Impact of Urban Form in the Yangtze River Delta of China on the Spatiotemporal Evolution of Carbon Emissions from Transportation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Study Area
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Estimating Carbon Emissions from Transportation
3.2. Analysis of the Spatial Structure of Urban Form
3.3. Econometric Modeling
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Analysis of Energy-Related CO2 Emissions from Transportation
4.2. Analysis of Urban Form
4.3. Estimation Results of the Panel Model
5. Conclusions and Policy Implications
5.1. Conclusions
5.2. Policy Implications
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, P.; He, J.; Hong, X.; Zhang, W.; Qin, C.; Pang, B.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y. Carbon sources/sinks analysis of land use changes in China based on data envelopment analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 204, 702–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, E.; Qi, Q.; Chen, L.; Wu, X. The spatial-temporal patterns and multiple driving mechanisms of carbon emissions in the process of urbanization: A case study in Zhejiang, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 358, 131954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, F.; Liao, X.; Shen, L.; Meng, C.; Lai, Y. Exploring the spatiotemporal impacts of urban form on CO2 emissions: Evidence and implications from 256 Chinese cities. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2022, 96, 106850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, D.; Xia, C.; Wang, Z.; Wang, H.; Liu, Y. Urban expansion simulation towards low-carbon development: A case study of Wuhan, China. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2020, 63, 102455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Fang, C.; Wang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Ma, H. Quantifying the relationship between urban development intensity and carbon dioxide emissions using a panel data analysis. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 49, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sargent, M.; Barrera, Y.; Nehrkorn, T.; Hutyra, L.R.; Gately, C.K.; Jones, T.; McKain, K.; Sweeney, C.; Hegarty, J.; Hardiman, B.; et al. Anthropogenic and biogenic co 2 fluxes in the boston urban region. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 7491–7496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Dong, Y.X.; Yang, R.; Zhang, H.O.; Wang, C.J.; Du, Z.W. Temporal and spatial differences in carbon emissions in the pearl river delta based on multi-resolution emission inventory modeling. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 214, 615–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Yang, Y.; Liu, S.; Li, Q. Research on transportation carbon emission peak prediction and judgment system in China. Sustainability 2023, 15, 14880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Fang, C.; Ma, H.; Wang, Y.; Qin, J. Spatial differences and multi-mechanism of carbon footprint based on gwr model in provincial China. J. Geogr. Sci. 2014, 24, 612–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clifton, K.; Ewing, R.; Knaap, G.J.; Song, Y. Quantitative analysis of urban form: A multidisciplinary review. J. Urban. Int. Res. Placemak. Urban Sustain. 2008, 1, 17–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.; Wang, S.; Li, G. Changing urban forms and carbon dioxide emissions in China: A case study of 30 provincial capital cities. Appl. Energy 2015, 158, 519–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Ou, W.; Guo, J.; Pueppke, S.G. How does urban form influence PM2.5 concentrations: Insights from 350 different-sized cities in the rapidly urbanizing Yangtze River Delta (YRD) region of China, 1998–2015. Cities 2020, 98, 102581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Sweeney, J. Modelling the impact of urban form on household energy demand and related CO2 emissions in the Greater Dublin Region. Energy Policy 2012, 46, 359–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, J.; Liu, X.; Li, X.; Chen, Y. Quantifying the relationship between urban forms and carbon emissions using panel data analysis. Landsc. Ecol. 2013, 28, 1889–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Lee, B. The influence of urban form on GHG emissions in the U.S. household sector. Energy Policy 2014, 68, 534–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resch, E.; Bohne, R.A.; Kvamsdal, T.; Lohne, J. Impact of Urban Density and Building Height on Energy Use in Cities. Energy Procedia 2016, 96, 800–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wang, F.; Kang, T.; Wang, C.; Chen, X.; Miao, Z.; Zhang, L.; Ye, Y.; Zhang, H. Exploring differentiated impacts of socioeconomic factors and urban forms on city-level CO2 emissions in China: Spatial heterogeneity and varying importance levels. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2022, 84, 104028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, K.; Yao, X. The impact of urban compactness on urban carbon emissions: A study of 281 Chinese cities. Urban Clim. 2024, 56, 102052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Huang, B.; Chen, M.; Huang, Z. Modeling urban vertical growth using cellular automata—Guangzhou as a case study. Appl. Geogr. 2014, 53, 172–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berardi, U. Building Energy Consumption in US, EU, and BRIC Countries. Procedia Eng. 2015, 118, 128–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falahatkar, S.; Rezaei, F. Towards low carbon cities: Spatio-temporal dynamics of urban form and carbon dioxide emissions. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2020, 18, 100317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, K.; Xu, T.; Li, Y.; Chen, Z.; Gong, W.; Wu, J.; Yu, B. Effects of urban forms on CO2 emissions in China from a multi-perspective analysis. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 262, 110300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sha, W.; Chen, Y.; Wu, J.; Wang, Z. Will polycentric cities cause more CO2 emissions? A case study of 232 Chinese cities. J. Environ. Sci. 2020, 96, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Zhang, G. Analysis of the measurement of transportation carbon emissions and the emission reduction path in the Yangtze River economic belt under the background of “dual carbon” goals. Energies 2024, 17, 3364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y. An analytical process of spatial autocorrelation functions based on Moran’s index. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0249589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Sun, Z.; Guo, H.; Wang, J.; Jiang, H.; Gao, J. Dataset of built-up areas of Chinese cities in 2020. Chin. Sci. Data 2022, 7, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J. Research on Urban Spatial Morphology and Urban Low-Carbon Development Quality. Master’s Thesis, Wuhan University, Wuhan, China, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, N. Urban form revisited—Selecting indicators for characterising European cities. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2010, 96, 29–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronchi, S.; Salata, S.; Arcidiacono, A. An indicator of urban morphology for landscape planning in Lombardy (Italy). Manag. Environ. Qual. Int. J. 2018, 29, 623–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Tang, L.; Xu, M.; Yang, X. Landscape pattern indices for evaluating urban spatial morphology—A case study of Chinese cities. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 99, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kupfer, J.A. Landscape ecology and biogeography: Rethinking landscape metrics in a post-fragstats landscape. Prog. Phys. Geogr. Earth Environ. 2012, 36, 400–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, L.; Wei, C.; Cai, S. Economic development and carbon dioxide emissions in China: Provincial panel data analysis. China Econ. Rev. 2012, 23, 371–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Mulali, U. Factors affecting CO2 emission in the middle east: A panel data analysis. Energy 2012, 44, 564–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Cheng, L.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J. Exploring the impact of explicit and implicit urban form on carbon emissions: Evidence from Beijing, China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 154, 110558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.; Huang, Y.; Sun, Y. Effects of urban form on carbon emissions in China: Implications for low-carbon urban planning. Land 2022, 11, 1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Fang, S.; Zhang, C.; Hu, S.; Nan, D.; Yang, Y. Exploring the impact of urban form on urban land use efficiency under low-carbon emission constraints: A case study in China’s yellow river basin. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 311, 114866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bereitschaft, B.; Debbage, K. Urban form, air pollution, and co 2 emissions in large u.s. metropolitan areas. Prof. Geogr. 2013, 65, 612–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egidi, G.; Cividino, S.; Vinci, S.; Sateriano, A.; Salvia, R. Towards local forms of sprawl: A brief reflection on Mediterranean urbanization. Sustainability 2020, 12, 582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iizuka, S.; Xuan, Y.; Takatori, C.; Nakaura, H.; Hashizume, A. Environmental impact assessment of introducing compact city models by downscaling simulations. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2020, 63, 102424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

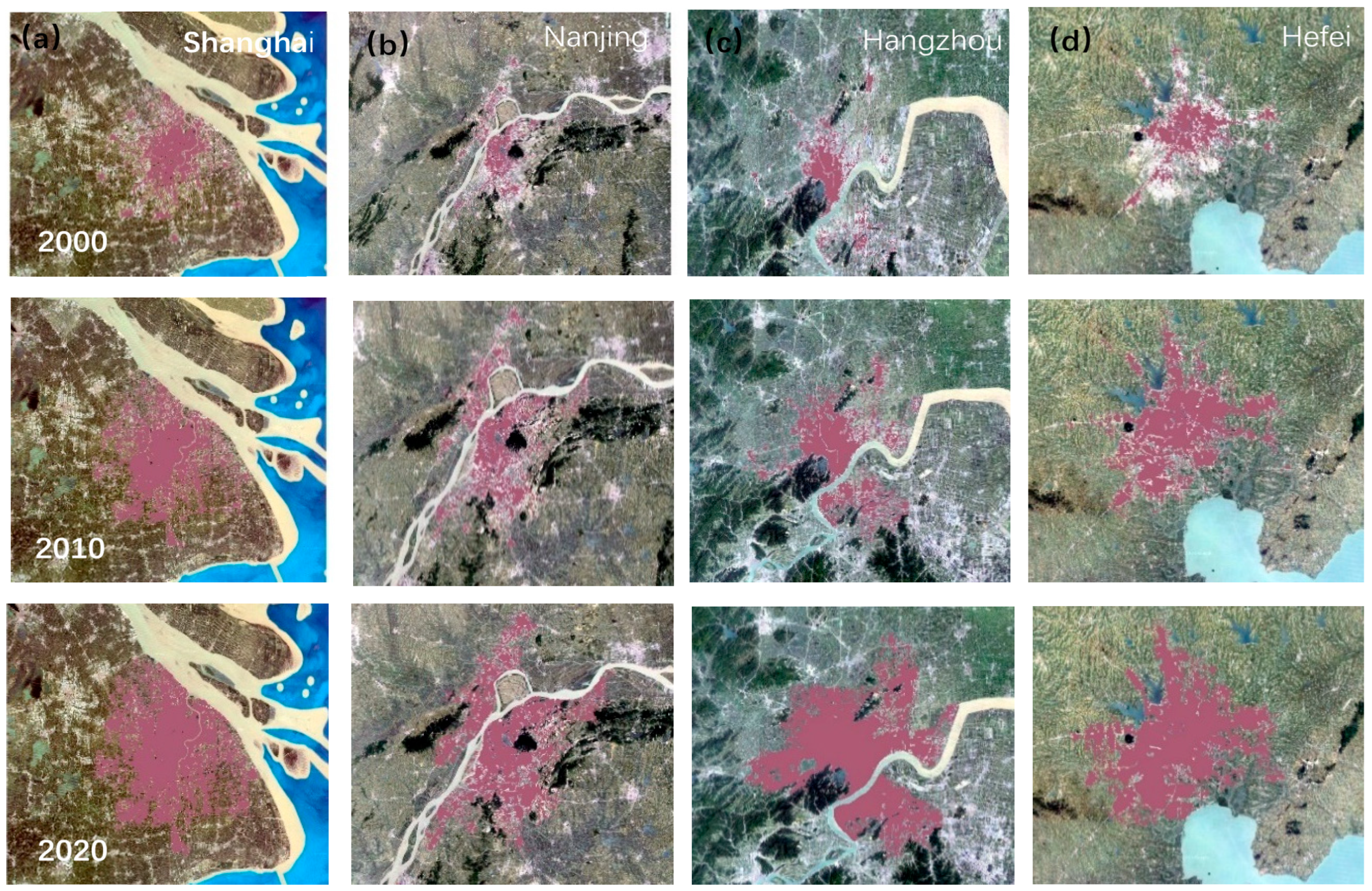
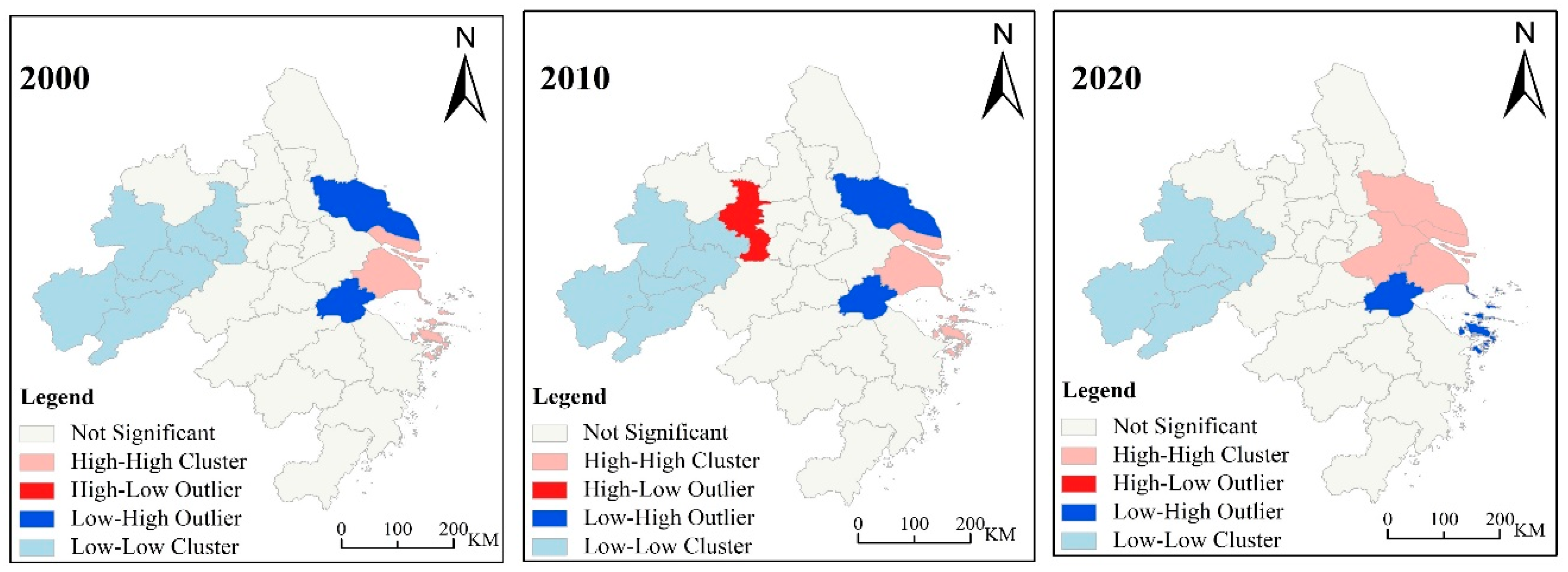
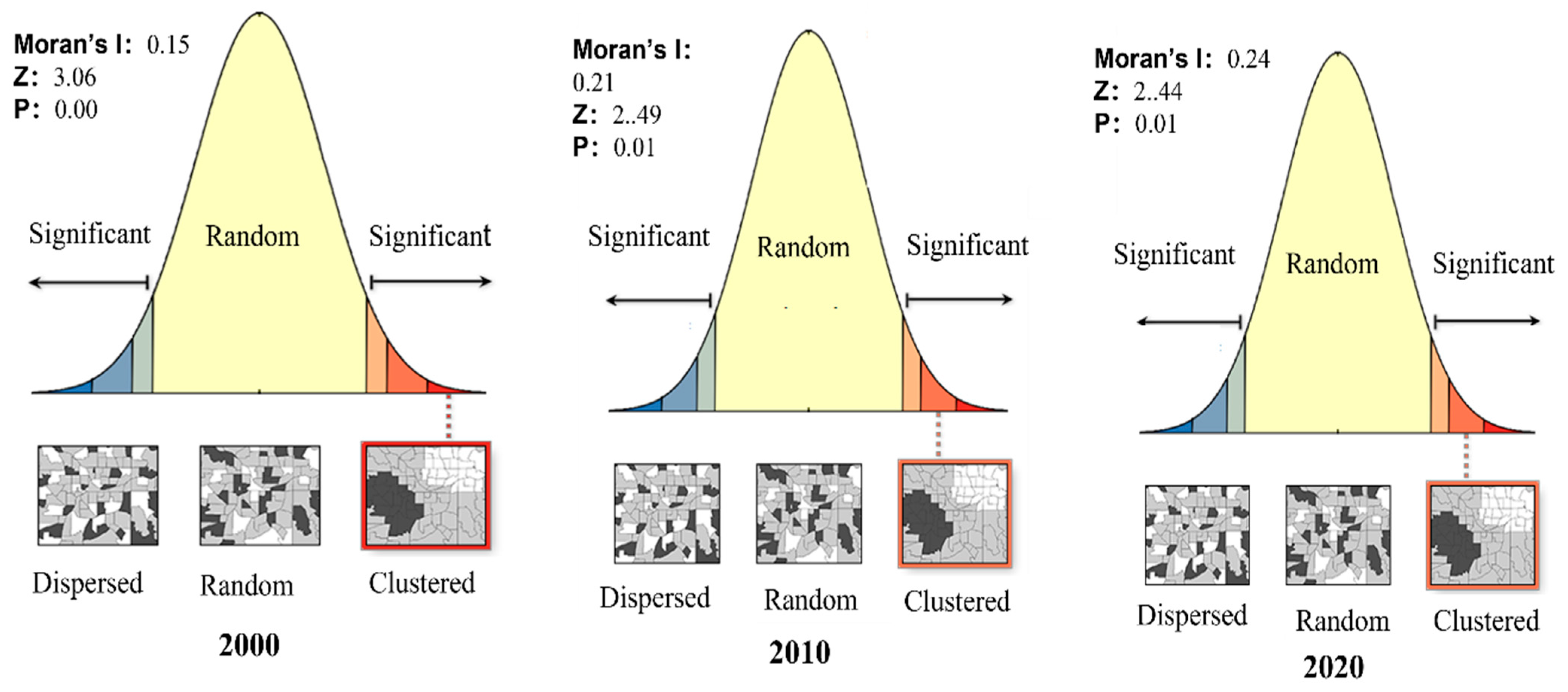

| Energy | Average Low Calorific Value (kJ/kg) | Standard Coal Conversion Factor | Carbon Content per Unit Calorific Value (tC/TJ) | Carbon Oxidation Rate | Carbon Emission Factor (kgCO2/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| raw coal | 20,934 | 0.7143 | 27.37 | 0.94 | 1.975 |
| coke | 28,470 | 0.9714 | 29.5 | 0.93 | 2.860 |
| gasoline | 43,124 | 1.4714 | 18.9 | 0.98 | 2.929 |
| kerosene | 43,124 | 1.4714 | 19.5 | 0.98 | 3.022 |
| diesel fuel | 42,705 | 1.4571 | 20.2 | 0.98 | 3.010 |
| fuel oil | 41,868 | 1.4286 | 21.1 | 0.98 | 3.171 |
| liquefied petroleum gas | 50,242 | 1.7143 | 17.2 | 0.98 | 3.105 |
| natural gas | 38,931 | 1.3300 | 15.32 | 0.99 | 2.162 |
| Indicators | Abbreviation | Equation |
|---|---|---|
| Total Area | TA | |
| Maximum Patch Index | LPI | |
| Area-Weighted Mean Shape Index | SHAPE_AM | |
| Area-Weighted Mean Patch Fractal Dimension Index | FRAC_AM | |
| Perimeter–Area Ratio Distribution | PARA_MN | |
| Percent of Similar Adjacent | PLADJ | |
| Patch Cohesion Index | COHESION | |
| Aggregation Index | AI | |
| Landscape Shape Index | LSI | |
| Patch Density | PD | |
| Road Network Density | RD | |
| Traffic Coupling Degree | CF |
| City | Area of Built-Up Area (km2) | City | Area of Built-Up Area (km2) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2000 | 2010 | 2020 | 2000 | 2010 | 2020 | ||
| Shanghai | 771.53 | 1371.47 | 1877.62 | Shaoxing | 75.87 | 148.68 | 243.07 |
| Nantong | 67.08 | 143.72 | 230.26 | Jinhua | 25.04 | 64.36 | 98.42 |
| Wuxi | 102.44 | 239.51 | 448.36 | Zhoushan | 17.87 | 32.19 | 57.80 |
| Suzhou | 79.06 | 219.66 | 418.60 | Taizhou | 22.74 | 102.96 | 174.99 |
| Yancheng | 35.75 | 67.54 | 155.66 | Wenzhou | 64.01 | 90.29 | 129.52 |
| Changzhou | 146.39 | 288.58 | 487.85 | Hefei | 148.66 | 389.45 | 649.94 |
| Nanjing | 188.99 | 365.61 | 687.11 | Wuhu | 44.90 | 97.97 | 163.10 |
| Yangzhou | 39.37 | 86.61 | 217.53 | Maanshan | 38.25 | 80.32 | 109.22 |
| Zhenjiang | 38.45 | 106.71 | 188.28 | Tongling | 22.02 | 39.31 | 77.35 |
| Taizhou | 27.02 | 68.78 | 130.15 | Anqing | 24.49 | 47.37 | 87.70 |
| Hangzhou | 143.65 | 372.45 | 765.30 | Chuzhou | 15.29 | 38.68 | 93.30 |
| Ningbo | 82.90 | 207.89 | 317.01 | Chizhou | 5.04 | 18.66 | 36.09 |
| Jiaxing | 18.87 | 62.18 | 140.24 | Xuancheng | 10.55 | 23.44 | 54.50 |
| Huzhou | 12.34 | 28.53 | 62.58 | ||||
| PD | LSI | PLADJ | COHESION | AI | TA | LPI | SHAPE_AM | FRAC_AM | PARA_MN | RD | CF | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| V1 | 1 | |||||||||||
| V2 | −0.102 | 1 | ||||||||||
| V3 | −0.786 ** | −0.031 | 1 | |||||||||
| V4 | −0.816 ** | 0.158 | 0.707 ** | 1 | ||||||||
| V5 | −0.772 ** | −0.103 | 0.995 ** | 0.691 ** | 1 | |||||||
| V6 | −0.313 ** | 0.802 ** | 0.339 ** | 0.356 ** | 0.293 ** | 1 | ||||||
| V7 | −0.546 ** | −0.160 | 0.632 ** | 0.819 ** | 0.646 ** | 0.161 | 1 | |||||
| V8 | −0.456 ** | 0.639 ** | 0.440 ** | 0.645 ** | 0.393 ** | 0.807 ** | 0.536 ** | 1 | ||||
| V9 | −0.572 ** | 0.534 ** | 0.424 ** | 0.811 ** | 0.372 ** | 0.581 ** | 0.640 ** | 0.889 ** | 1 | |||
| V10 | −0.409 ** | 0.029 | 0.467 ** | 0.588 ** | 0.450 ** | 0.166 | 0.621 ** | 0.527 ** | 0.640 ** | 1 | ||
| V11 | −0.472 ** | 0.461 ** | 0.496 ** | 0.546 ** | 0.455 ** | 0.633 ** | 0.387 ** | 0.764 ** | 0.696 ** | 0.550 ** | 1 | |
| V12 | −0.502 ** | 0.408 ** | 0.483 ** | 0.530 ** | 0.446 ** | 0.573 ** | 0.396 ** | 0.703 ** | 0.644 ** | 0.450 ** | 0.817 ** | 1 |
| Model | R | R2 | F | Significance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | 0.962 | 0.925 | 69.497 | p < 0.001 |
| Model | Variable | Coefficient | T | p | N |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | PD | −480.592 *** | −3.880 | 0.000 | 81 |
| LSI | −19.657 *** | −3.805 | 0.000 | 81 | |
| PLADJ | 2962.224 *** | 3.332 | 0.001 | 81 | |
| COHESION | 1111.889 | 1.790 | 0.078 | 81 | |
| AI | −3727.839 *** | −3.788 | 0.000 | 81 | |
| TA | 0.026 *** | 9.522 | 0.000 | 81 | |
| LPI | 6.586 | 1.859 | 0.067 | 81 | |
| SHAPE_AM | 63.212 *** | 5.658 | 0.000 | 81 | |
| FRAC_AM | −18,750.877 *** | −5.524 | 0.000 | 81 | |
| PARA_MN | 0.220 *** | 3.465 | 0.001 | 81 | |
| RD | 69.524 ** | 2.144 | 0.036 | 81 | |
| CF | −495.671 | −1.507 | 0.136 | 81 | |
| constant | −12,817.602 | −0.226 | 0.822 | 81 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, Y.; Chen, B.; Li, Q. Impact of Urban Form in the Yangtze River Delta of China on the Spatiotemporal Evolution of Carbon Emissions from Transportation. Sustainability 2024, 16, 9678. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16229678
Sun Y, Chen B, Li Q. Impact of Urban Form in the Yangtze River Delta of China on the Spatiotemporal Evolution of Carbon Emissions from Transportation. Sustainability. 2024; 16(22):9678. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16229678
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Yanming, Baozhong Chen, and Qingli Li. 2024. "Impact of Urban Form in the Yangtze River Delta of China on the Spatiotemporal Evolution of Carbon Emissions from Transportation" Sustainability 16, no. 22: 9678. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16229678
APA StyleSun, Y., Chen, B., & Li, Q. (2024). Impact of Urban Form in the Yangtze River Delta of China on the Spatiotemporal Evolution of Carbon Emissions from Transportation. Sustainability, 16(22), 9678. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16229678






