An Interdisciplinary Assessment of the Impact of Emerging Contaminants on Groundwater from Wastewater Containing Disodium EDTA
Abstract
1. Introduction
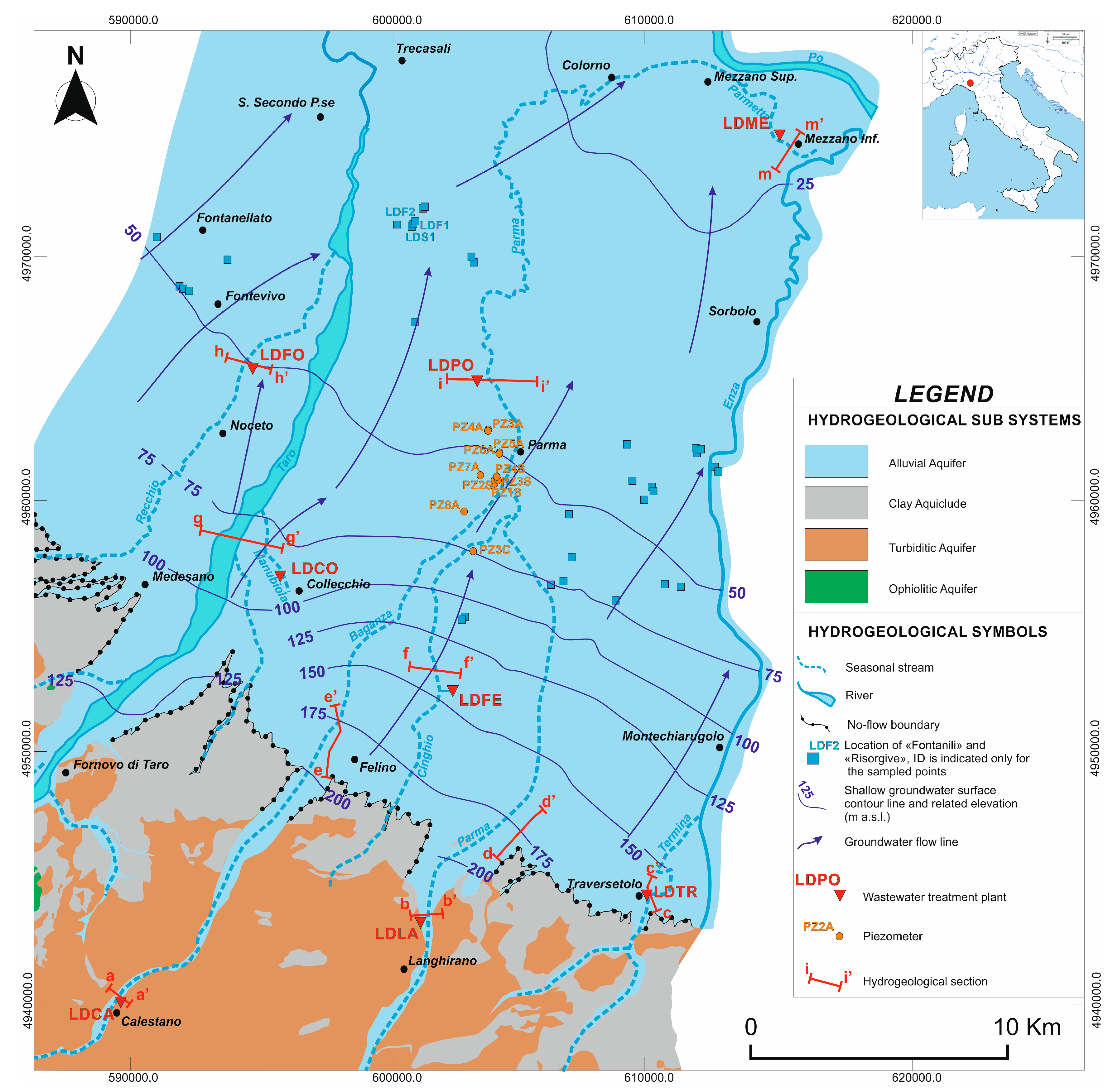
2. Study Area
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Geological Elaborations
3.2. Examination of Productive Activities in the Territory of Parma
3.3. Wastewater Discharge Selection and Sampling
3.4. Chemical Analysis
3.5. Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS) for Bacterial Community Analyses
4. Results
4.1. Hydrogeological Model
4.2. Productive Activities and Wastewater Treatment Plants
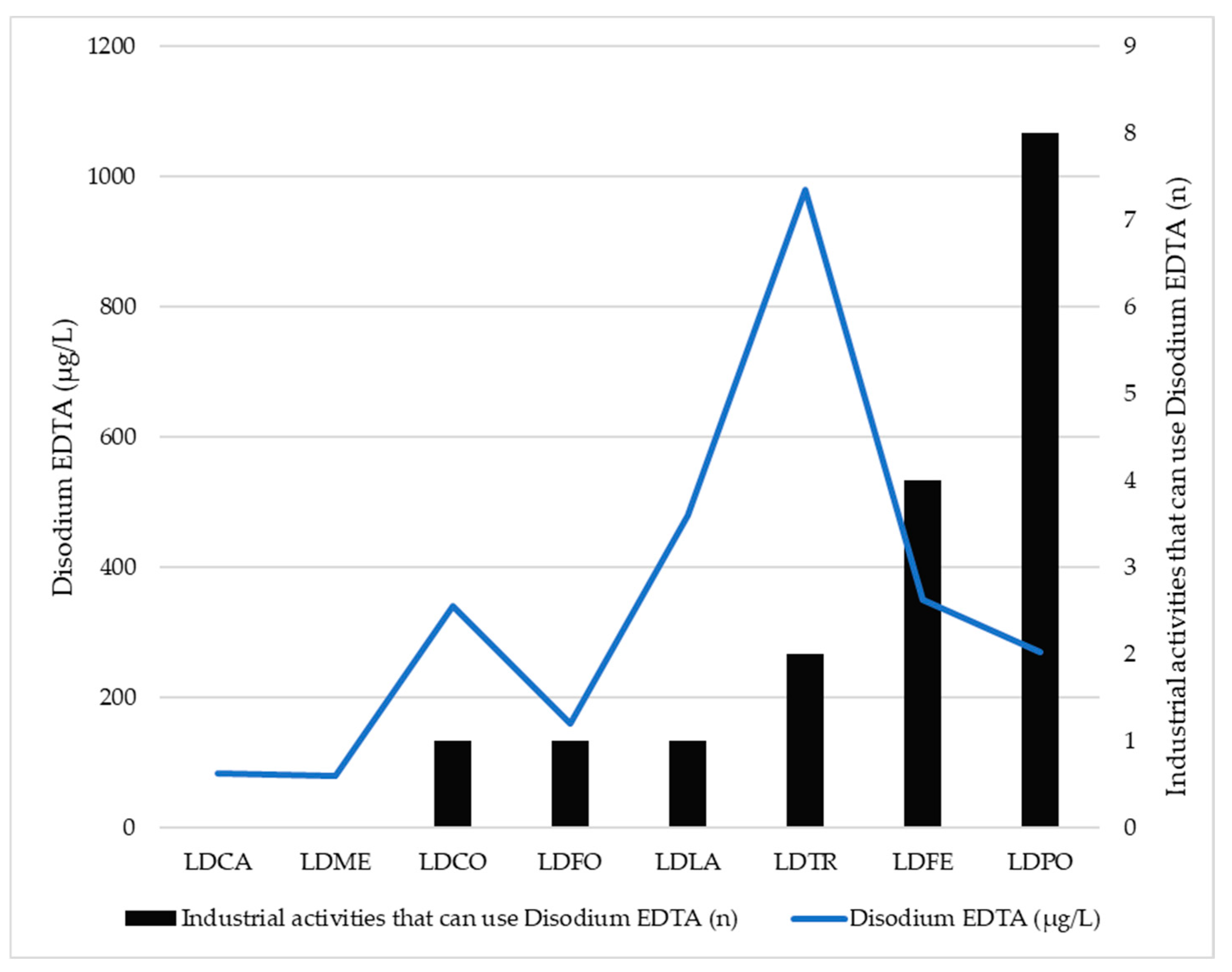
4.3. Chemical Results
4.4. Biomolecular Investigations
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Biel-Maeso, M.; Corada-Fernández, C.; Lara-Martín, P.A. Removal of personal care products (PCPs) in wastewater and sludge treatment and their occurrence in receiving soils. Water Res. 2019, 150, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, X.; Hu, J.; Li, S.; Yu, M. Occurrence, fate, and mass balance of selected pharmaceutical and personal care products (PPCPs) in an urbanized river. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 266, 115340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Branchet, P.; Castro, N.A.; Fenet, H.; Gomez, E.; Courant, F.; Sebag, D.; Gardon, J.; Jourdan, C.; Ngatcha, B.N.; Kengne, I.; et al. Anthropic impacts on Sub-Saharan urban water resources through their pharmaceutical contamination (Yaoundé, Center Region, Cameroon). Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 660, 886–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kahle, M.; Buerge, I.J.; Muller, M.D.; Poiger, T. Hydrophilic anthropogenic markers for quantification of wastewater contamination in ground- and surface waters. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2009, 28, 2528–2536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reh, R.; Licha, T.; Geyer, T.; Nodler, K.; Sauter, M. Occurrence and spatial distribution of organic micro-pollutants in a complex hydrogeological karst system during low flow and high flow periods, results of a two-year study. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 443, 438–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Ding, J.; Jiang, H.; Wang, Z.; Zheng, L.; Song, X.; Zou, H. Pharmaceuticals and Personal Care Products across Different Water Bodies in Taihu Lake Basin, China: Occurrence, Source, and Flux. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 11135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, M.; Tirkey, A.; Tiwari, A.; Lee, S.S.; Dubey, R.; Kim, K.H.; Pandey, S.K. The Environmental Significance of Contaminants of Concern in the Soil–Vegetable Interface: Sources, Accumulation, Health Risks, and Mitigation through Biochar. Sustainability 2022, 14, 14539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, K.; Kolpin, D.; Furlong, E.; Zaugg, S.; Meyer, M.; Barber, L. A national reconnaissance of pharmaceuticals and other organic wastewater contaminants in the United States I. Groundwater. Sci. Total Environ. 2008, 402, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabeza, Y.; Candela, L.; Ronen, D.; Teijón, G. Monitoring the occurrence of emerging contaminants in treated wastewater and groundwater between 2008 and 2010. The Baix Llobregat (Barcelona, Spain). J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 239–240, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thapa, B.S.; Pandit, S.; Patwardhan, S.B.; Tripathi, S.; Mathuriya, A.S.; Gupta, P.K.; Lal, R.B.; Tusher, T.R. Application of Microbial Fuel Cell (MFC) for Pharmaceutical Wastewater Treatment: An Overview and Future Perspectives. Sustainability 2022, 14, 8379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.S.; Ying, G.G.; Shareef, A.; Kookana, R.S. Simultaneous determination of benzotriazoles and ultraviolet filters in ground water, effluent and biosolid samples using gas chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2011, 1218, 5328–5335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B. (Ed.) . Emerging Contaminants in Soil and Groundwater Systems: Occurrence, Impact, Fate and Transport; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 1–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuart, M.E.; Manamsa, K.; Talbot, J.C.; Crane, E.J. Emerging Contaminants in Groundwater; British Geological Survey Open Report: Nottingham, UK, 2011; pp. 1–111. [Google Scholar]
- Stuart, M.E.; Lapworth, D.J.; Thomas, J.; Edwards, L. Fingerprinting groundwater pollution in catchments with contrasting contaminant sources using microorganic compounds. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 468–469, 564–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Oua, W.; Wang, C.; Wang, Z.; Huang, Q.; Jin, J.; Tan, J. Occurrence and ecological potential of pharmaceuticals and personal care products in groundwater and reservoirs in the vicinity of municipal landfills in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 490, 889–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rusiniak, P.; Kmiecik, E.; Wątor, K.; Duda, R.; Bugno, R. Pharmaceuticals and personal care products in the urban groundwater– preliminary monitoring (case study: Kraków, Southern Poland). Urban Water J. 2021, 14, 364–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Zhang, T. Mass flows and removal of antibiotics in two municipal wastewater treatment plants. Chemosphere 2011, 83, 1284–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Li, S.; Wang, X.; Li, Z.; Zhan, Y.; Chen, C. Efficient Degradation of 4-Acetamidoantipyrin Using a Thermally Activated Persulfate System. Sustainability 2022, 14, 14300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krzeminski, P.; Concetta, M.; Karaolia, P.; Langenhoff, A.; Almeida, C.M.R.; Felis, E.; Gritten, F.; Rasmus, H.; Fernandes, T.; Manaia, C.M.; et al. Performance of secondary wastewater treatment methods for the removal of contaminants of emerging concern implicated in crop uptake and antibiotic resistance spread: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 648, 1052–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzo, L.; Fiorentino, A.; Grassi, M.; Attanasio, D.; Guida, M. Advanced treatment of urban wastewater by sand filtration and graphene adsorption for wastewater reuse: Effect on a mixture of pharmaceuticals and toxicity. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2015, 3, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Li, Q.; Feng, W.; Zhang, X. Application Progress of O3/PMS Advanced Oxidation Technology in the Treatment of Organic Pollutants in Drinking Water. Sustainability 2022, 14, 11718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzo, L.; Malato, S.; Antakyali, D.; Beretsou, V.G.; Maja, B.Đ.; Gernjak, W.; Heath, E.; Ivancev-Tumbas, I.; Karaolia, P.; Lado, A.R.; et al. Consolidated vs new advanced treatment methods for the removal of contaminants of emerging concern from urban wastewater. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 655, 986–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krahnstöver, T.; Santos, N.; Georges, K.; Campos, L.; Antizar-Ladislao, B. Low-Carbon Technologies to Remove Organic Micropollutants from Wastewater: A Focus on Pharmaceuticals. Sustainability 2022, 14, 11686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molins-Delgado, D.; Díaz-Cruz, M.S.; Barceló, D. Introduction: Personal Care Products in the Aquatic Environment. In Personal Care Products in the Aquatic Environment; The Handbook of Environmental Chemistry 36; Díaz-Cruz, M.S., Barceló, D., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; ISBN 978-3-319-18808-9. ISSN 1867-979X. [Google Scholar]
- Molins-Delgado, D.; Díaz-Cruz, M.S.; Barceló, D. Removal of polar UV stabilizers in biological wastewater treatments and ecotoxicological implications. Chemosphere 2015, 119, S51–S57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molins-Delgado, D.; Díaz-Cruz, S.M.; Barceló, D. Ecological risk assessment associated to the removal of endocrine-disrupting parabens and benzophenone-4 in wastewater treatment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 310, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Cruz, M.S.; Molins-Delgado, D.; Serra-Roig, M.P.; Kalogianni, E.; Skoulikidis, N.T.; Barceló, D. Personal care products reconnaissance in EVROTAS river (Greece): Water-sediment partition and bioaccumulation in fish. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 651, 3079–3089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbosa, M.O.; Moreira, N.F.F.; Ribeiro, A.R.; Pereira, M.F.R.; Silva, A.M.T. Occurrence and removal of organic micropollutants: An overview of the watch list of EU Decision 2015/495. Water Res. 2016, 94, 257–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Archer, E.; Petrie, B.; Kasprzyk-Hordern, B.; Wolfaardt, G.M. The fate of pharmaceuticals and personal care products (PPCPs), endocrine disrupting contaminants (EDCs), metabolites and illicit drugs in a WWTW and environmental waters. Chemosphere 2017, 174, 437–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebele, A.J.; Oluseyi, T.; Drage, D.S.; Harrad, S.; Abdallah, M.A.-E. Occurrence, seasonal variation and human exposure to pharmaceuticals and personal care products in surface water, groundwater and drinking water in Lagos State, Nigeria. Emerg. Contam. 2020, 6, 124–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengar, A.; Vijayanandan, A. Human health and ecological risk assessment of 98 pharmaceuticals and personal care products (PPCPs) detected in Indian surface and wastewaters. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 807, 150677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeleye, A.S.; Xue, J.; Zhao, Y.; Taylor, A.A.; Zenobio, J.E.; Sun, Y.; Han, Z.; Salawu, O.A.; Zhud, Y. Abundance, fate, and effects of pharmaceuticals and personal care products in aquatic environments. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 424, 127284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gogoia, A.; Mazumder, P.; Tyagi, V.K.; Chaminda, G.G.T.; An, A.K.; Kumar, M. Occurrence and fate of emerging contaminants in water environment: A review. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2018, 6, 169–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Y.; Wu, H.; Li, L.; Ren, M.; Qie, H.; Lin, A. A review of distribution and risk of pharmaceuticals and personal care products in the aquatic environment in China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 213, 112044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, B.M.; Bečanová, J.; Scheringer, M.; Sharma, A.; Bharat, G.K.; Whitehead, P.J.; Klánová, J.; Nizzetto, L. Health and ecological risk assessment of emerging contaminants (pharmaceuticals, personal care products, and artificial sweeteners) in surface and groundwater (drinking water) in the Ganges River Basin, India. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 646, 1459–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, R.V.; Cerqueira, M.A.; Melo, M.T.C.; Figueiredo, D.R.; Keizer, J.J. Spatial patterns of surface water quality in the Certima River basin, central Portugal. J. Environ. Monit. 2010, 12, 189–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balmer, M.E.; Buser, H.-R.; Müller, M.D.; Poiger, T. Occurrence of some organic UV filters in wastewater, in surface waters, and in fish from Swiss lakes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 953–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barboza, L.G.A.; Gimenez, B.C.G. Microplastics in the marine environment: Current trends and future perspectives. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 97, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlumpf, M.; Schmid, P.; Durrer, S.; Conscience, M.; Maerkel, K.; Henseler, M.; Gruetter, M.; Herzog, I.; Reolon, S.; Ceccatelli, R.; et al. Endocrine activity and developmental toxicity of cosmetic UV filters: An update. Toxicology 2004, 205, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wee, S.Y.; Aris, A.Z. Occurrence and Public-Perceived Risk of Endocrine Disrupting Compounds in Drinking Water. NPJ Clean Water 2018, 2, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission (EC). Directive 2000/60/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 23 October 2000 establishing a framework for community action in the field of water policy. Off. J. Eur. Commun. 2000, L327, 1–72. [Google Scholar]
- Quevauville, P.; Carere, M.; Polesello, S. Chemical monitoring activity for the implementation of the Water Framework Directive. Trends Anal. Chem. 2012, 36, 1–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ducci, L.; Rizzo, P.; Pinardi, R.; Solfrini, A.; Maggiali, A.; Pizzati, M.; Balsamo, F.; Celico, F. What Is the Impact of Leaky Sewers on Groundwater Contamination in Urban Semi-Confined Aquifers? A Test Study Related to Fecal Matter and Personal Care Products (PCPs). Hydrology 2023, 10, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinardi, R.; Feo, A.; Ruffini, A.; Celico, F. Purpose Designed Hydrogeological Maps for Wide Interconnected Surface Groundwater Systems: The Test Example of Parma Alluvial Aquifer and Taro River Basin (Northern Italy). Hydrology 2023, 10, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanini, A.; Ghirardi, M.; Emiliani, R. A multidisciplinary approach to evaluate the effectiveness of natural attenuation at a contaminated site. Hydrology 2021, 8, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanini, A.; Petrella, E.; Sanangelantoni, A.M.; Angelo, L.; Ventosi, B.; Viani, L.; Rizzo, P.; Remelli, S.; Bartoli, M.; Bolpagni, R.; et al. Groundwater characterisation from an ecological and human perspective: An interdisciplinary approach in the Functional Urban Area of Parma, Italy. Rend. Lincei 2019, 30, 93–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Severini, E.; Ducci, L.; Sutti, A.; Robottom, S.; Sutti, S.; Celico, F. River–Groundwater Interaction and Recharge Effects on Microplastics Contamination of Groundwater in Confined Alluvial Aquifers. Water 2022, 14, 1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iacumin, P.; Venturelli, G.; Selmo, E. Isotopic features of rivers and groundwater of the Parma Province (Northern Italy) and their relationships with precipitation. J. Geochem. Explor. 2009, 102, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amorosi, A.; Bruno, L.; Cleveland, D.M.; Morelli, A.; Hong, W. Paleosols and associated channel-belt sand bodies from a continuously subsiding late Quaternary system (Po Basin, Italy): New insights into continental sequence stratigraphy. Bulletin 2017, 129, 449–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruno, L.; Amorosi, A.; Lugli, S.; Sammartino, I.; Fontana, D. Trunk river and tributary interactions recorded in the Pleistocene–Holocene stratigraphy of the Po Plain (northern Italy). Sedimentology 2021, 68, 2918–2943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossetti, G.; Pieri, V.; Martens, K. Recent ostracods (Crustacea, Ostracoda) found in lowland springs of the provinces of Piacenza and Parma (Northern Italy). Hydrobiologia 2005, 542, 287–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonaposta, D.; Segadelli, S.; De Nardo, M.T.; Alessandrini, A.; Pezzoli, S. Le potenzialità geologiche dei dati storici ambientali: Il caso delle sorgenti e dei fontanili in Emilia Romagna; Il Geologo dell’Emilia Romagna: Bologna, Italy, 2011; pp. 19–34. [Google Scholar]
- Kløve, B.; Ala-aho, P.; Bertrand, G.; Boukalova, Z.; Ertürk, A.; Goldscheider, N.; Ilmonen, J.; Karakaya, N.; Kupfersberger, H.; Kvoerner, J.; et al. Groundwater dependent ecosystems. Part I: Hydroecological status and trends. Environ. Sci. Policy 2011, 14, 770–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancini, M.C.; Arfini, F.; Guareschi, M. When Higher Education Meets Sustainable Development of Rural Areas: Lessons Learned from a Community–University Partnership. Soc. Sci. 2022, 11, 338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parma Manifactures Associations. Parma and Its Enterprises. 2020. Available online: www.upi.pr.it (accessed on 16 May 2024).
- Cinnirella, S.; Buttafuoco, G.; Pirrone, N. Stochastic analysis to assess the spatial distribution of groundwater nitrate concentrations in the Po catchment (Italy). Environ. Pollut. 2005, 133, 569–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassanino, M.; Sacco, D.; Zavattaro, L.; Grignani, C. Nutrient balance as a sustainability indicator of different agro-environments in Italy. Ecol. Indic. 2011, 11, 715–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laini, A.; Bartoli, M.; Castaldi, S.; Viaroli, P.; Capri, E.; Trevisan, M. Greenhouse gases (CO2, CH4 and N2O) in lowland springs within an agricultural impacted watershed (Po River Plain, northern Italy). Chem. Ecol. 2011, 27, 177–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelahad, N.; Bolpagni, R.; Jona Lasinio, G.; Vis, M.L.; Amadio, C.; Laini, A.; Keil, E.J. Distribution, morphology and ecological niche of Batrachospermum and Sheathia species (Batrachospermales, Rhodophyta) in the fontanili of the Po plain (northern Italy). Eur. J. Phycol. 2015, 50, 318–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Racchetti, E.; Salmaso, F.; Pinardi, M.; Quadroni, S.; Soana, E.; Sacchi, E.; Severini, E.; Celico, F.; Viaroli, P.; Bartoli, M. Is food irrigation a potential driver of river-groundwater interactions and diffuse nitrate pollution in agricultural watersheds? Water 2019, 11, 2304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Severini, E.; Magri, M.; Soana, E.; Bartoli, M.; Faggioli, M.; Celico, F. Irrigation practices affect relationship between reduced nitrogen fertilizer use and improvement of river and groundwater chemistry. Agric. Water Manag. 2023, 289, 108564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinardi, M.; Soana, E.; Severini, E.; Racchetti, E.; Celico, F.; Bartoli, M. Agricultural practices regulate the seasonality of groundwater-river nitrogen exchanges. Agric. Water Manag. 2022, 273, 107904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feo, A.; Pinardi, R.; Artoni, A.; Celico, F. Three-Dimensional High-Precision Numerical Simulations of Free-Product DNAPL Extraction in Potential Emergency Scenarios: A Test Study in a PCE-Contaminated Alluvial Aquifer (Parma, Northern Italy). Sustainability 2023, 15, 9166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ducci, L.; Rizzo, P.; Bucci, A.; Pinardi, R.; Monaco, P.; Celico, F. The Challenge Posed by Emerging Environmental Contaminants: An Assessment of the Effectiveness of Phenoxyethanol Biological Removal from Groundwater through Mesocosm Experiments. Sustainability 2024, 16, 2183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.J.; Kim, K.Y.; Hamm, S.Y.; Kim, M.; Kim, H.K.; Oh, J.E. Occurrence and distribution of pharmaceutical and personal care products, artificial sweeteners, and pesticides in groundwater from an agricultural area in Korea. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 659, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, N.H.; Hu, J.; Li, J.; Ong, S.L. Suitability of artificial sweeteners as indicators of raw wastewater contamination in surface water and groundwater. Water Res. 2014, 48, 443–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ISO/IEC 17025:2017; General requirements for the competence of testing and calibration laboratories. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017.
- ISO 16588:2002; Water quality—Determination of six complexing agents—Gas-chromatographic method. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2002.
- Bucci, A.; Naclerio, G.; Allocca, V.; Celico, P.; Celico, F. Potential use of microbial community investigations to analyze hydrothermal systems behaviour: The case of Ischia island, southern Italy. Hydrol. Process. 2011, 25, 1866–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griebler, C.; Lueders, T. Microbial biodiversity in groundwater ecosystems. Freshw. Biol. 2009, 54, 649–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hjorleifsdottir, S.; Skirnisdottir, S.; Hreggvidsson, G.O.; Holst, O.; Kristjansson, J.K. Species composition of cultivated and noncultivated bacteria from short filaments in an Icelandic hot spring at 88 °C. Microb. Ecol. 2001, 42, 117–125. [Google Scholar]
- Hobel, C.F.V.; Marteinsson, V.T.; Hreggvidsson, G.O.; Kristjansson, J.K. Investigation of the microbial ecology of intertidal hot springs by using diversity analysis of 16S rRNA and chitinase genes. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 2771–2776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Liu, H.; Tong, L.; Wang, Y.; Chen, R.; Liu, S.; Zhao, L.; Li, Z.; Cai, L. Relationships between microbial communities and groundwater chemistry in two pristine confined groundwater aquifers in central China. Hydrol. Process. 2019, 33, 1993–2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, Y.; Su, J.; Wang, J.; Dai, N.; Li, J.; Song, L.; Zuo, R. Soil microbial community response to seawater intrusion into coastal aquifer of Donghai Island, South China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 72, 3329–3338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amalfitano, S.; Del Bon, A.; Zoppini, A.; Ghergo, S.; Fazi, S.; Parrone, D.; Casella, P.; Stano, F.; Preziosi, E. Groundwater geochemistry and microbial community structure in the aquifer transition from volcanic to alluvial areas. Water Res. 2014, 65, 384–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebrun, M.; Miard, F.; Bucci, A.; Fougère, L.; Nandillon, R.; Naclerio, G.; Scippa, G.S.; Destandeau, E.; Morabito, D.; Bourgerie, S. The rhizosphere of Salix viminalis plants after a phytostabilization process assisted by biochar, compost, and iron grit: Chemical and (micro)-biological analyses. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 47447–47462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchum, R.M., Jr.; Vail, P.R.; Thompson, S., III. Seismic Stratigraphy and Global Changes of Sea Level: Part 2. The Depositional Sequence as a Basic Unit for Stratigraphic Analysis: Section 2. Application of Seismic Reflection Configuration to Stratigraphic Interpretation in M 26: Seismic Stratigraphy—Applications to Hydrocarbon Exploration; AAPG Special Volumes: Tulsa, OK, USA, 1977; pp. 53–62. [Google Scholar]
- Cherian, P.; Bergfeld, W.F.; Belsito, D.V.; Klaassen, C.D.; Liebler, D.C.; Marks, J.G.; Shank, R.C.; Slaga, T.J.; Snyder, P.W.; Fiume, M.; et al. EDTA and Salts. Int. J. Toxicol. 2023, 42 (Suppl. 3), 32S–36S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission Website. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/food/food-feed-portal/screen/food-additives/search/details/POL-FAD-IMPORT-3124 (accessed on 12 April 2024).
- Bernardet, J.-F.; Bowman, J.P. Flavobacterium. In Bergey’s Manual of Systematics of Archaea and Bacteria; Trujillo, M.E., Dedysh, S., DeVos, P., Hedlund, B., Kämpfer, P., Rainey, F.A., Whitman, W.B., Eds.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahn, M.W.; Kasalický, V.; Jezbera, J.; Brandt, U.; Šimek, K. Limnohabitans australis sp. nov., isolated from a freshwater pond, and emended description of the genus Limnohabitans. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2010, 60, 2946–2950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Kumari, S.; Anil Kumar, P.; Lal, R. Novosphingobium. In Bergey’s Manual of Systematics of Archaea and Bacteria; Trujillo, M.E., Dedysh, S., DeVos, P., Hedlund, B., Kämpfer, P., Rainey, F.A., Whitman, W.B., Eds.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peix, A.; Ramírez-Bahena, M.H.; Velázquez, E. Historical evolution and current status of the taxonomy of genus Pseudomonas. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2009, 9, 1132–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willems, A.; Gillis, M. Hydrogenophaga. In Bergey’s Manual of Systematics of Archaea and Bacteria; Trujillo, M.E., Dedysh, S., DeVos, P., Hedlund, B., Kämpfer, P., Rainey, F.A., Whitman, W.B., Eds.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, W.; Stewart, J.; Powell, D.; Gardner, T. Evaluation of Bacteroides markers for the detection of human faecal pollution. Letters Appl. Microbiol. 2008, 46, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nataro, J.P.; Bopp, C.A.; Fields, P.I.; Kaper, J.B.; Strockbine, N.A. Escherichia, Shigella, and Salmonella. In Manual of Clinical Microbiology, 11th ed.; ASM Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2011; pp. 603–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collado, M.C.; Donat, E.; Ribes-Koninckx, C.; Calabuig, M.; Sanz, Y. Imbalances in faecal and duodenal Bifidobacterium species composition in active and non-active coeliac disease. BMC Microbiol. 2008, 8, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdenelli, M.C.; Ghelfi, F.; Silvi, S.; Orpianesi, C.; Cecchini, C.; Cresci, A. Probiotic properties of Lactobacillus rhamnosus and Lactobacillus paracasei isolated from human faeces. Eur. J. Nutr. 2009, 48, 355–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zagato, E.; Pozzi, C.; Bertocchi, A.; Schioppa, T.; Saccheri, F.; Guglietta, S.; Fosso, B.; Melocchi, L.; Nizzoli, G.; Troisi, J.; et al. Endogenous murine microbiota member Faecalibaculum rodentium and its human homologue protect from intestinal tumour growth. Nat. Microbiol. 2020, 5, 511–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, R.A.; Lawlor, K.; Bailey, M.; Macaskie, L.E. Biodegradation of metal-EDTA complexes by an enriched microbial population. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1998, 64, 1319–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behbahaninia, A.; Mirbagheri, S.; Nouri, J. Effects of sludge from wastewater treatment plants on heavy metals transport to soils and groundwater. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2010, 7, 401–406. [Google Scholar]
- Hubbard, L.E.; Keefe, S.H.; Kolpin, D.W.; Barber, L.B.; Duris, J.W.; Hutchinson, K.J.; Bradley, P.M. Understanding the hydrologic impacts of wastewater treatment plant discharge to shallow groundwater: Before and after plant shutdown. Environ.Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2016, 2, 864–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karnjanapiboonwong, A.; Suski, J.G.; Shah, A.A.; Cai, Q.; Morse, A.N.; Anderson, T.A. Occurrence of PPCPs at a wastewater treatment plant and in soil and groundwater at a land application site. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2011, 216, 257–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fennell, C.; Misstear, B.; O’Connell, D.; Dubber, D.; Behan, P.; Danaher, M.; Moloney, M.; Gill, L. An assessment of contamination fingerprinting techniques for determining the impact of domestic wastewater treatment systems on private well supplies. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 268, 115687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| ATECO Code | ATECO Description of Economic Activities | Number of Industrial Activities in the Study Area |
|---|---|---|
| 10.85.09 | Production of ready meals and dishes from other food products | 7 |
| 21.10.00 | Manufacture of basic pharmaceutical products | 2 |
| 20.42.00 | Manufacture of toiletry products: perfumes, cosmetics, soaps, and similar items | 3 |
| 10.89.09 | Production of other food products not elsewhere classified (n.e.c.) | 2 |
| 82.92.10 | Packaging and wrapping of food products | 3 |
| Plant Capacity | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wastewater Treatment Plant | Average Daily Volume (m3/d) | Population Equivalent Units (n) | Inhabitants (n) | Industrial Activities (n) | Industrial Activities that Can Use Disodium EDTA (n) |
| LDCA | 450 | 4000 | 2062 | 1 | 0 |
| LDME | 450 | 9600 | 3168 | 4 | 0 |
| LDCO | 3000 | 20,000 | 14,711 | 22 | 1 |
| LDFE | 6700 | 50,000 | 9168 | 56 | 4 |
| LDFO | 3800 | 16,000 | 5543 | 15 | 1 |
| LDLA | 10,500 | 25,000 | 10,801 | 126 | 1 |
| LDPO | 24,000 | 168,000 | 100,015 | 61 | 8 |
| LDTR | 1800 | 9900 | 9591 | 31 | 2 |
| Sample | Parameter (CAS) | Technique | Analytical Method | Disodium EDTA (µg/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LDCA | Disodium EDTA (139-33-3) | GC-MS | EN ISO 16588 [68] | 83 |
| LDME | Disodium EDTA (139-33-3) | GC-MS | EN ISO 16588 [68] | 80 |
| LDCO | Disodium EDTA (139-33-3) | GC-MS | EN ISO 16588 [68] | 340 |
| LDFE | Disodium EDTA (139-33-3) | GC-MS | EN ISO 16588 [68] | 350 |
| LDFO | Disodium EDTA (139-33-3) | GC-MS | EN ISO 16588 [68] | 160 |
| LDLA | Disodium EDTA (139-33-3) | GC-MS | EN ISO 16588 [68] | 480 |
| LDPO | Disodium EDTA (139-33-3) | GC-MS | EN ISO 16588 [68] | 270 |
| LDTR | Disodium EDTA (139-33-3) | GC-MS | EN ISO 16588 [68] | 980 |
| Groundwater Sample | Final Read Number |
|---|---|
| Pz1S | 45,846 |
| Pz2S | 39,521 |
| Pz3S | 54,855 |
| Pz4S | 54,741 |
| Pz3A | 69,745 |
| Pz4A | 51,091 |
| Pz5A | 77,817 |
| Pz6A | 73,062 |
| Pz7A | 59,631 |
| Pz8A | 44,792 |
| Pz3C | 23,600 |
| Pz3A | Pz4A | Pz5A | Pz6A | Pz7A | |||||
| Methylobacter | 5.03% | Flavobacterium | 44.74% | Pseudomonas | 6.75% | Bacteroides | 8.15% | Limnohabitans | 22.31% |
| Methylotenera | 4.68% | Limnohabitans | 22.92% | Lactobacillus | 3.97% | Escherichia-Shigella | 6.06% | Herminiimonas | 22.01% |
| Methylomonas | 4.46% | Pseudarcicella | 4.28% | Streptococcus | 2.90% | Bifidobacterium | 3.61% | Pseudomonas | 11.69% |
| Pz1S | Pz2S | Pz3S | Pz4S | Pz8S | |||||
| Hydrogenophaga | 22.01% | Novosphingobium | 12.14% | Novosphingobium | 14.26% | Novosphingobium | 8.00% | Bacteroides | 7.21% |
| Silanimonas | 20.81% | Azospirillum | 6.00% | Limnohabitans | 5.17% | Azospirillum | 7.47% | Faecalibaculum | 6.88% |
| Roseococcus | 17.60% | Sphaerotilus | 5.93% | Sphingomonas | 3.60% | Flavobacterium | 6.26% | Lactobacillus | 6.57% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ducci, L.; Rizzo, P.; Pinardi, R.; Celico, F. An Interdisciplinary Assessment of the Impact of Emerging Contaminants on Groundwater from Wastewater Containing Disodium EDTA. Sustainability 2024, 16, 8624. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16198624
Ducci L, Rizzo P, Pinardi R, Celico F. An Interdisciplinary Assessment of the Impact of Emerging Contaminants on Groundwater from Wastewater Containing Disodium EDTA. Sustainability. 2024; 16(19):8624. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16198624
Chicago/Turabian StyleDucci, Laura, Pietro Rizzo, Riccardo Pinardi, and Fulvio Celico. 2024. "An Interdisciplinary Assessment of the Impact of Emerging Contaminants on Groundwater from Wastewater Containing Disodium EDTA" Sustainability 16, no. 19: 8624. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16198624
APA StyleDucci, L., Rizzo, P., Pinardi, R., & Celico, F. (2024). An Interdisciplinary Assessment of the Impact of Emerging Contaminants on Groundwater from Wastewater Containing Disodium EDTA. Sustainability, 16(19), 8624. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16198624









