An Evaluation of Sustainable Development in Chinese Counties Based on SDGs
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. System of Indicators for Evaluating Sustainable Development of Counties
2.2. Evaluation Area
2.3. Data Sources
2.4. Assessment and Analytical Methods
2.4.1. Indicator Weights
2.4.2. Coupling Coordination Analysis
2.4.3. Barrier Degree Analysis
2.4.4. Dagum Gini Coefficient Decomposition
3. Results
3.1. Sustainable Development in China’s Counties
3.2. Coupling Coordination Results
3.3. Analysis of Degree of Obstacles
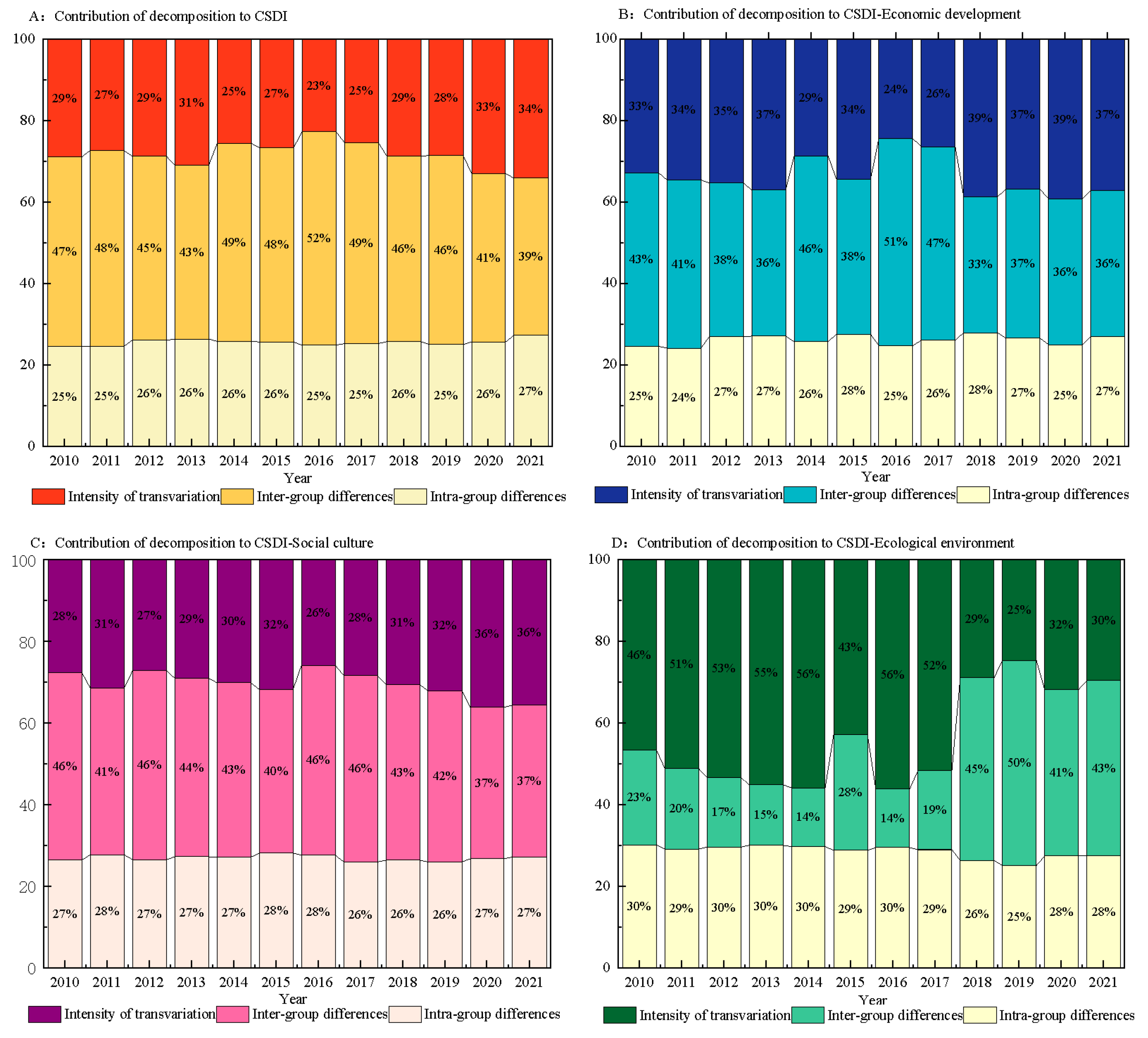
3.4. Dagum Decomposition
4. Discussion and Conclusions
4.1. Conclusions
4.2. Innovations and Limitations
4.3. Recommendations
- (1)
- Building mechanisms for regional differentiated development
- (2)
- Promoting synergy between ecological protection and economic development
- (3)
- Improvements in policy synergy and long-term guarantee mechanism
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hu, Z.G.; Wu, Q.; Li, J. The localization of SDGs in China: System construction, status assessment and development reflection. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 154, 110514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.C.; Chau, S.N.; Chen, X.Z.; Zhang, J.; Li, Y.J.; Dietz, T.; Wang, J.Y.; Winkler, J.A.; Fan, F.; Huang, B.R.; et al. Assessing progress towards sustainable development over space and time. Nature 2020, 577, 74–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhan, P.; Costa, L.; Rybski, D.; Lucht, W.; Kropp, J.P. A Systematic Study of Sustainable Development Goal (SDG) Interactions. Earths Future 2017, 5, 1169–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scoones, I.; Stirling, A.; Abrol, D.; Atela, J.; Charli-Joseph, L.; Eakin, H.; Ely, A.; Olsson, P.; Pereira, L.; Priya, R.; et al. Transformations to sustainability: Combining structural, systemic and enabling approaches. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 2020, 42, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biermann, F.; Hickmann, T.; Sénit, C.A.; Beisheim, M.; Bernstein, S.; Chasek, P.; Grob, L.; Kim, R.E.; Kotzé, L.J.; Nilsson, M.; et al. Scientific evidence on the political impact of the Sustainable Development Goals. Nat. Sustain. 2022, 5, 795–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, L.M.; Domingues, J.P.; Dima, A.M. Mapping the Sustainable Development Goals Relationships. Sustainability 2020, 12, 3359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Adamo, I.; Di Carlo, C.; Gastaldi, M.; Rossi, E.N.; Uricchio, A.F. Economic Performance, Environmental Protection and Social Progress: A Cluster Analysis Comparison towards Sustainable Development. Sustainability 2024, 16, 5049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.F.; Li, F.X.; Qiu, M.L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, X.; He, J.H. An integrated framework for measuring sustainable rural development towards the SDGs. Land Use Policy 2024, 147, 107339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warchold, A.; Pradhan, P.; Thapa, P.; Putra, M.; Kropp, J.P. Building a unified sustainable development goal database: Why does sustainable development goal data selection matter? Sustain. Dev. 2022, 30, 1278–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.T.; Fu, B.J.; Wang, S.; Song, S.; Li, Y.J.; Xu, Z.C.; Wei, Y.P.; Liu, J.G. Decoupling of SDGs followed by re-coupling as sustainable development progresses. Nat. Sustain. 2022, 5, 452–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ElMassah, S.; Mohieldin, M. Digital transformation and localizing the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). Ecol. Econ. 2020, 169, 106490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Hu, S.G.; Wu, S.; Song, J.R.; Li, H.Y. County-level land use carbon emissions in China: Spatiotemporal patterns and impact factors. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2024, 105, 105304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.C.; Bai, J.J.; Chen, J. An Improved Indicator System for Evaluating the Progress of Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) Sub-Target 9.1 in County Level. Sustainability 2019, 11, 4783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.; Wang, M.; Li, Y.; Wang, Q.; Tang, A.N. Spatial Pattern, Classification, and Influencing Factors of High-Quality County Development in China. J. Urban Plan. Dev. 2025, 151, 05024041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.Y.; Bai, J.J.; Chen, J. Measuring SDG 15 at the County Scale: Localization and Practice of SDGs Indicators Based on Geospatial Information. Isprs Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2019, 8, 515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.; Zhao, X.S.; Fan, D.Q.; Li, S.N. Geospatial Disaggregation of Population Data in Supporting SDG Assessments: A Case Study from Deqing County, China. Isprs Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2019, 8, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, R.; Huang, X.T.; Ye, X.Y.; Pan, Z.; Wang, H.; Luo, B.; Liu, D.M.; Hu, X.X. County Ecosystem Health Assessment Based on the VORS Model: A Case Study of 183 Counties in Sichuan Province, China. Sustainability 2022, 14, 11565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.J.; Wang, M.J.; Huang, B.; Li, S.C.; Lin, Y.H. Evaluation and Analysis of Poverty-Stricken Counties under the Framework of the UN Sustainable Development Goals: A Case Study of Hunan Province, China. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.T.; Wang, S.J. Analysis of the Impact of County-Levelization on Economic Growth and Public Service Development Based on Panel Data. Discret. Dyn. Nat. Soc. 2023, 2023, 6500191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, R.C.; Guo, Y.; Wu, Y.Z.; Amado, M. Exploration on the Innovation Model of County Urbanization Development with the Resource Constraints in China. Sustainability 2023, 15, 16129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, P.; Tao, H.J. Sustainable Development in Gansu Province: Theil Index and Cluster Analysis. Sustainability 2024, 16, 4518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.J.; Wang, Y.J.; Teng, F.; Li, S.C.; Lin, Y.H.; Cai, H.F. China’s poverty assessment and analysis under the framework of the UN SDGs based on multisource remote sensing data. Geo-Spat. Inf. Sci. 2024, 27, 111–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.Y.; Zhang, L.; Bai, L.Y.; Liao, J.J.; Chen, B.W.; Yan, M. Assessment of Localized Targets of Sustainable Development Goals and Future Development on Hainan Island. Sustainability 2023, 15, 8551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.J.; Zheng, S.Y.; Huang, Z.Q.; Song, L.; Long, Y.; Zhan, X.J.; Jiang, L.J.; Wang, Y.M.; Shu, Y.Q.; Zheng, C.M. Assessing progress towards sustainable development in Shenzhen 2005–2019. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 349, 131496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wang, L.; Zhai, J.; Feng, T.; Lei, Y.; Li, S.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Hu, Z.; Zhu, K.; et al. Assessing progress toward China's subnational sustainable development by Region Sustainable Development Index. Sustain. Horiz. 2024, 11, 100099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Zhou, D.; Fan, J. Spatial differences of Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) among counties (cities) on the northern slope of the Kunlun Mountains. Reg. Sustain. 2024, 5, 100108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Cao, S.S.; Du, M.Y.; Lu, L.L.; Guo, H.D.; Wang, S.R.; Liu, Y.; Li, X.X. Provincial localization framework for SDGs in China: Enhancing support for sustainable governance. Appl. Geogr. 2025, 175, 103505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, K.; Sheng, Q.Y.; Liu, Y.H.; Yang, Y.Z.; Dong, G.L.; Qiao, Z.; Wang, M.; Sun, C.H.; Han, D.R. A framework for achieving urban sustainable development goals (SDGs): Evaluation and interaction. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2024, 114, 105780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricciolini, E.; Rocchi, L.; Cardinali, M.; Paolotti, L.; Ruiz, F.; Cabello, J.M.; Boggia, A. Assessing Progress Towards SDGs Implementation Using Multiple Reference Point Based Multicriteria Methods: The Case Study of the European Countries. Soc. Indic. Res. 2022, 162, 1233–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, C.; Metternicht, G.; Wiedmann, T. Prioritising SDG targets: Assessing baselines, gaps and interlinkages. Sustain. Sci. 2019, 14, 421–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McArthur, J.W.; Rasmussen, K. Classifying Sustainable Development Goal trajectories: A country-level methodology for identifying which issues and people are getting left behind. World Dev. 2019, 123, 104608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Firoiu, D.; Ionescu, G.H.; Bandoi, A.; Florea, N.M.; Jianu, E. Achieving Sustainable Development Goals (SDG): Implementation of the 2030 Agenda in Romania. Sustainability 2019, 11, 2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Deng, H.; Zhang, D.W. Fine-grained sustainability assessment: County sustainable development in China from 2000 to 2017. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 425, 138798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, J.; Li, X. Interlinkages among County-Level Construction Indicators and Related Sustainable Development Goals in China. Land 2022, 11, 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, W.; Qu, Q.; Liang, S.; Jiang, W. Using granular computing to measure the similarity of sustainable development in China: Addressing goals 1, 3, 8, 10 and 15 of the SDGs. Environ. Dev. 2023, 47, 100886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.D.; Gao, M.; Cheng, S.L.; Hou, W.X.; Song, M.L.; Liu, X.; Liu, Y.; Shan, Y.L. County-level CO2 emissions and sequestration in China during 1997–2017. Sci. Data 2020, 7, 391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Chen, K.; Liu, J.S. A clustering algorithm based on the weighted entropy of conditional attributes for mixed data. Concurr. Comput. -Pract. Exp. 2021, 33, e6293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, K.; Han, J.M.; Wu, Q.R.; Xie, W.S.; He, W.B.; Yang, Z.Z.; Wang, Y.B.; Liu, J.C.; Shi, E.H. The coupling coordination and spatiotemporal evolution of industrial water-energy-CO2 in the Yellow River Basin. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 912, 169012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.Q.; Wang, F.; Ma, S.L. Research on the Coupled and Coordinated Relationship Between Ecological Environment and Economic Development in China and its Evolution in Time and Space. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2025, 34, 3333–3342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, C.; Chen, H.; Long, R. Coupling and coordination of China’s economy, ecological environment and health from a green production perspective. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 19, 4087–4106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, S.F.; Zhang, X.; Shu, W.J. Evaluation of internal coupling and coordination degree and diagnosis of obstacle factors for high-quality regional economic development: Evidence from Chongqing’s “One District, Two Groups”. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0312820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, K.; Yuan, Y.J. Spatiotemporal pattern assessment of China’s industrial green productivity and its spatial drivers: Evidence from city-level data over 2000-2017. Appl. Energy 2022, 307, 118248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Guo, Y. Spatiotemporal heterogeneity of green total factor productivity in Chinese cities under technological heterogeneity. Energy Rep. 2024, 11, 1535–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Yuan, K.; Niu, T.; Zhang, L.; Guan, Y. Study on the Spatial and Temporal Evolution Patterns of Green Innovation Efficiency and Driving Factors in Three Major Urban Agglomerations in China-Based on the Perspective of Economic Geography. Sustainability 2022, 14, 9239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Zeng, B. Urban Technology Transfer, Spatial Spillover Effects, and Carbon Emissions in China. Sustainability 2024, 16, 9662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klimczuk, A.; Gawron, G.P.; Toczyski, P. Editorial: Towards 2030: Sustainable development goal 1: No poverty. A sociological perspective. Front. Sociol. 2024, 9, 1487228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.; Ru, J. Goals of sustainable infrastructure, industry, and innovation: A review and future agenda for research. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 28446–28458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, X.; Wang, F.; Chen, J.; Zhang, Y. The Income Gap Between Urban and Rural Residents in China: Since 1978. Comput. Econ. 2018, 52, 1153–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajoary, P.K.; Balachandra, P.; Garza-Reyes, J.A. Industry 4.0 maturity and readiness assessment: An empirical validation using Confirmatory Composite Analysis. Prod. Plan. Control 2024, 35, 1779–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hager, C.; Hamagami, N. Local Renewable Energy Initiatives in Germany and Japan in a Changing National Policy Environment. Rev. Policy Res. 2020, 37, 386–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, S.; Agra, R.; Zolyomi, A.; Keith, H.; Nicholson, E.; de Lamo, X.; Portela, R.; Obst, C.; Alam, M.; Honzak, M.; et al. Using the system of environmental-economic accounting ecosystem accounting for policy: A case study on forest ecosystems. Environ. Sci. Policy 2024, 152, 103653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
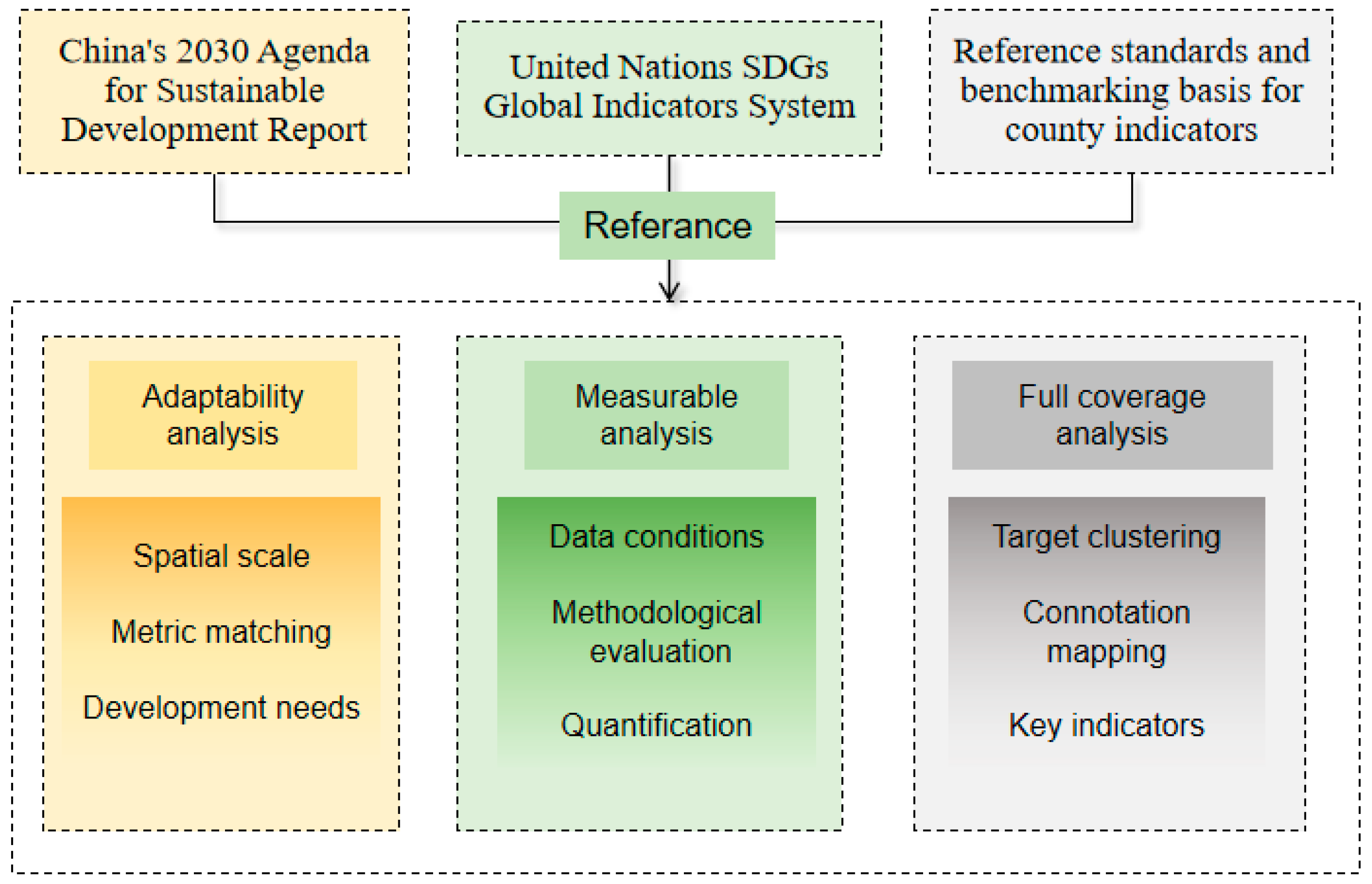



| Dimensions | Category | Existing Research Status | Key Contributions of This Study |
|---|---|---|---|
| Study area | National/Sub-national | Well established | - |
| Urban/Provinces | Extensive | - | |
| Rural/County | Limited (mostly rural) | Establish a “three-tier SDGs delivery framework” at county level | |
| Areas of concern | Economic Development | Well established | Incorporate urban-rural gap assessment in economic development system |
| Social Sustainability | Urban-focused | Focus on coordinated urban-rural societal progress | |
| Environment Resources | Extensive | - | |
| Analytical perspective | Spatiotemporal analysis | Mature methods | Develop “coordination-obstacle-Dagum decomposition” triple dynamic evaluation model |
| Regional differences | Provincial divisions | Adopt four-region division (east/central/west/northwest) aligning with national strategy | |
| System coordination | Mostly economy-environment | Conduct three-system (economic-environmental-social) Dagum Gini decomposition |
| No. | Dimension | Indicators | SDGs | Weights |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Economic development | Minimum standard salary | 2 | 0.0386 |
| 2 | Urban and rural basic public service expenditure as share of fiscal expenditure | 6 | 0.0382 | |
| 3 | Number of social welfare adoption units | 8 | 0.0774 | |
| 4 | Beds in health-care facilities | 9 | 0.0226 | |
| 5 | Pupil division ratio | 9 | 0.0097 | |
| 6 | Gender ratio of men to women | 10 | 0.0111 | |
| 7 | Average annual GDP growth | 11 | 0.0361 | |
| 8 | GDP per capita | 11 | 0.0538 | |
| 9 | Ratio of income between urban and rural areas | 16 | 0.0168 | |
| 10 | Ecological environment | Grain production per unit area | 1 | 0.0286 |
| 11 | Domestic sewage treatment rate | 1 | 0.0075 | |
| 12 | Water consumption per 10,000 GDP | 3 | 0.0469 | |
| 13 | Gas penetration rate | 3 | 0.0093 | |
| 14 | Green space coverage in built-up areas | 4 | 0.0194 | |
| 15 | Non-hazardous treatment rate of domestic waste | 5 | 0.0120 | |
| 16 | PM2.5 annual average concentration | 8 | 0.0566 | |
| 17 | Agricultural fertilizer use | 8 | 0.0422 | |
| 18 | Net carbon emissions per capita | 10 | 0.0462 | |
| 19 | Forest cover | 2 | 0.0502 | |
| 20 | Social cultural | Gross power of agricultural machinery | 6 | 0.0258 |
| 21 | Water supply penetration | 6 | 0.0028 | |
| 22 | Labor productivity | 7 | 0.0437 | |
| 23 | Number of industrial enterprises above scale | 11 | 0.0495 | |
| 24 | Total retail sales of consumer goods per capita | 11 | 0.0379 | |
| 25 | Gini coefficient (a measure of statistical dispersion) | 11 | 0.0422 | |
| 26 | Area occupied by construction land per unit of GDP | 12 | 0.0772 | |
| 27 | Urbanization rate of resident population | 13 | 0.0271 | |
| 28 | Financial self-sufficiency rate | 15 | 0.0706 |
| Key SDGs | Existing Problems | Development Proposals |
|---|---|---|
| SDG 7: Affordable and Clean Energy | Underutilized clean energy resources in western regions | Establish national clean energy bases in western counties |
| SDG9: Industry, Innovation and Infrastructure | Low innovation levels and R&D investment in counties | East: build AI innovation hubs; central: adopt eastern tech spillovers; west: develop cross-regional clean energy transmission |
| SDG11: Sustainable Cities and Communities | Inadequate public services (education and health-care) and rural infrastructure | Create a three-tier service network: “county-key town-village” |
| SDG 13: Climate Action, SDG 15: Life on Land | Insufficient ecological restoration in fragile western areas; high industrial emissions in the east | West: cross-province eco-compensation; east: carbon labeling for key industries |
| SDG 16: Peace, Justice and Strong Institutions, SDG 17: Partnerships for the Goals | Fragmented governance and lack of inter-regional collaboration | Establish cross-county industrial alliances to share technology, market, and ecological governance experience |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, Y.; Shao, C.; Zhan, X. An Evaluation of Sustainable Development in Chinese Counties Based on SDGs. Sustainability 2025, 17, 4704. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17104704
Zhao Y, Shao C, Zhan X. An Evaluation of Sustainable Development in Chinese Counties Based on SDGs. Sustainability. 2025; 17(10):4704. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17104704
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Yufei, Chaofeng Shao, and Xuesong Zhan. 2025. "An Evaluation of Sustainable Development in Chinese Counties Based on SDGs" Sustainability 17, no. 10: 4704. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17104704
APA StyleZhao, Y., Shao, C., & Zhan, X. (2025). An Evaluation of Sustainable Development in Chinese Counties Based on SDGs. Sustainability, 17(10), 4704. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17104704







