Geochemical Indicators on the Central Tibetan Plateau Lake Sediments: Historical Climate Change and Regional Sustainability
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
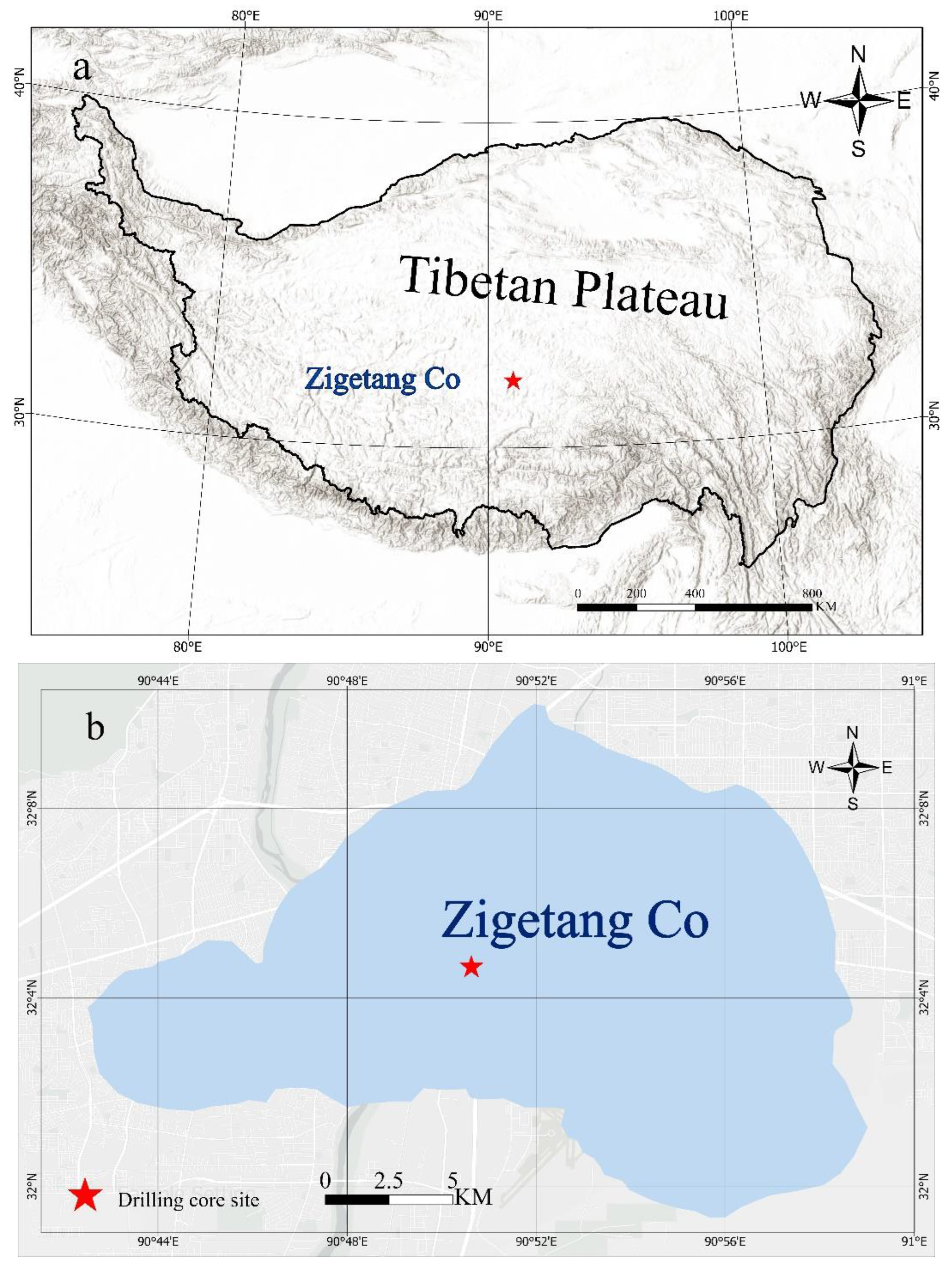
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sample Collection and Preparation
2.3. Analytical Methods
3. Results
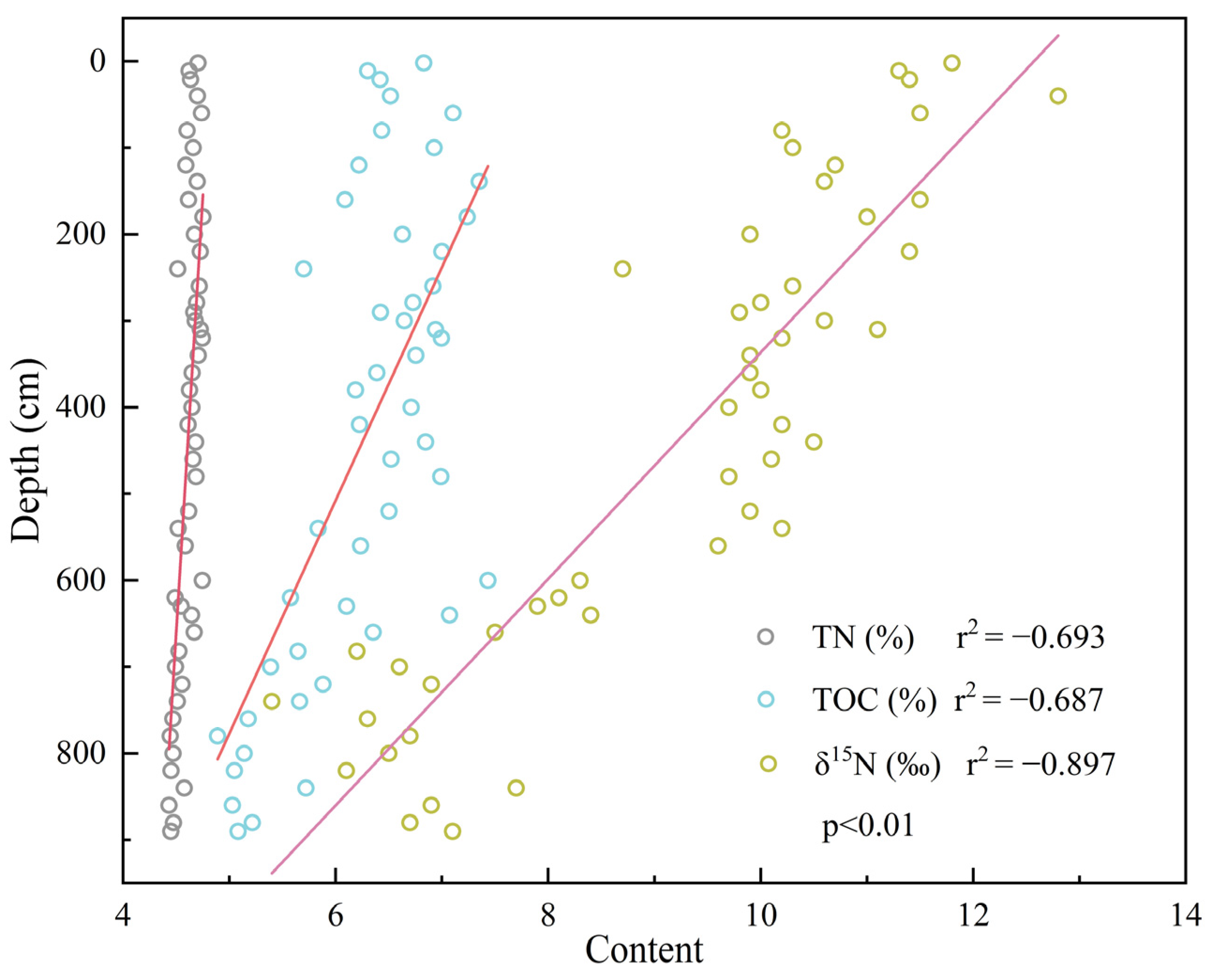
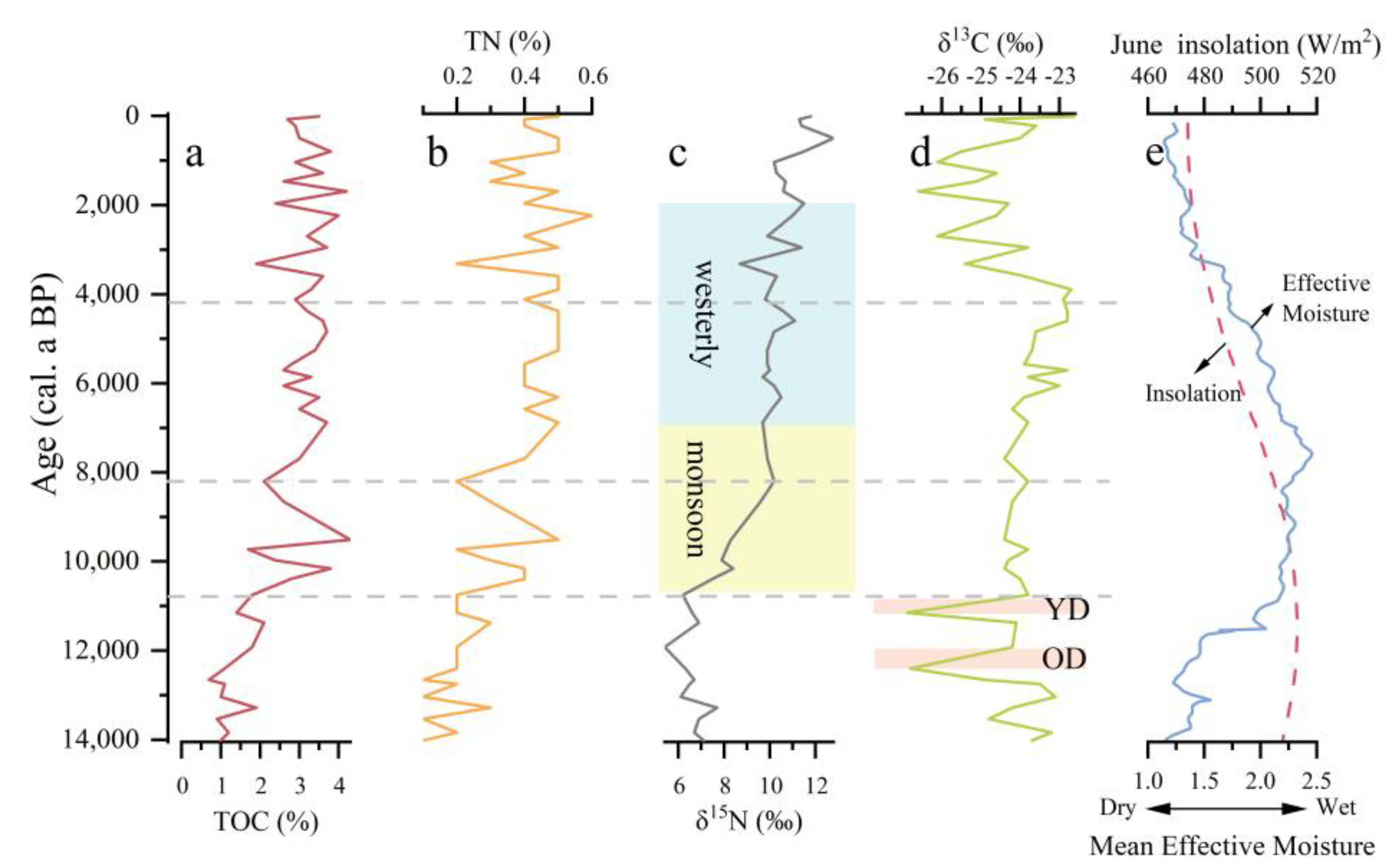
3.1. Variations in Geochemical Indicators
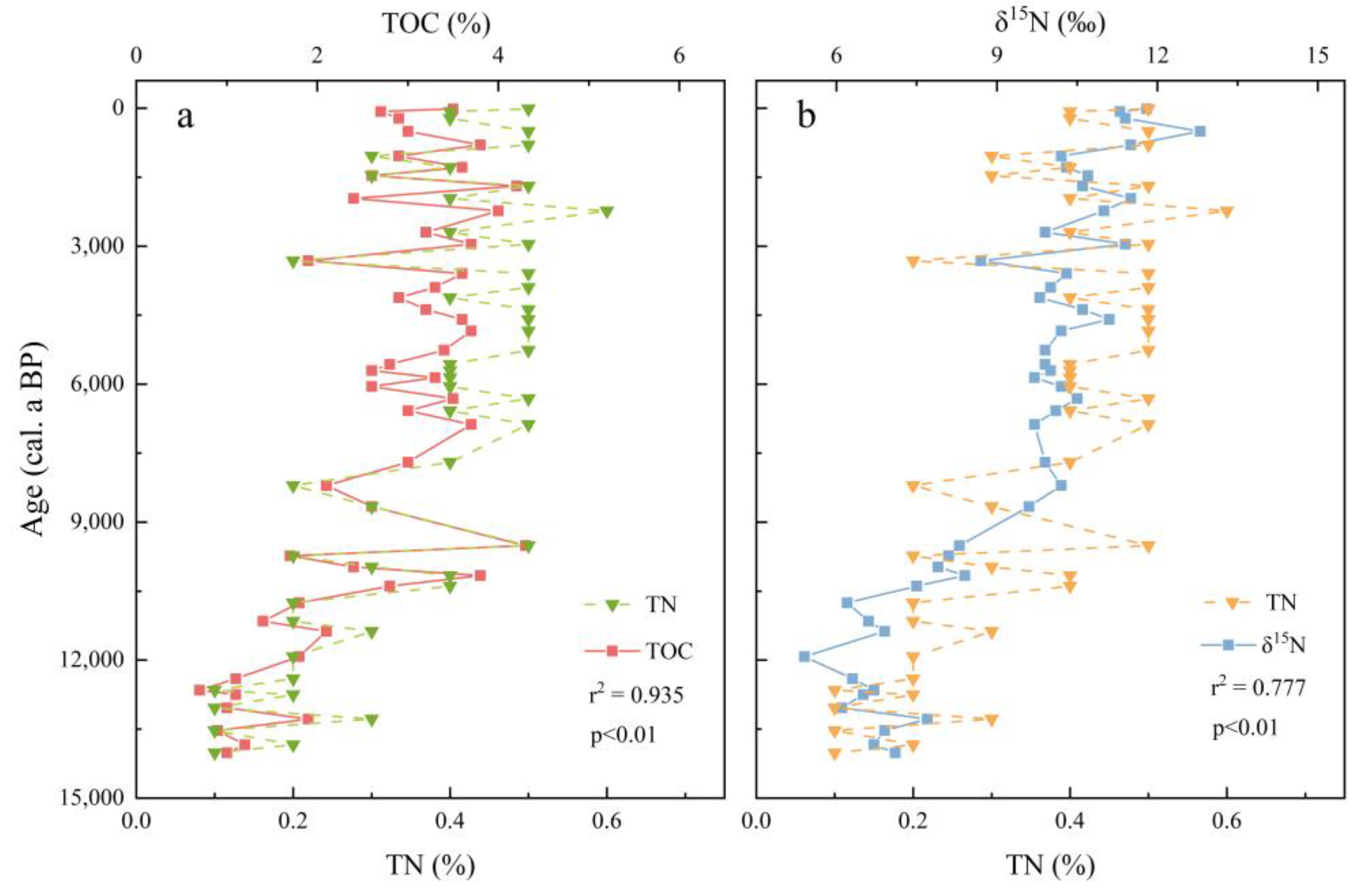
3.2. Characteristics of the δ13Corg and δ15N Variations
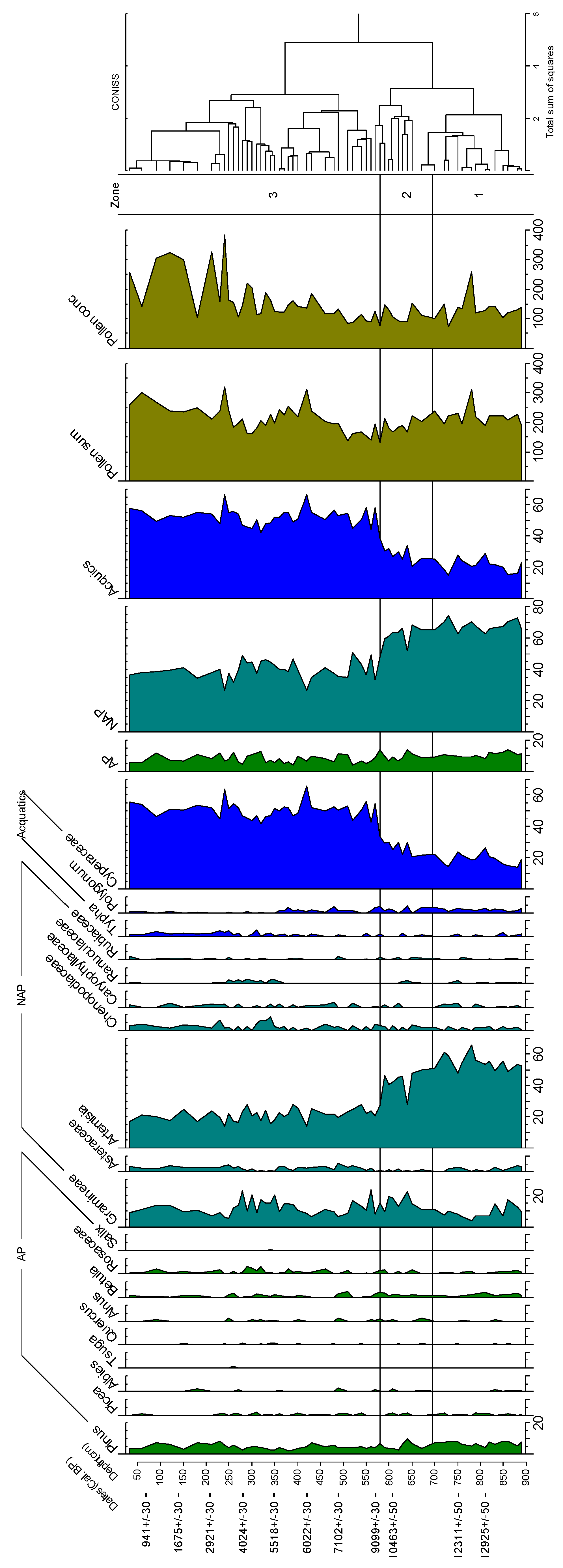
3.3. The Division and Characteristics of Pollen Assemblage Zones
4. Discussion
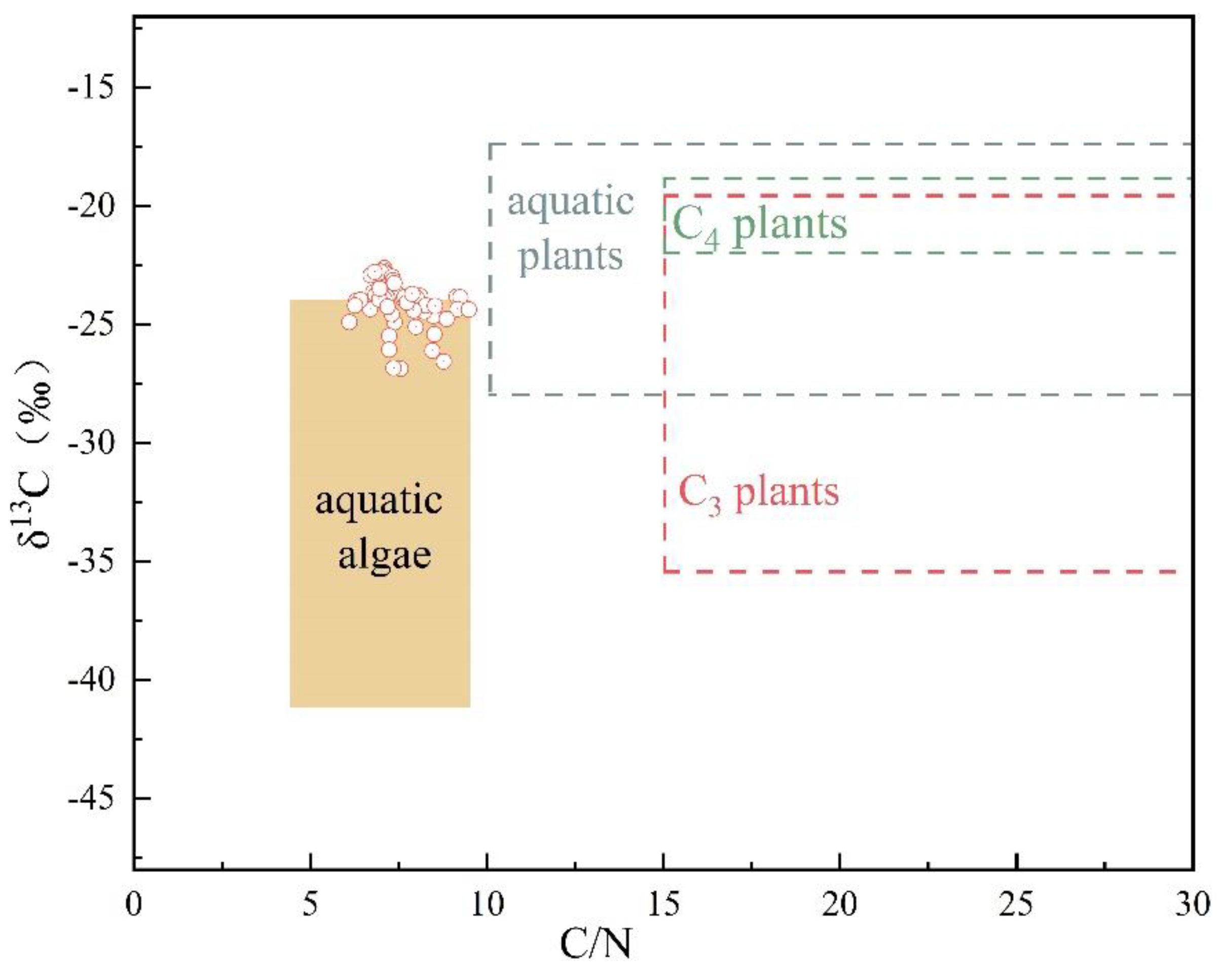
4.1. Sources of Lake Organic Matter
4.2. Geochemical Indicators and Climate-Environmental Changes
4.3. Reconstruction of the Past Climate of Zigetang Co
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- It was found that the climate was probably cold and dry during the Last Glacial Termination, which was not conducive to plant growth and development. These conditions resulted in low TOC and TN contents, as well as low δ15N values, and mainly consisted of pollen from the Gramineae and Artemisia families. Both the OD and YD events were documented during this stage. A warm and humid climate likely emerged during the early Holocene, leading to increases in TOC and TN contents, and δ15N values. This was consistent with the enhanced solar radiation and monsoon-induced precipitation. There were significant changes in pollen composition. However, the early Holocene climate exhibited instability and also documented specific cold events. In the mid to late Holocene, the high δ15N values likely indicated abundant precipitation in the basin. This was evidenced by the extensive growth of herbaceous plants, reflecting the rich precipitation consistent with the penetration of westerlies into the interior of the TP. The climate changes during the Last Glacial Termination and early Holocene were influenced by the monsoon, while in the mid to late Holocene, precipitation in the basin was influenced by the westerlies.
- (2)
- The research found that climate conditions had a significant impact on plant growth and regional human activities. In cold and dry climatic conditions, plant growth was limited, and it was necessary to reduce human activities to protect the ecosystem. In contrast, in warm and humid conditions, plant growth was enhanced and the potential for human activities increased, though sustainable development still needed to be considered. Understanding these relationships helps in formulating adaptive policies to balance environmental protection with economic development, achieving long-term sustainable development for the region.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, Y.; Qin, B.; Zhu, G.; Song, C.; Deng, J.; Xue, B.; Gong, Z.; Wang, X.; Wu, J.; Shi, K.; et al. Importance and main ecological and environmental problems of lakes in China. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2022, 67, 3503–3519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Members, C. Climatic Changes of the Last 18,000 Years: Observations and Model Simulations. Science 1988, 241, 1043–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuo, Y.; Zeng, W.; Ma, B.; Cui, D.; Xie, Y.; Wang, J. Spatiotemporal variation and influencing factors of nitrogen and phosphorus in lake sediments in China since 1850. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 368, 133170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anas, M.U.M.; Scott, K.A.; Wissel, B. Carbon budgets of boreal lakes: State of knowledge, challenges, and implications. Environ. Rev. 2015, 23, 275–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, N.; Singh, S.P.; Sahu, S.; Bhattacharyya, R.; Maurya, A.S.; Kumar, N.; Rout, R.K.; Tripathy, G.R. Isotopic evidence of autochthonous organic matter acting as a major sink of anthropogenic heavy metals in modern lacustrine sediments. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 349, 123964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Peng, H.; Jie, W.; Ding, H.; Hu, Y.; Fan, B.; Gao, Y.; Hong, B. Nitrogen isotopic composition of Jiulong Wetland sediments in Fanjing Mountain and Holocene climate evolution process. J. Lake Sci. 2023, 35, 1844–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edje, B.O.; Ishaque, A.B.; Chigbu, P. Spatial and Temporal Patterns of δ13C and δ15N of Suspended Particulate Organic Matter in Maryland Coastal Bays, USA. Water 2020, 12, 2345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasher, G.E.; Axford, Y.; Masterson, A.L.; Berman, K.; Larocca, L.J. Holocene temperature and landscape history of southwest Greenland inferred from isotope and geochemical lake sediment proxies. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2020, 239, 106358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, L.; Cao, J.; Jin, J.; Xiang, B.; Ma, W.; Wang, T. Response of nitrogen isotopes to paleo-environment and organic carbon accumulation in a Late Paleozoic alkaline lake, Junggar Basin. Chem. Geol. 2022, 602, 120884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Wang, N.; Zhang, L.; Li, Z.; Zhao, W.; Li, M.; Su, X.; Wang, Y. Palaeoenvironmental evolution of the Badain Jaran Desert hinterland during the Early to Middle Holocene: A multi-proxy reconstruction on Taoerlegetu paleolake, northwest China. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2023, 611, 111359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, A.; Xu, J.; Xie, L.; Cheng, R.; Wei, Z.; Zhong, W. Geochemical characteristics of sediments in the Xiaohai lagoon (Eastern Hainan) and implications for the paleo-typhoon activities. J. Lake Sci. 2019, 31, 1758–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.; Li, L.; Liu, C.; Yan, W.; Wang, L.; Zhang, M.; Wang, D. Historical variations of sedimentary organic matter sources and their relationships with human socio-economic activities in multiple habitats of a shallow lake. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 140, 109011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, W.; Zhang, J.; Yin, H.; Xue, J.; Cao, J.; Tang, X. Study on the Climatic and Environmental Implication of Stable Nitrogen Isotopes from the Holocene Lacustrine Sediments in Balikun Lake in Xinjiang. J. South China Norm. Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2013, 45, 182–188. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, J.; Huang, J.; Zhang, R.; Huang, C.; Liu, J. The variation of carbon and nitrogen isotopic compositions in the Dajiuhu sediments and climate changes since Late Pleistocene in the western Hubei of Central China. Quat. Sci. 2021, 41, 916–930. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Feng, Z.; Ran, M.; Zhang, D.; Lan, B.; Sun, A. Holocene vegetation and hydrology variations and their associations with climate changes: A multi-proxy analysis of a sediment core from an alpine basin in the middle Tianshan Mountains. Clim. Dyn. 2021, 56, 3835–3852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Punt, W.; Hoen, P.P.; Blackmore, S.; Nilsson, S.; Thomas, A.L. Glossary of pollen and spore terminology. Rev. Palaeobot. Palynol. 2007, 143, 1–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y.; Wang, W.; Hu, J.; Zhang, J.; Lai, Y. Vegetation and climate changes over the last 30,000 years on the Leizhou Peninsula, southern China, inferred from the pollen record of Huguangyan Maar Lake. Boreas 2017, 46, 525–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufman, D.; McKay, N.; Routson, C.; Erb, M.; Davis, B.; Heiri, O.; Jaccard, S.; Tierney, J.; Dätwyler, C.; Axford, Y.; et al. A global database of Holocene paleotemperature records. Sci. Data 2020, 7, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, T.; Xu, P.; Lu, Y.; Li, Z. Spatial-Temporal Characteristics and Influencing Factors of Tourism Activity Intensity in Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Ecol. Econ. 2023, 39, 140–146. [Google Scholar]
- Li, P.; Gao, C.; Luo, Y.; Guo, H.; Sun, W. Spatial differences and value conversion potential of ecological assets on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, China. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2024, 44, 1808–1821. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, J.; Jia, Y.; A, W.; Lv, W.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, M.; Tsechoe, D.; Wang, S. The main influencing factors of household income and expenditure of herdsmen in the northern Tibetan Plateau. Tibet. Sci. Technol. 2024, 46, 48–53. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, J.; Liu, X.; Guo, Y.; Ren, H. Study on vegetation change in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau from 1980 to 2015. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2021, 30, 288–296. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, S.; Chappellaz, J.; Jouzel, J.; Chu, P.C.; Masson-Delmotte, V.; Qin, D.; Raynaud, D.; Mayewski, P.A.; Lipenkov, V.Y.; Kang, S. Summer temperature trend over the past two millennia using air content in Himalayan ice. Clim. Past 2007, 3, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, X.; Wang, S.; Zhu, H.; Xu, Y.; Liang, E.; Yin, Z.-Y.; Xu, X.; Xiao, Y. A 3585-year ring-width dating chronology of Qilian juniper from the northeastern Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. IAWA J. 2009, 30, 379–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Song, B.; Zhang, S.; Li, S.; Qu, H.; Song, X.; Wang, J.; Zhou, S.; Chen, M.; Wan, X. Sporopollen records and implications for surface processes: A case study of Shell Ridge in the Qaidam Basin, Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Quat. Int. 2020, 565, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, Y.; Werne, J.P.; Meyers, P.A.; Zhang, H. Organic matter geochemical signatures of sediments of Lake Ngoring (Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau): A record of environmental and climatic changes in the source area of the Yellow River for the last 1500 years. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2020, 551, 109729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.; Jin, C.; Kang, S.; Li, S.; Chen, W. Paleoenvironmental changes of Cuona Lake on the central Tibetan Plateau over the last 13 kyrs based on organic geochemical proxies. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2024, 638, 112061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, S.; Liu, C.Q.; Mostofa, K.M.G.; Zhao, Z.; Luo, R. Hydrogeochemistry and δ13CDIC and δ18OH2O composition of three Chinese Tibetan Plateau lakes. Isot. Environ. Health Stud. 2017, 54, 89–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Li, S.; Shu, W. Pigments in the lake sediments: Environmental indicator. Mar. Geol. Quat. Geol. 2007, 27, 37–42. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Bernd, W.; Xia, W.; Yu, S.; Shen, D.; Jiang, Y. A preliminary study of the Holocene lake level changes and their causes derived from the sediment record of Zigetang Lake, Tibetan Plateau. Earth Sci. Front. 2009, 16, 162–167. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Liu, Q.; Li, S.; Fang, X.; Zhang, J.; Li, T. Holocene Environmental Changes Derived from Ostracode Shell Stable Isotopes in the Sediment Core of Zigetang Lake, Tibetan Plateau. Mt. Res. 2014, 32, 373–379. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, C.; Günther, F.; Li, S.; Jia, G.; Peng, P.A.; Gleixner, G. Reduced early Holocene moisture availability inferred from δD values of sedimentary n-alkanes in Zigetang Co, Central Tibetan Plateau. Holocene 2016, 26, 556–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lü, H.; Gu, Z.; Wu, N.; Wang, L.; Guo, Z.; Wu, H. Effect of altitude on the organic carbon-sotope composition of modern surface soils from Qinghai-XiZang Plateau. Quat. Sci. 2001, 21, 399–406. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Li, W. Hydrochemistry in meromictic Lake Zige Tangco, Central Tibetan Plateau. Asian J. Water Environ. Pollut. 2004, 1, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Li, S.; Yin, Y.; Ji, J.; Pu, P. The discovery of semi-mixed lakes and its significance on Tibetan Plateau. Sci. China Ser. D Earth Sci. 2001, 31, 269–272. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.; Qian, N.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, H. Pollen Flora of China; China Science Publishing & Media Ltd.: Beijing, China, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Guan, Z. Pollen and Spores Morphology of Common Aquatic Vascular Plants in China; China Science Publishing & Media Ltd.: Beijing, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, L.; Mao, L.; Shu, J.; Li, C.; Shen, C.; Zhou, Z. An Illustrated Handbook of Quaternary Pollen and Spores in China; China Science Publishing & Media Ltd.: Beijing, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Grimm, E.C. CONISS: A FORTRAN 77 program for stratigraphically constrained cluster analysis by the method of incremental sum of squares. Comput. Geosci. 1987, 13, 13–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, J.; Huang, X.; Xu, D.; Chen, W.; Song, B.; Cui, A.; Eric, G. The Latest Tilia Software: Chinese Manual and Practise Skills. Acta Palaeontol. Sin. 2018, 57, 260–272. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Chen, G.; Huang, L.; Kong, L.; Li, R.; Han, Q.; Li, P.; Suo, Q.; Zhou, Q. Synchronic changes of lake organic and inorganic carbon burial in response to catchment development over the past century: A case study of Shilin Karst area. J. Lake Sci. 2022, 34, 1751–1764. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Q.; Pang, Y.; Xiang, S.; Wan, L. Distribution characteristics and source analysis of organic matter in surface sediments of Luoma Lake. China Environ. Sci. 2021, 41, 4850–4856. [Google Scholar]
- Meyers, P.A. Organic geochemical proxies of paleoceanographic, paleolimnologic, and paleoclimatic processes. Org. Geochem. 1997, 27, 213–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendall, C.; Silva, S.R.; Kelly, V.J. Carbon and nitrogen isotopic compositions of particulate organic matter in four large river systems across the United States. Hydrol. Process. 2001, 15, 1301–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Andreas, L.; Bernd, W.; Li, S.; Wang, S. Holocene climate change in the Central Tibetan Plateau inferred by lacustrine sediment geochemical records. Sci. China Ser. D Earth Sci. 2007, 50, 1548–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Si, B.; Zhai, D.; Itoh, S.; Lomtatidze, Z. Hydrology of Dali Lake in central-eastern Inner Mongolia and Holocene East Asian monsoon variability. J. Paleolimnol. 2008, 40, 519–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Wu, J.; Si, B.; Liang, W.; Nakamura, T.; Liu, B.; Inouchi, Y. Holocene climate changes in the monsoon/arid transition reflected by carbon concentration in Daihai Lake of Inner Mongolia. Holocene 2006, 16, 551–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Chi, Y.; Xie, Y.; Kang, C.; Wu, P.; Sun, L.; Wei, Z. Paleofire events recorded by charcoal in Harbin loess since the middle-late Pleistocene with driving mechanism. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2022, 42, 10317–10328. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Liu, T.; Cao, Q.; Zhang, J.; Deng, H. Spatial distribution and stoichiometric characteristics of C, N, P in the sediment-Potamogeton crisp’s system in Dongping Lake. Environ. Chem. 2020, 39, 2263–2271. [Google Scholar]
- Kastner, S.; Ohlendorf, C.; Haberzettl, T.; Lücke, A.; Mayr, C.; Maidana, N.I.; Schäbitz, F.; Zolitschka, B. Southern hemispheric westerlies control the spatial distribution of modern sediments in Laguna Potrok Aike, Argentina. J. Paleolimnol. 2010, 44, 887–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglas, P.M.J.; Stratigopoulos, E.; Park, S.; Keenan, B. Spatial differentiation of sediment organic matter isotopic composition and inferred sources in a temperate forest lake catchment. Chem. Geol. 2022, 603, 120887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, J.; Wu, H.; Yang, H.; Wang, J.; Liu, J.; Tong, Y.; Wang, D.; Huang, M. Global warming induces the succession of photosynthetic microbial communities in a glacial lake on the Tibetan Plateau. Water Res. 2023, 242, 120213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, A.; Loutre, M.F. Insolation values for the climate of the last 10 million years. Quat. Sci. Rev. 1991, 10, 297–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, X.; Feng, X.; Hu, L.; Li, J.; Liu, X.; Wang, N.; Xiao, Q.; Wei, J. Coupled δ15NTN and δ13CTOC Insights into Methane Seepage Activities in Bulk Marine Sediments of the Qiongdongnan Basin, South China Sea. J. Ocean Univ. China 2022, 21, 1495–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Liu, X.; Wang, S.; Ryo, M. Palaeoclimatic changes in the Qinghai Lake area during the last 18,000 years. Quat. Int. 2005, 136, 131–140. [Google Scholar]
- Herzschuh, U. Palaeo-moisture evolution in monsoonal Central Asia during the last 50,000 years. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2006, 25, 163–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.; D’Andrea, W.J.; Wang, M.; He, Y.; Liang, J. Influence of the Indian monsoon and the subtropical jet on climate change on the Tibetan Plateau since the late Pleistocene. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2017, 163, 84–94. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, N.; Yao, T.; Thompson, L.G.; Henderson, K.A.; Davis, M.E. Evidence for cold events in the early Holocene from the Guliya ice core, Tibetan Plateau, China. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2002, 47, 818–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Günther, F.; Witt, R.; Schouten, S.; Mausbacher, R.; Daut, G.; Zhu, L.; Xu, B.; Yao, T.; Gleixner, G. Quaternary ecological responses and impacts of the Indian Ocean Summer Monsoon at Nam Co, Southern Tibetan Plateau. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2015, 112, 66–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Andreas, L.; Jin, Z.; Wang, S.; Schleser, G.H.; Battarbee, R.W.; Xia, W. Holocene climate development on the central Tibetan Plateau: A sedimentary record from Cuoe Lake. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2006, 234, 328–340. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, T.; Masson-Delmotte, V.; Gao, J.; Yu, W.; Yang, X.; Risi, C.; Sturm, C.; Werner, M.; Zhao, H.; He, Y.; et al. A review of climatic controls on δ18O in precipitation over the Tibetan Plateau: Observations and simulations. Rev. Geophys. 2013, 51, 525–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, C.; Li, S.; Chen, W.; Cao, C. Climate Changes on the Tibetan Plateau Inferred from Organic Geochemistry Records in Lake Sediments—A Case of Lake Zigetang Co. Bull. Mineral. Petrol. Geochem. 2016, 35, 625–633. [Google Scholar]
- He, Y.; Hou, J.; Brown, E.T.; Xie, S.; Bao, Z. Timing of the Indian Summer Monsoon onset during the early Holocene: Evidence from a sediment core at Linggo Co, central Tibetan Plateau. Holocene 2017, 28, 755–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Hou, J.; Wang, M.; He, Y. Influence of monsoon and westerlies on Holocene climate change in the Tibetan Plateau: Isotopic evidence. Quat. Sci. 2019, 39, 678–686. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Liang, J.; Hou, J.; Zhang, W. Centennial-scale climate variability during the past 2000 years on the central Tibetan Plateau. Holocene 2015, 25, 892–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, X.; Wang, X.; Gao, Y.; Yue, F.; Chen, W. Geochemical Indicators on the Central Tibetan Plateau Lake Sediments: Historical Climate Change and Regional Sustainability. Sustainability 2024, 16, 8186. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16188186
Ma X, Wang X, Gao Y, Yue F, Chen W. Geochemical Indicators on the Central Tibetan Plateau Lake Sediments: Historical Climate Change and Regional Sustainability. Sustainability. 2024; 16(18):8186. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16188186
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Xi, Xiaodan Wang, Yunlong Gao, Fujun Yue, and Wei Chen. 2024. "Geochemical Indicators on the Central Tibetan Plateau Lake Sediments: Historical Climate Change and Regional Sustainability" Sustainability 16, no. 18: 8186. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16188186
APA StyleMa, X., Wang, X., Gao, Y., Yue, F., & Chen, W. (2024). Geochemical Indicators on the Central Tibetan Plateau Lake Sediments: Historical Climate Change and Regional Sustainability. Sustainability, 16(18), 8186. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16188186






