Effect of Extending High-Temperature Duration on ARG Rebound in a Co-Composting Process for Organic Wastes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods and Materials
2.1. Composting Materials and Experimental Setup
2.2. Sampling and Physicochemical Analysis
2.3. Determination of Heavy Metals and Antibiotics
2.4. DNA Extraction, High-Throughput Sequencing, and Bioinformatics
2.5. High-Throughput Sequencing and Real-Time PCR for Determination of ARG and MGE Abundances
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
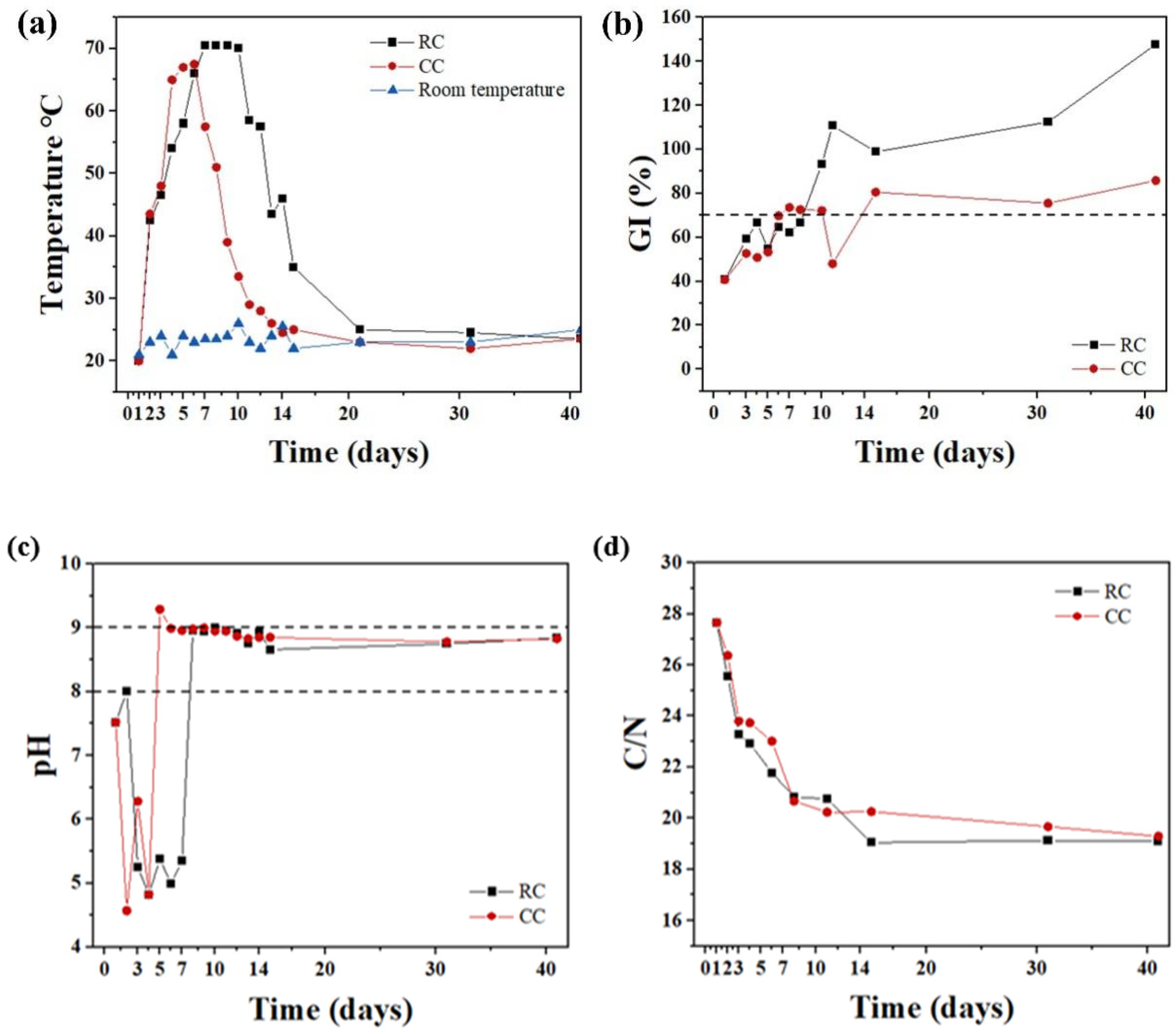
3.1. Changes in Environmental Parameters
3.2. Antibiotic and Heavy Metal Concentrations in the Composting System
3.3. Fate of ARGs and MGEs in the CC and RC Processes
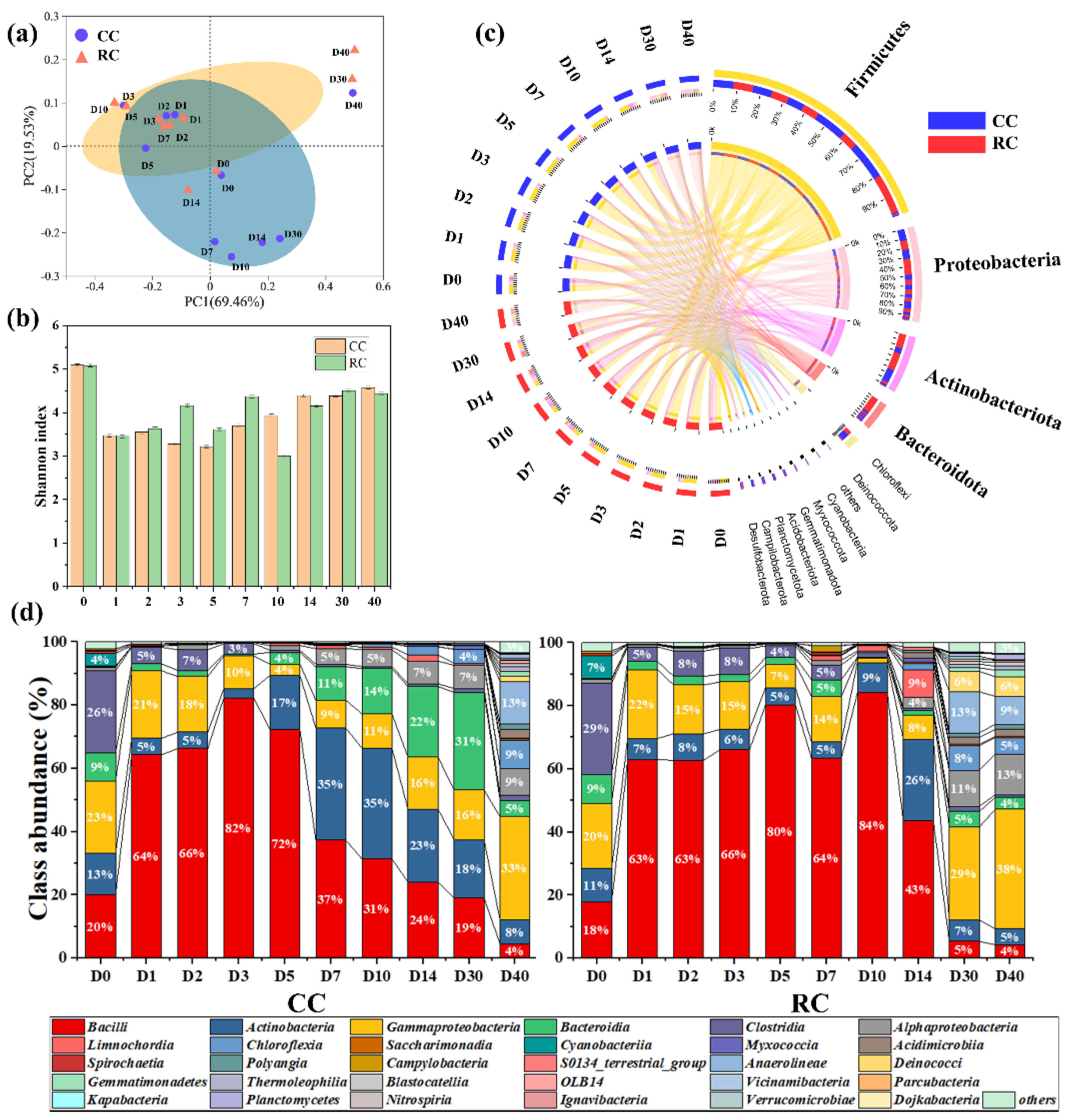
3.4. Composition and Succession of Microbial Communities
3.5. Potential Host Contributed to the Rebounding of ARGS
3.6. In Situ Drivers of ARGs in the Composting Process
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, B.T.; Yu, K.F.; Ahmed, I.; Gin, K.; Xi, B.D.; Wei, Z.M.; He, Y.L.; Zhang, B. Key factors driving the fate of antibiotic resistance genes and controlling strategies during aerobic composting of animal manure: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 791, 148372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, R.K.; Wang, J.; Ben, W.W.; Qiang, Z.M. The profile of antibiotic resistance genes in pig manure composting shaped by composting stage: Mesophilic-thermophilic and cooling-maturation stages. Chemosphere 2020, 250, 126181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sardar, M.F.; Zhu, C.X.; Geng, B.; Ahmad, H.R.; Song, T.T.; Li, H.N. The fate of antibiotic resistance genes in cow manure composting: Shaped by temperature-controlled composting stages. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 320, 124403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, H.P.; Zhao, Q.; Cui, P.; Chen, Z.; Yu, Z.; Geisen, S.; Friman, V.-P.; Zhou, S.G. Efficient reduction of antibiotic residues and associated resistance genes in tylosin antibiotic fermentation waste using hyperthermophilic composting. Environ. Int. 2019, 133, 105203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Huang, X.-H.; Sun, J.-Z.; Graham, D.W.; Xie, B. Antibiotic resistance genes and associated microbial community conditions in aging landfill systems. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 12859–12867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pehrsson, E.C.; Tsukayama, P.; Patel, S.; Mejía-Bautista, M.; Sosa-Soto, G.; Navarrete, K.M.; Calderon, M.; Cabrera, L.; Hoyos-Arango, W.; Bertoli, M.T.; et al. Interconnected microbiomes and resistomes in low-income human habitats. Nature 2016, 533, 212–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Yuan, Q.B.; Mathieu, J.; Stadler, L.; Senehi, N.; Sun, R.N.; Alvarez, P.J.J. Antibiotic resistance genes from livestock waste: Occurrence, dissemination, and treatment. NPJ Clean Water 2020, 3, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyrrell, C.; Burgess, C.M.; Brennan, F.P.; Walsh, F. Antibiotic resistance in grass and soil, Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2019, 47, 477–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, W.W.; Zhang, A.Y.; Chen, S.J.; He, X.P.; Jin, L.; Yu, X.M.; Yang, S.Z.; Li, B.; Fan, L.Q.; Pan, X.; et al. Heavy metals, antibiotics and nutrients affect the bacterial community and resistance genes in chicken manure composting and fertilized soil. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 257, 109980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, T.L.; Wu, D.; Zhang, L.X.; Zou, D.X.; Sun, Y.M.; Gao, M.; Wang, X.M. A comparison of antibiotics, antibiotic resistance genes, and bacterial community in broiler and layer manure following composting. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2021, 28, 14707–14719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.Z.; Lu, C.; Shen, D.; Liu, J.; Ma, Z.; Yang, B.; Ling, W.T.; Waigi, M.G. Elimination of the risks of colistin resistance gene (mcr-1) in livestock manure during composting. Environ. Int. 2019, 126, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, I.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, P.; Xie, Y.; Zhang, B. Sensitive response mechanism of ARGs and MGEs to initial designed temperature during swine manure and food waste co-composting. Environ. Res. 2023, 216, 114513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pu, C.J.; Yu, Y.; Diao, J.X.; Gong, X.Y.; Li, J.; Sun, Y. Exploring the persistence and spreading of antibiotic resistance from manure to biocompost, soils and vegetables. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 688, 262–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subirats, J.; Murray, R.; Scott, A.; Lau, C.H.-F.; Topp, E. Composting of chicken litter from commercial broiler farms reduces the abundance of viable enteric bacteria, Firmicutes, and selected antibiotic resistance genes. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 746, 141113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youngquist, C.P.; Mitchell, S.M.; Cogger, C.G. Fate of antibiotics and antibiotic resistance during digestion and composting: A review. J. Environ. Qual. 2016, 45, 537–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, H.P.; Lu, X.M.; Rensing, C.; Friman, V.-P.; Geisen, S.; Chen, Z.; Yu, Z.; Wei, Z.; Zhou, S.G.; Zhu, Y.G. Hyperthermophilic composting accelerates the removal of antibiotic resistance genes and mobile genetic elements in sewage sludge. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 266–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, Z.F.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, Z.J.; Ding, C.F.; Zhang, T.L.; Wan, L.P.; Wang, X.X. Antibiotic degradation dominates the removal of antibiotic resistance genes during composting. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 344, 126229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, H.P.; Friman, V.-P.; Geisen, S.; Zhao, Q.; Cui, P.; Lu, X.M.; Chen, Z.; Yu, Z.; Zhou, S.G. Horizontal gene transfer and shifts in linked bacterial community composition are associated with maintenance of antibiotic resistance genes during food waste composting. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 660, 841–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diehl, D.L.; LaPara, T.M. Effect of temperature on the fate of genes encoding tetracycline resistance and the integrase of class 1 integrons within anaerobic and aerobic digesters treating municipal wastewater solids. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 9128–9133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oshima, T.; Moriya, T. A preliminary analysis of microbial and biochemical properties of high-temperature compost. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2008, 1125, 338–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvam, A.; Wang, X.; Wong, J. Food Waste Composting: Challenges and Possible Approaches, Current Developments in Biotechnology and Bioengineering. In Current Developments in Biotechnology and Bioengineering; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 137–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, X.; Sun, W.; Gu, J.; Wang, X.J.; Zhang, Y.J.; Duan, M.L.; Li, H.C.; Zhang, R.R. Reducing antibiotic resistance genes, integrons, and pathogens in dairy manure by continuous thermophilic composting. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 220, 425–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, N.; Xie, S.Y.; Zeng, M.; Xu, X.Y.; Li, Y.; Liu, X.Y.; Wang, X.B. Impacts of pile temperature on antibiotic resistance, metal resistance and microbial community during swine manure composting. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 744, 140920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Zheng, J.; Tian, S.; Liu, C.; Liu, L.; Wei, L.; Fan, H.; Zhang, T.; Wang, L.; Zhu, G.; et al. Higher temperatures do not always achieve better antibiotic resistance gene removal in anaerobic digestion of swine manure. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2019, 85, e02878-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, P.Y.; Liu, B.T.; Ahmed, I.; Yang, J.; Zhang, B. Composting effect and antibiotic removal under a new temperature control strategy. Waste Manag. 2022, 153, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- NY/T 525-2021; Organic Fertilizer. Agricultural Standards of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2021.
- Liu, T.; He, B.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, G.; Lin, H. Application of improved BCR method in speciation analysis of heavy metals in activated sludge samples. Chin. J. Anal. Lab. 2007, 26, 17–20. [Google Scholar]
- Tran, N.H.; Chen, H.J.; Van Do, T.; Reinhard, M.; Ngo, H.H.; He, Y.L.; Gin, K.Y.-H. Simultaneous analysis of multiple classes of antimicrobials in environmental water samples using SPE coupled with UHPLC-ESI-MS/MS and isotope dilution. Talanta 2016, 159, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, Y.; Yu, G.; Shi, C.P.; Liu, L.M.; Guo, Q.; Han, C.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, L.; Liu, B.X.; Gao, H.; et al. Majorbio Cloud: A one-stop, comprehensive bioinformatic platform for multiomics analyses. iMeta 2022, 1, e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ezzariai, A.; Hafidi, M.; Khadra, A.; Aemig, Q.; El Fels, L.; Barret, M.; Merlina, G.; Patureau, D.; Pinelli, E. Human and veterinary antibiotics during composting of sludge or manure: Global perspectives on persistence, degradation, and resistance genes. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 359, 465–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garg, V.; Gupta, R. Optimization of cow dung spiked pre-consumer processing vegetable waste for vermicomposting using Eisenia fetida. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2011, 74, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, M.L.; Zhang, Y.H.; Zhou, B.B.; Wang, Q.J.; Gu, J.; Liu, G.H.; Qin, Z.L.; Li, Z.J. Changes in antibiotic resistance genes and mobile genetic elements during cattle manure composting after inoculation with Bacillus subtilis. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 292, 122011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.H.; Gu, J.; Wang, X.J.; Tuo, X.X.; Yu, J.; Zhan, R.R. Key role of cyromazine in the distribution of antibiotic resistance genes and bacterial community variation in aerobic composting. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 274, 418–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Dong, Y.H.; Wang, H. Residues of veterinary antibiotics in manures from feedlot livestock in eight provinces of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 1069–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estrella-González, M.J.; Suárez-Estrella, F.; Jurado, M.M.; López, M.J.; López-González, J.A.; Siles-Castellano, A.B.; Muñoz-Mérida, A.; Moreno, J. Uncovering new indicators to predict stability, maturity and biodiversity of compost on an industrial scale. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 313, 123557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, J.D.; Jin, Y.M.; Wen, X.; Mi, J.D.; Wu, Y.B. Adding a complex microbial agent twice to the composting of laying-hen manure promoted doxycycline degradation with a low risk on spreading tetracycline resistance genes. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 265, 114202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broussolle, V.; Carlin, F.; Lereclus, D.; Nielsen-LeRoux, C.; Sanchis, V. Beneficial and detrimental spore-formers: A world of diversity. Res. Microbiol. 2017, 168, 307–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.L.; Jia, Y.Y.; Zhang, X.M.; Feng, X.H.; Wu, J.J.; Wang, L.S.; Chen, G.J. Wheat straw: An inefficient substrate for rapid natural lignocellulosic composting. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 209, 402–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Guo, X.H.; Deng, H.; Dong, D.; Tu, Q.P.; Wu, W.X. New insights into the structure and dynamics of actinomycetal community during manure composting. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 98, 3327–3337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, J.S.; Mao, G.N.; Yin, X.L.; Ma, L.P.; Liu, L.; Bai, Y.H.; Zhang, T.; Qu, J.H. Identification and quantification of bacterial genomes carrying antibiotic resistance genes and virulence factor genes for aquatic microbiological risk assessment. Water Res. 2020, 168, 115160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gou, C.L.; Wang, Y.Q.; Zhang, X.Q.; Zhong, R.Z.; Gao, Y.H. Effects of chlorotetracycline on antibiotic resistance genes and the bacterial community during cattle manure composting. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 323, 124517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.Z.; Gu, J.; Wang, X.J.; Ma, J.Y.; Hu, T.; Peng, H.L.; Bao, J.F.; Zhang, R.R. Effects of nano-zerovalent iron on antibiotic resistance genes and mobile genetic elements during swine manure composting. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 258, 113654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, X.; Sun, W.; Gu, J.; Wang, X.-J.; Sun, J.-J.; Yin, Y.-N.; Duan, M.-L. Variable effects of oxytetracycline on antibiotic resistance gene abundance and the bacterial community during aerobic composting of cow manure. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 315, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, S.; Li, H.; Song, D.; Lin, X.; Wang, Y. Influence of zeolite and superphosphate as additives on antibiotic resistance genes and bacterial communities during factory-scale chicken manure composting. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 263, 393–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Q.X.; Zhang, H.; Guo, Y.; Tian, T.T. Influence of chicken manure fertilization on antibiotic-resistant bacteria in soil and the endophytic bacteria of pakchoi. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13, 662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, J.H.; Novak, J.T.; Knocke, W.R.; Pruden, A. Survival of antibiotic resistant bacteria and horizontal gene transfer control antibiotic resistance gene content in anaerobic digesters. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.Y.; Cheng, W.M.; Li, B.H.; Xu, Y.; Zheng, X.Q. The fate of antibiotic resistance genes during co-composting of swine manure with cauliflower and corn straw. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 300, 122669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.H.; Na, G.S.; Gao, H.; Wang, L.J.; Bao, C.G.; Yao, Z.W. Fate of sulfonamide resistance genes in estuary environment and effect of anthropogenic activities. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 527, 429–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Pankow, C.A.; Oh, M.; Heath, L.S.; Zhang, L.; Du, P.; Xia, K.; Pruden, A. Effect of antibiotic use and composting on antibiotic resistance gene abundance and resistome risks of soils receiving manure-derived amendments. Environ. Int. 2019, 128, 233–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.R.; Gu, J.; Wang, X.J.; Li, Y.; Zhang, K.Y.; Yin, Y.N.; Zhang, X. Contributions of the microbial community and environmental variables to antibiotic resistance genes during co-composting with swine manure and cotton stalks. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 358, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, X.; Sun, P.; Liu, B.; Ahmed, I.; Xie, Z.; Zhang, B. Effect of Extending High-Temperature Duration on ARG Rebound in a Co-Composting Process for Organic Wastes. Sustainability 2024, 16, 5284. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16135284
Yang X, Sun P, Liu B, Ahmed I, Xie Z, Zhang B. Effect of Extending High-Temperature Duration on ARG Rebound in a Co-Composting Process for Organic Wastes. Sustainability. 2024; 16(13):5284. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16135284
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Xi, Pengyu Sun, Botao Liu, Imtiaz Ahmed, Zhixiong Xie, and Bo Zhang. 2024. "Effect of Extending High-Temperature Duration on ARG Rebound in a Co-Composting Process for Organic Wastes" Sustainability 16, no. 13: 5284. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16135284
APA StyleYang, X., Sun, P., Liu, B., Ahmed, I., Xie, Z., & Zhang, B. (2024). Effect of Extending High-Temperature Duration on ARG Rebound in a Co-Composting Process for Organic Wastes. Sustainability, 16(13), 5284. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16135284




