Assessing the Scale Effects of Dynamics and Socio-Ecological Drivers of Ecosystem Service Interactions in the Lishui River Basin, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Source and Processing
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. Quantification of ESs
2.3.2. Unit Scale Division
2.3.3. Data Calculation and Sampling
2.3.4. Quantification of Trade-Offs/Synergies Among ESs
2.3.5. Identification of ES Bundles
2.3.6. Analysis of Socio-Ecological Drivers
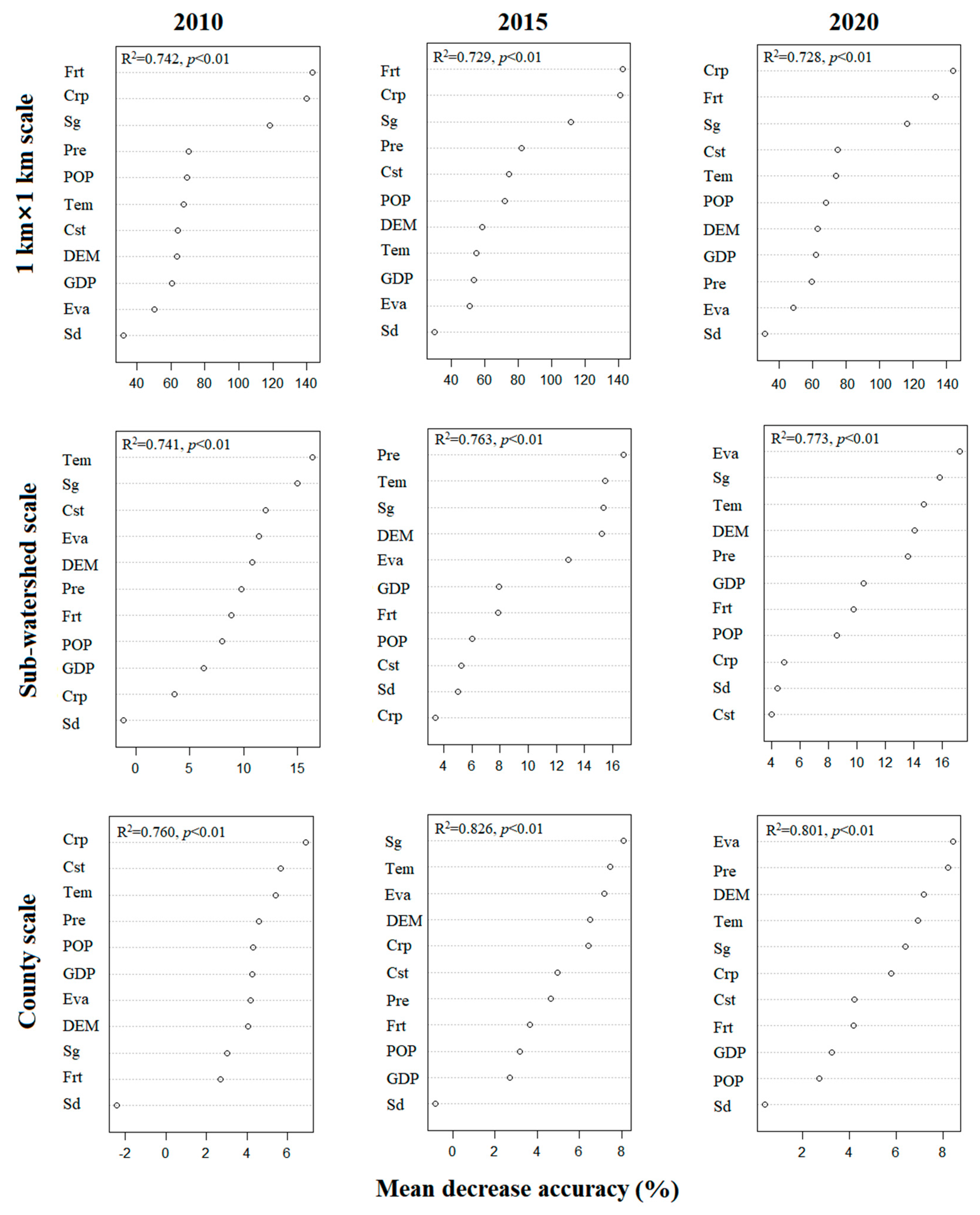
Driving Factors Selection
Random Forest Analysis
2.3.7. Other Statistic Analysis
3. Results
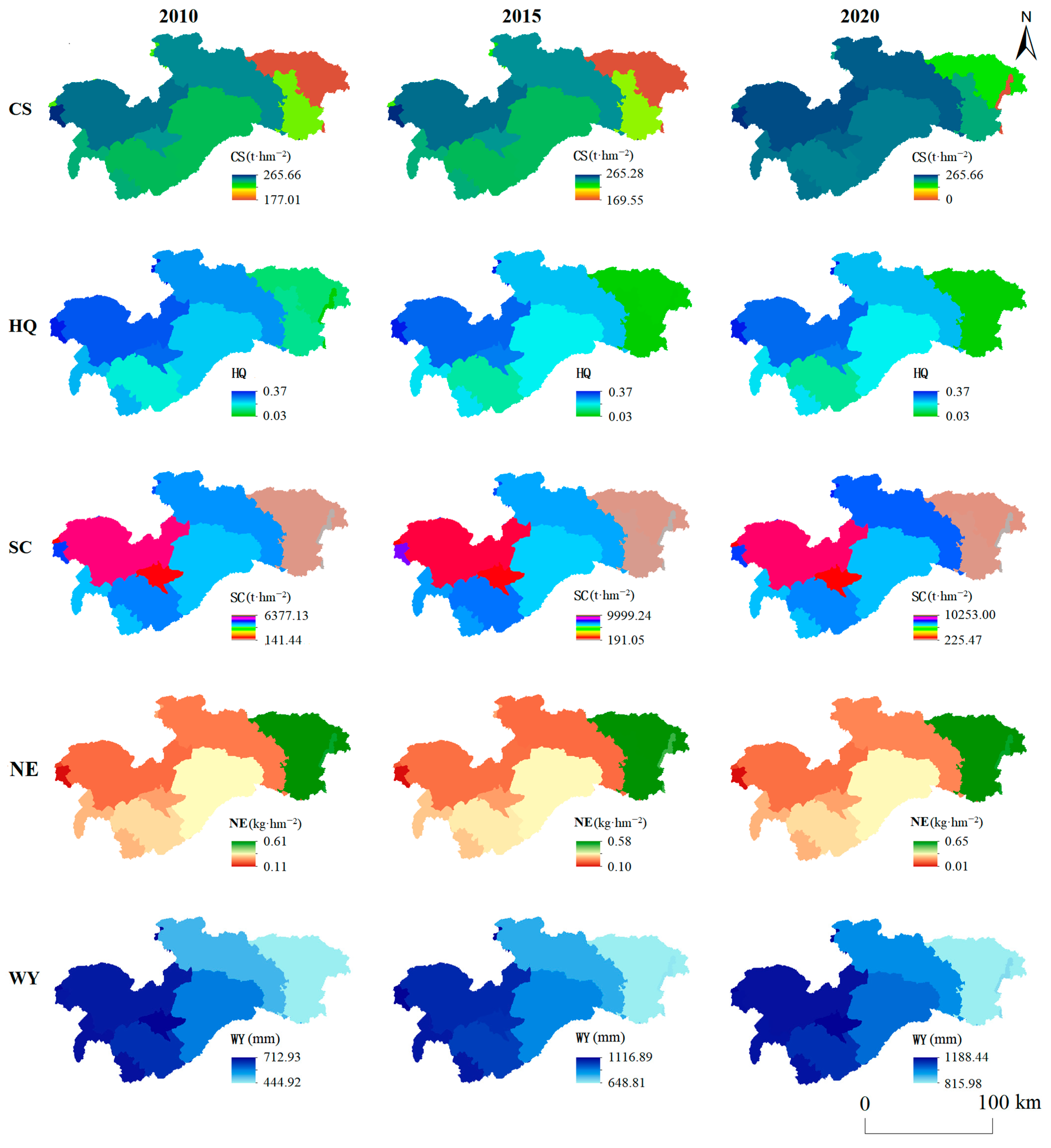
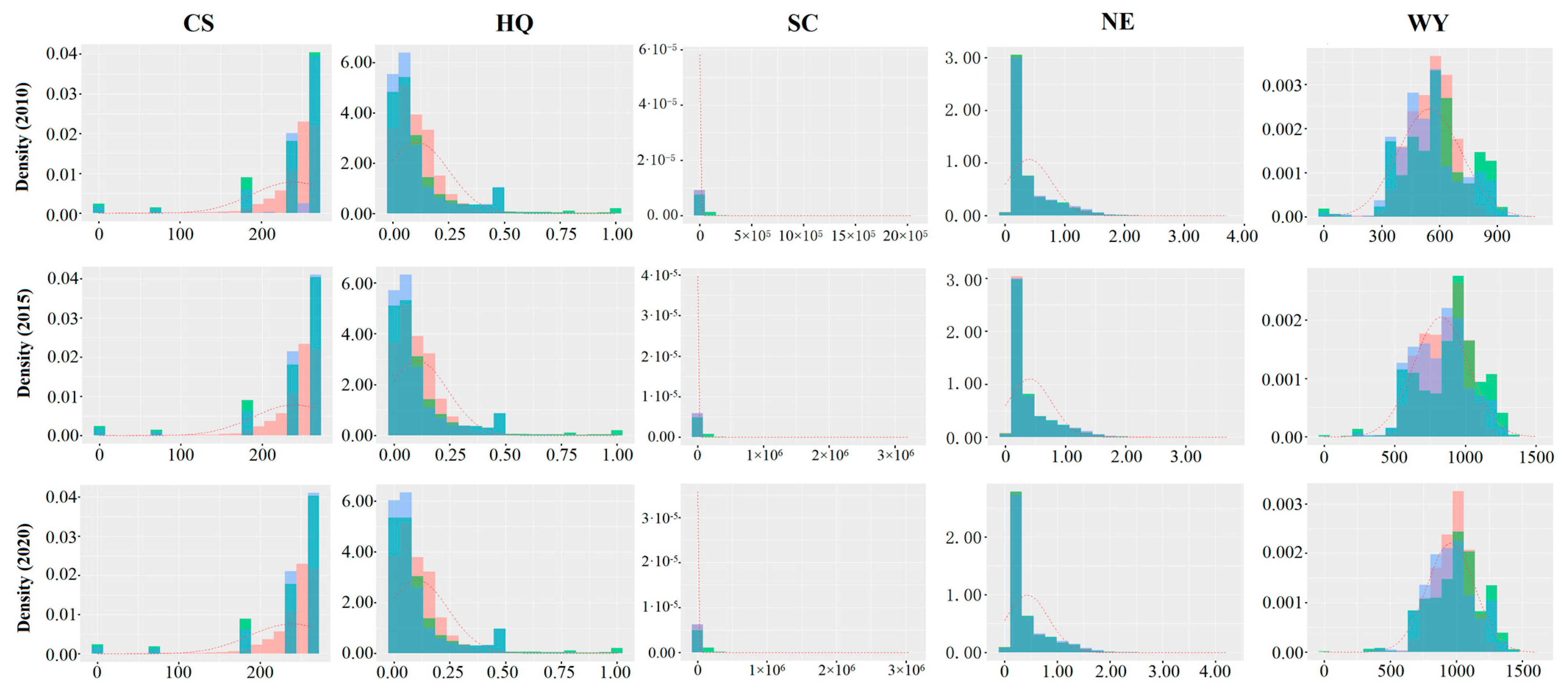
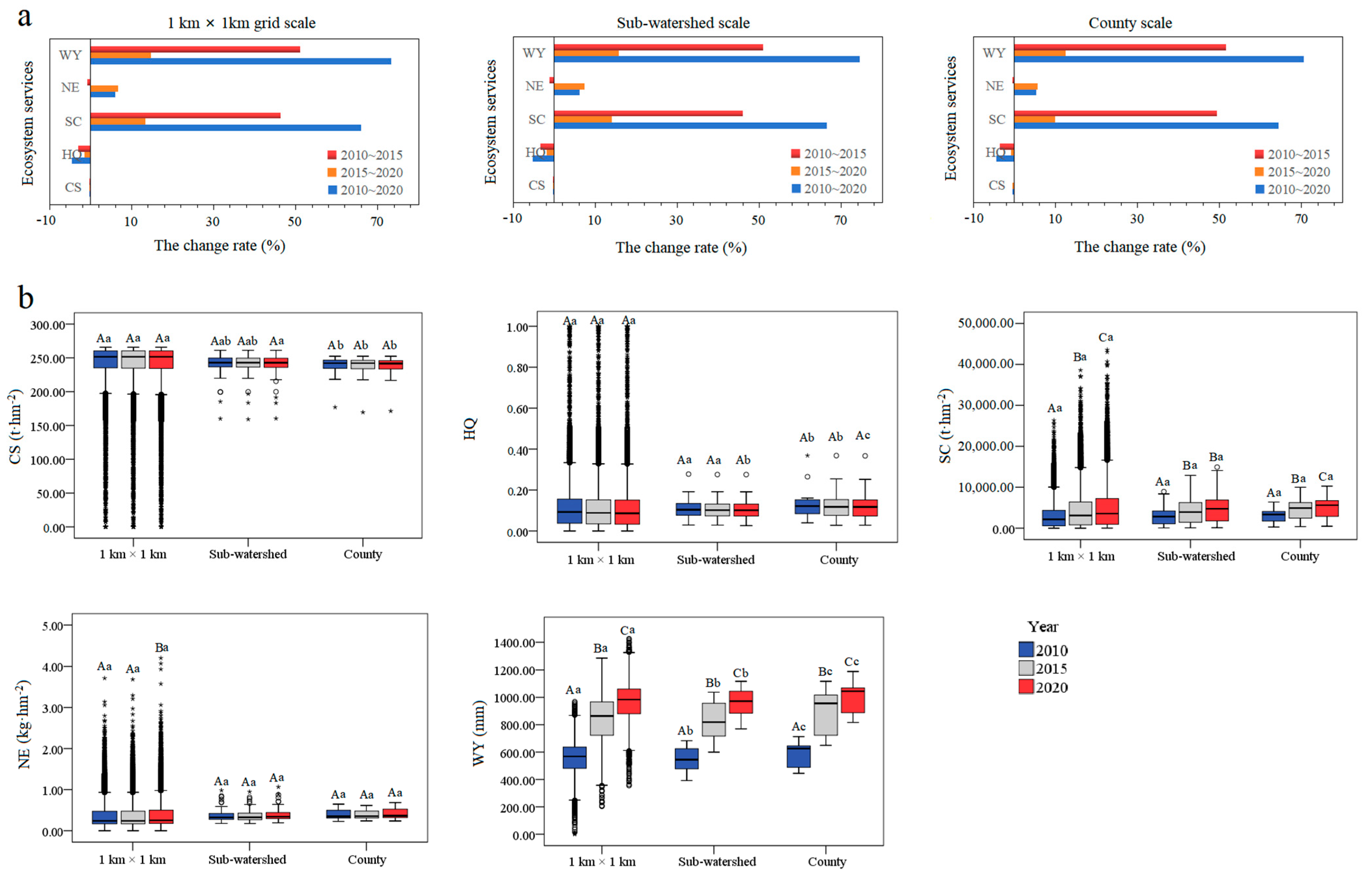
3.1. Spatiotemporal Distribution Characteristics of ESs
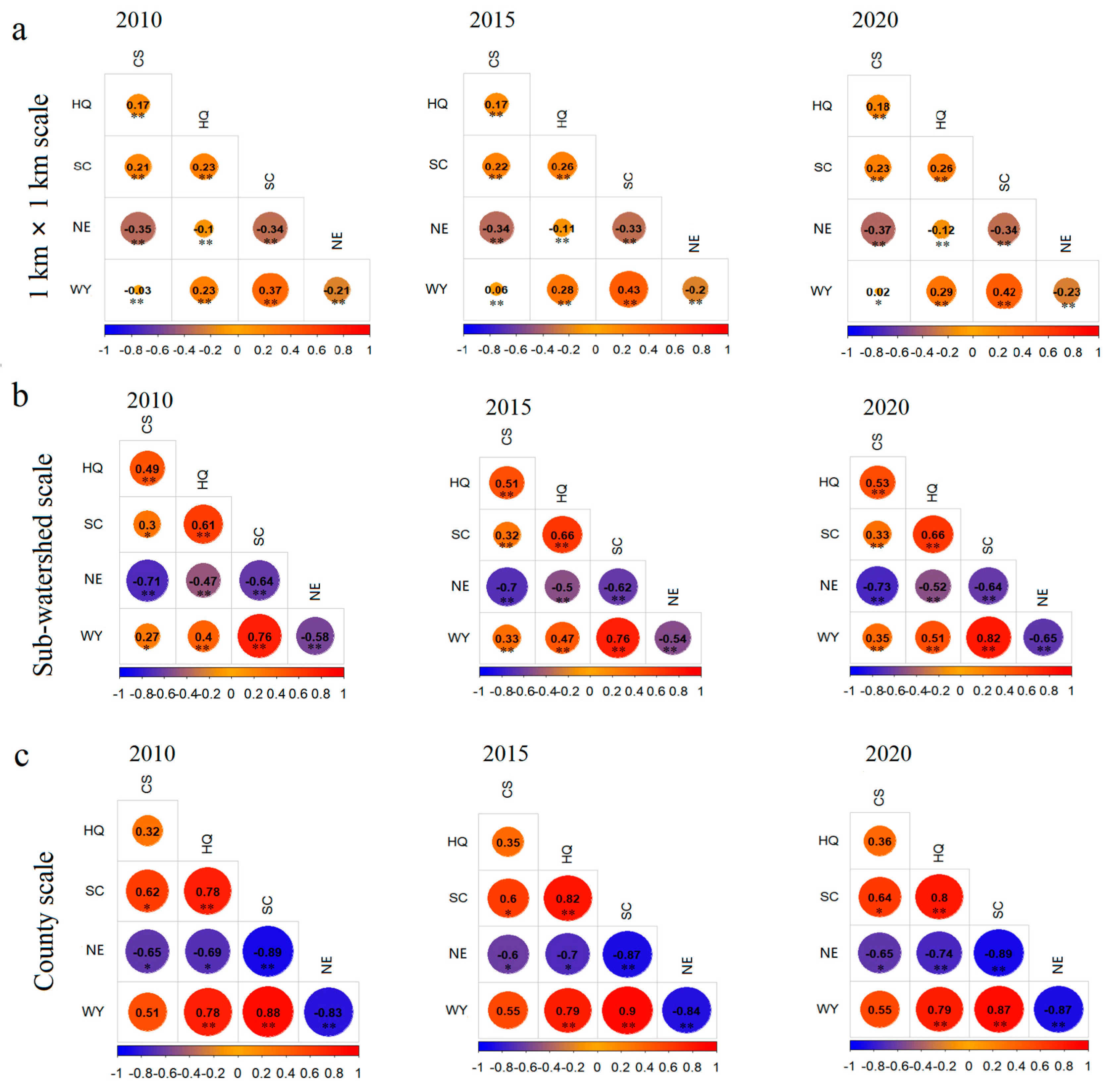
3.2. The Trade-Offs/Synergies Between ES Pairs
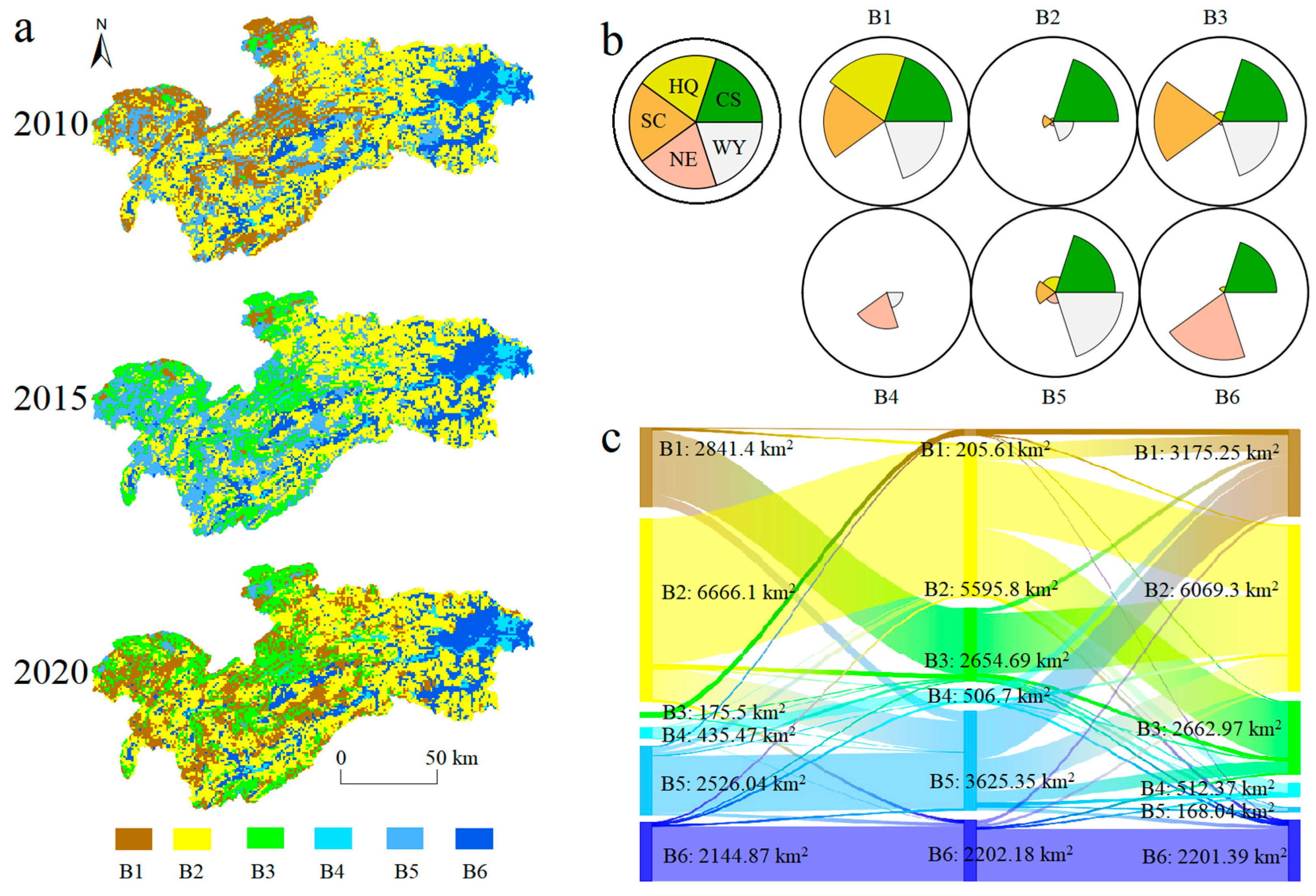
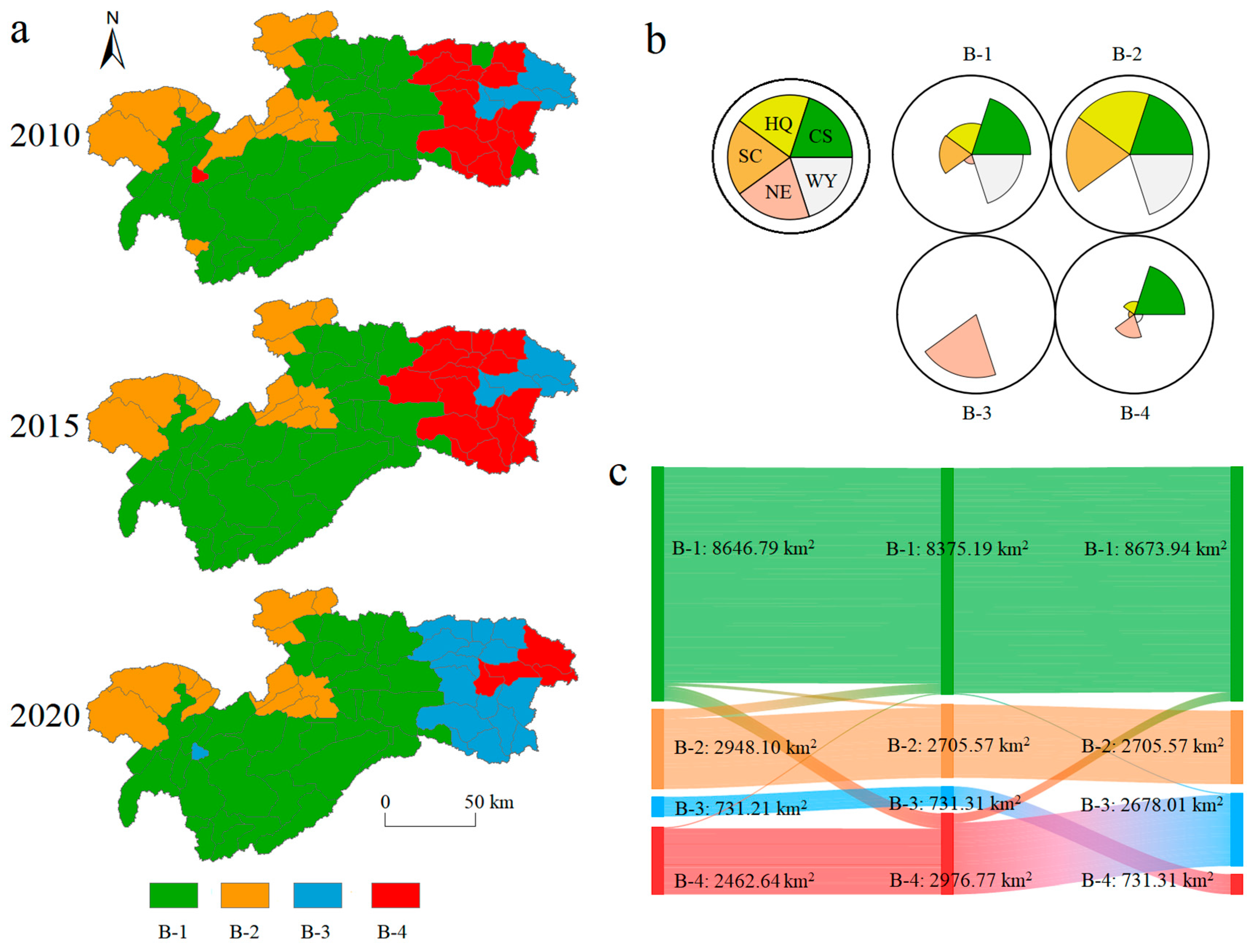
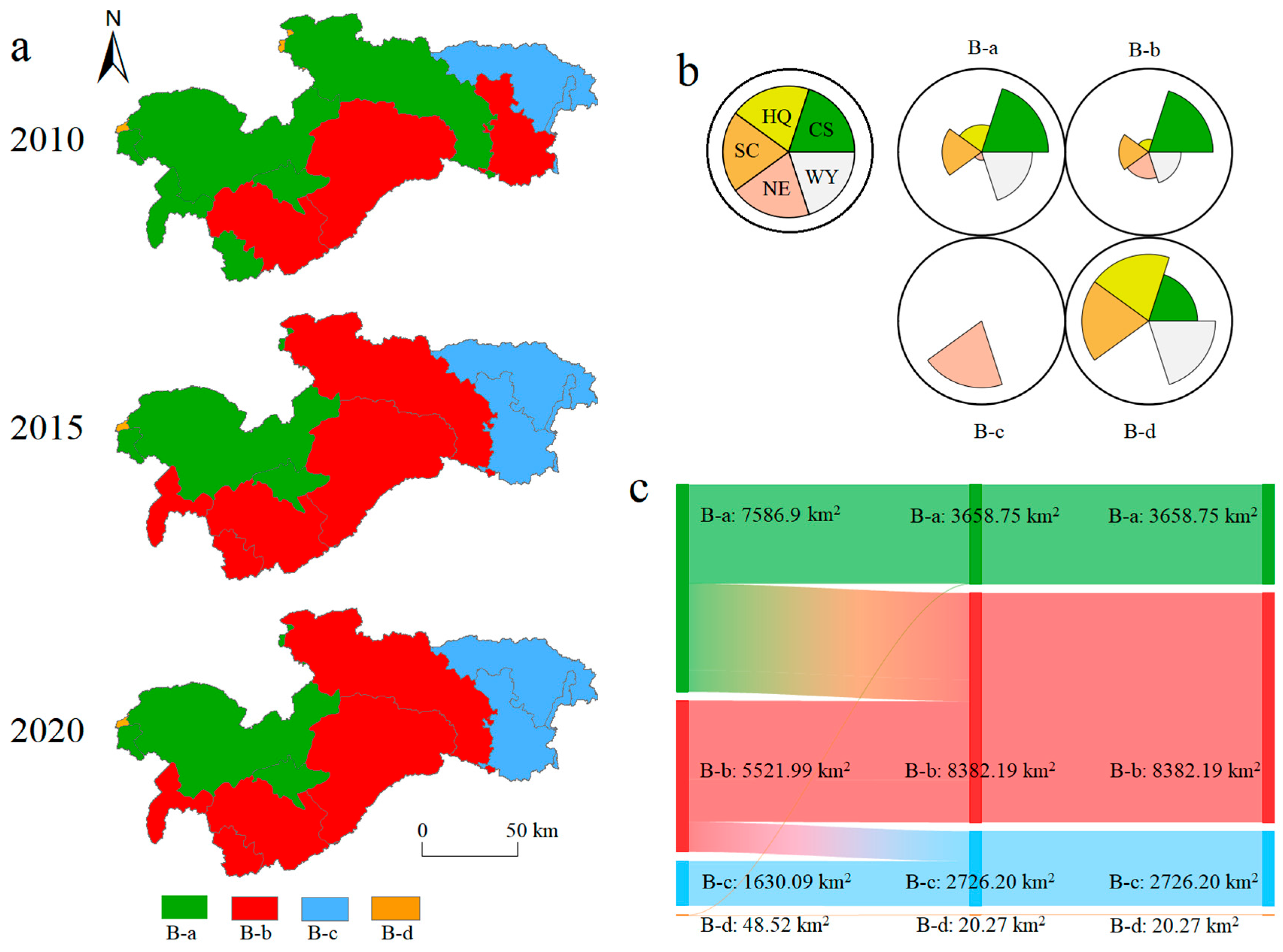
3.3. Spatial–Temporal Patterns of ES Bundles at Different Scales
3.4. Social–Ecological Influences of ESs Bundles Distribution Across Different Times and Scales
4. Discussion
4.1. Spatio-Temporal Characteristics of the Five ESs
4.2. The Scale Effect of Trade-Offs and Synergies Among ESs
4.3. Historical Patterns and Dynamics of ESBs Across Various Scales and Their Socio-Ecological Drivers
4.4. Limitations and Prospects
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jiang, C.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Z. Spatially explicit assessment of ecosystem services in China’s Loess Plateau: Patterns, interactions, drivers, and implications. Glob. Planet. Change 2018, 161, 41–52. [Google Scholar]
- Costanza, R.; d’Arge, R.; de Groot, R.; Farber, S.; Grasso, M.; Hannon, B.; Limburg, K.; Naeem, S.; O’Neill, R.V.; Paruelo, J.; et al. The value of the world’s ecosystem services and natural capital. Nature 1997, 387, 253–260. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Q.; Zhao, W.; Fu, B.; Ding, J.; Wang, S. Ecosystem service trade-offs and their influencing factors: A case study in the Loess Plateau of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 607–608, 1250–1263. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.G. Effects of changing scale on landscape pattern analysis: Scaling relations. Landsc. Ecol. 2004, 19, 125–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raudsepp-Hearne, C.; Peterson, G.D.; Bennett, E.M. Ecosystem service bundles for analyzing tradeoffs in diverse landscapes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 5242–5247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Zuo, L. Revealing ecosystem services relationships and their driving factors for five basins of Beijing. J. Geogr. Sci. 2021, 31, 111–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raudsepp-Hearne, C.; Peterson, G.D. Scale and ecosystem services: How do observation, management, and analysis shift with scale—Lessons from Québec. Ecol. Soc. 2016, 21, 16. [Google Scholar]
- Cord, A.F.; Bartkowski, B.; Beckmann, M.; Dittrich, A.; Hermans-Neumann, K.; Kaim, A.; Lienhoop, N.; Locher-Krause, K.; Priess, J.; Schröter-Schlaack, C.; et al. Towards systematic analyses of ecosystem service trade-offs and synergies: Main concepts, methods and the road ahead. Ecosyst. Serv. 2017, 28, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.; Turner, M.G. Spatial interactions among ecosystem services in an urbanizing agricultural watershed. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 12149–12154. [Google Scholar]
- Spake, R.; Lasseur, R.; Crouzat, E.; Bullock, J.M.; Lavorel, S.; Parks, K.E.; Schaafsma, M.; Bennett, E.M.; Maes, J.; Mulligan, M.; et al. Unpacking ecosystem service bundles: Towards predictive mapping of synergies and trade-offs between ecosystem services. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2017, 47, 37–50. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.C.; He, S.Y.; Xue, J.; Zhang, H.Y.; Li, Z.H.; Wang, L.; Li, K. Exploring ecosystem service trade-offs and their response to landscape configuration at multi-scales: A case study of Hubei Province. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2023, 43, 4835–4846. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xia, G.; Yuan, S.F.; Alexander, V.; Prishchepov, A.V. Spatial-temporal heterogeneity of ecosystem service interactions and their social-ecological drivers: Implications for spatial planning and management. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2023, 189, 106767. [Google Scholar]
- Karimi, J.D.; Corstanje, R.; Harris, J.A. Understanding the importance of landscape configuration on ecosystem service bundles at a high resolution in urban landscapes in the UK. Landsc. Ecol. 2021, 36, 2007–2024. [Google Scholar]
- Li, T.; Liang, X.Y.; Zhang, J.; Geng, Y.; Geng, T.W.; Shi, J.X. Ecosystem service trade-off and synergy relationship and its driving factor analysis based on Bayesian belief network: A case study of the Loess Plateau in northern Shanxi Province. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2023, 43, 6758–6771. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, D.; Wang, Y.; Hao, S.; Xu, W.; Lv, L.; Yu, S. Spatial-temporal variation and tradeoffs/synergies analysis on multiple ecosystem services: A case study in the Three-River Headwaters region of China. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 116, 106494. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, G.; Ge, Y.; Xue, H.; Yang, W.; Shi, Y.; Peng, C.; Du, Y.; Fan, X.; Ren, Y.; Chang, J. Using ecosystem service bundles to detect tradeoffs and synergies across urban–rural complexes. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2015, 136, 110–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gou, M.M.; Li, L.; Ouyang, S.; Wang, N.; La, L.M.; Liu, C.F.; Xiao, W.F. Identifying and analyzing ecosystem service bundles and their socioecological drivers in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 307, 127208. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Z.; Peng, J.; Wu, J.S. Ecosystem service bundles based approach to exploring the trajectories of ecosystem service spatiotemporal change: A case study of Shenzhen City. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2020, 40, 2545–2554. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Quintas-Soriano, C.; García-Llorente, M.; Norstrm, A.; Meacham, M.; Castro, A.J. Integrating supply and demand in ecosystem service bundles characterization across Mediterranean transformed landscapes. Landsc. Ecol. 2019, 34, 1619–1633. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.L.; Peng, J.; Hu, Y.N.; Wu, W.H. Ecological function zoning in Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region based on ecosystem service bundles. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2017, 28, 2657–2666. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Shen, J.S.; Liang, Z.; Liu, L.B.; Li, D.L.; Zhang, Y.T.; Li, S.C. Trade-offs and synergies of ecosystem service bundles in Xiong’an New Area. Geogr. Res. 2020, 39, 79–91. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Dou, H.S.; Li, X.B.; Li, S.K.; Dang, D.L.; Li, X.; Liu, X.; Li, M.Y.; Liu, S.Y. Mapping ecosystem services bundles for analyzing spatial trade-offs in inner Mongolia. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 256, 120444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Li, S.; Liu, L.; Liang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; Wu, S. Uncovering the relationships between ecosystem services and social-ecological drivers at different spatial scales in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 290, 125193. [Google Scholar]
- Renard, D.; Rhemtulla, J.M.; Bennett, E.M. Historical dynamics in ecosystem service bundles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 13411–13416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meacham, M.; Queiroz, C.; Norström, A.V.; Peterson, G.D. Social-ecological drivers of multiple ecosystem services: What variables explain patterns of ecosystem services across the Norrström drainage basin? Ecol. Soc. 2016, 21, 14. [Google Scholar]
- Dade, M.C.; Mitchell, M.G.; McAlpine, C.A.; Rhodes, J.R. Assessing ecosystem service trade-offs and synergies: The need for a more mechanistic approach. Ambio 2019, 48, 1116–1128. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, X.; Tang, H.; Yang, P.; Hu, G.; Liu, Z.; Wu, J. Spatiotemporal patterns and drivers of ecosystem service supply and demand across the conterminous United States: A multiscale analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 703, 135005. [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein, J.H.; Caldarone, G.; Duarte, T.K.; Ennaanay, D. Integrating ecosystem-service tradeoffs into land-use decisions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 7565–7570. [Google Scholar]
- Vallet, A.; Locatelli, B.; Levrel, H.; Wunder, S.; Seppelt, R.; Scholes, R.J.; Oszwald, J. Relationships between ecosystem services: Comparing methods for assessing tradeoffs and synergies. Ecol. Econ. 2018, 150, 96–106. [Google Scholar]
- Han, X.J.; Wang, J.J.; Wen, X. The scale effect and differentiation mechanism of the relationship between ecosystem services in the grain for green area: A case study of Ansai District. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2024, 44, 1791–1807. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Tomscha, S.A.; Sutherland, I.J.; Renard, D.; Gergel, S.E.; Rhemtulla, J.M.; Bennett, E.M.; Daniels, L.D.; Eddy, I.M.; Clark, E.E. A guide to historical data sets for reconstructing ecosystem service change over time. BioScience 2016, 66, 747–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Dong, B.; Li, S.; Lin, Y.; Shahtahmassebi, A.; You, S.; Zhang, J.; Gan, M.; Yang, L.; Wang, K. Identifying the trade-offs and synergies among land use functions and their influencing factors from a geospatial perspective: A case study in Hangzhou. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 314, 128026. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, Y.; Lu, Y.H.; Chen, W.P.; Fu, B.J. Temporal variation and spatial scale dependency of ecosystem service interactions: A case study on the central Loess Plateau of China. Landsc. Ecol. 2017, 32, 1201–1217. [Google Scholar]
- Schirpke, U.; Candiago, S.; Egarter Vigl, L.; Jäger, H.; Labadini, A.; Marsoner, T.; Meisch, C.; Tasser, E.; Tappeiner, U. Integrating supply, flow and demand to enhance the understanding of interactions among multiple ecosystem services. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 651, 928–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lautenbach, S.; Kugel, C.; Lausch, A.; Seppelt, R. Analysis of historic changes in regional ecosystem service provisioning using land use data. Ecol. Indic. 2011, 11, 676–687. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y. What factors affect the synergy and tradeoff between ecosystem services, and how, from a geospatial perspective? J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 257, 120454. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Z.; Jin, X.; Chen, T.; Wu, J. Understanding trade-offs and synergies of ecosystem services to support the decision-making in the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei region. Land Use Policy 2021, 106, 105446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamann, M.; Biggs, R.; Reyers, B. Mapping social-ecological systems: Identifying ‘green-loop’ and ‘red-loop’ dynamics based on characteristic bundles of ecosystem service use. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2015, 34, 218–226. [Google Scholar]
- O’Higgins, T.; Nogueira, A.A.; LillebøA, I.; O’Higgins, T.; Nogueira, A.A.; Lillebøa, I. A simple spatial typology for assessment of complex coastal ecosystem services across multiple scales. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 649, 1452–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Wu, J.; Tang, H.; Yang, P. An urban hierarchy-based approach integrating ecosystem services into multiscale sustainable land use planning: The case of China. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2022, 178, 106097. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, B.W.; Song, N.; Geng, S.H.; Chen, Q. Evolution characteristics and impacting factors of annual runoff and sediment in Lishui River during 1955–2009. Bull Soil Water Conserv. 2014, 34, 360–363. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Guo, R.Z.; Shen, H.J.; Yang, M.H. Studies on ecosystem service value and ecological compensation strategy in Lishui River Basin. Res. Environ. Sci. 2016, 29, 774–782. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Z.; Lotz, T.; Chang, N.B. Assessing the long-term effects of land use changes on runoff patterns and food production in a large lake watershed with policy implications. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 204, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Z.W.; Yang, H.; Ning, Q.M.; Tang, H. Temporal and spatial evolution of land use intensity and its impact on ecosystem services in Dongting Lake Zone. Econ. Geogr. 2022, 42, 176–185. [Google Scholar]
- Turner, M.G.; Donato, D.C.; Romme, W.H. Consequences of spatial heterogeneity for ecosystem services in changing forest landscapes: Priorities for future research. Landsc. Ecol. 2013, 28, 1081–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.L.; Zhuang, D.F.; Jia, S.F.; Hu, Y.F. Automatic extraction of drainages in China based on DEM in GIS environment. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Basin 2004, 13, 343–348. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Millennium Ecosystem Assessment (MEA). Ecosystems and Human Well-Being: Synthesis; Island Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, X.Y.; Shan, R.F.; Liu, F. Spatio-temporal quantification of patterns trade-offs and synergies among multiple hydrological ecosystem services in different topographic basins. J. Clean Prod. 2020, 268, 122338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.X.; Liu, Z.F.; He, C.Y.; Wu, J.G. Multi-scale analysis of ecosystem service trade-offs in urbanizing drylands of China: A case study in the Hohhot-Baotou-Ordos-Yulin region. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2016, 36, 4881–4891. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Zhou, P.Q.; Yuan, S.J.; Tan, X.; Lou, Z.F. Land Ecosystem Service Functions for Dongting Lake Ecological Economic Zone Based on InVEST Model. Bull Soil Water Conserv. 2022, 42, 267–272, 282. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Fu, B.; Xu, P.; Wang, Y.K.; Peng, Y.; Ren, J. Spatial pattern of water retention in Dujiangyan County. Geosciences 2013, 48, 856–866. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, G.; Long, X.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, D.; Wu, H.; Li, S. Identifying the drivers of water yield ecosystem service: A case study in the Yangtze River Basin, China. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 132, 108304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Li, P.; Cheng, W.J.; Xiao, Z.Y.; Mu, Y.L.; Zhi, L.H.; Li, X.W. Evaluation and complex relations analysis of ecosystem services based on spatial-temporal change of land use in Dongting Lake. Acta Sci. Circumstant. 2022, 42, 121–130. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Williams, J.R. The erosion-productivity impact calculator (EPIC) model: A case history. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 1990, 329, 421–428. [Google Scholar]
- Ouyang, L.Y. The Research on the Effects of LUCC on Ecosystem Services in Dongting Lake Region Based on InVEST Model; Central South University of Forestry and Technology: Hunan, China, 2022. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, T.; Liu, K.; Hu, S.; Bao, Y.B. Soil erosion and ecological benefits evaluation of Qinling Mountains based on the InVEST model. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Basin 2014, 23, 1242–1250. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ouyang, Z.; Hua, Z.; Yang, X.; Polasky, S.; Daily, G.C. Improvements in ecosystem services from investments in natural capital. Science 2016, 352, 1455–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharp, R.; Tallis, H.T.; Ricketts, T.; Nelson, E.; Ennaanay, D.; Wolny, S.; Olwero, N.; Vigerstol, K.; Aukema, J.; Diedenhoven, M.; et al. InVEST User’s Guide; The Natural Capital Project: Stanford, CA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, L.; He, N.; Yu, G. A dataset of carbon density in Chinese terrestrial ecosystems (2010s). China Sci. Data 2018, 3, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, L.L.; Wang, L.C.; Chen, W.X.; Sun, J.; Cao, Q.; Wang, S.Q.; Wang, L. Identifying the impacts of natural and human factors on ecosystem service in the Yangtze and Yellow River Basins. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 314, 127995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Du, Y.T. Study on the Spatio-Temporal Patterns of Habitat Quality and Its Terrain Gradient Effects of the Middle of the Yangtze River Economic Belt Based on InVEST Model. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Basin 2019, 28, 2429–2440. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Sharp, R.; Douglass, J.; Wolny, S.; Arkema, K.; Bermhardt, J.; Bierbower, W.; Cchaumont, N.; Denu, D.; Fisher, D.; Glowinski, K.; et al. InVEST 3.7.0 User’s Guide; Stanford University: Stanford, CA, USA; University of Minnesota: Minneapolis, MN, USA; The Nature Conservancy: Arlington County, VA, USA; World Wildlife Fund: Gland, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, J.B.; Mao, D.H.; Deng, M.R. Evaluation of typical ecosystem services and trade-offs/synergies in Dongting Lake Basin. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Basin 2024, 33, 310–321. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, W.; Fu, B.J.; Shu, Z.G.; Lv, Y.H.; Gao, G.Y.; Feng, X.M.; Schüler, S.; Wu, X.; Wang, C. Spatiotemporal drivers of Nature’s contributions to people: A county level study. Environ. Sci. Ecotechnol. 2024, 20, 100430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.Q.; Feng, Z.; Zhao, H.F.; Wu, K.N. Identification of ecosystem service bundles and driving factors in Beijing and its surrounding areas. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 711, 134687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.W.; Liu, J.F.; Kuang, Y.W.; Wang, Q.; Huang, R.Z.; Nie, W.; Sun, J.Y.; Zhao, Y.P. Spatiotemporal dynamics and driving forces of ecosystem service trade-offs and synergies in Jiangxi Province. Chin. J. Ecol. 2023, 42, 1234–1245. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yan, X.L.; Li, X.Y.; Liu, C.H.; Li, J.W.; Zhong, J.Q. Spatial evolution trajectory of ecosystem service bundles and its social-ecological driven by geographical exploration: A case study of Dalian. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2022, 42, 5734–5747. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Peng, J.; Tian, L.; Liu, Y.X.; Zhao, M.Y.; Hu, Y.N.; Wu, J.S. Ecosystem services response to urbanization in metropolitan areas: Thresholds identification. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 607–608, 706–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L. Random forest. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, A.M.; Iverson, L.R.; Liaw, A. Newer classification and regression tree techniques: Bagging and random forests for ecological prediction. Ecosystem 2006, 9, 181–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Xu, C. Geodetector: Principle and prospective. Acta Geograph. Sinic. 2017, 72, 116–134. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, T.J.; Zhang, S.P.; Cao, Q.; Wang, H.Y.; Li, Y.L. The spatiotemporal dynamics of ecosystem services bundles and the social-economic-ecological drivers in the Yellow River Delta region. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 137, 108573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Wang, S.; Xiao, Y.; Xie, G.; Lei, G. Mapping the spatiotemporal heterogeneity of ecosystem service relationships and bundles in Ningxia. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 294, 126216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.M.; Yang, K.; Li, L.X.; Zhu, Y.H.; Fan, X. Spatio-temporal heterogeneity and attribution analysis of hydrological ecosystem services tradeoffs and synergies in Dianchi Lake Basin. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2023, 43, 4876–4891. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Shen, J.; Li, S.; Liang, Z.; Liu, L.; Wu, S. Exploring the heterogeneity and nonlinearity of trade-offs and synergies among ecosystem services bundles in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei urban agglomeration. Ecosyst. Serv. 2020, 43, 101103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Tang, X.L.; Yuan, S.J.; Sun, Y.; Liu, C.; Wang, Y.B. Supply and demand of multi-scale ecosystem services and their influencing factors in Hu’nan Province. Bull Soil Water Conserv. 2023, 43, 272–281. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Pei, Y.J.; Luo, M.Y.; Zhao, Y.H.; Han, L.; Yang, S.Y.; Zhang, L. Trade-offs and synergies among ecosystem services at multiple scales. A case study of Yan’an City. Chin. J. Ecol. 2022, 41, 1351–1360. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Li, Z.J.; Zeng, H. Scale effects on ecosystem service trade-off and its influencing factors based on wavelet transform: A case study in the Pearl River Delta, China. Geogr. Res. 2022, 41, 1279–1297. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- de Groot, R.S.; Alkemade, R.; Braat, L.; Hein, L.; Willemen, L. Challenges in integrating the concept of ecosystem services and values in landscape planning, management and decision making. Ecol. Complex. 2010, 7, 260–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, X.N.; Gu, Y.Y.; Zou, C.X.; Xu, D.L.; Wang, L.; Yang, Y.; Huang, X.F. Temporal variation and spatial scale dependency of the trade-offs and synergies among multiple ecosystem services in the Taihu lake Basin of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 651, 218–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, C.H.; Dong, M.; Fu, B.J.; Liu, G.H. Scale effects of sediment retention, water yield, and net primary production: A case-study of the Chinese Loess Plateau. Land Degrad Dev. 2020, 31, 1408–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, X.N.; Yang, Z.; Yang, Y.J. Trade-off and Synergy of Ecosystem Services and Their Scale Effects in the Huaihe River Basin from 1995 to 2020. Areal. Res. Dev. 2023, 42, 150–154+166. [Google Scholar]
- Malinga, R.; Gordon, L.J.; Jewitt, G.; Lindborg, R. Mapping ecosystem services across scales and continents—A review. Ecosyst. Serv. 2015, 13, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.; Wu, X.; Zhang, J.J.; Zhang, Y.L.; Dang, H.; Lü, Y.H.; Wang, C.; Guo, J.Y. Spatiotemporal heterogeneity and driving factors of ecosystem service relationships and bundles in a typical agropastoral ecotone. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 156, 111074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.W.; Wu, D.; Li, H.; Liu, X.; Wang, Y.P.; Guo, J.Y. Spatio-temporal variations of ecosystem service bundles in Huaihe River Basin based on SOFM. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2024, 44, 4544–4557. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Pan, M.; Chen, T.W.; Huang, L.; Cao, W. Spatial and temporal variations in ecosystem services and its driving factors analysis in Jing-Jin-Ji region. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2020, 40, 5151–5167. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Kragt, M.E.; Robertson, M.J. Quantifying ecosystem services trade-offs from agricultural practices. Ecol. Econ. 2014, 102, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Zhao, W.; Liu, Y.; Wang, S.; Wang, J.; Zhai, R. Influence of land use change on the ecosystem service trade-offs in the ecological restoration area: Dynamics and scenarios in the Yanhe watershed. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 644, 556–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wu, J.; Liu, Y.; Hai, X.; Shanguan, Z.; Deng, L. Driving factors of ecosystem services and their spatiotemporal change assessment based on land use types in the Loess Plateau. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 311, 114835. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.J.; Liu, Z.T.; Chen, Y.X.; Fang, C.L. Factors influencing ecosystem services in the Pearl River Delta, China: Spatiotemporal differentiation and varying importance. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2021, 168, 105477. [Google Scholar]
- Dubovyk, O.; Sliuzas, R.; Flacke, J. Spatio-temporal modelling of informal settlement development in Sancaktepe district, Istanbul, Turkey. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2011, 66, 235–246. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, J.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, H.; Zuo, L. Identification of dominant factors affecting soil erosion and water yield within ecological red line areas. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munoz, J.D.; Steibel, J.P.; Snapp, S.; Kravchenko, A.N. Cover crop effect on corn growth and yield as influenced by topography. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2014, 189, 229–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
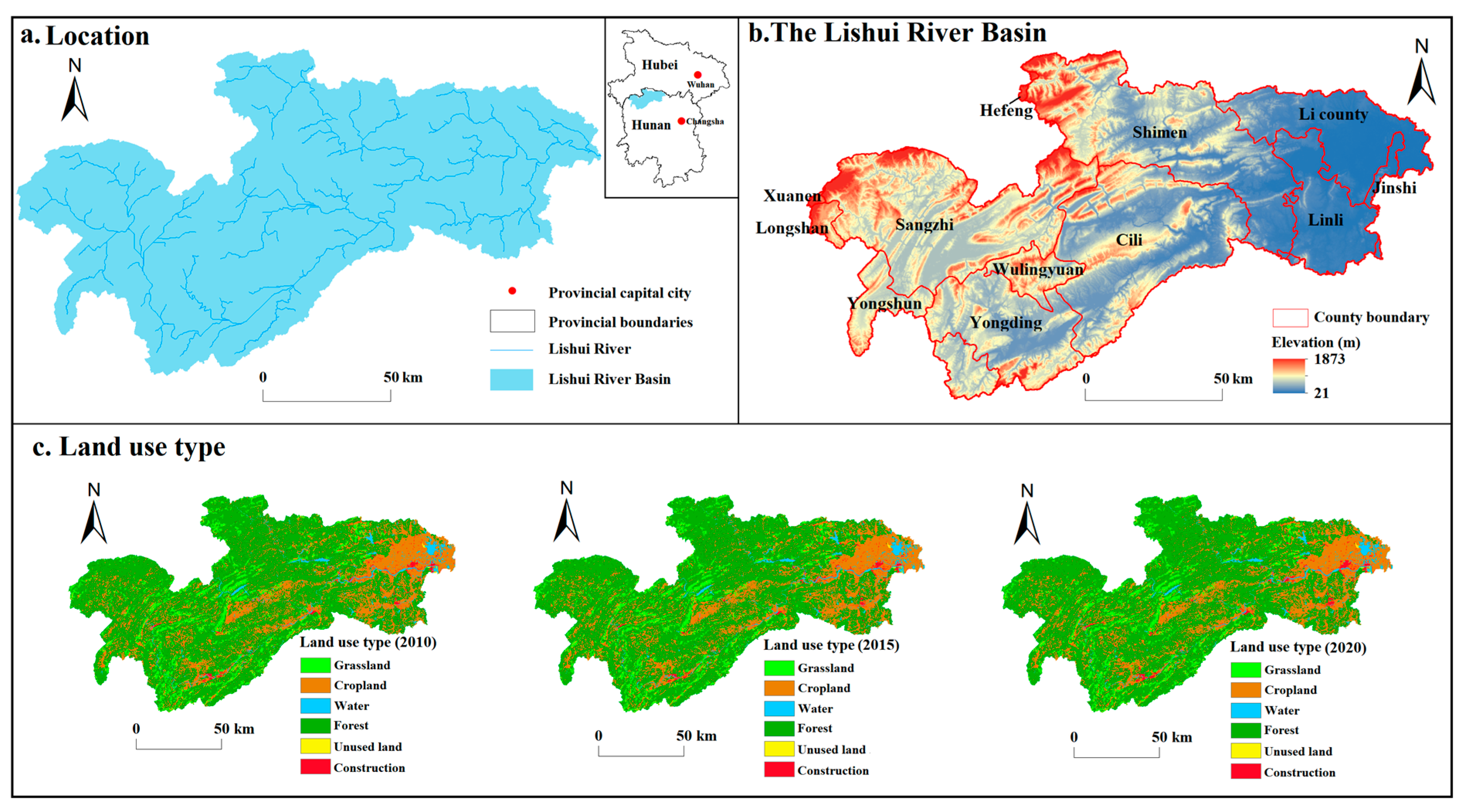
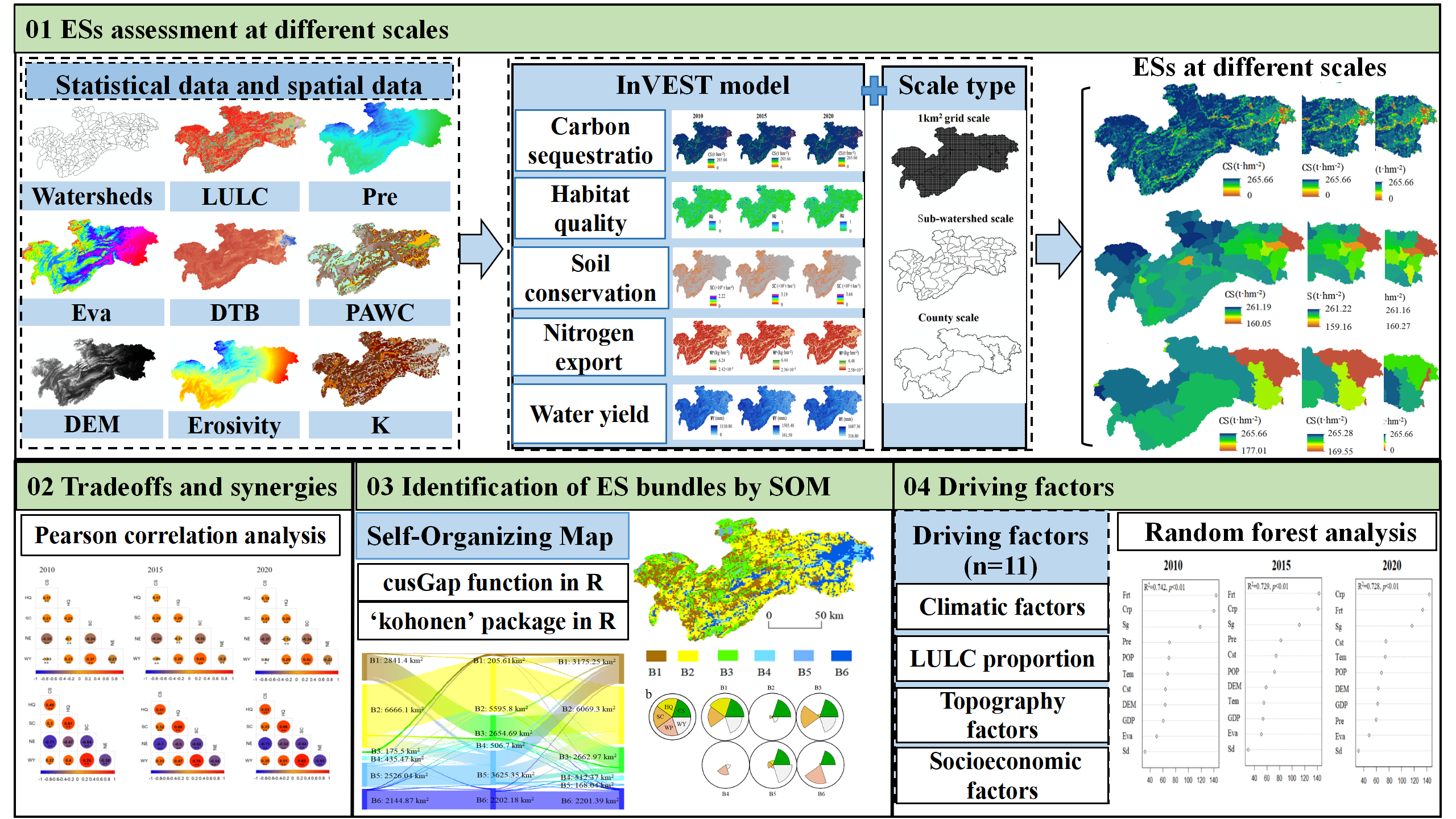
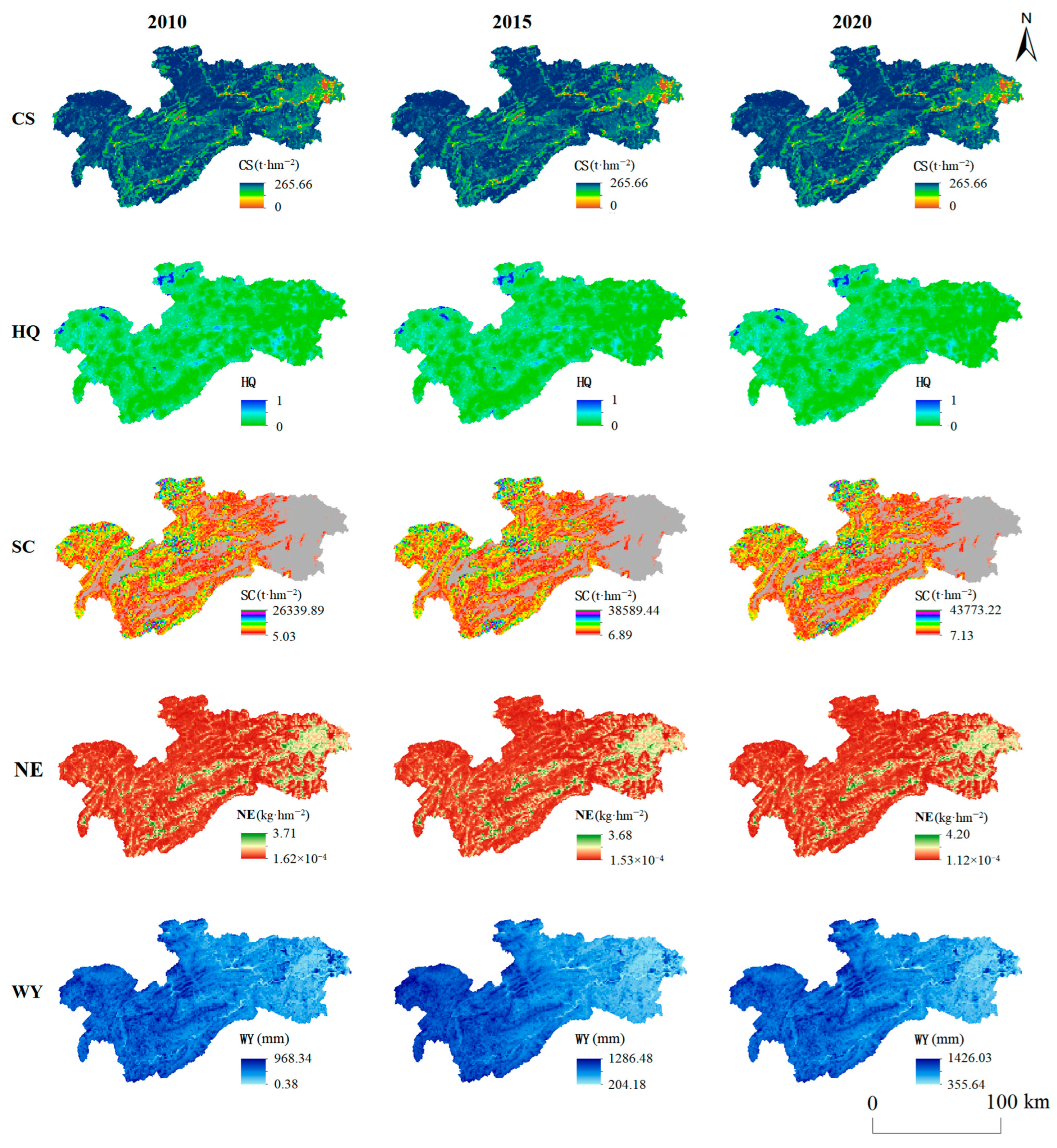
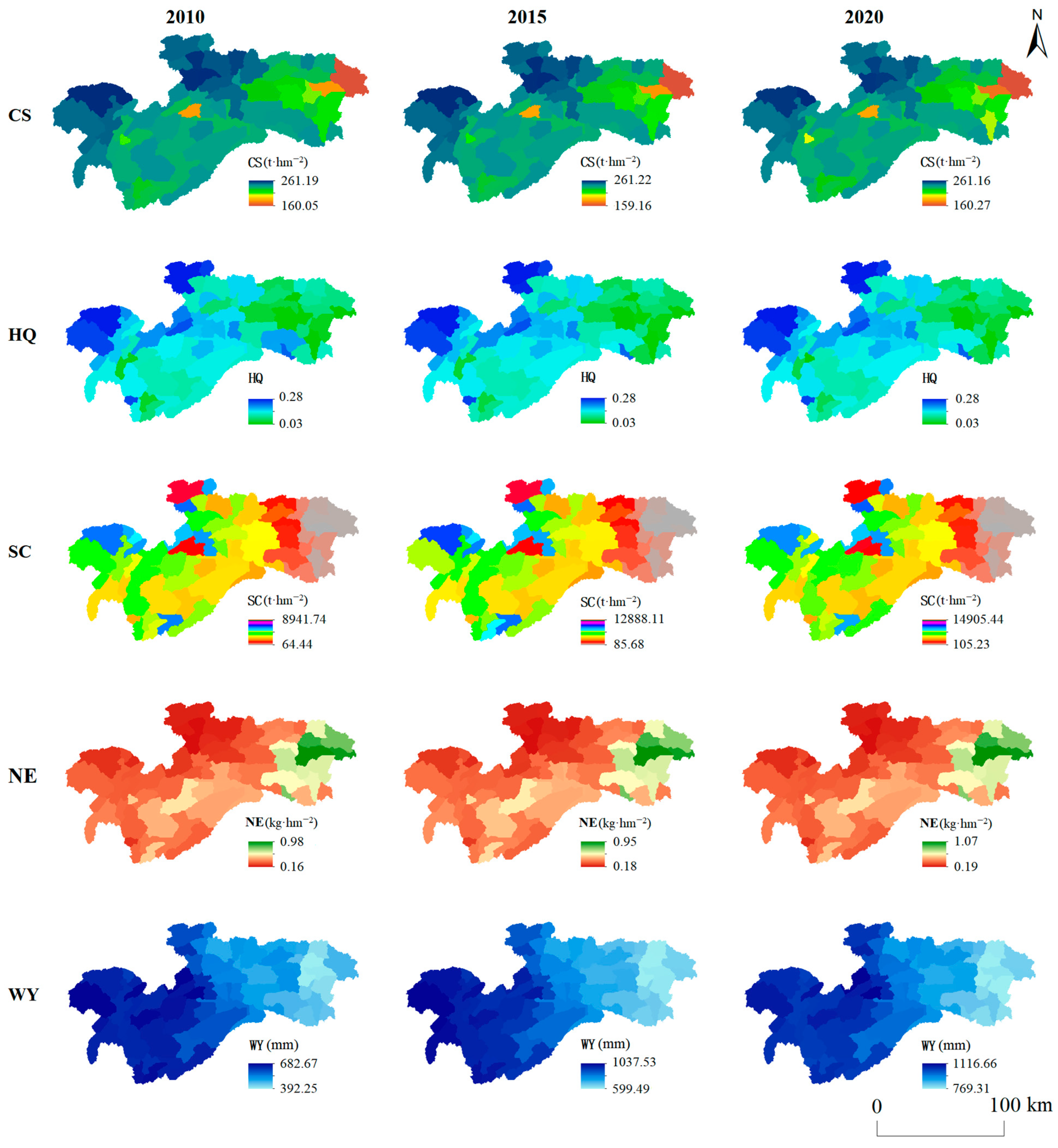
| Data | Data Source | Spatial Resolution | Year | Related Model |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rain (annual average precipitation, annual total precipitation) | China Meteorological Data Network (https://data.cma.cn) and Global Climate Database (http://www.worldclimate.com/), accessed on 13 June 2023 | 1000 m | 2010, 2015, 2020 | WY, NDR |
| Root restricting layer depth | Defined from land use types and InVEST user’s guide | 30 m | 2020 | WY |
| Digital elevation model | Geospatial Data Cloud (http://www.gscloud.cn/), accessed on 9 January 2024 | 30 m | 2020 | NDR, SDR |
| Plants’ available water content | Defined from land use types and InVEST user’s guide | 30 m | 2020 | WY |
| Rainfall erosivity | https://gda.bnu.edu.cn/sypt/sjgx/tdlytdfgsjj/index.html, accessed on 7 May 2024 | 1000 m | 2010, 2015, 2020 | SDR |
| Evapotranspiration | The National Tibetan Plateau Data Center (https://data.tpdc.ac.cn/zh-hans/data/8b11da09-1a40-4014-bd3d-2b86e6dccad4), accessed on 13 June 2023 | 1000 m | 2010, 2015, 2020 | WY |
| Soil erodibility | https://gda.bnu.edu.cn/sypt/sjgx/tdlytdfgsjj/index.html, accessed on 23 May 2024 | 30 m | 2020 | SDR |
| Watersheds | https://www.resdc.cn/DOI/DOI.aspx?DOIID=44, accessed on 29 June 2023 | 1 | 2019 | NDR, SDR, WY |
| LULC | Data Center for Resources and Environmental Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences (https://www.resdc.cn/), accessed on 6 February 2024 | 30 m | 2010, 2015, 2020 | CSS, HQ, NDR, SDR, WY, |
| Soil data | The National Tibetan Plateau Data Center (https://data.tpdc.ac.cn/), accessed on 16 June 2023 | 1000 m | 2010 | NDR, SDR, WY |
| Carbon density data | Derived from Chinese scientific data (http://csdata.org/), accessed on 5 June 2024 | 1000 m | 2020 | CSS |
| Biophysical Table | Based on literature and field studies, including LULC_veg, root_depth, Kc (the plant evapotranspiration coefficient), load of nutrients, and efficiency of nutrient retention, etc. | 1 | 2010, 2015, 2020 | NDR, SDR, WY |
| Mean annual temperature | China Meteorological Data Network (https://data.cma.cn), accessed on 18 October 2023 | 1000 m | 2010, 2015, 2020 | Some driving factors |
| Population density (POP) | WorldPop (https://www.worldpop.org/), accessed on 24 October 2023 | 1000 m | 2010, 2015, 2020 | |
| Gross Domestic Product (GDP) | National Earth System Science Data Center (http://www.geodata.cn/data/datadetails.html?dataguid=844414&docid=6666), accessed on 24 October 2023 | 1000 m | 2010, 2015, 2020 |
| Categories. | Ecosystem Services | Methods | Main Equation | Remarks | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Provisioning services | Water yield | WY | Equation (1) | Yx: annual water on grid x; AET: evapotranspiration; P: annual precipitation. | [12,51,52] |
| Regulating services | Nitrogen export | NDR | Equation (2) | : total nutrient export; loadsurf,i and loadsubs,i: local runoff potential. NDRsurf,i and NDRsubs,i: nutrient delivery factors of surface and subsurface runoff. | [11,53] |
| Soil conservation | SDR | Equation (3) | SCr: actual soil erosion; SCp: potential soil erosion; R: rainfall erosivity; K: soil erodibility. LS: slope length; P: conservation of soil and water; C: vegetation cover. | [54,55,56] | |
| Carbon sequestration | CSS | Equation (4) | : total CS; : carbon in aboveground biomass; : carbon in belowground biomass; : soil carbon; : carbon in dead matter. | [19,22,57,58,59,60] | |
| Supporting service | Habitat quality | HQ | Equation (5) | : HQ value of grid x; : habitat suitability of LULC type j; : habitat degradation degree; z: scaling parameter; k: the half-saturation constant. | [37,61] |
| Category | Indicator | Abbreviation |
|---|---|---|
| Proportion of land use types | Forest proportion | Frt |
| Cropland proportion | Crp | |
| Construction proportion | Cst | |
| Climatic | Annual average temperature | Tem |
| Mean annual precipitation | Pre | |
| Evapotranspiration | Eva | |
| Topographic factors | Elevation | DEM |
| Slope gradient | Sg | |
| Slope direction | Sd | |
| socio-economic factors | Population density | POP |
| Gross domestic product | GDP |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zeng, S.; Jiang, C.; Bai, Y.; Wang, H.; Guo, L.; Zhang, J. Assessing the Scale Effects of Dynamics and Socio-Ecological Drivers of Ecosystem Service Interactions in the Lishui River Basin, China. Sustainability 2024, 16, 8990. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16208990
Zeng S, Jiang C, Bai Y, Wang H, Guo L, Zhang J. Assessing the Scale Effects of Dynamics and Socio-Ecological Drivers of Ecosystem Service Interactions in the Lishui River Basin, China. Sustainability. 2024; 16(20):8990. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16208990
Chicago/Turabian StyleZeng, Suping, Chunqian Jiang, Yanfeng Bai, Hui Wang, Lina Guo, and Jie Zhang. 2024. "Assessing the Scale Effects of Dynamics and Socio-Ecological Drivers of Ecosystem Service Interactions in the Lishui River Basin, China" Sustainability 16, no. 20: 8990. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16208990
APA StyleZeng, S., Jiang, C., Bai, Y., Wang, H., Guo, L., & Zhang, J. (2024). Assessing the Scale Effects of Dynamics and Socio-Ecological Drivers of Ecosystem Service Interactions in the Lishui River Basin, China. Sustainability, 16(20), 8990. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16208990






