Building a Resilient Digital Entrepreneurship Landscape: The Importance of Ecosystems, Decent Work, and Socioeconomic Dynamics
Abstract
1. Introduction
General Research Objective
2. Literature Review
2.1. The Relationship between Entrepreneurship Ecosystems and Digital Entrepreneurship
2.2. The Relationship between Decent Work and Digital Entrepreneurship
2.3. Role of Economic Growth
2.4. Role of the Socioeconomic Status
3. Method
3.1. Sample and Process
3.2. Variables Measurement
4. Data Analysis Aggregation
4.1. Common Method Variance (CMV)
4.2. Measurement Model Assessment
4.3. Hypothesis Testing
5. Discussion and Implications
6. Limitations and Future Work
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Questionnaire
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Strongly Disagree | Disagree | Neutral | Agree | Strongly Agree | |||||
| MEE1 | Importance of support/incentives for internationalization: (i) Saudi Agency for Investment and Foreign Trade (AICEP) (ii) Institute for Support to Small and Medium-Sized Enterprises and Innovation (iii) Saudi Business Association (iv) Business Associations (v) Local/Municipal/Regional; (vi) Specific entities of the sector of activities (vii) Chambers of Commerce; Saudi Embassies and Consulates | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |||
| MOEE2 | Relevance of the following partners for the effectiveness of your company’sinternationalization: (i) Suppliers (ii) Customers (iii) Competitors (iv) Consultants (v) Universities (vi) Research Centers | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |||
| MOEE3 | The importance that you attribute to each of these factors for the effectiveness of the internationalization of your company: (i) Seniority of the company (ii) Size of the company; Specific skills of the employees (iii) international experience of the employees (iv) Strong entrepreneurial propensity and willingness to take risks on the part of key employees and the company management) Formal contact network (other companies) (vi) Informal contact network (friends, familiars members) (vii) Territorial proximity to new markets (viii) Linguistic | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Strongly Disagree | Disagree | Neutral | Agree | Strongly Agree | |||||
| Safe working conditions | |||||||||
| SWC1. | Have you received adequate training on emergency procedures and evacuation plans in case of a workplace hazard? | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |||
| SWC2. | Do you feel that your workplace takes sufficient measures to address health concerns, such as proper ventilation and sanitation? | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |||
| SWC3. | Have you ever encountered a safety issue, and if so, how was it addressed by your employer? | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |||
| Access to Healthcare | |||||||||
| AHC1. | Are you aware of the healthcare benefits offered by your employer, including coverage for medical consultations, prescriptions, and preventive care? | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |||
| AHC2. | Does your employer offer any preventive healthcare programs or initiatives, such as vaccination drives, health screenings, or wellness programs? | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |||
| AHC3. | Do you believe that the health insurance coverage provided by your employer is sufficient to meet your healthcare needs? | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |||
| Adequate Compensation | |||||||||
| AC1. | Have you experienced any challenges or disparities in terms of compensation within your workplace? | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |||
| AC2. | How transparent is your employer in communicating the criteria and process for determining compensation? | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |||
| AC3. | Would you value more flexibility in compensation structures, such as performance bonuses or stock options? | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |||
| Free Time and Rest | |||||||||
| FTR1. | Are there any specific factors or challenges that affect your ability to maintain a healthy work-life balance? | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |||
| FTR2. | Have you ever faced challenges in taking breaks or utilizing your allotted free time during working hours? | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |||
| FTR3. | Does your employer offer flexible working hours or arrangements to accommodate personal or family needs? | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |||
| Complementary Values | |||||||||
| CV1. | To what extent do you feel that the organizational culture promotes a sense of shared values and ethics among employees? | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |||
| CV2. | How inclusive do you perceive your workplace culture to be in embracing diverse perspectives, backgrounds, and values? | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |||
| CV3. | Have you ever faced a situation where you felt your values conflicted with a work-related decision, and if so, how was it resolved? | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Strongly Disagree | Disagree | Neutral | Agree | Strongly Agree | |||||
| INND1. | I believe that the organization actively seeks and implements innovative solutions to enhance its operations. | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |||
| INND2. | I feel that my team has the freedom to experiment with new approaches and solutions without fear of punitive measures. | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |||
| INND3. | Innovative contributions and achievements are acknowledged and celebrated within my organization. | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |||
| INND4. | There are channels and platforms in place for employees to share and collaborate on innovative ideas. | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |||
| INND5. | The organization allocates resources and budget for research and development, supporting innovative initiatives. | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |||
| SCS1 | Social Status: “On a scale from 1 to 10, where 1 represents the highest social status and 10 represents the lowest, how would you rate your social status relative to others in your community?” | 1–10 |
| SCS2 | Economic Status: “On a scale from 1 to 10, where 1 represents the highest economic status and 10 represents the lowest, how would you rate your economic status compared to others in your society?” | 1–10 |
| SCS3 | Overall Socioeconomic Standing: “Considering both your social and economic status, how would you rate your overall socioeconomic position on a scale from 1 to 10, where 1 is the highest status and 10 is the lowest?” | 1–10 |
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Strongly Disagree | Disagree | Neutral | Agree | Strongly Agree | |||||
| DE1. | I plan to start an e-business in the future. | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |||
| DE2. | I am determined to create my own e-business even though I will encounter difficulties. | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |||
| DE3. | I intend to start an e-business in the next five years. | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |||
| DE4. | I have very seriously thought about starting an e-business. | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |||
| DE5. | I am ready to do anything to be an e-entrepreneur. | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |||
| For the questions below, please indicate your response by placing a mark (√) in the appropriate space beside each item. | ||
| □ Male | □ Female |
| □ Below 25 Years | □ 25–30 Years |
| □ 31–40 Years | □ 41–50 Years | |
| □ Above 51 Years | ||
| □ High school | □ Diploma |
| □ Bachelor’s degree | □ Master’s Degree | |
| □ Doctorate’s degree | ||
| □ 2 Years and below | □ 3–5 Years |
| □ 6–10 Years | □ 11–15 Years | |
| □ 16 Years and above | ||
| □ Manufacturing | □ Technology |
| □ Medical organizations | □ Insurances | |
| □ Retails □ Telecommunication | □ legal □ Finance | |
References
- Nguyen PN, D.; Nguyen, H.H. Unveiling the link between digital entrepreneurship education and intention among university students in an emerging economy. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2024, 203, 123330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, J.; Alhassan, I.; Binsaif, N.; Singh, P. Digital entrepreneurship research: A systematic review. J. Bus. Res. 2023, 156, 113507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Halbusi, H.; AbdelFattah, F.; Ferasso, M.; Alshallaqi, M.; Hassani, A. Fear of failure for entrepreneurs in emerging economies: Stress, risk, finances, hard work, and social support. J. Small Bus. Enterp. Dev. 2024, 31, 95–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadhyay, N.; Upadhyay, S.; Al-Debei, M.M.; Baabdullah, A.M.; Dwivedi, Y.K. The influence of digital entrepreneurship and entrepreneurial orientation on the intention of family businesses to adopt artificial intelligence: Examining the mediating role of business innovativeness. Int. J. Entrep. Behav. Res. 2023, 29, 80–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachmann, N.; Rose, R.; Maul, V.; Hölzle, K. What makes for future entrepreneurs? The role of digital competencies for entrepreneurial intention. J. Bus. Res. 2024, 174, 114481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhakupov, Y.K.; Berzhanova, A.M.; Mukhanova, G.K.; Baimbetova, A.B.; Mamutova, K.K. The impact of entrepreneurship on the socio-economic development of regions. Bus. Strategy Dev. 2023, 6, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yáñez-Valdés, C.; Guerrero, M. Determinants and impacts of digital entrepreneurship: A pre-and post-COVID-19 perspective. Technovation 2024, 132, 102983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, X.; Nespoli, P.; Profita, F.; Huang, L.; Xu, Y. Digital entrepreneurship: Towards a knowledge management perspective. J. Knowl. Manag. 2024, 28, 341–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, B.; Wang, L.; Yu, X.; Feng, B. Data-driven analysis of digital entrepreneurship in medical supply resilience confronting the COVID-19 epidemic. Inf. Process. Manag. 2024, 61, 103502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Angelo, S.; Cavallo, A.; Ghezzi, A.; Di Lorenzo, F. Understanding corporate entrepreneurship in the digital age: A review and research agenda. In Review of Managerial Science; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2024; pp. 1–56. [Google Scholar]
- Al Halbusi, H. Digital entrepreneurship and personal resilience on new business models in the 21st century. In Handbook of Research on Entrepreneurship and Organizational Resilience during Unprecedented Times; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2023; pp. 331–351. [Google Scholar]
- Ghezzi, A.; Cavallo, A. Agile business model innovation in digital entrepreneurship: Lean startup approaches. J. Bus. Res. 2020, 110, 519–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bejjani, M.; Göcke, L.; Menter, M. Digital entrepreneurial ecosystems: A systematic literature review. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2023, 189, 122372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, C.; Ferreira, J.J.; Veiga, P.M.; Kraus, S.; Dabić, M. Digital entrepreneurship platforms: Mapping the field and looking towards a holistic approach. Technol. Soc. 2022, 70, 101979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gala, K.; Schwab, A.; Mueller, B.A. Star entrepreneurs on digital platforms: Heavy-tailed performance distributions and their generative mechanisms. J. Bus. Ventur. 2024, 39, 106347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ukata, P.F.; Amini, M.C. Digital entrepreneurial skills acquired by business education undergraduates for decent works in tertiary institutions in Rivers State. Int. J. Innov. Educ. Res. 2022, 10, 99–108. [Google Scholar]
- Braganza, A.; Chen, W.; Canhoto, A.; Sap, S. Productive employment and decent work: The impact of AI adoption on psychological contracts, job engagement and employee trust. J. Bus. Res. 2021, 131, 485–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ukko, J.; Nasiri, M.; Saunila, M.; Rantala, T. Sustainability strategy as a moderator in the relationship between digital business strategy and financial performance. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 236, 117626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dittes, S.; Richter, S.; Richter, A.; Smolnik, S. Toward the workplace of the future: How organizations can facilitate digital work. Bus. Horiz. 2019, 62, 649–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, Y.J.; Wang, I.Y. Exploring the development trajectory of decent work literature: An empowerment perspective. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2024, 201, 123230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blustein, D.L.; Kenny, M.E.; Di Fabio, A.; Guichard, J. Expanding the impact of the psychology of working: Engaging psychology in the struggle for decent work and human rights. J. Career Assess. 2019, 27, 3–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felicetti, A.M.; Corvello, V.; Ammirato, S. Digital innovation in entrepreneurial firms: A systematic literature review. Rev. Manag. Sci. 2024, 18, 315–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elia, G.; Margherita, A.; Passiante, G. Digital entrepreneurship ecosystem: How digital technologies and collective intelligence are reshaping the entrepreneurial process. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2020, 150, 119791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roshan, R.; Balodi, K.C.; Datta, S.; Kumar, A.; Upadhyay, A. Circular economy startups and digital entrepreneurial ecosystems. Bus. Strategy Environ. 2024, 33, 4843–4860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joel, O.T.; Oguanobi, V.U. Entrepreneurial leadership in startups and SMEs: Critical lessons from building and sustaining growth. Int. J. Manag. Entrep. Res. 2024, 6, 1441–1456. [Google Scholar]
- Sitaridis, I.; Kitsios, F. Digital entrepreneurship and entrepreneurship education: A review of the literature. Int. J. Entrep. Behav. Res. 2024, 30, 277–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stam, E.; Spigel, B. Entrepreneurial ecosystems around the globe and early-stage company growth dynamics. Entrep. Theory Pract. 2016, 40, 49–69. [Google Scholar]
- Autio, E.; Nambisan, S.; Thomas, L.D.; Wright, M. Digital affordances, spatial affordances, and the genesis of entrepreneurial ecosystems. Strateg. Entrep. J. 2018, 12, 72–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Audretsch, D.B.; Belitski, M. Entrepreneurial ecosystems in cities: Establishing the framework conditions. J. Technol. Transf. 2017, 42, 1030–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; van Gorp, D.; Kievit, H. Digital technology and national entrepreneurship: An ecosystem perspective. J. Technol. Transf. 2023, 48, 1077–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, A.B.; Endut, N. Do decent working conditions contribute to work–life balance: A study of small enterprises in Bangladesh. Asia Pac. J. Innov. Entrep. 2018, 12, 90–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herman, E. The interplay between digital entrepreneurship and sustainable development in the context of the EU digital economy: A multivariate analysis. Mathematics 2022, 10, 1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firlej, K.A.; Firlej, C.; Luty, L. Economic growth and decent work as a goal of sustainable development in the European Union in the pre-pandemic and pandemic period. Int. Entrep. Rev. 2023, 9, 61–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.W.; Umar, M.; Khaddage-Soboh, N.; Safi, A. From innovation to impact: Unraveling the complexities of entrepreneurship in the digital age. Int. Entrep. Manag. J. 2024, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubis, A.S.; Wijaya, C.; Sakapurnama, E. Analysis of entrepreneurial ecosystem factors on productive entrepreneurship of digital start-ups in Indonesia. Int. J. Bus. Ecosyst. Strategy 2023, 5, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yang, G.; Shao, T.; Yang, D.; Liu, Z. Does digital infrastructure promote individual entrepreneurship? Evidence from a quasi-natural experiment on the “Broadband China” strategy. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2024, 206, 123555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mtibaa, N.; Boudabbous, S. Entrepreneur digital (ED) et processus entrepreneurial: Schéma théorique et validation empirique. Rev. Int. Des Sci. De Gest. 2023, 6, 24–47. [Google Scholar]
- Kraus, S.; Vonmetz, K.; Orlandi, L.B.; Zardini, A.; Rossignoli, C. Digital entrepreneurship: The role of entrepreneurial orientation and digitalization for disruptive innovation. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2023, 193, 122638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hommel, K.; Bican, P.M. Digital entrepreneurship in finance: Fintechs and funding decision criteria. Sustainability 2020, 12, 8035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, E.S.; Von Briel, F.; Davidsson, P.; Kuckertz, A. Digital or not–The future of entrepreneurship and innovation: Introduction to the special issue. J. Bus. Res. 2021, 125, 436–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakry, D.S.; Daim, T.; Dabic, M.; Yesilada, B. An evaluation of the effectiveness of innovation ecosystems in facilitating the adoption of sustainable entrepreneurship. J. Small Bus. Manag. 2022, 62, 763–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, P.; Maas, G.; Dobson, S.; Newbery, R.; Agyapong, D.; Matlay, H. Entrepreneurship in Africa, part 1: Entrepreneurial dynamics in Africa. J. Small Bus. Enterp. Dev. 2018, 25, 346–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Halbusi, H.; Al-Sulaiti, K.; Abdelfattah, F.; Ahmad, A.B.; Hassan, S. Understanding consumers’ adoption of e-pharmacy in Qatar: Applying the unified theory of acceptance and use of technology. J. Sci. Technol. Policy Manag. 2024; ahead-of-print. [Google Scholar]
- Al Halbusi, H.; Soto-Acosta, P.; Popa, S. Entrepreneurial passion, role models and self-perceived creativity as antecedents of e-entrepreneurial intention in an emerging Asian economy: The moderating effect of social media. Asia Pac. J. Manag. 2022, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Xu, Y.; Wu, C.H.; Luo, Y. Fortune favors the experienced: Entrepreneurs’ Internet-Era Imprint, digital entrepreneurship and venture capital. Inf. Process. Manag. 2023, 60, 103406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Halbusi, H.; Klobas, J.E.; Ramayah, T. Green core competence and firm performance in a post-conflict country, Iraq. Bus. Strategy Environ. 2023, 32, 2702–2714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fairlie, R.W.; Robb, A.M. Why Are Black-Owned Businesses Less Successful than White-Owned Businesses? The Role of Families, Inheritances, and Business Human Capital. J. Labor Econ. 2007, 25, 289–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhajri, A.; Aloud, M. Female digital entrepreneurship: A structured literature review. Int. J. Entrep. Behav. Res. 2024, 30, 369–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermawan, E.; Vikaliana, R. The Relationship of Socio-Economic Status to Emotional and Consumptive Behavior. Asian J. Manag. Entrep. Soc. Sci. 2023, 3, 214–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.A.; Jain, R. Determinants of Micro-Entrepreneurship: A Study on Socio-Economic Factors in Context of Digital Bangladesh. Int. J. Bus. Econ. Res. 2017, 6, 37–42. [Google Scholar]
- Hammoda, B. Digital Technology in Entrepreneurship Education: An Overview of the Status Quo. In Digital Transformation for Entrepreneurship; World Scientific Publishing Co. Pte. Ltd.: Singapore, 2024; pp. 7–93. [Google Scholar]
- Oladapo, I.A.; Alkethery, N.M.; AlSaqer, N.S. Consequences of COVID-19 Shocks and Government Initiatives on Business Performance of Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises in Saudi Arabia. J. Small Bus. Strategy 2023, 33, 64–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, J.J.; Fernandes, C.I.; Veiga, P.M. The role of entrepreneurial ecosystems in SME internationalization. J. Bus. Res. 2023, 157, 113603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Autin, K.L.; Ezema, G.N. Validation of the Chinese decent work scale. J. Career Dev. 2023, 50, 37–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.; Zhou, Y. Measuring the green economic growth in China: Influencing factors and policy perspectives. Energy 2022, 241, 122518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Halbusi, H.; Soto-Acosta, P.; Popa, S. Analysing e-entrepreneurial intention from the theory of planned behaviour: The role of social media use and perceived social support. Int. Entrep. Manag. J. 2023, 19, 1611–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hair, J.F.; Hult, G.T.M.; Ringle, C.; Sarstedt, M. A Primer on Partial Least Squares Structural Equation Modeling (PLS-SEM), 2nd ed.; Sage: London, UK; Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Podsakoff, P.M.; MacKenzie, S.B.; Lee, J.Y.; Podsakoff, N.P. Common method biases in behavioral research: A critical review of the literature and recommended remedies. J. Appl. Psychol. 2003, 88, 879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Podsakoff, P.M.; MacKenzie, S.B.; Podsakoff, N.P. Sources of method bias in social science research and recommendations on how to control it. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 2012, 63, 539–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henseler, J.; Ringle, C.M.; Sarstedt, M. A new criterion for assessing discriminant validity in variance-based structural equation modeling. J. Acad. Mark. Sci. 2015, 43, 115–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawson, J.F. Moderation in management research: What, why, when, and how. J. Bus. Psychol. 2014, 29, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usman, M.; Vanhaverbeke, W.; Roijakkers, N. How open innovation can help entrepreneurs in sensing and seizing entrepreneurial opportunities in SMEs. Int. J. Entrep. Behav. Res. 2023, 29, 2065–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Chen, M.; Wang, Q.; Fang, Y. The study of value network reconstruction and business model innovation driven by entrepreneurial orientation. Int. Entrep. Manag. J. 2023, 19, 2013–2036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odeyemi, O.; Oyewole, A.T.; Adeoye, O.B.; Ofodile, O.C.; Addy, W.A.; Okoye, C.C.; Ololade, Y.J. Entrepreneurship in Africa: A review of growth and challenges. Int. J. Manag. Entrep. Res. 2024, 6, 608–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ordeñana, X.; Vera-Gilces, P.; Zambrano-Vera, J.; Jiménez, A. The effect of high-growth and innovative entrepreneurship on economic growth. J. Bus. Res. 2024, 171, 114243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzhengiz, T.; Patala, S. The role of cross-sector partnerships in the dynamics between places and innovation ecosystems. RD Manag. 2024, 54, 370–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okoye, K.; Hussein, H.; Arrona-Palacios, A.; Quintero, H.N.; Ortega, L.O.P.; Sanchez, A.L.; Ortiz, E.A.; Escamilla, J.; Hosseini, S. Impact of digital technologies upon teaching and learning in higher education in Latin America: An outlook on the reach, barriers, and bottlenecks. Educ. Inf. Technol. 2023, 28, 2291–2360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Błażejowski, M.; Kwiatkowski, J.; Gazda, J. Sources of economic growth: A global perspective. Sustainability 2019, 11, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chew, X.; Alnoor, A.; Khaw, K.W.; Sadaa, A.M.; Al Halbusi, H.; Muhsen, Y.R. Symmetric and asymmetric modeling to boost customers’ trustworthiness in livestreaming commerce. In Current Psychology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2024; pp. 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Al Halbusi, H.; Popa, S.; Alshibani, S.M.; Soto-Acosta, P. Greening the future: Analyzing green entrepreneurial orientation, green knowledge management and digital transformation for sustainable innovation and circular economy. Eur. J. Innov. Manag. 2024; ahead-of-print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| First-Order Constructs | Second-Order Constructs | Items | Loading (>0.5) | CR (>0.7) | AVE (>0.5) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Macro Entrepreneurial Ecosystem | MEE1 | 0.737 | 0.825 | 0.563 | |
| MEE2 | 0.813 | ||||
| MEE3 | 0.756 | ||||
| MEE4 | 0.826 | ||||
| MEE5 | 0.726 | ||||
| Meso Entrepreneurial Ecosystem | MOEE1 | 0.781 | |||
| MOEE2 | 0.745 | ||||
| MOEE3 | 0.845 | ||||
| MOEE4 | 0.777 | ||||
| Micro Entrepreneurial Ecosystem | MIEE1 | 0.881 | 0.877 | 0.655 | |
| MIEE2 | 0.780 | ||||
| MIEE3 | 0.778 | ||||
| MIEE4 | 0.800 | ||||
| Entrepreneurial Ecosystems | Macro Entrepreneurial Ecosystem | 0.745 | 0.875 | 0.668 | |
| Meso Entrepreneurial Ecosystem | 0.817 | ||||
| Micro Entrepreneurial Ecosystem | 0.868 | ||||
| Safe Working Conditions | SWC1 | 0.812 | 0.857 | 0.698 | |
| SWC2 | 0.812 | ||||
| SWC3 | 0.795 | ||||
| Access to Healthcare | ATHC1 | 0.783 | 0.857 | 0.685 | |
| ATHC2 | 0.827 | ||||
| ATHC3 | 0.841 | ||||
| Adequate Compensation | AC1 | 0.789 | 0.852 | 0.563 | |
| AC2 | 0.841 | ||||
| AC3 | 0.856 | ||||
| Free Time and Rest | FTR1 | 0.784 | 0.886 | 0.609 | |
| FTR2 | 0.786 | ||||
| FTR3 | 0.769 | ||||
| Complementary Values | CMV1 | 0.745 | 0.822 | 0.598 | |
| CMV2 | 0.831 | ||||
| CMV3 | 0.822 | ||||
| Decent Work | Safe working conditions | 0.842 | 0.891 | 0.749 | |
| Access to healthcare | 0.812 | ||||
| Adequate compensation | 0.786 | ||||
| Free time and rest | 0.736 | ||||
| Complementary values | 0.822 | ||||
| Economic Growth | ECG1 | 0.774 | 0.874 | 0.623 | |
| ECG2 | 0.814 | ||||
| ECG3 | 0.877 | ||||
| ECG4 | 0.873 | ||||
| ECG5 | 0.856 | ||||
| Socioeconomic Status | SCS1 | 0.798 | 0.811 | 0.588 | |
| SCS2 | 0.757 | ||||
| SCS3 | 0.847 | ||||
| Digital Entrepreneurship | DIE1 | 0.785 | 0.798 | 0.667 | |
| DIE2 | 0.877 | ||||
| DIE3 | 0.873 | ||||
| DIE4 | 0.856 | ||||
| DIE5 | 0.786 |
| Constructs | Mean | SD | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Entrepreneurial Ecosystems | 3.647 | 0.585 | 0.778 | ||||
| 2. Decent Work | 3.472 | 0.551 | 0.602 | 0.713 | |||
| 3. Economic Growth | 4.184 | 0.637 | 0.432 | 0.514 | 0.829 | ||
| 4. Socioeconomic Status | 4.513 | 0.519 | 0.134 | 0.165 | 0.483 | 0.809 | |
| 5. Digital Entrepreneurship | 4.211 | 0.549 | 0.335 | 0.583 | 0.472 | 0.305 | 0.742 |
| Constructs | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Entrepreneurial Ecosystems | ||||||
| 2. Decent Work | 0.454 | |||||
| 3. Economic Growth | 0.399 | 0.679 | ||||
| 4. Socioeconomic Status | 0.527 | 0.604 | 0.529 | |||
| 5. Digital Entrepreneurship | 0.189 | 0.264 | 0.359 | 0.558 |
| Bias and Corrected Bootstrap 95% CI | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hypothesis | Relationship | Std Beta | Std Error | t-Value | p-Value | BCI 95% LL | BCI 95% UL | Decision |
| H-1 | Entrepreneurial Ecosystems -> Digital Entrepreneurship | 0.312 | 0.088 | 3.484 | 0.000 | 0.125 | 0.289 | Supported |
| H-3 | Decent Work -> Digital Entrepreneurship | 0.202 | 0.054 | 3.115 | 0.000 | 0.313 | 0.553 | Supported |
| (1) Patient Empowerment Healthcare Sustainability | Bias and Corrected Bootstrap 95% CI | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hypothesis | Relationship | Std Beta | Std Error | t-Value | p-Values | BCI 95% LL | BCI 95% UL | Decision |
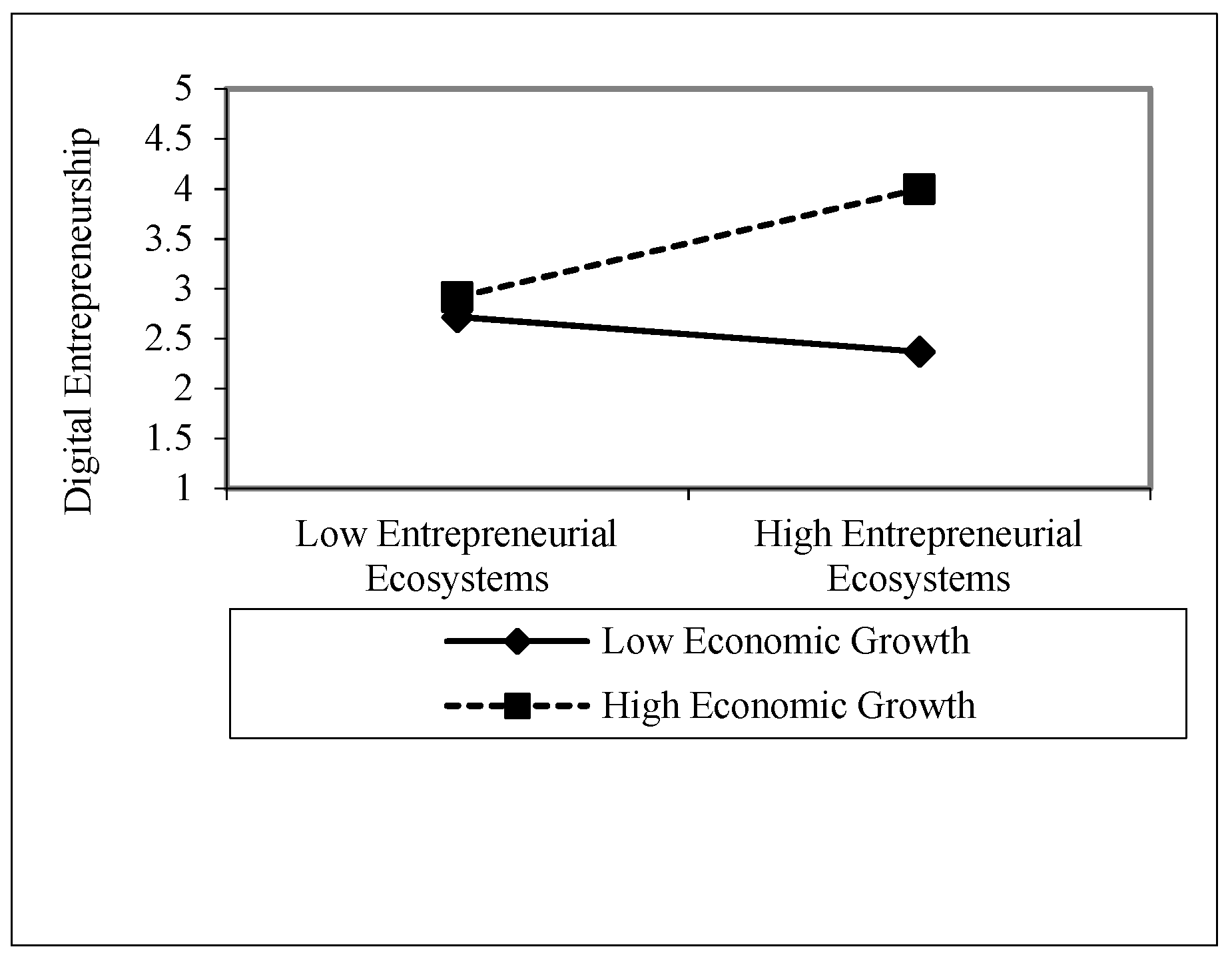
| H-3a | Entrepreneurial Ecosystems × Economic Growth --> Digital Entrepreneurship | 0.068 | 0.027 | 2.143 | 0.000 | 0.023 | 0.123 | Supported |
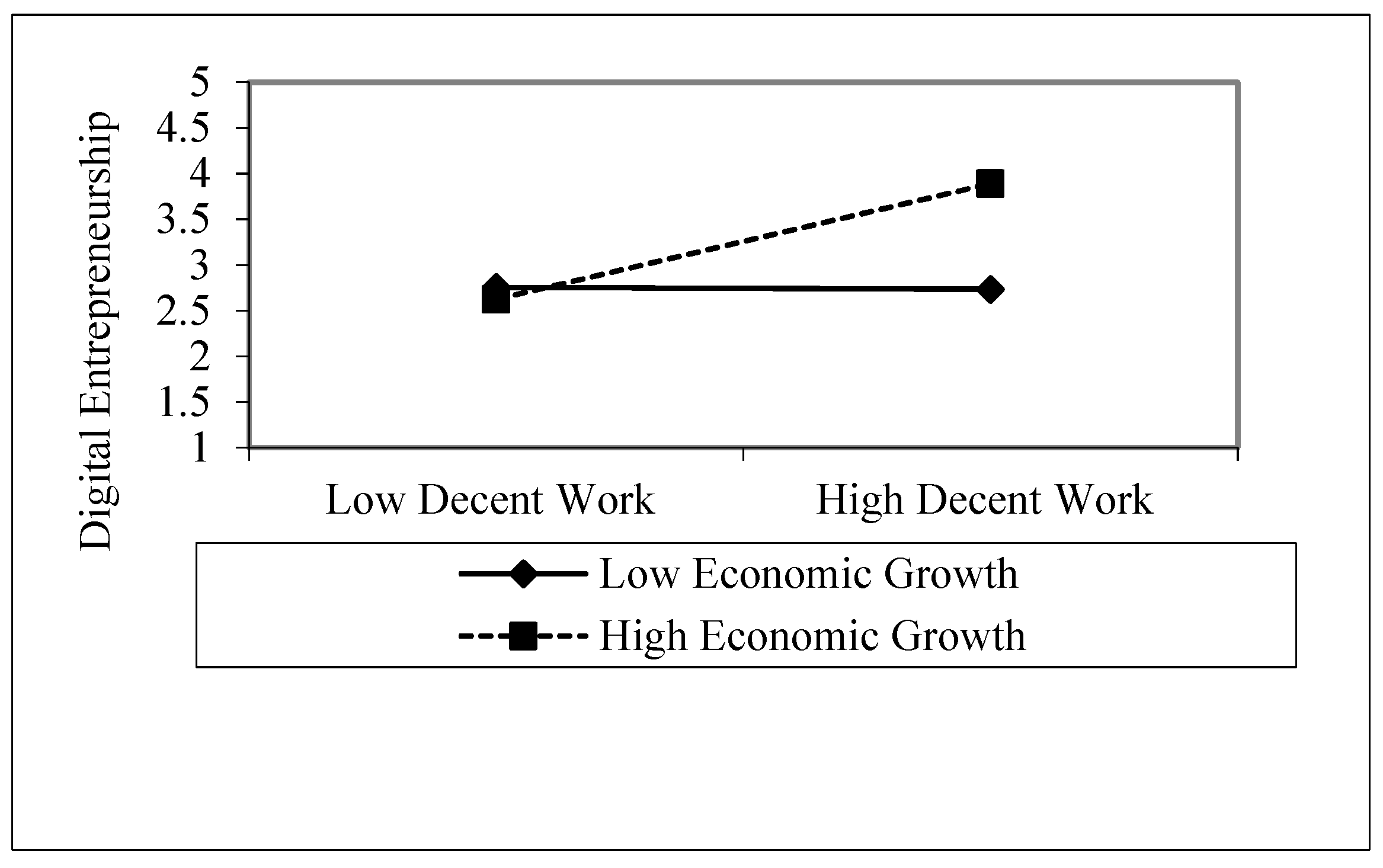
| H-3b | Decent Work × Economic Growth --> Digital Entrepreneurship | 0.166 | 0.096 | 2.239 | 0.000 | 0.010 | 0.274 | Supported |
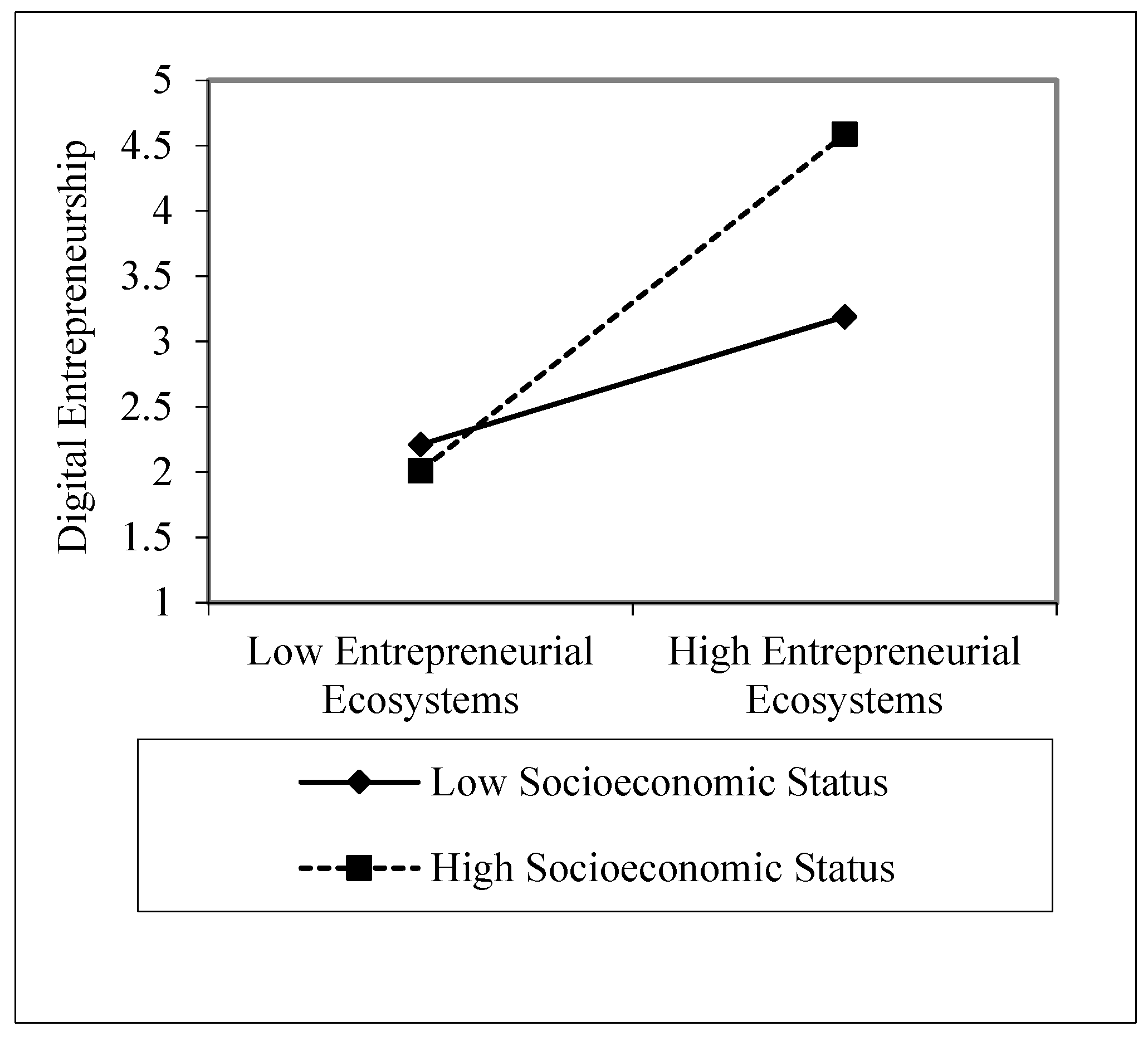
| H-3c | Entrepreneurial Ecosystems × Socioeconomic Status --> Digital Entrepreneurship | 0.289 | 0.088 | 3.722 | 0.000 | 0.020 | 0.076 | Supported |
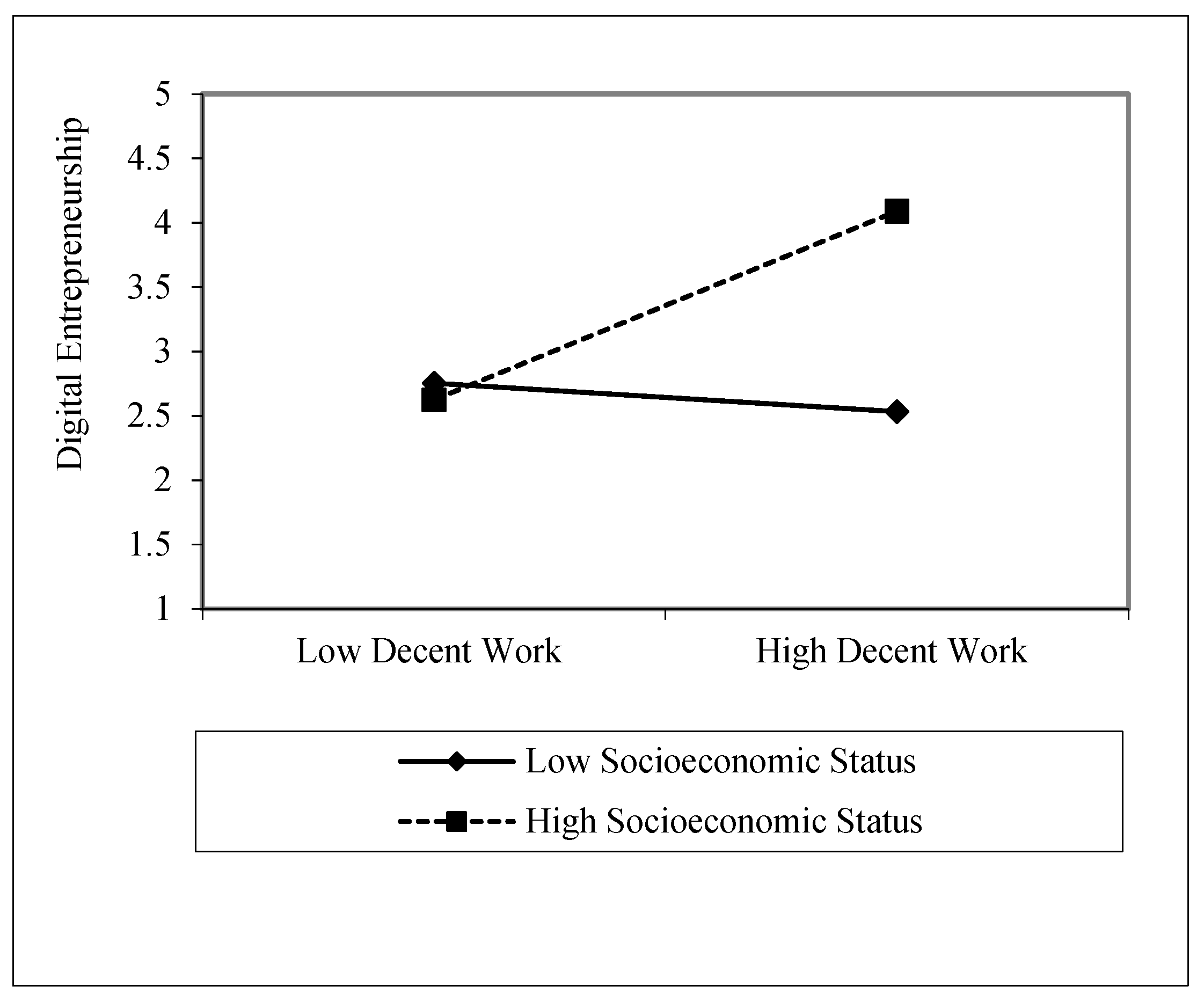
| H-53d | Decent Work × Socioeconomic Status --> Digital Entrepreneurship | 0.215 | 0.061 | 3.524 | 0.000 | 0.124 | 0.321 | Supported |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alzamel, S. Building a Resilient Digital Entrepreneurship Landscape: The Importance of Ecosystems, Decent Work, and Socioeconomic Dynamics. Sustainability 2024, 16, 7605. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16177605
Alzamel S. Building a Resilient Digital Entrepreneurship Landscape: The Importance of Ecosystems, Decent Work, and Socioeconomic Dynamics. Sustainability. 2024; 16(17):7605. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16177605
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlzamel, Samar. 2024. "Building a Resilient Digital Entrepreneurship Landscape: The Importance of Ecosystems, Decent Work, and Socioeconomic Dynamics" Sustainability 16, no. 17: 7605. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16177605
APA StyleAlzamel, S. (2024). Building a Resilient Digital Entrepreneurship Landscape: The Importance of Ecosystems, Decent Work, and Socioeconomic Dynamics. Sustainability, 16(17), 7605. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16177605






