibitory effects remain largely unresolved [74]. Among the hypothesized mechanisms, leachates containing Zn and other soluble compounds released from TWPs have attracted attention. While Zn is an essential micronutrient required for several enzymatic processes and membrane stabilization, excessive concentrations, often 5–500 times higher than those found in typical microplastic (MP) leachates, may lead to toxic outcomes [90]. Interestingly, studies have also shown that under certain concentrations, Zn released from tyre debris can stimulate plant growth, acting as a supplemental micronutrient. For example, Khoshgoftarmanesh et al. [94] reported enhanced growth of maize (Zea mays L.) and sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.) when tyre crumbs were used as a Zn source. This dual role of Zn underscores the complex dose-dependent effects of TWP-derived constituents on plant physiology [104].
Beyond essential micronutrients, TWPs also release a suite of organic compounds with known or suspected toxicity. Among these, PAHs, bisphenol A, and a range of tyre-specific additives—including diphenylguanidine (DPG), hexamethoxymethylmelamine (HMMM), and N-phenyl-N′-(1,3-dimethylbutyl)-p-phenylenediamine (6PPD)—have been detected in plant tissues following exposure [10,11,12,13,14]. Recent work by Castan et al. [12] demonstrated the uptake and biotransformation of such additives in lettuce, with concentrations in leaf tissues ranging from 0.75 µg g−1 for 6PPD to 20 µg g−1 for HMMM. Notably, the metabolic byproducts of these compounds may exhibit greater toxicity than their parent forms, raising concerns about bioaccumulation and food safety [108]. Despite this, direct mechanistic data linking specific organic constituents in TWP leachates to particular phytotoxic outcomes remain limited, warranting targeted research efforts [109]. Physical characteristics, such as particle size, surface charge (zeta potential), and shape, significantly influence the fate and behaviour of TWPs in plant–soil systems [28]. Nanometre-sized TWPs, like other engineered nanoplastics and microplastics, are capable of penetrating plant root cell walls and entering the vascular system, particularly when particles carry a negative surface charge [110]. Fan et al. [111] noted that TWPs exhibit a lower zeta potential compared to MPs, which may enhance their mobility and cellular uptake. These nano-sized particles have the potential to translocate into above-ground plant tissues, although the extent of their enrichment appears to be species-specific and remains poorly characterized due to the limited availability of experimental data [112].
Emerging evidence also suggests that TWPs impose considerable physiological and biochemical stress on plants (Table 3; Figure 2). At the cellular level, TWPs can trigger oxidative damage characterized by elevated ROS, particularly hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), and lipid peroxidation markers such as malondialdehyde (MDA), with levels reaching 12–18 nmol g−1 fresh weight. These oxidative responses are often accompanied by the upregulation of antioxidative defence genes such as catalase (CAT) and peroxidase (POD), whose expression may increase three- to six-fold [25,26,27]. Photosynthetic efficiency is similarly compromised, with studies documenting 25–40% reductions in the maximum quantum yield of photosystem II (Fv/Fm), along with chlorophyll (a + b) losses ranging from 35 to 55% [8,9,10]. Additionally, excessive Zn accumulation in aerial tissues, ranging from 200 to 800 mg kg−1 dry weight, has been linked to secondary deficiencies of iron (Fe) and manganese (Mn), exacerbating nutrient imbalances and further impairing photosynthesis and growth [5,6,7,8]. The implications of these stress responses extend to measurable losses in agronomic performance. Controlled-environment and field-based studies have revealed substantial yield reductions in key crops [92]. For example, wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) has shown a 20–35% decrease in shoot biomass at soil concentrations of 500 mg TWP kg−1, while rice (Oryza sativa L.) exhibited a 40–60% drop in grain yield under similar contamination levels, primarily due to compromised nutrient uptake [103]. Leafy vegetables exposed to TWP levels above 200 mg kg−1 soil developed visible chlorosis and necrosis [12]. On a broader scale, European surveillance programmes have reported 8–12% declines in crop yields near roadside agricultural plots, with TWPs estimated to account for up to 60% of observed growth impairments [18,113].

Table 3.
Toxic effects of tyre wear particles on agricultural crops.
Despite these alarming observations, significant gaps remain in our understanding of TWP–plant interactions, particularly concerning long-term ecological risks, plant species-specific susceptibilities, and the precise physicochemical traits that govern uptake and toxicity [46,47,48,49,50]. Furthermore, little is known about how TWP exposure affects soil microbial communities and rhizosphere dynamics, which are crucial for nutrient cycling and plant health [7,83,84,85]. Given the expanding footprint of vehicular pollution and the persistent nature of TWPs in the environment, there is an urgent need for comprehensive, mechanistic, and interdisciplinary studies to elucidate the pathways of plant exposure, uptake, translocation, and the resultant physiological consequences [92,93,94,95]. In summary, TWPs pose a multifaceted threat to terrestrial plant systems through both chemical and physical mechanisms. Their complex composition, including essential and toxic elements, persistent organic pollutants, and nanoplastic fragments, enables them to interfere with fundamental plant processes ranging from seed germination to photosynthesis and biomass production. Future research should integrate high-resolution imaging, molecular biology, and ecotoxicological modelling to develop a predictive understanding of TWPs behaviour in agroecosystems and their broader implications for food security and environmental sustainability.
6.3. Impact of TWPs on Humans
The insidious infiltration of TWPs into human systems represents a growing public health crisis with far-reaching consequences [31]. These complex environmental pollutants, generated through the constant abrasion of vehicle tyres against road surfaces, permeate our daily lives through multiple exposure pathways, each carrying distinct health risks [114]. Urban residents routinely inhale approximately 3200 TWPs daily, with the fine PM2.5 fraction penetrating deeply into lung tissue, where it triggers a cascade of adverse effects [30]. Clinical evidence links this exposure to significantly elevated asthma incidence rates (18–25% increase) near high-traffic areas, while controlled animal studies demonstrate more severe outcomes, including pulmonary fibrosis and restrictive lung dysfunction [103]. The carbon black component of TWPs appears particularly problematic, inducing persistent inflammation in bronchial epithelial cells and contributing to lung cancer risk through genotoxic mechanisms that researchers are only beginning to understand [115].
Beyond respiratory impacts, TWPs exert concerning effects on cardiovascular health through multiple pathological pathways [116]. Epidemiological studies consistently associate TWP exposure with substantially increased cardiovascular mortality rates, showing 12–15% higher risk for every 10 µg m−3 increment in particulate concentration [117]. At the mechanistic level, these particles compromise vascular function by inducing endothelial dysfunction, evidenced by measurable reductions (30%) in flow-mediated dilation among exposed populations [19,38,39,40]. The metal constituents of TWPs, particularly Zn and copper, appear to drive oxidative stress in vascular tissues, while organic additives like 6PPD disrupt critical cardiac ion channels even at nanomolar concentrations [5,72,73]. These cardiovascular effects may help explain the observed correlation between residential proximity to major roadways and increased incidence of hypertension, atherosclerosis, and other circulatory disorders [74,75,76]. Perhaps most alarmingly, emerging research reveals that TWPs pose significant developmental and reproductive risks [104]. Animal models have conclusively demonstrated the ability of TWP-derived nanoparticles to cross the placental barrier, with exposed offspring exhibiting a markedly higher incidence of low birth weight (a 2.3-fold increase) and various developmental delays [114]. The particles’ endocrine-disrupting properties manifest through their capacity to alter steroid hormone synthesis, interfere with thyroid function, and modify epigenetic markers in germ cells—effects that may have transgenerational consequences [92]. These findings raise particular concern for pregnant women and young children living in urban environments with high traffic density, where TWP exposure levels frequently exceed safety thresholds [61].
The systemic toxicity of TWPs extends to nearly every major organ system through complex and often synergistic mechanisms [118]. Gastrointestinal absorption of particles from contaminated food and water supplies leads to measurable disruptions in gut microbiome composition, with high-exposure groups showing 20–30% reductions in microbial diversity and specific depletion of beneficial Bacteroides species [74]. Neurological studies have documented the ability of TWPs to penetrate the blood–brain barrier in rodent models, where they induce microglial activation and oxidative damage in sensitive hippocampal regions. These findings may explain the growing epidemiological association between air pollution exposure and the risk of neurodegenerative disease [4]. The carcinogenic potential of TWPs stems from both their physical properties and chemical composition, with PAHs, such as benzo[a]pyrene, frequently exceeding WHO safety limits in roadside soils and 6PPD demonstrating acute cytotoxicity to human lymphocytes at minimal concentrations [12,119].
The global health burden attributable to TWP exposure remains underestimated by current risk assessment frameworks [38]. While the World Health Organization estimates that 7–12% of urban particulate-related deaths (approximately 250,000 annually) stem from non-exhaust sources like TWPs, this figure likely represents only the tip of the iceberg [113]. Existing assessments fail to account for chronic low-dose exposure effects, synergistic interactions with other pollutants, and long-latency outcomes such as neurodegeneration or developmental disorders [33]. The true cost of TWP pollution may only become apparent decades after exposure, creating an urgent need for proactive research and intervention strategies [63]. Critical knowledge gaps persist regarding the bioaccumulation kinetics of TWP additives, dose–response relationships for sensitive populations, and effective filtration technologies for indoor environments where people spend the majority of their time [92,93,94,95]. As global vehicle numbers continue their relentless rise, the public health impacts of TWPs will intensify without immediate, coordinated action across scientific, regulatory, and technological domains to address what may become one of the most significant environmental health challenges of our century.
6.4. Synthesis and Critical Discussion of Hazardous Effects
A critical synthesis of the reviewed literature reveals both consensus and ongoing debate regarding the mechanisms and severity of TWP impacts across biological systems [63]. There is broad agreement that TWPs disrupt soil structure, suppress beneficial microbial communities, impair plant health, and pose significant risks to human populations. However, the magnitude and specific pathways of these effects are highly context-dependent and often mechanistically complex [71]. For instance, inconsistencies in reported toxicity thresholds for soil organisms and plants can usually be traced to differences in TWP size, surface chemistry, and degree of environmental ageing, which modulate their bioavailability and interaction with biota [46,103]. Laboratory studies using pristine TWPs frequently report lower toxicity thresholds compared to field studies, where particles are more weathered and may carry co-contaminants, suggesting that environmental transformation processes (e.g., oxidation, aggregation, sorption of metals and organics) play a critical role in modulating hazard [12,20,61]. Mechanistically, TWPs exert their effects through both direct and indirect pathways: physically, by altering soil porosity, compaction, and water retention, and chemically, by leaching metals (notably Zn) and organic additives that disrupt cellular redox balance, enzyme function, and hormonal signalling in both microbes and plants [82,84]. The dual role of certain TWP-derived elements, such as Zn, which can be both essential and toxic depending on concentration and plant species, further complicates risk assessment and management [40]. In humans, the fine and ultrafine fractions of TWPs (PM2.5 and below) are particularly concerning due to their ability to penetrate deep into the lungs, cross biological barriers, and induce systemic oxidative stress and inflammation, mechanisms now linked to respiratory, cardiovascular, and neurodevelopmental disorders [53].
Emerging trends in the literature emphasize the importance of particle characteristics (size, charge, and shape), environmental context (soil type, climate, and co-pollutants), and biological factors (species sensitivity and trophic level) in determining the fate and effects of TWPs [5,69,83]. There is also increasing recognition of the potential for synergistic or antagonistic interactions with other pollutants, as well as the need for standardized, environmentally relevant testing protocols [98]. The current evidence base highlights the need to integrate mechanistic toxicology, environmental chemistry, and real-world exposure assessment to address these uncertainties [75,110]. Only through such interdisciplinary approaches can we accurately predict the long-term ecological and health risks of TWPs and design effective mitigation strategies [17,29]. Despite recent advances, significant knowledge gaps remain. There is a need for long-term field studies to assess the persistence and cumulative impacts of TWPs in diverse soil types and agroecosystems [38,46,56]. Mechanistic research is required to elucidate the pathways by which TWPs interact with soil biota, plants, and food webs, as well as to determine the bioavailability and toxicity of associated chemical additives under realistic environmental conditions [58,75]. Standardized methods for TWP detection, quantification, and toxicity assessment in soils are lacking, which hinders cross-study comparisons and risk evaluation [120]. Furthermore, the effectiveness and feasibility of emerging remediation strategies in real-world agricultural settings remain largely untested. Future research should prioritize integrated, multidisciplinary approaches that link laboratory findings with field observations, develop harmonized analytical protocols, and explore innovative mitigation and policy solutions to safeguard both ecosystem and human health.
7. Remediation Strategies
The persistent and multifaceted threat posed by TWPs has drawn increasing concern due to their ubiquitous distribution and potential toxicity to terrestrial and aquatic biota [45]. TWPs contain complex mixtures of polymers, heavy metals such as Zn, and diverse organic additives that leach into ecosystems upon deposition [121]. Addressing TWP toxicity requires a comprehensive, systems-level approach that encompasses prevention at the source, interception along environmental pathways, and removal or detoxification at affected sites [122]. A growing body of interdisciplinary research is now converging on integrated mitigation frameworks that target not only particle reduction but also limit their environmental fate, transport, and toxicity (Figure 3).
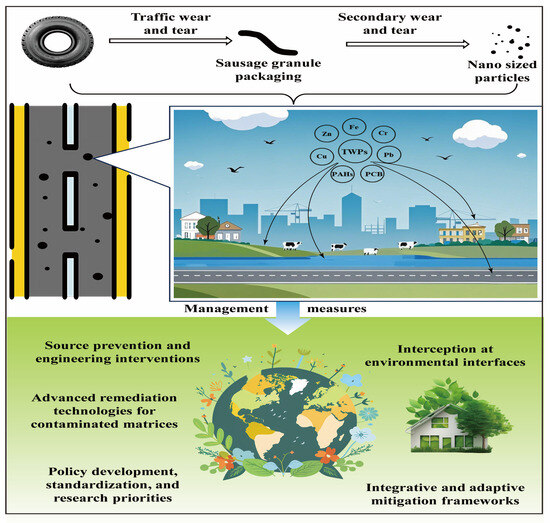
Figure 3.
Environmental impact and management of tyre wear particles (TWPs). The figure highlights the composition of TWPs and associated contaminants (e.g., heavy metals like Fe, Cr, Cu, and Pb, as well as additives such as PAHs and PCBs), their breakdown into nano-sized particles, and comprehensive mitigation strategies including source prevention, advanced remediation, policy measures, and ecosystem-based interception.
7.1. Source Prevention and Engineering Interventions
Preventing the generation of TWPs at their origin remains the most sustainable and cost-effective strategy to mitigate their environmental footprint [123]. Innovations in tyre materials and vehicle design have demonstrated considerable potential in minimizing wear rates [19,20,21]. The integration of advanced tread compounds—such as silica-reinforced elastomers and graphene-enhanced rubber—offers significantly enhanced abrasion resistance, reducing TWP production by up to 40% under laboratory conditions [124]. Moreover, tyre formulations utilizing biobased polymers and non-toxic plasticizers are emerging as promising alternatives, aligning material performance with environmental sustainability [58]. In addition to tyre and vehicle innovations, the choice of road surface material also influences TWP generation. Concrete roads are known to provide greater grip compared to asphalt surfaces, which can increase tyre abrasion and, consequently, TWP production. This highlights the importance of considering road construction materials in holistic mitigation strategies, as optimizing surface composition and texture could help reduce overall TWP emissions. Vehicle-level technologies also contribute to minimizing the formation of TWP. Intelligent tyre pressure monitoring systems, which maintain optimal inflation in real-time, have been shown to reduce uneven wear and prolong tyre life, thereby curbing particle release [61,88,89,90]. However, the widespread adoption of advanced tyre materials and vehicle technologies may be constrained by higher production costs, limited commercial availability, and the need for industry-wide standardization. Consumer acceptance and regulatory incentives will be critical for large-scale implementation. Similarly, the adoption of airless tyre systems and regenerative braking mechanisms diminishes frictional forces that accelerate tread degradation [125]. Electric vehicles (EVs), while presenting higher torque-induced wear, offer opportunities for integrated traction control and energy recovery systems that can be optimized for TWP mitigation [126,127]. From a policy standpoint, regulatory initiatives mandating tyre composition disclosures and encouraging low-emission product labelling can further incentivize manufacturers to prioritize environmentally benign designs [128]. Concurrently, promoting public awareness and behavioural shifts, such as smoother driving, proper vehicle maintenance, and timely tyre replacement, could contribute substantially to emission reduction at scale.
7.2. Interception at Environmental Interfaces
Despite preventive efforts, a considerable fraction of TWPs inevitably enter the environment, particularly through roadway runoff and atmospheric dispersion [51]. To arrest their migration into sensitive ecosystems, interception strategies targeting the interface between roads and the environment have gained prominence [129]. Engineered roadside infrastructure, including bioswales, vegetated buffer strips, and permeable pavements, plays a crucial role in physically trapping particulate matter [130]. Studies have reported capture efficiencies ranging from 60 to 80% for particles larger than 50 µm, particularly when systems incorporate subsurface filtration layers and sorptive media [131]. Innovative materials are enhancing these interception systems. For instance, mycelium-amended bioswales and biochar-infused substrates exhibit dual functionality by not only filtering particulates but also degrading associated organic contaminants through microbial and oxidative mechanisms [132]. Magnetic barriers and sedimentation basins further exploit the inherent ferrous content of TWPs, enabling passive separation via magnetic attraction or gravitational settling [132]. These systems, when integrated into urban stormwater management networks, act as critical control points to reduce particle loading into downstream water bodies [133]. On the atmospheric front, automated street-sweeping technologies equipped with advanced particle classifiers have shown promise in selectively targeting and removing deposited TWPs from road surfaces [134]. Despite their effectiveness, interception measures often require significant infrastructure investment, regular maintenance, and adaptation to local conditions. Their efficiency can vary with particle size, weather conditions, and urban design, potentially limiting their universal applicability. These interventions, though logistically demanding, are particularly effective in high-traffic urban corridors and industrial zones where ambient TWP concentrations are elevated.
7.3. Advanced Remediation Technologies for Contaminated Matrices
In scenarios where TWPs have already accumulated within environmental compartments, active remediation becomes necessary [135]. A suite of physical, chemical, and biological technologies is being developed to remediate TWP-contaminated soils and aquatic systems, with a particular focus on particle removal and detoxification of associated contaminants [136]. Electrokinetic remediation has emerged as a powerful technique for mobilizing and extracting TWPs from fine-grained soils [31,32,33,34]. This process involves applying an electric field across contaminated matrices, facilitating the directional migration of charged particles, which can then be captured or neutralized [132]. Reported removal efficiencies exceed 85%, making it a viable option for hotspot remediation [92]. Bioremediation techniques, particularly mycoremediation, harness the degradative capabilities of white-rot fungi, such as Phanerochaete chrysosporium L., to break down recalcitrant rubber polymers and associated PAHs [112]. These fungi secrete extracellular oxidative enzymes, including laccases and peroxidases, capable of fragmenting complex tyre-derived organics into less toxic byproducts [137]. The use of genetically engineered microbial strains, such as Zn-resistant Pseudomonas spp., further offers the potential for sequestering and detoxifying metal constituents within TWP matrices [48]. In aquatic environments, flotation techniques enhanced with nanobubble generation have demonstrated exceptional removal efficiencies [138]. By modifying surface tension and enhancing particle–bubble interactions, nanobubbles facilitate the rise and separation of TWPs from water columns with up to 95% efficiency [28]. Nevertheless, many advanced remediation technologies remain at the pilot or laboratory scale, with challenges including high operational costs, technical complexity, and potential secondary environmental impacts such as energy use or byproduct generation. Field-scale validation and cost–benefit analyses are needed to assess their practical feasibility. Membrane filtration, though currently limited by fouling and cost, is also under development for tertiary treatment applications in wastewater facilities [139].
7.4. Integrative and Adaptive Mitigation Frameworks
Due to the diverse physicochemical characteristics of TWPs and their dispersion across multiple environmental media, no singular strategy can offer universal efficacy [140]. Consequently, integrative approaches that combine multiple control points—from source prevention to environmental remediation—are essential for holistic mitigation [141]. Tailoring these interventions to site-specific conditions, such as traffic density, land use, and hydrology, can optimize outcomes [142]. For instance, a comprehensive mitigation scheme in urban areas might incorporate low-emission tyres, intelligent transport systems to reduce congestion, permeable road surfaces to intercept particles, and downstream treatment wetlands to polish runoff [143]. In industrial or port regions with high vehicular loads, integrating electrokinetic remediation with periodic street cleaning and magnetic separation may be more appropriate. The rise in electric and autonomous vehicles further underscores the need for dynamic strategies [17,21,22,23]. While heavier EVs may increase per-mile tyre wear, autonomous driving systems offer the potential to regulate acceleration and braking patterns, thereby minimizing abrupt tyre wear events [144]. These shifts highlight the importance of anticipating future mobility trends within TWP mitigation frameworks [103,114,115,116].
7.5. Policy Development, Standardization, and Research Priorities
Robust policy mechanisms and targeted research support are critical for mainstreaming TWP mitigation technologies. Currently, the lack of standardized methodologies for TWP quantification and toxicity assessment hinders cross-study comparisons and regulatory action [20,41,42,144]. For example, a recent inter-laboratory study by Tariq et al. [145] demonstrated that harmonized protocols for TWP sampling and analysis can reduce measurement variability by up to 30%, underscoring the need for urgent standardization. Establishing harmonized protocols for particle sampling, characterization, and toxicity testing is essential to inform evidence-based policy development and effective regulation [146]. Several real-world policy initiatives illustrate growing regulatory attention to TWP pollution. The European Union’s “Zero Pollution Action Plan” aims to reduce microplastic pollution, including emissions from tyre and road wear, by 30% by 2030, with specific measures targeting these sources [147]. In California, the Department of Toxic Substances Control has proposed regulations requiring tyre manufacturers to evaluate and potentially replace 6PPD, a tyre additive linked to aquatic toxicity [131]. Japan has implemented national standards for particulate matter from non-exhaust sources, including TWPs, within its broader air quality management framework [17]. Additionally, the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) has called for international cooperation to address microplastic pollution from tyre wear through global monitoring and best practice guidelines [10,11,12]. Research priorities should focus on real-world validation of emerging technologies. Pilot-scale trials of bioengineered filtration systems, for instance, have shown 60–80% TWP capture efficiency in urban stormwater runoff [145]. Long-term monitoring studies, such as those conducted in the Rhine River basin, have documented a 25% reduction in TWP concentrations following the implementation of green infrastructure and permeable pavements [146]. Particular emphasis should be placed on understanding the degradation pathways of TWP constituents, their bioaccumulation potential, and chronic toxicity effects on sentinel organisms [5,72,73]. Furthermore, life cycle assessments (LCAs) of remediation technologies are increasingly being used to ensure interventions do not introduce secondary environmental burdens. For example, a comparative LCA by Kim et al. [17] found that myco-remediation approaches had 40% lower greenhouse gas emissions and energy consumption compared to conventional chemical treatments. Policymakers can accelerate progress by mandating TWP monitoring in urban planning projects, incentivizing the development of green infrastructure, and supporting public–private partnerships for technological innovation [103,114,115,116]. International collaboration is also essential, as demonstrated by the EU’s “Zero Pollution Action Plan”, which sets a target to reduce microplastic pollution, including TWPs, by 30% by 2030 [129]. Such coordinated efforts are crucial given the transboundary nature and global prevalence of TWP pollution [31,32,33].
Addressing the environmental and health risks associated with TWP pollution requires a paradigm shift from reactive cleanup to proactive, preventive strategies. Advances in material science, microbial biotechnology, and urban infrastructure design have unlocked a wide array of tools for mitigating TWP generation and toxicity. However, their success depends on the integrated deployment across sectors, continuous investment in research, and supportive policy frameworks. A coordinated, multidisciplinary approach spanning environmental engineering, toxicology, urban planning, and regulatory science is essential to confront this emerging pollutant and safeguard ecological resilience in the face of growing anthropogenic pressures. Ultimately, sustained progress in mitigating TWP pollution will depend on strong collaboration among scientists, policymakers, industry leaders, and the public to ensure that innovative solutions are effectively implemented at local, national, and international levels.
8. Conclusions
TWPs are an emerging environmental pollutant with complex and far-reaching consequences for terrestrial ecosystems and human health. This review highlights that, although significant progress has been made in characterizing TWP sources, environmental pathways, and toxicological mechanisms, critical challenges remain. TWPs persist in soils due to their physicochemical stability and diverse composition, including synthetic polymers, heavy metals, and organic additives, which enables their accumulation and bioactivity across environmental compartments. Current evidence demonstrates that TWPs disrupt soil structure and microbial communities, impair plant growth, and introduce contaminants into food webs, ultimately posing risks to both ecological integrity and public health. Although a range of remediation strategies, such as source reduction, bioengineered filtration, and bioremediation, have been proposed, their field-scale effectiveness and long-term sustainability remain unclear. Future research should prioritize the following: (1) long-term field studies to assess the persistence and cumulative impacts of TWPs in different agroecosystems; (2) development of standardized protocols for TWP detection, quantification, and toxicity assessment in soils and crops; (3) mechanistic investigations into TWP interactions with soil biota and plant systems, including uptake, translocation, and transformation pathways; (4) evaluation of innovative remediation and mitigation technologies under realistic agricultural conditions; and (5) comprehensive risk assessments that integrate ecological, agronomic, and human health endpoints. To address the growing challenge of TWP pollution, coordinated action is urgently needed among researchers, policymakers, industry stakeholders, and the public. Implementing evidence-based policies, advancing interdisciplinary research, and promoting sustainable tyre and road technologies will be essential to mitigate TWP emissions and safeguard environmental and human health.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, F.U.H. and J.C.; methodology, B.D.; software, J.K.; validation, J.K., X.L. and T.L.; formal analysis, J.C.; resources, J.C. and F.U.H.; writing—original draft preparation, J.K., B.D., F.U.H. and H.; writing—review and editing, T.L., P.Z. and J.C., funding acquisition, P.Z. and J.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2024YFD15015051), the Young Scientists Innovation Funds of State Key Laboratory of Black Soils Conservation and Utilization, Northeast Institute of Geography and Agroecology (2023HTDGZ-QN-02), the Science and Technology Development Program of Jilin Province (YDZJ202401498ZYTS).
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding authors, upon reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Li, K.; Su, H.; Xiu, X.; Liu, C.; Hao, W. Tire wear particles in different water environments: Occurrence, behavior, and biological effects, a review and perspectives. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 90574–90594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weyrauch, S.; Seiwert, B.; Voll, M.; Reemtsma, T. Long term biodegradation study on tire and road wear particles and chemicals thereof. Sci. Total Environ. 2025, 975, 179240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, J.; Lv, M.; Zhu, D.; Leifheit, E.F.; Chen, Q.-L.; Wang, Y.-Q.; Chen, L.-X.; Rillig, M.C.; Zhu, Y.-G. Tire wear particles: An emerging threat to soil health. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 53, 239–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, Y.; Abdolahpur Monikh, F.; Jaffer, Y.D.; Mugani, R.; Ionescu, D.; Chen, G.; Yang, J.; Grossart, H. Effects of tire wear particles on freshwater bacterial-fungal community dynamics and subsequent elemental cycles using microcosms. J. Hazard. Mat. 2025, 487, 137062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundel, D.; Wiget, A.; Fliessbach, A.; Bigalke, M.; Weber, C.J. Tracks of travel: Unveiling tire particle concentrations in Swiss cantonal road soils. Microplastics Nanoplastics 2025, 5, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kole, P.J.; Löhr, A.J.; J Van Belleghem, G.A.; J Ragas, A.M. Wear and Tear of Tyres: A Stealthy Source of Microplastics in the Environment. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, S.; Hüffer, T.; Klöckner, P.; Wehrhahn, M.; Hofmann, T.; Reemtsma, T. Tire wear particles in the aquatic environment—A review on generation, analysis, occurrence, fate and effects. Water Res. 2018, 139, 83–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, B.; Wang, X.; Chen, L.A.; Ma, T.; Mendez-Jimenez, D.; Cobb, L.C.; Frederickson, C.; Fang, T.; Hwang, B.; Shiraiwa, M.; et al. Metal contents and size distributions of brake and tire wear particles dispersed in the near-road environment. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 883, 163561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, H.; Sukumaran, V.; Yeo, I.; Shim, K.; Lee, S.; Choi, H.; Ha, S.Y.; Kim, M.; Jung, J.; Lee, J.; et al. Phenotypic toxicity, oxidative response, and transcriptomic deregulation of the rotifer Brachionus plicatilis exposed to a toxic cocktail of tire-wear particle leachate. J. Hazard. Mat. 2022, 438, 129417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hüffer, T.; Wagner, S.; Reemtsma, T.; Hofmann, T. Sorption of organic substances to tire wear materials: Similarities and differences with other types of microplastic. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 113, 392–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azeem, I.; Adeel, M.; Shakoor, N.; Zain, M.; Bibi, H.; Azeem, K.; Li, Y.; Nadeem, M.; Manan, U.; Zhang, P.; et al. Coexposure to tire wear particles and nickel inhibits mung bean yield by reducing nutrient uptake. Environ. Sci. Process Impacts 2024, 26, 832–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castan, S.; Sherman, A.; Peng, R.; Zumstein, M.T.; Wanek, W.; Hüffer, T.; Hofmann, T. Uptake, metabolism, and accumulation of tire wear particle-derived compounds in lettuce. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 168–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolomijeca, A.; Parrott, J.; Khan, H.; Shires, K.; Clarence, S.; Sullivan, C.; Chibwe, L.; Sinton, D.; Rochman, C.M. Increased temperature and turbulence alter the effects of leachates from tire particles on Fathead Minnow (Pimephales promelas). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 1750–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, D.; Biswas, J.K.; Mulla, S.I.; Singh, R.; Shukla, R.; Ahanger, M.A.; Shekhawat, G.S.; Verma, K.K.; Siddiqui, M.W.; Seth, C.S. Micro and nanoplastics pollution: Sources, distribution, uptake in plants, toxicological effects, and innovative remediation strategies for environmental sustainability. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2024, 213, 108795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roubeau Dumont, E.; Gao, X.; Zheng, J.; Macairan, J.; Hernandez, L.; Baesu, A.; Bayen, S.; Robinson, S.; Ghoshal, S.; Tufenkji, N. Unraveling the toxicity of tire wear contamination in three freshwater species: From chemical mixture to nanoparticles. J. Hazard. Mat. 2023, 453, 131402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouredji, A.; Pourchez, J.; Forest, V. Biological effects of Tire and Road Wear Particles (TRWP) assessed by in vitro and in vivo studies—A systematic review. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 894, 164989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.W.; Leifheit, E.F.; Maaß, S.; Rillig, M.C. Time-Dependent Toxicity of Tire Particles on Soil Nematodes. Front. Environ. Sci. 2021, 9, 744668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leifheit, E.F.; Kissener, H.L.; Faltin, E.; Ryo, M.; Rillig, M.C. Tire abrasion particles negatively affect plant growth even at low concentrations and alter soil biogeochemical cycling. Soil Ecol. Lett. 2022, 4, 409–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; Zhou, X.; Su, Y.; Wang, H.; Yu, R.; Zhou, S.; Xu, E.G.; Xing, B. Environmental occurrence, fate, impact, and potential solution of tire microplastics: Similarities and differences with tire wear particles. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 795, 148902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wik, A.; Dave, G. Occurrence and effects of tire wear particles in the environment—A critical review and an initial risk assessment. Environ. Pollut. 2008, 157, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baensch-Baltruschat, B.; Kocher, B.; Kochleus, C.; Stock, F.; Reifferscheid, G. Tyre and road wear particles—A calculation of generation, transport, and release to water and soil with special regard to German roads. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 752, 141939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, J.; Zhu, D.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; Liang, A.; Sun, H.; Chen, Q.; Lassen, S.; Lv, M.; Chen, L. Exposure to heavy metal and antibiotic enriches antibiotic resistant genes on the tire particles in soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 792, 148417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fauser, P.; Tjell, J.; Mosbaek, H.; Pilegaard, K. Tire-tread and bitumen particle concentrations in aerosol and soil samples. Pet. Sci. Technol. 2002, 20, 127–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smolders, E.; Degryse, F. Fate and effect of zinc from tire debris in soil. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2002, 36, 3706–3710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherman, A.; Hämmerle, L.E.; Ben Mordechay, E.; Chefetz, B.; Hüffer, T.; Hofmann, T. Uptake of tire-derived compounds in leafy vegetables and implications for human dietary exposure. Front. Environ. Sci. 2024, 12, 1384506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeb, A.; Liu, W.; Ali, N.; Shi, R.; Lian, Y.; Wang, Q.; Wang, J.; Li, J.; Zheng, Z.; Liu, J.; et al. Integrating metabolomics and high-throughput sequencing to investigate the effects of tire wear particles on mung bean plants and soil microbial communities. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 340, 122872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, L.; Lee, T.; Kim, H.; An, Y. Toxicity assessment of tire particles released from personal mobilities (bicycles, cars, and electric scooters) on soil organisms. J. Hazard. Mat. 2022, 437, 129362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunningham, B.; Harper, B.; Brander, S.; Harper, S. Toxicity of micro and nano tire particles and leachate for model freshwater organisms. J. Hazard. Mat. 2022, 429, 128319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selonen, S.; Dolar, A.; Kokalj, A.J.; Sackey, L.N.; Skalar, T.; Fernandes, V.C.; van Gestel, C.A. Exploring the impacts of microplastics and associated chemicals in the terrestrial environment–Exposure of soil invertebrates to tire particles. Environ. Res. 2021, 201, 111495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baensch-Baltruschat, B.; Kocher, B.; Stock, F.; Reifferscheid, G. Tyre and road wear particles (TRWP)—A review of generation, properties, emissions, human health risk, ecotoxicity, and fate in the environment. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 733, 137823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehner, R.; Weder, C.; Petri-Fink, A.; Rothen-Rutishauser, B. Emergence of nanoplastic in the environment and possible impact on human health. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 1748–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vethaak, A.D.; Leslie, H.A. Plastic debris is a human health issue. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 6825–6826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, S.L.; Kelly, F. Plastic and human health: A micro issue? Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 6634–6647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Councell, T.B.; Duckenfield, K.U.; Landa, E.R.; Callender, E. Tire-wear particles as a source of zinc to the environment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 4206–4214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boots, B.; Russell, C.W.; Green, D.S. Effects of microplastics in soil ecosystems: Above and below ground. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 11496–11506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okoffo, E.D.; O’Brien, S.; Ribeiro, F.; Burrows, S.D.; Toapanta, T.; Rauert, C.; O’Brien, J.W.; Tscharke, B.J.; Wang, X.; Thomas, K.V. Plastic particles in soil: State of the knowledge on sources, occurrence and distribution, analytical methods and ecological impacts. Environ. Sci. Process Impacts 2021, 23, 240–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, F.; Su, Y.; Ji, Y.; Ji, R. Release of zinc and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons from tire crumb rubber and toxicity of leachate to Daphnia magna: Effects of tire source and photoaging. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2021, 107, 651–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattsson, K.; de Lima, J.A.; Wilkinson, T.; Järlskog, I.; Ekstrand, E.; Sköld, Y.A.; Gustafsson, M.; Hassellöv, M. Tyre and road wear particles from source to sea. Micro Nanoplastics 2023, 3, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, X.; Huang, H.; Jiao, R.; Liu, J. Experimental investigation on the characteristics of tire wear particles under different non-vehicle operating parameters. Tribol. Int. 2020, 150, 106354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreider, M.L.; Panko, J.M.; McAtee, B.L.; Sweet, L.I.; Finley, B.L. Physical and chemical characterization of tire-related particles: Comparison of particles generated using different methodologies. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 652–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, I.; Kim, H.; Lee, S. Characteristics of tire wear particles generated in a laboratory simulation of tire/road contact conditions. J. Aerosol Sci. 2018, 124, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panko, J.M.; Hitchcock, K.M.; Fuller, G.W.; Green, D. Evaluation of Tire Wear Contribution to PM2.5 in Urban Environments. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unice, K.M.; Kreider, M.L.; Panko, J.M. Comparison of tire and road wear particle concentrations in sediment for watersheds in France, Japan, and the United States by quantitative pyrolysis GC/MS analysis. Environ. Sci. Tech. 2013, 47, 8138–8147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stephensen, E.; Celander, M.; Hulander, M.; Parkkonen, J.; Hegelund, T.; Sturve, J.; Hasselberg, L.; Bengtsson, M.; Förlin, L. Biomarker responses and chemical analyses in fish indicate leakage of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and other compounds from car tire rubber. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2003, 22, 2926–2931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magni, S.; Tediosi, E.; Maggioni, D.; Sbarberi, R.; Noé, F.; Rossetti, F.; Fornai, D.; Persici, V.; Neri, M.C. Ecological Impact of End-of-Life-Tire (ELT)-Derived Rubbers: Acute and Chronic Effects at Organism and Population Levels. Toxics 2022, 10, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stack, M.; Hollman, K.; Mladenov, N.; Harper, B.; Pinongcos, F.; Sant, K.; Rochman, C.; Richardot, W.; Dodder, N.; Hoh, E. Micron-size tire tread particles leach organic compounds at higher rates than centimeter-size particles: Compound identification and profile comparison. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 334, 122116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, P.M.; Moran, K.D.; Miller, E.L.; Brander, S.M.; Harper, S.; Garcia-Jaramillo, M.; Carrasco-Navarro, V.; Ho, K.T.; Burgess, R.M.; Thornton Hampton, L.M.; et al. Where the rubber meets the road: Emerging environmental impacts of tire wear particles and their chemical cocktails. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 927, 171153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muresan, B.; Truong, X.; De Oliveira, T.; Lumière, L.; Cerezo, V.; Watanabe, N.; Do, M. A study of the direct emission of tire wear particles on different types of roads. Sci. Total Environ. 2025, 958, 178018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunze, M.; Feißel, T.; Ivanov, V.; Bachmann, T.; Hesse, D.; Gramstat, S. Analysis of TRWP Particle Distribution in Urban and Suburban Landscapes, Connecting Real Road Measurements with Particle Distribution Simulation. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Luo, Z.; Yu, R.; Yan, C.; Zhou, S.; Xing, B. Tire wear particles: Trends from bibliometric analysis, environmental distribution with meta-analysis, and implications. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 322, 121150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilliges, R.; Endres, M.; Tifert, A.; Brenner, E.; Marks, T. Characterization of road runoff with regard to seasonal variations, particle size distribution and the correlation of fine particles and pollut-ants. Water Sci. Technol. 2016, 75, 1169–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lundberg, J.; Gustafsson, M.; Janhäll, S.; Eriksson, O.; Blomqvist, G.; Erlingsson, S. Temporal Variation of Road Dust Load and Its Size Distribution—A Comparative Study of a Porous and a Dense Pavement. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2020, 231, 561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fussell, J.C.; Franklin, M.; Green, D.C.; Gustafsson, M.; Harrison, R.M.; Hicks, W.; Kelly, F.J.; Kishta, F.; Miller, M.R.; Mudway, I.S.; et al. A review of road traffic-derived non-exhaust particles: Emissions, physicochemical characteristics, health risks, and mitigation measures. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 6813–6835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Yang, H.; Wu, Y.; Pu, Q.; He, W.; Li, X. A review of tire wear particles: Occurrence, adverse effects, and control strategies. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 283, 116782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Zhang, M.; Ge, Y.; Wen, Y.; Luo, J.; Yin, D.; Wang, C.; Wang, C. Emission Characteristics of Tyre Wear Particles from Light-Duty Vehicles. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Wang, L.; Wang, R.; Jiang, W.; Du, L.; Huang, H.; Zhang, L.; Ding, Y. Fresh tire wear particles from moving vehicles: Dispersion dynamics, exposure, and prevention strategy. Emerg. Contam. 2025, 11, 100503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, S.; Cui, Y.; Brahney, J.; Mahowald, N.M.; Li, Q. Long-distance atmospheric transport of microplastic fibres influenced by their shapes. Nat. Geosci. 2023, 16, 863–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samara, C.; Voutsa, D. Size distribution of airborne particulate matter and associated heavy metals in the roadside environment. Chemosphere 2005, 59, 1197–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scerri, M.M.; Weinbruch, S.; Delmaire, G.; Mercieca, N.; Nolle, M.; Prati, P.; Massabò, D. Exhaust and non-exhaust contributions from road transport to PM10 at a Southern European traffic site. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 316, 120569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jandacka, D.; Durcanska, D.; Cibula, R. Concentration and inorganic elemental analysis of particulate matter in a road tunnel environment (Žilina, Slovakia): Contribution of non-exhaust sources. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 952577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torreggiani, G.; Manfrin, C.; Giglio, A.; Dissegna, A.; Chiandetti, C.; Giotta, P.; Renzi, M.; Anselmi, S.; Bentivoglio, T.; Babczyńska, A.; et al. The Effect of Tyre and Road Wear Particles on the Terrestrial Isopod Armadillidium pallasii. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mun, S.; Chong, H.; Lim, Y.; Kwon, S. Chemical Assessment of Real Driving Tire and Road Wear Particles in Urban and Suburban Seoul, Korea. Sustainability 2023, 16, 10395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, T.; Kim, H. An Experimental Study on the Component Analysis and Variation in Concentration of Tire and Road Wear Particles Collected from the Roadside. Sustainability 2022, 15, 12815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neukirchen, C.; Saraji-Bozorgzad, M.R.; Mäder, M.; Mudan, A.P.; Czasch, P.; Becker, J.; Di Bucchianico, S.; Trapp, C.; Zimmermann, R.; Adam, T. Comprehensive elemental and physical characterization of vehicle brake wear emissions from two different brake pads following the Global Technical Regulation methodology. J. Hazard. Mat. 2025, 482, 136609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seinfeld, J.H.; Bretherton, C.; Carslaw, K.S.; Coe, H.; DeMott, P.J.; Dunlea, E.J.; Feingold, G.; Ghan, S.; Guenther, A.B.; Kahn, R.; et al. Improving our fundamental understanding of the role of aerosol−cloud interactions in the climate system. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 5781–5790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolan, S.; Padhye, L.P.; Jasemizad, T.; Govarthanan, M.; Karmegam, N.; Wijesekara, H.; Amarasiri, D.; Hou, D.; Zhou, P.; Biswal, B.K.; et al. Impacts of climate change on the fate of contaminants through extreme weather events. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 909, 168388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Gao, T.; Kang, S.; Shi, H.; Mai, L.; Allen, D.; Allen, S. Current status and future perspectives of microplastic pollution in typical cryospheric regions. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2022, 226, 103924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wang, B.; Cui, P.; Ma, Y.; Wang, Y.; Hao, J.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Sun, L.; Wang, J.; et al. Disaster effects of climate change in High Mountain Asia: State of art and scientific challenges. Adv. Climate Change Res. 2024, 15, 367–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Sun, B.; Li, J. Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Sediments/Soils of the Rapidly Urbanized Lower Reaches of the River Chaohu, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 2302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zehetner, F.; Rosenfellner, U.; Mentler, A.; Gerzabek, M.H. Distribution of Road Salt Residues, Heavy Metals and Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons across a Highway-Forest Interface. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2009, 198, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamis, J.E.; Koelmans, A.A.; Dröge, R.; Kaag, N.H.; Keur, M.C.; Tromp, P.C.; Jongbloed, R.H. Environmental risks of car tire microplastic particles and other road runoff pollutants. Microplastics Nanoplastics 2021, 1, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Österlund, H.; Blecken, G.; Lange, K.; Marsalek, J.; Gopinath, K.; Viklander, M. Microplastics in urban catchments: Review of sources, pathways, and entry into stormwater. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 858, 159781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cremades, L.V.; Muñoz, A.; Gómez, M.E. Proposed Index for Assigning an Environmental Label to Passenger Cars. Sustainability 2023, 16, 7195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, M.E.; Harper, B.J.; Harper, S.L. Comparative Toxicity of Micro, Nano, and Leachate Fractions of Three Rubber Materials to Freshwater Species: Zebrafish and Daphnia. Microplastics 2025, 4, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampalo, M.; Gómez, M.; Almeda, R. Impact of tire particle leachates on microplankton communities in the Canary Islands. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2025, 291, 117787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, H.; Sablani, S.S.; Wu, Q. Recycling Functional Fillers from Waste Tires for Tailored Polystyrene Composites: Mechanical, Fire Retarding, Electromagnetic Field Shielding, and Acoustic Insulation Properties—A Short Review. Materials 2024, 17, 2675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roubeau Dumont, E.; Gagné, F. Nanoplastic Contamination in Freshwater Biofilms Using Gel Permeation Chromatography and Plasmonic Nanogold Sensor Approaches. Nanomaterials 2023, 14, 1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Przekop, R.E.; Sztorch, B.; Pakuła, D.; Konieczna, R.; Frydrych, M. Micro- and Nano-Pollutants from Tires and Car Brakes Generated in the Winter Season in the Poznan City Urban Environment. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 4235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagné, F.; André, C.; Auclair, J. Micro and Nanoplastic Contamination and Its Effects on Freshwater Mussels Caged in an Urban Area. J. Xenobiotics 2023, 13, 761–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdi, A.; Naseri, M. Effects of tire wear particles on the water retention of soils with different textures in the full moisture range. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2024, 264, 104345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, I.R.W.; Raj, A.S.; Viaroli, S. Microplastic removal, identification and characterization in Chennai sewage treatment plants. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 380, 125120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weinbruch, S.; Matthies, J.; Zou, L.; Kandler, K.; Ebert, M.; Bigalke, M. Deposition rates and air concentrations of tire and road wear particles near a motorway in Germany. Atmos. Environ. 2025, 352, 121228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Xu, Y.; Bi, M.; Li, H.; Li, G.; Rillig, M.C. Soil properties explain the variability in tire wear particle effects in soil based on a laboratory test with 59 soils. Environ. Pollut. 2025, 375, 126271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.; Pan, H.; Zhang, T.; Cao, L.; Wang, Y. The Dynamics of Soil Macropores and Hydraulic Conductivity as Influenced by the Fibrous and Tap Root Systems. Agriculture 2024, 14, 1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochman, C.M. Microplastics research-from sink to source. Science 2018, 360, 28–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, J.S.; Tiwari, S.K. The impact of end-of-life tires on the mechanical properties of fine-grained soil: A review. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2019, 21, 485–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redondo-Hasselerharm, P.E.; de Ruijter, V.N.; Mintenig, S.M.; Verschoor, A.; Koelmans, A. Ingestion and chronic effects of car tire tread particles on freshwater benthic macroinvertebrates. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 13986–13994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Shi, T.; Li, X.; Sun, H.; Xia, X.; Ji, X.; Zhang, J.; Liu, M.; Lin, Y.; Zhang, R.; et al. Inhaled tire-wear microplastic particles induced pulmonary fibrotic injury via epithelial cytoskeleton rearrangement. Environ. Int. 2022, 164, 107257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halle, L.L.; Palmqvist, A.; Kampmann, K.; Khan, F.R. Ecotoxicology of micronized tire rubber: Past, present and future considerations. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 706, 135694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michelangeli, M.E.; Brandsma, S.H.; Margalef, M.; Forsman, E.; Kuehr, S.; Spanu, D.; Gomes, T. Chemical leachates from car tyre granulates and PET bottles induce toxic effects on Mytilus edulis haemocytes. Environ. Chem. Ecotoxicol. 2024, 7, 776–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Souza Machado, A.A.; Lau, C.W.; Till, J.; Kloas, W.; Lehmann, A.; Becker, R.; Rillig, M.C. Impacts of microplastics on the soil biophysical environment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 9656–9665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calarnou, L.; Traïkia, M.; Leremboure, M.; Malosse, L.; Dronet, S.; Delort, A.; Besse-Hoggan, P.; Eyheraguibel, B. Assessing biodegradation of roadway particles via complementary mass spectrometry and NMR analyses. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 900, 165698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Broekhuizen, P.; Säämänen, A.; Schuurbiers, D.; Isigonis, P.; Jensen, K.A.; Kühnel, D.; Le Blansch, K. Tyre wear nanoparticles as test for a nano risk governance framework. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 1045246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, H.; He, W.; Sun, P.; Zhao, W.; Liu, M. Exploring the Potential Hormonal Effects of Tire Polymers (TPs) on Different Species Based on a Theoretical Computational Approach. Polymers 2022, 15, 1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linh, D.V.; Huong, N.L.; Tabata, M.; Imai, S.; Iijima, S.; Kasai, D.; Anh, T.K.; Fukuda, M. Characterization and functional expression of a rubber degradation gene of a Nocardia degrader from a rubber-processing factory. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2017, 123, 412–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoshgoftarmanesh, A.H.; Behzadan, H.Z.; SanaeiOstovar, A.; Chaney, R.L. Bacterial inoculation speeds zinc release from ground tire rubber used as Zn fertilizer for corn and sunffower in a calcareous soil. Plant Soil 2012, 361, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhodes, E.; Ren, Z.; Mays, D. Zinc leaching from tire crumb rubber. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 12856–12863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pochron, S.T.; Fiorenza, A.; Sperl, C.; Ledda, B.; Patterson, C.L.; Tucker, C.C.; Panico, N. The response of earthworms (Eisenia fetida) and soil microbes to the crumb rubber material used in artiffcial turf fields. Chemosphere 2017, 173, 557–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pochron, S.; Nikakis, J.; Illuzzi, K.; Baatz, A.; Demirciyan, L.; Dhillon, A.; Vaughan, D. Exposure to aged crumb rubber reduces survival time during a stress test in earthworms (Eisenia fetida). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 11376–11383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camponelli, K.M.; Casey, R.E.; Snodgrass, J.W.; Lev, S.M.; Landa, E.R. Impacts of weathered tire debris on the development of Rana sylvatica larvae. Chemosphere 2009, 74, 717–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.W.; Xu, Y.; Meidl, P.; Bi, M.; Zhu, Y.; Rillig, M.C. Soil storage conditions alter the effects of tire wear particles on microbial activities in laboratory tests. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2022, 9, 1037–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Zhu, D.; Wang, H.-T.; Lassen, S.B.; Chen, Q.; Li, G.; Lv, M.; Zhu, Y.-G. Dysbiosis in the gut microbiota of soil fauna explains the toxicity of tire tread particles. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 7450–7460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Sui, Y.; Haider, F.U.; Li, S.; Mu, P.; Zhang, P.; Wang, B.; Liu, T.; Lin, T.; Li, X. Tire wear particles (TWPs) induced toxicity in wheat (Triticum aestivum) by affecting osmotic regulation, redox homeostasis, photosynthesis, and microbial density. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2025. under review. [Google Scholar]
- Gualtieri, M.; Andrioletti, M.; Vismara, C.; Milani, M.; Camatini, M. Toxicity of tire debris leachates. Environ. Int. 2005, 31, 723–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wik, A.; Nilsson, E.; Källqvist, T.; Tobiesen, A.; Dave, G. Toxicity assessment of sequential leachates of tire powder using a battery of toxicity tests and toxicity identification evaluations. Chemosphere 2009, 77, 922–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menicagli, V.; Balestri, E.; Lardicci, C. Exposure of coastal dune vegetation to plastic bag leachates: A neglected impact of plastic litter. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 683, 737–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capolupo, M.; Sørensen, L.; Jayasena, K.D.R.; Booth, A.M.; Fabbri, E. Chemical composition and ecotoxicity of plastic and car tire rubber leachates to aquatic organisms. Water Res. 2020, 169, 115270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isa, V.; Saliu, F.; Becchi, A.; Spadaccino, G.; Quinto, M.; Veronelli, M.; Lasagni, M.; Galli, P.; Lavorano, S. Impacts of microplastics on reef-building corals: Disentangling the contribution of the chain scission products released by weathering. Sci. Total Environ. 2025, 975, 179239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reay, M.K.; Graf, M.; Murphy, M.; Li, G.; Yan, C.; Bhattacharya, M.; Osbahr, H.; Ma, J.; Chengtao, W.; Shi, X.; et al. Higher potential leaching of inorganic and organic additives from biodegradable compared to conventional agricultural plastic mulch film. J. Hazard. Mat. 2025, 488, 137147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alkio, M.; Tabuchi, T.M.; Wang, X. Stress responses to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in Arabidopsis include growth inhibition and hypersensitive response-like symptoms. J. Exp. Bot. 2005, 56, 2983–2994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chibwe, L.; Parrott, J.L.; Shires, K.; Khan, H.; Clarence, S.; Lavalle, C.; Sullivan, C.; O’Brien, A.M.; De Silva, A.O.; Muir, D.C.; et al. A Deep Dive into the Complex Chemical Mixture and Toxicity of Tire Wear Particle Leachate in Fathead Minnow. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2022, 41, 1144–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sieber, G.; Beisser, D.; Rothenberger, J.L.; Shah, M.; Schumann, M.; Sures, B.; Boenigk, J. Microbial community shifts induced by plastic and zinc as substitutes of tire abrasion. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, X.; Ma, Z.; Zou, Y.; Liu, J.; Hou, J. Investigation on the adsorption and desorption behaviors of heavy metals by tire wear particles with or without UV ageing processes. Environ. Res. 2021, 195, 110858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putar, U.; Turk, K.; Jung, J.; Kim, C.; Kalčíková, G. The dual impact of tire wear microplastics on the growth and ecological interactions of duckweed Lemna minor. Environ. Pollut. 2025, 368, 125681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gopinath, P.M.; Saranya, V.; Vijayakumar, S.; Mythili Meera, M.; Ruprekha, S.; Kunal, R.; Chandrasekaran, N. Assessment on interactive prospectives of nanoplastics with plasma proteins and the toxicological impacts of virgin, coronated and environmentally released-nanoplastics. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pronk, M.E.; Woutersen, M.; Herremans, J.M. Synthetic turf pitches with rubber granulate inffll: Are there health risks for people playing sports on such pitches? J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2020, 30, 567–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halle, L.L.; Palmqvist, A.; Kampmann, K.; Jensen, A.; Hansen, T.; Khan, F.R. Tire wear particle and leachate exposures from a pristine and road-worn tire to Hyalella azteca: Comparison of chemical content and biological effects. Aqua. Toxicol. 2021, 232, 105769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, F.R.; Halle, L.L.; Palmqvist, A. Acute and long-term toxicity of micronized car tire wear particles to Hyalella azteca. Aqua. Toxicol. 2019, 213, 105216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevenson, K.; Stallwood, B.; Hart, A.G. Tire rubber recycling and bioremediation: A review. Biorem. J. 2008, 12, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adachi, K.; Tainosho, Y. Characterization of heavy metal particles embedded in tire dust. Environ. Int. 2004, 30, 1009–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziajahromi, S.; Drapper, D.; Hornbuckle, A.; Rintoul, L.; Leusch, F.D. Microplastic pollution in a stormwater floating treatment wetland: Detection of tyre particles in sediment. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 713, 136356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kupiainen, K.; Denby, B.; Gustafsson, M.; Johansson, C.; Ketzel, M.; Kukkonen, J.; Norman, M.; Pirjola, L.; Bennet, C.; Blomqvist, G.; et al. Road Dust and PM10 in the Nordic Countries: Measures to Reduce Road Dust Emissions from Traffic; Nordic Council of Ministers: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Piscitello, A.; Bianco, C.; Casasso, A.; Sethi, R. Non-exhaust traffic emissions: Sources, characterization, and mitigation measures. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 766, 144440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patil, S.; Bafana, A.; Naoghare, P.K.; Krishnamurthi, K.; Sivanesan, S. Environmental prevalence, fate, impacts, and mitigation of microplastics-a critical review on present understanding and future research scope. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2021, 28, 4951–4974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panko, J.; Kreider, M.; Unice, K. Review of tire wear emissions. In Non-Exhaust Emissions. An Urban Air Quality Problem for Public Health; Amato, F., Ed.; Impact and Mitigation Measures; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; p. 147. [Google Scholar]
- Ozdemir, H. Mitigation impact of roadside trees on fine particle pollution. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 659, 1176–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kupiainen, K.; Stojiljkovic, A.; Paunu, V.V.; Karvosenoja, N.; Karppinen, A.; Kukkonen, J.; Kangas, L.; Kauhaniemi, M.; Denby, B.; Hänninen, O. Characteristics and mitigation of vehicular non-exhaust particle emissions in Nordic conditions. In Air Pollution Modeling and Its Application XXVI; Mensink, C., Gong, W., Hakami, A., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Gabbe, C.J.; Oxlaj, E.; Wang, J. Residential development and near-roadway air pollution: Assessing risk and mitigation in San Jose, California. J. Transp. Health 2019, 13, 78–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuller, M.; Bai, S.; Eisinger, D.; Niemeier, D. Practical mitigation measures for diesel particulate matter: Near-road vegetation barriers. In Contract AQ-04-01: Developing Effective and Quantifiable Air Quality Mitigation Measures; University of California: Davis, CA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- European TRWP Platform, Action Plan For TRWP Mitigation. 2019. Available online: https://www.etrma.org/key-topics/tyre-and-road-wear-particles/ (accessed on 18 February 2020).
- European TRWP Platform, Mitigation Actions—Progress Update. 2020. Available online: https://erticonetwork.com/ertico-presents-clean-mobility-project-to-the-european-trwp-platform/ (accessed on 18 February 2020).
- ETRMA, Workshop on Microplastics from Tyre Wear: Knowledge, Mitigation Measures, and Policy Options—ETRMA. 2020. Available online: https://www.etrma.org/library/workshop-on-microplastics-from-tyre-wear-knowledge-mitigation-measures-and-policy-options/ (accessed on 20 May 2020).
- Barr, B.C.; Andradóttir, H.Ó.; Thorsteinsson, T.; Erlingsson, S. Mitigation of Suspendable Road Dust in a Subpolar, Oceanic Climate. Sustainability 2021, 13, 9607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arias, A.H.; Alfonso, M.B.; Girones, L.; Piccolo, M.C.; Marcovecchio, J.E. Synthetic microfibers and tyre wear particles pollution in aquatic systems: Relevance and mitigation strategies. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 295, 118607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amato, F. (Ed.) Non-Exhaust Emissions. An Urban Air Quality Problem for Public Health. Impact and Mitigation Measures; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- AIRUSE. The Scientific Basis of Street Cleaning Activities as Road Dust Mitigation Measure. AIRUSE LIFE, 30 October 2013.
- Thodhal Yoganandham, S.; Daeho, K.; Heewon, J.; Shen, K.; Jeon, J. Unveiling the environmental impact of tire wear particles and the associated contaminants: A comprehensive review of environmental and health risk. J. Hazard. Mat. 2024, 480, 136155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovochich, M.; Parker, J.A.; Oh, S.C.; Lee, J.P.; Wagner, S.; Reemtsma, T.; Unice, K.M. Characterization of individual tire and road wear particles in environmental road dust, tunnel dust, and sediment. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2021, 8, 1057–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acarer, S. A review of microplastic removal from water and wastewater by membrane technologies. Water Sci. Technol. 2023, 88, 199–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neupert, J.W.; Venghaus, D.; Barjenbruch, M. Measures to Reduce the Discharge of tire Wear into the Environment. Microplastics 2024, 3, 305–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lackner, M.; Branka, M. Microplastics in Farmed Animals—A Review. Microplastics 2024, 3, 559–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neupert, J.W.; Stein, J.; Venghaus, D.; Barjenbruch, M. Tyre Wear Measurements Using the Marker SBR in a Technical Retrofit Sustainable Drainage System (SuDS). Microplastics 2025, 4, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwivedi, Y.K.; Hughes, L.; Baabdullah, A.M.; Ribeiro-Navarrete, S.; Giannakis, M.; Al-Debei, M.M.; Dennehy, D.; Metri, B.; Buhalis, D.; Cheung, C.M.; et al. Metaverse beyond the hype: Multidisciplinary perspectives on emerging challenges, opportunities, and agenda for research, practice and policy. Int. J. Infor. Manag. 2022, 66, 102542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Yu, K.; Zhang, Y.; Du, H.; Sioutas, C.; Wang, Q. Unveiling the mechanism secret of abrasion emissions of particulate matter and microplastics. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tariq, Z.; Williams, I.D.; Cundy, A.B.; Zapata-Restrepo, L.M. A critical review of sampling, extraction and analysis methods for tyre and road wear particles. Environ. Pollut. 2025, 377, 126440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meland, S.; Granheim, G.M.; Rundberget, J.T.; Rødland, E. Screening of tire derived chemicals and tire wear particles in a road tunnel wash water treatment basin. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2024, 11, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; Araminienė, V.; Uogintė, I.; Varnagirytė-Kabašinskienė, I.; Černiauskas, V.; Gudynaitė-Franckevičienė, V.; Džiugys, A.; Davulienė, L.; Misiulis, E.; Davtalab, M.; et al. Evaluating the role of urban green infrastructure in combating traffic-related microplastic pollution. Sci. Tot. Environ. 2025, 983, 179688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).