Exploring the Importance of Destination Attributes of Sustainable Urban Waterfronts: Text and Data Mining of Tourists’ Online Reviews
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. Sustainable Urban Waterfront Destinations
2.2. S–O–R Theory
2.3. Destination Attributes
- Natural, social, and historical factors;
- Entertainment and shopping facilities;
- Infrastructure;
- Food;
- Shelter.
2.4. Text and Data Mining in Online Reviews
- Pre-modeling (research questions, data evaluation, and preparation for data mining);
- Modeling (selecting analytical techniques, analyzing data, evaluating results, and final model identification);
- Post-modeling (applying and tracking the outcomes of data mining models).
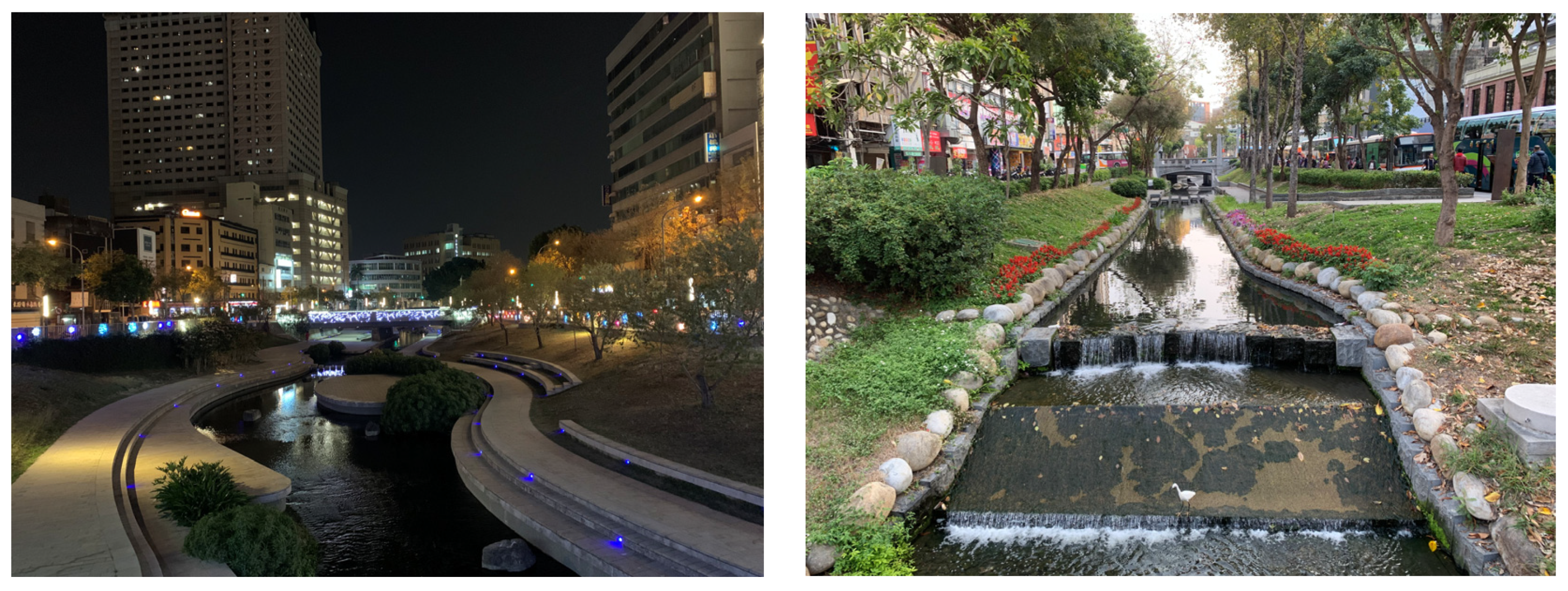
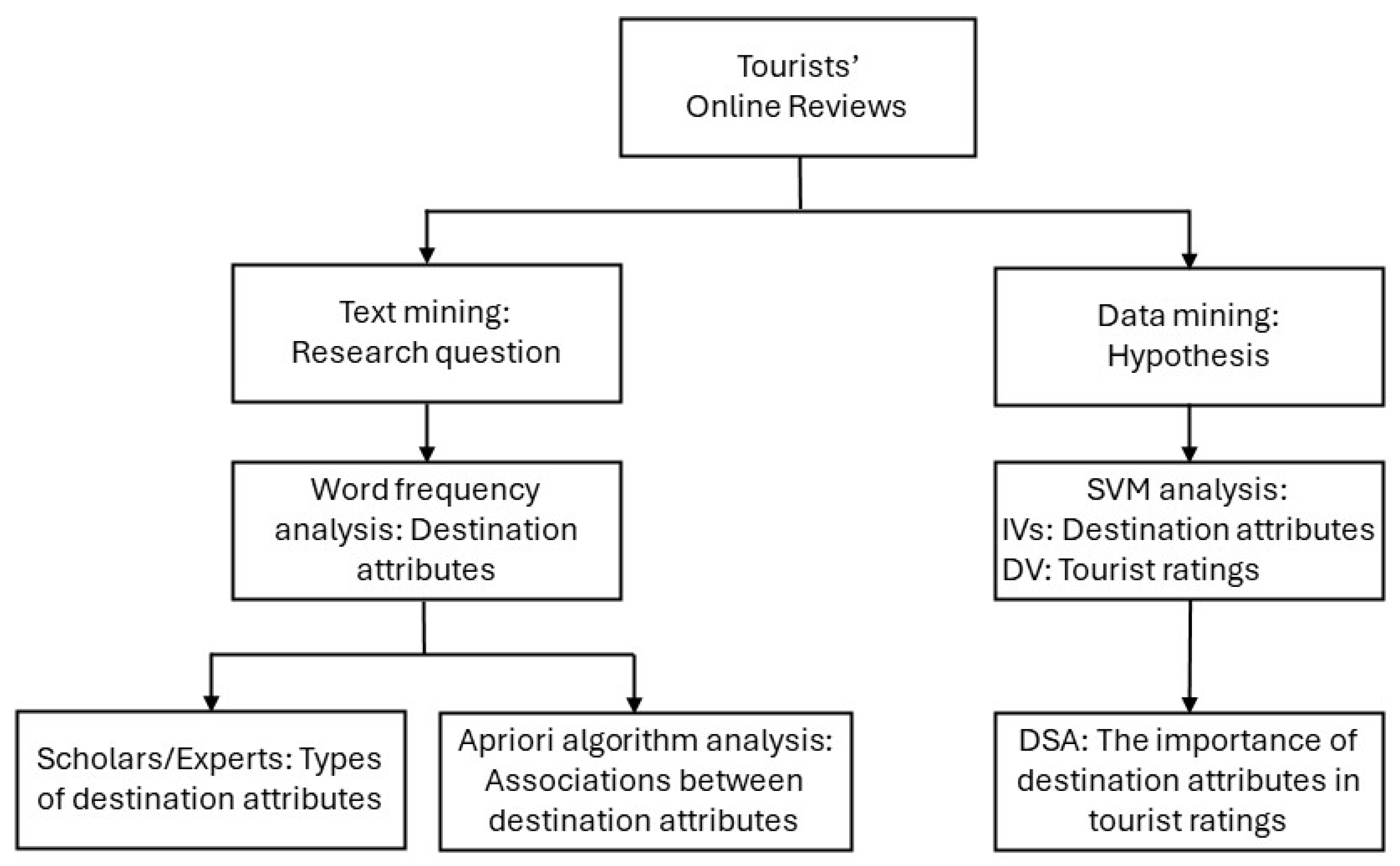
3. Methods
4. Results
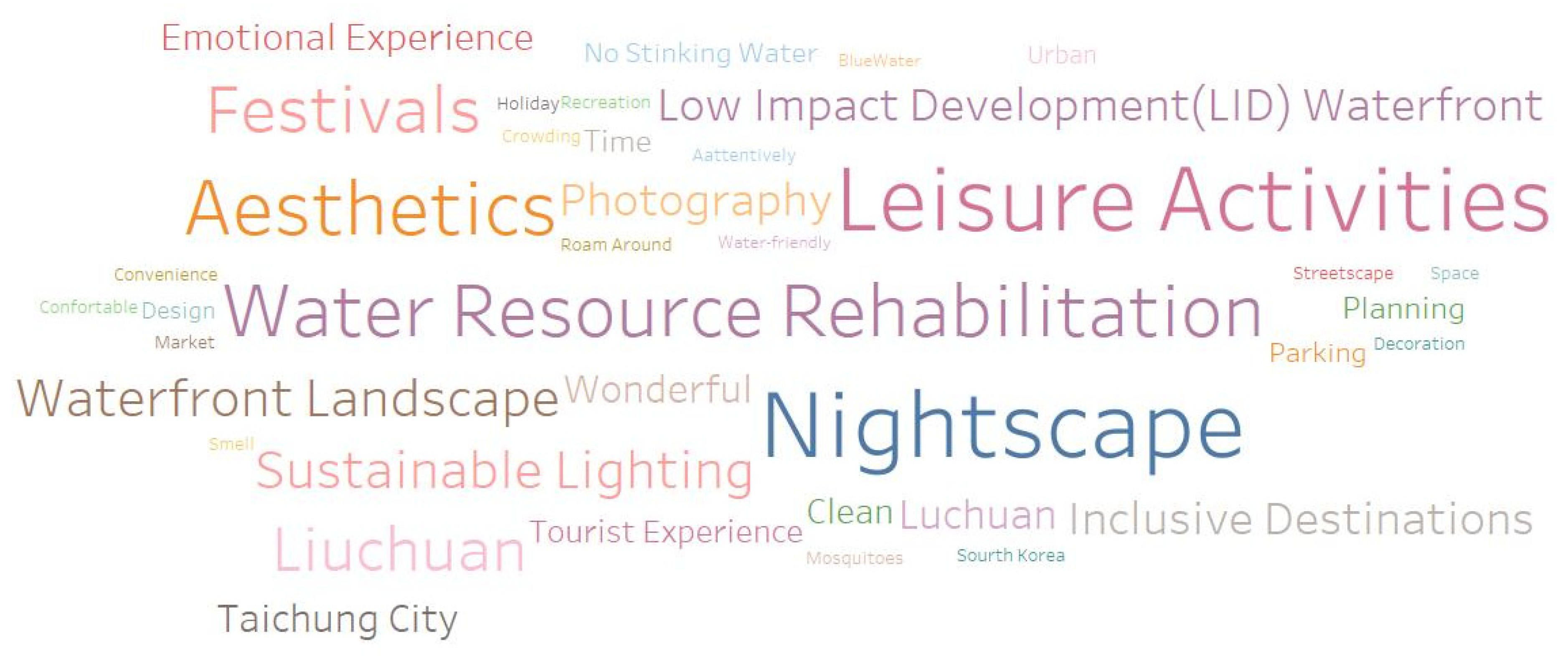
4.1. Destination Attributes of Sustainable Urban Waterfronts
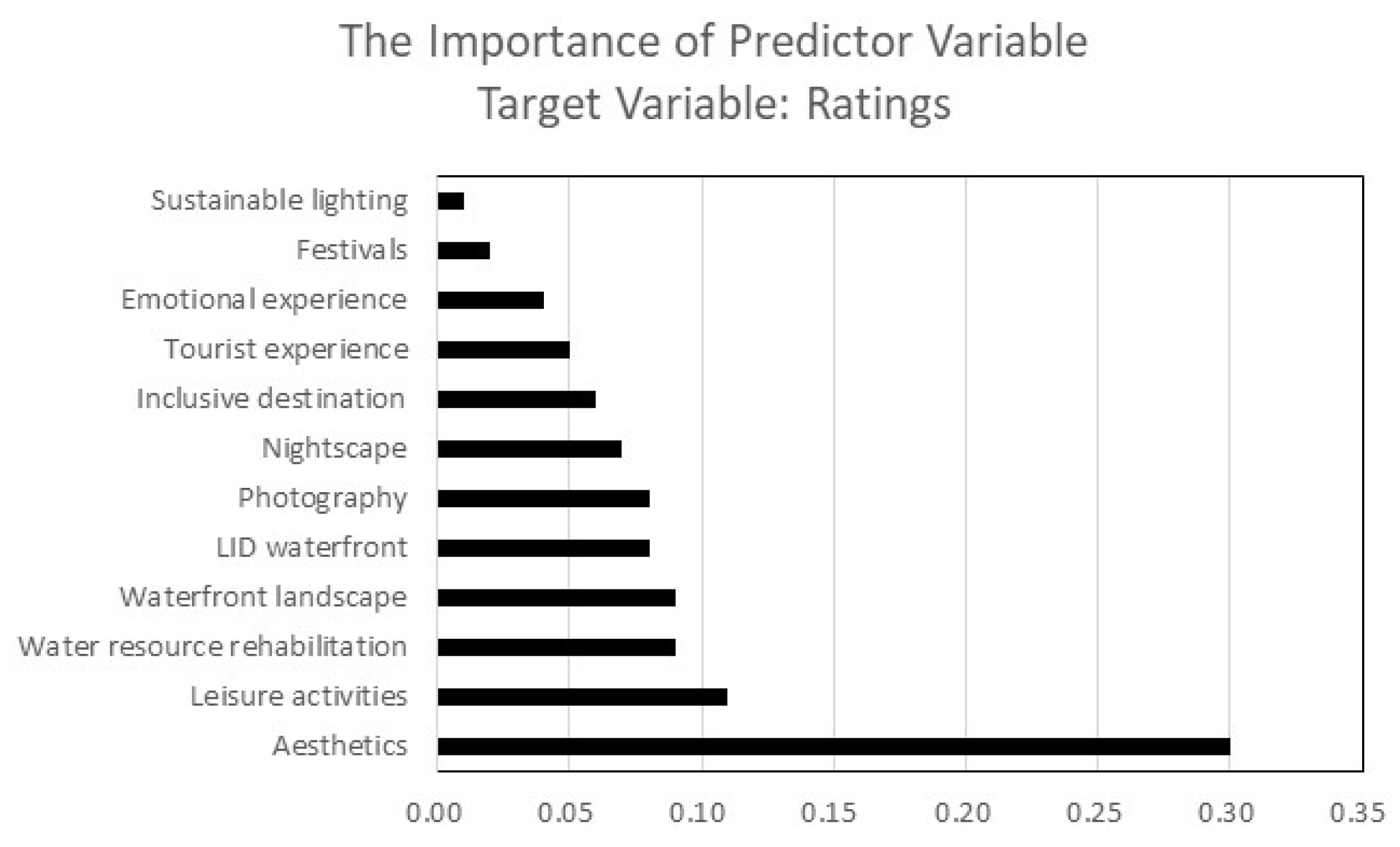
4.2. The Impacts of Destination Attributes on Tourists’ Ratings
- Aesthetics (0.30%);
- Leisure activities (0.11%);
- Water resource rehabilitation (0.09%);
- Waterfront landscape (0.09%);
- LID waterfront (0.08);
- Photography (0.08%);
- Nightscape (0.07%);
- Inclusive destinations (0.06%);
- Tourist experiences (0.05%);
- Emotional experiences (0.04%);
- Festivals (0.02%);
- Sustainable lighting (0.01%).
4.3. Associations between Destination Attributes
5. Discussion and Implications
6. Limitations and Further Research
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Giles-Corti, B.; Lowe, M.; Arundel, J. Achieving the SDGs: Evaluating indicators to be used to benchmark and monitor progress towards creating healthy and sustainable cities. Health Policy 2020, 124, 581–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pendlebury, J. The historical urban landscape of the Liverpool waterfront: The three graces in a new perspective. In Waterfronts revisited: European Ports in a Historic and Global Perspective; Porfyriou, H., Sepe, M., Eds.; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 108–122. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, P.F.; Gu, K. The changing urban morphology: Waterfront redevelopment and event tourism in New Zealand. Tour. Manag. Perspect. 2015, 15, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, A.; Thomas, H. Waterfront tourism and public art in Cardiff Bay and Lisbon’s Park of Nations. J. Policy Res. Tour. Leis. Events 2012, 4, 327–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, R.M.R. Sustainable urban waterfronts using sustainability assessment rating systems. Int. J. Civ. Environ. Struct. Constr. Archit. Eng. 2014, 8, 488–498. [Google Scholar]
- Morrison, A.M.; Maxim, C. World Tourism Cities: A Systematic Approach to Urban Tourism; Routledge: London, UK, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Giovinazzi, O.; Moretti, M. Port cities and urban waterfront: Transformations and opportunities. TeMaLab J. Mobil. Land Use Environ. 2010, 3, 57–64. [Google Scholar]
- Niemann, B.; Werner, T. Strategies for the sustainable urban waterfront. WIT Trans. Ecol. Environ. 2016, 204, 431–439. [Google Scholar]
- Lagarense, B.E.S.; Walansendow, A. Exploring residents’ perceptions and participation on tourism and waterfront development: The case of Manado waterfront development in Indonesia. Asia Pac. J. Tour. Res. 2015, 20, 223–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blasi, S.; Ganzaroli, A.; De Noni, I. Smartening sustainable development in cities: Strengthening the theoretical linkage between smart cities and SDGs. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2022, 80, 103793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixit, S.K.; Abraham, A. Tourism in Asian Cities; Dixit, S.K., Ed.; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2021; pp. 11–30. [Google Scholar]
- Aiesha, R.; Evans, G. VivaCity: Mixed-use urban tourism. In Tourism, Culture & Regeneration; Smith, M., Ed.; CAB International: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2007; pp. 35–48. [Google Scholar]
- Griffin, T.; Hayllar, B. Historic waterfronts as tourism precincts: An experiential perspective. Tour. Hosp. Res. 2007, 7, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doorne, S. Power, participation and perception: An insider’s perspective on the politics of the Wellington waterfront redevelopment. Curr. Issues Tour. 1998, 1, 129–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luka, N. Contested periurban amenity landscapes: Changing waterfront ‘countryside ideals’ in central Canada. Landsc. Res. 2017, 42, 256–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritchie, J.R.B.; Crouch, G.I. The Competitive Destination: A Sustainable Tourism Perspective; CABI: Wallingford, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Reyes-Menendez, A.; Correia, M.; Matos, N.; Adap, C. Sustainability Understanding Online Consumer Behavior and eWOM Strategies for Sustainable Business Management in the Tourism Industry. Sustainability 2020, 12, 8972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, F.J.; Braesemann, F.; Teubner, T. Measuring sustainable tourism with online platform data. EPJ Data Sci. 2022, 11, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Echtner, C.M.; Ritchie, J.R.B. The measurement of destination image: An empirical assessment. J. Travel Res. 1993, 31, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, K.; Li, X. Tourism destination image: Conceptual problems and definitional solutions. J. Travel Res. 2016, 55, 1065–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, S. Measuring tourists’ meal experience by mining online user generated content about restaurants. Scand. J. Hosp. Tour. 2019, 19, 371–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, A.; Murphy, H.; Fierro, J.C. Hospitality and travel: The nature and implications of user-generated content. Cornell Hosp. Q. 2012, 53, 220–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsiakali, K. User-generated-content versus marketing-generated-content: Personality and content influence on traveller’s behavior. J. Hosp. Mark. Manag. 2018, 27, 946–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantallops, A.S.; Salvi, F. New consumer behavior: A review of research on eWOM and hotels. Int. J. Hosp. Manag. 2014, 36, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, C.; Taneja, U. Electronic word of mouth for the choice of wellness tourism destination image and the moderating role of COVID-19 pandemic. J. Tour. Futures, 2023; ahead-of-print. [Google Scholar]
- Banerjee, S.; Chua, A.Y.K. In search of patterns among travellers’ hotel ratings in TripAdvisor. Tour. Manag. 2016, 53, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariani, M.; Borghi, M. Environmental discourse in hotel online reviews: A big data analysis. J. Sustain. Tour. 2021, 29, 829–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salah, M.H.A.; Abdou, A.H.; Hassan, T.H.; El-Amin, M.A.-M.M.; Kegour, A.B.A.; Alboray, H.M.M.; Mohamed, A.S.D.; Ali, H.S.A.M.; Mohammed, E.F.A. Power of eWOM and Its Antecedents in Driving Customers’ Intention to Revisit: An Empirical Investigation on Five-Star Eco-Friendly Hotels in Saudi Arabia. Sustainability 2023, 15, 9270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauri, A.G.; Minazzi, R. Web reviews influence on expectations and purchasing intentions of hotel potential customers. Int. J. Hosp. Manag. 2013, 34, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toral, S.L.; Martínez-Torres, M.R.; Gonzalez-Rodriguez, M.R. Identification of the unique attributes of tourist destinations from online reviews. J. Travel Res. 2018, 57, 908–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casalo, L.V.; Flavian, C.; Guinaliu, M.; Ekinci, Y. Do online hotel rating schemes influence booking behaviors? Int. J. Hosp. Manag. 2015, 49, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tucker, C.E. Social networks, personalized advertising, and privacy controls. J. Mark. Res. 2014, 51, 546–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, M.; Jeon, M.M. Customer reviews of hotel experiences through consumer generated media (CGM). J. Hosp. Leis. Mark. 2008, 17, 121–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermeulen, I.E.; Seegers, D. Tried and tested the impact of online hotel reviews on consumer consideration. Tour. Manag. 2009, 30, 123–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baloglu, S.; Mangaloglu, M. Tourism destination images of Turkey, Egypt, Greece, and Italy as perceived by US-based tour operators and travel agents. Tour. Manag. 2001, 22, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stepchenkova, S.; Li, X.R. Destination image: Do top-of-mind associations say it all? Ann. Tour. Res. 2014, 45, 46–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calheiros, A.C.; Moro, S.; Rita, P. Sentiment classification of consumer generated online reviews using topic modeling. J. Hosp. Mark. Manag. 2017, 26, 675–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sparks, B.A.; Browning, V. The impact of online reviews on hotel booking intentions and perception of trust. Tour. Manag. 2011, 32, 1310–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moro, S.; Rita, P.; Coelho, J. Stripping customers’ feedback on hotels through data mining: The case of Las Vegas Strip. Tour. Manag. Perspect. 2017, 23, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Dewancker, B.J.; Qi, Q. Citizens’ preferences and attitudes towards urban waterfront spaces: A case study of Qiantang riverside development. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 45787–45801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyer, M.C. The City of Collective Memory; MIT Press: London, UK, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Fernandes, J.; Chamusca, P.; Pinto, J.; Tenreiro, J.; Figueiredo, P. Urban rehabilitation and tourism: Lessons from Porto (2010–2020). Sustainability 2023, 15, 6581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, C.; Harris, S.; Taufen, A.; Livesley, J.; Crommelin, L. What does it mean for a transitioning urban waterfront to “work” from a sustainability perspective? J. Urban. Int. Res. Placemaking Urban Sustain. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leporelli, E.; Santi, G. From psychology of sustainability to sustainability of urban spaces: Promoting a primary prevention approach for well-being in the healthy city designing. A Waterfr. Case Study Livorno. Sustain. 2019, 11, 760. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, A. On the water’s edge: Developing cultural regeneration paradigms for urban waterfronts. In Tourism, Culture Regeneration; Smith, M., Ed.; CABI: Wallingford, UK, 2007; pp. 143–150. [Google Scholar]
- Craig-Smith, S. The role of tourism in inner-harbor redevelopment: A multinational perspective. In Recreation and Tourism as a Catalyst for Urban Waterfront Redevelopment: An International Survey; Craig-Smith, S., Fagence, M., Eds.; Praeger: Westport, CT, USA, 1995; pp. 16–35. [Google Scholar]
- Kipfer, S.; Keil, R. Planning Inc.? Planning the competitive city in the New Toronto. Antipode 2002, 34, 227–264. [Google Scholar]
- Law, C.M. Introduction. In Tourism in Major Cities; Law, C.M., Ed.; International Thomson Business Press: London, UK, 1996; pp. 1–22. [Google Scholar]
- Mehrabian, A.; Russell, J.A. An Approach to Environmental Psychology; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1974. [Google Scholar]
- Eroglu, S.A.; Machleit, K.A.; Davis, L.M. Atmospheric qualities of online retailing: A conceptual model and implications. J. Bus. Res. 2001, 54, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loureiro, S.; Ribeiro, L. The effect of atmosphere on emotions online shopping intention: Age differentiation. In Conference Book Proceeding of ANZMAC Conference–Marketing in the Age of Consumerism: Jekyll or Hyde? MacCarthy, M., Ed.; ANZMAC: Sydney, Australia, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Bigne, E.; Chatzipanagiotou, K.; Ruiz, C. Pictorial content, sequence of conflicting online reviews and consumer decision-making: The stimulus-organism-response model revisited. J. Bus. Res. 2020, 115, 403–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; So, K.K.F.; Hu, X.; Poomchaisuwan, M. Travel for affection: A stimulus-organism-response model of honeymoon tourism experiences. J. Hosp. Tour. Res. 2022, 46, 1187–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lew, A.A. A framework for tourist attraction research. Ann. Tour. Res. 1987, 14, 553–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H. The antecedents of memorable tourism experiences: The development of a scale to measure the destination attributes associated with memorable experiences. Tour. Manag. 2014, 44, 34–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prayag, G. Exploring the relationship between destination image and brand personality of a tourist destination: An application of projective techniques. J. Travel Tour. Res. 2007, 2, 111–130. [Google Scholar]
- Gearing, C.; Swart, W.; Var, T. Establishing a measure of touristic attractiveness. J. Travel Res. 1974, 12, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, C.; Fletcher, J.; Gilbert, D.; Wanhill, S. Tourism: Principles and Practice; Longman Scientific Technical: Harlow, UK, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Buhalis, D. Marketing the competitive destination of the future. Tour. Manag. 2000, 21, 97–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, H.G.; Han, H. Tourist experience quality and loyalty to an island destination: The moderating impact of destination image. J. Travel Tour. Mark. 2018, 36, 43–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlesinger, W.; Cervera-Taulet, A.; Pérez-Cabaña, C. Exploring the links between destination attributes, quality of service experience and loyalty in emerging Mediterranean destinations. Tour. Manag. Perspect. 2020, 35, 100699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathnaweera, D.U.; Weerakoon, K.G.P.K. Sustainability of urban recreational waterfront development in Colombo urban area, Sri Lanka. Geogr. Malays. J. Soc. Space 2021, 17, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaki, S.K.; Hegazy, I.R. Investigating the challenges and opportunities for sustainable waterfront development in Jeddah City. Int. J. Low-Carbon Technol. 2023, 18, 809–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, E.E.; Gill, J. A positioning strategy for a tourist destination, based on analysis of customers’ perceptions and satisfactions. Mark. Intell. Plan. 2005, 23, 172–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, C.; Deb, S.K.; Hasan, A.A.T.; Khandakar, M.S.A. Mediating effect of tourists’ emotional involvement on the relationship between destination attributes and tourist satisfaction. J. Hosp. Tour. Insights 2021, 4, 490–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, C.G.; Qu, H. Examining the relationship between tourists’ attribute, satisfaction and overall satisfaction. J. Hosp. Mark. Manag. 2009, 18, 4–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozdemir, B.; Aksu, A.; Ehtiyar, R.; Cizel, B.; Cizel, R.B.; Icigen, E.T. Relationships among tourist profile, satisfaction and destination loyalty examining empirical evidence in Antalya region in Turkey. J. Hosp. Mark. Manag. 2012, 21, 506–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Žabkar, V.; Brenčič, M.; Dmitrović, T. Modelling perceived quality, visitor satisfaction and behavioural intentions at the destination level. Tour. Manag. 2010, 31, 537–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, T.K.; Wan, D.; Ho, A. Tourists’ satisfaction, recommendation and revisiting Singapore. Tour. Manag. 2007, 28, 965–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations World Tourism Organization. Tourism in the 2030 Agenda. 2023. Available online: https://www.unwto.org/tourism-in-2030-agenda (accessed on 24 December 2023).
- Sotiriadis, M.D.; Van Zyl, C. Electronic word-of-mouth and online reviews in tourism services: The use of Twitter by tourists. Electron. Commer. Res. 2013, 13, 103–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Reilly, T.; Battelle, J. Web Squared: Web 2.0 Five Years on; O’Reilly Media, Inc.: Newton, MA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Tham, A.; Croy, G.; Mair, J. Social media in destination choice: Distinctive electronic word-of-mouth dimensions. J. Travel Tour. Mark. 2013, 30, 144–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papathanassis, A.; Knolle, F. Exploring the adoption and processing of online holiday reviews: A grounded theory approach. Tour. Manag. 2011, 32, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akehurst, G. User generated content: The use of blogs for tourism organisations and tourism consumers. Serv. Bus. 2009, 3, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Royds, D. The big data analysis challenge for landscape architecture. J. Digit. Landsc. Archit. 2018, 3, 191–199. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, W.L.; Stepchenkova, S. User-generated content as a research mode in tourism and hospitality applications: Topics, methods, and software. J. Hosp. Mark. Manag. 2015, 24, 119–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Torres, M.R.; Rodriguez-Piñero, F.; Toral, S.L. Customer preferences versus managerial decision-making in open innovation communities: The case of Starbucks. Technol. Anal. Strateg. Manag. 2015, 27, 1226–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Q.; Duan, W.; Gan, Q. Exploring determinants of voting for the ‘Helpfulness’ of online user reviews: A text mining approach. Decis. Support Syst. 2011, 50, 511–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlou, P.A.; Dimoka, A. The nature and role of feedback text comments in online marketplaces: Implications for trust building, price premiums, and seller differentiation. Inf. Syst. Res. 2006, 17, 392–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.; Lehto, X.Y.; Morrison, A.M. Destination image representation on the web: Content analysis of Macau travel related websites. Tour. Manag. 2007, 28, 118–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youn Kim, H.; Yoon, J.H. Examining national tourism brand image: Content analysis of Lonely Planet Korea. Tour. Rev. 2013, 68, 56–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.L.; Stepchenkova, S. Ecotourism experiences reported online: Classification of satisfaction attributes. Tour. Manag. 2012, 33, 702–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, S.E.; Duan, W.; Boo, S. An analysis of one-star online reviews and responses in the Washington, DC, lodging market. Cornell Hosp. Q. 2013, 54, 49–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turban, E.; Aronson, J.E.; Liang, T.P.; Sharda, R. Decision Support and Business Intelligence Systems, 8th ed.; Pearson Education: London, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Moro, S.; Cortez, P.; Rita, P. A data-driven approach to predict the success of bank telemarketing. Decis. Support Syst. 2014, 62, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liberty Times Net. Four Projects in Taichung City, Including LiuChuan, LuChuan, and DongDaxi Canals, Were Honored with the “2022 Architecture and Landscape Architecture Award”! 2023. Available online: https://news.ltn.com.tw/news/life/breakingnews/4042774 (accessed on 23 July 2023).
- Taichung City Government Tourism and Travel Bureau. LuChuan River Shore Walkway. 2020. Available online: https://travel.taichung.gov.tw/zh-tw/Attractions/Intro/1104/%E6%9F%B3%E5%B7%9D%E6%B0%B4%E5%B2%B8%E6%AD%A5%E9%81%93 (accessed on 31 July 2020).
- Taichung City Government Tourism and Travel Bureau. LiuChuan Waterfront Corridor. 2020. Available online: https://travel.taichung.gov.tw/zh-tw/Attractions/Intro/1260/%E7%B6%A0%E5%B7%9D%E6%B0%B4%E5%B2%B8%E5%BB%8A%E9%81%93 (accessed on 31 July 2020).
- Environmental Protection Administration Executive Yuan, Taiwan. The “River Water Quality Maintenance and Improvement Program” Won the National Sustainable Development Award from the Executive Yuan. 2023. Available online: https://enews.epa.gov.tw/Page/3B3C62C78849F32F/5273464f-49d6-4d31-a1ec-a552e8071cca (accessed on 23 July 2023).
- Wang, W.-C.; Lin, C.-H. Using Big Data for Predicting Tourists’ Reviews on Urban Waterfront: The Case of LuChuan and LiuChuan Canals of Taichung City. In Proceedings of the 2020 the 22st Leisure, Recreation, and Tourism Research Symposium, Taipei, Taiwan, 27 September 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Vapnik, V. The Nature of Statistical Learning Theory; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Godnov, U.; Redek, T. Application of text mining in tourism: Case of Croatia. Ann. Tour. Res. 2016, 58, 162–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCallum, A.; Nigam, K. Text classification by bootstrapping with keywords, EM and shrinkage. In Proceedings of the ACL Workshop for Unsupervised Learning in Natural Language Processing, College Park, MD, USA, 21 June 1999; Kehler, A., Stolcke, A., Eds.; University of Maryland: College Park, MD, USA, 1999; pp. 52–58. [Google Scholar]
- Bengio, Y.; Grandvalet, Y. No unbiased estimator of the variance of k-fold crossvalidation. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2004, 5, 1089–1105. [Google Scholar]
- Refaeilzadeh, P.; Tang, L.; Liu, H. Cross-validation In Encyclopedia of Database Systems; Liu, L., Özsu, M.T., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2009; pp. 532–538. [Google Scholar]
- Moro, S.; Rita, P. Forecasting tomorrow’s tourist. Worldw. Hosp. Tour. Themes 2016, 8, 643–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teoh, T.T.; Rong, Z. Association rules. In Artificial intelligence with Python. Machine learning: Foundations, Methodologies, and Applications; Tan, K.C., Tao, D., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2022; pp. 219–224. [Google Scholar]
- Kostopoulou, S. On the revitalized waterfront: Creative milieu for creative tourism. Sustainability 2013, 5, 4578–4593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahana, H.; Nizar, S.A. Waterfront development: A tool to restore the neighbourhood. Int. J. Sci. Res. 2020, 9, 1027–1033. [Google Scholar]
- Tung, V.W.S.; Ritchie, J.B. Exploring the essence of memorable tourism experiences. Ann. Tour. Res. 2011, 38, 1367–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodside, A.G.; Dubelaar, C. A general theory of tourism consumption systems: A conceptual framework and an empirical exploration. J. Travel Res. 2002, 41, 120–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.; Khan, S.S.; Alharbi, Y. Text mining challenges and applications: A Comprehensive review. Int. J. Comput. Sci. Netw. Secur. 2020, 20, 138–148. [Google Scholar]

| Rule | Consequence | Antecedent | Support | Confidence | Lift |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Leisure activities | Photography | 17.577 | 37.654 | 1.724 |
| 2 | Nightscape | Sustainable lighting | 12.839 | 37.746 | 2.418 |
| 3 | Aesthetics | Nightscape | 5.353 | 37.838 | 1.712 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, W.-C.; Lin, C.-H. Exploring the Importance of Destination Attributes of Sustainable Urban Waterfronts: Text and Data Mining of Tourists’ Online Reviews. Sustainability 2024, 16, 2271. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16062271
Wang W-C, Lin C-H. Exploring the Importance of Destination Attributes of Sustainable Urban Waterfronts: Text and Data Mining of Tourists’ Online Reviews. Sustainability. 2024; 16(6):2271. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16062271
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Wei-Ching, and Chung-Hsien Lin. 2024. "Exploring the Importance of Destination Attributes of Sustainable Urban Waterfronts: Text and Data Mining of Tourists’ Online Reviews" Sustainability 16, no. 6: 2271. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16062271
APA StyleWang, W.-C., & Lin, C.-H. (2024). Exploring the Importance of Destination Attributes of Sustainable Urban Waterfronts: Text and Data Mining of Tourists’ Online Reviews. Sustainability, 16(6), 2271. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16062271






