Abstract
The production of municipal solid waste incineration fly ash (MSWI-FA) and municipal sludge (MS) has been increasing annually, raising concerns about proper disposal. In this study, a thermal treatment method with attributes of energy efficiency and complete detoxification was applied to synergistically convert MSWI-FA and MS into precursors for the synthesis of high-strength alkali-activated materials (AAMs). The impact of mass ratios of MSWI-FA and MS on the mineralogy, microstructure, and reactivity of obtained precursors were investigated. The mechanism of alkali activation was deeply studied by characterizing the evolution of reaction products. The strength development of synthesized AAMs was characterized in a one-year time scale, as well as the environmental compatibility. The results revealed that strength, with values ranging from 12.8–33.0 MPa at 3 d, 29.5–44.1 MPa at 28 d and 39.3–54.8 MPa at 365 d. Furthermore, after one year of curing, the release of Ni, Cr, Cu, Pb, Zn, Mn, and Ba from synthesized AAMs into both deionized water and acetic acid were far below the regulatory limits in China. All these contribute to promoting the safe disposal and effective valorization of MSWI-FA and MS.
1. Introduction
The continuous improvement in living standards has led to an increase in the generation of urban domestic waste, posing significant challenges to society and the environment [1]. The per capita waste generation in some cities of China has increased from 0.15 tons/year in 2002 to 0.50 tons/year in 2022 [2]. Currently, the methods for municipal solid waste treatment include anaerobic digestion, composting, incineration, landfilling, and recycling [3]. Landfilling and incineration are the two primary strategies employed for treating municipal solid waste. Incineration, due to its numerous advantages such as low footprint, high reduction capacity, and effective recovery of heat energy, has become a popular technology for waste disposal [4]. Data from the National Statistical Yearbook in 2022 show that the incineration rate of domestic municipal waste has steadily increased from 18% in 2009 to 72% in 2021 [5]. The incineration method complies with the principles of waste reduction, harmlessness, and resource utilization [6]. However, the substantially high amounts of municipal solid waste incineration fly ash (MSWI-FA) generated during the incineration process pose a challenge to the industry [7]. MSWI-FA contains a complex mixture of heavy metals and is enriched with pollutants like dioxins and chlorides [8]. Its leaching concentration exceeds the upper limit of hazardous waste worldwide [9]. Inappropriate treatment methods can have harmful effects on the environment, causing significant damage. Therefore, various ecologically harmless and resource-based disposal processes for MSWI-FA have emerged. The selection of suitable technologies is crucial for the stable operation of power plants for the incineration of domestic waste.
Currently, the most commonly used methods for the treatment of MSWI-FA include stabilization/solidification, followed by landfilling [10]. However, these approaches not only annihilate land resources but also cause long-term pollutant migration. Processes such as cement kiln co-processing [11], high-temperature sintering [12], plasma melting [13], molten salt cyclic thermal treatment [14], the hydrothermal method [15], and low-temperature pyrolysis [16] have gained significant attention. The amount of MSWI-FA used in cement kilns is limited, whereas the hydrothermal treatment technology is still at the laboratory stage, with numerous challenges for its widespread implementation [11]. Currently, heat treatment can stabilize heavy metals and destroy dioxins, making it a hot topic of research [17]. However, heat treatment methods require higher temperatures, which increase energy consumption and processing costs.
In recent years, China has made significant progress in the collection and treatment of domestic sewage in urban and rural regions [18]. Municipal sludge (MS), a by-product of sewage treatment, has become a challenging issue for environmental management, as 50% to 80% of the heavy metals in wastewater end up in the MS during the treatment process. [19,20]. Additionally, MS contains toxic organic compounds, hormones, microplastics, parasites, and pathogenic microorganisms [21]. Inappropriate handling or indiscriminate discharge of MS can disrupt the ecosystem and also pollute the water and soil [19].
Currently, the main disposal methods for MS include landfilling, incineration, composting, and utilization in construction materials. Landfilling leads to the waste of land and risks such as leachate seepage. Incineration is energy-intensive and may produce secondary pollutants. In addition, Elmi et al. [22] noted that the phytotoxicity of heavy metals in MS limits its long-term land utilization. Utilization in construction materials can be transformed into a valuable resource for social production [23]. Statistical data show that the proportion of MS disposal through the construction materials production method in China has been increasing year by year, accounting for only 9.2% in 2009 and rising to 15.9% in 2019 [24]. The proper treatment of MS resources helps in balancing economic growth and protecting the environment. Increasing the utilization rate of MS and enhancing its value contribute to environmental protection and safeguards the health of residents.
Alkali-activated materials (AAMs) are substances that use alkali activators to catalyze the hydration reaction of mineral-rich materials [25,26]. These materials have gained popularity in the construction industry, due to their numerous advantages. Compared to the production of cement, the production of AAMs offers several advantages, such as minimal consumption of natural resources, production at normal temperatures, utilization of a wide range of solid wastes, and efficient solidification of heavy metals [27,28]. The current focus on environmental and climatic concerns is driving the need for more efficient and sustainable materials and production processes to reduce the extraction of natural resources, processing emissions, and waste generation [29]. Precursors from different sources can be used to prepare AAMs. Industrial by-products such as fly ash from coal combustion or slag from ironmaking are commonly used [30,31]. Recently, a wide range of municipal and industrial by-products are expected to be utilized, such as ash from incineration of municipal waste, MS, and wastes from construction industry, agriculture, and mining [32,33].
Although the use of MSWI-FA in the preparation of AAMs can effectively immobilize heavy metals [34,35], the efficiency of utilization of MSWI-FA remains limited. AAMs based on MSWI-FA possess lower mechanical properties, as compared to other industrial waste, necessitating the requirement of additional phases rich in silica or alumina to enhance their reactivity [36,37]. MS faces similar challenges, since some proportions of its SiO2, Al2O3, and CaO exist in the form of silica and alumina crystals, which impact the depolymerization of Si and Al tetrahedra [38]. Additionally, conventional pretreatment methods struggle to eliminate dioxins from MSWI-FA, with only heat treatment proving to be effective. This raises concerns about the potential leakage of dioxins from AAMs [39]. This can pose significant risks of environmental pollution. To address these concerns and minimize the adverse effects during the preparation of AAMs from solid waste or hazardous waste, this study proposes a pre-thermal treatment method for MSWI-FA and MS.
According to previous studies, heat treatment of MSWI-FA and MS synergistically leads to low energy consumption [40]. Collaborative processing can lower the temperature of heat treatment and reduce energy consumption. Moreover, heat treatment also decreases the levels of chlorine and heavy metals [41], which is advantageous, since excessive chlorine can corrode the equipment and negatively impact the performance of alkaline-active materials [42,43]. The residue remaining after heat treatment of MSWI-FA and MS contains elements like Ca, Si, Al, and Fe, akin to auxiliary bonding materials [44,45]. Exploitation of this resource for the production of alkaline-active materials not only reduces the dependence on mineral resources but is also cost-saving. Studies have shown that the mixing ratio of the above solid waste can reach 20–70% [46]. The annual production of MSWI-FA in China has exceeded 10 million tons [47],;thus, it can generate more than approximately 14 million tons/year of AAMs. Furthermore, this approach effectively solves the problem of the inability of alkaline-active materials to eliminate toxic and harmful substances (such as dioxins) from MSWI-FA, thereby mitigating the risk of environmental pollution.
Based on previous research, this paper reports the optimization of the heat treatment process in the preparation of highly active precursors from solid products. Furthermore, it investigates the possibility of the utilization of MSWI-FA and MS for the production of alkaline-activated materials. This study also delves into the phase transformation, microstructure, distribution of elements, and leaching behavior of heavy metals, providing new insights and potential solutions for the utilization of MSWI-FA and MS.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
MSWI-FA was obtained from a municipal solid waste incineration facility located in Hunan. The MS, with a moisture level of 75.9%, was procured from a wastewater treatment facility in Hubei, after centrifugal separation. The chemical composition was analyzed using X-ray fluorescence (XRF) equipment from the S4 Pioneer series (Brooke, Germany). The findings are presented in Table 1, which shows that MSWI-FA contained high levels of CaO, SO3, and Cl, accounting for 58.44%, 7.08%, and 15.31%, respectively. The main components in the MS were SiO2, Al2O3, and Fe2O3, in proportions of 49.76%, 15.47%, and 12.84%, respectively.

Table 1.
Chemical composition of MSWI-FA and MS /%.
The phase compositions of MSWI-FA and MS can be studied from their XRD patterns in Figure 1. MSWI-FA showed a complex mixture of phases, primarily calcium and chloride salts, such as CaCO3 and CaSO4, NaCl, KCl, CaClOH, and a small amount of SiO2. In contrast, the phase composition of MS was relatively simple, mainly consisting of SiO2 and a small amount of KAl2(AlSi3O10)(OH)2.
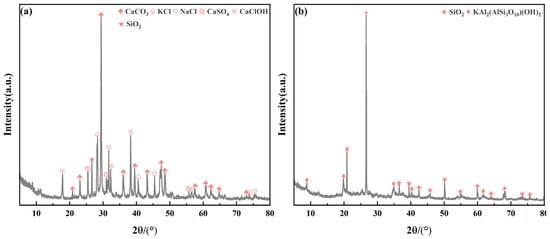
Figure 1.
XRD patterns of raw material: (a) MSWI-FA; (b) MS.
Figure 2 presents the SEM images of MSWI-FA and MS. In Figure 2(a1), the particles of MSWI-FA appeared predominantly spherical. Figure 2(a2,a3) provided a closer morphological view of a single spherical particle of MSWI-FA, revealing its loosened interior structure with obvious agglomeration. The MSWI-FA sample displayed a flake-like and spherical micromorphology. The micromorphology of MS in Figure 2(b1) showed noticeable agglomeration of particles and denser composition, as compared to MSWI-FA. The magnified view (Figure 2(b2,b3)) showed the accumulation and aggregation of numerous lamellar crystals in layers.

Figure 2.
SEM images of raw materials: (a1–a3) MSWI-FA; (b1–b3) MS.
TG-DSC analyses of MSWI-FA and MS raw materials were conducted to study their thermal weight-loss processes, and the results are presented in Figure 3. Figure 3a shows the thermal weight-loss process of MSWI-FA in the presence of air, which could be categorized into three stages. The first stage, with 3.3% weight loss, occurred between 30 and 530 °C and involved the elimination of water (adsorbed water and crystalline water) and the decarboxylation of organic matter. The second stage occurred between 530–738 °C, showing a significant endothermic peak at 695 °C. It was attributed mainly to the decomposition of carbonate, resulting in a total weight loss of 19.8%. The third stage, with weight loss of 9.3%, occurred in the range of 738–1200 °C and was primarily characterized by the volatilization of metal chlorides with low boiling points. As seen in Figure 3b, the thermal weight loss of MS in the air atmosphere can also be divided into three stages. The first stage was characterized by an endothermic peak between 30 and 200 °C, mainly due to the removal of moisture from MS, resulting in a weight loss of 6.5%. The DSC curve showed an exothermic peak at 327 °C, corresponding to the second stage, which was primarily attributed to the combustion of the organic matter and fixed carbon in MS. The weight loss in this stage was 19.6%. The third stage occurred in the temperature range of 600–1200 °C. Only a small endothermic peak was observed at around 1150 °C in the DSC curve, possibly due to an endothermic reaction or the decomposition of different components in the MS. The weight loss in this stage was 1.5%, which was low. Overall, the weight loss of MSWI-FA during the thermal process in the temperature range of 30–1200 °C was slightly higher than that of MS.
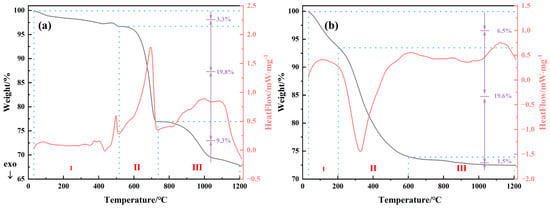
Figure 3.
TG-DSC curves of the raw materials: (a) MSWI-FA; (b) MS.
2.2. Preparation of the Precursor
According to the “Determination of fusibility of coal ash” (GB/T219-2008), the characteristic temperatures for MSWI-FA, MS, and their mixtures were assessed using the triangular cone test method. Figure 4 shows the flow temperature (FT) of MSWI-FA alone was remarkably high, reaching 1490 °C. Additionally, the FT of MS was slightly lower than that of MSWI-FA, but still reached 1325 °C. The addition of different amounts of MS showed a decreasing and then increasing trend in FT. Notably, for 60% of MS, the FT reached its lowest point at 1211 °C. Considering the melting characteristics of the mixture and to achieve energy conservation through temperature reduction, the temperature for the precursor preparation was set at 1200 °C.
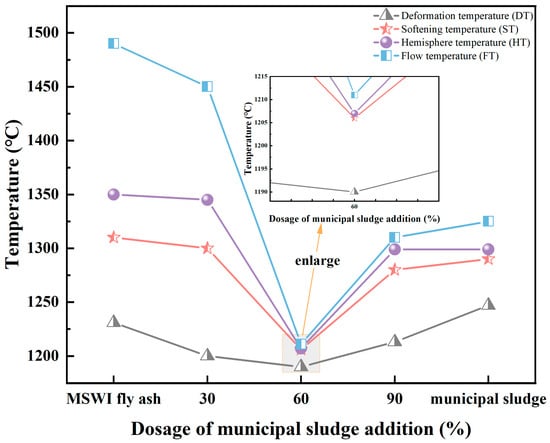
Figure 4.
Characteristic melting temperatures of the raw materials and their mixtures.
The specific method for the preparation of the precursor was as follows: Firstly, dried MSWI-FA and MS were weighed according to their proportions and mixed in a mortar for 20 min. Then, the mixture was transferred to a muffle furnace for calcination, and the temperature gradually increased from room temperature to 1200 °C at a rate of 10 °C/min. It was then heated at 1200 °C for 30 min. After completion of the roasting process, the sample was promptly removed and immersed in a stainless steel bucket filled with water for rapid cooling. Following this, the cooled calcined product was dried to obtain the precursor.
2.3. Reactivity Test
The reactivities of the obtained precursors were determined by the strength activity index method. In brief, 42.5 R Portland cement was used for the preparation of the mortar specimen. The control sample (sample ID: control) was prepared using a water-to-ordinary Portland cement (OPC)-to-sand mass ratio of 0.5:1:3.25%. The OPC (by weight) was replaced by the precursor to prepare the test specimens, which were labeled as OPC-MS-0.3, OPC-MS-0.6, and OPC-MS-0.9, based on the proportion of the precursor.
Homogeneous mixtures were obtained by mixing weighed materials in a planetary mixer for 5 min, followed by casting these mixtures into molds with dimensions of 40 × 40 × 160 mm3 and vibrating them for 2 min to remove entrapped air bubbles. The molds were then covered with a glass plate and subjected to curing in a box at 20 °C and 100% relative humidity (RH). After 24 h of curing, the samples were demolded and stored under water prior to measurement of strength.
2.4. AAM Synthesis and Strength Measurement
The activator used in the synthesis of AAMs was a sodium silicate solution containing 13.7% SiO2, 9.5% Na2O, and 76.8% H2O. The modulus, i.e. molar ratio of SiO2/Na2O, was 1.5. The precursors were thermally treated MSWI-FA and MS in different mass ratios. To synthesize AAMs, each precursor prepared in Section 2.2 was combined with an activator and mixed for 5 min. The mass ratio of solution-to-precursor was 0.45 for all mixtures. Both the activator modulus and solution-to-precursor ratio were determined on the basis of extensive pre-tests [48,49]. The main focus was on the micro-, mechanical, and environmental properties of the obtained AAMs; the evaluation of technological advancements in thermal treatment of MSWI-FA and MS; and the feasibility of converting thermal products into cementitious materials. Table 2 presents the specific mixing proportions. After mixing, the pastes were poured into molds having dimensions of 40 × 40 × 40 mm³ and then vibrated for 2 min to eliminate the trapped air bubbles. Thereafter, the casted pastes along with the molds were covered with glass plates and placed in a curing box set at 20 °C and approximately 100% relative humidity for 24 h. The samples were then demolded, wrapped in PE foil, and stored at 20 °C till further testing.

Table 2.
Mixing proportions of AAM mortars.
The compressive strengths of the synthesized AAMs were measured and documented after aging for 7, 14, 28, 90, 180, and 365 days. A constant force of 2.4 kN/s was applied during the measurement of strength, and at least three samples from each set were measured.
2.5. XRD and FTIR Analyses
X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis was used to determine the mineral compositions of the raw materials MSWI-FA and MS after thermal treatment and the synthesized AAMs. In the case of AAM pastes, the samples were crushed and milled at specific time intervals. At an early stage, the chemical reaction between the precursor and activator could be continuous and extensive. Thus, crushed samples (with particle sizes less than 1 mm) were immersed in anhydrous ethanol to arrest the alkali activation process, according to the procedure documented in the RILEM TC-238 method [50,51]. The resulting grains were then dried at 40 °C, ground to a less-than-0.074 mm particle size, and further analyzed by XRD.
The XRD patterns of all the samples were acquired using an X’Pert Pro Diffractometer (PANalytical, Netherlands) in the theta-two theta geometry and 2θ range of 5–80°. The X-rays from a CuKα source were produced from a tube operating at 40 mA and 40 kV. More information regarding the procedure for data analysis is available in an earlier report [51,52].
FTIR spectroscopy was employed to determine the chemical groups in the synthesized geopolymer gel in this study. The analysis was conducted on a NEXUS 670 (Nicolet, MN, USA) spectrometer in the absorbance mode. The slurry was prepared and treated following the same procedure as that described for XRD analysis. FTIR absorption spectra were recorded in the range of 4000–400 cm−1, with a sensitivity of 2 cm−1.
2.6. SEM-EDS Measurement
Morphological characterization of the AAM paste and its precursor was conducted using the TESCAN MIRA3 scanning electron microscope (SEM). Prior to SEM analysis, a small amount of the fractured sample from the AAM paste was dried under vacuum at 40 °C for 24 h. Both the precursor and paste were sputter coated with gold to improve the conductivity. Additionally, EDS maps were generated to quantitatively map individual elements in specific areas. The selection of these areas was guided by backscattered electron (BSE) images, which provided clear contrast based on chemical composition. The accelerating voltage for the analysis was set at 20 kV.
2.7. Leaching of Synthesized AAMs
Leaching of heavy metals (Ni, Cr, Cu, Pb, Zn, Mn, Ba) from synthesized AAMs was characterized according to HJ/T300-2007 and HJ 557-2010. Briefly, the AAM pastes, after curing for 28 d, were crushed and transferred to a 2 L PE bottle with a screw cap and an inner cap. The bottle was then filled with acetic acid solution to obtain a pH of 2.64. The mass ratio of acetic acid solution to crushed paste was 20:1, in which the intimal water content of AAM pastes was considered. The bottles were then fixed in a device and subjected to a rotary speed of 30 rpm at 25 °C for 18 h. The leachate was filled, and concentrations of above heavy metals were determined by ICP-MS. After testing in an acidic condition, the leaching experiments were also conducted in deionized water, wherein the mass ratio of deionized water to crushed paste was 10:1. The leaching of heavy metals from the samples after curing for one year was also studied to evaluate the long-term environmental compatibility of the obtained AAMs. Blank tests were also conducted, in which no AAM paste was added in the PE bottle. Each proportion of AAM mix was tested two times; i.e., two individual samples in each system were tested.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Physiochemical Property of Precursors
Figure 5 presents the XRD patterns of MSWI-FA and MS mixtures in different proportions, after subjecting them to heat treatment at 1200 °C with a 30-min heat retention period. When the MS doping amount was small (30%), the mixture had a higher Ca content. The predominant crystalline phase observed after heat treatment was Ca2Al2SiO7, along with certain amounts of Ca12Al14O33 and Ca2SiO4. Combining Figure 1 and Figure 3, it can be seen that before 800 °C (the second stage in Figure 3a), CaCO3 in MSWI-FA decomposes, providing CaO that reacts with MS. The reactions that occur are as follows:
CaCO3 →CaO +CO2
2CaO + SiO2 + Al2O3 → Ca2Al2SiO7
12CaO + 7Al2O3 → Ca12Al14O33
2CaO + SiO2 → Ca2SiO4
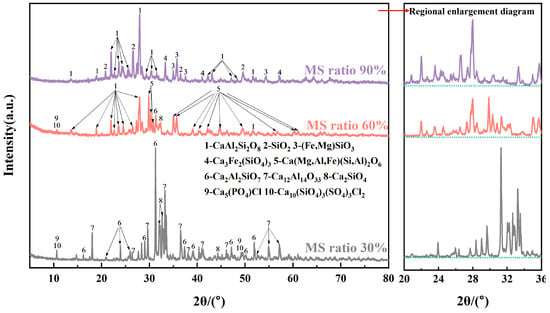
Figure 5.
XRD patterns of mixtures with different ratios of MS after heat treatment.
Additionally, due to the higher Cl content in MSWI-FA and the higher P content in MS, small quantities of Ca5(PO4)Cl and Ca10(SiO4)3(SO4)3Cl2 were present in the product [53]. As the MS proportion increased (60%), the amounts of Si, Al, and Fe in the mixture also increased, which caused a change in the main crystal phase to CaAl2SiO8 and Ca(Mg,Al,Fe)(Si,Al)2O6 after heat treatment. When the MS proportion reached 90%, the primary mineral phase observed in the mixture after heat treatment was CaAl2Si2O8, with some amount of unreacted SiO2. As the proportion of MS increased, the Ca content in the mixture decreased, while the Si, Al, and Fe contents continued to increase, which led to the formation of Fe-containing phases like (Fe,Mg)SiO3 and Ca2Fe2(SiO4)3. The above reactions are as follows:
CaO + SiO2 + Al2O3 → CaAl2SiO8
Fe2O3 + MgO + SiO2 → (Fe,Mg)SiO3
2CaO + 3SiO2 + Fe2O3 → Ca2Fe2(SiO4)3
CaO + SiO2 + Al2O3 + Fe2O3 + MgO → Ca(Mg,Al,Fe)(Si,Al)2O6
Overall, when the MS proportion was 30%, the crystallinity of the mixture improved after heat treatment. However, as the MS content increased to 60% and 90%, the crystallinity decreased. In the range of 20° to 35°, a broad peak was noticed, indicating an increase in the disorderliness of the atomic arrangement in the material. At this point, the mixture contained a certain amount of amorphous phase.
The SEM images of MSWI-FA and MS mixtures in various proportions after heat treatment at 1200 °C for 30 min are presented in Figure 6. In Figure 6a, the mixture appeared agglomerated after roasting but still relatively loose, with dispersed particles. Upon magnification, rod-shaped and small block crystals could be observed. As the amount of MS increased (Figure 6b,c), the mixtures became denser after roasting, indicating increased consolidation of the raw materials and clear signs of partial melting. Upon magnification, the internal grain boundaries appeared blurred, revealing smooth, glassy regions and a few columnar crystals. Overall, when the content of MS was relatively low (30%), its reactivity was lower, while at MS contents of 60% and 90%, its reactivity increased. According to the research by Yuyang Long et al [54], an appropriate ratio of CaO, SiO2, and Al2O3 could reduce the temperature required for heat treatment. These findings were consistent with the melting temperatures observed in Figure 4 and the distinct broad peak in Figure 5.
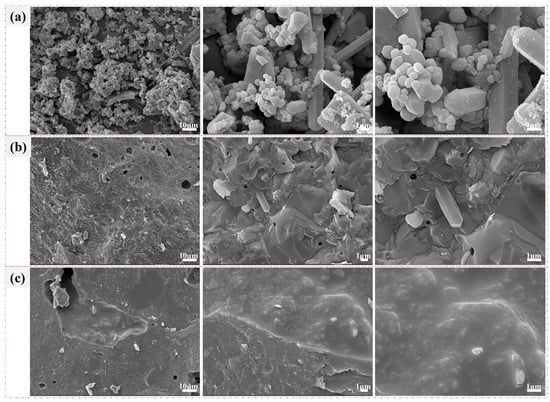
Figure 6.
SEM images of mixtures with different ratios of MS after heat treatment: (a) 30%; (b) 60%; (c) 90%.
In order to further obtain a clear picture of the phase transformation and distribution of elements during heat treatment, EDS analysis of the roasted mixture was performed, and the results are shown in Figure 7. When the MS proportion was 30% (Figure 7a), the main elements at Point 1 were O, Ca, Si, P, S, and Cl, while the main elements at Point 2 were O, Ca, and Si. This information when combined with the XRD phase analysis in Figure 5 showed that the main phases present were Ca10(SiO4)3(SO4)3Cl2, Ca5(PO4)Cl, and Ca2SiO4. Moving on to Figure 7b, the main elements observed were O, Ca, Si, Fe, Al, and a small amount of Mg. The contents of elements at this point were consistent with Ca(Mg, Al, Fe)(Si, Al)2O6 and CaAl2SiO8 in Figure 5. The two phases corresponded to each other, and Point 2 represented the region of molten vitrification, which indicated that part of CaAl2SiO8 melted to form an amorphous phase.
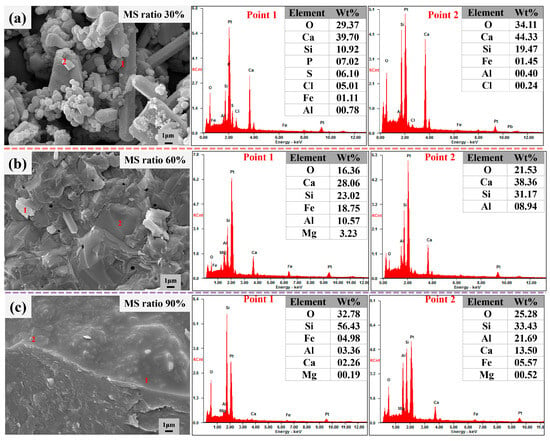
Figure 7.
EDS of mixtures with different ratios of MS after heat treatment.
When the MS content increased to 90% (Figure 7c), a melting zone could be observed in the microstructure. The main elements at Point 1 were O (32.78%) and Si (56.43%), accounting for more than 89% of the composition, suggesting that the main phase was SiO2. At Point 2, the main elements detected were O, Si, Al, and Ca, with small amounts of Fe and Mg. The analysis of Figure 5 indicated that the main phases at this time were CaAl2Si2O8 and a small amount of (Fe, Mg) SiO3. These findings were consistent with the results from Figure 7b.
3.2. Reactivities of Precursors
The strength activity indexes of precursors prepared in this work are presented in Table 3. The compressive strengths of all the samples increased on prolongation of curing time. Though OPC-MS-0.9 after curing for 3 d and 7 d showed lower strength, it showed higher strength than the control sample after 28 d of curing. This indicated that the reaction rate of MS-0.9 increased with time. This was reflected by the obvious increase in the strength activity index, which was even higher than 1 after 28 d of curing. The high reactivity of MS-0.9 contributed to the improvement in strength of the OPC-MS-0.9 mortar.

Table 3.
Compressive strength and strength activity indexes of samples.
OPC-MS-0.6 exhibited strength comparable with that of OPC-MS-0.9 after 3 d and 7 d of curing, suggesting similar early reactivity. However, the sample containing MS-0.6 after 28 d had strength lower than that of its MS-0.9 counterpart. In contrast, the compressive strength was obviously lower than that of the control sample for OPC-MS-0.3 for all curing times. This indicated that the hydration of the cement could not compensate for the dilution effect caused by the replacement of the precursor. Meanwhile, the strength activity index of MS-0.3 on day 28 was higher than 0.75, the mass ratio of cement in solid binder, suggesting that it can be used as supplementary cementitious material.
3.3. Alkali Activation Mechanisms
Figure 8 shows the XRD patterns of AAMs after 28 days of curing. The figure shows that with 30% of MS doping, the main phase observed was Ca12Al14O33, along with Ca2Al2SiO7, Ca3Mg(SiO4), and Ca3Si2O7. When compared to the sample before activation (Figure 5), the content of Ca2Al2SiO7 after activation decreased, whereas the proportion of Ca12Al14O33 increased, indicating that more of Ca2Al2SiO7 was converted to Ca12Al14O33. With higher doping amounts of MS (60% and 90%), the main crystal phases observed were (Ca, Na)(Si, Al)2Si2O8 and Ca2Al2SiO7. Overall, the amorphous hump after activation increased as the MS proportion increased. This was consistent with the changes in Si and amorphous phase contents in the precursors.
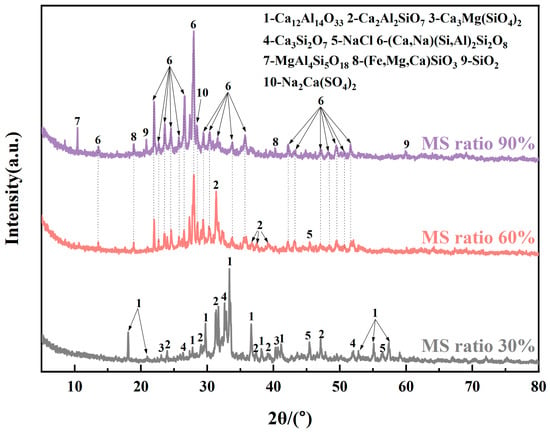
Figure 8.
XRD patterns of AAMs after 28 days of curing.
Figure 9 shows the microstructures of AAMs after 28 d of curing. In Figure 9a, the sample with 30% MS showed numerous cracks, with massive particles seen on magnification. These particles were interconnected by gel-like substances, resulting in their aggregation and stacking in large quantities. As depicted in Figure 9b, with the increase in MS content, the cracks in the sample decreased. Magnification showed a significant number of rod-like crystals and some gel materials. Furthermore, in Figure 9c, when the MS content was further increased to 90%, the surface cracks of the sample decreased further. The magnified image showed a substantial amount of gel. Additionally, short columnar crystals were enveloped by the gel, resulting in an overall highly dense material structure.
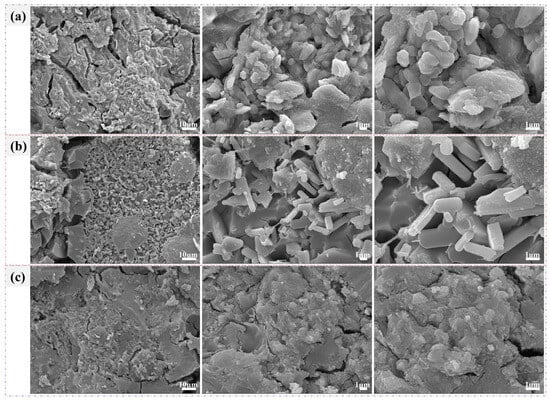
Figure 9.
SEM images of AAMs with different ratios of MS after 28 d of curing: (a) 30%, (b) 60%, and (c) 90%.
The above results indicated that when the content of MS in the precursor was relatively low, the internal linkages within the activated AAMs were weak. As the amount of MS added increased, the internal particles interconnected through a gel-like substance, forming a large number of aggregations and accumulations, resulting in a more complete and dense microstructure. This highlighted the good reactivity of the precursor with 90% MS content, demonstrating excellent polymerization effects and gelation activity.
To obtain further insight into the phase transition and distribution of elements during the alkali-activated process, EDS analysis was conducted at different points on various AAM samples. The results are presented in Figure 10 and Table 4, and the phase composition analysis was performed based on Figure 10.
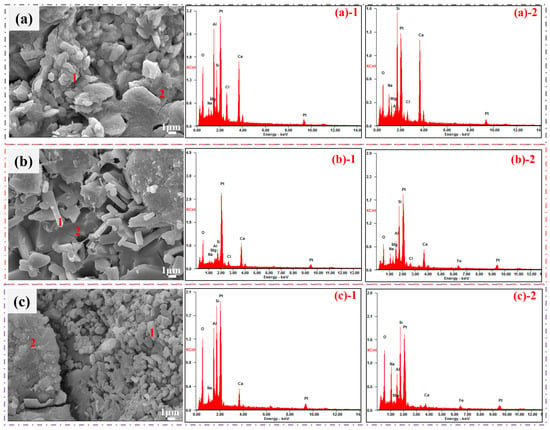
Figure 10.
EDS mapping of elements of AAMs with different ratios of MS after 28 d of curing: (a) 30%, (b) 60%, (c) 90%.

Table 4.
Chemical compositions at selected points as shown in Figure 10 (weight%).
The main elements at Point (a)-1 were O, Ca, and Al, whereas the main elements at Point (a)-2 were O, Ca, and Si, with very little amount of Al. Combining these results with XRD analysis showed that the main phases at these points were Ca12Al14O33 and Ca3Si2O7, respectively.
As shown in Figure 10b, the main elements at Point (b)-1 were O, Ca, and Si, and certain amounts of Al and Na. Its main phase could be (Ca,Na)(Si,Al)2Si2O8. The main elements at Point (b)-2 were O, Si, Ca, Fe, and Al, so the main phases could be (Ca,Na)(Si,Al)2Si2O8 and (Fe,Mg,Ca)SiO3. At all the above points, certain amounts of Na and Cl were present, which corresponded to the diffraction peak of NaCl in the XRD patterns.
The main elements at Point (c)-1 were O, Si, Ca, Al, and Na, and its phase was (Ca,Na)(Si,Al)2Si2O8. The main elements at Point (c)-2 were O, Si, Na, Al, and Fe, while the Ca content was relatively low. The main phases included Na-enriched (Ca,Na)(Si,Al)2Si2O8 and (Fe,Mg,Ca)SiO3.
Figure 11 shows the FTIR spectra of AAMs prepared using different precursor systems to investigate changes in their molecular structures and chemical bonds. The spectral peaks in the range of 460–760 cm−1 in all alkali-activated samples were attributed to the in-plane bending vibrations of the Si-O and Al-O bonds, as well as the bending vibrations of the Si-O-Si and O-Al-O bonds [55]. It was observed that the center of the peak between 979 cm−1 and 1003 cm−1 was shifted towards a higher wavenumber, with an increase in the amount of MS proportion. The peak seen initially at 979 cm−1 shifted to 996 cm−1 and finally reached 1003 cm−1. These peaks were attributed to the vibrational stretching modes of asymmetric silicates (Si-O-Al) and silicon–oxygen bonds (Si-O-Si) [56]. As compared to AAM-30%MS and AAM-60%MS, AAM-90%MS had broad spectral peaks, which indicated an increase in amorphous features [57,58]. This result was consistent with the results in Figure 5.
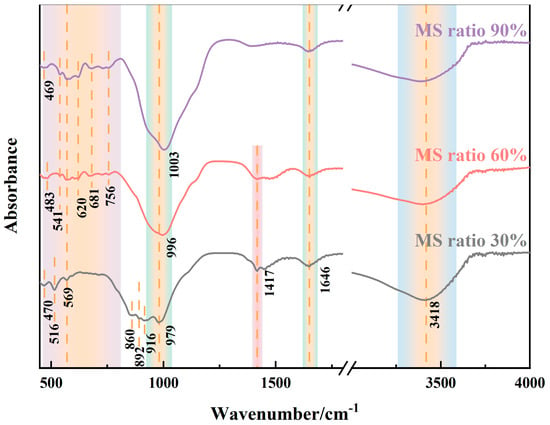
Figure 11.
FTIR spectra of AAMs after 28 d of curing.
The peaks at 1646 cm−1 and 3418 cm−1 in the spectra could be assigned to the H-O-H bending vibrations and Al-OH stretching vibrations, respectively. These peaks could either be due to weak bonds formed within the structure during water quenching [59], or they may be the O-H bending vibrations in [Al(OH)6]3- and the stretching vibrations of Al-OH groups [60]. The small peak at 1417 cm−1 was consistent with the asymmetric stretching vibrations of the O-C-O bond of CO32−, caused due to the atmospheric carbonization on the sample surface, which was only found in the case of AAM-30%MS and AAM-60%MS. This could be ascribed to the higher internal Ca content [56]. Small and sharp peaks at 860 cm−1, 892 cm−1, and 916 cm−1 corresponded to the symmetric vibrations of Al-O-Si or Si-O-Si [61]. As per the Beer–Lambert law [62], higher absorbance bands indicated increased product quantities. The Si-O bands’ intensity showed a gradual rise with MS incorporation. Additionally, specific Si-O vibration bands shifted to higher wavenumbers, indicating a formation of a more interconnected gel, consistent with XRD findings.
3.4. Mechanical Properties of Synthesized AAM Mortar
Figure 12 shows the evolution of compressive strength in synthesized AAM pastes. The strength was significantly influenced by the formulation of the binder. AAMs produced from MS-0.6 and MS-0.9 achieved comparable strength even when cured for shorter periods (7, 14, and 28 d), which were higher than that of the counterpart synthesized using MS-0.3. This could be due to the differences in reactivity and formulation.
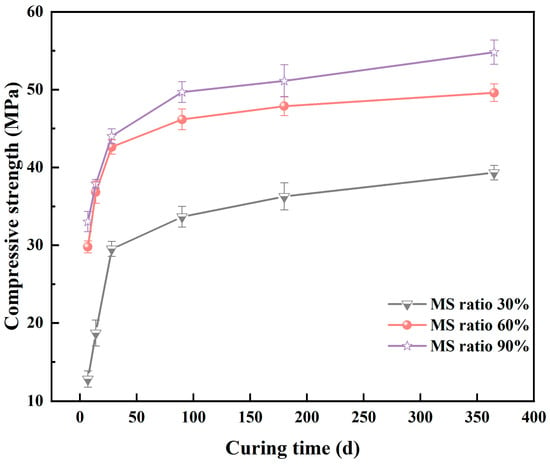
Figure 12.
Compressive strengths of synthesized AAMs mortars.
As described in Section 2.2, larger amounts of anorthite (CaAl2Si2O8,) pyroxene (Ca(Mg,Al,Fe)(Si,Al)2O6), and calcium aluminosilicate (Ca2Al2SiO7) were formed in the precursor after calcination at 1200 °C. These minerals played a role in the alkaline activation process and contributed to the strengthening of the products [63]. Meanwhile, the compressive strength increased on addition of MS to the precursor. For the same roasting process, AAMs prepared by adding 60% and 90% MS exhibited compressive strengths approximately 1.4–2.6 times higher than those prepared with 30% MS. As the MS content was increased, there was a decrease in the molar ratio of CaO/SiO2 from 1.96 to 0.18. Although calcium was not essential for the formation of geopolymer products, some studies suggested that a reduction in the CaO content improved the compressive strength and processability of AAM [64]. These findings were consistent with the results presented in Section 3.1 (reactivity). Additionally, Figure 4 and Figure 5 demonstrated that an increase in the amount of MS could effectively lower the FT of the mixture, thereby enabling the generation of a greater amount of amorphous phase at the same preparation temperature. In conclusion, appropriate proportions of MSWI-FA and MS could reduce the temperature required for the preparation of the precursor and minimize energy consumption.
In all samples, the strength increased with an increase in the curing period. This was particularly obvious for shorter periods of curing. The compressive strength increased from 12.8–33.0 MPa for a 3 d cured product to 29.5–44.1 MPa for a 28 d cured product. Further extension of curing time also contributed to the enhancement of compressive strength, but to little extent. After one year of curing at 25 °C, the compressive strength of the obtained AAMs reached 39.3–54.8 MPa. This was similar to the results of alkali-activated MSWI-FA or metakaolin geopolymers [65]. In other studies [40], the long-term strength evolution of MSWI-FA and metakaolin geopolymer were thoroughly studied and correlated with gel chemistry. The effect of curing time was more significant for AAMs prepared with the precursors of lower reactivity, due to the minute dissolution and gelation of reactive components. Long-term curing was necessary to achieve a considerable reaction degree. In contrast, precursors with high reactivity (such as metakaolin and granulated ground blast furnace slag) normally speed up the alkali activation, resulting in high strength of hardened mixtures early on [52].
Notably, the samples for strength measurement in this work were prepared and cured at ambient temperature, and elevated temperature curing was not required to achieve considerable strength. Based on the properties of early aging and long-term strength, the synthesized AAMs, in particular those with MS ratios of 60% and 90%, could be used for a wide range of common construction projects.
3.5. Environmental Compatibility
The results of leaching of Ni, Cr, Cu, Pb, Zn, Mn, and Ba from AAMs produced using thermally treated MSWI-FA and MS, with the sample IDs being AAM-0.3, AAM-0.6, and AAM-0.9, are presented in Figure 13.
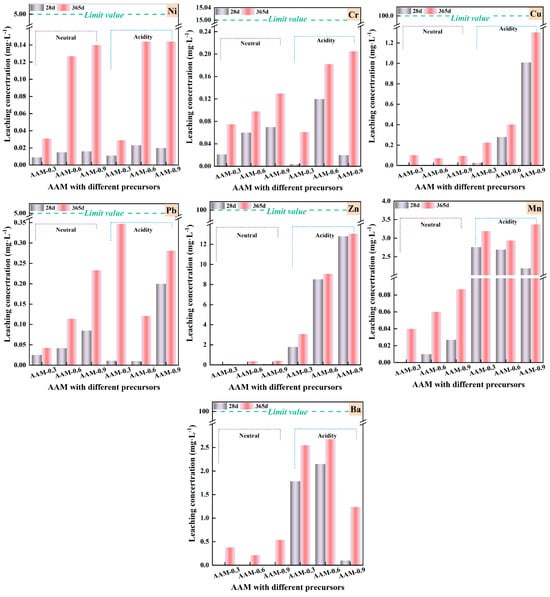
Figure 13.
Leaching toxicity of AAM produced from thermally treated MSWI-FA and MS.
It was evident that the release of the above metals from AAMs into the liquid, both deionized water and acetic acid, was very low. Even after 365 d of curing, only limited amounts of heavy metals were released into the leachate. For example, Zn, with the highest concentration among studied elements of 13.046 ppm, had a concentration far below the threshold.
It could be inferred from Figure 13 that higher amounts of heavy metals were detected when acetic acid was applied. In literature [66], the influence of leachate pH on the leaching characteristics of heavy metals from geopolymers was investigated. For most of the heavy metal elements, the leached amounts were maximum in an extremely acidic pH, particularly pH <2. Zn, Pb, Mn, and Ba were leached as cations in high concentrations under extremely acidic conditions, and their concentrations progressively decreased as the pH increased. The primary controlling factor was the low solubility of components containing these elements in alkaline conditions [67]. Typically, these elements were effectively immobilized within AAM [68,69]. Research [66] showed that Cu and Ni exhibited amphoteric leaching behavior, whereas Cr was released as anions. In the former case, the concentration increased in both acidic and alkaline conditions. Engelman et al. [70] stated that hydrous ferric oxide (HFO) and dissolved organic carbon (DOC) had significant influence on the leaching of Cu and Ni from cementitious materials. For elements that leached in their oxyanionic forms, the maximum leaching concentration was observed under the most acidic conditions, as well as the natural pH of the material. Natural pH refers to the pH value of the mixture containing only AAM grains and deionized water, without the addition of acidic or alkaline chemicals. This refers to Cr, which has the tendency to form oxyanions. The concentrations of Cr in acetic acid solution and deionized water, shown in Figure 13, were comparable, and they could be roughly considered to be the maximum releases from synthesized AAMs. All these demonstrated the environmental compatibility of the AAMs produced from MSWI-FA and MS in this work.
4. Summary and Conclusions
In this work, MSWI-FA and MS were thermally treated to prepare precursors for environmentally compatible AAMs. The influence of the mass ratio of MSWI-FA and MS on the phase composition of the precursor, reactivity, compressive strength, microstructure, reaction products, and environmental compatibility of the synthesized AAMs was studied. The following conclusions were drawn:
(1) When the MS addition was 60% and 90%, the microstructure of the prepared precursors exhibited greater densification, and areas of partial melting were visible, with the main phase composition being anorthite (CaAl2Si2O8).
(2) The strength-activity indexes of the precursor prepared in this work indicated that as the proportion of MS increased, the reaction activity index significantly increased. High reactivity contributed to enhancing the strength of the synthetic AAM mortar. After 28 days, AAMs with the addition of 90% MS exhibited the highest compressive strength of 44.1 MPa, which further increased to 54.8 MPa after 365 days.
(3) After 365 d of solidification, the amounts of heavy metals released from AAM into liquids, both deionized water and acetic acid, were very low. The AAMs produced in this work were environmentally compatible.
The results of this study confirmed the feasibility of preparing AAMs with MSWI-FA and MS. It could serve as a building material in the construction industry, offering an alternative to Portland cement. Additionally, its good environmental compatibility enables it to resist the erosion of acidic environments.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Z.S. and J.X.; data curation, Z.J. and X.L.; investigation, X.L. and M.G.; methodology, J.X.; supervision, X.F.; writing—original draft, Z.S. and J.X.; writing—review and editing, Z.S. and J.X. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was financially supported by the Natural Science Foundation (No. 52204357) and Hunan Provincial Department of Education and Scientific Research Project (No. 23A0004).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors on request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Lu, M.; Ge, W.; Xia, Y.; Sun, C.; Lin, X.; Tsang, D.C.W.; Ling, T.-C.; Hu, Y.; Wang, L.; Yan, J. Upcycling MSWI fly ash into green binders via flue gas-enhanced wet carbonation. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 440, 141013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Gao, X.; Fei, X. Generation and management of municipal solid waste in top metropolitans of China: A comparison with Singapore. Circ. Econ. 2023, 2, 100041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Leng, B.; Xi, J. Assessing the social cost of municipal solid waste management in Beijing: A systematic life cycle analysis. Waste Manag. 2024, 173, 62–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Ge, W.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, L.; Xia, Y.; Lin, X.; Huang, Q.; Lu, S.; Tsang, D.C.W.; Yan, J. Designing low-carbon cement-free binders for stabilization/solidification of MSWI fly ash. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 339, 117938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Bureau of Statistics of China. China Statistical Yearbook; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, Z.; Cai, G.; Gao, L.; Wu, M.; Kong, L.; Bai, J.; Bai, Z.; Li, H.; Li, W. The physical encapsulation and chemical fixation of Zn during thermal treatment process of municipal solid waste incineration (MSWI) fly ash. Waste Manag. 2023, 166, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, T.-H.; Siao, H.-J.; Gau, S.-H.; Kuo, J.-H.; Li, M.-G.; Sun, C.-J. Life-Cycle Assessment of Municipal Solid Waste Incineration Fly Ash Recycling as a Feedstock for Brick Manufacturing. Sustainability 2023, 15, 10284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dongyang, H.; Hongyun, H.; Facun, J.; Wu, Z.; Changqi, L.; Hao, X.; Lu, D.; Xinye, W. Thermal separation of heavy metals from municipal solid waste incineration fly ash: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 467, 143344. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, D.; Wang, X.; Wu, C.; Li, T.; Wang, M.; Liu, S.; Wang, Q.; Shimaoka, T. Dechlorination of Municipal Solid Waste Incineration Fly Ash by Leaching with Fermentation Liquid of Food Waste. Sustainability 2020, 12, 4389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clavier, K.A.; Liu, Y.; Intrakamhaeng, V.; Townsend, T.G. Re-evaluating the TCLP’s Role as the Regulatory Driver in the Management of Municipal Solid Waste Incinerator Ash. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 7964–7973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bie, R.; Chen, P.; Song, X.; Ji, X. Characteristics of municipal solid waste incineration fly ash with cement solidification treatment. J. Energy Inst. 2016, 89, 704–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindberg, D.; Molin, C.; Hupa, M. Thermal treatment of solid residues from WtE units: A review. Waste Manag. 2015, 37, 82–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, W.; Shi, W.; Shi, Y.; Chen, D.; Liu, B.; Chu, C.; Li, D.; Li, Y.; Chen, G. Plasma vitrification and heavy metals solidification of MSW and sewage sludge incineration fly ash. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 408, 124809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Hu, H.; Guo, G.; Gong, L.; Liu, H.; Yao, H. Investigation of properties change in the reacted molten salts after molten chlorides cyclic thermal treatment of toxic MSWI fly ash. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 421, 126536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, X.; Yuan, R.; Gan, M.; Ji, Z.; Sun, Z. Subcritical hydrothermal treatment of municipal solid waste incineration fly ash: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 865, 160745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, P.C.; Chen, Q.H.; Chang, M.B. Pyrolysis of MWI fly ash—Effect on dioxin-like congeners. Chemosphere 2013, 92, 857–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, C.; Chen, C.; Shi, X.; Wu, S.; Jia, Y.; Du, B.; Liu, J. Recovery of metals from municipal solid waste incineration fly ash and red mud via a co-reduction process. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2020, 154, 104600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.; Liu, Z.; Xu, C.; Huang, X. A new efficient paradigm of energy and resource recovery from sewage: AnMBR treating chemically pre-precipitated concentrate in sidestream. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 478, 147309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, D.; Cheng, S.; Zhang, Y.; Ullah, F.; Ji, G.; Li, A. Relation between hydrophilic/hydrophobic characteristics of sludge extracellular polymeric substances and sludge moisture-holding capacity in hot-pressing drying. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 916, 170233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Un, C. Enhancing Sewage Sludge Treatment with Hydrothermal Processing: A Case Study of Adana City. Sustainability 2024, 16, 4174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Li, A.; Chang, Y. Hydrothermal treatment coupled with mechanical expression at increased temperature for excess sludge dewatering: Heavy metals, volatile organic compounds and combustion characteristics of hydrochar. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 297, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmi, A.; Al-Khaldy, A.a.; AlOlayan, M. Sewage sludge land application: Balancing act between agronomic benefits and environmental concerns. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 250, 119512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Detho, A.; Kadir, A.A.; Ahmad, S. Utilization of wastewater treatment sludge in the production of fired clay bricks: An approach towards sustainable development. Results Eng. 2024, 21, 101708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Zhu, F.; Li, Q.; Xue, C.; Xia, X.; Yu, H.; Zhao, Q.; Jiang, J.; Bai, S. Development, current state and future trends of sludge management in China: Based on exploratory data and CO2-equivaient emissions analysis. Environ. Int. 2020, 144, 106093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luukkonen, T.; Abdollahnejad, Z.; Yliniemi, J.; Kinnunen, P.; Illikainen, M. One-part alkali-activated materials: A review. Cem. Concr. Res. 2018, 103, 21–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ślosarczyk, A.; Fořt, J.; Klapiszewska, I.; Thomas, M.; Klapiszewski, Ł.; Černý, R. A literature review of the latest trends and perspectives regarding alkali-activated materials in terms of sustainable development. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 25, 5394–5425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elzeadani, M.; Bompa, D.V.; Elghazouli, A.Y. One part alkali activated materials: A state-of-the-art review. J. Build. Eng. 2022, 57, 104871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tositti, L.; Masi, G.; Morozzi, P.; Zappi, A.; Chiara Bignozzi, M. Cleaner, sustainable, and safer: Green potential of alkali-activated materials in current building industry, radiological good practice, and a few tips. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 409, 133879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Wang, B.; Zhang, S. Dispersion, properties, and mechanisms of nanotechnology-modified alkali-activated materials: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2024, 192, 114215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ailar, H.; van Deventer, J.S.J. Characterisation of One-Part Geopolymer Binders Made from Fly Ash. Waste Biomass Valorization 2016, 8, 225–233. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, K.-t.; Du, L.-q.; Lv, X.-s.; He, Y.; Cui, X.-m. Preparation of drying powder inorganic polymer cement based on alkali-activated slag technology. Powder Technol. 2017, 312, 204–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kravchenko, E.; Lazorenko, G.; Jiang, X.; Leng, Z. Alkali-activated materials made of construction and demolition waste as precursors: A review. Sustain. Mater. Technol. 2024, 39, e00829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahutjane, T.C.; Tchadjié, L.N.; Sithole, T.N. The feasibility of utilizing sewage sludge as a source of aluminosilicate to synthesise geopolymer cement. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 25, 3314–3323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, X.; Wang, L.; Hu, C.; Gong, J.; Xu, T.; Li, J.; Yang, L.; Bai, J.; Zhong, S. Co-disposal of MSWI fly ash and electrolytic manganese residue based on geopolymeric system. Waste Manag. 2018, 82, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Min, X.; Ke, Y.; Liu, D.; Tang, C. Preparation of red mud-based geopolymer materials from MSWI fly ash and red mud by mechanical activation. Waste Manag. 2019, 83, 202–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, X.; Rao, F.; Leon-Patino, C.A.; Song, S. Effects of aluminum on the expansion and microstructure of alkali-activated MSWI fly ash-based pastes. Chemosphere 2020, 240, 124986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Hu, L.; Tang, L.; Ren, J. Utilisation of municipal solid waste incinerator (MSWI) fly ash with metakaolin for preparation of alkali-activated cementitious material. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 402, 123451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Godoy, L.G.G.; Rohden, A.B.; Garcez, M.R.; da Costa, E.B.; Da Dalt, S.; de Oliveira Andrade, J.J. Valorization of water treatment sludge waste by application as supplementary cementitious material. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 223, 939–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Li, L.; Wen, Z.; Yan, D.; Liu, M.; Huang, Q.; Zhu, Z. Removal of dioxins from municipal solid waste incineration fly ash by low-temperature thermal treatment: Laboratory simulation of degradation and ash discharge stages. Waste Manag. 2023, 168, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, M.; Xing, J.; Tang, Q.; Ji, Z.; Fan, X.; Zheng, H.; Sun, Z.; Chen, X. Basic Research on Co-treatment of Municipal Solid Waste Incineration Fly Ash and Municipal Sludge for Energy-Saving Melting. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 45153–45164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Huang, Y.; Yu, M.; Cheng, H.; Li, Z.; Xu, W. Mineral phase evolution and heavy metals migration during the hydrothermal treatment of municipal solid waste incineration fly ash. Fuel 2024, 357, 129790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Zhu, N.; Li, X.; Xi, Y.; Shen, W.; Wu, P. Triggered heavy metals and chlorine simultaneous removal from hazardous waste incineration fly ash. Process Saf. Saf. Environ. Environ. Prot. Prot. 2023, 175, 796–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Guo, M.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, T.; Fang, Y.; Sui, L.; Gong, G. Chloride binding mechanism and free chloride reduction method of alkali-activated slag/fly ash mixed with seawater. Constr. Constr. Build. Build. Mater. Mater. 2023, 409, 134079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ascensão, G.; Marchi, M.; Segata, M.; Faleschini, F.; Pontikes, Y. Reaction kinetics and structural analysis of alkali activated Fe–Si–Ca rich materials. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 246, 119065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, M.X.; Chen, F.X.; Zhang, X.Y.; Wang, R.K.; Yu, R. Effect of Ca/Si ratio on the characteristics of alkali-activated ultra-high performance concrete (A-UHPC): From hydration kinetics to microscopic structure development. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 394, 132158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Perumal, P.; Aghabeyk, F.; Adediran, A.; Illikainen, M.; Ye, G. Advances in using municipal solid waste incineration (MSWI) bottom ash as precursor for alkali-activated materials: A critical review. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2024, 204, 107516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Sun, Y.; Li, W.; Nie, Y.; Wang, F.; Bian, R.; Wang, H.; Wang, Y.N.; Gong, Z.; Lu, J.; et al. Solidification/stabilization pre-treatment coupled with landfill disposal of heavy metals in MSWI fly ash in China: A systematic review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 478, 135479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Hu, L.; Dong, Z.; Tang, L.; Xing, F.; Liu, J. Effect of silica fume on the mechanical property and hydration characteristic of alkali-activated municipal solid waste incinerator (MSWI) fly ash. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 295, 126317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Xie, G.; Wang, Z.; Zeng, C.; Fan, X.; Li, Z.; Ren, J.; Xing, F.; Zhang, W. Manufacture of alkali-activated cementitious materials using municipal solid waste incineration (MSWI) ash: Immobilization of heavy metals in MSWI fly ash by MSWI bottom ash. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 392, 131848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scrivener, K.L.; Lothenbach, B.; De Belie, N.; Gruyaert, E.; Skibsted, J.; Snellings, R.; Vollpracht, A. TC 238-SCM: Hydration and microstructure of concrete with SCMs. Mater. Struct. 2015, 48, 835–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Vollpracht, A. Isothermal calorimetry and in-situ XRD study of the NaOH activated fly ash, metakaolin and slag. Cem. Concr. Res. 2018, 103, 110–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Vollpracht, A. One year geopolymerisation of sodium silicate activated fly ash and metakaolin geopolymers. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2019, 95, 98–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Ren, Q.; Li, S.; Lu, Q. Effect of Phosphorus on the Behavior of Potassium during the Co-combustion of Wheat Straw with Municipal Sewage Sludge. Energy Fuels 2013, 27, 5923–5930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Y.; Song, Y.; Yang, Y.; Huang, H.; Fang, H.; Shen, D.; Geng, H.; Ruan, J.; Gu, F. Co-vitrification of hazardous waste incineration fly ash and hazardous waste sludge based on CaO–SiO2–Al2O3 system. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 338, 117776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-Jiménez, A.; Palomo, A. Composition and microstructure of alkali activated fly ash binder: Effect of the activator. Cem. Concr. Res. 2005, 35, 1984–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchakouté, H.K.; Fotio, D.; Rüscher, C.H.; Kamseu, E.; Djobo, J.N.Y.; Bignozzi, M.C.; Leonelli, C. The effects of synthesized calcium phosphate compounds on the mechanical and microstructural properties of metakaolin-based geopolymer cements. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 163, 776–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajimohammadi, A.; Provis, J.L.; van Deventer, J.S. Time-resolved and spatially-resolved infrared spectroscopic observation of seeded nucleation controlling geopolymer gel formation. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 357, 384–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz, A.G.; Bueno, S.; Villarejo, L.P.; Eliche-Quesada, D. Improved strength of alkali activated materials based on construction and demolition waste with addition of rice husk ash. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 413, 134823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Wang, H.; Yang, R.; Kong, F.; Hong, T. The potential of copper slag as a precursor for partially substituting blast furnace slag to prepare alkali-activated materials. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 434, 140283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, C.; Wang, B.; Ai, H.; Liu, Z. A comparative study on characteristics and leaching toxicity of fluidized bed and grate furnace MSWI fly ash. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 305, 114345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, H.; Provis, J.L.; Bullen, F.; Reid, A.; Zhu, Y. Quantitative kinetic and structural analysis of geopolymers. Part 1. The activation of metakaolin with sodium hydroxide. Thermochim. Acta 2012, 539, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Li, J.-S.; Zhan, B.-J.; Sharma, U.; Poon, C.S. Compressive strength and microstructural properties of dry-mixed geopolymer pastes synthesized from GGBS and sewage sludge ash. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 182, 597–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Londono-Zuluaga, D.; Tobón, J.I.; Aranda, M.A.G.; Santacruz, I.; De la Torre, A.G. Clinkering and hydration of belite-alite-ye’elimite cement. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2017, 80, 333–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashad, A.M. A comprehensive overview about the influence of different admixtures and additives on the properties of alkali-activated fly ash. Mater. Des. 2014, 53, 1005–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garanayak, L. Behavior of alkali activated fly ash slag paste at room temperature. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 43, 1865–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Vollpracht, A.; van der Sloot, H.A. pH dependent leaching characterization of major and trace elements from fly ash and metakaolin geopolymers. Cem. Concr. Res. 2019, 125, 105889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartwich, P.; Vollpracht, A. Influence of leachate composition on the leaching behaviour of concrete. Cem. Concr. Res. 2017, 100, 423–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Provis, J.L.; Feng, D.; van Deventer, J.S.J. The role of sulfide in the immobilization of Cr(VI) in fly ash geopolymers. Cem. Concr. Res. 2008, 38, 681–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Provis, J.L.; van Deventer, J.S.J. Geopolymers: Structure, Processing, Properties and Industrial Applications; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Engelsen, C.J.; van der Sloot, H.A.; Wibetoe, G.; Justnes, H.; Lund, W.; Stoltenberg-Hansson, E. Leaching characterisation and geochemical modelling of minor and trace elements released from recycled concrete aggregates. Cem. Concr. Res. 2010, 40, 1639–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).