Can Public Environmental Concern Drive Changes in Residents’ Green Consumption Behavior?
Abstract
1. Introduction
- March 2015: Under the Dome documentary raises awareness of environmental issues related to coal burning.
- March 2017: The 2017 Work Plan for Air Pollution Prevention and Control in the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei Region and surrounding areas was officially released.
- March 2018: Pilot implementation of the household waste classification system begins.
- September 2020: The “dual carbon” targets are officially proposed.
- Data source: Baidu search index; Note: Data visualization using Python 3.13.3
2. Literature Review and Research Hypotheses
2.1. Research on Public Environmental Concern
2.2. Research on Green Consumption
2.3. Critical Review of the Literature
2.4. Influence Mechanism and Research Hypothesis
3. Residents’ Green Consumption Measurement
3.1. Indicator System
3.2. Data Sources
3.3. Calculation Methods
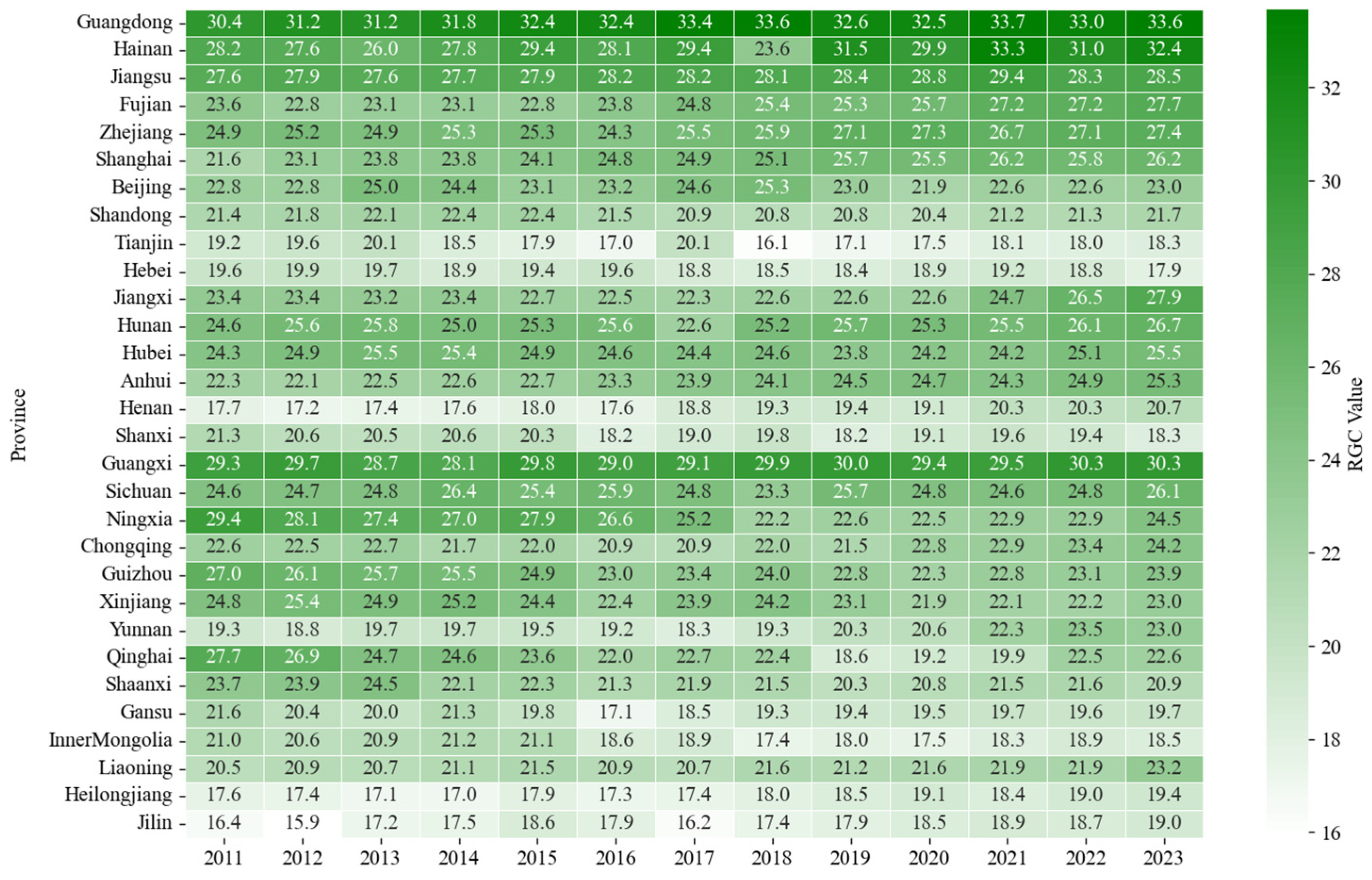
3.4. Current Development of RGC
4. Research Framework
4.1. Model Framework Design
4.2. Variable Selection
4.3. Descriptive Statistics
5. Empirical Results Examination
5.1. Baseline Regression
5.2. Mechanism Analysis
5.3. Robustness Tests
5.3.1. Changing Sample Period
5.3.2. Lagging Independent Variables
5.3.3. Substituting the Independent Variable
5.4. Endogeneity Test
5.5. Heterogeneity Analysis
5.5.1. Regional Heterogeneity
5.5.2. Pollution Emission Heterogeneity
5.5.3. Innovation Foundation Heterogeneity
6. Discussion
7. Conclusion and Recommendations
7.1. Research Conclusion
7.2. Policy Implications
7.3. Limitations and Future Research Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yu, X.; Wang, P. Economic Effects Analysis of Environmental Regulation Policy in the Process of Industrial Structure Upgrading: Evidence from Chinese Provincial Panel Data. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 753, 142004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, M. The Influence of Environmental Regulation on Industrial Structure Upgrading: Based on the Strategic Interaction Behavior of Environmental Regulation among Local Governments. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2021, 170, 120930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, C.; Wang, R.; Gong, X. The Influence of Environmental Cognition on Green Consumption Behavior. Front. Psychol. 2022, 13, 988585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Yu, Z.; Liu, H.; Cai, X.; Zhang, Z. Green Consumption, Environmental Regulation and Carbon Emissions—An Empirical Study Based on a PVAR Model. Sustainability 2024, 16, 1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkington, J.; Hailes, J. The Green Consumer Guide: From Shampoo to Champagne—Highstreet Shopping for a Better Environment; Gollancz: London, UK, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, L.; Keh, H.T.; Chen, J. Assimilating and Differentiating: The Curvilinear Effect of Social Class on Green Consumption. J. Consum. Res. 2021, 47, 914–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, J. The Governance of China, Volume I; Foreign Languages Press: Beijing, China, 2014; p. 101. [Google Scholar]
- Du, W.; Li, M.; Fan, Y.; Liang, S. Can Public Environmental Concern Inhibit the Market Entry of Polluting Firms: Micro Evidence from China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 154, 110528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Xue, Y.; Yang, J. Impact of Environmental Regulations on Green Technological Innovative Behavior: An Empirical Study in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 188, 763–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Environmental Protection Law of the People’s Republic of China (2015 Revision). National People’s Congress. Available online: https://www.mee.gov.cn/ywgz/fgbz/fl/201404/t20140425_271040.shtml (accessed on 28 May 2025).
- General Office of the CPC Central Committee; General Office of the State Council. Guiding Opinions on Building a Modern Environmental Governance System. Available online: https://www.gov.cn/zhengce/2020-03/03/content_5486380.htm (accessed on 30 May 2025).
- Chen, J.; Pan, J.; Xu, Y. Sources of Authoritarian Responsiveness: A Field Experiment in China. Am. J. Political Sci. 2016, 60, 383–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Hong, J.; Rong, J.; Ma, H.; Lv, M.; Wu, M. Impact of Environmental Regulations on High-Quality Development of Energy: From the Perspective of Provincial Differences. Sustainability 2022, 14, 11712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Lin, W.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, H.; Liu, X.; Liu, B. Does the Environment Information Announcement Promote Green Innovation? A Quasi-Natural Experimental Evidence from the City-Level of China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 136, 108720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Yang, G.; Li, X. Correlation between PM2.5 Pollution and Its Public Concern in China: Evidence from Baidu Index. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 293, 126091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Zhu, S. Public Environmental Concerns, Environmental Regulations and Energy-Intensive Industrial Dynamics in China. J. Nat. Resour. 2020, 35, 2744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Ji, X.; Zhang, D.; Yang, J.; Wang, Y. How Public Environmental Concern Affects the Sustainable Development of Chinese Cities: An Empirical Study Using Extended DEA Models. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 251, 109619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, F.; Liu, J.; Zheng, L. The Effects of Public Environmental Concern on Urban-Rural Environmental Inequality: Evidence from Chinese Industrial Enterprises. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2022, 80, 103787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Shi, M.; Liu, J.; Tan, Z. Public Environmental Concern, Government Environmental Regulation and Urban Carbon Emission Reduction—Analyzing the Regulating Role of Green Finance and Industrial Agglomeration. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 924, 171549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Ho, K.C.; Yan, C.; Gozgor, G. Public Environmental Concern, CEO Turnover, and Green Investment: Evidence from a Quasi-Natural Experiment in China. Energy Econ. 2021, 100, 105379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, Z. Will Public Environmental Concerns Foster Green Innovation in China’s Automotive Industry? An Empirical Study Based on Multi-Sourced Data Streams. Front. Energy Res. 2021, 9, 623638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Tang, C.; Liu, Z.; Huang, Y. How Does Public Environmental Supervision Affect the Industrial Structure Optimization? Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 1485–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emekci, S. Green Consumption Behaviours of Consumers within the Scope of TPB. J. Consum. Mark. 2019, 36, 410–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, J.; Modi, A.; Patel, J. Predicting Green Product Consumption Using Theory of Planned Behavior and Reasoned Action. J. Retail. Consum. Serv. 2016, 29, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Guo, S.; Bai, C.; Wang, W. Study on the Impact of Haze Pollution on Residents’ Green Consumption Behavior: The Case of Shandong Province. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 219, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, S.; Salladarré, F.; Brécard, D. Green Consumption and Peer Effects: Does It Work for Seafood Products? Food Policy 2018, 76, 44–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Liu, N.; Zhao, M. Factors and Mechanisms Affecting Green Consumption in China: A Multilevel Analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 209, 481–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akehurst, G.; Afonso, C.; Martins Gonçalves, H. Re-examining Green Purchase Behaviour and the Green Consumer Profile: New Evidences. Manag. Decis. 2012, 50, 972–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, K.; Pang, X. Investigation into the Factors Affecting the Green Consumption Behavior of China Rural Residents in the Context of Dual Carbon. Sustainability 2024, 16, 5797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J. Public Participation in China: The Case for Environmental Enforcement. J. Chin. Gov. 2022, 7, 159–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Sun, Q.; Ma, X. Promotion or Inhibition? Understanding the Impact of Public Environmental Concerns on Energy Transition in China. Energy 2024, 313, 133768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buntaine, M.T.; Greenstone, M.; He, G.; Liu, M.; Wang, S.; Zhang, B. Does the Squeaky Wheel Get More Grease? The Direct and Indirect Effects of Citizen Participation on Environmental Governance in China. Am. Econ. Rev. 2024, 114, 815–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Kuai, Y.; Liu, X. Stock Market Response to Environmental Policies: Evidence from Heavily Polluting Firms in China. Econ. Model. 2020, 86, 306–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Q.; Wan, L.; Wang, S.; Chen, Z.; Li, J.; Wu, J.; Song, M. Will Informal Environmental Regulation Induce Residents to Form a Green Lifestyle? Evidence from China. Energy Econ. 2023, 125, 106835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, Q.; Anders, S.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, L. The Roles of Pollution Concerns and Environmental Knowledge in Making Green Food Choices: Evidence from Chinese Consumers. Food Res. Int. 2020, 130, 108881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordon, W. Brand Green: Mainstream or Forever Niche? Green Alliance: London, UK, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Ajzen, I. The Theory of Planned Behavior. Organ. Behav. Hum. Decis. Process. 1991, 50, 179–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Du, J.; Khan, M.A.S.; Jin, S.; Altaf, M.; Anwar, F.; Sharif, I. Effects of Subjective Norms and Environmental Mechanism on Green Purchase Behavior: An Extended Model of Theory of Planned Behavior. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 779629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, W.; Qu, G.; Zhang, X.; Robert, D. The Impact of Public Participation in Environmental Behavior on Haze Pollution and Public Health in China. Econ. Model. 2021, 98, 319–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.B.; Yang, M.M.; Sun, K.G. Impact of Public Environmental Attention on Environmental Governance of Enterprises and Local Governments. China Popul. Resour. Environ. 2022, 32, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, B.; Böhmelt, T.; Ward, H. Public Opinion and Environmental Policy Output: A Cross-National Analysis of Energy Policies in Europe. Environ. Res. Lett. 2017, 12, 114011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, M.H. Creating Public Value: Strategic Management in Government; Harvard University Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, P.; Song, Y.; Zhang, M. Mediating and Spatial Spillover Effects of Public Participation in Environmental Pollution Governance Mediated via Traditional and New Media. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 342, 118046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, M.E.; van der Linde, C. Toward a New Conception of the Environment-Competitiveness Relationship. J. Econ. Perspect. 1995, 9, 97–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Huang, Z.; Su, Y. New Media Environment, Environmental Regulation and Corporate Green Technology Innovation: Evidence from China. Energy Econ. 2023, 119, 106545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Yao, Z.; Zhong, K. Do Environmental Regulations of Carbon Emissions and Air Pollution Foster Green Technology Innovation: Evidence from China’s Prefecture-Level Cities. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 350, 131537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Ouadghiri, I.; Guesmi, K.; Peillex, J.; Ziegler, A. Public Attention to Environmental Issues and Stock Market Returns. Ecol. Econ. 2021, 180, 106836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Ho, K.-C.; Xia, S.; Yan, C. Do Public Environmental Concerns Promote New Energy Enterprises’ Development? Evidence from a Quasi-Natural Experiment. Energy Econ. 2022, 109, 105967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neu, D.; Saxton, G.D.; Rahaman, A.S. Correction: Social Accountability, Ethics, and the Occupy Wall Street Protests. J. Bus. Ethics 2022, 180, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Ma, X.; Fu, T.; Guan, S. Does Public Concern over Haze Pollution Matter? Evidence from Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 755, 142397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Li, K.; Gao, Y. How the Internet Affects China’s Green Consumption Development: Empirical Research Based on Baidu Index Data. Sustainability 2023, 15, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Fu, Y.; Song, M. Coupling Relationship between Green Production and Green Consumption: Case of the Yangtze River Delta Area. Nat. Resour. Model. 2020, 33, e12239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Z.Q.; Xia, J.C. Green Financial Policies and Green Consumption Development—Based on Green Financial Reform and Innovation Pilot Zones and Composite Control Method. China Bus. Mark. 2023, 8, 101–115. [Google Scholar]
- Suining Development and Reform Commission. Promoting Green Development through Green Consumption: Suining’s Green Consumption Evaluation Index System Passed the Review. Available online: https://sfzggw.suining.gov.cn/xinwen/show/202af0b9f0fe4c2fa188977e17381cc0.html (accessed on 27 May 2025).
- Zhang, G.; Deng, N.; Mou, H.; Zhang, Z.G.; Chen, X. The Impact of the Policy and Behavior of Public Participation on Environmental Governance Performance: Empirical Analysis Based on Provincial Panel Data in China. Energy Policy 2019, 129, 1347–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Ishikawa, M.; Liu, X.; Hamori, S. The Determinants of Citizen Complaints on Environmental Pollution: An Empirical Study from China. J. Clean. Prod. 2011, 19, 1306–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Y.; Liu, L.; Yang, B. Different Types of Environmental Concerns and Heterogeneous Influence on Green Total Factor Productivity: Evidence from Chinese Provincial Data. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 428, 139295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Ren, Y. Public Environmental Concern and Corporate ESG Performance. Financ. Res. Lett. 2024, 61, 104991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Yin, W.; Jin, Y. Analyzing Public Environmental Concerns at the Threshold to Reduce Urban Air Pollution. Sustainability 2023, 15, 15420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Liu, Y.; Yu, X. The Impact of Public Environmental Concern on Environmental Pollution: The Moderating Effect of Government Environmental Regulation. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0290255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, J.; Pan, W. Regional Characteristics and Impact Mechanisms of New Urbanization and Green Development Level in China at the Provincial Level. Econ. Geogr. 2023, 43, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Baron, R.M.; Kenny, D.A. The Moderator–Mediator Variable Distinction in Social Psychological Research: Conceptual, Strategic, and Statistical Considerations. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 1986, 51, 1173–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, P.; Wang, X.; Choi, B.; Huan, X. Green Finance, International Technology Spillover and Green Technology Innovation: A New Perspective of Regional Innovation Capability. Sustainability 2023, 15, 1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhang, S.; Chen, F.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y. Does Chinese Companies’ OFDI Enhance Their Own Green Technology Innovation? Financ. Res. Lett. 2023, 56, 104113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Jiang, J.; Bian, J.; Liu, Y.; Lin, G.; Yin, Y. Are Environmental Regulations Holding Back Industrial Growth? Evidence from China. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 306, 127007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.; Li, X.; Yuan, B.; Li, D.; Chen, X. The Effects of Three Types of Environmental Regulation on Eco-Efficiency: A Cross-Region Analysis in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 173, 245–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, R.; Yuan, Y. Different Types of Environmental Regulations and Heterogeneous Influence on Energy Efficiency in the Industrial Sector: Evidence from Chinese Provincial Data. Energy Policy 2020, 145, 111747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Ai, B.; Li, C.; Pan, X.; Yan, Y. Dynamic Relationship among Environmental Regulation, Technological Innovation and Energy Efficiency Based on Large Scale Provincial Panel Data in China. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2019, 144, 428–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Hunt, A.; Morley, B. The Impact of Heterogeneous Environmental Regulation Tools on Economic Growth: Can Environmental Protection and Economic Growth Be Win-Win? Sustainability 2024, 16, 5585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wu, L.; Hao, L.; Yu, X.; Streimikiene, D. Does the Import of Green Products Encourage Green Technology Innovation? Empirical Evidence from China. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2024, 200, 123137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Wen, J.; Wang, X.-Y.; Ma, J.; Chang, C.-P. Green Innovation, Natural Extreme Events, and Energy Transition: Evidence from Asia-Pacific Economies. Energy Econ. 2023, 121, 106638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.; Li, B.; Zhang, D. ESG Implementation, Public Environmental Concern, and Corporate Green Technology Innovation: Analysis Based on the Background of China’s “Dual Carbon” Targets. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2024, 1–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, X.Y.; Gu, N.H. Does the Establishment of Intellectual Property Model Cities Affect Innovation Quality? J. Financ. Econ. 2021, 47, 49–63. [Google Scholar]
- Blundell, W.; Gowrisankaran, G.; Langer, A. Escalation of Scrutiny: The Gains from Dynamic Enforcement of Environmental Regulations. Am. Econ. Rev. 2020, 110, 2558–2585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wu, S.; Qin, X.; La, M.; Zuo, H. Informal Environment Regulation, Green Technology Innovation and Air Pollution: Quasi-Natural Experiments from Prefectural Cities in China. Sustainability 2022, 14, 6333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Q.; Teo, T.S.H.; Sun, T. Effects of Official and Unofficial Environmental Regulations on Environmental Quality: Evidence from the Yangtze River Economic Belt, China. Environ. Res. 2023, 226, 115667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Long, H.; Zhang, X.; Tan, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Zang, C.; Tu, C. The Interaction Effect between Public Environmental Concern and Air Pollution: Evidence from China. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 391, 136231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zheng, T. Can Dual Pilot Policy of Innovative City and Low Carbon City Promote Green Lifestyle Transformation of Residents? J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 405, 136711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Hu, Z.; Cao, J.; Xu, X. The Impact of Environmental Accountability on Air Pollution: A Public Attention Perspective. Energy Policy 2022, 161, 112733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Wu, S.; Li, G.; Yuan, Y. Explore Public Concerns about Environmental Protection on Sina Weibo: Evidence from Text Mining. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 104067–104085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Primary Indicator | Secondary Indicator | Unit | Indicator Attribute | Weight |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Green manufacturing processes | Fertilizer applied per unit of cultivated and irrigated land | Tons per hectare | − | 0.0993 |
| Per capita solar water heater area in rural areas | Square meters per person | + | 0.1286 | |
| Sulfur dioxide emissions relative to GDP | Tons per RMB 1 billion | − | 0.0438 | |
| Energy consumption intensity | Tons of standard coal per RMB 10,000 | − | 0.0459 | |
| Sustainable lifestyles | Daily energy consumption per person | Tons of standard coal per person | − | 0.0558 |
| Per capita public bus and electric vehicle operations | Vehicles per 10,000 people | + | 0.1189 | |
| Per capita private car ownership | Vehicles per person | − | 0.1154 | |
| Per capita daily water consumption | Liters | − | 0.0810 | |
| Environmental ecosystems | Proportion of household waste subjected to harmless treatment | % | + | 0.0556 |
| Per capita park green space area | Square meters per person | + | 0.0891 | |
| Urban green coverage rate | % | + | 0.1015 | |
| Percentage of GDP spent on energy saving and environmental protection | % | + | 0.0651 |
| Variable | N | Mean | sd | Min | Max | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dependent Variable | RGC | 390 | 3.128 | 0.164 | 2.765 | 3.517 |
| Core Independent Variable | PEC | 390 | 4.577 | 0.431 | 2.878 | 5.372 |
| Control Variables | URB | 390 | −0.519 | 0.194 | −1.049 | −0.110 |
| RES | 390 | 10.09 | 0.443 | 9.043 | 11.35 | |
| GOV | 390 | −1.434 | 0.384 | −2.254 | −0.277 | |
| EDU | 390 | 8.595 | 1.089 | 6.004 | 12.16 | |
| LE | 390 | 12.22 | 0.753 | 9.410 | 15.04 | |
| IND | 390 | 0.228 | 0.386 | −0.640 | 1.739 | |
| Variables | (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | (7) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PEC | 0.107 *** | 0.222 *** | 0.226 *** | 0.307 *** | 0.308 *** | 0.313 *** | 0.261 *** |
| (0.0210) | (0.0764) | (0.0779) | (0.0697) | (0.0697) | (0.0696) | (0.0668) | |
| URB | −1.176 *** | −1.145 *** | −1.311 *** | −1.314 *** | −1.313 *** | −1.287 *** | |
| (0.113) | (0.150) | (0.134) | (0.134) | (0.134) | (0.128) | ||
| RES | −0.0635 | 0.401 ** | 0.458 ** | 0.444 ** | 0.454 ** | ||
| (0.203) | (0.187) | (0.194) | (0.193) | (0.184) | |||
| GOV | 0.473 *** | 0.484 *** | 0.479 *** | 0.350 *** | |||
| (0.0493) | (0.0501) | (0.0501) | (0.0522) | ||||
| EDU | −0.0372 | −0.0404 | −0.0346 | ||||
| (0.0321) | (0.0321) | (0.0305) | |||||
| LE | 0.0169 | 0.0188 * | |||||
| (0.0104) | (0.00994) | ||||||
| IND | 0.219 *** | ||||||
| (0.0360) | |||||||
| Constant | 2.915 *** | 0.773 ** | 1.380 | −2.794 | −3.038 * | −3.103 * | −3.210 * |
| (0.0986) | (0.357) | (1.976) | (1.811) | (1.822) | (1.818) | (1.730) | |
| Time Fixed | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| Region Fixed | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| N | 390 | 390 | 390 | 390 | 390 | 390 | 390 |
| adj. R2 | 0.086 | 0.409 | 0.409 | 0.534 | 0.536 | 0.539 | 0.584 |
| Variables | (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GTI | RGC | CER | RGC | MER | RGC | |
| PEC | 0.203 * | 0.233 *** | 1.133 | 0.258 *** | 0.711 *** | 0.259 *** |
| (0.108) | (0.0811) | (10.79) | (0.0875) | (0.3232) | (0.0915) | |
| GTI | 0.139 *** | |||||
| (0.0364) | ||||||
| CER | 0.00224 *** | |||||
| (0.000647) | ||||||
| MER | 0.00226 *** | |||||
| (0.00106) | ||||||
| Constant | −30.96 *** | 1.020 | −557.6 *** | −2.023 | −470.1 ** | −2.435 |
| (2.364) | (2.551) | (160.2) | (2.263) | (199.4) | (4.739) | |
| Controls | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| Time Fixed | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| Region Fixed | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| N | 390 | 390 | 390 | 390 | 390 | 390 |
| adj. R2 | 0.994 | 0.846 | 0.678 | 0.850 | 0.814 | 0842 |
| Variables | (1) | (2) | (3) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Changing Sample Period | Lagging Independent Variables | Replacing Independent Variable | |
| L.RGC | |||
| PEC | 0.217 *** | ||
| (0.0597) | |||
| L.PEC | 0.221 *** | ||
| (0.0619) | |||
| PEC2 | 0.0624 ** | ||
| (0.0270) | |||
| Constant | 1.961 | −2.745 | 1.252 |
| (1.823) | (1.666) | (1.463) | |
| Controls | YES | YES | YES |
| Time Fixed | YES | YES | YES |
| Region Fixed | YES | YES | YES |
| N | 300 | 360 | 390 |
| adj. R2 | 0.251 | 0.591 | 0.239 |
| AR(1) | |||
| AR(2) | |||
| Hansen Test |
| Variables | (1) SYS-GMM | (2) Add Control Variables | (3) First Stage | (4) Second Stage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RGC | RGC | PEC | RGC | |
| L.RGC | 0.554 *** | |||
| (0.0403) | ||||
| PEC | 0.228 ** | 0.223 ** | 0.7084 *** | |
| (0.0933) | (0.0914) | (0.2488) | ||
| IV | 0.0004 *** | |||
| (0.0001) | ||||
| Constant | −0.0403 | −2.536 | ||
| (0.442) | (4.696) | |||
| Controls | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| Time Fixed | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| Region Fixed | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| N | 360 | 390 | 390 | 390 |
| adj. R2 | 0.844 | |||
| AR (1) | 0.005 | |||
| AR (2) | 0.645 | |||
| Hansen Test | 0.716 | |||
| Kleibergen–Paap LM | 14.34 | |||
| Kleibergen–Paap rk Wald F | 16.23 | |||
| Hansen J | 0.000 |
| Variables | Region | Pollution Emission | Innovation Foundation | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (1) Eastern | (2) Central–Western | (3) High | (4) Low | (5) High | (6) Low | |
| PEC | 0.141 ** | 0.405 *** | 0.276 *** | 0.068 | 0.331 *** | 0.258 *** |
| (0.066) | (0.092) | (0.104) | (0.064) | (0.120) | (0.073) | |
| Constant | −9.692 *** | −2.696 | 4.118 | −3.746 | −2.868 | 3.772 |
| (2.060) | (2.859) | (3.743) | (2.273) | (2.325) | (2.671) | |
| Controls | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| Time Fixed | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| Region Fixed | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| adj. R2 | 0.5420 | 0.6754 | 0.7261 | 0.5103 | 0.4858 | 0.7138 |
| N | 143 | 247 | 195 | 195 | 195 | 195 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, J.; Li, Y.; Wu, T.; Jiang, W. Can Public Environmental Concern Drive Changes in Residents’ Green Consumption Behavior? Sustainability 2025, 17, 5352. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17125352
Zhao J, Li Y, Wu T, Jiang W. Can Public Environmental Concern Drive Changes in Residents’ Green Consumption Behavior? Sustainability. 2025; 17(12):5352. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17125352
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Jing, Yaya Li, Tian Wu, and Wen Jiang. 2025. "Can Public Environmental Concern Drive Changes in Residents’ Green Consumption Behavior?" Sustainability 17, no. 12: 5352. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17125352
APA StyleZhao, J., Li, Y., Wu, T., & Jiang, W. (2025). Can Public Environmental Concern Drive Changes in Residents’ Green Consumption Behavior? Sustainability, 17(12), 5352. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17125352






