Identifying Critical Links in Degradable Road Networks Using a Traffic Demand-Based Indicator
Abstract
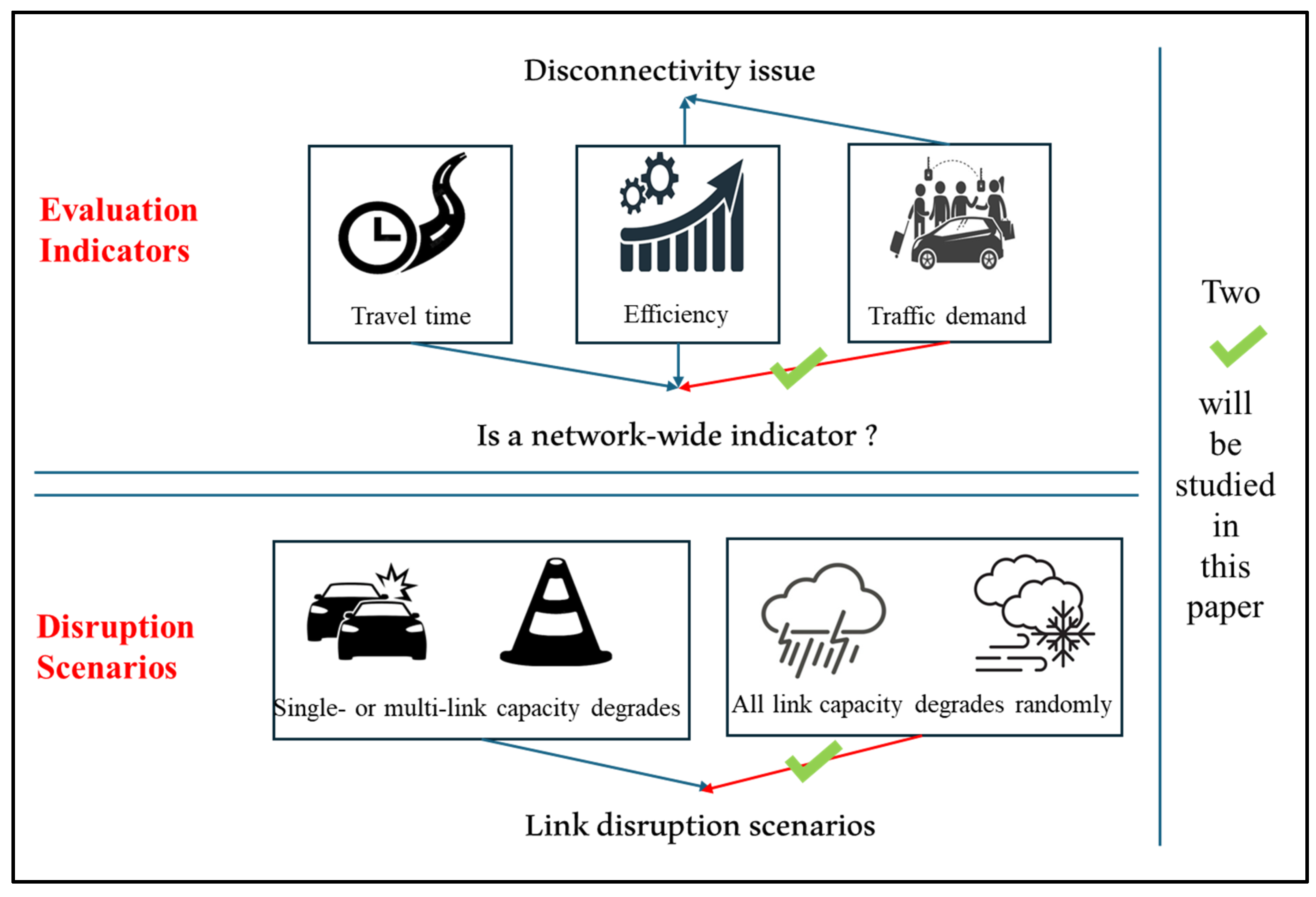
1. Introduction
- (1)
- A new traffic demand-based indicator called late arrival demand is proposed, which can capture the impact of link disruptions on the traffic demand of both connected and disconnected OD pairs.
- (2)
- We propose a late arrival rate-based user equilibrium model and design the corresponding algorithm to estimate the late arrival demand in degradable road networks.
- (3)
- We execute numerical experiments based on two traffic benchmark networks, including the Nguyen–Dupuis network and the Sioux Falls network, to identify critical links by various indicators and perform correlation analyses.
2. Problem Statements and Methodology
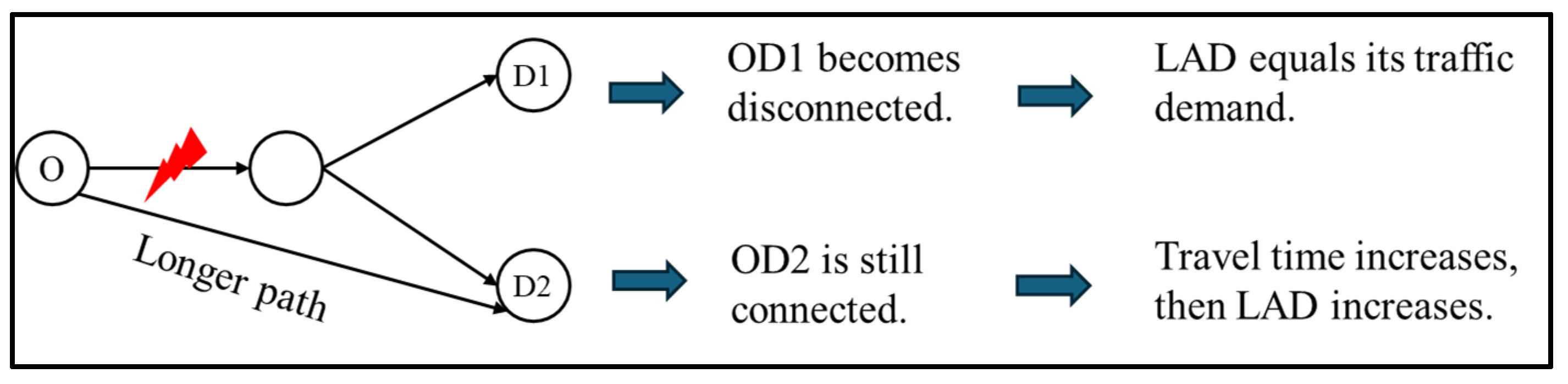
2.1. The Indicator of Late Arrival Demand
2.2. The LAR-Based UE Model
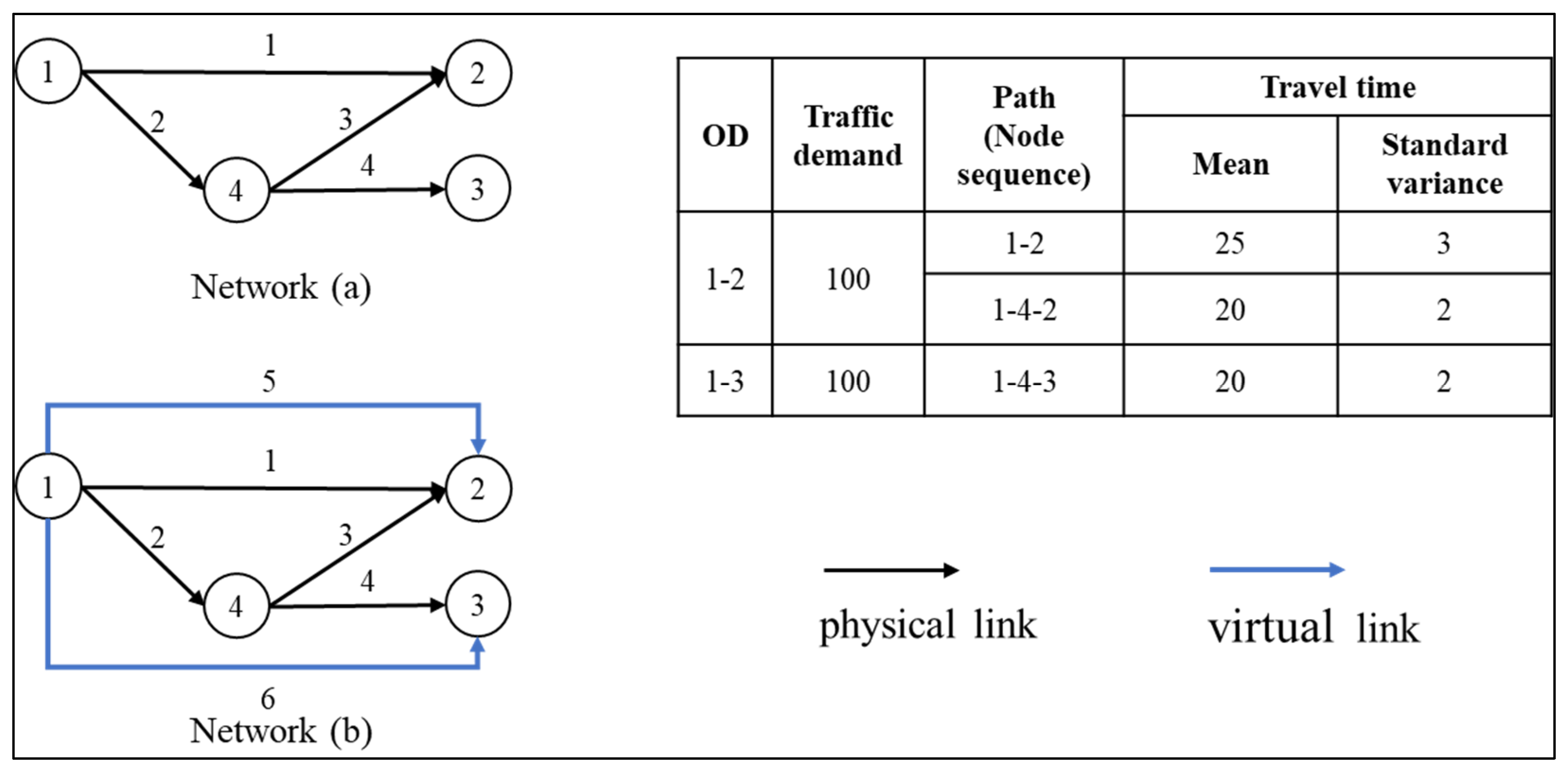
2.2.1. Path Travel Time Distribution
2.2.2. TTB and LAR
2.2.3. LAR-Based UE Model and Solution Algorithm
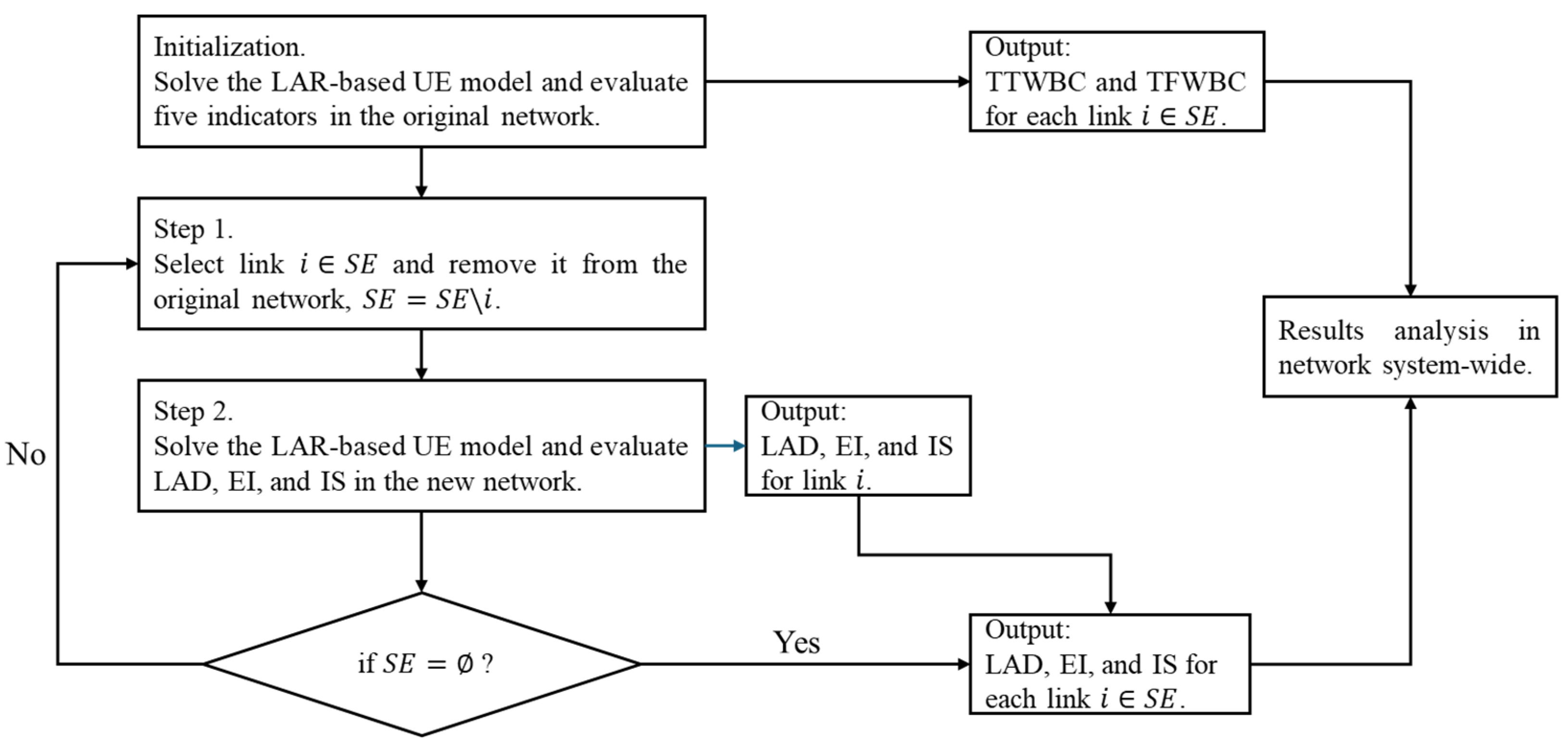
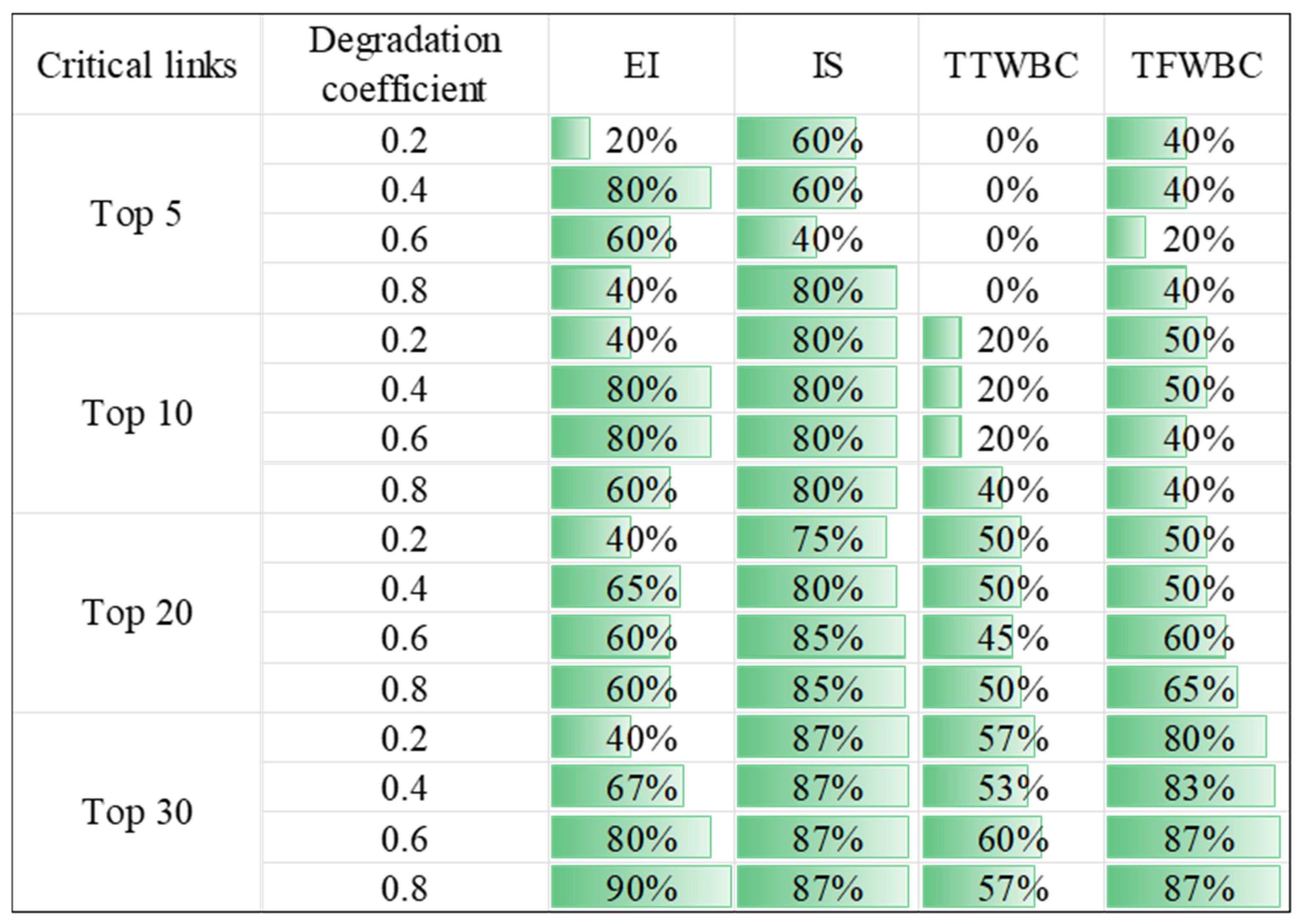
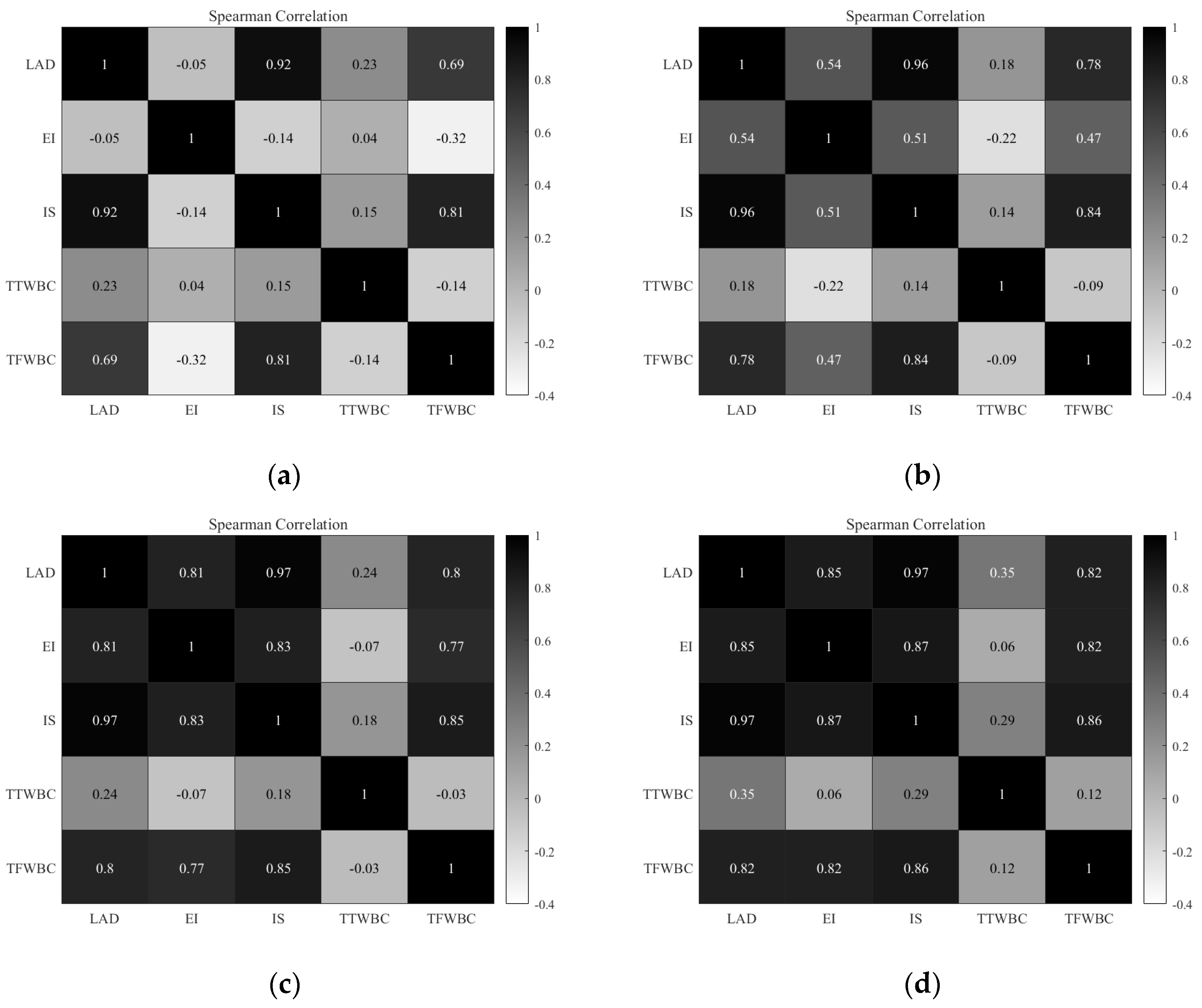
2.3. Identify Critical Links by Different Indicators
3. Numerical Experiments
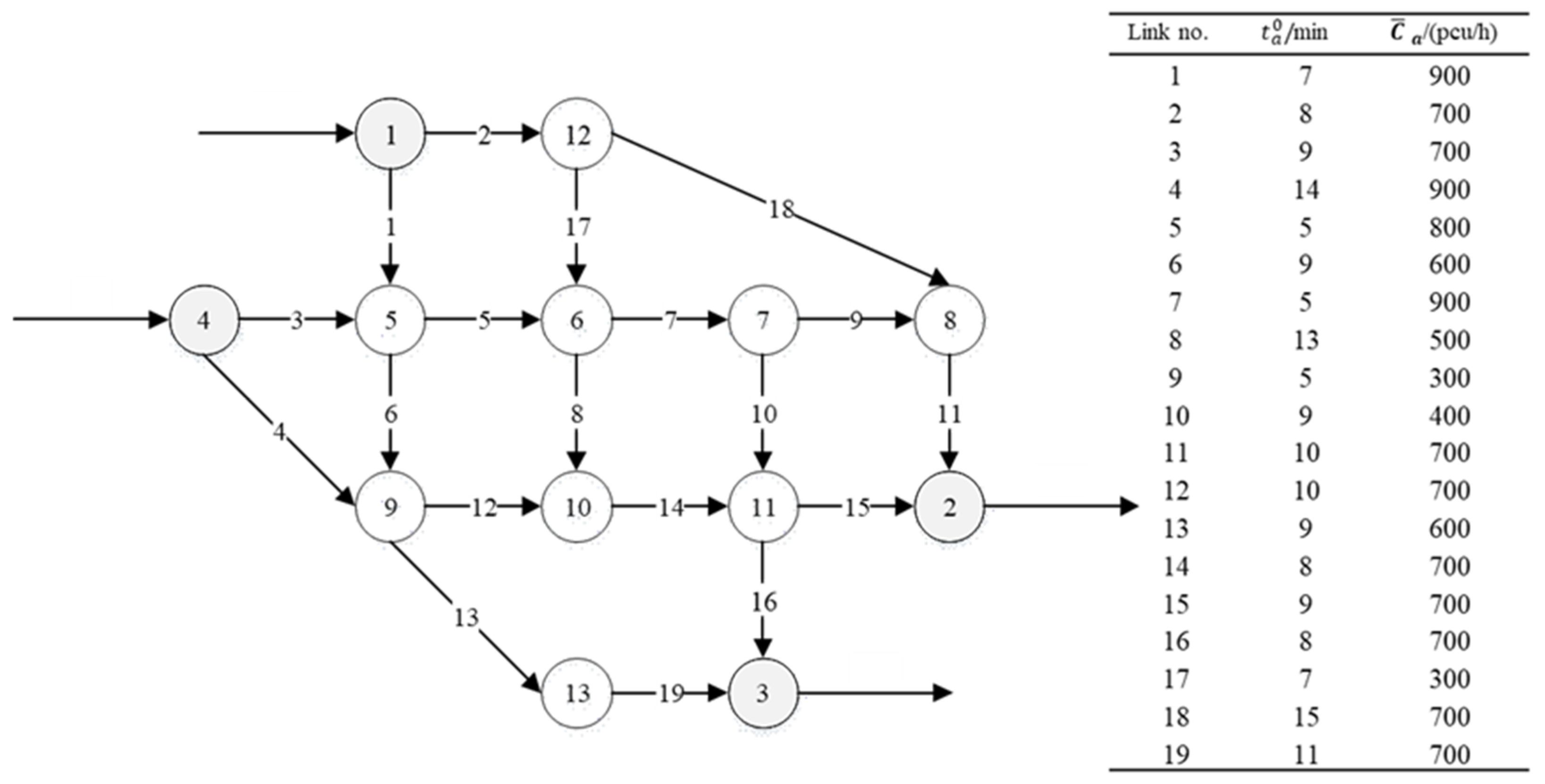
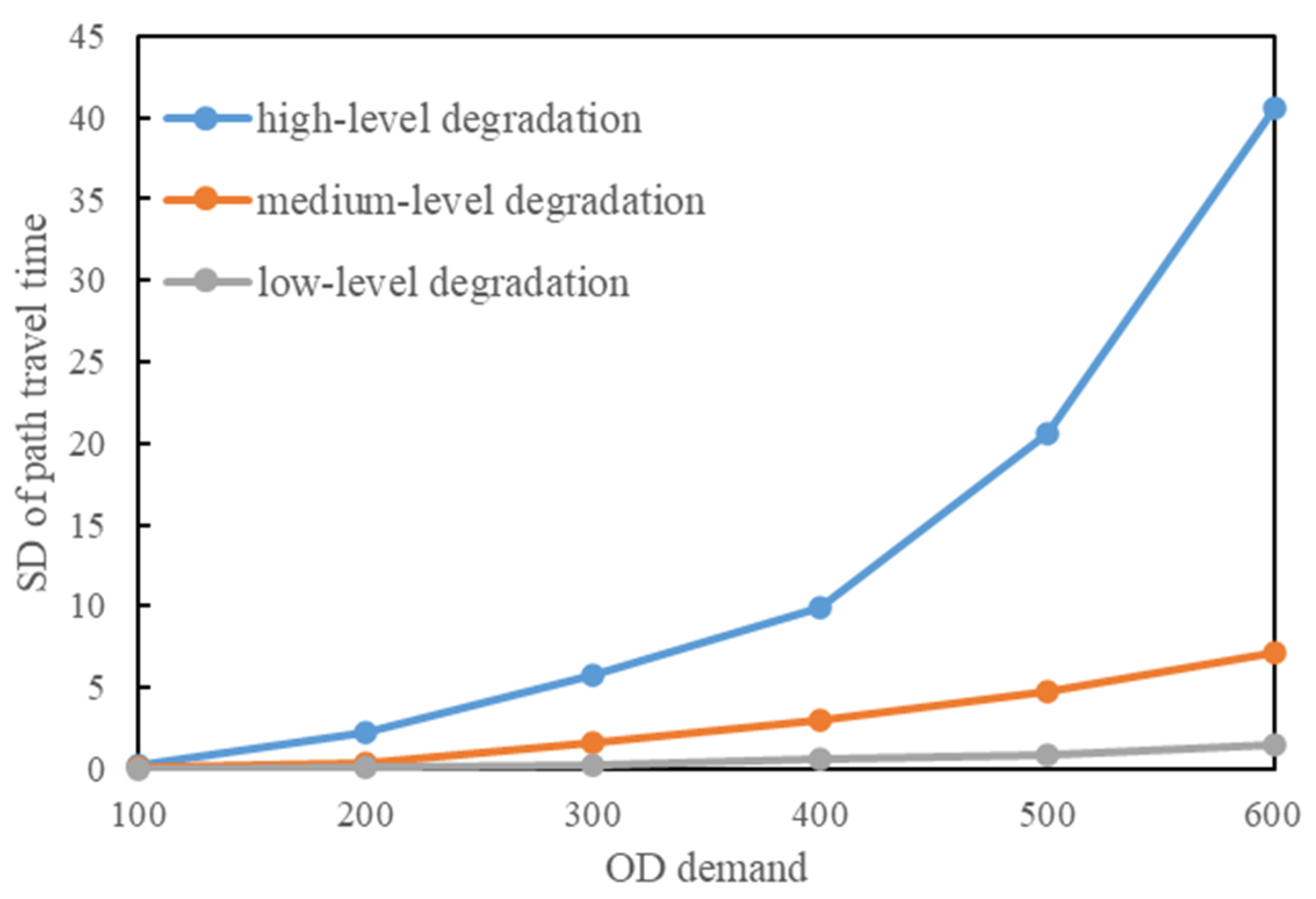
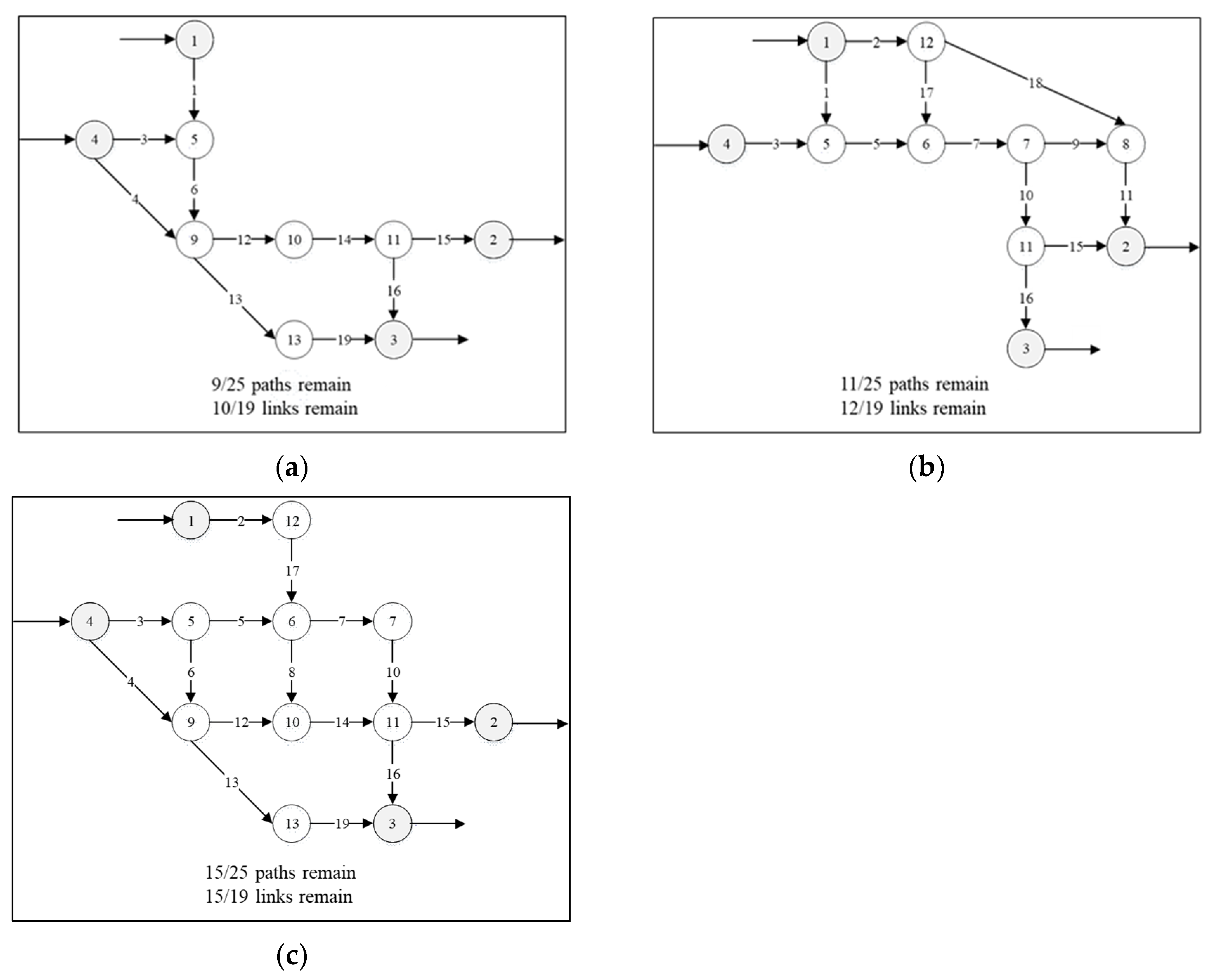
3.1. Nguyen–Dupuis Network
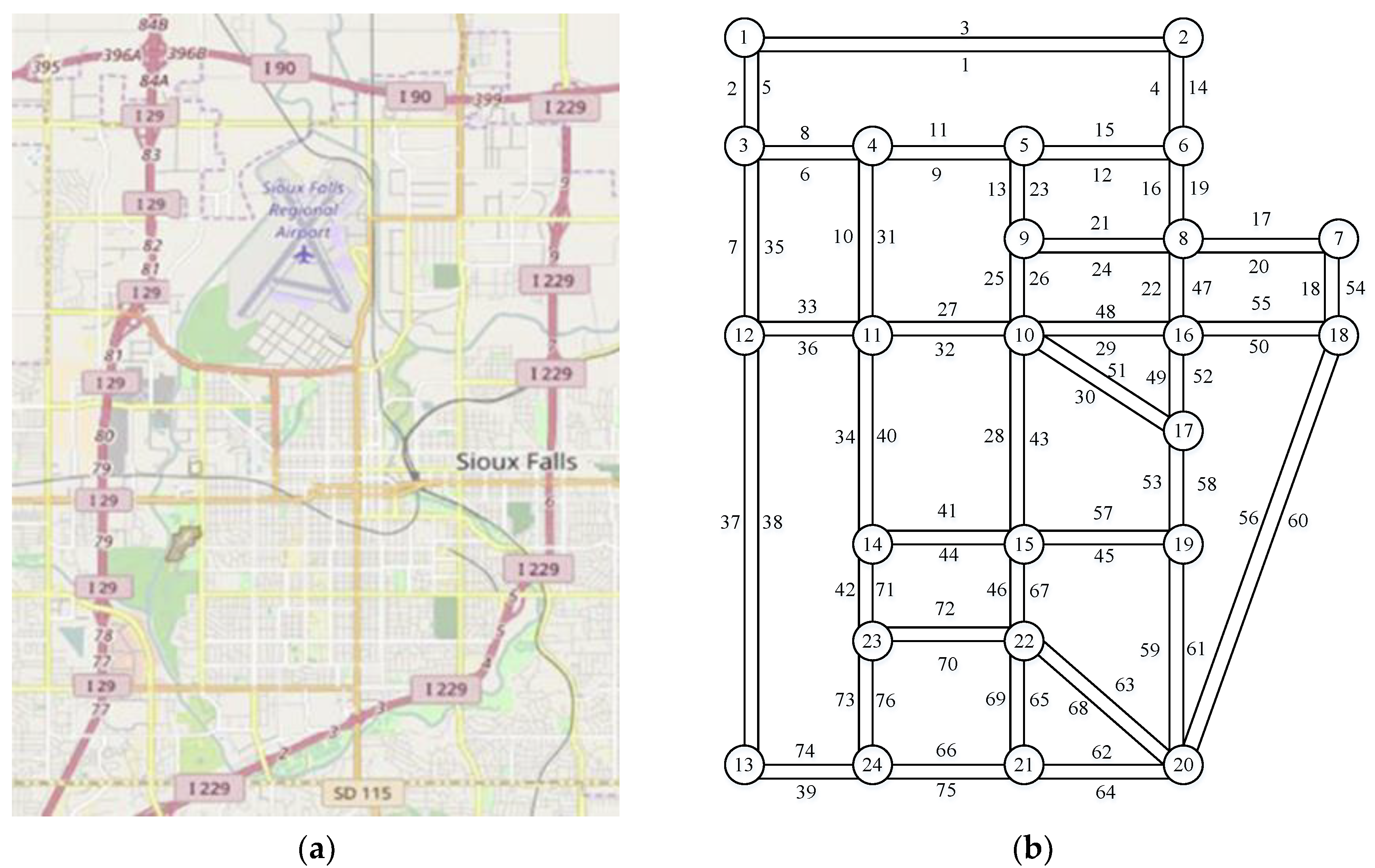
3.2. Sioux Falls Network
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ye, Q.; Kim, H. Assessing Network Vulnerability Using Shortest Path Network Problems. J. Transp. Saf. Secur. 2019, 13, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Chen, C.; Zhang, J.; Gu, X.; Huang, X. Vulnerability Assessment of Urban Road Traffic Systems Based on Traffic Flow. Int. J. Crit. Infrastruct. Prot. 2022, 38, 100536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takhtfiroozeh, H.; Golias, M.; Mishra, S. Topological-Based Measures with Flow Attributes to Identify Critical Links in a Transportation Network. Transp. Res. Rec. 2021, 2675, 863–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.Y.; Lam, W.H.K.; Sumalee, A.; Li, Q.; Li, Z.-C. Vulnerability Analysis for Large-Scale and Congested Road Networks with Demand Uncertainty. Transp. Res. Part A Policy Pract. 2012, 46, 501–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almotahari, A.; Yazici, A. A Computationally Efficient Metric for Identification of Critical Links in Large Transportation Networks. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2021, 209, 107458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almotahari, A.; Yazici, M.A. A Link Criticality Index Embedded in the Convex Combinations Solution of User Equilibrium Traffic Assignment. Transp. Res. Part A Policy Pract. 2019, 126, 67–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagurney, A.; Qiang, Q. A Network Efficiency Measure with Application to Critical Infrastructure Networks. J. Glob. Optim. 2008, 40, 261–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Jia, H.; Luo, Q.; Li, Y.; Yang, L. Identification of Critical Links in a Large-Scale Road Network Considering the Traffic Flow Betweenness Index. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0227474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, J.L.; Novak, D.C.; Aultman-Hall, L.; Scott, D.M. Identifying Critical Road Segments and Measuring System-Wide Robustness in Transportation Networks with Isolating Links: A Link-Based Capacity-Reduction Approach. Transp. Res. Part A Policy Pract. 2010, 44, 323–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenelius, E.; Petersen, T.; Mattsson, L.-G. Importance and Exposure in Road Network Vulnerability Analysis. Transp. Res. Part A Policy Pract. 2006, 40, 537–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohouenou, P.Y.R.; Neves, L.A.C.; Christodoulou, A.; Christidis, P.; Lo Presti, D. Using a Hazard-Independent Approach to Understand Road-Network Robustness to Multiple Disruption Scenarios. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2021, 93, 102672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, K.; Wang, W.; Li, X.; Hua, X.; Chen, S.; Qin, S. Identifying the Critical Road Combination in Urban Roads Network under Multiple Disruption Scenarios. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2022, 607, 128192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, C.U.I.; Qingchang, L.U.; Jianyu, L.I. Key Station Identification of Urban Rail Transit Based on Network Redundancy. China Saf. Sci. J. 2022, 32, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, K.; Wang, W.; Li, X.; Chen, S.; Qin, S.; Hua, X. Cascading Failure in Urban Rail Transit Network Considering Demand Variation and Time Delay. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2023, 630, 129290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, J.; Sun, J.; Zhu, Y.; Jin, H.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, F.; Huang, J.; Wang, X. STP-TrellisNets+: Spatial-Temporal Parallel TrellisNets for Multi-Step Metro Station Passenger Flow Prediction. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2022, 35, 7526–7540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.Z.W.; Liu, H.; Szeto, W.Y.; Chow, A.H.F. Identification of Critical Combination of Vulnerable Links in Transportation Networks—A Global Optimisation Approach. Transp. A Transp. Sci. 2016, 12, 346–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Fu, X.; Liu, Z.; Xu, X.; Chen, A. Performance of Transportation Network under Perturbations: Reliability, Vulnerability, and Resilience. Transp. Res. Part E Logist. Transp. Rev. 2020, 133, 101809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Tang, Y.; Mohmand, Y.T.; Xu, P. Modifying Link Capacity to Avoid Braess Paradox Considering Elastic Demand. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2022, 605, 127951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almotahari, A.; Yazici, A. Impact of Topology and Congestion on Link Criticality Rankings in Transportation Networks. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2020, 87, 102529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, H.K.; Luo, X.W.; Siu, B.W.Y. Degradable Transport Network: Travel Time Budget of Travelers with Heterogeneous Risk Aversion. Transp. Res. Part B Methodol. 2006, 40, 792–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Wang, S.; Xu, X.; Shen, L. Identification of Critical Links Based on the Optimal Reliable Path in Stochastic Traffic Networks. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0301272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di, Z.; Yang, L.; Qi, J.; Gao, Z. Transportation Network Design for Maximizing Flow-Based Accessibility. Transp. Res. Part B Methodol. 2018, 110, 209–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Khani, A. Identifying Critical Links in Transportation Network Design Problems for Maximizing Network Accessibility. Transp. Res. Rec. 2020, 2674, 237–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.; Cheng, L.; Du, M.; Sun, C.; Ma, J.; Ge, H. Charging Station Location Problem for Maximizing the Space-Time-Electricity Accessibility: A Lagrangian Relaxation-Based Decomposition Scheme. Expert Syst. Appl. 2023, 222, 119801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zannat, K.; Choudhury, C.F.; Hess, S. Modeling Departure Time Choice of Car Commuters in Dhaka, Bangladesh. Transp. Res. Rec. 2022, 2676, 247–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gore, N.; Arkatkar, S.; Joshi, G.; Antoniou, C. Modified Bureau of Public Roads Link Function. Transp. Res. Rec. J. Transp. Res. Board 2023, 2677, 966–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Li, D.; Cheng, L.; Lou, X.; Sun, C.; Tang, W. Link Restriction: Methods of Testing and Avoiding Braess Paradox in Networks Considering Traffic Demands. J. Transp. Eng. Part A Syst. 2018, 144, 04017076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Yao, E.; Yang, Y. Degradable Transportation Network with the Addition of Electric Vehicles: Network Equilibrium Analysis. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0184693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, Z.; Xu, X.; Qu, K.; Chen, R.; Chen, A. Travel Time Reliability in Transportation Networks: A Review of Methodological Developments. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 2022, 143, 103866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhao, L.; Hu, X.; Zhao, X.; Wang, H. A Reliability-Based Traffic Equilibrium Model with Boundedly Rational Travelers Considering Acceptable Arrival Thresholds. Sustainability 2023, 15, 6988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Liao, F.; Gao, Z.; Timmermans, H. A Generalized Mean-Variance Metric of Route Choice Model under Travel Time Uncertainty. Transp. A Transp. Sci. 2022, 18, 299–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Cheng, L.; Ma, J. Travel Time Reliability with Boundedly Rational Travelers. Transp. A Transp. Sci. 2018, 14, 210–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, Q.; Cheng, L.; Li, D.; Ma, J.; Sun, C. Stochastic Transportation Network Considering ATIS with the Information of Environmental Cost. Sustainability 2018, 10, 3861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, Q.; Li, M.; Wu, Y. A Reliability-Based Network Equilibrium Model with Electric Vehicles and Gasoline Vehicles. Promet-Traffic Transp. 2024, 36, 83–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, Q.; Cheng, L.; Li, D.; Ma, J.; Sun, C. Traffic Paradox Under Different Equilibrium Conditions Considering Elastic Demand. Promet-Traffic Transp. 2019, 31, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yen, J.Y. Finding the K Shortest Loopless Paths in a Network. Manag. Sci. 1971, 17, 712–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, D.; Zhang, C.; Song, M.; Zhang, H.; Chen, J.; Zhang, K. Analysis of Urban Electric Vehicle Adoption Based on Operating Costs in Urban Transportation Network. Systems 2023, 11, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonett, D.G.; Wright, T.A. Sample Size Requirements for Estimating Pearson, Kendall and Spearman Correlations. Psychometrika 2000, 65, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schober, P.; Boer, C.; Schwarte, L.A. Correlation Coefficients: Appropriate Use and Interpretation. Anesth. Analg. 2018, 126, 1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spearman, C. The Proof and Measurement of Association between Two Things. In Studies in Individual Differences: The Search for Intelligence; Appleton-Century-Crofts: East Norwalk, CT, USA, 1961; p. 58. [Google Scholar]
- Myers, J.L.; Well, A.D.; Lorch, R.F., Jr. Research Design and Statistical Analysis: Third Edition, 3rd ed.; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2010; ISBN 978-0-203-72663-1. [Google Scholar]
- Kurmankhojayev, D.; Li, G.; Chen, A. Link Criticality Index: Refinement, Framework Extension, and a Case Study. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Safe 2024, 243, 109889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, X.; Liu, H.X. Boundedly Rational Route Choice Behavior: A Review of Models and Methodologies. Transp. Res. Part B Methodol. 2016, 85, 142–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Ge, H.; Cheng, R. An Extended Macro Model Accounting for the Driver’s Timid and Aggressive Attributions and Bounded Rationality. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2020, 540, 122988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Zhang, Y.; Hang, J.; Feng, X.; Xie, Z.; Zhang, D.; Yang, Y. CARPG: Cross-City Knowledge Transfer for Traffic Accident Prediction via Attentive Region-Level Parameter Generation. In Proceedings of the 32nd ACM International Conference on Information and Knowledge Management, Birmingham, UK, 21–25 October 2023; ACM: New York, NY, USA; pp. 2939–2948. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Yu, X.; Fei, J.; Jin, X.; Bai, W.; Yao, Z. Regional Traffic Congestion Coordination Control Based on Critical Links. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2024, 647, 129913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, M.; Jiang, X.; Chen, A. Identifying Critical Links Using Network Capacity-Based Indicator in Multi-Modal Transportation Networks. Transp. B Transp. Dyn. 2022, 10, 1126–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, K.; Wang, Z. A Parallel Computing Approach to Solve Traffic Assignment Using Path-Based Gradient Projection Algorithm. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 2020, 120, 102809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almotahari, A.; Yazici, A. Practice Friendly Metric for Identification of Critical Links in Road Networks. Transp. Res. Rec. 2020, 2674, 219–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| UD | TTT | EI | LAD | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Link Rank | UD Value | Link Rank | TTT Value | Link Rank | EI Value | Link Rank | LAD Value |
| 2 | 100 | 2 | + 2500 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 115.87 |
| 4 | 100 | 4 | + 2000 | 4 | 2.5 | 4 | 101.27 |
| 1 | 0 | 3 | 4500 | 3 | 4.5 | 3 | 17.14 |
| 3 | 0 | 1 | 4000 | 1 | 5 | 1 | 2.54 |
| Indicator | Formulation | Variable Description |
|---|---|---|
| LAD | ; . | |
| EI | ; ; is the number of OD pairs. | |
| IS | works when disconnected ODs exist. is the expected total travel time of the road network. is the set of disconnected OD pairs. | |
| TTWBC | ; ; . | |
| TFWBC | . |
| Degradation Levels | OD | Path No. | Sequence of Links | Low-Level Demand | Medium-Level Demand | High-Level Demand | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LAR | Path Flow | LAR | Path Flow | LAR | Path Flow | ||||
| Low-level | 1–3 | 1 | 1–5–7–10–16 | 0.124 | 200 | 0.121 | 328 | 0.120 | 508 |
| 2 | 1–6–13–19 | 0.185 | 0 | 0.121 | 72 | 0.120 | 92 | ||
| 3 | 2–17–7–10–16 | 0.238 | 0 | 0.204 | 0 | 0.196 | 0 | ||
| 4 | 1–5–8–14–16 | 0.458 | 0 | 0.310 | 0 | 0.134 | 0 | ||
| 5 | 1–6–12–14–16 | 0.511 | 0 | 0.320 | 0 | 0.127 | 0 | ||
| 6 | 2–17–8–14–16 | 0.631 | 0 | 0.440 | 0 | 0.217 | 0 | ||
| 4–2 | 7 | 3–5–7–9–11 | 0.123 | 200 | 0.119 | 338 | 0.120 | 305 | |
| 8 | 3–5–7–10–15 | 0.202 | 0 | 0.119 | 62 | 0.135 | 0 | ||
| 9 | 4–12–14–15 | 0.389 | 0 | 0.138 | 0 | 0.120 | 295 | ||
| 10 | 3–5–8–14–15 | 0.579 | 0 | 0.298 | 0 | 0.150 | 0 | ||
| 11 | 3–6–12–14–15 | 0.630 | 0 | 0.307 | 0 | 0.143 | 0 | ||
| Medium-level | 1–3 | 1 | 1–5–7–10–16 | 0.124 | 200 | 0.138 | 340 | 0.185 | 135 |
| 2 | 1–6–13–19 | 0.171 | 0 | 0.138 | 60 | 0.185 | 19 | ||
| 3 | 2–17–7–10–16 | 0.234 | 0 | 0.222 | 0 | 0.191 | 0 | ||
| 4 | 1–5–8–14–16 | 0.436 | 0 | 0.227 | 0 | 0.185 | 123 | ||
| 5 | 1–6–12–14–16 | 0.483 | 0 | 0.229 | 0 | 0.185 | 323 | ||
| 6 | 2–17–8–14–16 | 0.606 | 0 | 0.347 | 0 | 0.190 | 0 | ||
| 4–2 | 7 | 3–5–7–9–11 | 0.124 | 200 | 0.150 | 233 | 0.203 | 163 | |
| 8 | 3–5–7–10–15 | 0.193 | 0 | 0.150 | 3 | 0.203 | 280 | ||
| 9 | 4–12–14–15 | 0.352 | 0 | 0.150 | 164 | 0.203 | 157 | ||
| 10 | 3–5–8–14–15 | 0.545 | 0 | 0.243 | 0 | 0.205 | 0 | ||
| 11 | 3–6–12–14–15 | 0.591 | 0 | 0.245 | 0 | 0.206 | 0 | ||
| High-level | 1–3 | 1 | 1–5–7–10–16 | 0.178 | 168 | 0.384 | 250 | 0.468 | 260 |
| 2 | 1–6–13–19 | 0.178 | 32 | 0.384 | 5 | 0.468 | 14 | ||
| 3 | 2–17–7–10–16 | 0.264 | 0 | 0.385 | 0 | 0.468 | 108 | ||
| 4 | 1–5–8–14–16 | 0.288 | 0 | 0.384 | 75 | 0.468 | 184 | ||
| 5 | 1–6–12–14–16 | 0.300 | 0 | 0.384 | 19 | 0.468 | 27 | ||
| 6 | 2–17–8–14–16 | 0.425 | 0 | 0.384 | 51 | 0.468 | 7 | ||
| 4–2 | 7 | 3–5–7–9–11 | 0.209 | 120 | 0.390 | 81 | 0.466 | 199 | |
| 8 | 3–5–7–10–15 | 0.209 | 6 | 0.390 | 15 | 0.466 | 20 | ||
| 9 | 4–12–14–15 | 0.209 | 74 | 0.390 | 74 | 0.466 | 91 | ||
| 10 | 3–5–8–14–15 | 0.337 | 0 | 0.390 | 3 | 0.466 | 33 | ||
| 11 | 3–6–12–14–15 | 0.350 | 0 | 0.390 | 226 | 0.466 | 257 | ||
| Degradation Levels | LAD | EI | IS | TTWBC | TFWBC | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Link No. | Value | Link No. | Value | Link No. | Value | Link No. | Value | Link No. | Value | |
| Low-level | 11 | 720.13 | 11 | 9.02 | 11 | 7.04 | 11 | 19.42 | 11 | 1107.52 |
| 16 | 562.01 | 13 | 9.78 | 16 | 3.99 | 19 | 17.31 | 5 | 1091.70 | |
| 1 | 491.76 | 19 | 9.78 | 1 | 3.87 | 18 | 15.38 | 7 | 1091.70 | |
| 13 | 457.70 | 16 | 9.81 | 13 | 3.59 | 13 | 14.73 | 13 | 708.26 | |
| 19 | 457.70 | 1 | 9.83 | 19 | 3.59 | 4 | 14.13 | 19 | 708.26 | |
| Medium-level | 11 | 1000.39 | 11 | 7.64 | 16 | 13.45 | 4 | 20.68 | 11 | 843.72 |
| 4 | 802.32 | 16 | 8.19 | 11 | 13.17 | 11 | 19.57 | 4 | 752.00 | |
| 13 | 776.76 | 4 | 8.26 | 4 | 9.52 | 19 | 18.64 | 13 | 689.20 | |
| 19 | 776.76 | 13 | 8.36 | 1 | 9.45 | 13 | 16.75 | 19 | 689.20 | |
| 16 | 733.90 | 19 | 8.36 | 13 | 8.54 | 18 | 16.12 | 5 | 672.60 | |
| High-level | 11 | 1086.35 | 11 | 2.54 | 16 | 168.18 | 13 | 27.97 | 5 | 825.76 |
| 13 | 1073.83 | 13 | 2.87 | 11 | 116.52 | 4 | 26.77 | 1 | 615.09 | |
| 19 | 1073.83 | 19 | 2.87 | 1 | 93.63 | 19 | 24.52 | 4 | 568.10 | |
| 2 | 1047.05 | 14 | 3.25 | 13 | 93.13 | 11 | 23.28 | 14 | 538.78 | |
| 14 | 1032.26 | 4 | 3.42 | 19 | 93.13 | 14 | 22.19 | 7 | 528.74 | |
| Demand Levels | LAD | EI | IS | TTWBC | TFWBC | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Link No. | Value | Link No. | Value | Link No. | Value | Link No. | Value | Link No. | Value | |
| Low-level | 11 | 257.72 | 11 | 5.15 | 11 | 4.28 | 11 | 21.49 | 5 | 1002.06 |
| 13 | 200.25 | 13 | 5.38 | 13 | 2.70 | 4 | 14.02 | 7 | 1002.06 | |
| 19 | 200.25 | 19 | 5.38 | 19 | 2.70 | 5 | 13.05 | 11 | 799.18 | |
| 7 | 193.47 | 7 | 5.39 | 7 | 2.65 | 7 | 12.84 | 1 | 301.85 | |
| 5 | 174.41 | 2 | 5.45 | 5 | 2.16 | 19 | 11.05 | 9 | 301.23 | |
| Medium-level | 11 | 1000.39 | 11 | 7.64 | 16 | 13.45 | 4 | 20.68 | 11 | 843.72 |
| 4 | 802.32 | 16 | 8.19 | 11 | 13.17 | 11 | 19.57 | 4 | 752.00 | |
| 13 | 776.76 | 4 | 8.26 | 4 | 9.52 | 19 | 18.64 | 13 | 689.20 | |
| 19 | 776.76 | 13 | 8.36 | 1 | 9.45 | 13 | 16.75 | 19 | 689.20 | |
| 16 | 733.90 | 19 | 8.36 | 13 | 8.54 | 18 | 16.12 | 5 | 672.60 | |
| High-level | 11 | 2006.56 | 11 | 6.32 | 16 | 76.66 | 10 | 20.83 | 5 | 1665.17 |
| 13 | 1920.29 | 13 | 6.95 | 11 | 53.80 | 11 | 19.66 | 7 | 1237.17 | |
| 19 | 1920.29 | 19 | 6.95 | 1 | 43.10 | 4 | 18.89 | 1 | 1111.02 | |
| 14 | 1781.56 | 4 | 7.82 | 13 | 42.79 | 5 | 17.29 | 16 | 825.57 | |
| 2 | 1763.59 | 14 | 7.99 | 19 | 42.79 | 16 | 15.14 | 11 | 758.70 | |
| Ranking | LAD | EI | IS1 | IS2 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Two-Links | Value | Two-Links | Value | Two-Links | Value | Two-Links | Value | |
| 1 | (2,5) | 1511.86 | (13,14) | 4.18 | (1,11) | 143.87 | (1,2) | 800 |
| 2 | (11,13) | 1425.44 | (14,19) | 4.18 | (1,18) | 132.85 | (3,4) | 800 |
| 3 | (11,19) | 1425.44 | (11,14) | 4.20 | (13,14) | 127.22 | (11,15) | 800 |
| 4 | (2,7) | 1415.45 | (11,13) | 4.28 | (14,19) | 127.22 | (13,16) | 800 |
| 5 | (7,11) | 1415.45 | (11,19) | 4.28 | (2,15) | 97.20 | (16,19) | 800 |
| 6 | (7,18) | 1415.45 | (2,5) | 4.73 | (15,18) | 95.72 | (1,16) | 400 |
| 7 | (10,11) | 1415.45 | (1,11) | 4.80 | (11,13) | 74.59 | (1,17) | 400 |
| 8 | (11,14) | 1393.98 | (11,15) | 5.24 | (11,19) | 74.59 | (3,12) | 400 |
| 9 | (2,13) | 1339.54 | (13,16) | 5.29 | (11,14) | 73.38 | (3,14) | 400 |
| 10 | (2,19) | 1339.54 | (16,19) | 5.29 | (7,13) | 48.53 | (3,15) | 400 |
| 11 | (4,11) | 1332.72 | (1,2) | 5.39 | (7,19) | 48.53 | (5,12) | 400 |
| 12 | (11,16) | 1286.34 | (1,18) | 5.43 | (2,5) | 45.69 | (5,14) | 400 |
| 13 | (4,6) | 1262.99 | (2,15) | 5.55 | (4,16) | 29.27 | (5,15) | 400 |
| 14 | (12,13) | 1262.99 | (7,13) | 5.65 | (4,11) | 28.31 | (6,16) | 400 |
| 15 | (12,19) | 1262.99 | (7,19) | 5.65 | (2,7) | 27.85 | (7,14) | 400 |
| 16 | (2,4) | 1261.89 | (3,4) | 5.67 | (7,11) | 27.85 | (7,15) | 400 |
| 17 | (5,13) | 1261.43 | (15,18) | 5.71 | (7,18) | 27.85 | (9,15) | 400 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tu, Q.; He, H.; Lai, X.; Jiang, C.; Zheng, Z. Identifying Critical Links in Degradable Road Networks Using a Traffic Demand-Based Indicator. Sustainability 2024, 16, 8020. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16188020
Tu Q, He H, Lai X, Jiang C, Zheng Z. Identifying Critical Links in Degradable Road Networks Using a Traffic Demand-Based Indicator. Sustainability. 2024; 16(18):8020. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16188020
Chicago/Turabian StyleTu, Qiang, Han He, Xiaomin Lai, Chuan Jiang, and Zhanji Zheng. 2024. "Identifying Critical Links in Degradable Road Networks Using a Traffic Demand-Based Indicator" Sustainability 16, no. 18: 8020. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16188020
APA StyleTu, Q., He, H., Lai, X., Jiang, C., & Zheng, Z. (2024). Identifying Critical Links in Degradable Road Networks Using a Traffic Demand-Based Indicator. Sustainability, 16(18), 8020. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16188020








