Spatial Differentiation and Influencing Factors of Available Potassium in Cultivated Soil in Mountainous Areas of Northwestern Hubei Province, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Research Methods and Data Sources
2.1. Overview of the Study Area
2.2. Data Source and Processing
2.2.1. Sampling Point Data
2.2.2. Impact Factor Data
2.2.3. Geodetector
2.3. Data Preprocessing
3. Results
3.1. Statistical Characteristics of Soil AK
3.2. Spatial Variation in Soil AK
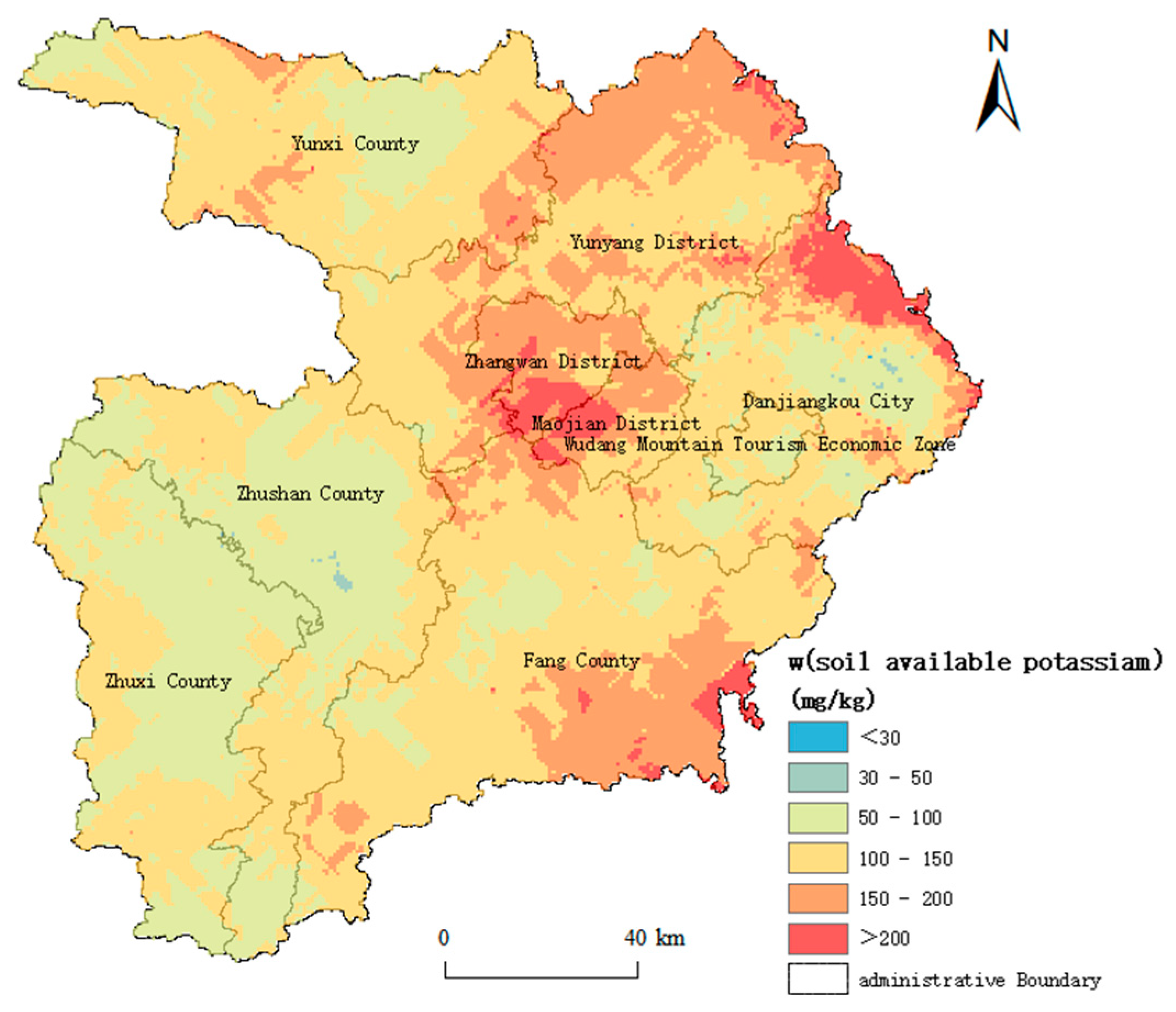
3.3. Spatial Distribution Characteristics of Soil AK
3.4. Geodetector Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. Influence of Terrain Factors on Spatial Variation in AK
4.1.1. Altitude
4.1.2. Slope
4.2. Effect of Climate Factors on Spatial Variability of AK
4.2.1. Mean Annual Temperature
4.2.2. Annual Precipitation
4.3. Effect of Soil Factors on Spatial Variability of AK
4.3.1. Soil Parent Material
4.3.2. Soil Type
4.3.3. Soil pH
4.4. Effects of Human Activities on Spatial Variability of AK
4.4.1. Cropping System
4.4.2. Plow Layers
4.5. The Impact of Interaction Factors on AK Spatial Variation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ismail, C. Potassium for better crop production and quality. Plant Soil. 2010, 335, 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, X.J.; Simpson, M.J. Temperature and substrate controls on microbial phospholipid fatty acid composition during incubation of grassland soils contrasting in organic matter quality. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2009, 41, 804–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dent, D. Soil as World Heritage; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Du, H.; Wang, K.L.; Peng, W.X.; Zeng, F.P.; Song, T.Q.; Zhang, H.; Lu, S.Y. Spatial heterogeneity of soil mineral oxide components in depression between karst hills, Southwest China. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2014, 24, 163–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, S.M.; Hou, J.Q.; Zhao, J.S.; Clarke, N.; Kempenaar, C.; Chen, X.L. Predicting soil organic matter, available nitrogen, available phosphorus and available potassium in a black soil using a nearby hyperspectral sensor system. Sensors 2024, 24, 2784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sardans, J.; Pe·uelas, J. Potassium: Aneglected nutrient in global change. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2015, 24, 261–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.L.; Zhang, X.Y.; Liu, X.B.; Liu, W.; Liu, Z.H. Spatial distribution of soil nutrient at depth in black soil of Northeast China:a case study of soil AK. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosystems 2013, 95, 319–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Chen, Y.P.; Jiang, Y.; Mu, J.H.; Wang, H. Spatial and Temporal variation of soil available potassium and Its Influencing Factors in Shaanxi Province. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2021, 35, 296–302+311. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, Q.W.; Wang, X.; Li, L.D.; You, H.D.; Bi, J. Vertical variation of soil physical and chemical properties at different altitudes in xiaowutai mountain. J. Soil. Water Conserv. 2019, 33, 241–247. [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson, S.R.; Stuedemann, J.A.; Belesky, D.P. Soil potassium distribution in grazed K-31 tall fescue pastures as affected by fertilization and endophytic fungus infection level. Agron. J. 1989, 81, 508–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallarino, A.P.; Borges, R. Phosphorus and potassium distribution in soil following long-term deep-band fertilization in different tillage systems. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2006, 70, 702–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.H.; Wang, C.Q.; Li, Q.Q.; Li, B.; Yu, L.Z.; Chen, Y.L.; Zhou, Y.G. Geostatistics and GIS analysis of soil available potassium in Mountainous Southwestern Sichuan. Southwest China J. Agric. Sci. 2016, 29, 651–657. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, J.; Mamat, Z.; Ye, Q. Spatial heterogeneity of soil nutrients and salinization risk assessment of a small-scale farmland in Ebinur Basin in northwest China. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2017, 37, 819–828. [Google Scholar]
- Dos Santos, R.O.; Franco, L.B.; Silva, S.A.; Sodré, G.A.; Menezes, A.A. Spatial variability of soil fertility and its relation with cocoa yield. Revista Brasileira de Engenharia Agrícola e Ambiental 2017, 21, 88–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.J.; Li, Z.W.; Wang, C.; Zheng, D.C.; Du, H.L. Prediction of available potassium content in cinmamon soil using hyperspectral imaging technology. Spectrosc. Spectr. Anal. 2019, 39, 1579–1585. [Google Scholar]
- Han, Y.; Jing, Y.F.; Guo, X.; Li, Z.L.; Lin, W.L.; Chen, L.; Yi, D. Study on the factors influencing the spatial variability of soil potassium in cultivated land in Poyang Lake Plain based on boosted regression tree. J. Plant Nutr. Fertil. 2020, 26, 622–634. [Google Scholar]
- Blanchet, G.; Libohova, Z.; Joost, S.; Rossier, N.; Schneider, A.; Jeangros, B.; Sinaj, J. Spatial variability of potassium in agricultural soils of the canton of Fribourg, Switzerland. Geoderma 2017, 290, 107–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.F.; Xu, C.D. Geodetector: Principle and prospective. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2017, 72, 116–134. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.F.; Hu, Y. Environmental health risk detection with GeoDetector. Environ. Model. Softw. 2012, 33, 114–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Xiao, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, L.; Tang, L. Interactive effects of natural and anthropogenic factors on heterogenetic accumulations of heavy metals in surface soils through geodetector analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 789, 147937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Ruan, Y.; Xuan, W.; Bao, H.; Du, Z. Risk assessment and spatial regulation on urban ground collapse based on geo-detector: A case study of Hangzhou urban area. Nat. Hazards 2023, 118, 525–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.J.; Wang, J.Y.; Wang, Y. Effect of land prices on the spatial differentiation of housing prices: Evidence from cross-county analyses in China. J. Geogr. Sci. 2018, 28, 725–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Notice of the Ministry of Agriculture on Issuing the Technical Specifications for Soil Testing and Formula Fertilization (Revised Edition in 2011). Available online: http://www.moa.gov.cn/ztzl/ctpfsf/gzdt/201109/t20110922_2293389.htm (accessed on 23 August 2024).
- Taghizadeh-Toosi, A.; Olesen, J.E.; Kristensen, K.; Elsgaard, L.; Østergaard, H.S.; Lagdsmand, M.; Greve, M.H.; Christensen, B.T. Changes in carbon stocks of Danish agricultural mineral soils between 1986 and 2009. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2014, 65, 730–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antwi, M.; Duker, A.A.; Fosu, M.; Abaidoo, R.C. Geospatial approach to study the spatial distribution of major soil nutrients in the Northern region of Ghana. Cogent Geosci. 2016, 2, 1201906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.Z.; Liu, G.M.; Yang, J.S.; Zhang, M.M. Spatial variability and distribution pattern of soil nutrients in Bohai coastala area. Acta Pedol. Sin. 2014, 51, 944–952. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.Q.; Jiao, J.Y.; Chen, T.D.; Chen, Y.L.; Lin, H.; Xu, Q.; Cheng, Y.Z.; Zhao, W.T. Soil nutrient evaluation of alluvial fan in the middle and lower reaches of Lhasa River Basin. J. Plant Nutr. Fertil. 2022, 28, 2082–2096. [Google Scholar]
- Cambardclla, C.A.; Moorman, T.B.; Novak, J.M.; Parkin, T.B.; Konopka, A.E. Field-scale variability of soil properties in central Iowa soils. Soil. Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1994, 58, 1501–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, R. Quantitative spatial analysis of soil in the field. Adv. Soil Sci. 1985, 3, 1–70. [Google Scholar]
- Kuchenbuch, R.; Claassen, N.; Jungk, A. Potassium availability in relation to soil moisture. Plant Soil 1986, 95, 233–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, O.P.; Zhou, X.; Huang, P.P.; Deng, L.J. Correlations between spatial variability of soil nutrients and topographic factors in the Purple Hilly Region of Sichuan. Resour. Sci. 2013, 35, 2434–2443. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Qi, Y.B.; Wang, Y.Y.; Zhang, L.L.; Liu, J.J. Spatial variability and factors affecting soil available potassium in the central Qinling-Daba Mountain area. Res. Environ. Sci. 2017, 30, 257–266. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, W.D.; Wang, Z.Q.; Su, G.P.; Ding, G.W. Quantitative determination of red-soil erosion by an Eu tracer method. Soil Tillage Res. 2008, 101, 52–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, M.Q.; Peng, Y.Y.; Wang, P.; Feng, L.; Chen, L.Y.; Du, X.Y.; Li, Q.Q.; Wang, C.Q. Spatial Variability Characteristic and Its Influencing Factors of Tobacco Planting Soil Available N, P and K in Yanyuan County of Sichuan, China. Soils 2016, 48, 984–991. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, L.J.; Yu, J.; Shi, J.S.; Wang, C.M.; Bi, Z.W.; Gao, J. Study on the evolution law of potassium with long time scale climate change in Jiangjun loess of the middle reaches of the jinghe river. J. Shanghai Jiaotong Univ. Agric. Sci. 2006, 34, 69–73. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, J.Y.; Gao, G.L.; Wang, Z.L.; Zhang, N.F. Temperature effects on quantity and intensity (Q/I) relationship of potassium in selected soils. Acta Pedol. Sin. 1992, 29, 137–141. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X.Y.; Ma, Y.J.; Zhang, R.P. Research progress in transformation of soil potassium in relation to pottash application. Chin. J. Soil. Sci. 2003, 34, 489–492. [Google Scholar]
- He, P.; Yang, L.P.; Xu, X.P.; Zhao, S.C.; Chen, F.; Li, S.T.; Tu, S.H.; Jin, J.Y.; Johnston, A.M. Temporal and spatial variation of soil available potassium in China (1990–2012). Field Crops Res. 2015, 173, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.E.; Shung, W.Y.; Yun, A.P.; Niu, L.A.; Hu, K.L. Spatio-temporal variability and the influencing factors of soil available potassium in 30 years in quzhou county, Hebei province. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2014, 47, 923–933. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, L.B.; Fang, B.; Dong, L.K. Spatial distribution characteristics of available potassium in typical tea gardens in Jiangsu Province and Zhejiang Province. Mt. Res. 2017, 35, 160–169. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, X.H.; Yang, L.L.; Zhou, M.L.; Tian, M.C.; Tian, F.; Feng, X.H.; Wu, Q.M. Distribution of available potassium contents of tobacco-growing soil and its influencing factors in karst region of Xiangxi. Mt. Res. 2013, 31, 519–526. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, G.W. Forms of aluminium in cation exchangers. Trans. Int. Congr. Soil Sci. 1960, 2, 364–369. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Chang, Q.R.; Huang, Y.; Shi, B.T.; Luo, L.L. Driving Factors and Interaction of STN Spatial Variation in Shaanxi Province Based on Geo-D. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2021, 52, 161–169. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Y.S.; Ma, K.; Zhou, H.; Llu, W.B.; Fang, F.M.; Zhi, J.J. Spatial variation and driving factors of soil pH in cultivated land of Anhui Province based on geomorphic unit. Acta Sci. Circumstantiae 2023, 43, 318–330. [Google Scholar]


| Rating | Range (mg/kg) | Sampling Number | Proportion (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| I (very rich) | 350.00–200.00 | 70 | 9.99 |
| II (rich) | 150.00–200.00 | 116 | 16.55 |
| III (moderate) | 100.00–150.00 | 197 | 28.10 |
| IV (low) | 50.00–100.00 | 239 | 34.09 |
| V (very low) | 30.00–50.00 | 69 | 9.84 |
| VI (extremely low) | 15.00–30.00 | 10 | 1.43 |
| AK average value | 118.95 |
| Sample Points | Minimum (mg/kg) | Maximum (mg/kg) | Mean (mg/kg) | SD (mg/kg) | C.V. (%) | Skewness | Kurtosis |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 701 | 17.00 | 350.00 | 118.95 | 64.30 | 54.06 | 1.08 | 1.10 |
| Model | Nugget | Sill | Nugget Coefficient | Range (m) | R2 | RSS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spherical | 0.0081 | 0.2952 | 0.027 | 7500 | 0.549 | 2.821 × 10−3 |
| Exponential | 0.0262 | 0.2944 | 0.089 | 8400 | 0.499 | 3.123 × 10−3 |
| Gaussian | 0.0458 | 0.2946 | 0.156 | 6409 | 0.546 | 2.825 × 10−3 |
| Linear | 0.2908 | 0.2908 | 0.000 | 102,158 | 0.000 | 2.82 × 10−3 |
| Impact Factor | Terrain | Climate | Soil Factors | Human Factor | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X1 | X2 | X3 | X4 | X5 | X6 | X7 | X8 | X9 | |
| Q | 0.0372 *** | 0.0556 *** | 0.1007 *** | 0.0837 *** | 0.1065 *** | 0.0949 *** | 0.1599 *** | 0.0321 ** | 0.0348 *** |
| Xi ∩ Xj | q (Xi) | q (Xj) | q (Xi∩Xj) | q (Xi) + q (Xj) | Interaction Type | Xi ∩ Xj | q (Xi) | q (Xj) | q (Xi ∩ Xj) | q (Xi) + q (Xj) | Interaction Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X1 ∩ X2 | 0.0372 | 0.0556 | 0.1146 | 0.0928 | non-linear | X3 ∩ X7 | 0.1007 | 0.0556 | 0.2124 | 0.1563 | non-linear |
| X1 ∩ X3 | 0.0372 | 0.1007 | 0.1366 | 0.1379 | two-factor | X3 ∩ X8 | 0.1007 | 0.0556 | 0.1597 | 0.1563 | non-linear |
| X1 ∩ X4 | 0.0372 | 0.0837 | 0.1215 | 0.1209 | non-linear | X3 ∩ X9 | 0.1007 | 0.0556 | 0.1516 | 0.1563 | two-facor |
| X1 ∩ X5 | 0.0372 | 0.1065 | 0.1518 | 0.1437 | non-linear | X4 ∩ X5 | 0.0837 | 0.1065 | 0.2083 | 0.1902 | non-linear |
| X1 ∩ X6 | 0.0372 | 0.0944 | 0.1354 | 0.1316 | non-linear | X4 ∩ X6 | 0.0837 | 0.0944 | 0.1795 | 0.1781 | non-linear |
| X1 ∩ X7 | 0.0372 | 0.1599 | 0.1895 | 0.1971 | two-factor | X4 ∩ X7 | 0.0837 | 0.1599 | 0.1874 | 0.2436 | two-factor |
| X1 ∩ X8 | 0.0372 | 0.0321 | 0.1084 | 0.0693 | non-linear | X4 ∩ X8 | 0.0837 | 0.0321 | 0.1568 | 0.1158 | non-linear |
| X2 ∩ X9 | 0.0372 | 0.0348 | 0.1049 | 0.0720 | non-linear | X4 ∩ X9 | 0.0837 | 0.0348 | 0.1364 | 0.1185 | non-linear |
| X2 ∩ X3 | 0.0556 | 0.1007 | 0.1633 | 0.1563 | non-linear | X5 ∩ X6 | 0.1065 | 0.0944 | 0.1809 | 0.2009 | two-factor |
| X2 ∩ X4 | 0.0556 | 0.0837 | 0.1588 | 0.1393 | non-linear | X5 ∩ X7 | 0.1065 | 0.1599 | 0.2318 | 0.2664 | two-factor |
| X2 ∩ X5 | 0.0556 | 0.1065 | 0.2016 | 0.1621 | non-linear | X5 ∩ X8 | 0.1065 | 0.0321 | 0.2200 | 0.1386 | non-linear |
| X2 ∩ X6 | 0.0556 | 0.0944 | 0.1792 | 0.1500 | non-linear | X5 ∩ X9 | 0.1065 | 0.0348 | 0.1767 | 0.1413 | non-linear |
| X2 ∩ X7 | 0.0556 | 0.1599 | 0.2366 | 0.2155 | non-linear | X6 ∩ X7 | 0.0944 | 0.1599 | 0.2099 | 0.2543 | two-factor |
| X2 ∩ X8 | 0.0556 | 0.0321 | 0.1261 | 0.0877 | non-linear | X6 ∩ X8 | 0.0944 | 0.0321 | 0.1773 | 0.1265 | non-linear |
| X5 ∩ X9 | 0.0556 | 0.0348 | 0.1115 | 0.0904 | non-linear | X6 ∩ X9 | 0.0944 | 0.0348 | 0.1571 | 0.1292 | non-linear |
| X3 ∩ X4 | 0.1007 | 0.0837 | 0.1595 | 0.1844 | two-factor | X7 ∩ X8 | 0.1599 | 0.0321 | 0.2291 | 0.1920 | non-linear |
| X3 ∩ X5 | 0.1007 | 0.1065 | 0.2145 | 0.2072 | non-linear | X7 ∩ X9 | 0.1599 | 0.0348 | 0.1970 | 0.1947 | non-linear |
| X3 ∩ X6 | 0.1007 | 0.0944 | 0.1857 | 0.1951 | two-factor | X8 ∩ X9 | 0.0321 | 0.0348 | 0.1095 | 0.0669 | non-linear |
| Environmental Variable | Altitude | Slope | Precipitation | Temperature | Topsoil Depth | Soil pH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pearson correlation coefficient | −0.138 ** | −0.146 ** | −0.268 ** | 0.287 ** | −0.080 * | 0.324 ** |
| p-value | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.035 | 0.000 |
| Altitude | Sample Number | Range | Average Value | Standard Deviation | Coefficient of Variation (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ≤200 | 73 | 25–299 | 139.25 | 66.94 | 48.07 |
| 200–300 | 182 | 17–350 | 133.06 | 74.76 | 56.19 |
| 300–400 | 121 | 26–321 | 117.53 | 66.11 | 56.25 |
| 400–500 | 98 | 27.58–302.00 | 106.67 | 49.52 | 46.42 |
| 500–600 | 104 | 20.79–327.00 | 108.43 | 56.82 | 52.40 |
| 600–700 | 53 | 31.46–255.00 | 94.02 | 47.26 | 50.27 |
| >700 | 70 | 39.00–303.00 | 115.31 | 56.75 | 49.22 |
| Slope | Sample Number | Range | Average Value | Standard Deviation | Coefficient of Variation (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ≤2° | 7 | 119–340.00 | 182.57 | 78.21 | 42.84 |
| 2–6° | 66 | 33–274.00 | 108.87 | 52.85 | 48.54 |
| 6–15° | 357 | 20.79–350.00 | 127.39 | 69.95 | 54.91 |
| 15–25° | 261 | 17.00–350.00 | 108.26 | 55.75 | 51.50 |
| >25° | 10 | 50.65–252.00 | 118.77 | 62.87 | 52.93 |
| Range | Sample Number | Range | Average Value | Standard Deviation | Coefficient of Variation (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ≤15.00 | 110 | 27.58–221.34 | 88.72 | 39.51 | 44.53% |
| 15.00–15.50 | 159 | 20.79–327.00 | 105.09 | 51.37 | 48.88% |
| 15.50–16.00 | 135 | 32.00–281.00 | 112.76 | 50.80 | 45.05% |
| 16.00–16.50 | 138 | 36.00–350.00 | 143.19 | 71.61 | 50.01% |
| >16.50 | 159 | 17.00–340.00 | 137.96 | 78.91 | 57.20% |
| Range | Sample Number | Range | Average Value | Standard Deviation | Coefficient of Variation (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ≤750 | 25 | 62.00–321.00 | 165.24 | 52.27 | 31.63 |
| 750–850 | 129 | 32.00–350.00 | 161.13 | 76.05 | 47.20 |
| 850–950 | 205 | 17.00–340.00 | 114.59 | 65.77 | 57.40 |
| 950–1050 | 218 | 20.79–281.00 | 97.16 | 45.01 | 46.33 |
| >1050 | 124 | 36.48–303.00 | 111.28 | 54.73 | 49.18 |
| Parent Material Type | Sample Number | Range | Average Value | Standard Deviation | Coefficient of Variation (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Purple rock weathering | 9 | 28–201 | 105.63 | 53.855 | 50.98 |
| Carbonate weathering | 53 | 43–299 | 146.30 | 70.641 | 48.29 |
| Quartzite weathering | 43 | 39–213 | 118.16 | 46.370 | 39.24 |
| Argillaceous weathering | 400 | 17–350 | 107.31 | 59.698 | 55.63 |
| Crystalline rock weathering | 16 | 34–321 | 134.54 | 81.185 | 60.34 |
| Red sandstone weathering | 60 | 36–350 | 177.74 | 77.456 | 43.58 |
| River and lake flushing (sinking) deposits | 40 | 32–199 | 117.33 | 38.877 | 33.13 |
| Quaternary old alluvium | 80 | 21–302 | 114.60 | 59.431 | 51.86 |
| Soil Types | Sample Number | Range | Average Value | Standard Deviation | Coefficient of Variation (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tide soil | 5 | 102–164 | 144.28 | 25.527 | 17.69 |
| Yellow cinnamon soil | 28 | 50–281 | 154.86 | 61.144 | 39.48 |
| Yellow-brown soil | 280 | 17–350 | 109.90 | 61.197 | 55.68 |
| Limestone | 31 | 43–299 | 150.42 | 68.583 | 45.59 |
| Paddy soil | 319 | 28–350 | 113.79 | 60.324 | 53.01 |
| Purple soil | 34 | 36–345 | 175.91 | 76.964 | 43.75 |
| Brown soil | 4 | 56–303 | 153.50 | 108.709 | 70.82 |
| Soil pH | Sample Number | Range | Average Value | Standard Deviation | Coefficient of Variation (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ≤4.5 | 1 | 83.38 | 83.38 | 0.00 | 0.00% |
| 4.5–5.5 | 85 | 20.79–350.00 | 109.18 | 64.80 | 59.35% |
| 5.5–6.5 | 326 | 17.00–302.00 | 99.04 | 49.80 | 50.28% |
| 6.5–7.5 | 174 | 32.00–350.00 | 133.94 | 67.54 | 50.43% |
| 7.5–8.5 | 115 | 32.00–345.00 | 160.26 | 70.85 | 44.21% |
| Cropping System | Sample Number | Range | Average Value | Standard Deviation | Coefficient of Variation (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tea fruit | 79 | 17.00–288.00 | 98.03 | 56.70 | 57.83% |
| Vegetable | 15 | 34.00–340.00 | 142.84 | 84.94 | 59.47% |
| Rice monoculture | 55 | 28.92–201.00 | 100.81 | 44.60 | 44.24% |
| Rice-rape rotation | 28 | 36.44–350.00 | 110.08 | 68.26 | 62.01% |
| Wheat-rice rotation | 24 | 42.00–208.00 | 126.92 | 51.93 | 40.92% |
| Maize-wheat rotation | 106 | 38.00–350.00 | 127.46 | 69.99 | 54.91% |
| Corn monoculture | 87 | 37.00–302.00 | 132.84 | 61.01 | 45.92% |
| Maize-rice rotation | 43 | 30.00–316.00 | 152.91 | 76.37 | 49.95% |
| Maize-potato intercropping | 71 | 20.00–256.41 | 94.38 | 49.64 | 52.60% |
| Canola-corn rotation | 193 | 25.00–321.00 | 121.67 | 65.03 | 53.45% |
| Topsoil Depth | Sample Number | Range | Average Value | Standard Deviation | Coefficient of Variation (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15–18 | 13 | 93–279 | 167.923 | 71.555 | 42.61 |
| 18–21 | 320 | 20–350 | 126.918 | 64.718 | 50.99 |
| 21–24 | 171 | 17–262 | 98.536 | 51.785 | 52.55 |
| 24–27 | 129 | 26–340 | 118.638 | 64.977 | 54.70 |
| 27–30 | 68 | 28–350 | 124.059 | 74.88 | 60.36 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Xu, L. Spatial Differentiation and Influencing Factors of Available Potassium in Cultivated Soil in Mountainous Areas of Northwestern Hubei Province, China. Sustainability 2024, 16, 7311. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16177311
Wu Z, Zhou Y, Xu L. Spatial Differentiation and Influencing Factors of Available Potassium in Cultivated Soil in Mountainous Areas of Northwestern Hubei Province, China. Sustainability. 2024; 16(17):7311. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16177311
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Zhengxiang, Yong Zhou, and Lei Xu. 2024. "Spatial Differentiation and Influencing Factors of Available Potassium in Cultivated Soil in Mountainous Areas of Northwestern Hubei Province, China" Sustainability 16, no. 17: 7311. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16177311
APA StyleWu, Z., Zhou, Y., & Xu, L. (2024). Spatial Differentiation and Influencing Factors of Available Potassium in Cultivated Soil in Mountainous Areas of Northwestern Hubei Province, China. Sustainability, 16(17), 7311. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16177311






