Abstract
The coupling coordination of new urbanization (NU) and rural revitalization (RR) is the key research that focuses on promoting integrated development between urban and rural areas. The entropy weight method, coupling coordination model, and obstacle model were used to explore the development level, coupling coordination degree, and obstacle factors of NU and RR in the basin area of Sichuan Province from 2013 to 2021 in this study. The results show the following: The levels of NU and RR in the basin area of Sichuan Province show an uptrend. Central cities exhibit higher levels of RR and NU. Under the influence of a central city, regional central cities have obvious growth in RR and NU. There are fluctuations in the RR and NU indicators in node cities. The coupling coordination degree of NU and RR in the basin area of Sichuan Province continues to rise, and the coordination levels are mainly basic coordination and moderate coordination. The coupling coordination degree is higher in central and regional central cities, while the coupling coordination degree of node cities is relatively lower. The levels of agricultural modernization, public infrastructure and medical resources, and rural governance are the main factors influencing the coupling coordination of NU and RR in the basin area of Sichuan Province. Affected by terrain, economy, and other factors, the level of urban–rural integration in the basin area of Sichuan Province is obviously different. With the continuous improvement of policies, the coupling coordination level of NU and RR is gradually developing towards a positive trend.
1. Introduction
Urban and rural areas constitute a dynamically interconnected system, and the relationship between urban and rural areas is the most basic economic and social relationship. The interactions between urban and rural areas are reflected in the flow of resources, labor, and culture, influencing both economic development and social reform [1,2]. The integration of urban and rural development has gradually emerged with the acceleration of urbanization. The attraction of urban areas for rural population, land, and capital is becoming increasingly obvious. However, it has also caused a series of problems in rural areas such as a shortage of rural labor, a reduction in arable land, a decline in agricultural status, and so on [3]. In urban areas, the dual structure of urban and rural regions underscores issues such as traffic congestion, strained residential land and employment resources, and worsening environmental pollution [4]. There is a global consensus that the urban–rural development gap impedes sustainable economic and social development [5]. Due to varying historical and cultural contexts, different measures for coordinated urban–rural development are adopted by countries. Under the influence of the “return to rural living” concept, the number of people returning to the countryside promotes the flow of urban and rural labor factors and alleviates the problem of rural labor loss in Japan in the 21st century [6]. Germany attaches great importance to the balanced development among urban and rural areas. In 1950, the country promoted the integration of urban and rural development with the idea of “urban and rural equivalence” [7]. The United States, as a highly urbanized developed country, also pays attention to the development of agricultural modernization. After the 1920s, the model of urban–rural development was built by the United States, which relies on metropolises and the roles of technology and the market [8,9].
As the largest developing country, China has a huge population. Since the 1980s, urbanization in China has developed rapidly, and the integration of urban and rural areas has continued to advance. The imbalance between urban and rural development is still the main issue that restricts the sustainable development of China [10]. So, new urbanization (NU) and rural revitalization (RR) strategies were proposed in China [11]. Under NU, being people-oriented has been emphasized, with simultaneous promotion of industrialization, information technology, and agricultural modernization. In contrast to traditional urbanization, NU places greater emphasis on the sustainable development of cities. RR focuses on “rural areas, agriculture and farmers”, which aims to improve the level of rural governance and development and to realize rural modernization. Coordinating the development strategies of NU and RR is an important way to achieve the integrated development of urban and rural areas in China [12].
Urban–rural relations have always been the focus of research on the economy, politics, and society. Before the 1950s, early urban and rural thoughts such as More’s Utopia [13], Howard’s “Garden City” [14], and Fourier’s “Harmonious Society” [15] emphasized connections between urban and rural areas. The proposal of the dual structure theory [16] changed the research focus of urban–rural relations. The growth pole theory [17], core and periphery theory [18], and urban bias theory [19] divided cities and rural areas, and the idea of urban priority development became the mainstream in this period based on dual structure theory. After the 1980s, the idea of urban–rural separation was broken [20]. Subsequently, theories such as the “Desakota” model [21], “Regional Network Model” [22], and “Urban–Rural Continuum” [23] were proposed in developing countries, which promoted the development of urban–rural integration. In the 21st century, scholars have focused on the interaction between urban–rural “connections” and “flows” [24] and explored urban–rural integration from the perspective of sustainable development [25,26]. The research focus shifted from European and American countries to developing countries gradually. In the context of globalization, the research perspective has shifted from regional to global sustainable development.
In China, the research on the relationship between NU and RR mainly focuses on the mechanism of action and empirical research [27]. In terms of the mechanism of action, coordinating NU and RR is conducive to breaking the urban–rural divide [28], in which RR provides conditions for the development of NU and NU has become an engine to make up for the shortcomings of rural areas [29]. In addition, the internal mechanisms of NU and RR are highly compatible, and there is an inevitable coupling mechanism [30]. In the empirical aspect, scholars established indicator systems according to different study areas. The main and objective valuation methods were used to measure the development levels of NU and RR, and the coupling characteristics of the two systems according to the relevant models were analyzed. In terms of methods, the analytic hierarchy process [31] and the entropy weight method [32,33] were used to calculate the comprehensive levels of each system. Meanwhile, the coupling coordination model [34] was adopted to measure the coupling degree between NU and RR. Nuclear density estimation [35,36], Global Moran’s I [37], and other methods were used to analyze the coordinated spatiotemporal pattern and spatial relationship between NU and RR. In terms of research objects, most scholars have analyzed the coupling characteristics of RR and NU at the provincial scale [38,39], while a few scholars analyzed them at the city scale [40] and county scale [41].
Many studies on the coupling coordination relationship between NU and RR have made the foundation for subsequent studies. However, most scholars have analyzed the relationship between NU and RR qualitatively [42,43]. In recent years, some scholars have conducted studies from a quantitative perspective [44], but the spatial and temporal coupling characteristics and influencing factors of the two systems are seldom analyzed at the urban scale. In the application of methods, the entropy weight method is based on the principle of information theory, using the variability of each index and information entropy to calculate the weight, which ensures the objectivity and scientific measurement of weight distribution [45]. In contrast, the analytic hierarchy relies on subjective expert judgment, which may lead to the results being influenced by personal bias and diminish the reliability of academic research. Therefore, this paper uses the entropy weight method to measure the comprehensive index of RR and NU [46]. The traditional coupling degree formula usually causes the coupling degree to be excessively concentrated in a certain range [47,48], thus reducing the interpretive validity of the coupling degree [49].
Therefore, the entropy weight method, the revised coupling coordination model, and the obstacle degree model were used to analyze the levels of NU, RR, and the coupling coordination characteristics in the basin area of Sichuan Province from 2013 to 2021. The main obstacle factors affecting the coupling of the two systems were explored. The decision-making reference for consolidating the achievements of poverty alleviation can be provided, and the bottlenecks and challenges in NU and RR and development in the basin area of Sichuan Province can be identified.
2. Overview and Data Sources of the Study Area
2.1. Overview of the Study Area
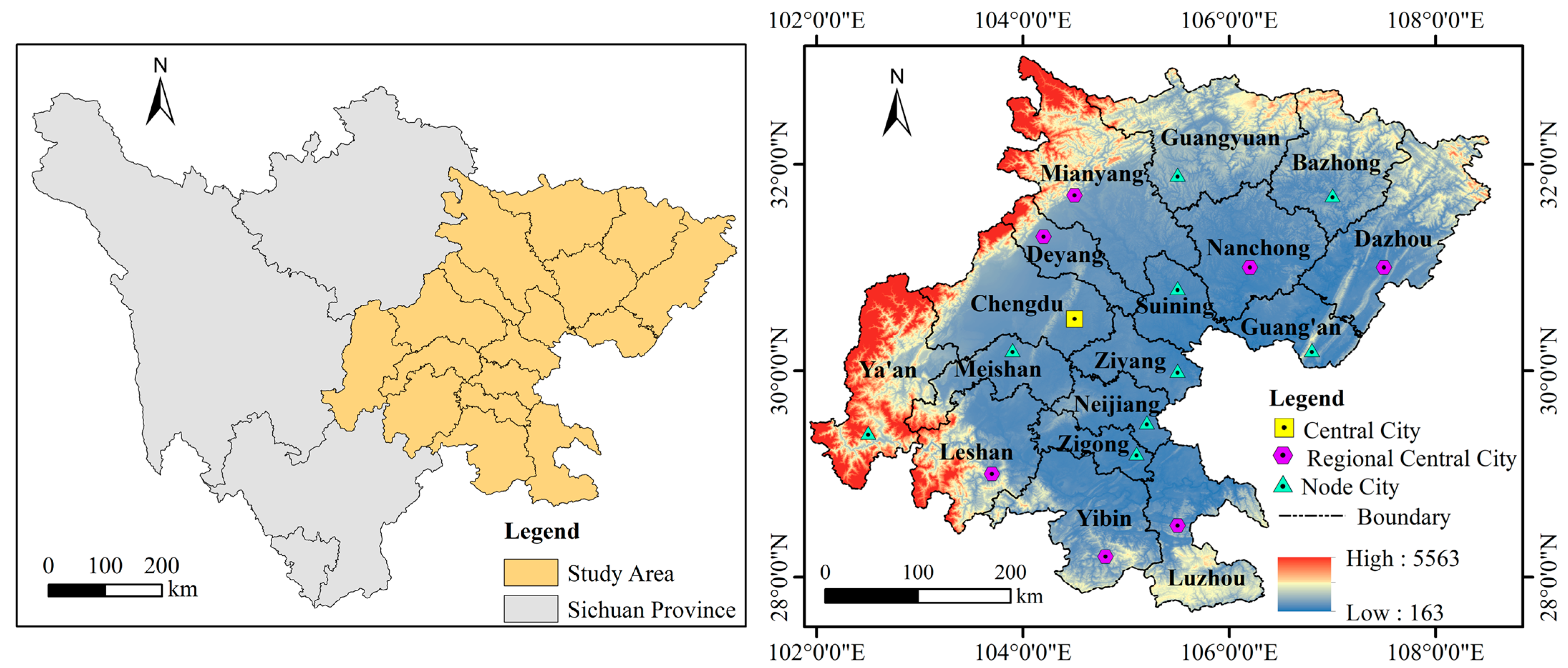
Sichuan Province is located in the hinterland of southwest China, where Bashu culture is prosperous. The topography of the province is complex and diverse, mainly mountain, plateau, and basin. It belongs to the subtropical monsoon climate area, with the annual temperature averaging about 17 °C and the annual precipitation about 900–1000 mm. The basin area of Sichuan Province is located in the eastern part of Sichuan Province, encompassing 17 prefecture-level cities including Bazhong, Chengdu, Dazhou, Deyang, Guang’an, Guangyuan, Leshan, Luzhou, Meishan, Mianyang, Nanchong, Neijiang, Suining, Ya’an, Yibin, Ziyang, and Zigong. The basin area of Sichuan Province is 1.86 × 105 km2, accounting for 38% of the total area of Sichuan Province. The resident population accounts for 90% of the total resident population of Sichuan Province. The GDP of the study area accounts for 93% of the province, and the GDP of agriculture, forestry, animal husbandry and fishery reaches CNY 820.7 billion. Most of the economic pillar industries of Sichuan Province are located in this area, and residents’ income is relatively high. Therefore, the basin area holds enormous potential for the future development of NU and RR. However, the contradiction between people and land and the unbalanced development of urban and rural areas are prominent. This region is still facing huge challenges at the NU and RR development levels (Figure 1).
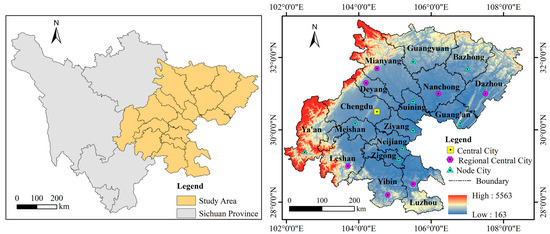
Figure 1.
Study area location map. Data from 30 m DEM (the left picture shows the position of the basin area of Sichuan Province within Sichuan Province, and the right picture shows the elevation of the basin area of Sichuan Province; digital elevation model (accessed on 4 September 2023): http://www.gscloud.cn/). Note: This map is based on the standard map No. GS (2024)0605 downloaded from the standard map service website of the National Administration of Surveying, Mapping and Geographic Information, and the base map has not been modified.
2.2. Data Sources
The primary sources of research data mainly include the “China Statistical Yearbook”, “China Urban-Rural Construction Statistical Yearbook”, and “Sichuan Statistical Yearbook” from 2013 to 2021. In addition, there are national economic and social economic development bulletins of 17 prefecture-level cities in the basin area of Sichuan Province and obtained from the China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI) official website (download data through CNKI user account permissions), while the missing data were supplemented by the linear interpolation method.
3. Index System Construction and Research Methods
3.1. Index System Construction
In this study (Table 1), the rural revitalization index was selected according to five dimensions. The dimensions include industrial revitalization, ecological livability, rural civilization, effective governance, and affluent living, found in the “Outline of the National Rural Revitalization Strategy (2012–2018)”. The new urbanization index was selected based on the “National New Urbanization Plan (2014–2020)” and the “14th Five-Year Plan for New Urbanization Implementation”, which include population urbanization, economic urbanization, land urbanization, social urbanization, and environmental urbanization. In rural revitalization, evaluation indicators are selected from industry, ecology, culture, organization, and livelihood perspectives. The dimensions are as follows: (1) Industrial revitalization is an important embodiment of the rural economy’s comprehensive ability. Rural economic development is closely linked to various factors, including the agricultural mechanization level, the comprehensive grain production capacity, the effective irrigation area, the amount of rural employment, and the total output value of agriculture, forestry, animal husbandry, and fishery [37,50]. (2) Effective governance can improve the quality of rural public services, enhance farmers’ sense of participation and access, and promote social stability. The per-unit application of chemical fertilizers, the per capita rural electricity consumption, the village clinic, and rural doctors and workers constitute the indicators of the rural living environment [51,52]. (3) The development of spiritual–cultural construction is reflected by rural civilization. Comprehensive television coverage, comprehensive radio coverage, and the number of cultural centers in rural areas are important factors of cultural communication [53]. (4) Effective governance can improve the quality of rural public services, increase the sense of participation among the inhabitants, and promote social stability. The role of the village committees, the number of people receiving minimum living security in rural areas, the number of special rural hardship individuals receiving assistance and support, and the number of village groups cannot be ignored [54]. (5) Affluent living entails enhancing the living standards and happiness of rural residents. The household consumption ability and quality of life are affected by the per capita current housing construction area in rural areas, the per capita disposable income of rural residents, the number of medical personnel per thousand people, and the Engel’s coefficient of rural residents [55].
In new urbanization, evaluation indicators such as population, economy, land, social, and environment are constructed, as follows: (1) Population urbanization is influenced by population migration. The urbanization rate, the population density, and the urban registered unemployment rate are the key indicators, which jointly affect the quality and sustainability of population urbanization [55]. (2) Industrial transformation, industrial upgrading, and diversified development of the urban economy are focused on by economic urbanization. The core driving forces of economic urbanization, which promote sustainable development in the region, are constituted by the increase in the per capita regional GDP, the proportion of the second industry in GDP, the proportion of the third industry in GDP, and the per capita disposable income of urban residents [56]. (3) Improving urban governance and service levels is the focus of social urbanization. The number of hospital beds per thousand people and increases in water and gas coverage rates will improve the social service system and enhance residents’ sense of happiness and belonging [57]. (4) The effective use of land resources promotes the development of land urbanization. The intensive and sustainable use of land can be promoted by reasonable planning of the per capita urban road area and the density of water supply pipelines in built-up areas [37]. (5) In the process of urbanization, the development of the ecological environment and the sustainability of resources are concerns of environmental urbanization. This dimension includes urban greening, pollution control, and the use of renewable energy, aiming to achieve a harmonious coexistence between humans and nature [51].
3.2. Methods
3.2.1. Data Preprocessing
Since the measurement units of the original data are not uniform, the dimensionless processing method proposed by Yanfei Zhang et al. [45] was adopted in this study to ensure data validity.
Positive indicator:
Negative indicator:
where = 1, 2, 3 …, n; = 1, 2, 3 …, m; denotes the indicator of the th prefecture-level city ; denotes the maximum value of the same indicators; denotes the minimum value of the same indicators; and denotes the standardized value.

Table 1.
New urbanization and rural revitalization evaluation index system.
Table 1.
New urbanization and rural revitalization evaluation index system.
| System Level | Dimension Level | Indicator Level | Index Interpretation | Unit | Indicating Direction |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rural revitalization | Industrial revitalization (A) | Agricultural mechanization level (A1) | Agricultural modernization | Kilowatts per hectare | + |
| Comprehensive grain production capacity (A2) | Food security | Tons per hectare | + | ||
| Effective irrigated area (A3) | Thousand hectares | + | |||
| Rural employment (A4) | Rural employment situation | Ten thousand people | + | ||
| Total output value of agriculture, forestry, animal husbandry, and fisheries (A5) | Agricultural production | Billion CNY | + | ||
| Ecological livability (B) | Per-unit application of chemical fertilizers (B1) | Resource consumption | Tons per hectare | - | |
| Per capita rural electricity consumption (B2) | Kilowatt-hours per person | - | |||
| Village clinic (B3) | Medical and health environment | Units | + | ||
| Rural doctors and health workers (B4) | People | + | |||
| Rural civilization (C) | Comprehensive television coverage in rural areas (C1) | Conditions of cultural transmission | % | + | |
| Comprehensive radio coverage in rural areas (C2) | % | + | |||
| Rural cultural centers (C3) | Units | + | |||
| Effective governance (D) | village committees (D1) | Rural autonomy | Units | + | |
| The number of people receiving minimum living security in rural areas (D2) | Social security situation | People | - | ||
| The number of special rural hardship individuals receiving assistance and support (D3) | People | - | |||
| Village groups (D4) | Rural norms | Units | + | ||
| Affluent living (E) | Per capita current housing construction area in rural areas (E1) | Income and expenditure conditions | Square meters per person | + | |
| Per capita disposable income of rural residents (E2) | CNY | + | |||
| The number of medical personnel per thousand people (E3) | Medical resource allocation conditions | Medical personnel per thousand people | + | ||
| Engel’s coefficient of rural residents (E4) | Distribution of income and expenditure | % | - | ||
| New urbanization | Population urbanization (F) | Urbanization rate (F1) | % | + | |
| Population density (F2) | Population migration | People per square kilometer | + | ||
| Urban registered unemployment rate (F3) | Employment environment | % | - | ||
| Economic urbanization (G) | Per capita regional gross domestic product (G1) | National economic | Billion CNY per person | + | |
| The proportion of the second industry in GDP (G2) | % | + | |||
| The proportion of the third industry in GDP (G3) | % | + | |||
| Per capita disposable income of urban residents (G4) | Income and expenditure conditions | CNY per person | + | ||
| Land urbanization (H) | Per capita urban road area (H1) | Utilization rate of land resources | Square meters per person | + | |
| The density of water supply pipelines in built-up areas (H2) | Kilometers per square kilometer | + | |||
| Social urbanization (I) | The number of hospital beds per thousand people (I1) | Medical and health conditions | Sheets per thousand people | + | |
| Water coverage rate (I2) | Infrastructure construction | % | + | ||
| Gas coverage rate (I3) | % | + | |||
| Environmental urbanization (J) | Per capita green park area (J1) | Ecological environment | Square meters per person | + | |
| Green coverage rate in built-up areas (J2) | % | + | |||
| Green area rate in built-up areas (J3) | % | + | |||
| Household waste treatment rate (J4) | Pollution treatment | % | + | ||
| Sewage treatment rate (J5) | % | + |
3.2.2. Entropy Weight Method
The entropy weight method is an objective weighting method, the core of which is to reflect the difference of information according to the entropy value of each index and determine the importance of each index scientifically. On the one hand, the entropy weight method can avoid the interference of subjective judgment on the weight of each evaluation index effectively to make the evaluation results more consistent. On the other hand, the entropy weight method can evaluate the amount of information quantitatively by calculating the entropy value of each index [58]. The Comprehensive index of RR and NU is used to evaluate the development of rural revitalization and new urbanization. The comprehensive index of RR can be understood as an indicator of assessing the effectiveness of policies to improve rural livelihoods. It reflects the ability of rural areas to adapt and develop in a rapidly changing socio-economic environment. The comprehensive index of NU captures the dynamics of urban growth and transformation, focusing on aspects such as infrastructure development, population density, and service accessibility. In order to comprehensively and accurately reflect most of the information content of the basic data and improve the objectivity and accuracy of the evaluation, this study uses the entropy weight method to calculate the comprehensive index of RR and NU [59]. The calculation formula of entropy weight method is as follows:
(1) Calculate the weight of the th indicator for the th evaluation object.
(2) Calculate the entropy value for the th indicator.
(3) Calculate the coefficient of variation for the th indicator.
(4) Calculate the weight of the th indicator relative to all the other indicators.
(5) Finally, the linear weighting method is used to sum up and calculate the comprehensive index for each city:
where indicates the year; denotes the standardized value; refers to the proportion of the th indicator in th year; refers to the index entropy; refers to the weight of the th indicator; refers to the difference coefficient of the th indicator; and refers to the comprehensive index of new urbanization or rural revitalization.
3.2.3. Coupling Coordination Model
The interrelationship between different subsystems can be reflected in the coupling coordination model by quantifying the coupling degree. A comprehensive evaluation and study of the entire system was allowed. However, traditional coupling models often result in coupling degree values being overly concentrated within a specific range, which diminishes the validity of the interrelationship interpretations among subsystems. Therefore, the method proposed by Shujia Wang et al. [49] was adopted to calculate the coupling coordination degree.
where is the number of subsystems; is the weight of the subsystem; is the value of each subsystem; is the value of the largest subsystem; is the coupling degree; is the comprehensive evaluation index; and is the degree of coordinated development.
3.2.4. Obstacle Degree Model
The obstacle degree model assesses the extent to which various obstructive factors hinder the achievement of objectives by quantifying their impacts. The obstacle degree model was used to analyze the factors that impede the coupling and coordination between new urbanization and rural revitalization [60].
where denotes the degree of deviation of the th indicator of the th evaluation object and denotes the degree of obstacle of the th indicator of the th evaluation object.
4. Result Analysis
4.1. Analysis of the Level of Rural Revitalization
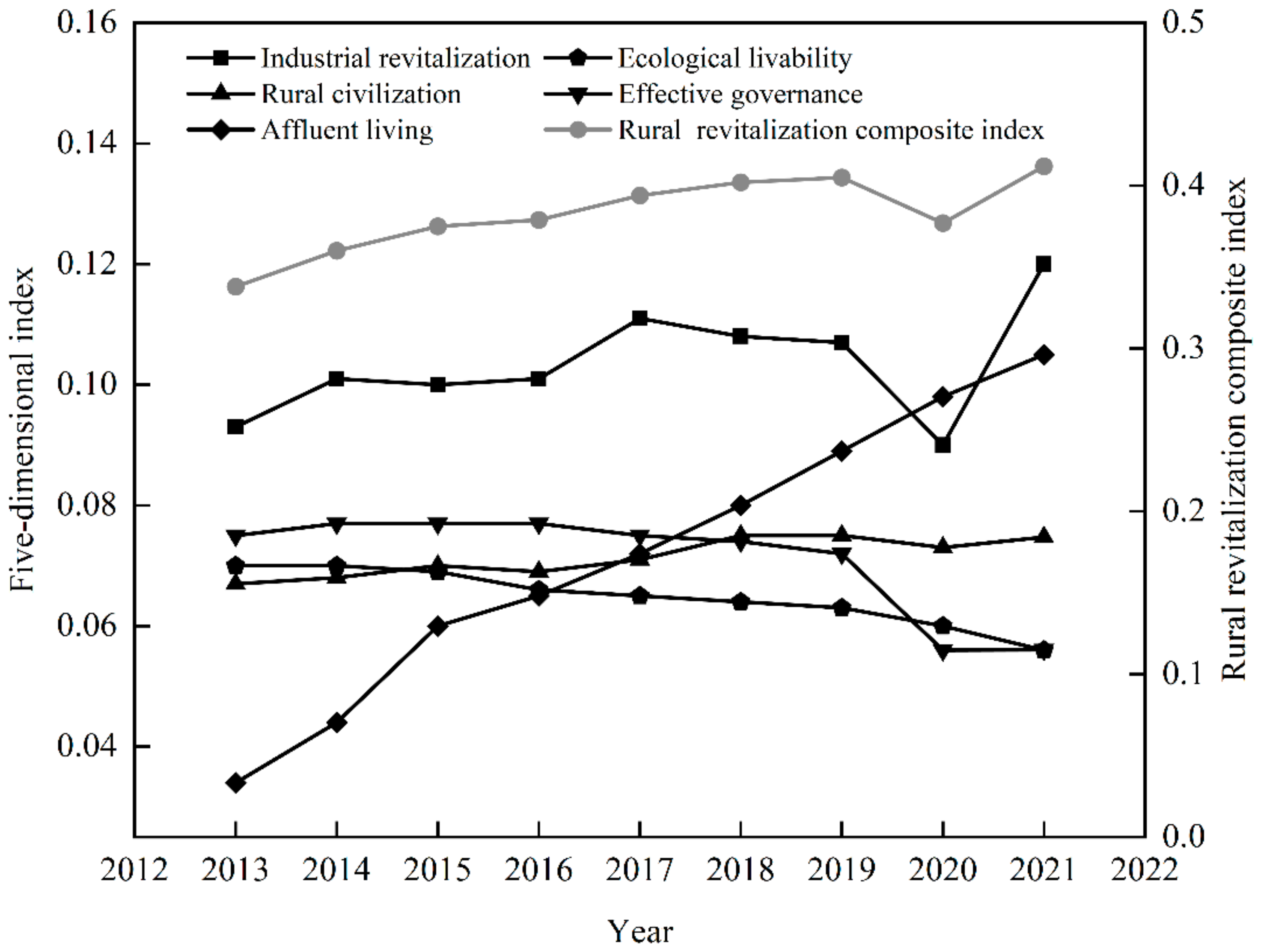
The overall level of RR in the basin area of Sichuan Province showed an uptrend (Figure 2). With the nationally targeted poverty alleviation, RR strategy, and other policies, the RR level in the study area increased from 0.338 (2013) to 0.453 (2021), with a 9-year mean value of 0.382. In 2020, the RR index decreased by 6.9% due to the impact of the COVID-19 epidemic. However, after the epidemic situation improved, the economy gradually recovered in all aspects, and the RR index of the basin area of Sichuan Province increased by 9.3% in 2021. From various dimensions, the study area exhibited a stable growth trend in the dimension of affluent living, increasing from 0.340 to 0.105. The dimensions of ecological livability and effective governance showed a downward trend. With the continuous development of urbanization and the blind rise of communities, the number of indicators of village clinics, rural doctors, and village groups has decreased by 20% and 25% in the indices of ecological livability and effective governance, respectively. It is noteworthy that the dimension of industrial revitalization and rural civilization declined in 2020. This may be caused by the decline in food production capacity and rural employment during COVID-19.
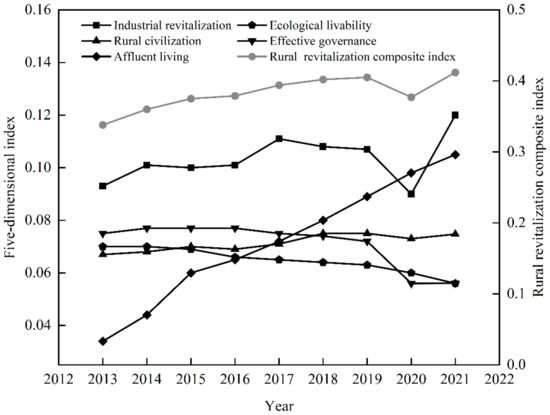
Figure 2.
Trends in the comprehensive index of rural revitalization and dimensional indices. (The figure uses double ordinates to display each dimension index, in which the dimensions of industrial revitalization, ecological livability, rural civilization, effective governance, and affluent living refer to the left ordinate, and the rural revitalization comprehensive index refers to the right coordinate).
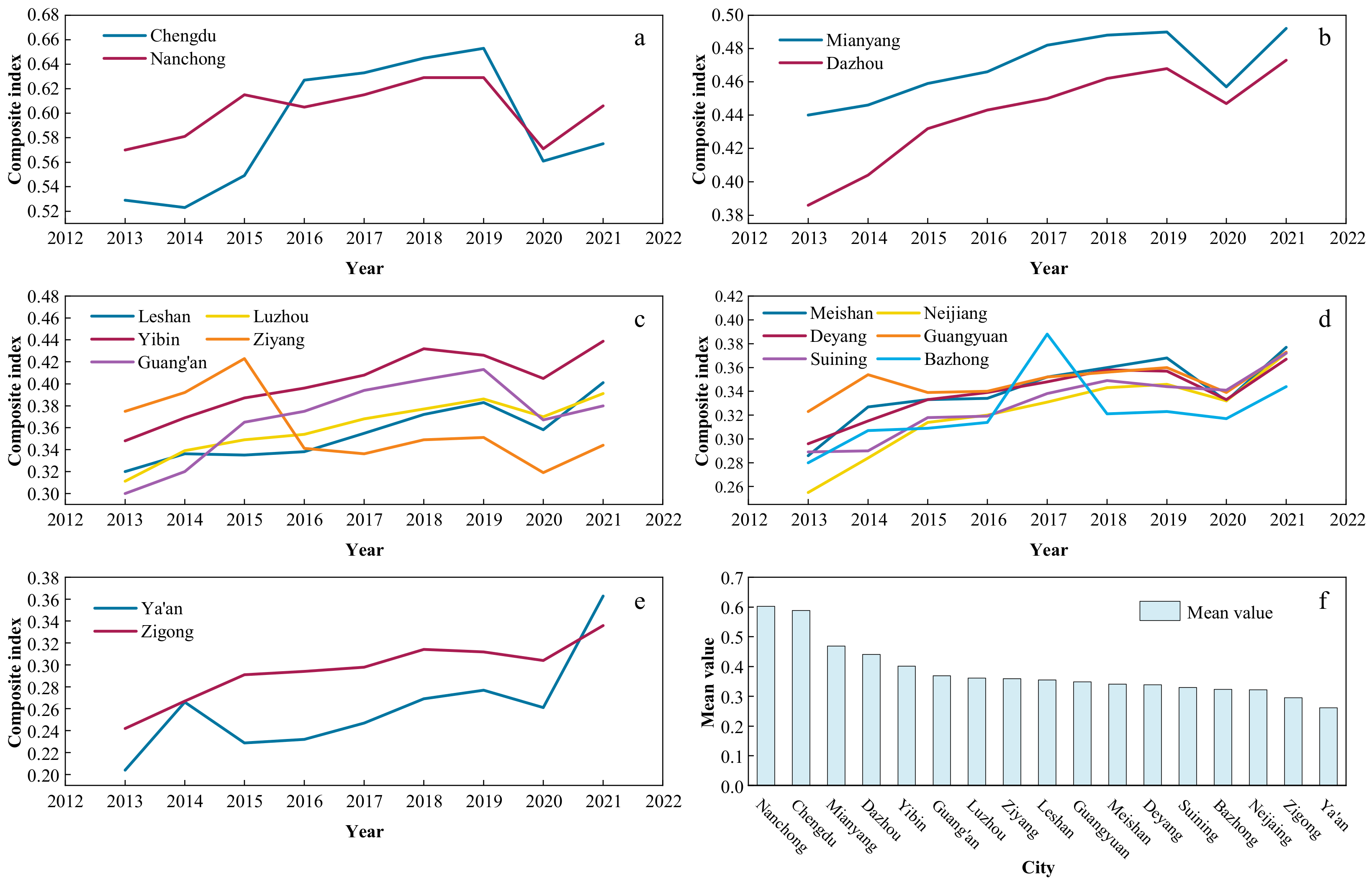
In Figure 3, it is apparent that there are obvious disparities in the RR development levels among the 17 prefecture-level cities in the basin area of Sichuan Province. Additionally, the comprehensive indices of RR in all cities in the area exhibited a downtrend in 2020. The highest mean value is 0.602 (for Nanchong), while the lowest is 0.261 (for Ya’an). Cities with mean values exceeding 0.4 include Nanchong, Chengdu, Mianyang, Dazhou, and Yibin, while the rest of the cities’ mean values are distributed in the range of 0.261 to 0.369. Specifically, Nanchong is not only a typical agricultural city in Sichuan Province but also the city with the second largest population in Sichuan Province. The city has a relatively high number of village committees, village groups, and village clinics, resulting in extensive service coverage. This abundance contributes to the city’s remarkable performance in effective governance, elevating the overall RR level in Nanchong. As the capital city of Sichuan Province, the mean value of Chengdu was 0.014 lower than that of Nanchong. This may result from urban expansion, the prominent contradiction between people and land, and the rural surplus labor force affecting the level of Chengdu’s RR development. The level of RR in Mianyang, Dazhou, Yibin, Luzhou, Deyang, and other cities showed uptrend, except for a decline in 2020 due to the impact of the pandemic. The RR index of Ziyang fluctuated significantly, especially from 0.423 (2015) to 0.26 (2016), which was mainly due to the effective irrigated area being less than 40% of the cultivated land area, and the decline in the total value of agriculture, forestry, animal husbandry, and fishery production led to a large decline in the RR index in 2016. Ba Zhong is located at the junction of Sichuan and Shanxi provinces and is a typical revolutionary base area and remote mountainous region. The RR index in Bazhong fluctuated greatly from 2016 to 2018, increasing from 0.314 (2016) to 0.388 (2017) and then decreasing to 0.321 (2018). This may be influenced by the development of tourism [61]. The level of RR in Zigong (0.295) and Ya’an (0.261) ranked low in the basin area of Sichuan Province. The limited area of Zigong, combined with its low level of agricultural mechanization due to terrain constraints and a relatively large rural population as well as a shortage of employment opportunities, has hindered the development of RR in Zigong. As of the end of 2021, rural employment in Zigong accounted for 34% of the total rural population. Ya’an is situated on the western edge of the Sichuan Basin. Its rural public healthcare level is relatively low, with the fewest number of village clinics and rural doctors among the 17 prefecture-level cities. Moreover, factors such as limited arable land and low grain output further constrain the improvement of RR levels in the area.
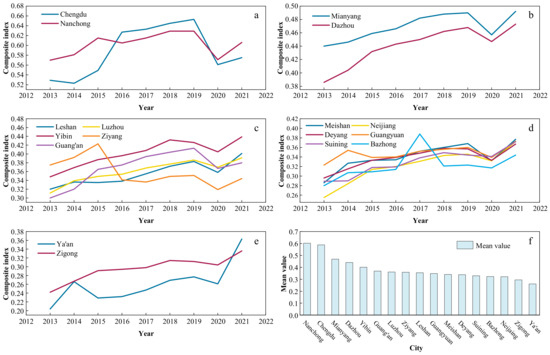
Figure 3.
Comprehensive index of rural revitalization in 17 prefecture-level cities from 2013 to 2021. (The level of RR is classified into five levels from high to low based on the natural breakpoint method. (a–e) show the comprehensive rural revitalization index of 17 prefecture-level cities, and (f) shows the average RR index of 17 prefecture-level cities from 2013 to 2021).
4.2. Analysis of the Level of New Urbanization
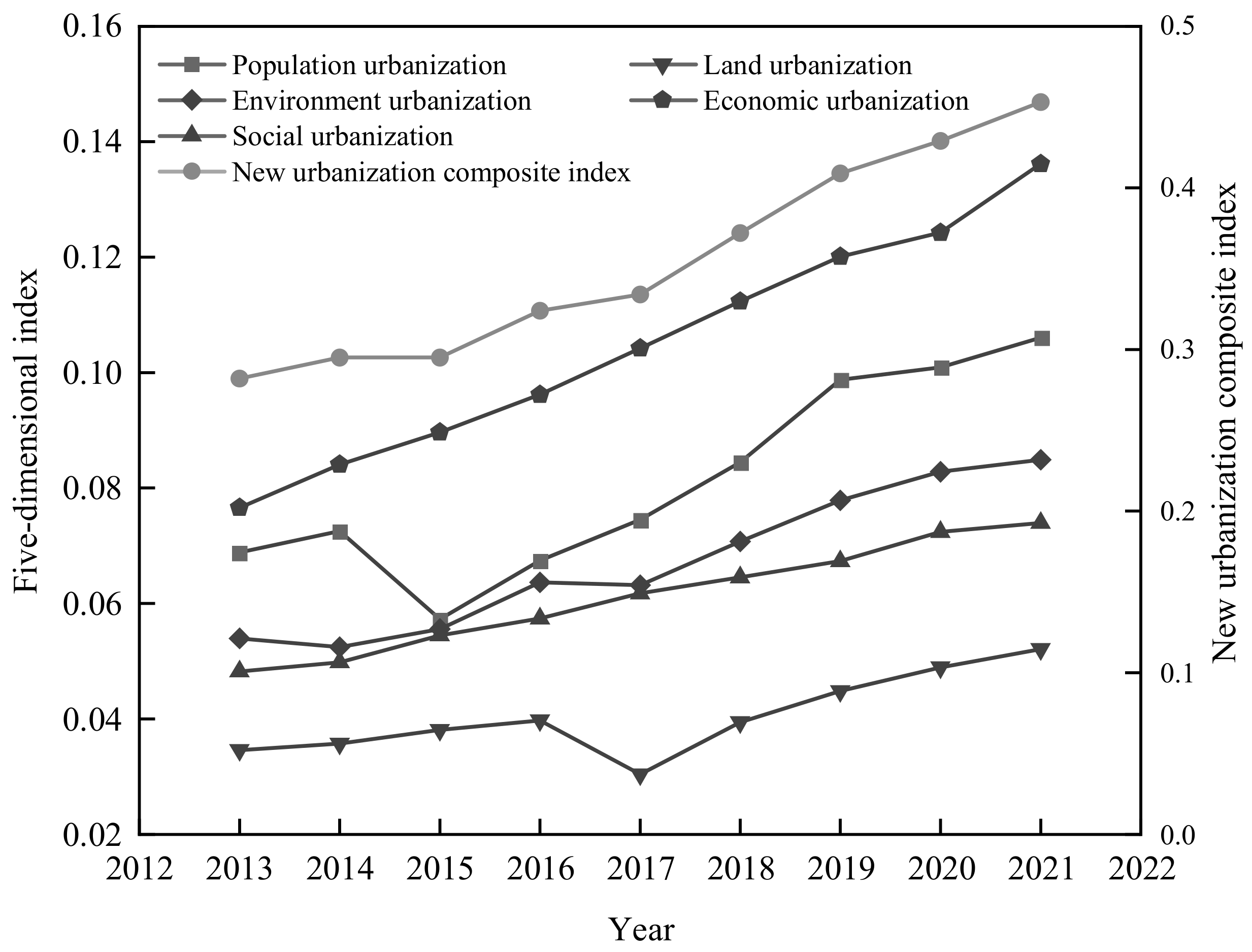
The overall NU level in the basin area of Sichuan Province exhibited a steady uptrend (Figure 4). According to the “New Urbanization of Sichuan Province (2014–2020)”, strategic deployment and NU construction are carried out in Sichuan constantly. From 2013 to 2021, The level of NU in the basin area of Sichuan Province increased by 60%. Between 2017 and 2018, the comprehensive NU index increased by 11%. According to the Urbanization Development Report of Sichuan Province [62], the region entered the middle stage of urbanization planning around 2017, achieving a historic transformation from a rural-type society to an urban-type society. In addition, the index of all dimensions in the study area showed fluctuating growth in general. The economic urbanization and social urbanization indices showed stable growth, with annual average growth rates of 7.5% and 5.5%, respectively. However, the population urbanization index showed a downward trend in 2015, primarily due to declining population density in cities such as Deyang and Meishan, which became significant obstacles for this dimension. The land urbanization index decreased clearly in 2017, despite an increase of 216.66 square kilometers in the built-up area of Sichuan Province from 2016 to 2017. The density of water supply pipelines decreased by 9%, impacting the land urbanization index. In 2018, influenced by national policies [63], Sichuan Province accelerated the construction of Chengdu–Chongqing city clusters, promoted the continuous improvement of the land spatial planning system, and enhanced municipal facilities, making this dimension index rise year by year.
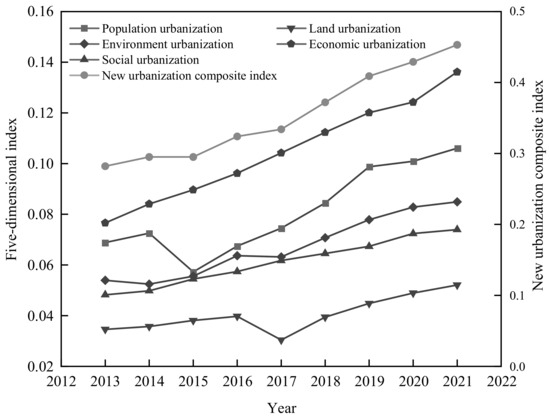
Figure 4.
Trends in the comprehensive index of NU and dimensional indices. (The figure uses double ordinates to display each dimension index, in which the dimensions of population urbanization, economic urbanization, land urbanization, social urbanization, and environmental urbanization refer to the left ordinate, and the new urbanization comprehensive index refers to the right coordinate).
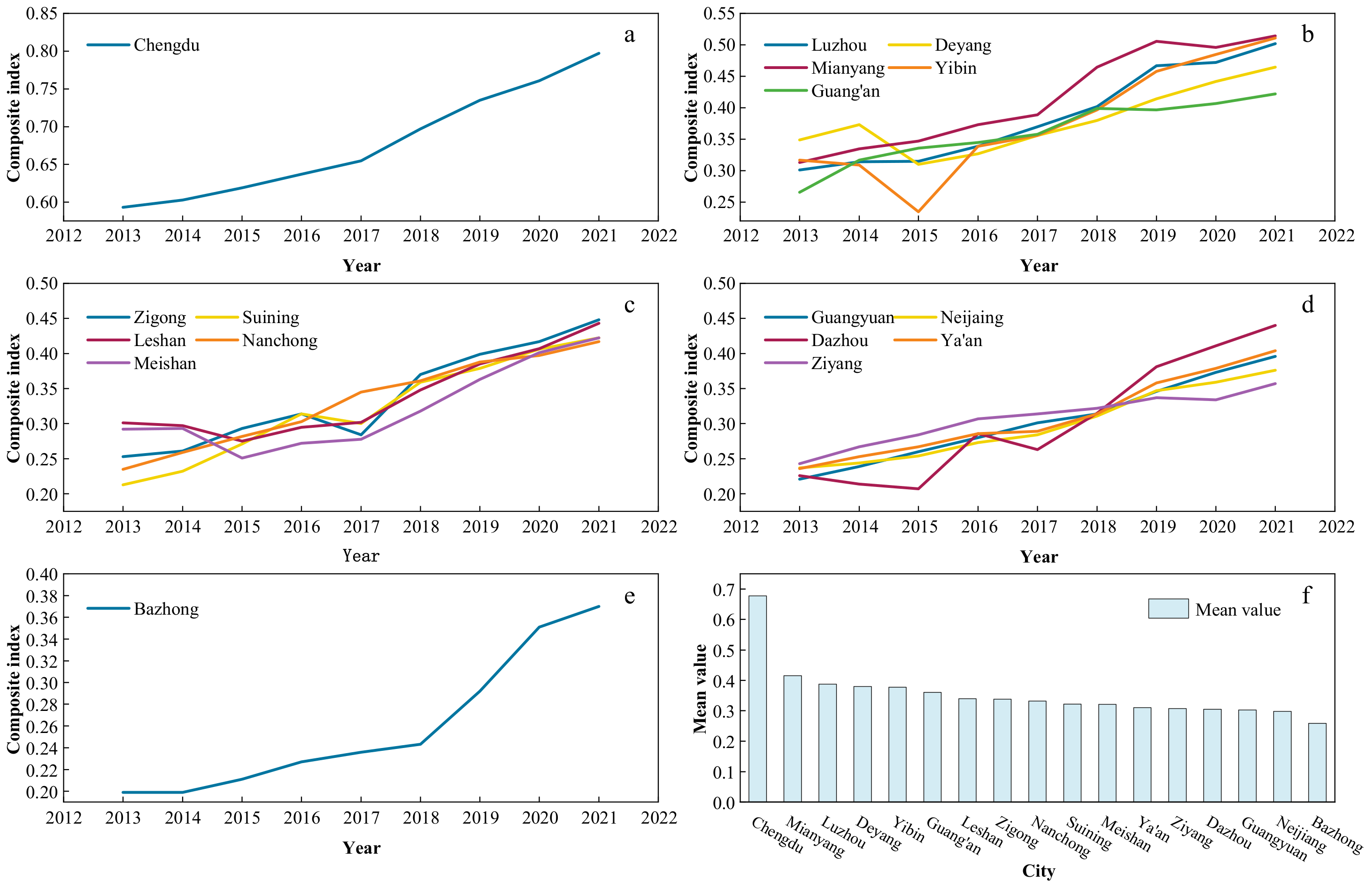
Analyzed by region (Figure 5), the level of NU among cities exhibits an uptrend, yet obvious heterogeneities persist across regions. The city with the highest average NU index in the basin area of Sichuan Province region is Chengdu, where the annual NU index consistently exceeds 0.55, notably peaking at 0.797 in 2021. As a national central city, Chengdu City exhibits a relatively high level of urbanization, achieving a rate of 79.5% in 2021. Moreover, indicators such as residents’ disposable income and per capita gross regional product are comparatively elevated, positioning Chengdu prominently in the NU index. Cities with lower NU indices include Bazhong and Neijiang, with Bazhong recording the lowest mean value at 0.259. This is due to the low per capita disposable income and per capita GDP of the city, as well as the inadequate urban infrastructure, which have led to the low level of NU in Bazhong. There has been an increase in the NU index of Neijiang from 0.237 (in 2013) to 0.376 (in 2021), but the overall average remains relatively low. The city started urbanization construction relatively late and pursued a more singular development approach. Moreover, factors such as overall low urban and rural incomes have constrained NU development in Neijiang. Mianyang, Deyang, Yibin, Luzhou, and other cities demonstrate relatively high NU indices, accompanied by substantial growth rates. Under the radiating role of the central city and the construction of regional central cities, the GDP and urbanization rate continue to increase, which promotes the development of NU.
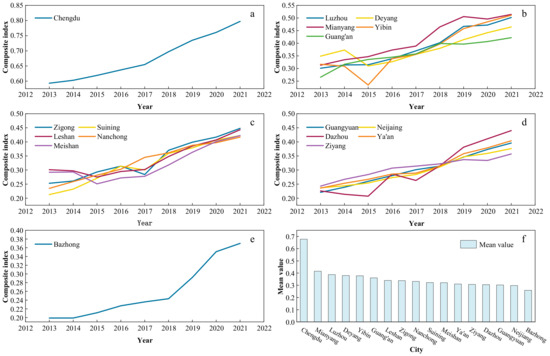
Figure 5.
Comprehensive index of new urbanization in 17 prefecture-level Cities from 2013 to 2021. (The level of NU was classified into five levels from high to low based on the natural breakpoint method. (a–e) show the comprehensive new urbanization index of 17 prefecture-level cities, and (f) shows the average new urbanization index of 17 prefecture-level cities from 2013 to 2021).
4.3. Coupling Coordination Analysis
Drawing on previous research [64,65], the coupling degree is categorized into seven levels (Table 2), and the results are as follows.

Table 2.
Coupling coordination levels.
As shown in Table 3, the coupling coordination degree of NU and RR in the basin area of Sichuan Province as a whole continues to rise from 0.53 (in 2013) to 0.624 (in 2021), with an average value of approximately 0.58. Before 2018, the overall average of each city was at an essential coordination level. After 2018, it reached a moderate coordination stage. This indicates that since the 19th National Congress of the Communist Party of China, there has been an improvement in the coordinated development between NU and RR due to the deepening integration of urban and rural areas. At the regional scale, from 2013 to 2021, Chengdu consistently ranked first in terms of coupling and coordination, whereas Bazhong maintained the lowest average degree of coupling and coordination. In the study area, there is a good coordination level in Chengdu. Mianyang, Nanchong, and Yibin are at a moderate coordination level. Moreover, cities reaching an essential coordination level constitute 76% of the total, highlighting obvious regional disparities in coupling coordination between NU and RR across the 17 prefecture-level cities due to uneven economic development. There has been a consistent coupling coordination degree exceeding 0.7 in Chengdu, maintaining a good or higher level of coordination over the past nine years. This indicates that greater harmony and balance have been achieved between various dimensions of NU and RR in Chengdu. The level of urban–rural integration has further improved against the backdrop of a gradually narrowing urban–rural gap and phased progress. Mianyang, Yibin, and Nanchong, whose coupling coordination average is between 0.6 and 0.7, are the regional centers of Sichuan Province and have apparent regional advantages. These cities promote factor flow between urban and rural areas by constantly improving welfare policies, actively encouraging talents to return home and start businesses, reforming medical insurance, and improving land mobilization mechanisms. There are a total of 13 cities (excluding Chengdu, Mianyang, Nanchong, and Yibin) whose coupling coordination average is between 0.5 and 0.6. The increasing coordination degree of NU and RR in these cities is due to the continuous improvement of agricultural mechanization level, urbanization rate, public health and environmental quality, and the reduction of the urban–rural income gap under the guidance of the “National New Urbanization Plan (2014–2020)”. These policies are expected to foster a positive trend in the coupling coordination of NU and RR.

Table 3.
Coupling coordination degree and ranking of 17 prefecture-level cities from 2013 to 2021. (The coupling coordination degrees corresponding to the colors in the table refer to the grading standards in Table 2).
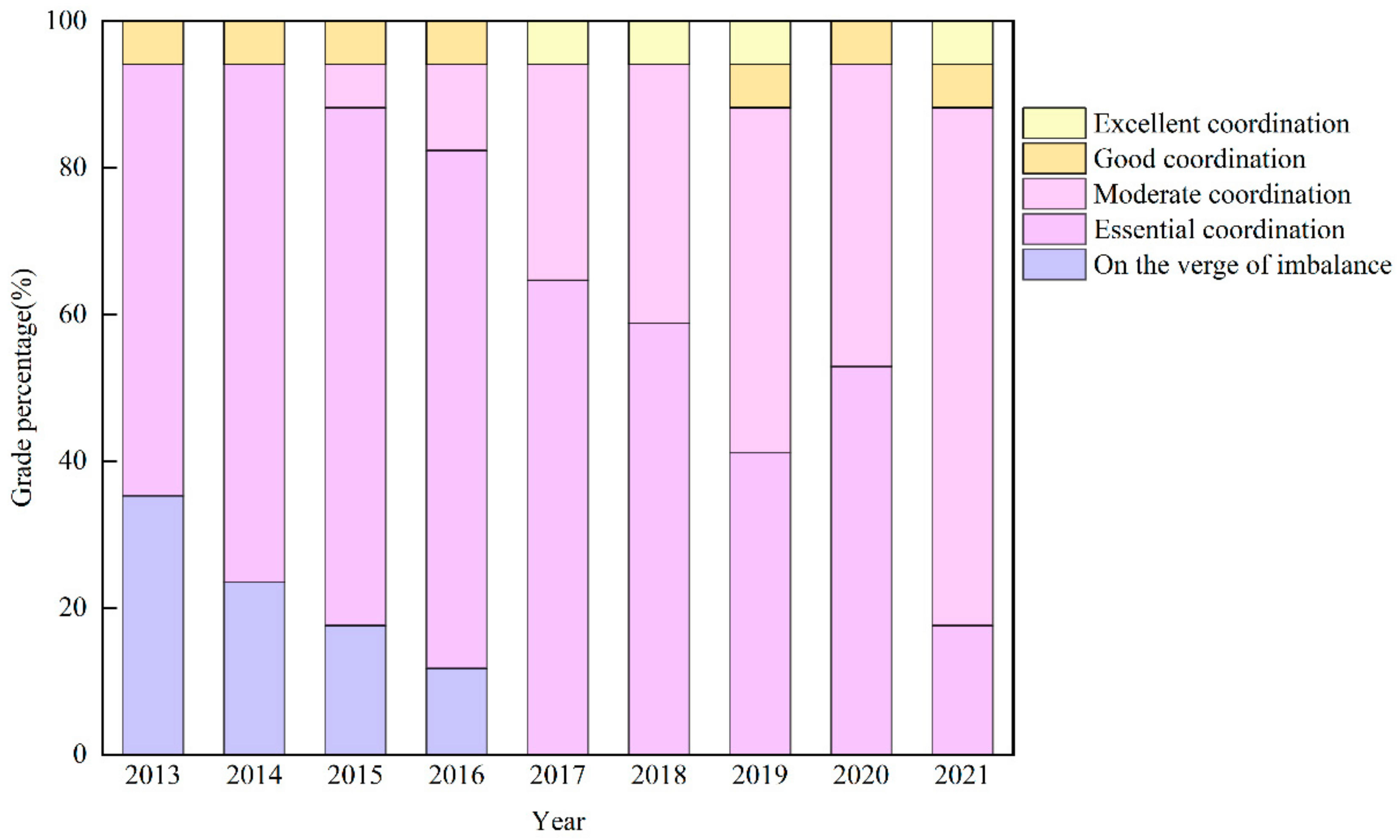
The coupling coordination type of most cities in the basin area of Sichuan Province gradually changed to the middle and high coordination levels (Figure 6). From 2013 to 2016, cities with coupling coordination types on the verge of imbalance transitioned towards an essential level of coordination. This shift indicates that targeted poverty alleviation measures have effectively improved rural conditions across diverse regions, thereby promoting urban–rural integration. Between 2017 and 2021, all cities with coupling coordination levels on the verge of imbalance successfully transitioned to at least an essential level of coordination. Additionally, there was a gradual decrease in cities at the essential coordination level coupled with an increase in those at a moderate coordination level. This trend underscores that coordinated policies such as the “Thirteenth Five-Year Plan”, which emphasizes human-centered approaches, prioritizes agricultural transformation, enhances rural development, and accelerates NU [66], have continually strengthened the coupling between NU and RR.
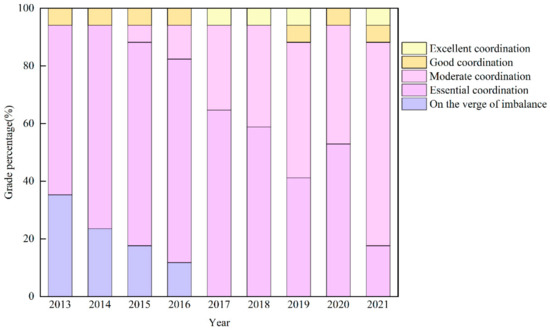
Figure 6.
Proportion of coupling coordination levels in 17 prefecture-level cities from 2013 to 2021. (The lengths of the five color bar plots in the figure represent the percentage of the regional coupling coordination level in the basin area of Sichuan Province from 2013 to 2021).
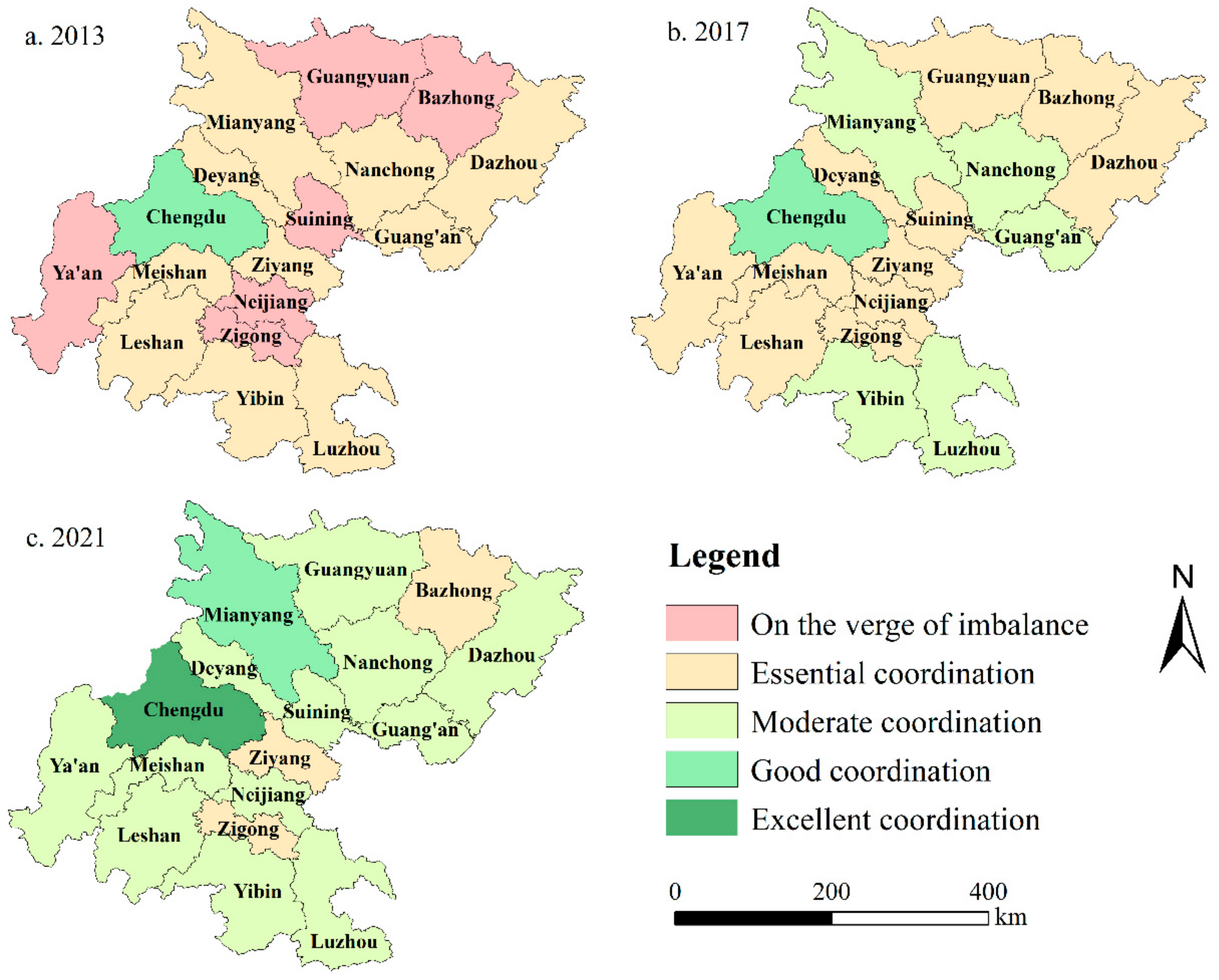
From a spatial evolution perspective (Figure 7), Chengdu stood out as the sole city with a high coordination degree between NU and RR in 2013, showcasing a pronounced primacy effect as the central city of Sichuan Province. There were 10 cities at an essential coordination level (including Dazhou, Guang’an, Nanchong, Mianyang, Deyang, Ziyang, Meishan, Leshan, Yibin, and Luzhou), roughly forming an “M”-shape distribution pattern at approximately 90 degrees. In 2017, five cities (including Mianyang, Nanchong, Guang’an, Yibin, and Luzhou) transitioned from an essential to a moderate coordination level. Chengdu maintained its high level of coordination. Meanwhile, six cities (including Ya’an, Guangyuan, Bazhong, Suining, Neijiang, and Zigong) were elevated from the verge of imbalance to an essential coordination level. Although the coordination types of cities such as Leshan, Meishan, Ziyang, Deyang, and Dazhou remained unchanged, their coupling coordination indices steadily increased. In 2021, the number of cities at a moderate coordination level increased, with Bazhong, Ziyang, and Zigong maintaining their coupling coordination types at an essential level. Chengdu’s coupling coordination shifted from a good level to an excellent level. Mianyang improved from moderate to good coordination, and eight cities—including Dazhou, Deyang, and Suining—progressed from essential to moderate coordination levels. Overall, the high coupling coordination between NU and RR is predominantly concentrated in central cities and regional central cities. This indicates that these cities have relatively concentrated industrial structures, resulting in a higher degree of integration between NU and rural areas. The rapid development of infrastructure such as transportation hubs has facilitated the flow of factors between urban and rural areas, gradually promoting coordination between NU and RR. While node cities may develop at a slower pace, they possess significant growth potential. Strengthening policy guidance is crucial to organizing node cities and regional central cities effectively, with the latter acting as primary drivers and node cities as supporting elements, thereby collectively advancing the overall urban–rural integration in Sichuan Province.
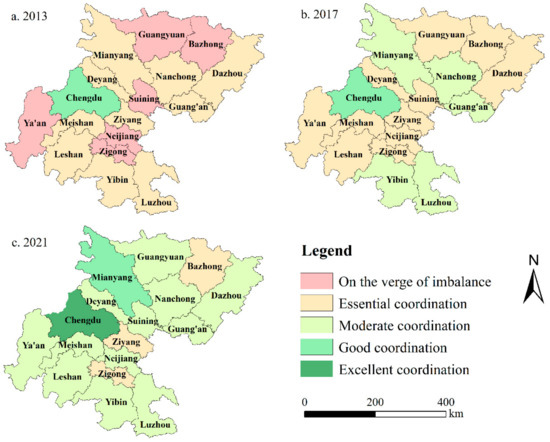
Figure 7.
Distribution map of coupling coordination levels of 17 prefecture-level cities in the basin area of Sichuan Province in 2013, 2017, and 2021. The base map is the standard map No. GS (2024)0605 downloaded from the standard map service website of the National Administration of Surveying, Mapping and Geographic Information (bzdt.ch.mnr.gov.cn, accessed on 3 September 2024), without modification.
4.4. Obstacle Factor Analysis
Three time periods (2013, 2017, and 2021) were selected, as was the obstacle degree model to analyze the dimensions of NU and RR in the basin area of Sichuan Province (Table 4). The results show obvious differences in the obstacle degree among all dimensions. From 2013 to 2017, the obstacle degree decreased the most in the dimension of affluent living, followed by the dimension of economic urbanization. This indicates that since the 18th National Congress of the Communist Party of China, various regions have implemented economic development policies, leading to a rapid increase in residents’ income and a gradual reduction in the urban–rural income gap. Conversely, the obstacles in ecological livability and land urbanization dimensions increased by 16.77% and 14.1%, respectively. This rise is attributed to the accelerated urbanization process within the study area during this period, leading to a surge in urban population and a reduction in per capita urban road area. Furthermore, the inclusion of certain areas within urban administrative boundaries, causing the blurring of distinctions between communities and rural areas, has resulted in a decrease in the number of rural health clinics and hospitals, thereby impeding the development of both dimensions. From 2017 to 2021, the obstacles decreased in the dimensions of affluent living and environmental urbanization due to improvements in rural housing conditions and employment environments following the RR strategy. Concurrently, the obstacles increased in effective governance, ecological livability, and social urbanization dimensions. Effective governance emerged as a primary constraint, notably influenced by initiatives like “Turning Villages into Communities”, which reduced village groups and healthcare facilities. After the implementation of the “Provincial Township Administrative Division and Village Level System Adjustment Reform” in Sichuan Province, the villagers’ committees were abolished and changed into community residents’ committees in the urban center or the surrounding rural areas that are included in the urban construction land [67]. While this initiative enhanced the rural employment environment and economic structure, its unilateral implementation led to challenges such as organizational inefficiencies, talent shortages, and excessive administrative functions [68].

Table 4.
Change rate of obstacle degree in each dimension.
To specifically analyze the obstacle factors influencing the coupling coordination between NU and RR, the top three were selected as important factors (Table 5). According to the frequency of obstacle factors, in the RR index system, A1 emerges as the most frequent and important obstacle factor restricting the development of RR in the basin area of Sichuan Province. The agricultural mechanization level in most urban areas of this region faces numerous challenges due to the unique topography and terrain. In the NU index system, I1 occurs most frequently due to the uneven distribution and insufficient utilization of medical and health resources in the study area [69]. Insufficient availability of hospital beds stands as the primary barrier obstructing NU development. Therefore, it is imperative for the basin area of Sichuan Province to adjust the medical and health structure, optimize medical and health resources. Particularly in the post-pandemic era, further enhancing the medical and health service system becomes especially crucial.

Table 5.
The top three obstacle factors of each city in 2013, 2017, and 2021.
To specifically analyze the differences among individuals (Table 5), this paper takes 2021 as an example to analyze the factors of the coupling coordinated development of NU and RR in each city in the study area. In terms of RR, the top three obstacles identified across 12 cities, including Chengdu, Zigong, Luzhou, and Bazhong, are A1, D1, and C3. Although the level of agricultural mechanization and industrialization in Chengdu is the highest in Sichuan Province, the level of agricultural machinery is still the biggest obstacle to the development of RR in Chengdu when all indicators tend to be balanced. In addition, there is a high level of urbanization in Chengdu. The “Turning Villages into Communities” initiative has had a great impact, particularly affecting A1 and D4, which affect the development of RR. There are complex topography, uneven distribution of resources, and relatively poor agricultural basic conditions in Zigong, Bazhong, Neijiang, and other cities. Under the influence of unreasonable community, the number of village committees has decreased, which affects the improvement of RR. Moreover, Leshan, Nanchong, and Ya’an are also affected by the indicators of D4, A4, and A3. There is a large area in Leshan, and the number of villagers’ groups has decreased with the continuous development of urbanization. From 2013 to 2021, D4 has seen a decrease of more than 4000 in Leshan. As of 2021, there is a large rural population in Nanchong, with the rural population reaching over 5 million. However, the number of rural employed individuals is only slightly over 1.7 million. Ya’an faces challenges due to its small geographical area and terrain constraints, resulting in limited arable land and low grain production capacity. As of 2021, its effective irrigated area was only 53.93 hectares, significantly lower than the other 16 prefecture-level cities in comparison.
In terms of NU, Chengdu is affected by factors such as G2 and J1. The transformation and upgrading of many traditional industries and the development of the tertiary industry affect the secondary industry to a certain extent. The sizeable population has contributed to environmental pollution in Chengdu. Additionally, the economic repercussions of the epidemic have also affected various aspects, collectively restricting the coordinated development of Chengdu’s NU and RR efforts. I1, F2, and F3 are the main obstacle factors in eight cities, including Zigong, Deyang, Guangyuan, and Suining. These cities face challenges stemming from their relatively low population density, limited industrial diversity, and strained employment conditions. Especially after the COVID-19 pandemic, there has been a high unemployment rate, compounded by the conflicting impact between public healthcare resources and the increasing population demands. Luzhou, Mianyang, Guang’an, and Meishan are also affected by F1. To strengthen their economic strength, it is necessary to strengthen the exchange and cooperation with the surrounding areas, improve the employment environment, improve the level of medical and health services, promote economic development, and improve the relevant household registration system to promote the settlement of the floating population. Yibin and Dazhou are also affected by H2 in built-up areas. During the development of regional central cities, the built-up areas gradually expand, and the relevant infrastructure is slow to follow up, thus affecting the development of NU. In addition, Bazhong is also affected by G2 due to its rugged terrain and relatively backward infrastructure. Development in the secondary industry in Bazhong is relatively inadequate, resulting in an overall weak economy [70]. Future strategies should focus on improving construction policies, restructuring the industrial sector, and leveraging local advantages such as cultivating high-quality tea and developing red tourism resources. These initiatives will diversify the job market, boost employment rates, and stimulate economic development.
5. Discussion
Conducting research on the coordinated development of NU and RR can provide valuable insights into achieving high-quality development in urban and rural areas in China. By studying the spatiotemporal differentiation of NN and RR levels, coupled with spatiotemporal characteristics and obstacle factors in the basin area of Sichuan Province, this paper has enriched the achievements of urban–rural integration development and provided a reference for the urban–rural integration development in Sichuan Province. The terrain of Sichuan Province is complex and diverse, and the reasons affecting regional differences are also different under different index systems.
In terms of level measurement, from 2013 to 2021, the levels of NU and RR in the basin area of Sichuan Province showed an overall growth trend. The research results from 2013 to 2019 were consistent with the urban–rural development level of 21 prefecture-level cities in Sichuan Province [71]. The changes from 2013 to 2020 were similar to those of Yunnan Province [72] and Guizhou Province [73]. It may be related to economic development, geographic location, and the similarity of indicators. The terrain of Sichuan Province is complex and diverse, and the reasons affecting regional differences are different under different index systems and different research areas. This paper holds that industrial revitalization and economic urbanization have a great impact on RR and NU in the basin area of Sichuan Province, which is different from other scholars. For example, Jin Liu [74] took 21 prefecture-level cities in Sichuan Province as research objects, constructed 66 indicators from the perspectives of industry, ecology, and governance, and believed that ecology and industry have a great impact on rural development. Yuling Huang [75] took Luzhou City as an example to construct 30 indicators and believed that ecological livability and urban infrastructure construction contributed a lot. In addition, Xiaohui Gao et al. [71] believed that the comprehensive level of RR in Chengdu ranks first, which is quite different from this study. This is mainly caused by the difference in indicators in rural governance. The scholar only considered output value, income, and employment when constructing the indicators, while rural governance and civilization may be ignored. In this study, the indicators of effective governance are constructed from the aspects of village committees, village groups, and rural assistance. As a typical large agricultural city in Sichuan Province, there are a large number of villages and towns in Nanchong, which can be given more samples in RR.
In terms of coupling features, the coupling coordination level of NU and RR in the basin area of Sichuan Province showed an overall growth trend, and there is apparent spatial heterogeneity among regions. This is consistent with the research results of Tianzhe Sun et al. [76]. However, there are obvious differences in the calculation of coupling degree with these scholars, which was mainly caused by the differences in coupling and coordination models. The coupling and coordination degree between NU and RR in 21 cities (prefectures) of Sichuan Province calculated by these scholars was concentrated in the range of 0.9–1.0, which was likely to reduce the interpretive validity of the coupling degree. However, the revised coupling and coordination model was adopted in this study, which can make up for this shortcoming. The coupling and coordination process of NU and RR in the basin area of Sichuan Province is affected by many factors. The level of agricultural mechanization is one of the main obstacle factors affecting the coupling and coordinated development of NU and RR in the basin area of Sichuan Province. In the process of urban–rural development, the level of agricultural mechanization (A1) serves as a vital factor not only in enhancing grain production and reducing labor costs but also in promoting the modernization of urban and rural areas. The level of agricultural mechanization (A1) plays a key role in promoting the coordinated development of RR and NU [77]. Another major obstacle factor is the number of medical and health beds per thousand population (I1), which plays a crucial role in evaluating the accessibility and quality of the healthcare system. Particularly in the process of NU and RR, the adequacy of public health services becomes increasingly critical. The level of development of public health services has profound implications for the integrated development of urban and rural areas [78]. This not only involves the allocation of medical resources but also directly affects the health status of urban and rural residents and stable socioeconomic development. Therefore, a comprehensive understanding and exploration of the impact mechanism of public health services on the integrated development of urban and rural areas are of great significance for optimizing the allocation of health resources, enhancing the health level of urban and rural residents, and promoting integrated urban–rural development.
This study found that COVID-19 caused a series of negative impacts on RR and NU development. In terms of RR, the epidemic caused delays in farming time and insufficient production materials, which affected the efficiency of agricultural planting and harvesting directly [79]. Furthermore, traditional agriculture was affected, medical and health service facilities needed to be improved, and employment opportunities were reduced, which affects the living conditions of the population. The epidemic has also brought challenges to the new type of urbanization. During the epidemic period, the urbanization process was affected by restricted population movement, rising unemployment rate, impact on urban economic activities, and insufficient urban public services and social governance. Consequently, the COVID-19 epidemic has exacerbated the imbalance between urban and rural development. The future development of rural and urban areas should be improved in the quality of medical care and the connection of medical resources between rural and urban areas to enhance the ability to cope with public health crises in the future.
However, there are still some shortcomings in this paper. First, the evaluation index system of NU and RR involves political, economic, cultural, social, and other aspects, and how to achieve benign coupling and coordinated development between the two still needs to be explored. Due to the difficulty in obtaining data in some regions, this paper had to abandon certain indicators when constructing indicators, so the evaluation index system constructed needs to be further refined, especially in the effective dimension of governance evaluation indicators. In the future, field research can be carried out to improve the evaluation index system according to local conditions and obtain a complete data link. Second, “village transformation into community” involves many aspects. At present, the boundary between village and community is relatively vague, which is also a place to be improved in this paper. In the future, for the definition of “village to community”, it is necessary to fully consider the actual situation and development requirements of different regions and distinguish the data of villages and communities. Third, this paper carries out the analysis from the city scale, and more detailed research can start from the county and township scale in order to coordinate the NU and RR to provide a more accurate basis.
6. Conclusions
Based on the panel data of the basin area of Sichuan Province from 2013 to 2021, an evaluation index system was established for the coupling coordination between NU and RR. This study delved into the spatiotemporal characteristics of coupling coordination between the two systems at both the regional and municipal levels in the basin area of Sichuan Province by using the entropy method, the coupling coordination model, and the obstacle degree model. Furthermore, the factors that influence the coupled coordination of NU and RR were revealed. The conclusions of the research are as follows:
(1) Overall, the levels of NU and RR in the basin area of Sichuan Province exhibit an uptrend, but obvious differences exist among various dimensions and regions. Central cities exhibit higher levels of RR and NU. Under the influence of a central city, regional central cities have obvious growth in RR and NU. There are fluctuations in node cities in the RR and NU indicators. In the RR system, the dimension of affluent living increased steadily, while the dimensions of rural civilization and industrial prosperity declined in 2020. The dimensions of ecological livability and effective governance in some areas were affected by the “Turning Villages into Communities” initiative, and the index declined. In the new urban system, the dimensions of economic urbanization and social urbanization grew steadily. The dimension of population urbanization showed a downward trend in 2015, which was influenced by the unemployment rate. The dimension of land urbanization decreased under the influence of putting forward the RR strategy but rebounded with the promotion of the urban–rural integration policy.
(2) The coupling coordination degree of NU and RR in the basin area of Sichuan Province rose continuously until 2020. Some cities achieved transformation from the verge of imbalance to essential coordination and above after 2017. Spatially, the coordination level of the coupling degree between NU and RR of 17 prefecture-level cities is very different. Regions with high coupling coordination are concentrated in central cities and regional central cities, while the coupling degree of node cities is relatively low.
(3) The levels of agricultural modernization, public infrastructure and medical resources, and rural governance are the main factors influencing the coupling coordination of NU and RR in the basin area of Sichuan Province. The level of agricultural mechanization (A1) and the number of hospital beds per thousand people (I1) have become the main obstacle factors. Analysis of the indicators in 2015, 2016, and 2017 shows that the obstacle degrees of dimensions such as affluent living, environmental urbanization, and economic urbanization have decreased, while those of dimensions including effective governance, ecological livability, social urbanization, land urbanization, population urbanization, rural civilization, and industrial revitalization have increased. In addition, it is necessary to set the conditions strictly for the transformation from village to community and strengthen the construction of medical and health resources in the future and to promote the coordinated development of urban and rural areas.
Author Contributions
L.Z.: writing—original draft, data curation, methodology. W.L.: conceptualization, methodology, writing—review, supervision. Z.C.: software, supervision. Z.Y., R.H., C.Q. and X.L.: data collection and processing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Regional Cultural Research Center of the Sichuan Provincial Social Science Key Research Base Annual Project, grant number CQYYJC2101; the National Innovation and Entrepreneurship Training Program for College Students, grant number S202010638090; the Scientific Research Fund of Sichuan Provincial Education Department, grant number 18ZA0476; the Meritocracy Research Funds of China West Normal University, grant number 17YC112; the Educational Reform Project of China West Normal University, grant number 403995.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Due to the inclusion of potentially sensitive indicators or data, the authors confirm that access to the dataset will be provided upon request to the corresponding author, rather than making it publicly available.
Acknowledgments
We appreciate the valuable help and insightful feedback provided by Rui Wang. We sincerely thank the reviewers for their valuable time and constructive comments.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Fang, C. On integrated urban and rural development. J. Geogr. Sci. 2022, 32, 1411–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.S. Research on the urban-rural integration and rural revitalization in the new era in China. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2018, 73, 637–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Kong, X.S.; Li, Y.J. Identifying the static and dynamic relationships between rural population and settlements in Jiangsu Province. China Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2020, 30, 810–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.Z.; Wang, J.Y. Spatio-temporal patterns of urban-rural transformation and optimal decision-making in China. Prog. Geogr. 2021, 40, 1799–1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, Y. Revitalize the world’s countryside. Nature 2017, 548, 275–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, N.Y. Return to the countryside: An ethnographic study of young urbanites in Japan’s shrinking regions. J. Rural Stud. 2024, 107, 103254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, R.W. Urban-rural integration and rural revitalization: Theoretical discussion, mechanism explanation and realization path. Geogr. Res. 2018, 37, 2127–2140. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Jiang, H. Urban-rural integration: Foreign model, experience and realization path. Agric. Econ. Probl. 2024, 2, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conley, K.L.; Whitacre, B.E. Does broadband matter for rural entrepreneurs and creative class employees. Rev. Reg. Stud. 2016, 46, 171–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.B.; Ye, C.; Yue, W.Z.; Ma, L.B.; Luo, Z.D.; Yang, R.; Lyu, X.; Wang, C.; Li, C.W.; Zhang, G.J.; et al. Urban-rural integrated development in China in the New Era: Challenges and paths. J. Nat. Resour. 2024, 39, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P. Analysis on the Coordinated Promotion Path of New Urbanization and Rural Revitalization: A Case Study Based on the Practice Exploration in Shaanxi. J. Northwest AF Univ. (Soc. Sci. Ed.) 2022, 22, 34–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The National Development and Reform Commission of the People’s Republic of China. Where Is the Newness of New Urban-Rural Relations? 2023. Available online: https://www.ndrc.gov.cn/wsdwhfz/202304/t20230411_1353479.html (accessed on 5 September 2023).
- More, T. Utopia: Thomas More; The Commercial Press: Beijing, China, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Howard, E. Garden Cities of Tomorrow; First Published 1898; S. Sonnenschein & Co., Ltd.: London, UK, 1949. [Google Scholar]
- Fourie, C. Selected Works of Fourier; The Commercial Press: Beijing, China, 2009; 118p. [Google Scholar]
- Lewis, W.A. Economic Development with Unlimited Supplies of Labour. Manch. Sch. Econ. Soc. Stud. 1954, 22, 139–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perroux, F. Economic Space: Theory and Applications. Q. J. Econ. 1950, 64, 89–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedmann, J.R. Regional Development Policy: A Case of Venezuela; MIT Press: Cambrige, MA, USA, 1966. [Google Scholar]
- Lipton, M. Why Poor People Stay Poor: A Study of Urban Bias in World Development; Temple Smith: London, UK, 1977; pp. 28–35. [Google Scholar]
- Preston, D.A. Rural-Urban and Inter-Settlement Interaction: Theory and Analytical Structure. Area 1975, 7, 171–174. Available online: https://www.jstor.org/stable/20001000 (accessed on 2 October 2023).
- McGee, T.G. Urbanisasi or Kotadesasi? Evolving patterns of urbanization in Asia. In Urbanization in Asia: Spatial Dimensions and Policy Issues; Costa, F.J., Dutt, A.K., Ma, L.J.C., Noble, A.G., Eds.; University of Hawaii Press: Honolulu, HI, USA, 1989; pp. 93–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglass, M. A Regional Network Strategy for Reciprocal Rura-urban Linkages. An Agenda for Policy Research with Reference to Indonesia. Third World Plan. Rev. 1998, 20. [Google Scholar]
- Tacoli, C. Rural-Rrban Interactions: A Guide to The Literature. Environ. Urban. 1998, 10, 147–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, K. Rural-Urban Interaction in the Developing World; Routledge: London, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somanje, A.N.; Mohan, G.; Lopes, J.; Mensah, A.; Gordon, C.; Zhou, X.; Moinuddin, M.; Saito, O.; Takeuchi, K. Challenges and Potential Solutions for Sustainable Urban-Rural Linkages in a Ghanaian Context. Sustainability 2020, 12, 507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baffoe, G.; Zhou, X.; Moinuddin, M.; Somanje, A.N.; Kuriyama, A.; Mohan, G.; Saito, O.; Takeuchi, K. Urban-Rural Linkages: Effective Solutions for Achieving Sustainable Development in Ghana from an SDG Interlinkage Perspective. Sustain. Sci. 2021, 16, 1341–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.T.; Li, S.; Wei, Y.P.; Si, B. Research on the Spatio-Temporal Coupling Coordination and Driving Factors of New Urbanization and Rural Revitalization. Dev. Financ. Res. 2024, 1, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.K. Accurately Grasping the Scientific Connotation of Coordinating New Urbanization and Comprehensive Rural Revitalization. China Rural Econ. 2024, 1, 2–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.N. Research on the Strategic Coupling Mechanism of New Urbanization and Rural Revitalization. Contemp. Econ. Manag. 2019, 41, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.F.; Song, C.Q.; Shi, P.J. Benign Coupling of Rural Revitalization and New Urbanization: Scientific Connotations and Era Choices of Chinese Urban-Rural Modernization Development. Econ. Geogr. 2023, 43, 154–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.B.; Wang, Y.K.; Zhu, M.; Wang, K. Construction and demonstration of evaluation index system of rural revitalization level. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2020, 36, 236–243. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, L.; Liu, Z.; Jin, C. How Does the Integration of Cultural Tourism Industry Affect Rural Revitalization? The Mediating Effect of New Urbanization. Sustainability 2023, 15, 10824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.F.; Shi, P.J.; Zhang, W.P.; Cai, W.; Li, X.; Li, Y. Evaluation and Spatial Pattern of Agricultural and Rural Innovation Development in County Areas under the Background of Rural Revitalization: A Case Study of Gansu Province. J. Nat. Resour. 2022, 37, 291–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.F.; Han, X.L. Research on the Coupling and Coordinated Development of Rural Revitalization, New Urbanization, and Ecological Environment: A Case Study of Five Prefecture-level Cities in Ningxia. Agric. Technol. 2023, 43, 156–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Zhang, X. The Spatial-Temporal Characteristics and Driving Forces of the Coupled and Coordinated Development between New Urbanization and Rural Revitalization. Sustainability 2023, 15, 16487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, G.; Wang, L.; Du, P. Contradiction or Harmony? Spatial and Temporal Relationships between New Urbanization and Rural Revitalization in the Yellow River Basin from a Coupling Perspective. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0288600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.X.; Li, L.; Zhou, J.P.; Liu, C.J. Dynamic Evolution and Driving Mechanism of Coupled and Coordinated Development between Rural Revitalization and New Urbanization. J. Nat. Resour. 2020, 35, 2044–2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.X.; Liu, Y.F.; Feng, J.M.; He, S. Spatio-temporal Pattern and Influencing Factors of Provincial New Urbanization and Urban-Rural Integration Development in China. J. Earth Sci. Environ. 2023, 45, 781–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Wang, X.Y. Research on the Coupling Coordination and Dynamic Relationship between New Urbanization and Rural Revitalization: A Case Study of Zhejiang Province. Stat. Manag. 2022, 37, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.K.; Ma, F.C. Spatio-temporal Evolution of Coordinated Development between New Urbanization and Rural Revitalization in the Yellow River Basin: A Case Study of 36 Cities (Prefectures) along the Yellow River. J. Hebei Agric. Univ. (Soc. Sci. Ed.) 2022, 24, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.Y.; Liang, Y.T.; Ma, Z.Y. Relationship between New Urbanization and Regional Economic Coordinated Development: A Case Study of Maoming City, Guangdong Province. Jiangsu Agric. Sci. 2020, 48, 327–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.L.; Shen, Z.Y. Research on the coupled and coordinated development of rural revitalization and new urbanization. Reg. Econ. Rev. 2021, 4, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, M.Y. Progress of research on new urbanization in China from the perspective of geography. Geogr. Res. Dev. 2022, 41, 46–51. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, J.; Yu, M.; Zhen, F.; Zhou, L.; Miao, Z. Assessment of coordinated development of new urbanization and rural revitalization, taking Zhejiang Province as an example. Econ. Geogr. 2023, 43, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.F.; Zhu, H.Y. Empirical Study on Coupling Coordination of Cultural Performing Arts and Tourism Flow in Southwest China. Econ. Geogr. 2014, 34, 182–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, C.M. Comprehensive evaluation and analysis on the level of green agricultural development in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei from the perspective of rural revitalization. Chin. J. Agric. Resour. Reg. Plan. 2023, 44, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Li, X.N. Research on the coupled and coordinated development of new urbanization and rural revitalization in Shaanxi Province. China Agric. Resour. Zoning 2024, 45, 170–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, J.J.; Xiao, J. Research on the coupling and coordination mechanism of rural revitalization and new urbanization in the middle and lower reaches of the Yellow River. Prog. Geogr. Sci. 2024, 43, 417–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.J.; Kong, W.; Ren, L.; Zhi, D.D.; Dai, B.T. Misconceptions and Corrections of Domestic Coupling Coordination Models. J. Nat. Resour. 2021, 36, 793–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, L. Coupling degree between new urbanization and new rural construction in Hubei. J. China Agric. Resour. Reg. Plan. 2020, 41, 181–186. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, G.X. Coupling analysis of new urbanization and rural revitalization in Henan. J. China Agric. Resour. Reg. Plan. 2020, 41, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.W. Study on regional difference, dynamic evolution and spatial convergence of rural revitalization level. Stat. Decis. 2023, 39, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, R.L. Measurement and Spatio-temporal Evolution of Coupling Coordination between Tourism Efficiency and Rural Revitalization in China. Geogr. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2023, 39, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, M.C. Construction and empirical analysis of the index system of rural revitalization in western China. Commer. Econ. 2021, 12, 121–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Wang, Y.Y. Spatio-temporal Pattern and Influencing Factors of Coupled and Coordinated Development between New Urbanization and Rural Revitalization. Stat. Decis. 2023, 39, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Wang, Y.Y. Measurement of coordination level between new urbanization and rural revitalization in Gansu Province and its influencing factors. J. Desert Res. 2022, 42, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, C.C.; Yang, F.J.; Guo, Q.R.; Chen, Z. Study on the coupled and coordinated development of new industrialization, new urbanization and rural revitalization levels. Stat. Decis. 2020, 36, 71–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhang, M.; Chi, G.T. Science and technology evaluation model based on entropy weight method and its empirical research. J. Manag. 2010, 7, 34–42. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, C.S.; Teng, Y.; Huang, L. Construction and Empirical Analysis of Evaluation Index System for China’s Food Security. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2015, 31, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.B.; Yue, L.; Liu, Y.X.; Dong, G.; Miao, C. Spatio-temporal Pattern and Obstacle Factors of Urban Residents’ Quality of Life in the Yellow River Basin under the Goal of High-quality Development. J. Geogr. Sci. 2021, 41, 1303–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The National Development and Reform Commission of the People’s Republic of China. Notice on Issuing the Revitalization and Development Plan for the Revolutionary Old Areas in Sichuan and Shaanxi. 2016. Available online: https://www.gov.cn/xinwen/2016-08/04/content_5097513.htm (accessed on 20 September 2023).
- Pishu.com. Sichuan’s Urbanization Rate Exceeds 50%, Achieving Historic Breakthrough. 2019. Available online: https://www.pishu.cn/psgd/535248.shtml (accessed on 10 September 2023).
- The National Development and Reform Commission of the People’s Republic of China. Circular of the National Development and Reform Commission on the Implementation of Key Tasks for Promoting New Urbanization in 2018. 2018. Available online: https://www.ndrc.gov.cn/xwdt/ztzl/xxczhjs/ghzc/202012/t20201224_1260110.html (accessed on 20 September 2023).
- Ma, X.F.; Zhou, H.; Tan, J.X.; Zhang, D. Coupling Paths and Mechanisms of Tourism Destination Growth and the Formation of High-level Scenic Spots: A Case Study of Zhangjiajie. Econ. Geogr. 2021, 41, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.Y.; Du, Y.X.; Li, H.; Wang, W. Spatio-temporal Changes in the Coupling Relationship between Urbanization and Ecosystem Services in the Middle Reaches of the Yellow River. J. Nat. Resour. 2021, 36, 131–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.L.; Xu, X. Rural Transformation and Planning Response during the “13th Five-Year Plan” Period. Urban Plan. 2015, 39, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Sichuan Provincial People’s Government. The Adjustment and Reform of Township Administrative Divisions in Sichuan Have Been Completed, and the Total Number of Townships (Streets) in Sichuan Has Been Reduced by 1509. 2021. Available online: https://www.sc.gov.cn/10462/10464/10797/2021/1/15/bcb86495b9484a0e877a2ffc4ed46ea0.shtml (accessed on 2 October 2024).
- Lin, F. Research on the Issues and Optimization Paths of “Village to Residential Area” Community Governance: A Case Study of Dezhou Development Zone. Mod. Agric. Res. 2023, 29, 103–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.S.; Qu, W. Research on the Current Situation and Optimization Strategies of Medical and Health Resources in Sichuan Province. Chongqing Med. 2021, 50, 711–720. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, H.H. Analysis of Industrial Structure in Bazhong City. Shandong Text. Econ. 2017, 12, 19–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.H. Spatio-Temporal Differentiation of Coupling Coordination Between Urban and Rural Development in Sichuan Province. Master’s Thesis, Sichuan Academy of Social Sciences, Chengdu, China, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.D.; Yang, Z.S. The Coupling Coordination and Influencing Factors of Rural Revitalization, New Urbanization and Ecological Environment in Yunnan Province. Resour. Dev. Mark. 2024, 40, 533–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.X. Spatio-temporal differentiation characteristics of coordinated development of new urbanization and rural revitalization, taking Guizhou Province as an example. Mod. Agric. 2022, 6, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Meng, Q. Construction and Empirical Analysis of Evaluation Index System for Rural Revitalization in Sichuan Province. West. Econ. Manag. Forum 2021, 32, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.L. Research on the Coordinated Development of Rural Revitalization and New Urbanization in Luzhou City. Master’s Thesis, Chongqing Normal University, Chongqing, China, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.Z. Research on the Coupled and Coordinated Development of Rural Revitalization and New Urbanization in Sichuan Province. Master’s Thesis, Jilin University, Changchun, China, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.R.; Lin, R.R. Measurement and Influencing Factors of Coupling Coordination between Rural Revitalization and New Urbanization. J. Zhejiang Agric. Sci. 2023, 35, 2477–2489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.Q.; Deng, S.J. Research on Urban-Rural Integration in Gansu Province from the Perspective of Coupling between Rural Revitalization and New Urbanization. J. Arid Land Agric. Sci. 2023, 2, 369–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.P.; Yang, D.; Guo, C. The impact of COVID-19 on China’s agricultural development and countermeasures. Reform 2020, 3, 5–13. Available online: http://www.reform.net.cn (accessed on 2 October 2023).
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).