Enhancing Urban Sustainability and Resilience: Employing Digital Twin Technologies for Integrated WEFE Nexus Management to Achieve SDGs
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
3. Methods
3.1. Data Collection Methods
3.2. Machine Learning Integration
3.2.1. Natural Language Processing (NLP) in Digital Twin Technology
3.2.2. Random Forest (RF)
4. Findings
4.1. Machine Learning Application Results
4.2. Digital Twin Assessment
5. Enhancing WEFE Nexus Management in Irbid Camp: A Call for Integrated Digital Solutions
5.1. Beyond Resource Efficiency: Comprehensive Community Empowerment
5.2. Need for Inclusive Support and Adaptive Policies
5.3. Empowering Community through Technological Engagement
5.4. Advocating for Structural and Technological Paradigm Shifts
6. Strategic Policy Guidelines for Enhancing Digital Twin Integration in Refugee Camps
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aldeek, Z.A.; Alibrahim, M.M.; Zeadeh, S. Requalifying the Irbid Refugee Camp: Towards Integrated Urban Development in Jordan. Int. J. Sustain. Dev. Plan. 2023, 18, 2769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, H.H.; Al-Betawi, Y.N.; Al-Qudah, H.S. Effects of urban form on social sustainability—A case study of Irbid, Jordan. Int. J. Urban Sustain. Dev. 2019, 11, 203–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chomiak-Orsa, I.; Hauke, K.; Perechuda, K.; Pondel, M. The use of Digital Twin in the sustainable development of the city on the example of managing parking resources. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2023, 225, 2183–2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purcell, W.; Neubauer, T. Digital Twins in Agriculture: A State-of-the-art review. Smart Agric. Technol. 2023, 3, 100094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Amore, G.; Di Vaio, A.; Balsalobre-Lorente, D.; Boccia, F. Artificial Intelligence in the Water–Energy–Food Model: A Holistic Approach towards Sustainable Development Goals. Sustainability 2022, 14, 867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dayıoğlu, M.A.; Turker, U. Digital transformation for sustainable future-agriculture 4.0: A review. J. Agric. Sci. 2021, 27, 373–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henriksen, H.J.; Schneider, R.; Koch, J.; Ondracek, M.; Troldborg, L.; Seidenfaden, I.K.; Kragh, S.J.; Bøgh, E.; Stisen, S. A New Digital Twin for Climate Change Adaptation, Water Management, and Disaster Risk Reduction (HIP Digital Twin). Water 2023, 15, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahmasebinia, F.; Lin, L.; Wu, S.; Kang, Y.; Sepasgozar, S. Exploring the Benefits and Limitations of Digital Twin Technology in Building Energy. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 8814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leck, H.; Conway, D.; Bradshaw, M.; Rees, J. Tracing the Water–Energy–Food Nexus: Description, Theory and Practice. Geogr. Compass 2015, 9, 445–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bieber, N.; Ker, J.H.; Wang, X.; Triantafyllidis, C.; van Dam, K.H.; Koppelaar, R.H.E.M.; Shah, N. Sustainable planning of the energy-water-food nexus using decision making tools. Energy Policy 2018, 113, 584–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cevher, C. Determination of the Main Socio-Economic Factors of the Sustainable Production of Forage Crops: Research of Kayseri Province. J. Agric. Sci. 2019, 25, 474–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namany, S.; Govindan, R.; Martino, M.D.; Pistikopoulos, E.N.; Linke, P.; Avraamidou, S.; Al-Ansari, T. An Energy-Water-Food Nexus-based Decision-making Framework to Guide National Priorities in Qatar. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 75, 103342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abegaz, B.W.; Datta, T.; Mahajan, S.M. Sensor technologies for the energy-water nexus—A review. Appl. Energy 2018, 210, 451–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, S. Implementing the Urban Nexus approach for improved resource-efficiency of developing cities in Southeast-Asia. City Cult. Soc. 2018, 13, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keyhanpour, M.J.; Musavi Jahromi, S.H.; Ebrahimi, H. System dynamics model of sustainable water resources management using the Nexus Water-Food-Energy approach. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2021, 12, 1267–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravar, Z.; Zahraie, B.; Sharifinejad, A.; Gozini, H.; Jafari, S. System dynamics modeling for assessment of water–food–energy resources security and nexus in Gavkhuni basin in Iran. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 108, 105682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, Q.; Wu, H.; Wang, Y.; Guo, P. Achieving sustainable development goals in agricultural energy-water-food nexus system: An integrated inexact multi-objective optimization approach. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2021, 174, 105833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albrecht, T.R.; Crootof, A.; Scott, C.A. The Water-Energy-Food Nexus: A systematic review of methods for nexus assessment. Environ. Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 043002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishant, R.; Kennedy, M.; Corbett, J. Artificial intelligence for sustainability: Challenges, opportunities, and a research agenda. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2020, 53, 102104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almadi, A.I.M.; Al Mamlook, R.E.; Ullah, I.; Alshboul, O.; Bandara, N.; Shehadeh, A. Vehicle collisions analysis on highways based on multi-user driving simulator and multinomial logistic regression model on US highways in Michigan. Int. J. Crashworthiness 2023, 28, 770–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Shboul, K.F.; Almasabha, G.; Shehadeh, A.; Alshboul, O. Exploring the efficacy of machine learning models for predicting soil radon exhalation rates. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2023, 37, 4307–4321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshboul, O.; Al Mamlook, R.E.; Shehadeh, A.; Munir, T. Empirical exploration of predictive maintenance in concrete manufacturing: Harnessing machine learning for enhanced equipment reliability in construction project management. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2024, 190, 110046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshboul, O.; Almasabha, G.; Shehadeh, A.; Al-Shboul, K. A comparative study of LightGBM, XGBoost, and GEP models in shear strength management of SFRC-SBWS. Structures 2024, 61, 106009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvestre, B.S.; Ţîrcă, D.M. Innovations for sustainable development: Moving toward a sustainable future. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 208, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshboul, O.; Almasabha, G.; Al-Shboul, K.F.; Shehadeh, A. A comparative study of shear strength prediction models for SFRC deep beams without stirrups using Machine learning algorithms. Structures 2023, 55, 97–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almasabha, G.; Shehadeh, A.; Alshboul, O.; Al Hattamleh, O. Structural performance of buried reinforced concrete pipelines under deep embankment soil. Constr. Innov. 2023; ahead-of-print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Vaio, A.; Hassan, R.; Alavoine, C. Data intelligence and analytics: A bibliometric analysis of human–Artificial intelligence in public sector decision-making effectiveness. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2022, 174, 121201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Vaio, A.; Palladino, R.; Hassan, R.; Escobar, O. Artificial intelligence and business models in the sustainable development goals perspective: A systematic literature review. J. Bus. Res. 2020, 121, 283–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caprani, L. Five ways the sustainable development goals are better than the millennium development goals and why every educationalist should care. Manag. Educ. 2016, 30, 102–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, W.; Chen, Y.; Zou, S.; Nover, D. Managing the water-climate- food nexus for sustainable development in Turkmenistan. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 220, 212–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwivedi, Y.K.; Hughes, L.; Ismagilova, E.; Aarts, G.; Coombs, C.; Crick, T.; Duan, Y.; Dwivedi, R.; Edwards, J.; Eirug, A.; et al. Artificial Intelligence (AI): Multidisciplinary perspectives on emerging challenges, opportunities, and agenda for research, practice and policy. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2021, 57, 101994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Fang, S.; Dong, H.; Xu, C. Review of digital twin about concepts, technologies, and industrial applications. J. Manuf. Syst. 2021, 58, 346–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, R.; Aguilar, J.; Toro, M.; Pinto, A.; Rodríguez, P. A systematic literature review on the use of machine learning in precision livestock farming. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2020, 179, 105826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovarelli, D.; Bacenetti, J.; Guarino, M. A review on dairy cattle farming: Is precision livestock farming the compromise for an environmental, economic and social sustainable production? J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 262, 121409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, J.; Berger, H.; Henriksen, H.J.; Sonnenborg, T.O. Modelling of the shallow water table at high spatial resolution using random forests. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2019, 23, 4603–4619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, J.; Gotfredsen, J.; Schneider, R.; Troldborg, L.; Stisen, S.; Henriksen, H.J. High resolution water table modeling of the shallow groundwater using a knowledge-guided gradient boosting decision tree model. Front. Water 2021, 3, 701726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, R.; Koch, J.; Troldborg, L.; Henriksen, H.J.; Stisen, S. Machine-learning-based downscaling of modelled climate change impacts on groundwater table depth. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2022, 26, 5859–5877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skobelev, P.; Laryukhin, V.; Simonova, E.; Goryanin, O.; Yalovenko, V.; Yalovenko, O. Multi-agent approach for developing a digital twin of wheat. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Smart Computing (SMARTCOMP), Bologna, Italy, 14–17 September 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Purcell, W.; Neubauer, T.; Mallinger, K. Digital Twins in agriculture: Challenges and opportunities for environmental sustainability. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 2023, 61, 101252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsolakis, N.; Bechtsis, D.; Bochtis, D. AgROS: A Robot Operating System Based Emulation Tool for Agricultural Robotics. Agronomy 2019, 9, 403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

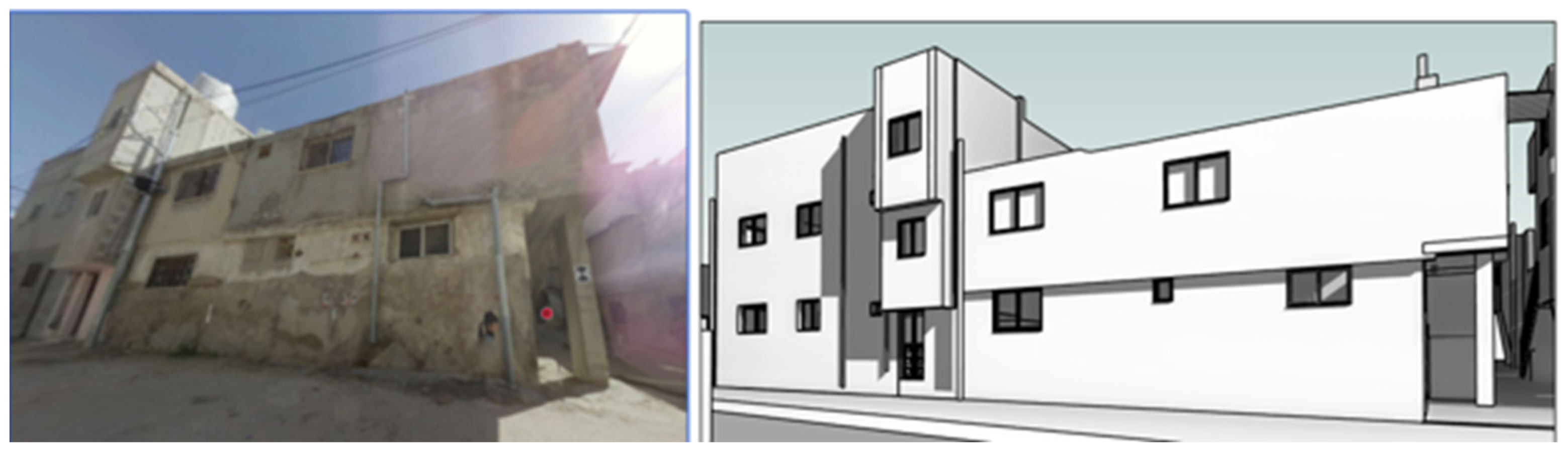
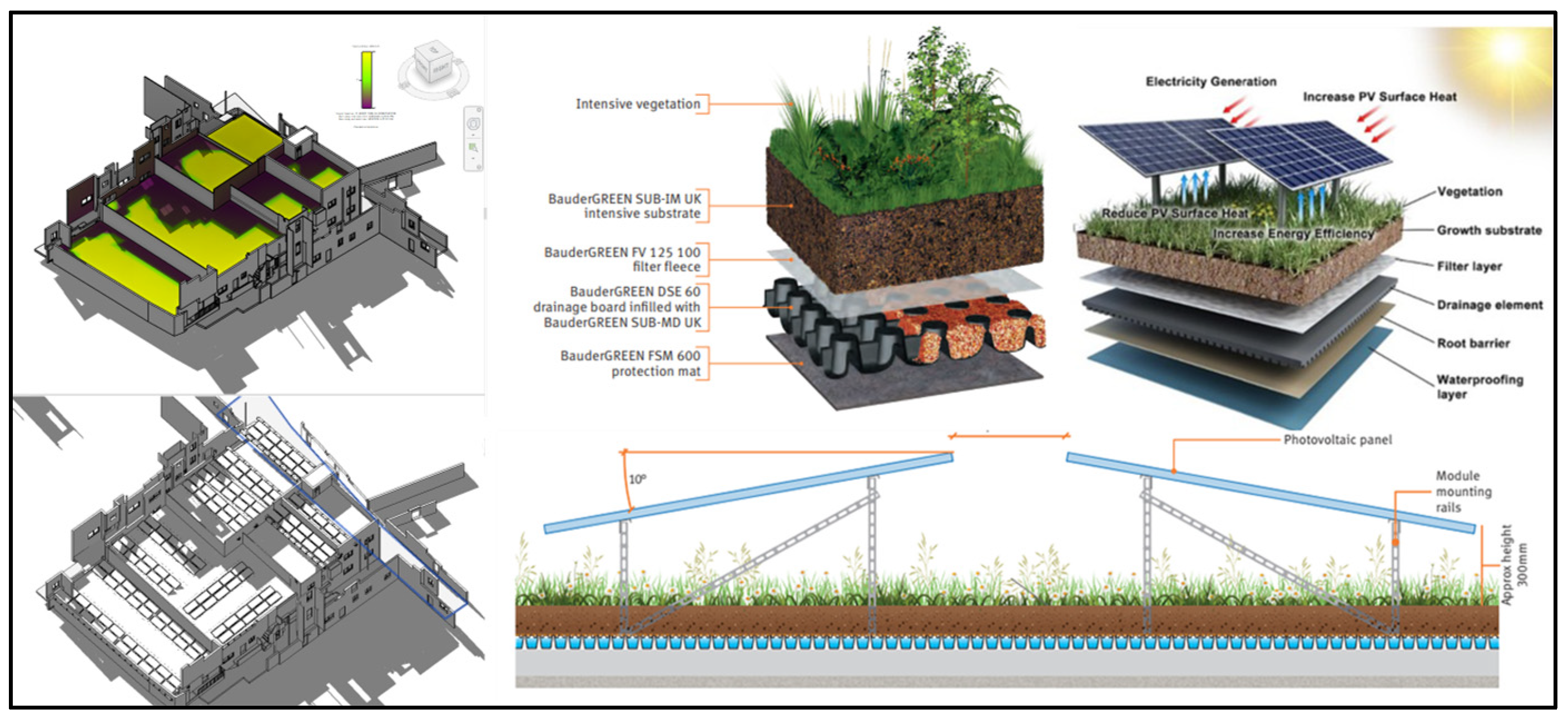



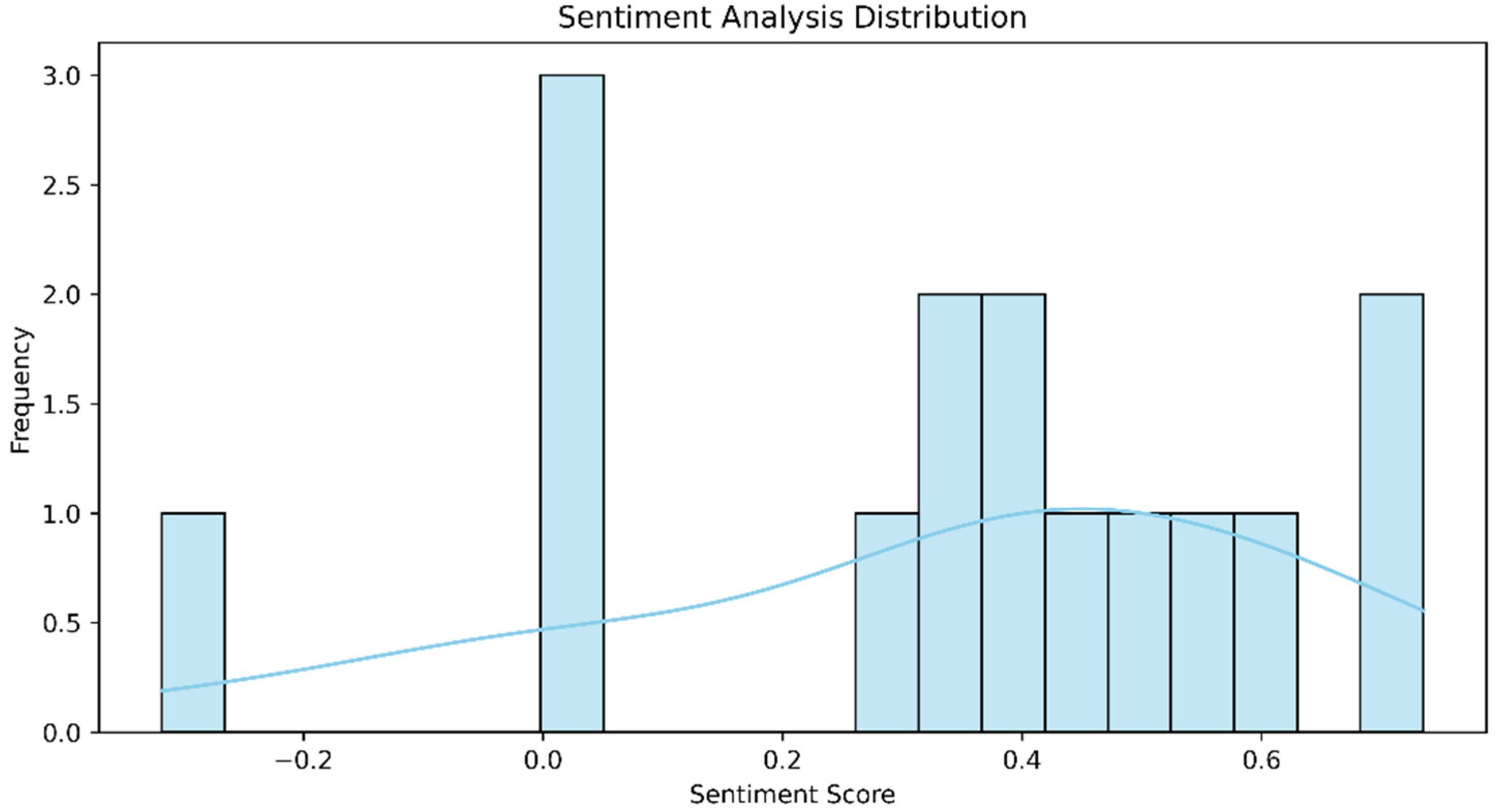
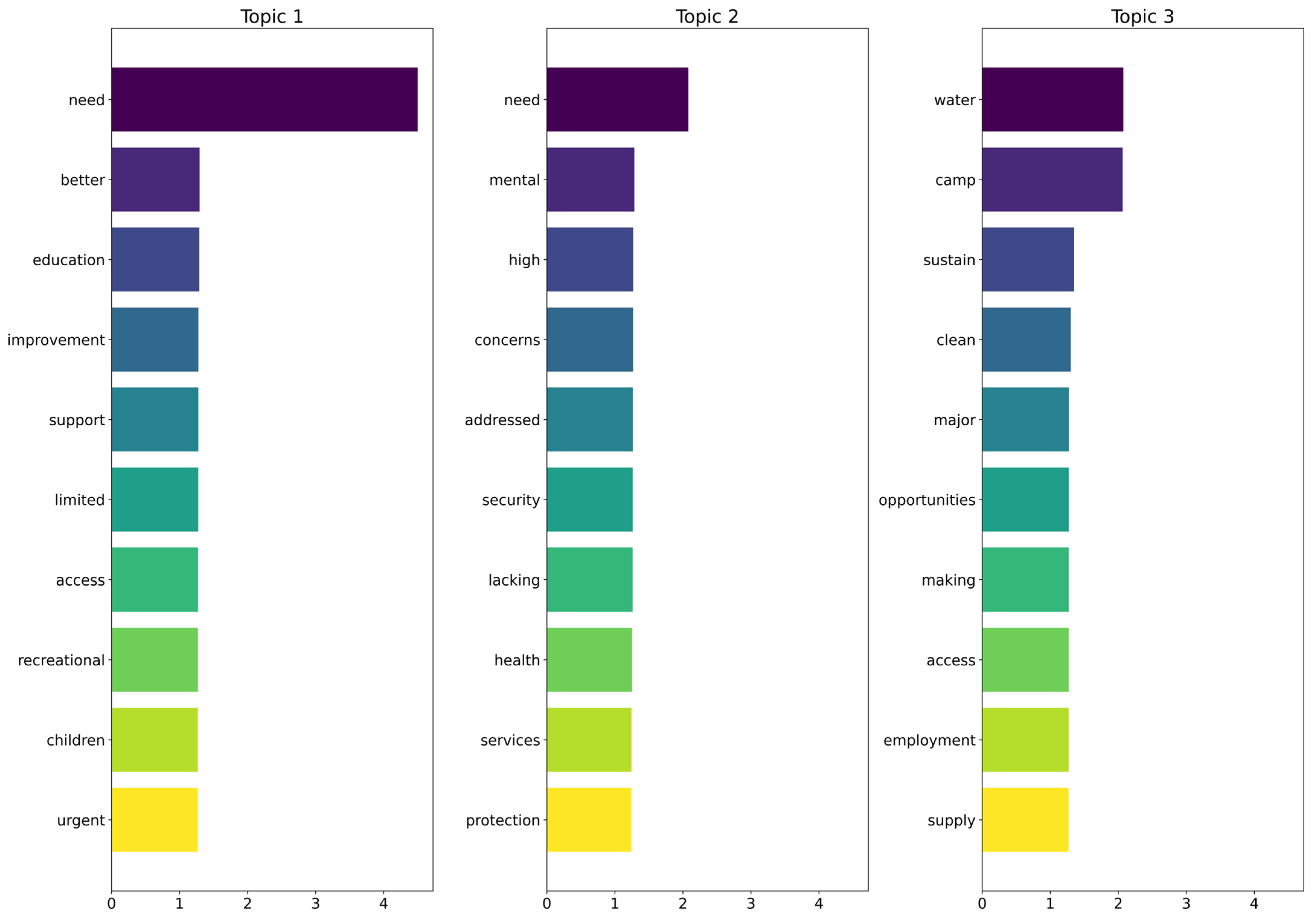
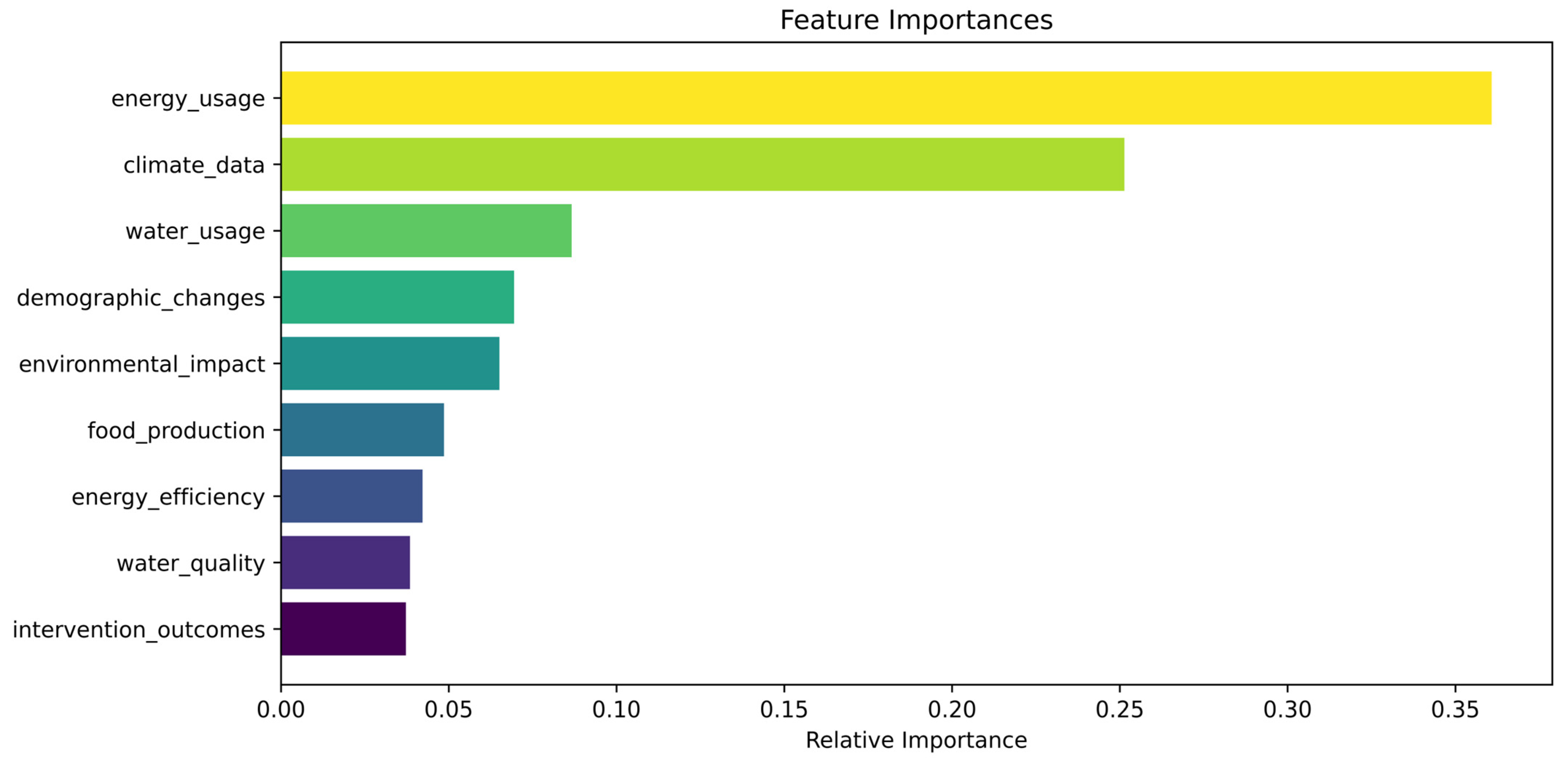



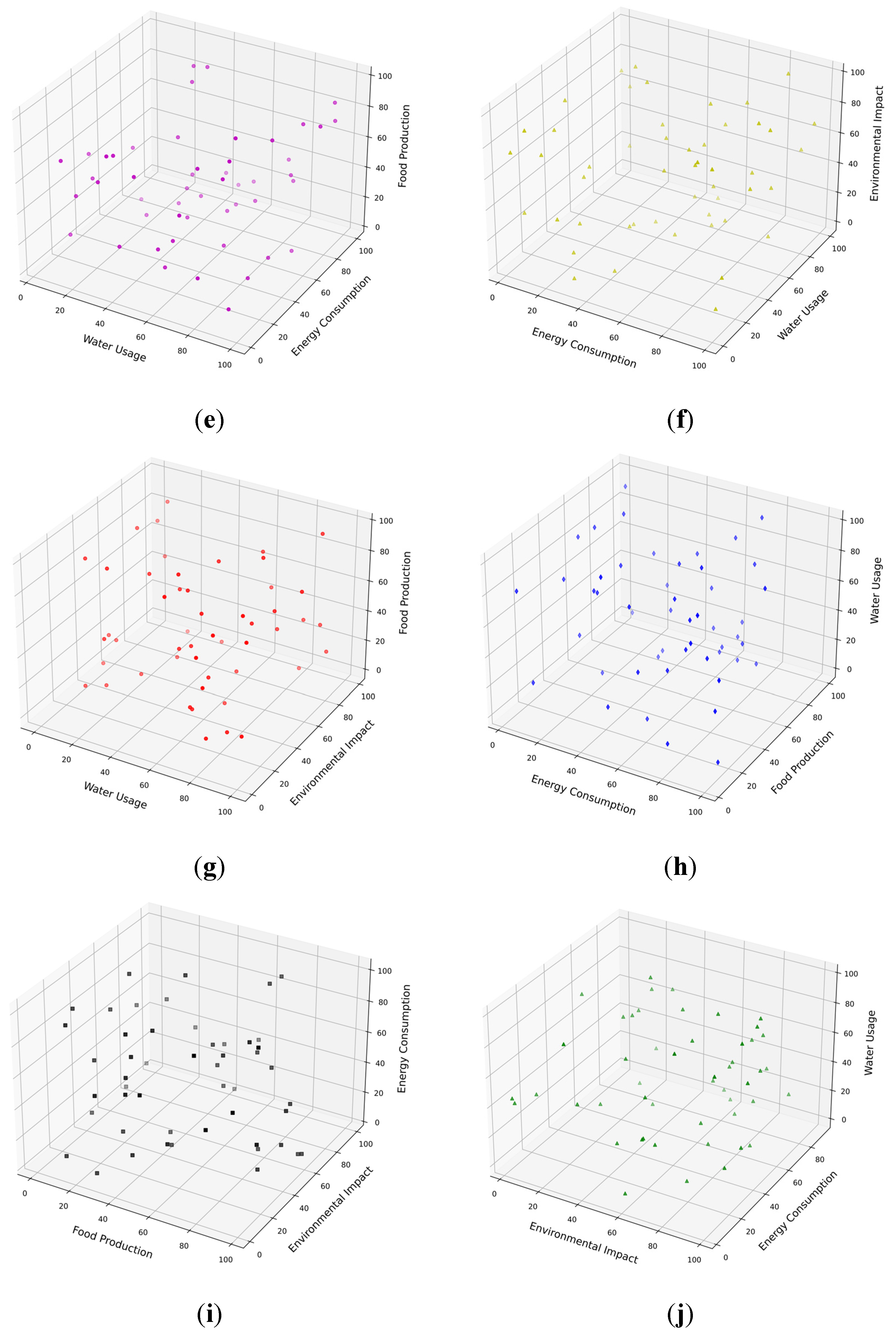
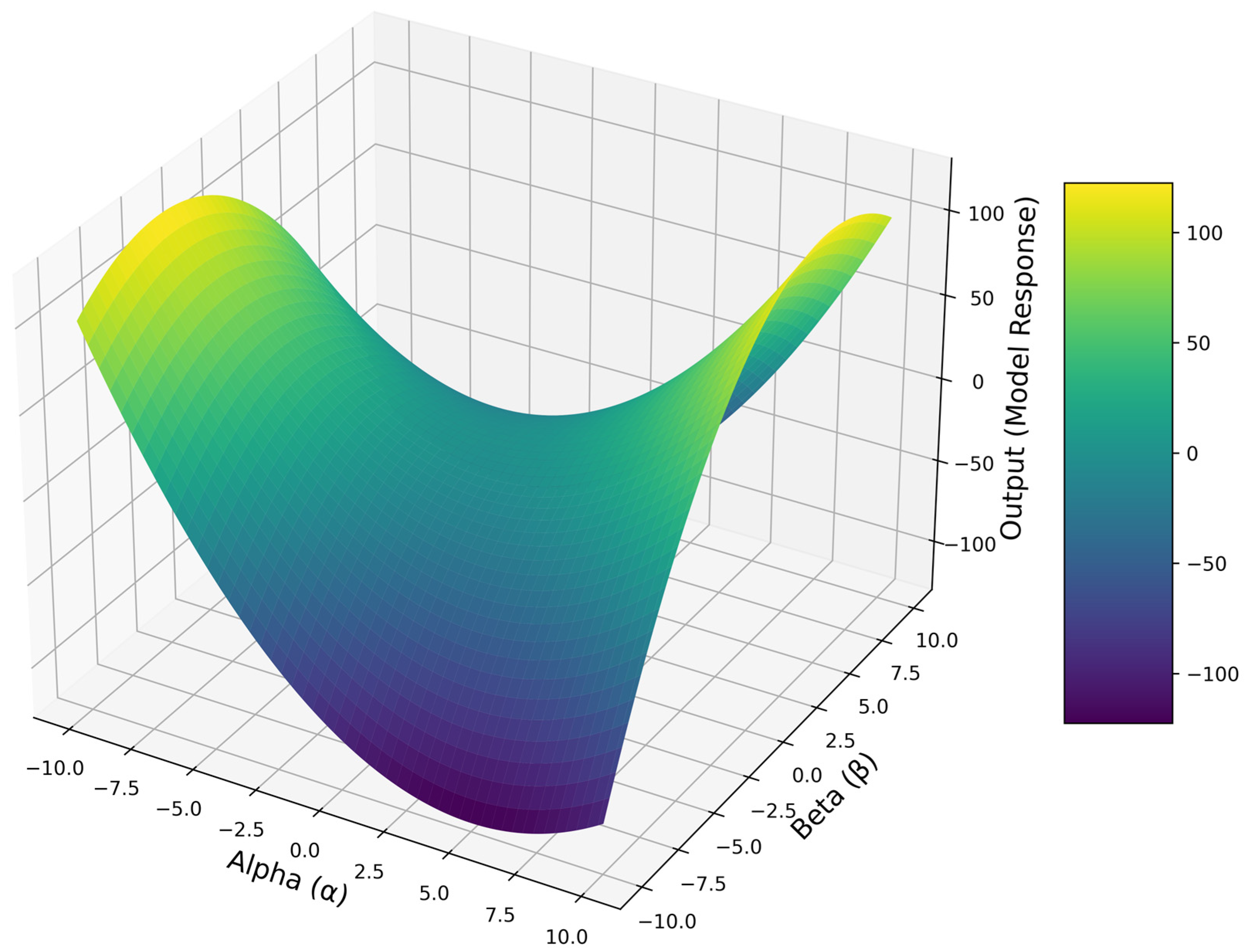
| Metric/Model | The Proposed Model | Support Vector Machine (SVM) | Logistic Regression |
|---|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | 0.92 | 0.85 | 0.87 |
| Recall | 0.90 | 0.80 | 0.83 |
| Precision | 0.94 | 0.88 | 0.89 |
| F1-Score | 0.92 | 0.84 | 0.86 |
| AUC-ROC | 0.96 | 0.90 | 0.88 |
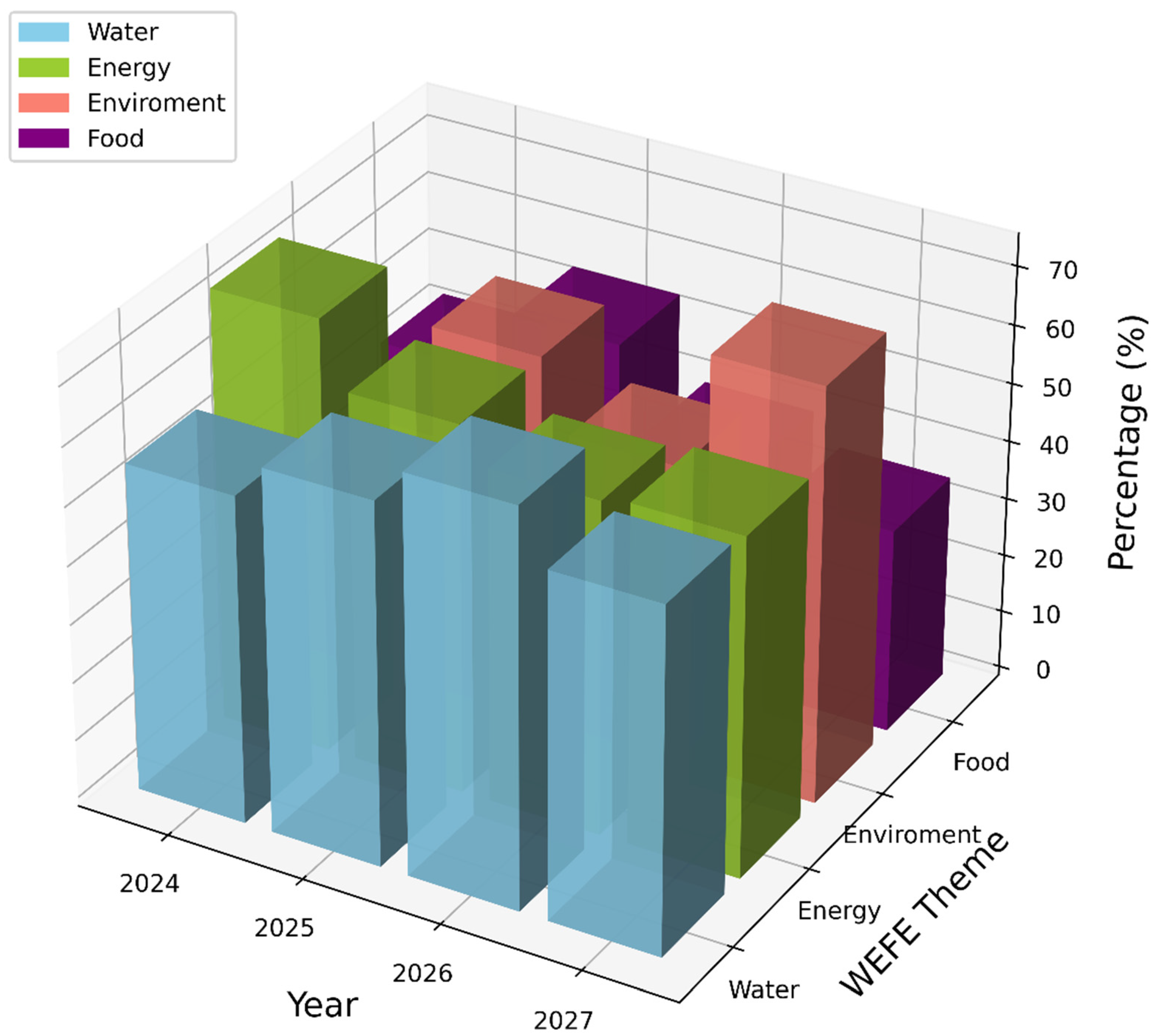
| WEFE Component | Baseline Metrics before Implementation | Metrics after Implementation | Percentage Improvement |
|---|---|---|---|
| Water | Water leakage: 15% Water conservation awareness: 80% Satisfaction with water management: 35% | Water leakage: 5% Water conservation awareness: 95% Satisfaction with water management: 80% | Water leakage reduction: 66.7% Awareness increase: 18.8% Satisfaction increase: 128.6% |
| Energy | Renewable energy usage: 20% Energy shortages: 25% Satisfaction with energy supply: 40% | Renewable energy usage: 50% Energy shortages: 10% Satisfaction with energy supply: 75% | Renewable energy usage increase: 150% Energy shortage reduction: 60% Satisfaction increase: 87.5% |
| Food | Optimized food distribution: 60% Own food production: 25% Nutritional adequacy: 50% | Optimized food distribution: 85% Own food production: 55% Nutritional adequacy: 75% | Food distribution optimization increase: 41.7% Own food production increase: 120% Nutritional adequacy increase: 50% |
| Environment | Green space availability: 10% Waste recycling rate: 30% Air quality index: 55 (Fair) | Green space availability: 20% Waste recycling rate: 60% Air quality index: 85 (Very Good) | -Green space availability increase: 100% Waste recycling rate increase: 100% Air quality improvement: 21.4% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shehadeh, A.; Alshboul, O.; Arar, M. Enhancing Urban Sustainability and Resilience: Employing Digital Twin Technologies for Integrated WEFE Nexus Management to Achieve SDGs. Sustainability 2024, 16, 7398. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16177398
Shehadeh A, Alshboul O, Arar M. Enhancing Urban Sustainability and Resilience: Employing Digital Twin Technologies for Integrated WEFE Nexus Management to Achieve SDGs. Sustainability. 2024; 16(17):7398. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16177398
Chicago/Turabian StyleShehadeh, Ali, Odey Alshboul, and Mai Arar. 2024. "Enhancing Urban Sustainability and Resilience: Employing Digital Twin Technologies for Integrated WEFE Nexus Management to Achieve SDGs" Sustainability 16, no. 17: 7398. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16177398
APA StyleShehadeh, A., Alshboul, O., & Arar, M. (2024). Enhancing Urban Sustainability and Resilience: Employing Digital Twin Technologies for Integrated WEFE Nexus Management to Achieve SDGs. Sustainability, 16(17), 7398. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16177398







