Human Capital Investment, Technological Innovation, and Resilience of Chinese High-End Manufacturing Enterprises
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Definition of Enterprise Resilience and Measurement of High-End Manufacturing Enterprise Resilience
2.1. Definition of Enterprise Resilience
2.2. Construction of Resilience Evaluation Index System for High-End Manufacturing Enterprises
2.3. Resilience Evaluation Methods for High-End Manufacturing Enterprises
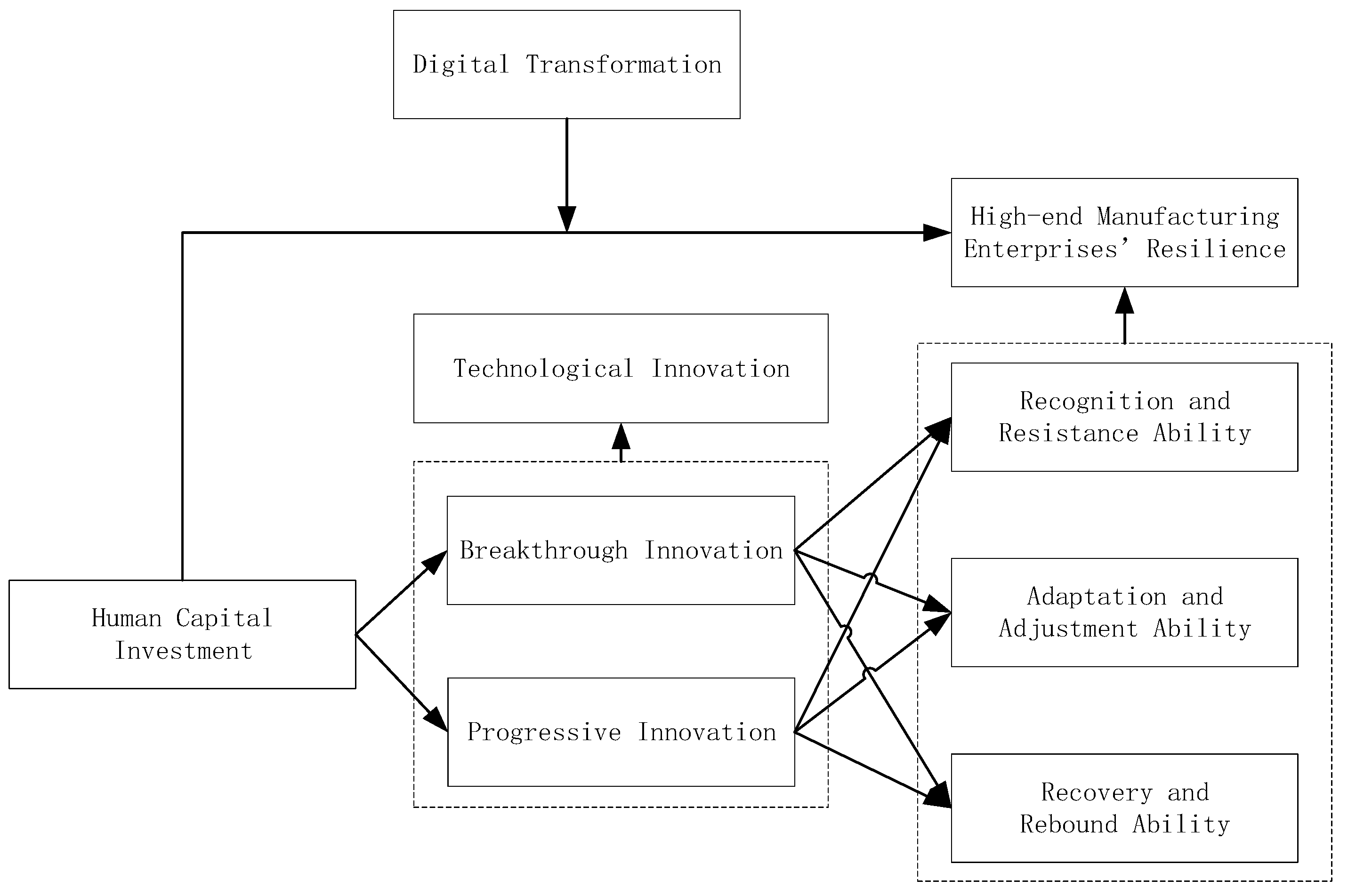
3. Internal Mechanism Analysis
4. Research Design
4.1. Sample Selection and Data Sources
4.2. Variable Design
4.2.1. Explained Variables
4.2.2. Explaining Variables
4.2.3. Mediating Variables
4.2.4. Control Variables
4.3. Construction of Models
5. Empirical Analysis and Results
5.1. Descriptive Statistics and Correlation Analysis
5.2. Basic Regression Analysis
5.3. Robustness Test
5.3.1. Changing Sample Size
5.3.2. Robustness Test Based on Bootstrap
5.4. Endogeneity Test
6. Further Analysis
6.1. Threshold Effect Analysis
6.2. Heterogeneity Analysis
6.2.1. Heterogeneity Analysis Based on Segmented Capabilities of Enterprise Resilience
6.2.2. Heterogeneity Analysis Based on the Nature of Property Rights
6.2.3. Heterogeneity Analysis Based on the Enterprise Size
7. Research Conclusions and Limitations
7.1. Conclusions and Implications
- (1)
- Adhere to the people-oriented concept and attach importance to human capital investment. Human capital is a critical factor in cultivating and enhancing the resilience of high-end manufacturing enterprises. These enterprises need managers with strategic decision-making abilities and excellent leadership abilities, as well as employees with professional competence, a sense of identity in the corporate culture, and conscientious and responsible qualities. Therefore, they should pay attention to cultivating, uniting, and leading talent and constantly strengthen the construction of the talent team. This requires high-end manufacturing enterprises in the recruitment process to thoughtfully select candidates based on education, experience, ability, and other aspects; at the same time, they should systematically strengthen staff training and development to constantly improve the staff’s professional competence and comprehensive quality and enhance the staff’s sense of identity to the corporate culture. In addition, it is also necessary to build an effective incentive mechanism to continuously enhance staff’s sense of belonging and sense of mission, as well as their sense of responsibility.
- (2)
- Adjust human capital investment strategies and optimize the human capital structure. In the face of a complex and changing living environment, high-end manufacturing enterprises need to update the concept of human capital, adjust the human capital investment strategy, and cultivate many strategic safeguard talents, first-class scientific and technological leaders, and innovation teams in crucial core areas to ensure that the enterprise owns abundant frontrunners in the field of core technology and many pioneers in cutting-edge areas. In addition, enterprises should improve their talent management systems and manage to trust, respect, treat, and tolerate talent to make it talent-oriented. They should give first-class talents greater rights to decide on technical routes, allocate research and development funds, and dispatch resources. They must make efforts to create an open, tolerant, equal, and accessible working environment for all kinds of talent.
- (3)
- Maintain strategic strength and continue to strengthen human capital investments and technological innovation. In the process of cultivating and enhancing high-end manufacturing enterprises’ resilience, human capital investment and technological innovation have multiple threshold effects; therefore, these firms need to maintain strategic determination, adhere to long-term, and continue to strengthen human capital investment and technological innovation to promote more high-end manufacturing enterprises to accomplish qualitative leaps through quantitative accumulation and significantly enhance enterprise resilience.
7.2. Limitations and Prospect
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Barghouti, Z.; Guinot, J.; Chiva, R. Compassion and altruism in organizations: A path for firm survival. Int. J. Manpow. 2023, 44, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duchek, S. Organizational resilience: A capability-based conceptualization. Bus. Res. 2020, 13, 215–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Yang, Z.; He, B. Does Digital Infrastructure Improve Urban Economic Resilience? Evidence from the Yangtze River Economic Belt in China. Sustainability 2023, 15, 14289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, P.; Fung, A.; Fung, H.-G.; Ma, X. Resilient leadership and outward foreign direct investment: A conceptual and empirical analysis. J. Bus. Res. 2022, 144, 729–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avolio, B.J.; Walumbwa, F.O.; Weber, T.J. Leadership: Current Theories, Research, and Future Directions. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 2009, 60, 421–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmić, A. Strategic Sustainability Orientation Influence on Organizational Resilience: Moderating Effect of Firm Size. Bus. Syst. Res. 2022, 13, 169–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, P.; Bu, W. The Impact of Organizational Learning on Organizational Resilience in Construction Projects. Buildings 2024, 14, 975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, H.; Budhwar, P.; Shipton, H.; Nguyen, H.-D.; Nguyen, B. Building organizational resilience, innovation through resource-based management initiatives, organizational learning and environmental dynamism. J. Bus. Res. 2022, 141, 808–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Kong, Z.; Han, Y.; Zeng, R. Can Aid Interventions Facilitate Project Resilience Performance? An Inverted U-Shaped Relationship Investigation. IEEE Trans. Eng. Manag. 2024, 71, 11078–11090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Zhang, R.; Yu, Z.; Zhu, S.; Qie, X.; Wu, J.; Li, P. Revisiting the porter hypothesis within the economy-environment-health framework: Empirical analysis from a multidimensional perspective. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 349, 119557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Zhu, S.; Guo, J.; Peng, S.; Qie, X.; Yu, Z.; Wu, J.; Li, P. Exploring ways to improve China’s ecological well-being amidst air pollution challenges using mixed methods. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 364, 121457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gagalyuk, T.; Kovalova, M. Digital technologies as a driver of resilience and institutional transformation: The case of Ukrainian agroholdings. Int. Food Agribus. Manag. Rev. 2024, 27, 5–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Deng, F. Can digitalization improve enterprise sustainability?–Evidence from the resilience perspective of Chinese firms. Heliyon 2023, 9, e14607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chowdhury, M.; Prayag, G.; Orchiston, C.; Spector, S. Postdisaster Social Capital, Adaptive Resilience and Business Performance of Tourism Organizations in Christchurch, New Zealand. J. Travel Res. 2019, 58, 1209–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Sánchez, A.; Guinot, J.; Chiva, R.; López-Cabrales, A. How to emerge stronger: Antecedents and consequences of organizational resilience. J. Manag. Organ. 2021, 27, 442–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.; Zhu, H.; Sun, X. Manufacturing intelligentization and technological innovation: Perspectives on intra-industry impacts and inter-industry technology spillovers. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2024, 204, 123418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wu, Y.; Cao, D.; Wang, Y. Organizational mindfulness towards digital transformation as a prerequisite of information processing capability to achieve market agility. J. Bus. Res. 2021, 122, 700–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramdani, B.; Binsaif, A.; Boukrami, E.; Guermat, C. Business models innovation in investment banks: A resilience perspective. Asia Pac. J. Manag. 2022, 39, 51–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heredia, J.; Rubiños, C.; Vega, W.; Heredia, W.; Flores, A. New Strategies to Explain Organizational Resilience on the Firms: A Cross-Countries Configurations Approach. Sustainability 2022, 14, 1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Xu, F.; Wang, L.; Taslima, A. Impact of capital enrichment on resource allocation efficiency in China’s manufacturing industry. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 2021, 41, 4079–4095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Yang, Z.; He, B. Empowerment of Digital Technology for the Resilience of the Logistics Industry: Mechanisms and Paths. Systems 2024, 12, 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Meng, Z.; Zhang, X.; Wu, J. The role of institutional quality in the nexus between green financing and sustainable development. Res. Int. Bus. Finance 2025, 73, 102531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verreynne, M.-L.; Ford, J.; Steen, J. Strategic factors conferring organizational resilience in SMEs during economic crises: A measurement scale. Int. J. Entrep. Behav. Res. 2023, 29, 1338–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; He, W. Resilience Measurement and Enhancement Strategies for Meizhou Bay Port Enterprises. Sustainability 2024, 16, 5708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DesJardine, M.; Bansal, P.; Yang, Y. Bouncing Back: Building Resilience Through Social and Environmental Practices in the Context of the 2008 Global Financial Crisis. J. Manag. 2019, 45, 1434–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, W.; Wei, Y.; Li, X.; Lin, L. What Dimension of CSR Matters to Organizational Resilience? Evidence from China. Sustainability 2019, 11, 1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan-Taylor, B.; Branicki, L. Creating resilient SMEs: Why one size might not fit all. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2011, 49, 5565–5579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hameed, W.U.; Nisar, Q.A.; Wu, H.-C. Relationships between external knowledge, internal innovation, firms’ open innovation performance, service innovation and business performance in the Pakistani hotel industry. Int. J. Hosp. Manag. 2021, 92, 102745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Wu, J.; Peng, J.; Lu, L. The perceived impact of the Covid-19 epidemic: Evidence from a sample of 4807 SMEs in Sichuan Province, China. Environ. Hazards 2020, 19, 323–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefani, U.; Schiavone, F.; Laperche, B.; Burger-Helmchen, T. New tools and practices for financing novelty: A research agenda. Eur. J. Innov. Manag. 2020, 23, 314–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, N.D.K.; Ali, I.; Gupta, S.; Chen, R.; Naresho, B.S. Bridging the Nexus Between Cloud ERP and Enterprise Resilience. J. Glob. Inf. Manag. 2024, 32, 336556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, T.; Qiao, L.; Yao, X.; Chen, S.; Tang, X. A Profit Framework Model for Digital Platforms Based on Value Sharing and Resource Complementarity. Sustainability 2022, 14, 11954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Cui, D.; Jin, C. The Value of Internal Control during a Crisis: Evidence from Enterprise Resilience. Sustainability 2023, 15, 513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, B.; Tian, S.; Zhang, X. Does the pilot free trade zone policy increase regional innovation ability? Evidence from China. Appl. Econ. Lett. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, H.; Ameen, K. The role of resilience capabilities in shaping how firms respond to disruptions. J. Bus. Res. 2018, 88, 535–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R. Safeguarding Enterprise Prosperity: An In-depth Analysis of Financial Management Strategies. J. Knowl. Econ. 2024, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Shan, Y.; Li, Y. Heterogeneous Partners, R&D cooperation and corporate innovation capability: Evidence from Chinese manufacturing firms. Technol. Soc. 2023, 72, 102183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Yuan, K.; Li, W.; Ding, W. An Emerging Fuzzy Feature Selection Method Using Composite Entropy-Based Uncertainty Measure and Data Distribution. IEEE Trans. Emerg. Top. Comput. Intell. 2023, 7, 76–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J. Impact of enterprise human capital on technological innovation based on machine learning and SVM algorithm. J. Ambient. Intell. Humaniz. Comput. 2021, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shela, V.; Ramayah, T.; Hazlina, A.N. Human capital and organisational resilience in the context of manufacturing: A systematic literature review. J. Intellect. Cap. 2021, 24, 535–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Peng, Y.; Yang, J.; Hossain, S. Human Capital Structure and Innovation Efficiency Under Technological Progress: Evidence from China. SAGE Open 2024, 14, 21582440241277165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X. A Human Resource Demand Forecasting Method Based on Improved BP Algorithm. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2022, 2022, 3534840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, G.; He, B. Does foreign direct investment affect wage inequality in Chinese manufacturing sector? Appl. Econ. Lett. 2023, 30, 80–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, H.; Wang, Z.; Xiong, Y. Is “Well-Paid Employment” Worth It? Evidence from Corporate Investment in China. Emerg. Mark. Finance Trade 2023, 59, 800–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bustinza, O.F.; Vendrell-Herrero, F.; Perez-Arostegui, M.; Parry, G. Technological capabilities, resilience capabilities and organizational effectiveness. Int. J. Hum. Resour. Manag. 2019, 30, 1370–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Bureau of Statistics of China. Available online: https://www.stats.gov.cn/xxgk/tjbz/gjtjbz/201710/t20171017_1758922.html (accessed on 25 October 2024).
- Neukam, M.; Bollinger, S. Encouraging creative teams to integrate a sustainable approach to technology. J. Bus. Res. 2022, 150, 354–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Hu, J. Employee equity incentive, executive psychological capital, and enterprise innovation. Front. Psychol. 2023, 14, 1132550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyun, J.; He, B. The Evolution of Job Reallocation in the Korean Manufacturing Sector. Korea World Econ. 2018, 19, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, D.; Chen, J. Managerial overconfidence and corporate resilience. Finance Res. Lett. 2024, 62, 105087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, M.; Prayag, G.; Patwardhan, V. The Bright and Dark Sides of the Relationship Between Relational Capital and Organizational Resilience: The Moderating Role of Human Capital. Int. J. Hosp. Tour. Adm. 2024, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, H.-N.; Do, N.B.; Nguyen, T.K.; Nguyen, T.M. Unveiling the impact of technological innovation and SMEs resilience: The moderating role of firms’ social sustainability orientation. Eur. J. Innov. Manag. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, R.; Li, Y.; Huang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, R.; Dunlop, E. Psychological capital and breakthrough innovation: The role of tacit knowledge sharing and task interdependence. Front. Psychol. 2023, 14, 1097936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, M.; Tang, D.; Wei, C.; Xu, A. Can Transformational Leadership Affect the Two Dimensional Creativity of Middle Managers in Retail Enterprises? The Mediating Role of Psychological Security. SAGE Open 2023, 13, 21582440231206965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Zhu, Y.; Lee, C.-C.; Morrison, A.M. The effects of foreign product demand-labor transfer nexus on human capital investment in China. Humanit. Soc. Sci. Commun. 2023, 10, 610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Edafioghor, T.E.; Wu, C.; Doherty, B. Building organisational resilience capability in small and medium-sized enterprises: The role of high-performance work systems. Hum. Resour. Manag. J. 2023, 33, 806–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Li, H.; Ghosal, V. Firm-level human capital and innovation: Evidence from China. China Econ. Rev. 2020, 59, 101388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| First-Grade Index | Second-Grade Index | Third-Grade Index |
|---|---|---|
| Recognition and Resistance Ability | Corporate Operating Scale [27] | Total Profit [27] |
| Operating Revenue [27] | ||
| Corporate Talent Resource [28] | Number of R&D Personnel [28] | |
| Enterprise “Hematopoietic” Ability [29] | Net Cash Flow from Operating Activities [29] | |
| Enterprise “Transfusion” Ability [30] | Net Cash Flow from Financing Activities [30] | |
| Adaptation and Adjustment Ability | Corporate Operating Efficiency [31] | Current Asset Turnover [31] |
| Fixed Asset Turnover [31] | ||
| Resource Allocation Flexibility [32] | The Proportion of Expenditure on Capital, R&D, and Advertising in Sample Enterprises [32] | |
| Government Support [34] | Government Subsidies [33] | |
| Recovery and Rebound Ability | Corporate Profitability [35] | Rate of Return on Total Asset [36] |
| Corporate Innovation Ability [35] | Number of Patent Applications [37] | |
| Corporate Growth Ability [35] | Growth Rate of Total Asset [35] | |
| Growth Rate of Operating Revenue [35] |
| Variable | Variable Name | Variable Code | Variable Definition |
|---|---|---|---|
| Explained variable | Enterprise resilience | ER | Comprehensively calculate by entropy value method. |
| Explaining variable | Human capital investment [51] | HCI | Ln (payroll payable) [43] |
| Mediating variable | Technological innovation [52] | TI | Ln (R&D expenditure) [47] |
| Breakthrough innovation [53] | BI | The proportion of R&D expenditure to operating income is greater than or equal to 75 quantiles. | |
| Progressive innovation [54] | PI | The proportion of R&D expenditure to operating income is less than 75 quantiles. | |
| Moderating variable | Digital transformation [3] | DT | Use the Python tool to extract the key feature word “digital” in the annual reports of listed companies and take the logarithm of the sum of the feature words’ frequency [3]. |
| Control variable | Enterprise age [50] | Age | Take the natural logarithm of the number of that accounting year minus the listing year of the company and add one [50]. |
| Asset-liability ratio [50] | Lev | Total liabilities/total assets [50] | |
| Nature of property right [50] | Soe | For state-owned enterprises, the value is 1, otherwise it is 0. State-owned enterprises are those whose capital is owned or controlled by the state [50]. | |
| Enterprise size [49] | Size | Ln (total assets) [49] |
| Variables | ER | HCI | TI | DT | Age | Lev | Soe | Size |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ER | 1 | |||||||
| HCI | 0.471 *** | 1 | ||||||
| TI | 0.549 *** | 0.738 *** | 1 | |||||
| DT | 0.125 *** | 0.332 *** | 0.399 *** | 1 | ||||
| Age | 0.180 *** | 0.253 *** | 0.312 *** | 0.224 *** | 1 | |||
| Lev | 0.184 *** | 0.331 *** | 0.328 *** | 0.271 *** | 0.255 *** | 1 | ||
| Soe | −0.133 *** | −0.227 *** | −0.257 *** | −0.160 *** | −0.463 *** | −0.230 *** | 1 | |
| Size | 0.583 *** | 0.743 *** | 0.873 *** | 0.300 *** | 0.430 *** | 0.398 *** | −0.335 *** | 1 |
| Min | 0.003 | 7.893 | 13.737 | 3.127 | 0.000 | 0.014 | 1.000 | 18.334 |
| Max | 0.878 | 23.305 | 23.796 | 4.392 | 3.497 | 2.471 | 2.000 | 26.832 |
| Mean | 0.057 | 17.712 | 18.714 | 3.703 | 2.229 | 0.402 | 1.708 | 22.328 |
| Std.Dev | 0.086 | 1.465 | 1.363 | 0.263 | 0.862 | 0.187 | 0.455 | 1.189 |
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | (7) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ER | ER | ER | BI | ER | PI | ER | |
| HCI | 0.004 *** | −0.023 *** | 0.123 *** | 0.007 *** | 0.117 *** | 0.002 * | |
| (4.722) | (−3.016) | (6.178) | (3.711) | (7.549) | (1.758) | ||
| DT | −0.142 *** | ||||||
| (−3.769) | |||||||
| HCI × DT | 0.008 *** | ||||||
| (3.573) | |||||||
| BI | 0.012 *** | ||||||
| (3.129) | |||||||
| PI | 0.012 *** | ||||||
| (6.840) | |||||||
| Age | −0.012 *** | −0.011 *** | −0.010 *** | 0.022 | −0.013 *** | 0.016 | −0.010 *** |
| (−5.977) | (−5.825) | (−5.276) | (0.430) | (−2.879) | (0.496) | (−4.531) | |
| Lev | −0.008 * | −0.009 ** | −0.009 ** | −0.182 | −0.010 | 0.007 | −0.011 ** |
| (−1.787) | (−2.190) | (−2.107) | (−1.638) | (−1.006) | (0.102) | (−2.174) | |
| Soe | 0.004 | 0.004 | 0.004 | 0.089 | −0.007 | 0.052 | 0.004 |
| (1.333) | (1.317) | (1.413) | (0.947) | (−0.864) | (1.035) | (1.258) | |
| Size | 0.035 *** | 0.032 *** | 0.031 *** | 0.710 *** | 0.020 *** | 0.703 *** | 0.024 *** |
| (21.114) | (18.091) | (18.002) | (17.459) | (4.333) | (23.084) | (9.755) | |
| _cons | −0.693 *** | −0.700 *** | 0.000 | 1.123 | −0.696 *** | 0.630 | −0.705 *** |
| (−19.477) | (−19.743) | (0.357) | (1.348) | (−9.419) | (0.997) | (−16.084) | |
| Firm fixed effect | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| Year fixed effect | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| N | 2983 | 2983 | 2983 | 698 | 698 | 2192 | 2192 |
| R2 | 0.972 | 0.972 | 0.972 | 0.986 | 0.976 | 0.978 | 0.975 |
| F | 91.530 | 80.695 | 62.891 | 86.285 | 19.561 | 147.390 | 50.257 |
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ER | ER | BI | ER | PI | ER | |
| HCI | 0.003 *** | 0.148 *** | 0.004 * | 0.091 *** | 0.002 * | |
| (3.362) | (5.837) | (1.746) | (5.124) | (1.670) | ||
| BI | 0.013 *** | |||||
| (3.198) | ||||||
| PI | 0.011 *** | |||||
| (5.915) | ||||||
| Age | −0.008 *** | −0.008 *** | −0.003 | −0.008 * | 0.063 | −0.006 ** |
| (−3.777) | (−3.742) | (−0.046) | (−1.659) | (1.612) | (−2.510) | |
| Lev | −0.010 ** | −0.011 ** | −0.054 | −0.006 | −0.006 | −0.013 *** |
| (−2.205) | (−2.494) | (−0.441) | (−0.617) | (−0.079) | (−2.647) | |
| Soe | 0.003 | 0.003 | 0.088 | −0.005 | 0.047 | 0.005 |
| (0.921) | (0.846) | (0.847) | (−0.569) | (0.856) | (1.267) | |
| Size | 0.036 *** | 0.034 *** | 0.708 *** | 0.020 *** | 0.685 *** | 0.027 *** |
| (19.586) | (17.521) | (14.889) | (4.252) | (18.494) | (10.035) | |
| _cons | −0.731 *** | −0.739 *** | 0.731 | −0.666 *** | 1.432 * | −0.773 *** |
| (−18.143) | (−18.365) | (0.745) | (−8.557) | (1.832) | (−15.278) | |
| Firm fixed effect | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| Year fixed effect | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| N | 2439 | 2439 | 587 | 587 | 1759 | 1759 |
| R2 | 0.982 | 0.982 | 0.988 | 0.983 | 0.982 | 0.983 |
| F | 78.001 | 67.262 | 63.565 | 14.214 | 87.752 | 42.630 |
| Observed Coefficient | Bootstrap Std. Err. | z | p > z | Normal | Based | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [95% Conf. Interval] | |||||||
| ER | Indirect Eff | 0.019 | 0.002 | 12.150 | 0.000 | 0.016 | 0.022 |
| Direct Eff | 0.008 | 0.002 | 3.850 | 0.000 | 0.004 | 0.013 | |
| Total Eff | 0.028 | 0.002 | 13.600 | 0.000 | 0.024 | 0.032 | |
| (1) | (2) | |
|---|---|---|
| ER | ER | |
| L_HCI | 0.002 ** | |
| (2.464) | ||
| Age | −0.012 *** | −0.013 *** |
| (−5.962) | (−4.024) | |
| Lev | −0.008 * | −0.007 * |
| (−1.806) | (−1.656) | |
| Soe | 0.004 | 0.002 |
| (1.311) | (0.551) | |
| Size | 0.034 *** | 0.035 *** |
| (20.998) | (17.697) | |
| _cons | −0.694 *** | −0.743 *** |
| (−19.502) | (−17.233) | |
| Firm fixed effect | YES | YES |
| Year fixed effect | YES | YES |
| N | 2983 | 2214 |
| R2 | 0.972 | 0.983 |
| F | 76.490 | 51.550 |
| Under-Identification Test (Kleibergen-Paap rk LM Statistic) | Weak Identification Test (Cragg-Donald Wald F Statistic) | Weak Identification Test Critical Values (Stock-Yogo Weak ID F Test Critical Values) |
|---|---|---|
| 202.051 *** | 63,000 | 16.38 (10% maximal IV size) |
| Basic Regression | 2sls-IV | |
|---|---|---|
| ER | ER | |
| HCI | 0.004 *** | 0.012 *** |
| (4.722) | (5.42) | |
| Age | −0.011 *** | −0.003 |
| (−5.825) | (−1.53) | |
| Lev | −0.009 ** | −0.248 *** |
| (−2.190) | (−3.20) | |
| Soe | 0.004 | 0.008 ** |
| (1.317) | (2.21) | |
| Size | 0.032 *** | 0.035 *** |
| (18.091) | (10.17) | |
| _cons | −0.700 *** | −0.948 *** |
| (−19.743) | (−16.30) | |
| Firm fixed effect | YES | YES |
| Year fixed effect | YES | YES |
| N | 2983 | 2983 |
| R2 | 0.972 | 0.546 |
| F | 80.695 | 63.000 |
| Threshold Variable | Number of Thresholds | F Value | p-Value | Threshold Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | ||||
| Human capital Investment (HCI) | Single threshold | 3074.71 | 0.000 | 19.8349 | ||
| Double threshold | 437.88 | 0.045 | 19.8349 | 20.6095 | ||
| Triple threshold | 347.6 | 0.572 | 19.8349 | 20.6095 | 21.523 | |
| Technological Innovation (TI) | Single threshold | 2464.48 | 0.000 | 21.3422 | ||
| Double threshold | 401.5 | 0.081 | 21.3422 | 22.0317 | ||
| Triple threshold | 303.17 | 0.089 | 21.3422 | 22.0317 | 22.5573 |
| Threshold Variable | Interval | Regression Coefficient | T Value | p-Value | Number of Samples |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Human capital investment (HCI) | φ < 19.8349 | 0.0031 | 2.29 | 0.022 | 2789 |
| 19.8349 < φ < 21.523 | 0.0045 | 3.26 | 0.001 | 180 | |
| φ > 21.523 | 0.0073 | 4.02 | 0.000 | 30 | |
| Technological innovation (TI) | ϕ < 21.3422 | 0.0035 | 2.63 | 0.009 | 2879 |
| 21.3422 < ϕ < 22.0317 | 0.0048 | 3.39 | 0.001 | 60 | |
| 22.0317 < ϕ < 22.5573 | 0.0085 | 4.60 | 0.000 | 29 | |
| ϕ > 22.5573 | 0.0105 | 4.87 | 0.000 | 31 |
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | (7) | (8) | (9) | (10) | (11) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ER1 | ER2 | ER3 | BI | ER1 | ER2 | ER3 | PI | ER1 | ER2 | ER3 | |
| HCI | 0.006 *** | 0.005 *** | −0.003 | 0.123 *** | 0.009 *** | 0.009 *** | −0.006 * | 0.117 *** | 0.004 *** | 0.002 * | −0.003 |
| (5.476) | (4.661) | (−1.456) | (6.178) | (4.033) | (3.969) | (−1.674) | (7.549) | (2.720) | (1.704) | (−1.317) | |
| BI | 0.013 *** | 0.017 *** | −0.005 | ||||||||
| (2.643) | (3.604) | (−0.605) | |||||||||
| PI | 0.013 *** | 0.011 *** | 0.010 *** | ||||||||
| (5.889) | (5.845) | (2.710) | |||||||||
| Age | −0.016 *** | −0.012 *** | −0.001 | 0.022 | −0.016 *** | −0.019 *** | 0.016 * | 0.016 | −0.017 *** | −0.010 *** | 0.001 |
| (−6.219) | (−5.559) | (−0.173) | (0.430) | (−2.827) | (−3.621) | (1.671) | (0.496) | (−5.669) | (−4.026) | (0.116) | |
| Lev | −0.010 * | −0.011 ** | −0.004 | −0.182 | −0.010 | −0.006 | −0.025 | 0.007 | −0.011 * | −0.011 ** | −0.011 |
| (−1.797) | (−2.137) | (−0.428) | (−1.638) | (−0.769) | (−0.515) | (−1.176) | (0.102) | (−1.684) | (−1.991) | (−0.983) | |
| Soe | 0.007 | 0.006 | −0.007 | 0.089 | −0.012 | −0.007 | 0.003 | 0.052 | 0.009 * | 0.005 | −0.005 |
| (1.611) | (1.623) | (−1.119) | (0.947) | (−1.165) | (−0.743) | (0.171) | (1.035) | (1.902) | (1.181) | (−0.656) | |
| Size | 0.039 *** | 0.031 *** | 0.027 *** | 0.710 *** | 0.027 *** | 0.017 *** | 0.018 * | 0.703 *** | 0.030 *** | 0.022 *** | 0.024 *** |
| (17.053) | (15.107) | (7.563) | (17.459) | (4.707) | (3.151) | (1.889) | (23.084) | (9.212) | (7.943) | (4.604) | |
| _cons | −0.877 *** | −0.697 *** | −0.480 *** | 1.123 | −0.896 *** | −0.751 *** | −0.168 | 0.630 | −0.886 *** | −0.680 *** | −0.590 *** |
| (−19.033) | (−16.904) | (−6.596) | (1.348) | (−9.580) | (−8.521) | (−1.071) | (0.997) | (−15.215) | (−13.468) | (−6.265) | |
| Firm fixed effect | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| Year fixed effect | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| N | 2983 | 2983 | 2983 | 698 | 698 | 698 | 698 | 2192 | 2192 | 2192 | 2192 |
| R2 | 0.972 | 0.960 | 0.881 | 0.986 | 0.973 | 0.969 | 0.878 | 0.978 | 0.974 | 0.962 | 0.885 |
| F | 76.650 | 59.789 | 10.459 | 86.285 | 19.270 | 17.572 | 2.113 | 147.390 | 45.879 | 35.302 | 8.619 |
| Soe = 1 | Soe = 0 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ER | ER1 | ER2 | ER3 | ER | ER1 | ER2 | ER3 | |
| HCI | 0.002 | 0.006 *** | 0.002 | −0.002 | 0.006 *** | 0.007 *** | 0.007 *** | −0.003 |
| (1.518) | (2.955) | (1.085) | (−0.629) | (4.992) | (4.484) | (5.215) | (−1.170) | |
| Age | −0.006 | −0.017 | −0.006 | 0.011 | −0.010 *** | −0.013 *** | −0.012 *** | 0.000 |
| (−0.754) | (−1.646) | (−0.687) | (0.700) | (−5.015) | (−4.993) | (−4.850) | (0.013) | |
| Lev | −0.008 | −0.015 | −0.012 | 0.019 | −0.009 ** | −0.009 | −0.010 * | −0.010 |
| (−0.770) | (−1.101) | (−0.980) | (0.874) | (−2.013) | (−1.454) | (−1.784) | (−1.016) | |
| Size | 0.042 *** | 0.047 *** | 0.043 *** | 0.033 *** | 0.029 *** | 0.037 *** | 0.027 *** | 0.024 *** |
| (9.941) | (8.738) | (9.127) | (3.855) | (14.897) | (14.675) | (11.851) | (6.091) | |
| _cons | −0.923 *** | −1.068 *** | −0.950 *** | −0.679 *** | −0.661 *** | −0.844 *** | −0.656 *** | −0.428 *** |
| (−9.936) | (−8.917) | (−9.144) | (−3.569) | (−17.497) | (−17.062) | (−14.557) | (−5.480) | |
| Firm fixed effect | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| Year fixed effect | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| N | 861 | 861 | 861 | 861 | 2103 | 2103 | 2103 | 2103 |
| R2 | 0.977 | 0.976 | 0.969 | 0.902 | 0.968 | 0.968 | 0.952 | 0.859 |
| F | 21.488 | 20.253 | 17.630 | 3.049 | 62.942 | 58.919 | 45.057 | 7.130 |
| Large-Scale Enterprise | Small-Scale Enterprise | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ER | ER1 | ER2 | ER3 | ER | ER1 | ER2 | ER3 | |
| HCI | 0.006 *** | 0.008 *** | 0.007 *** | −0.005 | 0.001 | 0.002 *** | 0.001 | −0.000 |
| (3.695) | (4.154) | (3.864) | (−1.450) | (1.541) | (3.368) | (1.008) | (−0.196) | |
| Age | −0.009 * | −0.014 ** | −0.009 | −0.003 | −0.004 *** | 0.001 | −0.004 *** | −0.010 *** |
| (−1.688) | (−1.999) | (−1.448) | (−0.287) | (−3.163) | (0.470) | (−2.810) | (−3.753) | |
| Lev | −0.009 | −0.005 | −0.014 | 0.006 | −0.001 | 0.003 | 0.000 | −0.009 |
| (−0.796) | (−0.367) | (−1.099) | (0.262) | (−0.231) | (1.200) | (0.063) | (−1.497) | |
| Soe | 0.004 | 0.006 | 0.005 | −0.004 | 0.000 | 0.002 | 0.001 | −0.005 |
| (0.810) | (0.889) | (0.867) | (−0.345) | (0.012) | (0.840) | (0.230) | (−0.923) | |
| Size | 0.047 *** | 0.060 *** | 0.047 *** | 0.036 *** | 0.014 *** | 0.011 *** | 0.013 *** | 0.022 *** |
| (13.070) | (12.780) | (11.049) | (4.756) | (9.935) | (8.049) | (8.019) | (6.593) | |
| _cons | −1.099 *** | −1.406 *** | −1.122 *** | −0.645 *** | −0.275 *** | −0.240 *** | −0.264 *** | −0.383 *** |
| (−13.867) | (−13.727) | (−12.070) | (−3.927) | (−9.993) | (−8.977) | (−8.094) | (−5.888) | |
| Firm fixed effect | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| Year fixed effect | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| N | 1463 | 1463 | 1463 | 1463 | 1458 | 1458 | 1458 | 1458 |
| R2 | 0.974 | 0.973 | 0.962 | 0.880 | 0.958 | 0.967 | 0.934 | 0.890 |
| F | 39.293 | 38.857 | 29.956 | 4.043 | 21.183 | 21.824 | 13.714 | 8.699 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chao, K.; Wang, S.; Wang, M. Human Capital Investment, Technological Innovation, and Resilience of Chinese High-End Manufacturing Enterprises. Sustainability 2025, 17, 247. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17010247
Chao K, Wang S, Wang M. Human Capital Investment, Technological Innovation, and Resilience of Chinese High-End Manufacturing Enterprises. Sustainability. 2025; 17(1):247. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17010247
Chicago/Turabian StyleChao, Kun, Shixue Wang, and Meijia Wang. 2025. "Human Capital Investment, Technological Innovation, and Resilience of Chinese High-End Manufacturing Enterprises" Sustainability 17, no. 1: 247. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17010247
APA StyleChao, K., Wang, S., & Wang, M. (2025). Human Capital Investment, Technological Innovation, and Resilience of Chinese High-End Manufacturing Enterprises. Sustainability, 17(1), 247. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17010247





