Spatial-Temporal Evolution of Carbon Sequestration and Emission Reduction Capacity of Agricultural Cultivation in Different Functional Grain Areas
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
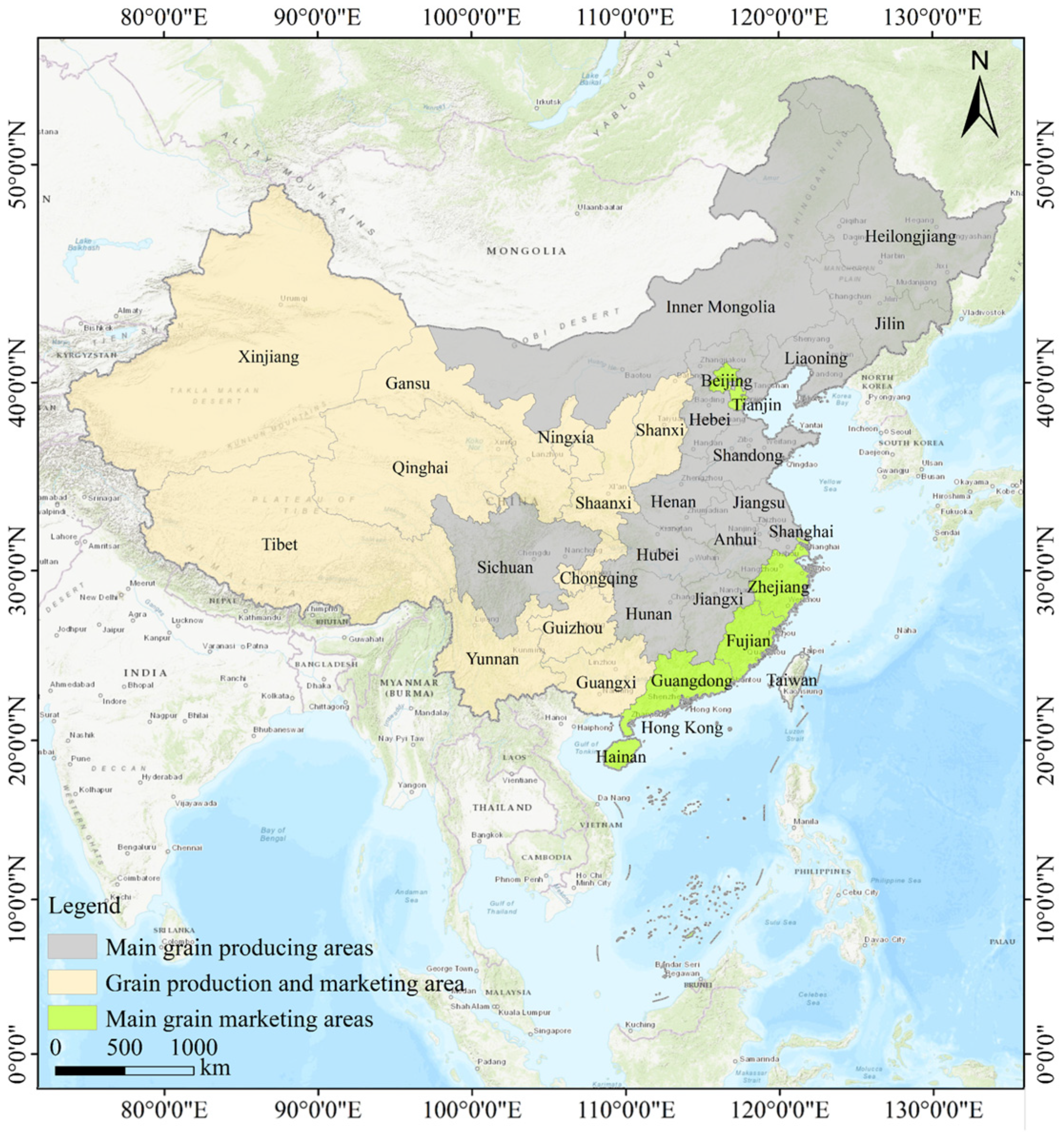
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Sources
2.3. Methodology
2.3.1. Characterization of the Carbon Sequestration and Emission Reduction Capacity of Agricultural Cultivation
2.3.2. Spatial Correlation Analysis
2.3.3. Theil Index
2.3.4. Kernel Density Estimation
3. Results
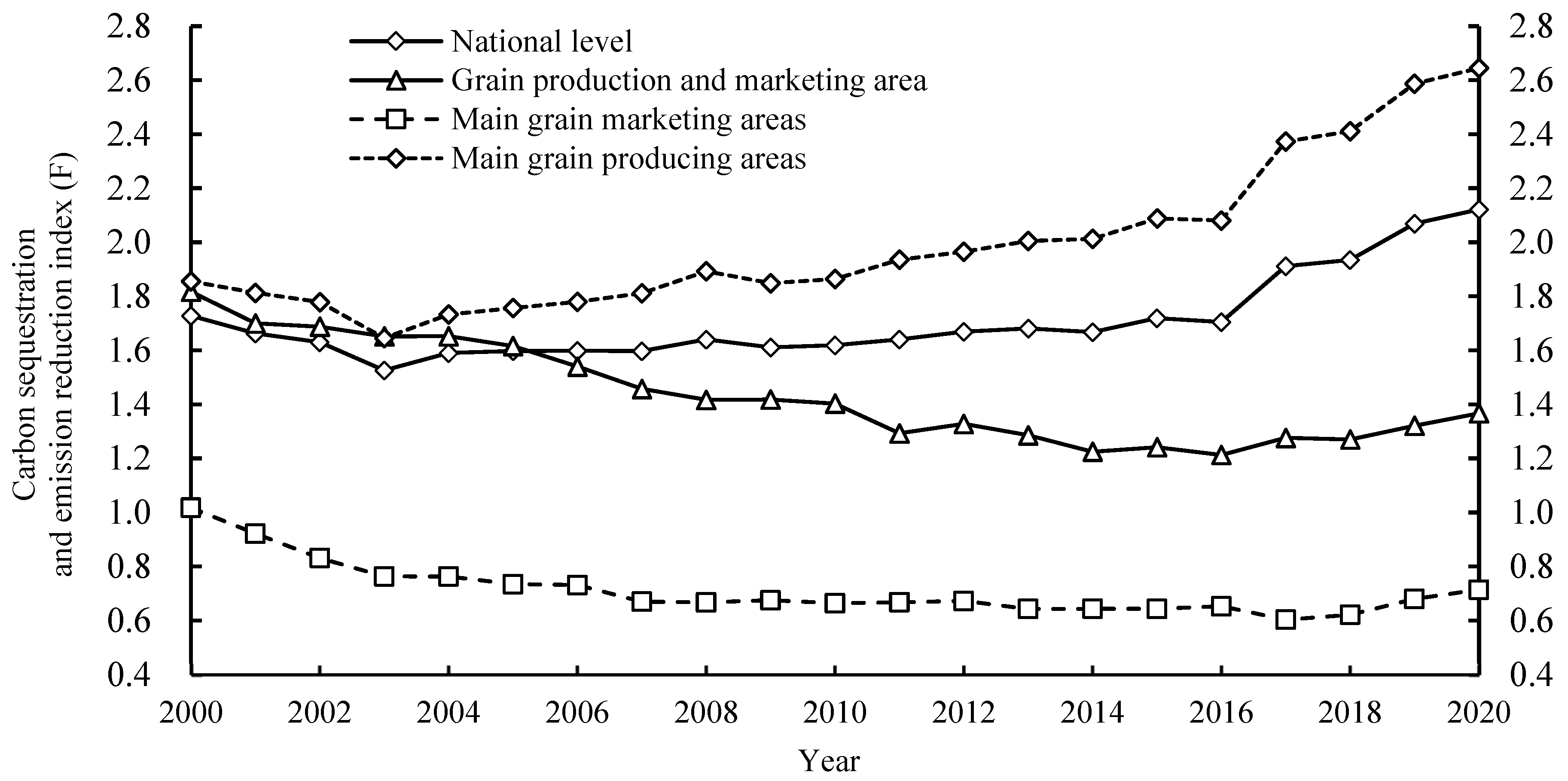
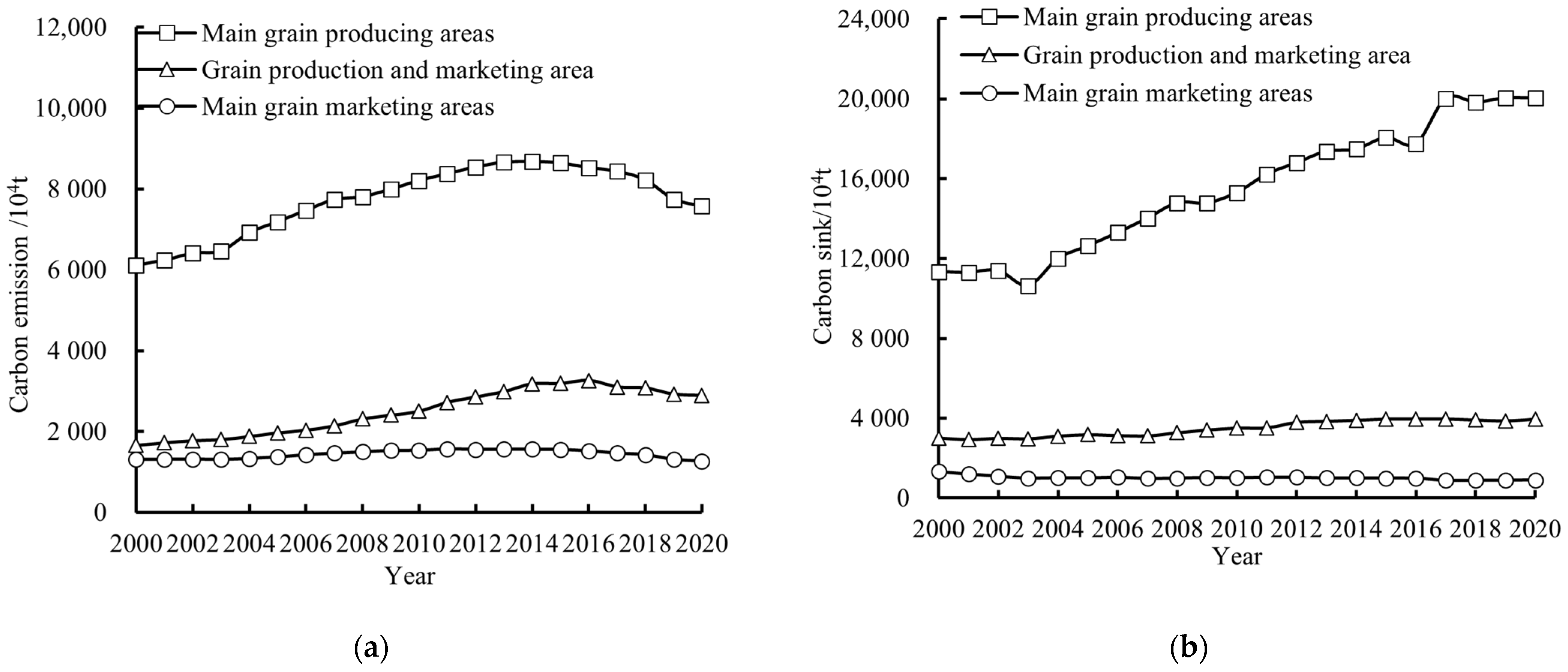
3.1. Spatial and Temporal Changes in Carbon Sequestration and Emission Reduction Capacity of Agricultural Cultivation
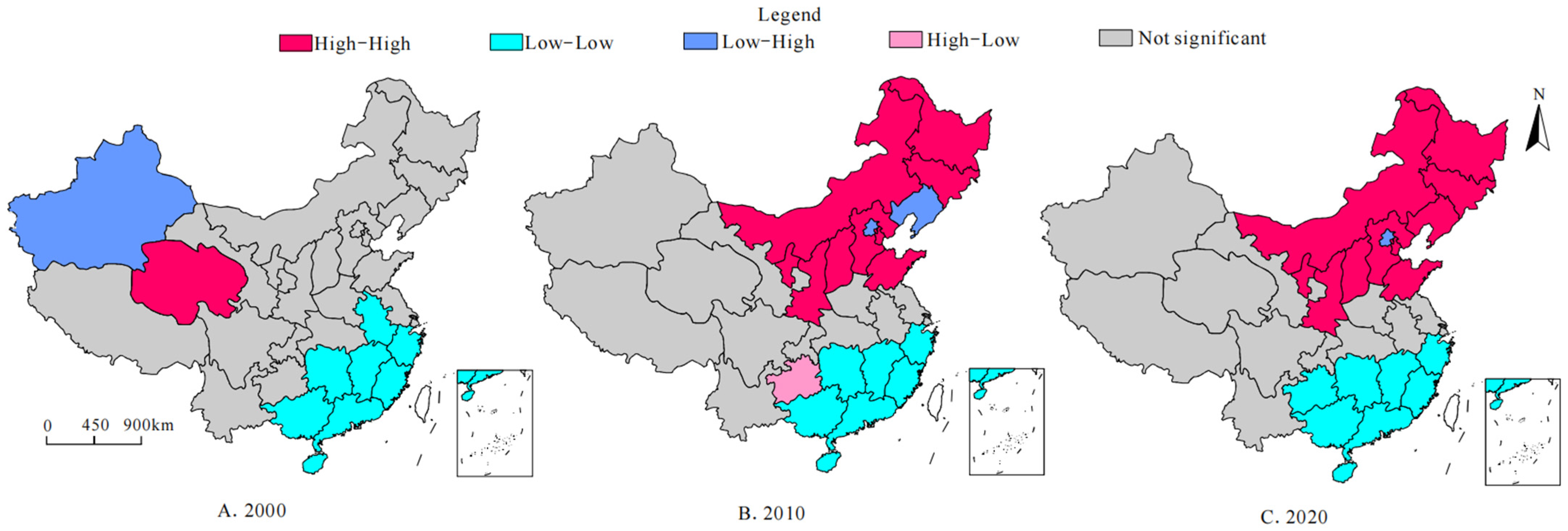
3.2. Characteristics of Spatial Correlation of Carbon Sequestration and Emission Reduction Capacity of Agricultural Cultivation
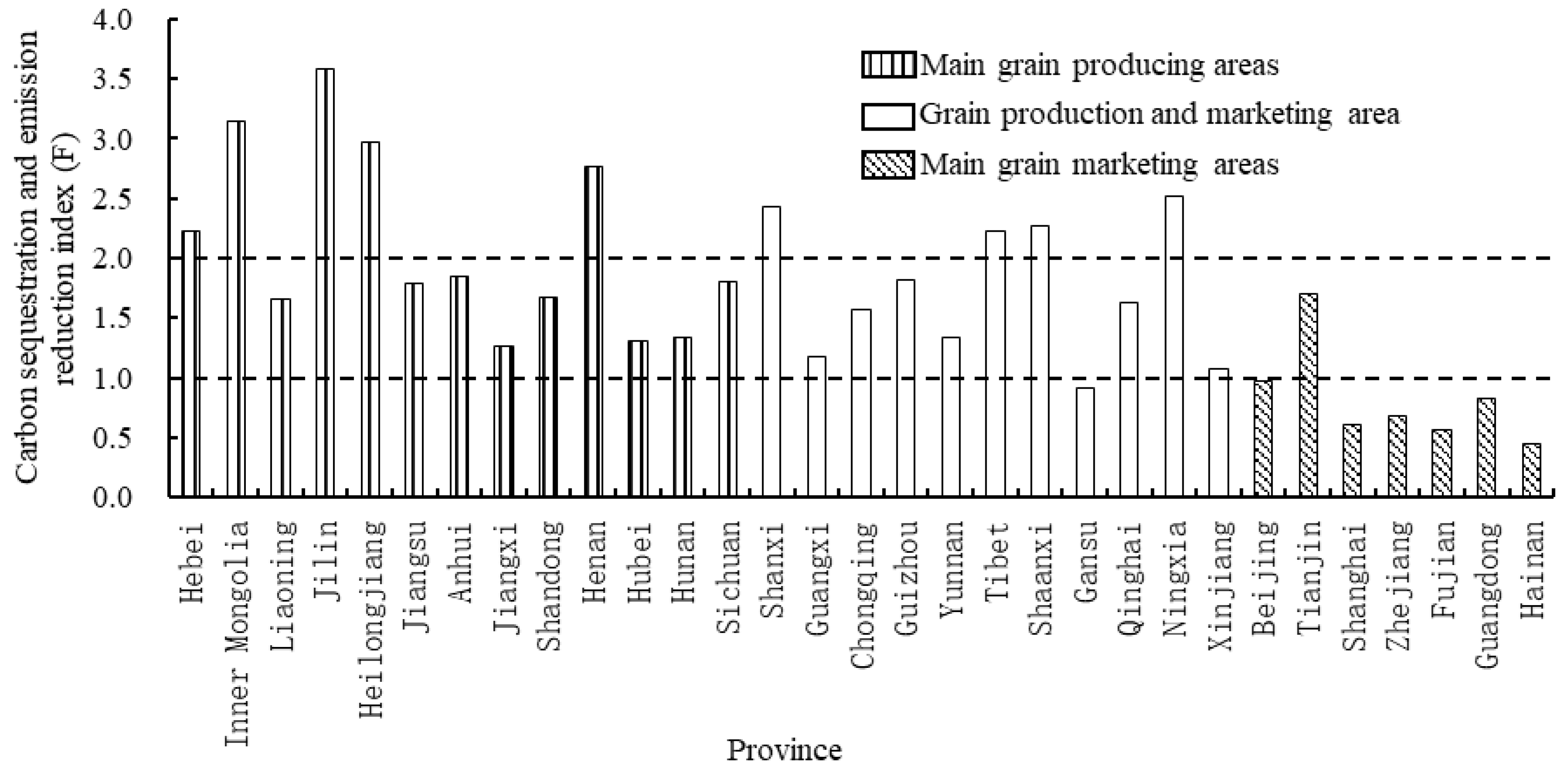
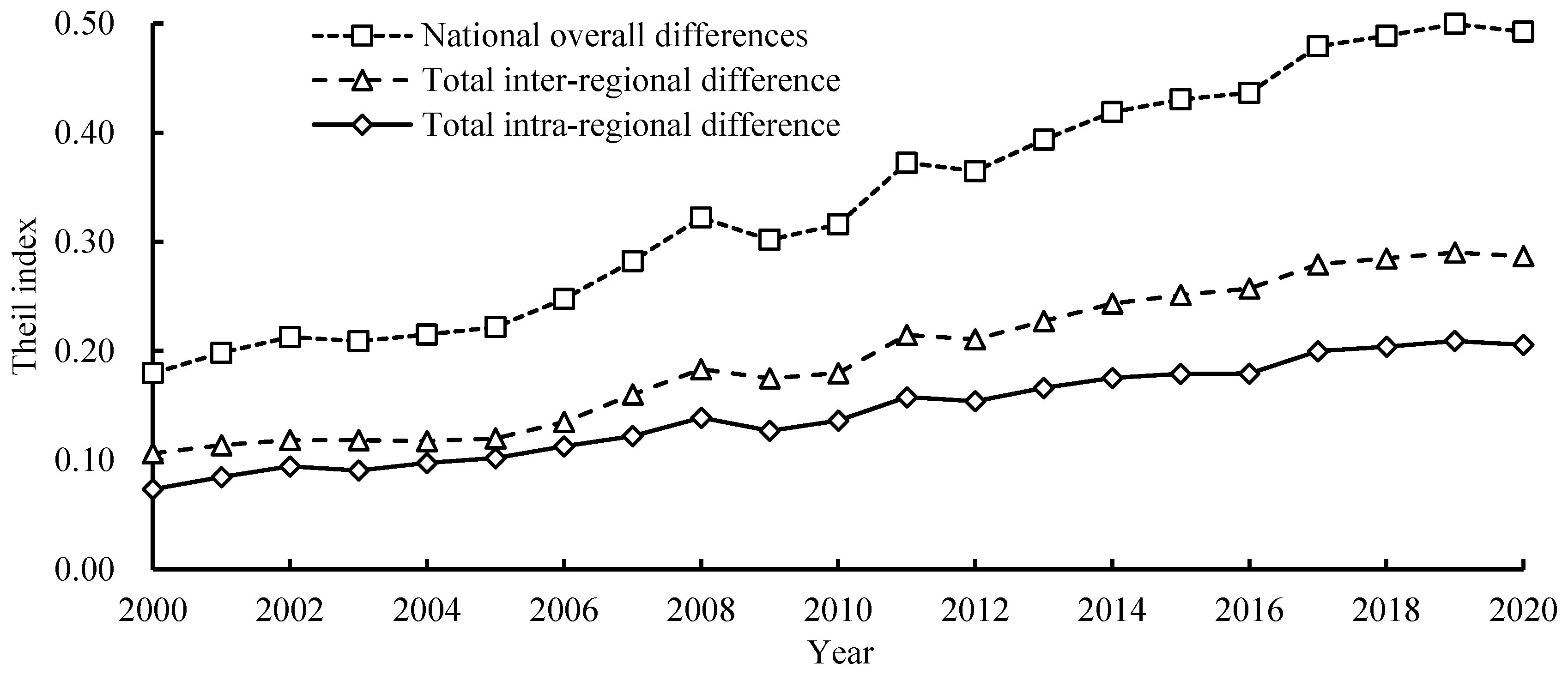
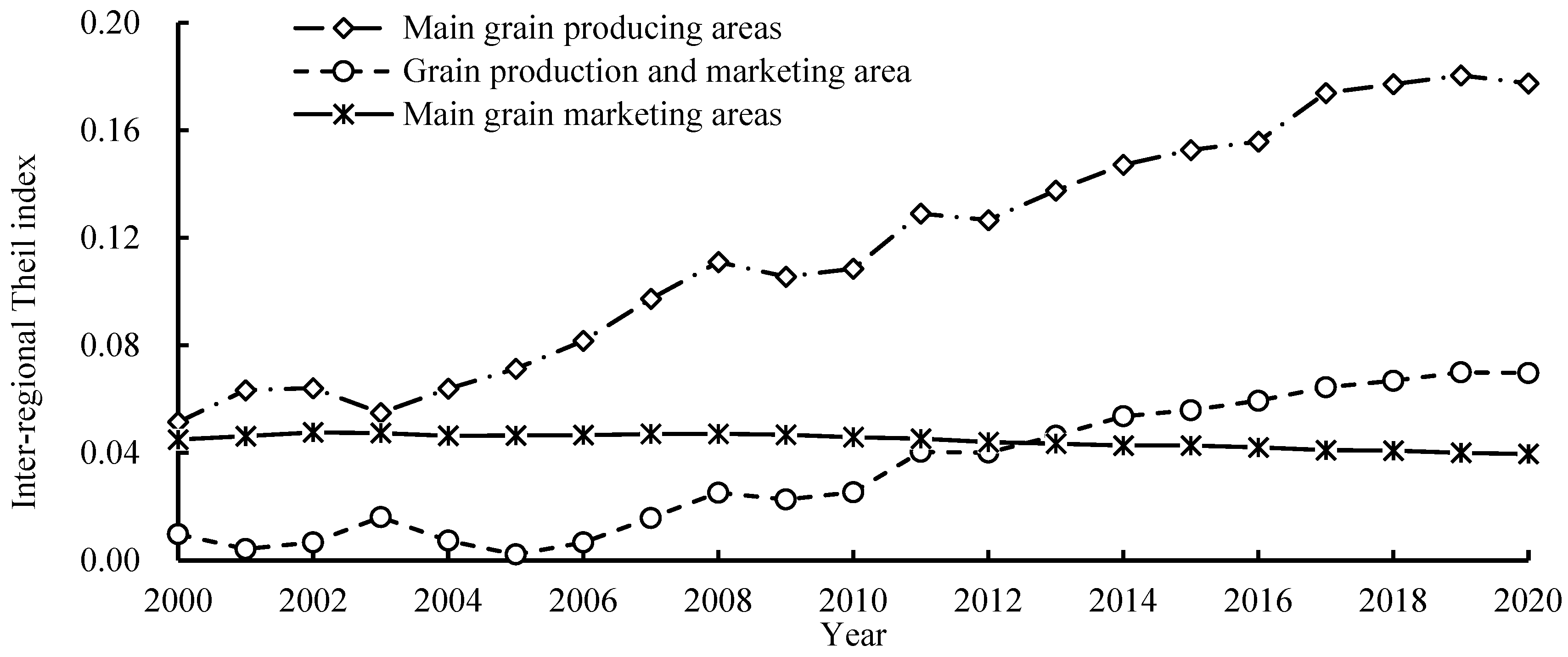
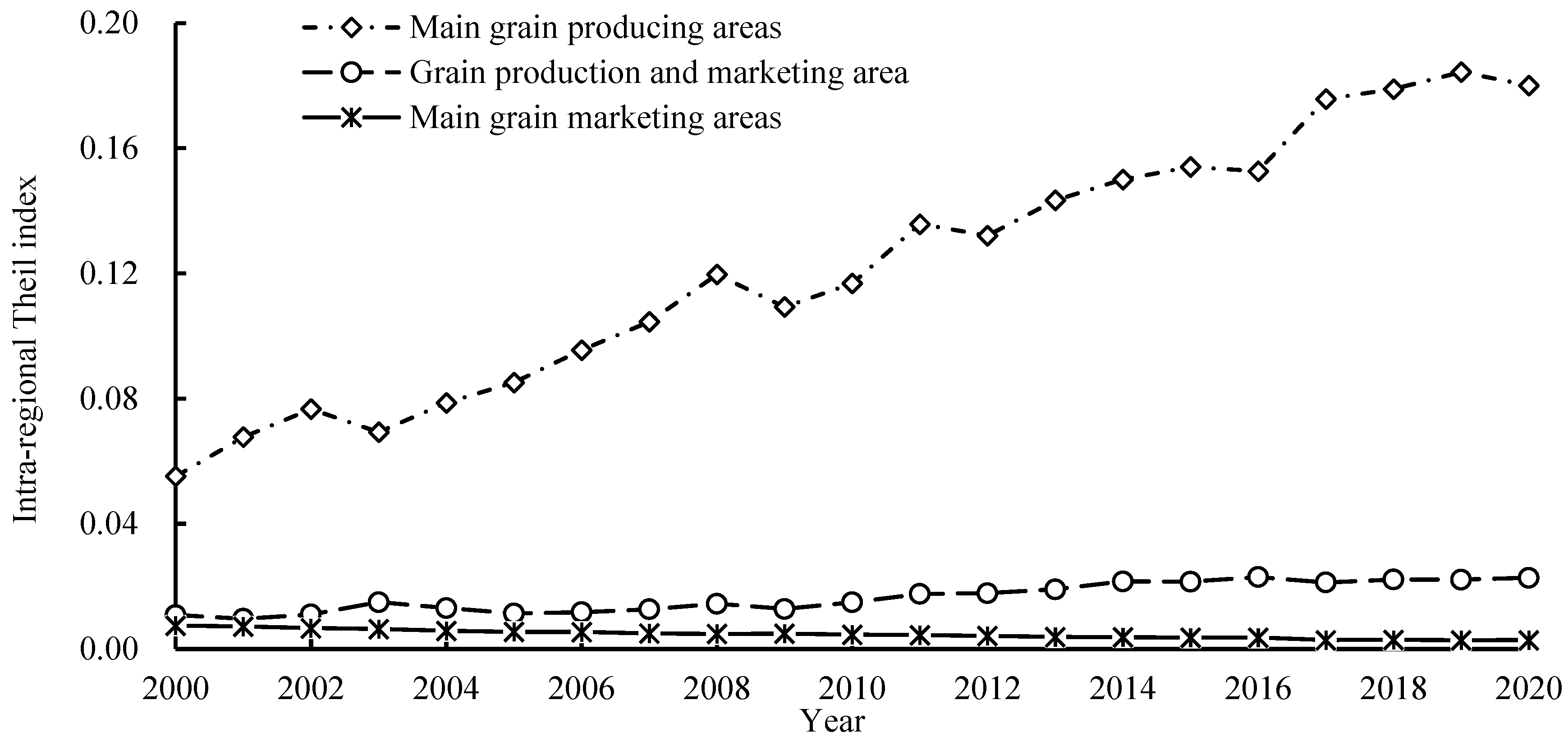
3.3. Analysis of Regional Differences in Carbon Sequestration and Emission Reduction Capacity of Agricultural Cultivation
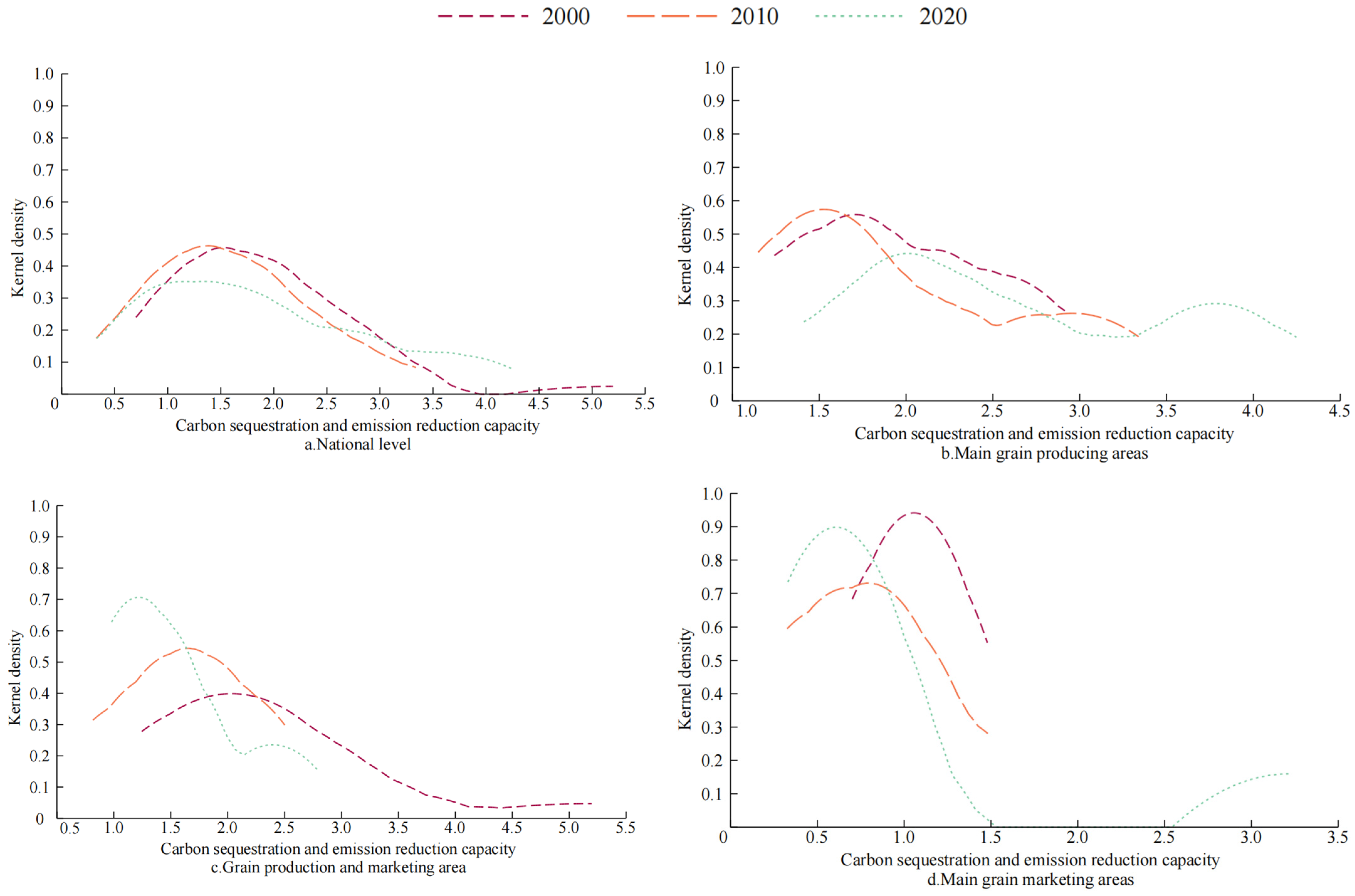
3.4. Dynamic Evolution of Carbon Sequestration and Emission Reduction Capacity of Agricultural Cultivation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xue, Y.; Li, C.H.; Li, J.W.; Lyu, H.; Lai, Q.Y.; Kang, Z.L.; Yao, P.; Li, J.H. Analysis of spatial and temporal characteristics and drivers of agricultural carbon emissions in China. Chin. J. Eco-Agric. 2024, 32, 1805–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asumadu-Sarkodie, S. The Relationship between Carbon Dioxide and Agriculture in Ghana: A Comparison of VECM and ARDL Model. Env. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 10968–10982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goglio, P. A Comparison of Methods to Quantify Greenhouse Gas Emissions of Cropping Systems in LCA. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 172, 4010–4017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grace, P.R.; Antle, J.; Aggarwal, P.K.; Ogle, S.; Paustian, K.; Basso, B. Soil Carbon Sequestration and Associated Economic Costs for Farming Systems of the Indo-Gangetic Plain: A Meta-Analysis. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2012, 146, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Just, C.; Armbruster, M.; Barkusky, D.; Baumecker, M.; Diepolder, M.; Döring, T.F.; Heigl, L.; Honermeier, B.; Jate, M.; Merbach, I.; et al. Soil Organic Carbon Sequestration in Agricultural Long-Term Field Experiments as Derived from Particulate and Mineral-Associated Organic Matter. Geoderma 2023, 434, 116472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Don, A.; Seidel, F.; Leifeld, J.; Kätterer, T.; Martin, M.; Pellerin, S.; Emde, D.; Seitz, D.; Chenu, C. Carbon Sequestration in Soils and Climate Change Mitigation—Definitions and Pitfalls. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2024, 30, e16983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, J.; Yang, G.; Yu, F.W. Agricultural greenhouse gases emissions and influencing factors in China. Chin. J. Eco-Agric. 2015, 23, 354–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.S.; Fu, B.J. Measurement of agricultural carbon emission and pressure of emission reduction in main grain-producing areas of China. Ecol. Econ. 2019, 35, 99–104. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, G.; Chen, Y. China’s agriculture carbon sink estimation and its coupling analysis with agricultural economy development. China Popul. Resour. Environ. 2016, 26, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Yin, M.H. Re-evaluation of China’s agricultural carbon emissions: Basic status, dynamic evolution and spatial spillover effects. Chin. Rural. Econ. 2022, 3, 104–127. [Google Scholar]
- He, Y.Q.; Chen, R.; Wu, H.Y.; Xu, J.; Song, Y. Spatial dynamics of agricultural carbon emissions in China and the related driving factors. Chin. J. Eco-Agric. 2018, 26, 1269–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Liu, Y.Y.; Zhang, Y.H.; Dong, S.H. Spatial and temporal distribution of carbon source/sink and decomposition of influencing factors in farmland ecosystem in Henan Province. Acta Sci. Circumstantiae 2022, 42, 410–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, P.F.; Zhu, X.Q.; Li, W. Dynamic evolution and influencing factors analysis of carbon emissions in Chinese agriculture. World Agric. 2018, 4, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.Y.; Liu, J.D.; Yang, L.S. Dynamic Evolution of China’s Agricultural Carbon Emission Intensity and Carbon Offset Potential. China Popul. Resour. Environ. 2021, 31, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.Q.; He, T.T. Spatiotemporal of agricultural carbon emission and decoupling in China during 1997-2018: An empirical research based on spatial and distribution dynamics method. J. Yunnan Agric. Univ. (Soc. Sci.) 2022, 16, 78–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lessmann, M.; Ros, G.H.; Young, M.D.; De Vries, W. Global Variation in Soil Carbon Sequestration Potential through Improved Cropland Management. Glob. Change Biol. 2022, 28, 1162–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B.; Fang, J.; Xu, Q.T.; Li, Y.B.; Lu, X.L. Dynamic change and analysis of reduction potential of agricultural carbon emissions in Baicheng city. J. Chin. Agric. Mech. 2016, 37, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ge, Y.X.; Liu, A.H.; Liang, Y. Research on agricultural ecological compensation mechanism based on carbon sequestration function of grain crops. Agric. Econ. Issues 2014, 35, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.W.; Zhang, J.H.; Wu, F.W. Analysis of carbon emissions and emission reduction pathways in China’s grain production. Stat. Decis. Mak. 2018, 34, 168–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.R.; Wang, L.G. Carbon sequestration and greenhouse gas mitigation paths and modes in a typical agroecosystem in northern China. Chin. J. Eco-Agric. 2022, 30, 641–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.J.; Deng, A.X.; Shang, Z.Y.; Tang, Z.W.; Chen, C.Q.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, W.J. Characteristics of carbon emission and approaches of carbon mitigation and sequestration for carbon neutrality in China’s crop production. Acta Agron. Sin. 2022, 48, 930–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Gao, W.; Wei, J.F.; Jiang, Z.F.; Zhang, Y.; Lyu, J.X. Spatiotemporal evolution and comprehensive zoning of net carbon sink in cultivated land use in China. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2022, 38, 239–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.Y.; Meng, Y.; Huang, H.J.; Chen, W.K. Spatiotemporal Coupling Between the Net Carbon Sequestration of Cropland Use and Agricultural Production in China. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2022, 36, 361–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, S.; Hu, Y.; Liu, H. Measurement and Spatial–Temporal Characteristics of Agricultural Carbon Emission in China: An Internal Structural Perspective. Agriculture 2022, 12, 1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Fan, J.; Chen, J. Spatial and Temporal Characteristics and Drivers of Agricultural Carbon Emissions in Jiangsu Province, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 12463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.Q.; Qu, Y.B.; Zhan, L.Y.; Su, D.S.; Wei, C.C. Dynamic evolution and driving effects of carbon emissions from grain production in China. Acta Geograhica Sin. 2023, 78, 2186–2208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Q.; Zhai, Y.J.; Hu, L.L. Spatial differential and dynamic evolution of carbon emission efficiency of grain production in five provinces of Huang-Huai-Hai region. Bull. Soil Water Conserv. 2024, 44, 389–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, L.W.; He, Z.H. The spatiotemporal distribution and driving factors of agricultural net carbon sink in northeast agricultural areas. J. Agric. Resour. Environ. 2024, 41, 505–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.F.; Li, B.; Zhang, R.Q. Spatiotemporal evolution and influencing factors of agricultural carbon emissions in Hebei Province at the county scale. Chin. J. Eco-Agric. 2022, 30, 570–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Zhao, R.; Zhan, Y. Land Comprehensive Carrying Capacity of Major Grain-Producing Areas in Northeast China: Spatial–Temporal Evolution, Obstacle Factors and Regulatory Policies. Sustainability 2022, 14, 11322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Wu, H.T. Research on fairness of agricultural carbon emissions in China major grain producing areas from the perspective of industrial structure. Agric. Technol. Econ. 2020, 1, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Wang, C.Y.; Zhang, J.B. Dynamic evolution and spatial spillover of China agricultural net carbon sink. China Popul. Resour. Environ. 2019, 29, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.N.; Zhang, Q.L.; Chen, W. Study on provincial agricultural carbon emission and emission reduction potential based on carbon sink function: Taking China three main grain crops as an example. Chong Qing Soc. Sci. 2022, 5, 58–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.X.; Zhang, H.B.; Yu, Y.P. Spatial and temporal dynamics in carbon source/sink and equity of the farmland ecosystem in Jiangsu coastal area, China. Chin. J. Agric. Resour. Reg. Plan. 2021, 42, 56–64. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, H.L. Advances on carbon storage in crops of China. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2014, 23, 692–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.Y.; Meng, Y.L.; Xu, J.; Hu, Y.; Zhou, Z.G. Temporal and spatial difference in carbon footprint of regional farmland ecosystem ─Taking Jiangsu Province as a Case. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2012, 31, 1034–1041. [Google Scholar]
- Han, B.; Wang, X.K.; Lu, F.; Duan, X.N.; Ouyang, Z.Y. Soil carbon sequestration and its potential by cropland ecosystems in China. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2008, 2, 612–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Si, X.H.; Wang, J. The measurement and its distribution dynamic evolution of grain production efficiency in China under the goal of reducing pollution emissions and increasing carbon sink. J. Nat. Resour. 2022, 37, 600–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, H.; Zhao, Z.H. Research on the effects of grain crop planting changes on agricultural carbon emissions between provinces in China. Chin. J. Agric. Resour. Reg. Plan. 2023, 44, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.; Wang, B.C.; Zhou, M.S. Spatiotemporal evolution and driving factors of China’s agricultural carbon emissions. Chin. J. Eco-Agric. 2024, 32, 1097–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pergner, I.; Lippert, C. On the Effects That Motivate Pesticide Use in Perspective of Designing a Cropping System without Pesticides but with Mineral Fertilizer—A Review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2023, 43, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostafaeipour, A.; Bidokhti, A.; Fakhrzad, M.-B.; Sadegheih, A.; Zare Mehrjerdi, Y. A New Model for the Use of Renewable Electricity to Reduce Carbon Dioxide Emissions. Energy 2022, 238, 121602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.L.; Zheng, L.Q.; Lian, H.F.; Tian, B.L.; Chen, Z.Y. The spatiotemporal dynamics and drivers of China’s agricultural net carbon sink. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2024, 38, 198–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y. Regional Difference Decomposition and Its Spatiotemporal Dynamic Evolution of Chinese Agricultural Carbon Emission: Considering Carbon Sink Effect. Env. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 38909–38928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C. Regional Differential Decomposition and Convergence of Rural Green Development Efficiency: Evidence from China. Env. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 22364–22379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.J.; Cyan, S.J.; Czhang, J.; Cjiang, Y.; Cdeng, A.X. Win-win strategy for national food security and agricultural double-carbon goals. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2021, 54, 3892–3902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Agricultural Materials | Carbon Emission Coefficient | Data Sources |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical fertilizer | 898.40/(kg/t) | ORAL |
| Pesticides | 4940.15/(kg/t) | ORAL |
| Agricultural film | 5180.00/(kg/t) | IREEA |
| Agricultural diesel | 592.70/(kg/t) | Wu et al. [14] |
| Farmland plowing | 312.60/(kg/hm2) | IREEA |
| Irrigation of farmland | 266.48/(kg/hm2) | Li et al. [32] |
| Main Grain Crops | Moisture Content (Wi) | Economic Coefficient (Li) | Carbon Absorption Rate (Bi) | Root Shoot Rate (Ri) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wheat | 0.120 | 0.400 | 0.485 | 0.166 |
| Corn | 0.130 | 0.400 | 0.471 | 0.170 |
| Rice | 0.120 | 0.450 | 0.414 | 0.125 |
| Year | National Level | Main Production Area | Production and Marketing Area | Main Marketing Area | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IG | Z | p-Value | IG | Z | p-Value | IG | Z | p-Value | IG | Z | p-Value | |
| 2000 | 0.165 | 2.630 | 0.009 | −0.113 | −0.180 | 0.481 | −0.357 | −1.721 | 0.022 | 0.605 | 1.851 | 0.041 |
| 2010 | 0.326 | 4.745 | 0.001 | 0.128 | 1.248 | 0.119 | −0.129 | −0.193 | 0.467 | 0.727 | 2.226 | 0.050 |
| 2020 | 0.428 | 6.287 | 0.001 | 0.295 | 2.235 | 0.025 | 0.166 | 1.357 | 0.098 | −0.201 | −0.314 | 0.359 |
| Year | MPA | PMA | MMA | Year | MPA | PMA | MMA | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2000 | 48.50 75.05 | 9.19 14.72 | 42.31 10.23 | 59.11 | 40.89 | 2011 | 60.11 86.05 | 18.79 11.14 | 21.09 2.81 | 57.64 | 42.36 |
| 2001 | 55.66 80.08 | 3.72 11.44 | 40.62 8.48 | 57.37 | 42.63 | 2012 | 60.08 85.74 | 19.04 11.56 | 20.88 2.70 | 57.77 | 42.23 |
| 2002 | 54.12 81.27 | 5.66 11.67 | 40.22 7.06 | 55.68 | 44.32 | 2013 | 60.50 86.24 | 20.39 11.46 | 19.10 2.30 | 57.78 | 42.22 |
| 2003 | 46.37 76.49 | 13.60 16.48 | 40.03 7.03 | 56.64 | 43.36 | 2014 | 60.44 85.57 | 22.02 12.31 | 17.54 2.13 | 58.14 | 41.86 |
| 2004 | 59.33 80.65 | 6.25 13.41 | 39.42 5.94 | 54.67 | 45.33 | 2015 | 60.75 85.98 | 22.24 12.01 | 17.00 2.02 | 58.38 | 41.62 |
| 2005 | 59.44 83.53 | 1.84 11.12 | 38.72 5.35 | 54.09 | 45.91 | 2016 | 60.58 85.15 | 23.09 12.84 | 16.33 2.01 | 58.93 | 41.07 |
| 2006 | 60.52
84.75 | 4.94 10.42 | 34.53 4.83 | 54.51 | 45.49 | 2017 | 62.27 87.95 | 23.06 10.63 | 14.68 1.42 | 58.30 | 41.70 |
| 2007 | 60.78 85.57 | 9.85 10.36 | 29.37 4.07 | 56.74 | 43.26 | 2018 | 62.21 87.71 | 23.46 10.87 | 14.34 1.42 | 58.27 | 41.73 |
| 2008 | 60.57 86.14 | 13.74 10.40 | 25.69 3.46 | 56.89 | 43.11 | 2019 | 62.14 88.07 | 24.08 10.58 | 13.78 1.35 | 58.11 | 41.89 |
| 2009 | 60.34 86.10 | 12.96
10.05 | 26.70 3.84 | 57.96 | 42.04 | 2020 | 61.87 87.57 | 24.32
11.04 | 13.81 1.38 | 58.25 | 41.75 |
| 2010 | 60.39 85.72 | 14.12 10.92 | 25.50 3.36 | 56.87 | 43.13 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Liu, X.; Song, M. Spatial-Temporal Evolution of Carbon Sequestration and Emission Reduction Capacity of Agricultural Cultivation in Different Functional Grain Areas. Sustainability 2024, 16, 10455. https://doi.org/10.3390/su162310455
Wang Y, Liu X, Song M. Spatial-Temporal Evolution of Carbon Sequestration and Emission Reduction Capacity of Agricultural Cultivation in Different Functional Grain Areas. Sustainability. 2024; 16(23):10455. https://doi.org/10.3390/su162310455
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yidi, Xianzhao Liu, and Mengru Song. 2024. "Spatial-Temporal Evolution of Carbon Sequestration and Emission Reduction Capacity of Agricultural Cultivation in Different Functional Grain Areas" Sustainability 16, no. 23: 10455. https://doi.org/10.3390/su162310455
APA StyleWang, Y., Liu, X., & Song, M. (2024). Spatial-Temporal Evolution of Carbon Sequestration and Emission Reduction Capacity of Agricultural Cultivation in Different Functional Grain Areas. Sustainability, 16(23), 10455. https://doi.org/10.3390/su162310455







