Arid Urban Green Areas Reimagined: Transforming Landscapes with Native Plants for a Sustainable Future in Aksu, Northwest China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
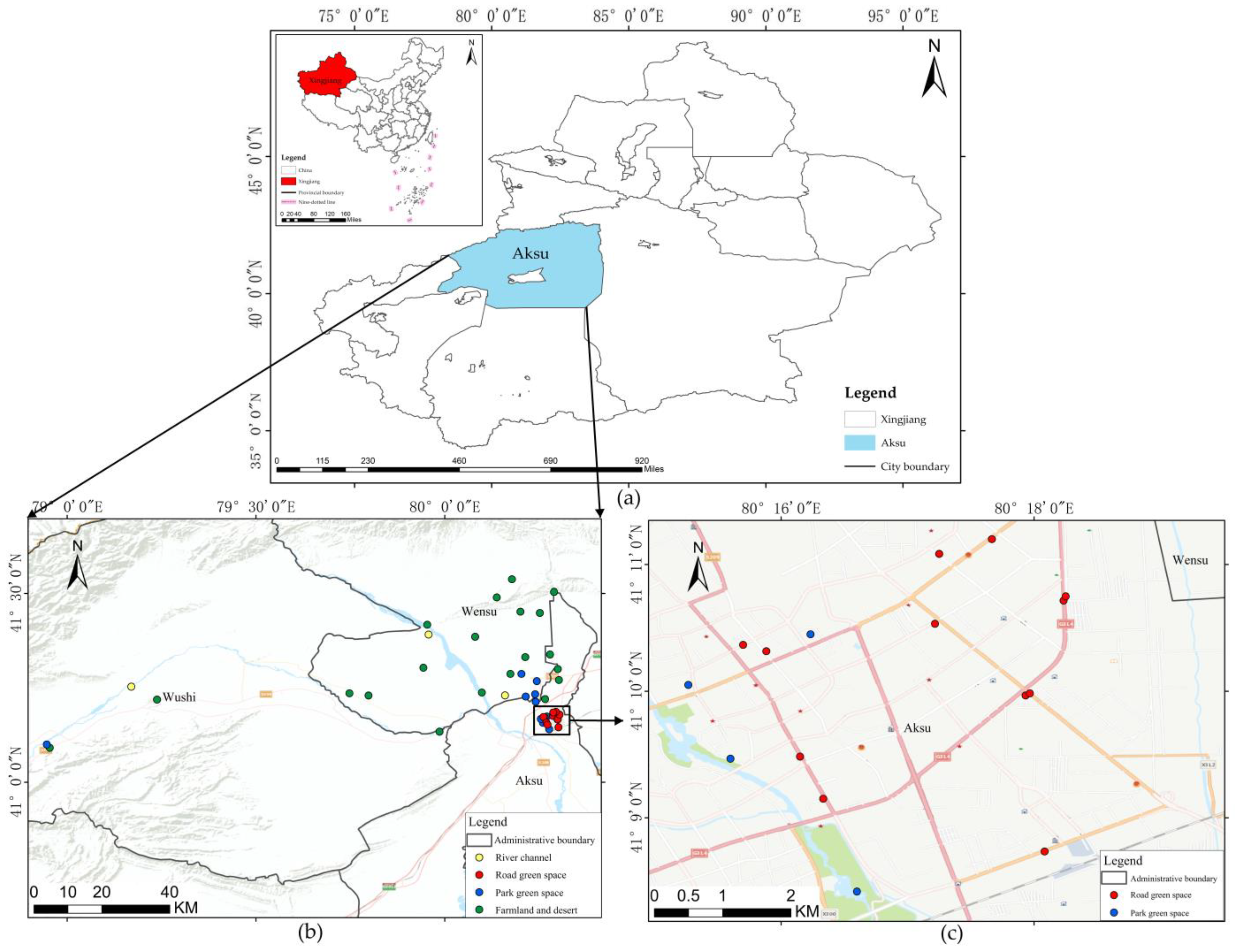
2.1. Study Area
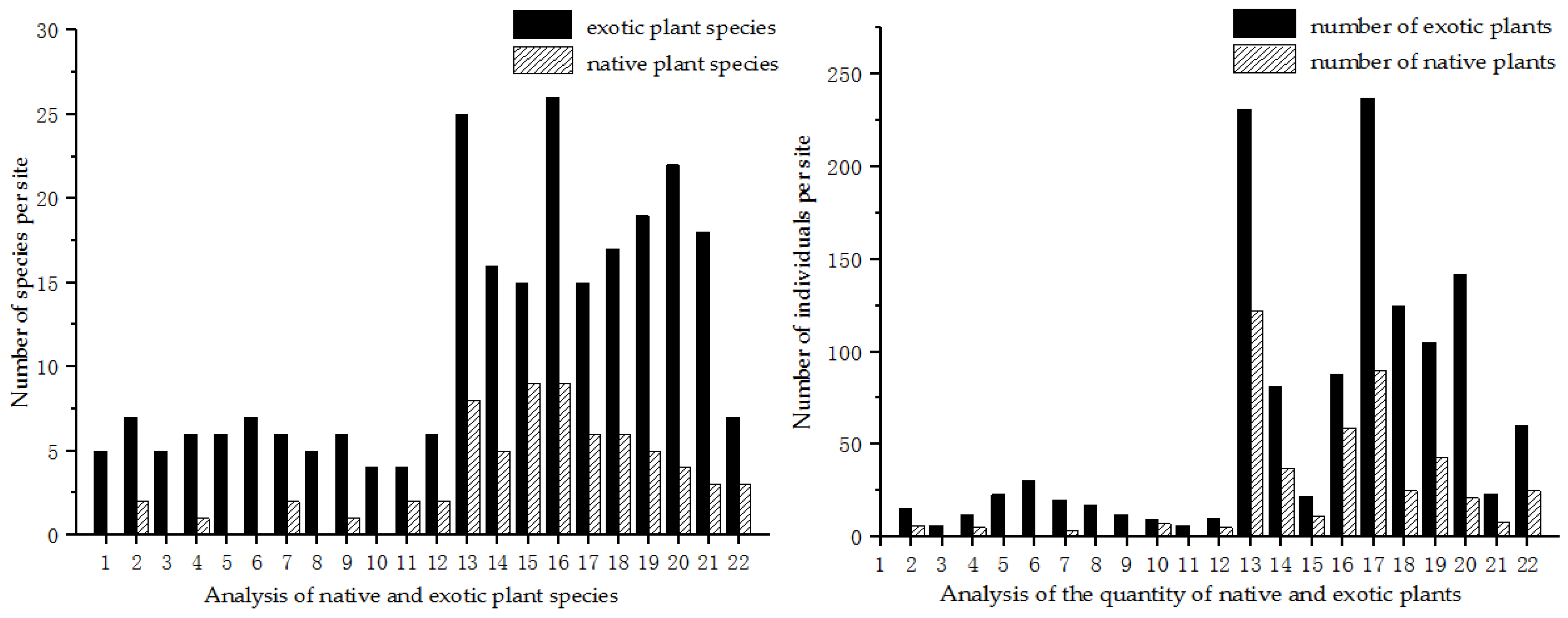
2.2. Plant Species Survey
2.3. Data Processing and Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Analysis of Native Plant Applications
3.1.1. Urban Landscaping Plants
3.1.2. Native Plant Resources
3.2. Functional Analysis of Native Plants
3.2.1. Dust Retention
3.2.2. Windbreak and Sand Fixation
3.2.3. Landscape Functions
4. Discussion
4.1. Application of Native Plants in Public Green Spaces
4.2. The Potential to Substitute Exotic Plants with Native Plants in Urban Landscaping
4.2.1. Substitutability in Terms of Ecological Functions
4.2.2. Native Plants’ Potential in Terms of Landscaping
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Batista, D.A.M.; Maciel, E.A.; Machado, D.L.; Coelho, C.P.; Guilherme, F.A.G. Urban greening dynamics in a Brazil Central city as a subsidy for public policies. Urban Ecosyst. 2023, 26, 845–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jim, C.Y.; Chen, W.Y. Perception and attitude of residents toward urban green spaces in Guangzhou (China). Environ. Manag. 2006, 38, 338–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gopal, D.; Nagendra, H.; Manthey, M. Vegetation in Bangalore’s Slums: Composition, Species Distribution, Density, Diversity, and History. Environ. Manag. 2015, 55, 1390–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, B.Y.; Keremu, R.; Muheiyate, L.; Zhaerhengbieke, H.; Yang, X.D. Priority analysis of native plants and exotic plants in urban greening in Urumqi. J. Xinjiang Univ. 2020, 37, 75–85+93. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.M.; Jeong, M.S.; Han, B.H.; Park, S.-C. A Study on the Planting Design for the Renewal of Urban Neighborhood Park-In Case of Okgu Neighborhood Park, Siheung, Gyeonggi-do, Korea. J. Korean Inst. Landsc. Archit. 2019, 47, 88–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berthon, K.; Thomas, F.; Bekessy, S. The role of ‘nativeness’ in urban greening to support animal biodiversity. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2021, 205, 103959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Slik, F. Are street trees friendly to biodiversity? Landsc. Urban Plan. 2022, 218, 104304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irmak, M.A. Use of native woody plants in urban landscapes. J. Food Agric. Environ. 2013, 11, 1305–1309. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, S.S.; Zhou, J.S.; Chen, H.F. The Investigation of Indigenous Groundcover Plants of Shenzhen City and Their Landscape Application. Chin. Landsc. Archit. 2007, 09, 81–84. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, J.W.; Bai, W.L.; Yao, H.J. Study on General Technology for Selecting Wild Landscape Pant. Chin. Landsc. Archit. 2012, 28, 18–22. [Google Scholar]
- Smetana, S.M.; Crittenden, J.C. Sustainable plants in urban parks: A life cycle analysis of traditional and alternative lawns in Georgia, USA. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2014, 122, 140–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotzen, B.; Branquinho, C.; Prasse, R. Does the exotic equal pollution? Landscape methods for solving the dilemma of using native versus non-native plant species in drylands. Land Degrad. Dev. 2020, 31, 2925–2935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.R.; Song, G.F. On Plant Configuration in Ecological Landscape Design. Chin. Landsc. Archit. 2011, 27, 86–90. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.J.; Hao, R.M. Development Suggestions on Native Woody Plants Based on Plant Survey of Main Urban Green Space of Nanjing. Chin. Landsc. Archit. 2015, 31, 82–85. [Google Scholar]
- Kimball, S.; Lulow, M.; Sorenson, Q.; Balazs, K.; Fang, Y.; Davis, S.J.; O’Connell, M.; Huxman, T.E. Cost-effective ecological restoration. Restor. Ecol. 2015, 23, 800–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Yang, Y.C.; Jin, C.; Dai, J.L.; Hu, S.W. Application of Native Plants in Residences under Different Concepts of Native Plants: A Case Study of Chongqing Main Urban Area. Chin. Landsc. Archit. 2022, 38, 26–31. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, S.; Qi, M.; Huang, L.; Zhao, L.; Lin, D.; Yang, Y. Biotic homogenization of China’s urban greening: A meta-analysis on woody species. Urban For. Urban Green. 2016, 18, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.J. The Advantage of Local Plants and the Reasons of Lacking of Their Application in City Greening. Chin. Landsc. Archit. 2004, 20, 73–74. [Google Scholar]
- Wilde, H.D.; Gandhi, K.J.; Colson, G. State of the science and challenges of breeding landscape plants with ecological function. Hortic. Res. 2015, 2, 14069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.J.; Zhao, J.J.; Liu, S.Y.; Song, C.C.; Jiang, N. Study on the Functional Diversity and the Species Diversity of Plant Communities in Mountain City Parks——A Case Study of the Main Urban Area of Chongqing. Chin. Landsc. Archit. 2021, 37, 124–129. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Zhu, Y. Conservation and Application of Native Plants in Country Parks—A Case Study of Pujiang Country Park Phase I Reconstruction in Shanghai. Landsc. Archit. Academic J. 2020, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baidourela, A.; Halik, U.; Aishan, T.; Abliz, A.; Welp, M. Dust retention capacities of urban trees and the influencing factors in Aksu, xinjiang. China. J. Desert Res. 2015, 35, 322–329. [Google Scholar]
- Nurmamat, K.; Halik, U.; Baidourela, A.; Nasirdin, N. Characterization and Valuation of Dust Retention of the Main Species of Strect Trees in Aksu. City. Sci. Silvae Sin. 2017, 53, 101–107. [Google Scholar]
- Tuerxun, M.; Halik, U.; Maimaiti, Z.; Ailiyasi, A. Relationship between Morphological Structure and Dust-holding Capacity of Ten Fruit Tree Leaves in Peri-urban Area of Aksu. J. Northwest For. Univ. 2016, 31, 279–283+304. [Google Scholar]
- de Sousa, M.P.; Rabbani, A.R.C.; Crepaldi, M.O.S.; da Silva, A.B.F. Arborização viária e sua relação com a infraestrutura urbana em Almenara, MG, Brasil. Terra Plur. 2020, 14, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, Y.C.; Machado, M.; dos Santos Silva, L.; Estevam, R.; Neto, F.F.; Caxambu, M.G. Análise quali-quantitativa da arborização de ruas do município de Godoy Moreira-PR. Rev. da Soc. Bras. Arborização Urbana. 2015, 10, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, C.; Zheng, M.; Huang, L.; Qian, S.; Jim, C.; Lin, D.; Zhao, L.; Minor, J.; Coggins, C.; Chen, B.; et al. Co-existence between humans and nature: Heritage trees in China’s yangtze River region. Urban For. Urban Green. 2020, 54, 126748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zencirkiran, M. Determination of native woody landscape plants in Bursa and Uludag. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2009, 8, 5737–5746. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, W.; Hu, G.; Zhang, Z.; He, Z. Shielding effect of oasis-protection systems composed of various forms of wind break on sand fixation in an arid region: A case study in the Hexi Corridor, northwest China. Ecol. Eng. 2008, 33, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Guan, D.; Peart, M.R. The morphological structure of leaves and the dust-retaining capability of afforested plants in urban Guangzhou, South China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2012, 19, 3440–3449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prusty, B.A.K.; Mishra, P.C.; Azeez, P.A. Dust accumulation and leaf pigment content in vegetation near the national highway at Sambalpur, Orissa, India. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2005, 60, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schleicher, N.J.; Norra, S.; Chai, F.; Chen, Y.; Wang, S.; Cen, K.; Yu, Y.; Stüben, D. Temporal variability of trace metal mobility of urban particulate matter from Beijing–A contribution to health impact assessments of aerosols. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 7248–7265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.; Li, J.; Ma, Y.; Shan, L.; Li, X.; Wei, L. A wind tunnel study of the airflow field and shelter efficiency of mixed windbreaks. Aeolian Res. 2019, 41, 100544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, K.; Liu, S.; Yang, Z.; Fang, E.; Zhou, L.; Huang, N. Effects of sand-fixing and windbreak forests on wind flow: A synthesis of results from field experiments and numerical simulations. J. Arid Land 2017, 9, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, R.J.; Liu, X.K.; Li, J.F.; Zhao, C. Effects of Typical Sand-Fixing Plant on Soil Improvement in Qinghai Lake Area. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2015, 2, 177–181. [Google Scholar]
- He, Y.; Xu, M.J. The Impact of Urbanization on the Diversity of Local Garden Plant Resources. Mol. Plant Breed. 2023, 21, 8234–8238. [Google Scholar]
- Ouyang, Y.F. The Constructing of Natural Plant Landscape. J. Anhui Agric. Sci. 2012, 40, 5391–5393. [Google Scholar]
- Abad, C.J.P. Environmental recovery of abandoned mining areas in Spain: Sustainability and new landscapes in some case studies. J. Sustain. Res. 2019, 1, e190003. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, L. Analysis of the Artistic Effect of Garden Plant Landscaping in Urban Greening. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2022, 2022, 2430067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ocokoljić, M.; Petrov, D.; Galečić, N.; Skočajić, D.; Košanin, O.; Simović, I. Phenological Flowering Patterns of Woody Plants in the Function of Landscape Design: Case Study Belgrade. Land 2023, 12, 706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da, L.J. Urban Near-to-nature Biocoenose Landmark Construction for the Restoration of Native Biodiversity: Concepts and Practices in Shanghai. Chin. Landsc. Archit. 2021, 37, 20–24. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, T.; Chen, Y.; Wang, W.; Chen, Y.; Liu, X. Characteristics of Plant Community in Rural Public Space in Nanjing. J. Northwest For. Univ. 2022, 37, 175–182. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, F.X.; Zhang, J.Q.; Zhao, D.Y.; Dong, L. Characteristics of Alien Plants in Country Parks in Suburb of Beijing. J. Northwest For. Univ. 2018, 33, 8. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, W.; Huang, L.; Yu, F.H. Increasing soil configurational heterogeneity promotes plant community evenness through equalizing differences in competitive ability. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 750, 142308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlóci, L.; Fekete, A. Ornamental Plants and Urban Gardening. Plants 2023, 12, 4096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, H.; Khattak, J.Z.K.; Ppoyil, S.B.T.; Kurup, S.S.; Ksiksi, T.S. Landscaping with native plants in the UAE: A review. Emir. J. Food Agric. 2017, 29, 729–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
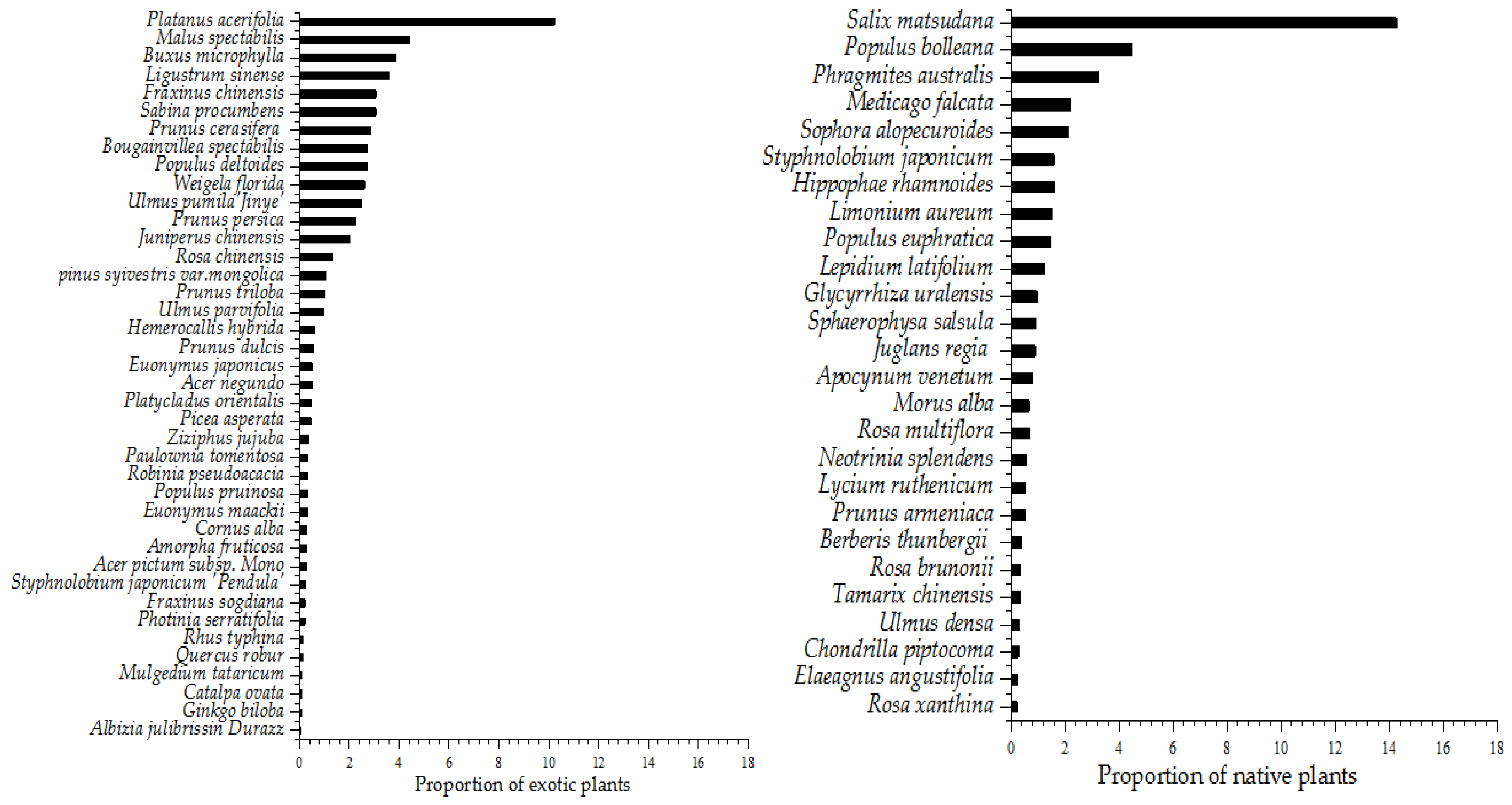
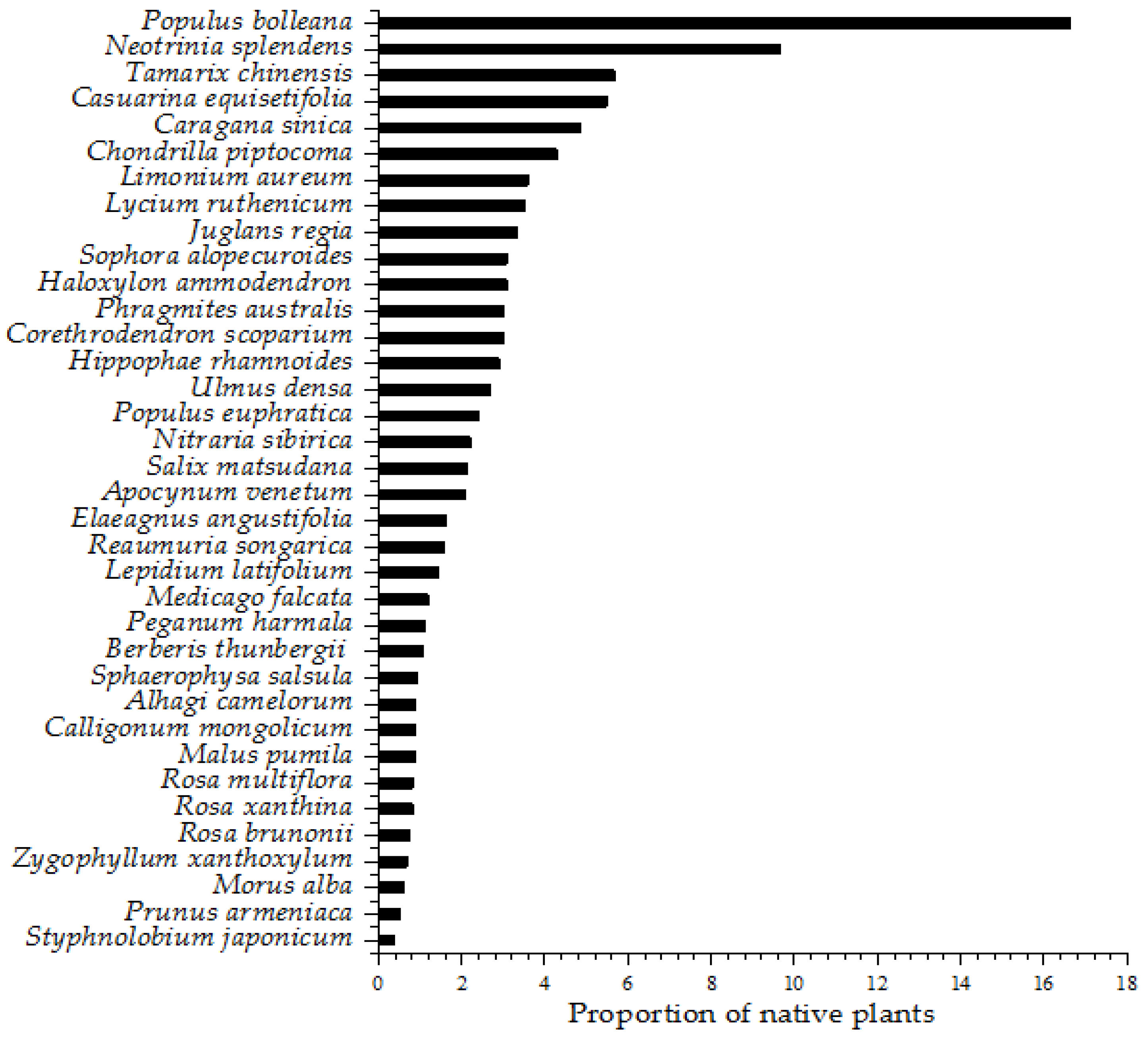
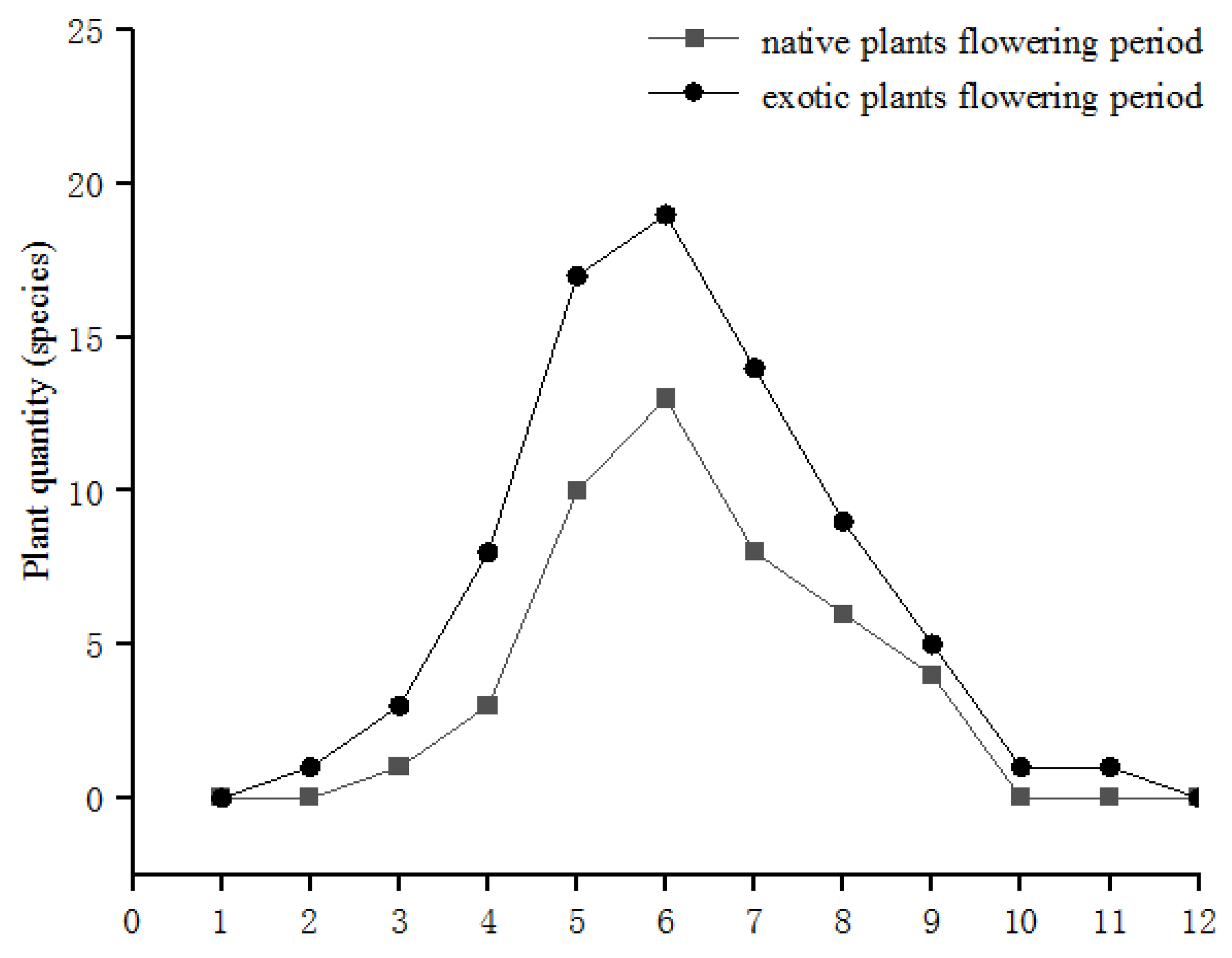
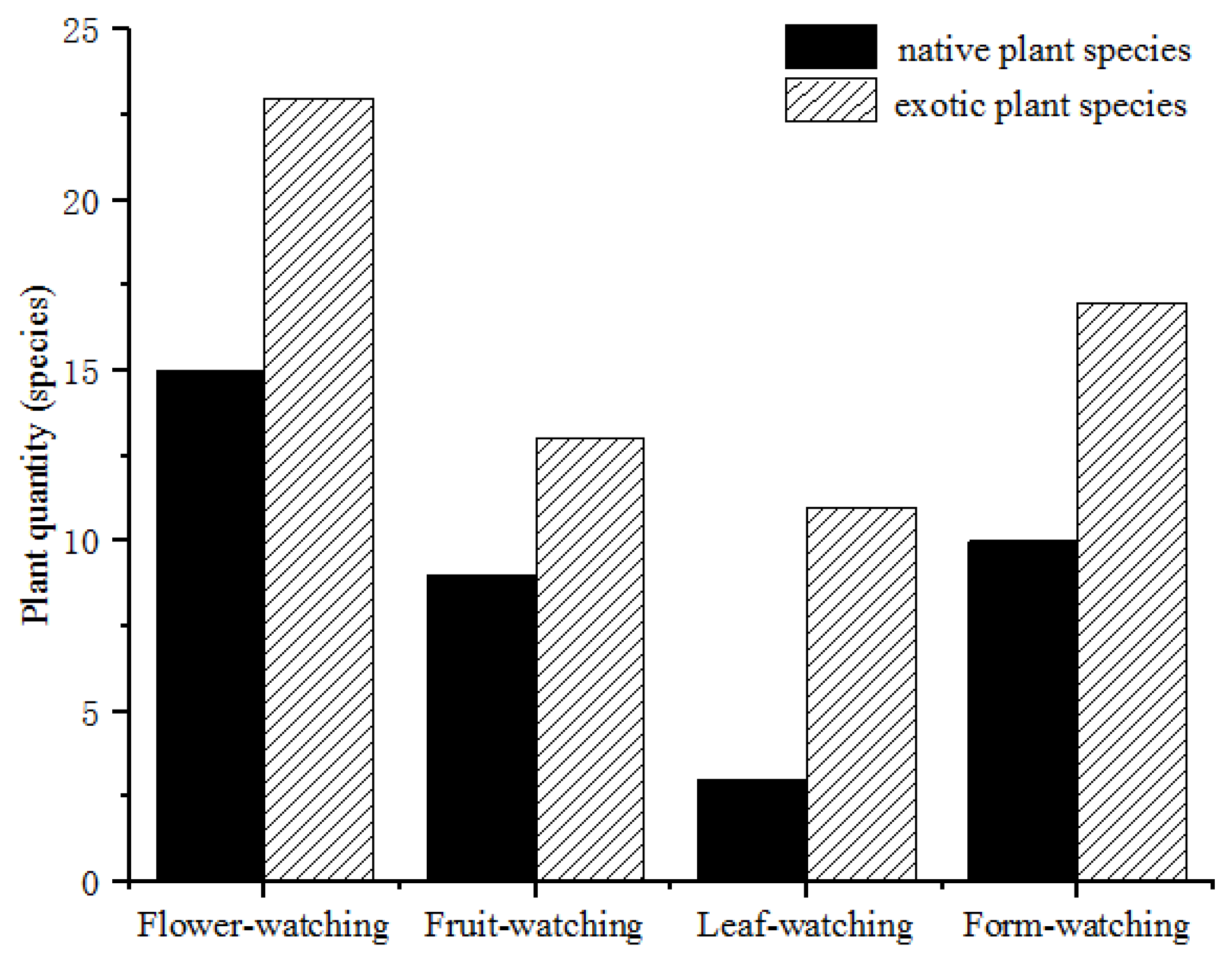
| Plant Type | Species Name | Frequency of Occurrence |
|---|---|---|
| Exotic plant | Platanus acerifolia | 17 |
| Ligustrum sinense | 15 | |
| Ulmus pumila’Jinye’ | 15 | |
| Prunus cerasifera | 14 | |
| Fraxinus chinensis | 12 | |
| Malus spectabilis | 13 | |
| Native plant | Salix matsudana | 13 |
| Populus bolleana | 7 | |
| Styphnolobium japonicum | 7 |
| Plant Type | Latin Name | Leaf Characteristics | Crown Diameter (m) | LAI | Dust Adhering per Leaf Area (g·m−2) | Single-Plant Dust-Adhering Capacity (g·m−2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Exotic plant | Platanus acerifolia | Large leaves with fuzz, leaf stalks with fuzz | 5.70 | 9.66 | 9.15 | 985.09 |
| Prunus cerasifera | Hairless on both sides | 2.68 | 11.17 | 4.27 | 251.96 | |
| Fraxinus sogdiana | Smooth surface | 3.34 | 6.93 | 4.06 | 242.85 | |
| Native plant | Styphnolobium japonicum | Surface with fuzz | 4.77 | 9.19 | 6.75 | 656.50 |
| Ulmus densa | Smooth surface, fuzzy in vein axils on the back | 3.57 | 9.71 | 6.21 | 388.46 | |
| Salix matsudana | Long fuzz on leaf surface, short leaf stalk | 2.75 | 10.45 | 3.29 | 248.10 | |
| Populus bolleana | Smooth surface, fuzzy on the back | 2.49 | 12.42 | 6.54 | 241.74 | |
| Elaeagnus angustifolia | Hairless on both sides | 2.30 | 9.46 | 4.62 | 157.07 | |
| Morus alba | Large leaves, smooth surface, fuzzy on leaf surface | 2.12 | 8.91 | 6.66 | 125.85 |
| Plant Type | Latin Name | Spacing (m) | Height (m) | Crown Diameter (m) | Canopy Density (%) | Windbreak Distance(m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Exotic plant | Platanus acerifolia | 3.5 | 15–20 | 3.35 | 26.26 | 45–100 |
| Robinia pseudoacacia | 5 | 14–17 | 4.7 | 18.80 | 42–85 | |
| Fraxinus chinensis | 4.5 | 4–8 | 2.56 | 10.24 | 12–40 | |
| Juniperus chinensis | 3 | 4–5 | 1.32 | 13.52 | 12–25 | |
| Malus spectabilis | 5 | 3–5 | 0.5 | 2.00 | 9–25 | |
| Native plant | Populus bolleana | 1.52 | 20–30 | 2.49 | 100 | 60–150 |
| Populus euphratica | 3.2 | 20–25 | 3.42 | 26.81 | 60–125 | |
| Styphnolobium japonicum | 5 | 20–25 | 4.77 | 19.08 | 60–125 | |
| Salix matsudana | 3.47 | 8–10 | 3.89 | 30.50 | 24–50 | |
| Morus alba | 2.3 | 3–10 | 2.12 | 33.92 | 9–50 |
| Viewing Type | Latin Name |
|---|---|
| Flower-watching | Caragana sinica; Nitraria sibirica; Tamarix chinensis; Rosa multiflora; Apocynum venetum; Sphaerophysa salsula; Chondrilla piptocoma; Corethrodendron scoparium; Prunus armeniaca; Rosa xanthina; Rosa brunonii; Sophora alopecuroides; Limonium aureum; Lepidium latifolium; Peganum harmala |
| Leaf-watching | Berberis thunbergii; Populus euphratica; Morus alba |
| Fruit-watching | Elaeagnus angustifolia; Juglans regia; Malus pumila; Prunus armeniaca; Nitraria sibirica; Lycium ruthenicum; Hippophae rhamnoides; Calligonum mongolicum; Morus alba |
| Form-watching | Styphnolobium japonicum; Salix matsudana; Ulmus densa; Populus bolleana; Morus alba; Populus euphratica; Prunus armeniaca; Tamarix chinensis; Juglans regia; Malus pumila |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, X.; Li, C.; Zhao, X.; Zhu, T. Arid Urban Green Areas Reimagined: Transforming Landscapes with Native Plants for a Sustainable Future in Aksu, Northwest China. Sustainability 2024, 16, 1546. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16041546
Liu X, Li C, Zhao X, Zhu T. Arid Urban Green Areas Reimagined: Transforming Landscapes with Native Plants for a Sustainable Future in Aksu, Northwest China. Sustainability. 2024; 16(4):1546. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16041546
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Xiaocao, Chengzhi Li, Xiaobing Zhao, and Tianyu Zhu. 2024. "Arid Urban Green Areas Reimagined: Transforming Landscapes with Native Plants for a Sustainable Future in Aksu, Northwest China" Sustainability 16, no. 4: 1546. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16041546
APA StyleLiu, X., Li, C., Zhao, X., & Zhu, T. (2024). Arid Urban Green Areas Reimagined: Transforming Landscapes with Native Plants for a Sustainable Future in Aksu, Northwest China. Sustainability, 16(4), 1546. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16041546








