Geochemical Characteristics of the Minghuazhen Formation in the Cangdong Sag, Bohai Bay Basin: Implications for Provenance, Paleoclimate, and Hydrocarbon Exploration
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
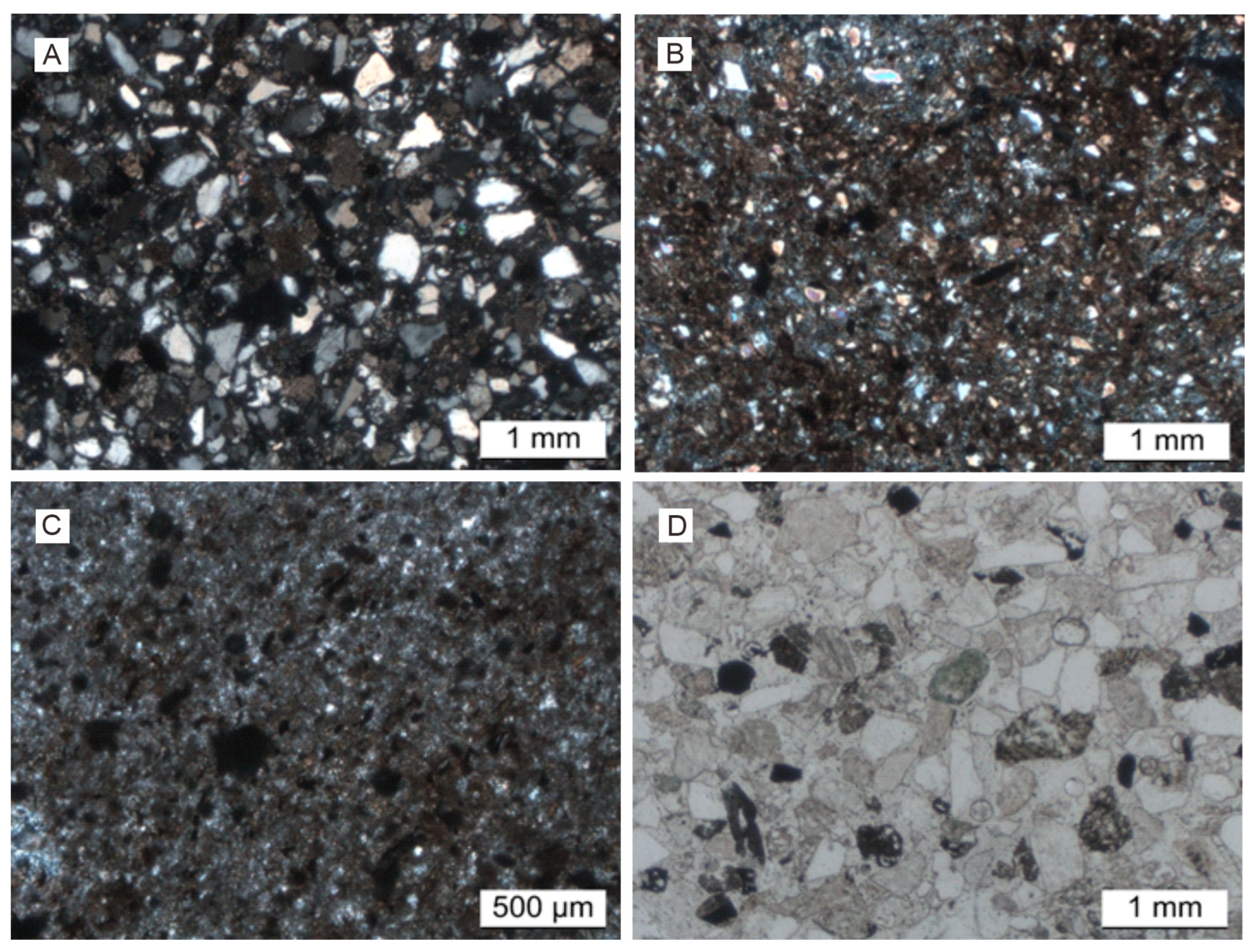
3.1. Petrographic Characteristics of Representative Samples
3.1.1. CZ1-b52: Fine to Medium Sandstone
3.1.2. CZ1-b54: Calcareous Core, Silty Fine Sand with Clay
3.1.3. CZ1-b67: Mudstone
3.1.4. CZ1-b80: Medium Sandstone
3.1.5. Overall Petrographic Characteristics
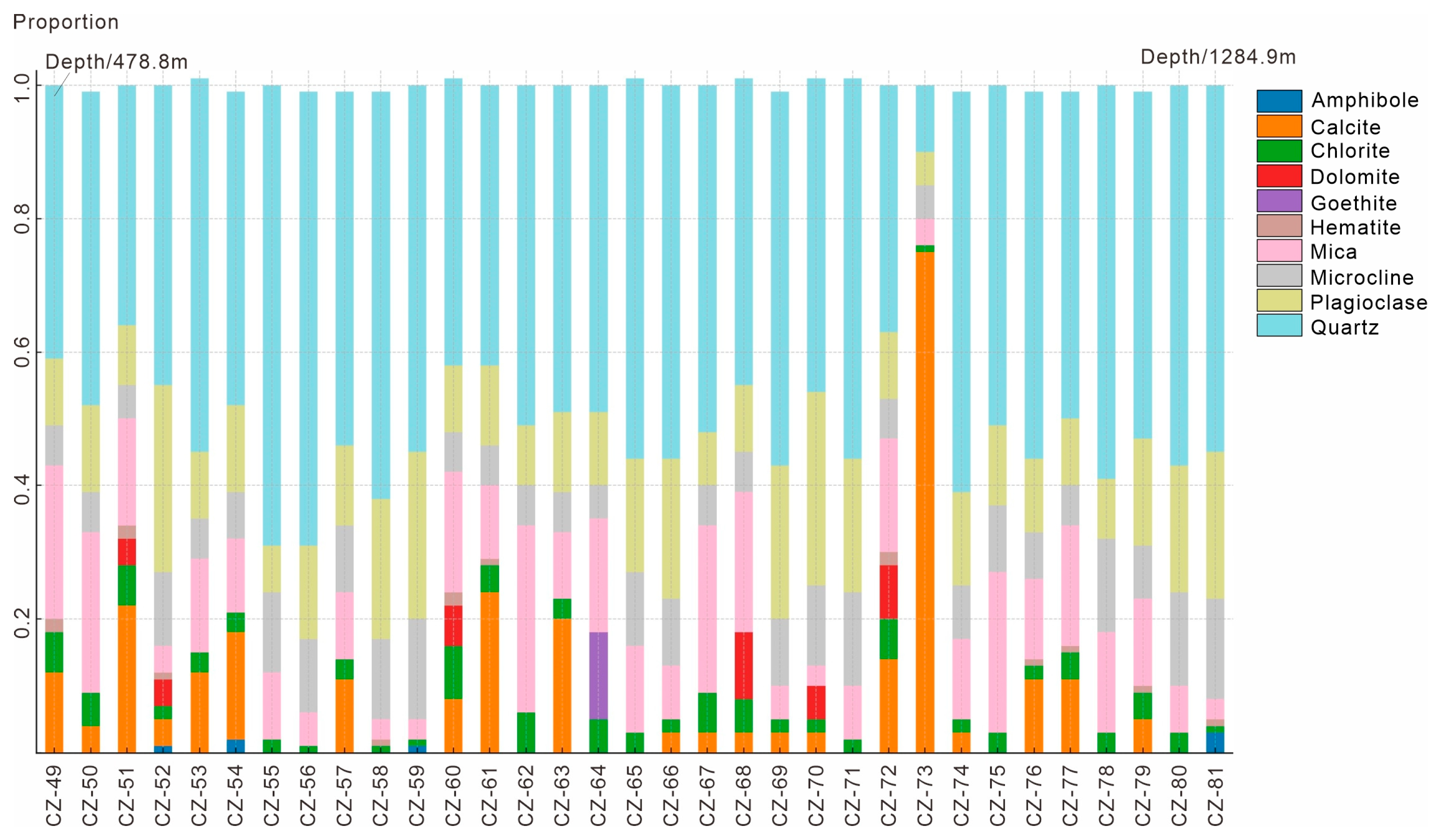
3.2. XRD Analysis
3.3. Major and Trace Elements
3.3.1. Major Element Characteristics
3.3.2. Trace Element Characteristics
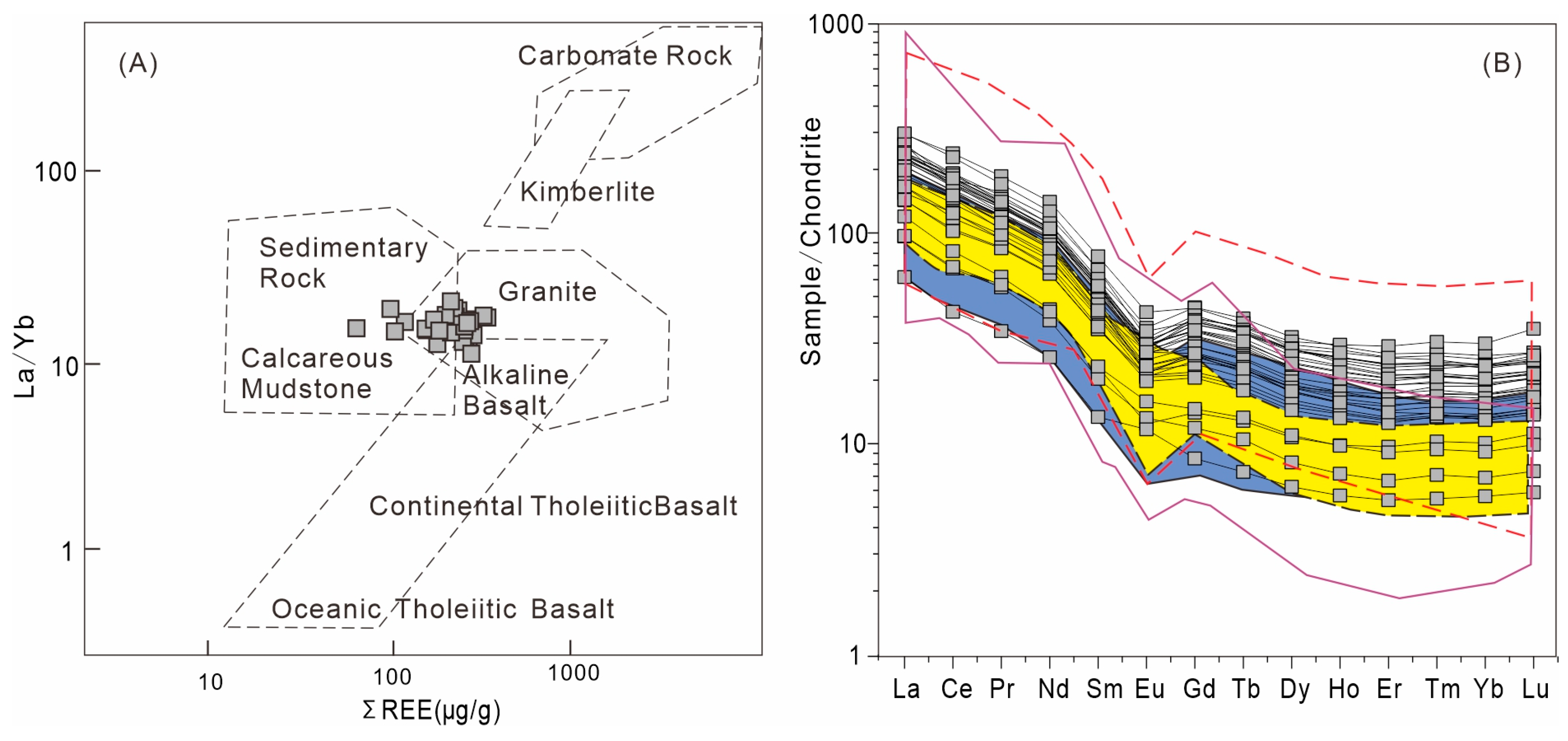
3.3.3. Rare Earth Element Characteristics
4. Discussion
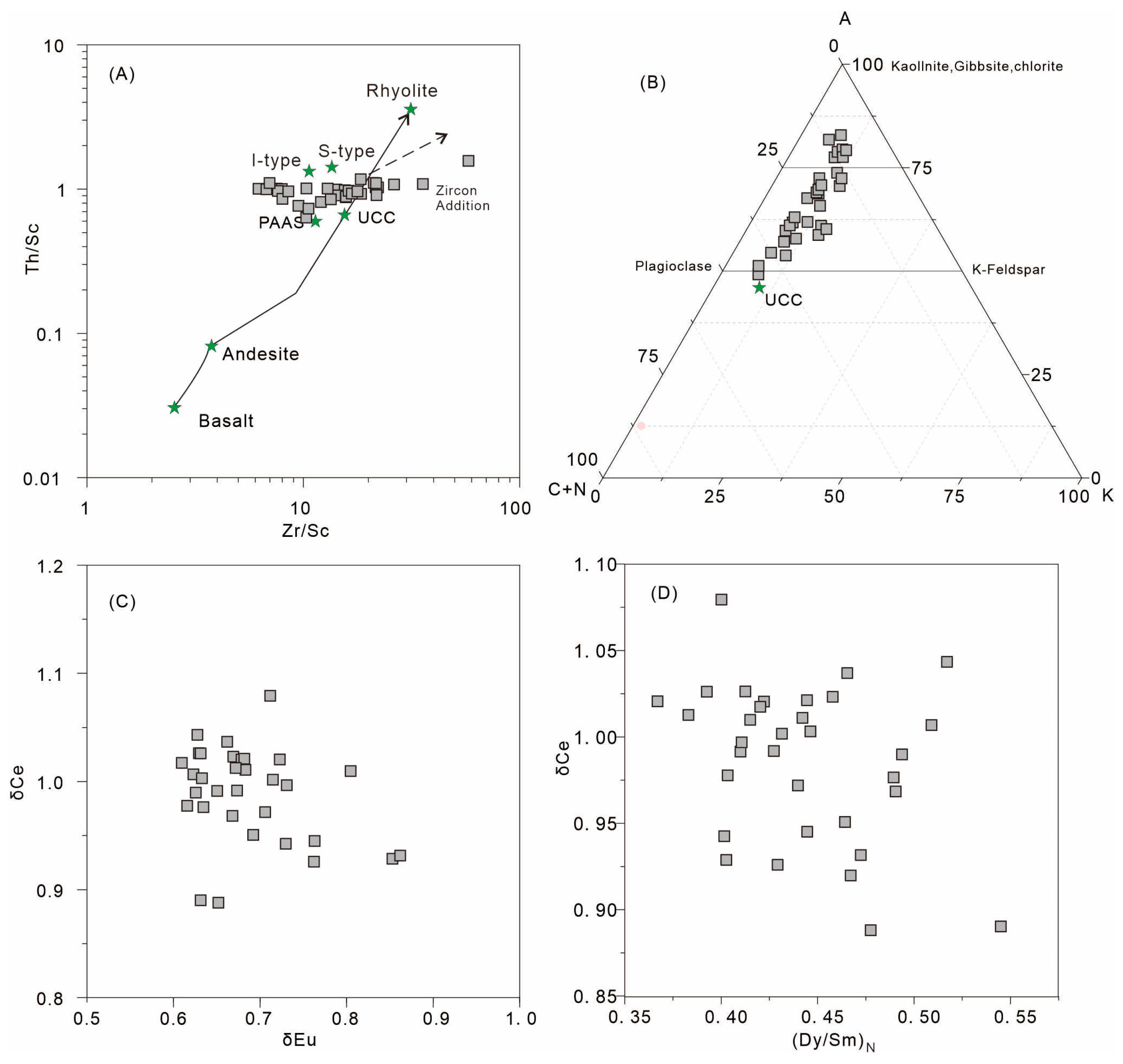
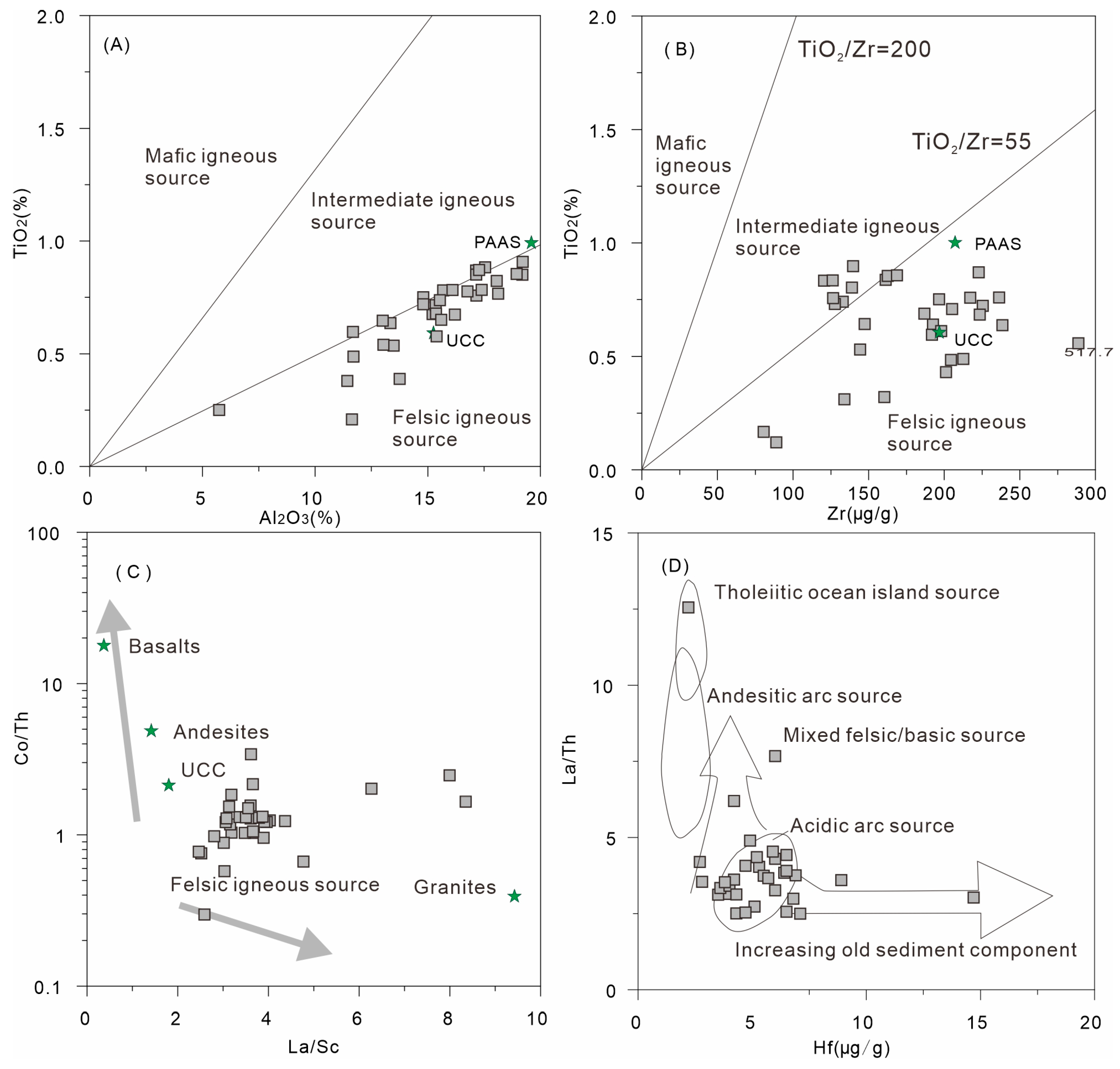
4.1. Provence of the Minghuazhen Formation
4.2. Paleoenvironment Reconstruction
4.2.1. Paleoclimate Characteristics
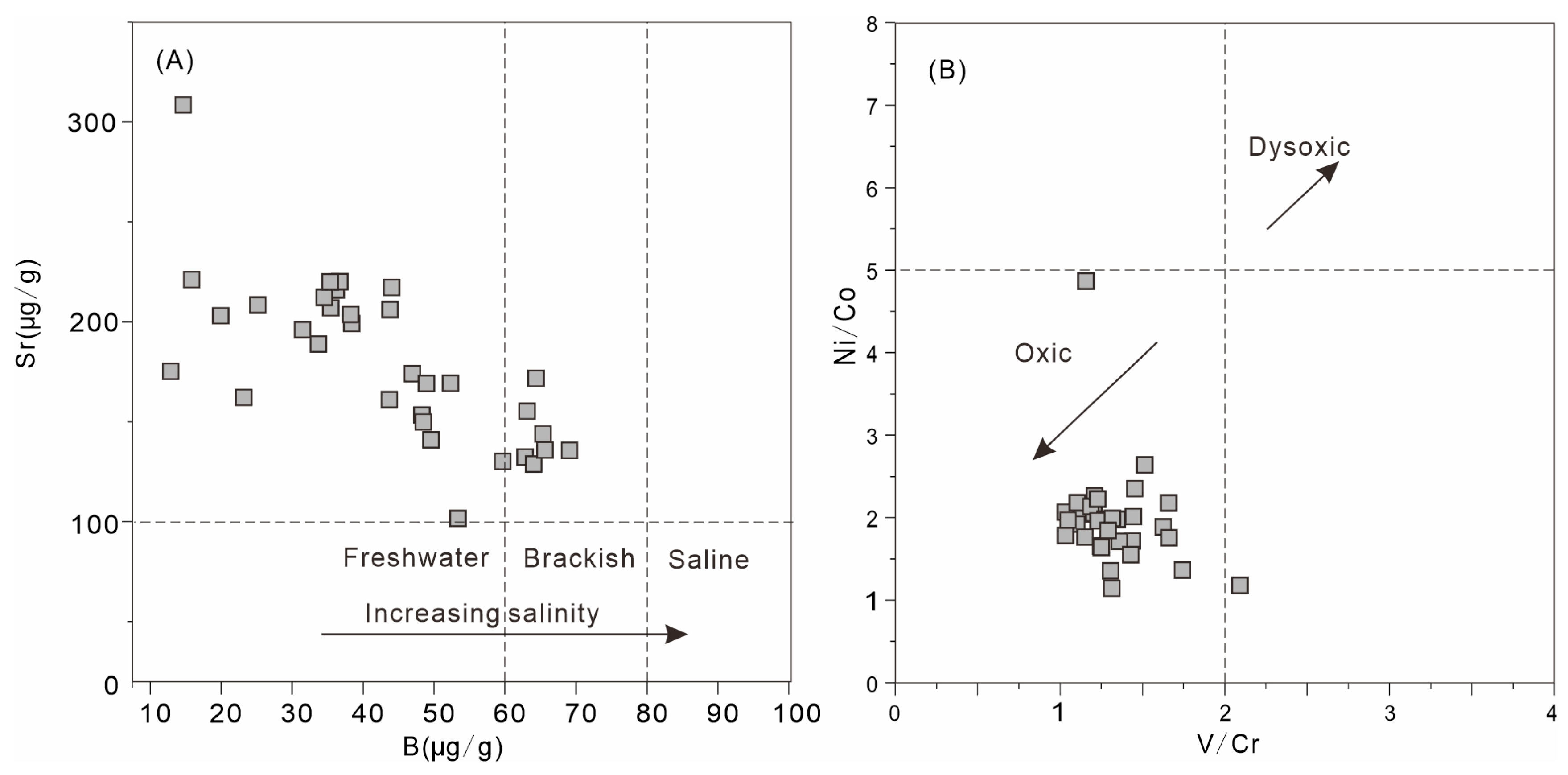
4.2.2. Paleosalinity Characteristics
4.2.3. Redox Conditions
4.3. Paleoclimatic Implications for Hydrocarbon Generation During the Sedimentation of the Minghuazhen Formation in the Cangdong Depression
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Correction Statement
References
- Algeo, T.J.; Hong, H.; Wang, C. The chemical index of alteration (CIA) and interpretation of ACNK diagrams. Chem. Geol. 2025, 671, 122474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Cui, H.; Li, S.; Spicer, R.A.; Li, S.; Su, T.; Zhou, Z.; Witkowski, C.R.; Lauretano, V.; Wei, G. Orbital-paced silicate weathering intensity and climate evolution across the Eocene-Oligocene transition in the southeastern margin of the Tibetan plateau. Glob. Planet. Change 2024, 234, 104388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapolas, A.; Finzel, E.S.; Horkley, L.K.; Peate, D.W. The effects of weathering and sediment source mixing on whole-rock geochemical provenance studies, cook inlet forearc basin, south-central Alaska, USA. GSA Bull. 2024, 136, 4353–4363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Hao, F.; Xu, C.; Zou, H. Paleolimnological environments and the formation of high quality source rocks in the Bohai bay basin: An integrated geochemical study of biomarkers, stable carbon and oxygen isotopes, and trace elements. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2020, 195, 107753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arfaoui, I.; Hamdi, O.; Boulvain, F. Geochemical and mineralogical characterizations of Silurian “hot” shales: Implications for shale gas/oil reservoir potential in Jeffara basin-southeastern Tunisia, north Africa. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2024, 212, 105213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, S.R.; McLennan, S.M. The Continental Crust: Its Composition and Evolution; Blackwell: Oxford, UK, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Nesbitt, H.W.; Young, G.M. Prediction of some weathering trends of plutonic and volcanic rocks based on thermodynamic and kinetic considerations. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1984, 48, 1523–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLennan, S.M.; Hemming, S.; McDaniel, D.K.; Hanson, G.N.; Johnsson, M.J.; Basu, A. Geochemical approaches to sedimentation, provenance, and tectonics. In Special Papers (Geological Society of America); Geological Society of America: Boulder, CO, USA, 1993; Volume 284, pp. 21–40. [Google Scholar]
- Huyan, Y.; Zhang, B.; Wang, X.; Lu, Y.; Liu, F. Geochemistry of the Lancang river (upper Mekong river) overbank sediments: Implications for provenance, weathering and sedimentary characteristics. Appl. Geochem. 2023, 156, 105747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.Q.; Esteban, M. Paleoclimatic controls on sedimentation, diagenesis, and reservoir quality; Lessons from Miocene carbonates. AAPG Bull. 1994, 78, 519–543. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, M.J. Weathering of the primary rock-forming minerals: Processes, products and rates. Clay Miner. 2004, 39, 233–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, R.; Lowe, D.R.; Cullers, R.L. The influence of sediment recycling and basement composition on evolution of mudrock chemistry in southwestern United States. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1995, 59, 1940–2919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Du, Y.; Yu, W.; Algeo, T.J.; Zhou, Q.; Xu, Y.; Qi, L.; Yuan, L.; Pan, W. The chemical index of alteration (CIA) as a proxy for climate change during glacial-interglacial transitions in earth history. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2020, 201, 103032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, R.; Cai, J.; Zeng, X.; Cheng, S. Detrital clay mineral input reconstructed based on weathering records and its influence on organic matter enrichment: A case study of the Paleogene Shahejie formation in the Dongpu sag, Bohai bay basin. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2024, 276, 106360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngia, N.R.; Menkem, E.F.; Fuanya, C.; Agyingi, C.M. Multiproxy analysis of Paleo-redox conditions, Paleo-productivity and organic matter enrichment in cretaceous Mudrocks of bombe-ediki and environs in the Douala sub-basin. Solid Earth Sci. 2025, 10, 100210. [Google Scholar]
- Condie, K.C.; Dengate, J.; Cullers, R.L. Behavior of rare earth elements in a Paleoweathering profile on granodiorite in the front range, Colorado, USA. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1995, 59, 279–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, C.; Mao, L.; Tan, Z.; Zhou, L.; Liu, L. Geochemistry of major and trace elements in sediments from the Lubei plain, China: Constraints for paleoclimate, paleosalinity, and paleoredox environment. J. Asian Earth Sci. X 2021, 6, 100071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, C.; Liu, S.; Liu, W.; Cheng, X.; Liu, X.; Dong, J.; Wang, R.; Li, Y.; Guan, M.; Tian, Q.; et al. Organic matter accumulation driven by land-sea interactions during the late cretaceous: A geochemical study of the Nenjiang formation, Songliao basin. Org. Geochem. 2025, 199, 104901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnamurthy, R.V.; Bhattacharya, S.K.; Kusumgar, S. Palaeoclimatic changes deduced from 13C/12C and C/N ratios of Karewa lake sediments, India. Nature 1986, 323, 150–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyers, P.A.; Ishiwatari, R. Organic Matter Accumulation Records in Lake Sediments. In Physics and Chemistry of Lakes; Lerman, A., Imboden, D.M., Gat, J.R., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1995; pp. 279–328. [Google Scholar]
- Twichell, S.C.; Meyers, P.A.; Diester-Haass, L. Significance of high C/N ratios in organic-carbon-rich Neogene sediments under the Benguela current upwelling system. Org. Geochem. 2002, 33, 715–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tribovillard, N.; Algeo, T.J.; Lyons, T.; Riboulleau, A. Trace metals as paleoredox and paleoproductivity proxies: An update. Chem. Geol. 2006, 232, 12–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, B.; Manning, D.A.C. Comparison of geochemical indices used for the interpretation of palaeoredox conditions in ancient mudstones. Chem. Geol. 1994, 111, 111–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Mao, Z.; Mao, R.; Li, Z.; Guan, Q.; Chen, X. Families of reservoired crude oils from the Cangdong sag, Bohai bay basin, China. Org. Geochem. 2018, 122, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, G.Q.; Yang, J.L.; Zhao, C.R.; Wang, Q.; Xu, Q.M.; Hu, Y.Z.; Qin, Y.F.; Li, J. Magnetostratigraphy of drill hole G2 in the Tianjin coastal area and its tectonic significance. Geol. Bull. China 2014, 33, 1642–1650. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Liu, Y.; Lin, G.; Zhou, Y.; Gong, F.; Zhang, D. REE geochemical characteristics and geological significance of mudstones from Neogene, Nanpu sag, Bohai basin. Geoscience 2006, 20, 449–456. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Liu, K.; Pu, X.; Chen, S.; Han, W.; Zhang, W.; Wang, H.; Liang, C.; Chen, B.; Zhai, M.; et al. Lithofacies characteristics and formation environments of mixed fine-grained sedimentary rocks in second member of Kongdian formation in Cangdong depression, Bohai bay basin. Earth Sci. 2020, 45, 3779–3796. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, W.; Xie, X.; Wang, X. Comparison of results analyzed by Chinese and European laboratories for FOREGS geochemical baselines mapping samples. Geosci. Front. 2011, 2, 247–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Zhang, C.; Xu, Q.; Hu, Y.; Zhou, X.; Xiao, G. Late Miocene geochemical weathering records and significance in the Bohai Bay, eastern China. Acta Geol. Sin. 2024, 99, 976–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesbitt, H.W.; Young, G.M. Early Proterozoic climates and plate motions inferred from major element chemistry of Lutites. Nature 1982, 299, 715–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedo, C.M.; Nesbitt, H.W.; Young, G.M. Unraveling the effects of potassium metasomatism in sedimentary rocks and paleosols, with implications for paleoweathering conditions and provenance. Geology 1995, 23, 921–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudnick, R.L.; Gao, S. Composition of the Continental Crust. In Treatise on Geochemistry, 2nd ed.; Holland, H.D., Turekian, K.K., Eds.; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2014; pp. 1–51. [Google Scholar]
- Haskin, L.A.; Frey, F.A. Dispersed and not-so-rare earths. Science 1966, 152, 299–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, G.M.; Nesbitt, H.W. Paleoclimatology and provenance of the glaciogenic Gowganda formation (paleoproterozoic), Ontario, Canada: A chemostratigraphic approach. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 1999, 111, 264–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, P.; Wang, L.; Wang, C.; Wu, X.; Wei, Y. Organic-matter accumulation of the lacustrine Lunpola oil shale, central Tibetan plateau: Controlled by the paleoclimate, provenance, and drainage system. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2015, 147–148, 58–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huyan, Y.; Yao, W. Geochemical comparisons of weathering, provenance and tectonics in the fluvial sediments from Yarlung zangbo to Brahmaputra river. Catena 2022, 210, 105944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes, L.D.C.; Santos, T.J.S.D.; Gomes, N.B. Geochemistry and provenance of the metasedimentary rocks surrounding the Santa Quitéria magmatic arc, NE Brazil: Tectonic and paleogeographic implications for the assembly of west Gondwana. Precambrian Res. 2021, 356, 106063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasanzu, C.; Maboko, M.A.H.; Manya, S. Geochemistry of fine-grained clastic sedimentary rocks of the Neoproterozoic Ikorongo group, NE Tanzania; Implications for provenance and source rock weathering. Precambrian Res. 2008, 164, 201–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shields, G.; Stille, P. Diagenetic constraints on the use of cerium anomalies as palaeoseawater redox proxies: An isotopic and REE study of Cambrian phosphorites. Chem. Geol. 2001, 175, 29–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wesolowski, D.J. Aluminum speciation and equilibria in aqueous solution: I. The solubility of gibbsite in the system Na-K-Cl-OH-Al(OH)4 from 0 to 100 °C. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1992, 56, 1065–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floyd, P.A.; Leveridge, B.E. Tectonic environment of the Devonian gramscatho basin, south Cornwall: Framework mode and geochemical evidence from turbiditic sandstones. J. Geol. Soc. 1987, 144, 531–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Condie, K.C. Chemical composition and evolution of the upper continental crust: Contrasting results from surface samples and shales. Chem. Geol. 1993, 104, 1–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, K.I.; Fujisawa, H.; Holland, H.D.; Ohmoto, H. Geochemistry of ~1.9 Ga sedimentary rocks from northeastern Labrador, Canada. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1997, 61, 4115–4137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allègre, C.J.; Michard, G. Introduction to Geochemistry, Geophysics and Astrophysics Monographs; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1974. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q. Synergistic Effect of Source and Climate and Its Implications for the Development of Organic-Rich Shale in Typical Hydrocarbonrich Sags in the Bohai Bay Basin; China University of Geosciences: Wuhan, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Hu, R.; Gao, S.; Feng, C.; Qi, L.; Zhong, H.; Xiao, T.; Qi, Y.; Wang, T.; Coulson, I.M. Zircon u–pb geochronology and major, trace elemental and Sr–Nd–Pb isotopic geochemistry of mafic dykes in western Shandong province, east China: Constrains on their petrogenesis and geodynamic significance. Chem. Geol. 2008, 255, 329–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.; Dai, K.; Zhang, C.; Liu, L.; Jing, T.; Li, J.; Zhao, W.; Chen, F. Cenozoic sedimentary archives of a strike-slip fault zone in the Tanhai region, Bohai bay basin, northeastern China. J. Struct. Geol. 2024, 186, 105203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhopadhyay, S.S. Weathering of soil minerals and distribution of elements: Pedochemical aspects1. Clay Res. 2005, 24, 183–199. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, J.; Guo, X.; Wang, Q.; Yan, N.; Wang, J. Geochemistry of REE in QH1 sediments of Qinghai lake since late Holocene and its paleoclimatic significance. J. Lake Sci. 2003, 15, 28–34. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, X.; Zhang, T.; Cheng, Y.; Liu, X.; Hu, P.; Wu, Z. Element geochemical characteristics of the middle—Late Jurassic Microclastic rock in the eastern Junggar basin: Implications for tracing sediment sources and paleoenvironment restoration. Geol. Bull. China 2022, 41, 1950–1966. [Google Scholar]
- Nelson, B.W. Sedimentary phosphate method for estimating paleosalinities. Science 1967, 158, 917–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Jia, J.; Liu, B.; Fu, X.; Li, H.; Xing, J.; Guan, J. Quantitative and comparative analysis of main controlling factors of organic matter enrichment in shallow lake-deep lacustrine shale: A case study of the first member of Qingshankou Formationin Changling sag, Songliao basin. Acta Geol. Sin. 2024, 98, 3773–3787. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, H.; Zheng, R.; Tang, F.; Zheng, A.; Sang, T.; Chen, S.; Li, G.; Li, L. Reconstruction and analysis of paleosalanity and paleoenvironment of the chang 6 member in the gengwan region, ordos basin. J. Mineral. Petrol. 2008, 28, 114–120. [Google Scholar]
- Hatch, J.R.; Leventhal, J.S. Relationship between inferred redox potential of the depositional environment and geochemistry of the upper Pennsylvanian (Missourian) stark shale member of the Dennis limestone, Wabaunsee county, Kansas, U.S.A. Chem. Geol. 1992, 99, 65–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elderfield, H.; Greaves, M.J. The rare earth elements in seawater. Nature 1982, 296, 214–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaller, M.; Ehlers, T. Vegetation and climate effects on soil production, chemical weathering, and physical erosion rates. Earth Surf. Dyn. Discuss. 2021, 2021, 1–26. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Jiang, Z.; Xian, B.; Li, Z.; Wan, J.; Wang, S. The discovery and significance of lacustrine environment-delta in Minghuazhen Formation, Nanpu sag. J. Northeast Pet. Univ. 2013, 37, 18–24. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, D.; Yao, Y.; Han, Y.; Yin, Z.; Zhang, H. Astrostratigraphic research on the Neogene Minghuazhen Formation in Dongying sag, Shandong province. J. Palaeogeogr. 2008, 10, 287–296. [Google Scholar]
- Holtvoeth, J.; Wagner, T.; Schubert, C. Organic matter in river-influenced continental margin sediments: The land-ocean and climate linkage at the late quaternary congo fan (ODP site 1075). Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 2003, 4, 1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| SiO2 | Al2O3 | TFe2O3 | MgO | CaO | Na2O | K2O | CIA | ICV | TC | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Minghuazheng Formation (n = 32) | mean | 61.2 | 15.2 | 6.33 | 1.96 | 4.82 | 1.56 | 2.34 | 67.4 | 1.30 | 0.96 |
| min | 21.5 | 5.73 | 2.20 | 0.761 | 0.685 | 0.435 | 0.785 | 49.2 | 0.49 | 0.04 | |
| max | 76.3 | 19.2 | 32.0 | 3.69 | 38.5 | 3.26 | 3.23 | 78.8 | 7.88 | 8.10 | |
| G 2 borehole in Bohai Bay (n = 573) [29] | min | 35.3 | 9.23 | 1.08 | 0.82 | 0.71 | 0.53 | 1.18 | 50 | / | / |
| max | 74.38 | 25.34 | 27.16 | 4.07 | 23.12 | 3.49 | 3.86 | 88.1 | / | / | |
| UCC | 66.62 | 15.40 | 5.04 | 2.48 | 3.59 | 3.27 | 2.80 | ||||
| B | Co | Cr | Hf | Mn | Nb | Ni | Rb | Sc | Sr | ||
| Minghuazheng Formation | mean | 43.2 | 16.0 | 70.0 | 5.42 | 721.8 | 12.9 | 30.1 | 97.4 | 13.2 | 179.3 |
| min | 12.90 | 3.41 | 15.60 | 2.20 | 137.7 | 5.84 | 12.06 | 33.10 | 4.01 | 101.6 | |
| max | 65.6 | 46.5 | 117.0 | 14.7 | 3699.0 | 18.0 | 63.1 | 134.3 | 20.6 | 308.5 | |
| UCC | 17 | 17.3 | 92 | 5.3 | 774.5 | 12 | 47 | 84 | 14.0 | 320 | |
| Ta | Th | Ti | U | V | Zr | N | P | S | TOC | ||
| Minghuazheng Formation | mean | 1.11 | 12.7 | 4074.5 | 2.54 | 90.2 | 185.8 | 151.6 | 402.8 | 166.1 | 0.10 |
| min | 0.37 | 4.12 | 1251.2 | 1.00 | 27.2 | 80.6 | 27.7 | 99.9 | 48.8 | 0.04 | |
| max | 1.53 | 20.6 | 5448.0 | 6.64 | 191.0 | 517.7 | 302.2 | 744.2 | 1428.3 | 0.49 | |
| UCC | 0.9 | 10.5 | 3835.7 | 2.7 | 97 | 193 | 83 | 654.7 | 621 |
| La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | Y | ΣREE | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CZ-49 | 55.8 | 112 | 13.3 | 48.9 | 8.88 | 1.73 | 8.13 | 1.33 | 7.51 | 1.58 | 4.25 | 0.67 | 4.26 | 0.68 | 43.1 | 312.1 |
| CZ-50 | 60.9 | 117 | 14.2 | 51.6 | 8.78 | 1.57 | 6.99 | 1.10 | 5.87 | 1.18 | 3.28 | 0.53 | 3.61 | 0.56 | 27.8 | 305.4 |
| CZ-51 | 53.6 | 104 | 12.5 | 46.0 | 8.48 | 1.64 | 7.57 | 1.25 | 6.95 | 1.45 | 3.97 | 0.62 | 3.88 | 0.62 | 39.9 | 292.9 |
| CZ-52 | 42.5 | 84.4 | 10.0 | 37.1 | 6.53 | 1.25 | 5.56 | 0.88 | 4.84 | 0.98 | 2.69 | 0.44 | 2.89 | 0.46 | 25.1 | 225.8 |
| CZ-53 | 36.7 | 76.5 | 8.92 | 32.9 | 6.07 | 1.20 | 5.09 | 0.84 | 4.69 | 0.96 | 2.69 | 0.44 | 2.91 | 0.46 | 23.9 | 204.3 |
| CZ-54 | 54.3 | 105 | 12.9 | 48.2 | 8.72 | 1.79 | 7.75 | 1.26 | 7.10 | 1.46 | 3.94 | 0.61 | 4.00 | 0.62 | 38.4 | 295.6 |
| CZ-55 | 28.4 | 50.1 | 5.88 | 20.3 | 3.53 | 0.72 | 2.88 | 0.48 | 2.72 | 0.56 | 1.60 | 0.26 | 1.71 | 0.28 | 15.9 | 135.3 |
| CZ-56 | 22.8 | 41.4 | 5.25 | 18.0 | 3.10 | 0.77 | 2.44 | 0.39 | 2.07 | 0.41 | 1.10 | 0.18 | 1.17 | 0.19 | 11.3 | 110.6 |
| CZ-57 | 62.5 | 110 | 14.8 | 55.5 | 10.3 | 2.06 | 9.12 | 1.47 | 8.14 | 1.63 | 4.42 | 0.69 | 4.45 | 0.69 | 44.0 | 329.8 |
| CZ-58 | 22.9 | 42.2 | 5.38 | 19.8 | 3.55 | 0.92 | 3.00 | 0.50 | 2.78 | 0.55 | 1.50 | 0.24 | 1.56 | 0.25 | 15.4 | 120.6 |
| CZ-59 | 14.6 | 25.9 | 3.25 | 12.0 | 2.05 | 0.68 | 1.75 | 0.27 | 1.59 | 0.32 | 0.89 | 0.14 | 0.96 | 0.15 | 10.5 | 75.02 |
| CZ-60 | 55.3 | 112 | 13.1 | 47.0 | 8.41 | 1.54 | 6.66 | 1.07 | 5.75 | 1.14 | 3.12 | 0.50 | 3.24 | 0.52 | 29.3 | 289.0 |
| CZ-61 | 52.1 | 102 | 12.5 | 46.9 | 8.71 | 1.68 | 7.56 | 1.24 | 7.07 | 1.45 | 3.91 | 0.62 | 4.04 | 0.64 | 39.2 | 289.2 |
| CZ-62 | 51.7 | 104 | 11.9 | 41.9 | 6.93 | 1.26 | 5.38 | 0.82 | 4.51 | 0.89 | 2.49 | 0.41 | 2.71 | 0.43 | 21.7 | 257.1 |
| CZ-63 | 52.5 | 108 | 12.6 | 47.1 | 8.45 | 1.69 | 7.12 | 1.18 | 6.42 | 1.31 | 3.48 | 0.55 | 3.52 | 0.56 | 32.2 | 286.3 |
| CZ-64 | 56.8 | 117 | 13.4 | 49.5 | 9.03 | 1.74 | 8.03 | 1.34 | 7.75 | 1.67 | 4.81 | 0.77 | 5.08 | 0.89 | 48.0 | 326.1 |
| CZ-65 | 55.0 | 111 | 12.8 | 46.7 | 8.12 | 1.62 | 6.62 | 1.05 | 5.68 | 1.16 | 3.15 | 0.49 | 3.29 | 0.52 | 29.1 | 285.9 |
| CZ-66 | 44.7 | 90.1 | 10.7 | 39.5 | 7.13 | 1.45 | 5.92 | 0.95 | 5.23 | 1.07 | 2.85 | 0.46 | 2.93 | 0.48 | 27.7 | 241.1 |
| CZ-67 | 46.2 | 90.5 | 10.8 | 40.2 | 6.96 | 1.29 | 5.30 | 0.84 | 4.73 | 1.00 | 2.84 | 0.48 | 3.19 | 0.52 | 24.7 | 239.6 |
| CZ-68 | 53.4 | 108 | 12.7 | 46.8 | 8.35 | 1.71 | 7.04 | 1.12 | 6.15 | 1.25 | 3.39 | 0.54 | 3.42 | 0.55 | 33.8 | 288.6 |
| CZ-69 | 33.9 | 63.9 | 8.12 | 30.2 | 5.36 | 1.22 | 4.50 | 0.72 | 3.95 | 0.80 | 2.16 | 0.35 | 2.27 | 0.36 | 20.7 | 178.4 |
| CZ-70 | 34.0 | 62.4 | 8.03 | 29.8 | 5.33 | 1.20 | 4.36 | 0.70 | 3.80 | 0.78 | 2.12 | 0.34 | 2.23 | 0.36 | 19.3 | 174.8 |
| CZ-71 | 69.6 | 146 | 17.6 | 65.6 | 11.8 | 2.44 | 9.04 | 1.39 | 7.20 | 1.37 | 3.68 | 0.58 | 3.99 | 0.61 | 31.2 | 372.2 |
| CZ-72 | 70.2 | 140 | 16.2 | 59.0 | 10.2 | 1.84 | 8.34 | 1.30 | 7.13 | 1.41 | 3.82 | 0.60 | 3.92 | 0.63 | 35.6 | 360.3 |
| CZ-73 | 62.3 | 98.5 | 11.8 | 45.0 | 7.92 | 1.63 | 7.93 | 1.27 | 7.17 | 1.53 | 4.23 | 0.64 | 3.98 | 0.67 | 53.6 | 308.2 |
| CZ-74 | 49.2 | 96.4 | 11.4 | 42.5 | 7.37 | 1.58 | 5.95 | 0.94 | 5.02 | 1.00 | 2.69 | 0.43 | 2.79 | 0.45 | 25.9 | 253.7 |
| CZ-75 | 48.9 | 97.2 | 11.3 | 41.0 | 7.00 | 1.36 | 5.49 | 0.85 | 4.44 | 0.88 | 2.37 | 0.38 | 2.49 | 0.41 | 21.5 | 245.6 |
| CZ-76 | 42.0 | 89.6 | 9.84 | 36.0 | 6.18 | 1.28 | 4.91 | 0.77 | 4.10 | 0.82 | 2.21 | 0.36 | 2.33 | 0.37 | 20.1 | 220.9 |
| CZ-77 | 57.3 | 115 | 13.8 | 51.9 | 9.26 | 1.98 | 7.81 | 1.25 | 6.62 | 1.33 | 3.53 | 0.54 | 3.42 | 0.54 | 34.5 | 308.4 |
| CZ-78 | 39.2 | 72.0 | 8.93 | 31.9 | 5.50 | 1.15 | 4.22 | 0.67 | 3.66 | 0.75 | 2.07 | 0.34 | 2.31 | 0.37 | 18.1 | 191.3 |
| CZ-79 | 56.4 | 111 | 13.4 | 49.0 | 8.58 | 1.71 | 7.09 | 1.14 | 6.08 | 1.23 | 3.37 | 0.53 | 3.45 | 0.54 | 30.7 | 294.4 |
| CZ-80 | 39.3 | 75.9 | 9.32 | 34.8 | 6.42 | 1.36 | 5.38 | 0.86 | 4.69 | 0.93 | 2.54 | 0.40 | 2.65 | 0.42 | 23.9 | 208.9 |
| CZ-81 | 47.0 | 92.1 | 10.6 | 39.4 | 6.54 | 1.58 | 5.51 | 0.85 | 4.50 | 0.89 | 2.33 | 0.35 | 2.20 | 0.35 | 25.2 | 239.4 |
| TOC | TC | S | N | P | SiO2 | Al2O3 | TFe2O3 | MgO | CaO | Na2O | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TC | −0.128 | ||||||||||
| S | 0.855 ** | 0.103 | |||||||||
| N | 0.527 ** | −0.281 | 0.372 * | ||||||||
| P | −0.028 | 0.149 | −0.117 | 0.191 | |||||||
| SiO2 | 0.196 | −0.809 ** | −0.001 | −0.022 | −0.236 | ||||||
| Al2O3 | 0.128 | −0.553 ** | 0.0001 | 0.711 ** | 0.085 | 0.111 | |||||
| TFe2O3 | −0.083 | −0.128 | −0.099 | 0.281 | 0.016 | −0.399 * | 0.327 * | ||||
| MgO | −0.164 | 0.057 | −0.069 | 0.347 * | 0.621 ** | −0.401 ** | 0.556 ** | 0.288 | |||
| CaO | −0.173 | 0.998 ** | 0.057 | −0.308 * | 0.125 | −0.808 * | −0.565 ** | −0.127 | 0.030 | ||
| Na2O | 0.039 | −0.383 * | 0.027 | −0.450 ** | −0.091 | 0.716 * | −0.477 ** | −0.393 * | −0.508 ** | −0.378 * | |
| K2O | 0.201 | −0.620 ** | 0.081 | 0.129 | 0.095 | 0.698 * | 0.081 | −0.165 | −0.100 | −0.630 ** | 0.625 * |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, J.; Li, Y.; Gong, J.; Duan, Z.; Hu, S.; Tang, L.; Su, W.; Gao, J.; Wang, Z.; Lin, L.; et al. Geochemical Characteristics of the Minghuazhen Formation in the Cangdong Sag, Bohai Bay Basin: Implications for Provenance, Paleoclimate, and Hydrocarbon Exploration. Sustainability 2025, 17, 5293. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17125293
Yang J, Li Y, Gong J, Duan Z, Hu S, Tang L, Su W, Gao J, Wang Z, Lin L, et al. Geochemical Characteristics of the Minghuazhen Formation in the Cangdong Sag, Bohai Bay Basin: Implications for Provenance, Paleoclimate, and Hydrocarbon Exploration. Sustainability. 2025; 17(12):5293. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17125293
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Jianzhou, Yong Li, Jingjing Gong, Zhuang Duan, Shuqi Hu, Liling Tang, Wenli Su, Jianweng Gao, Zhenliang Wang, Lujun Lin, and et al. 2025. "Geochemical Characteristics of the Minghuazhen Formation in the Cangdong Sag, Bohai Bay Basin: Implications for Provenance, Paleoclimate, and Hydrocarbon Exploration" Sustainability 17, no. 12: 5293. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17125293
APA StyleYang, J., Li, Y., Gong, J., Duan, Z., Hu, S., Tang, L., Su, W., Gao, J., Wang, Z., Lin, L., Zhao, K., & Gong, S. (2025). Geochemical Characteristics of the Minghuazhen Formation in the Cangdong Sag, Bohai Bay Basin: Implications for Provenance, Paleoclimate, and Hydrocarbon Exploration. Sustainability, 17(12), 5293. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17125293




