Antibiotic Resistance Genes and Faecal Sterols in Marine Sediments: An Evidence of Their Presence away from Point Sources–Kuwait’s Example
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Sterol Analysis
2.2. DNA Isolation
2.3. Bacterial Counts by qPCR
2.4. Shotgun Metagenomic Sequencing
3. Results
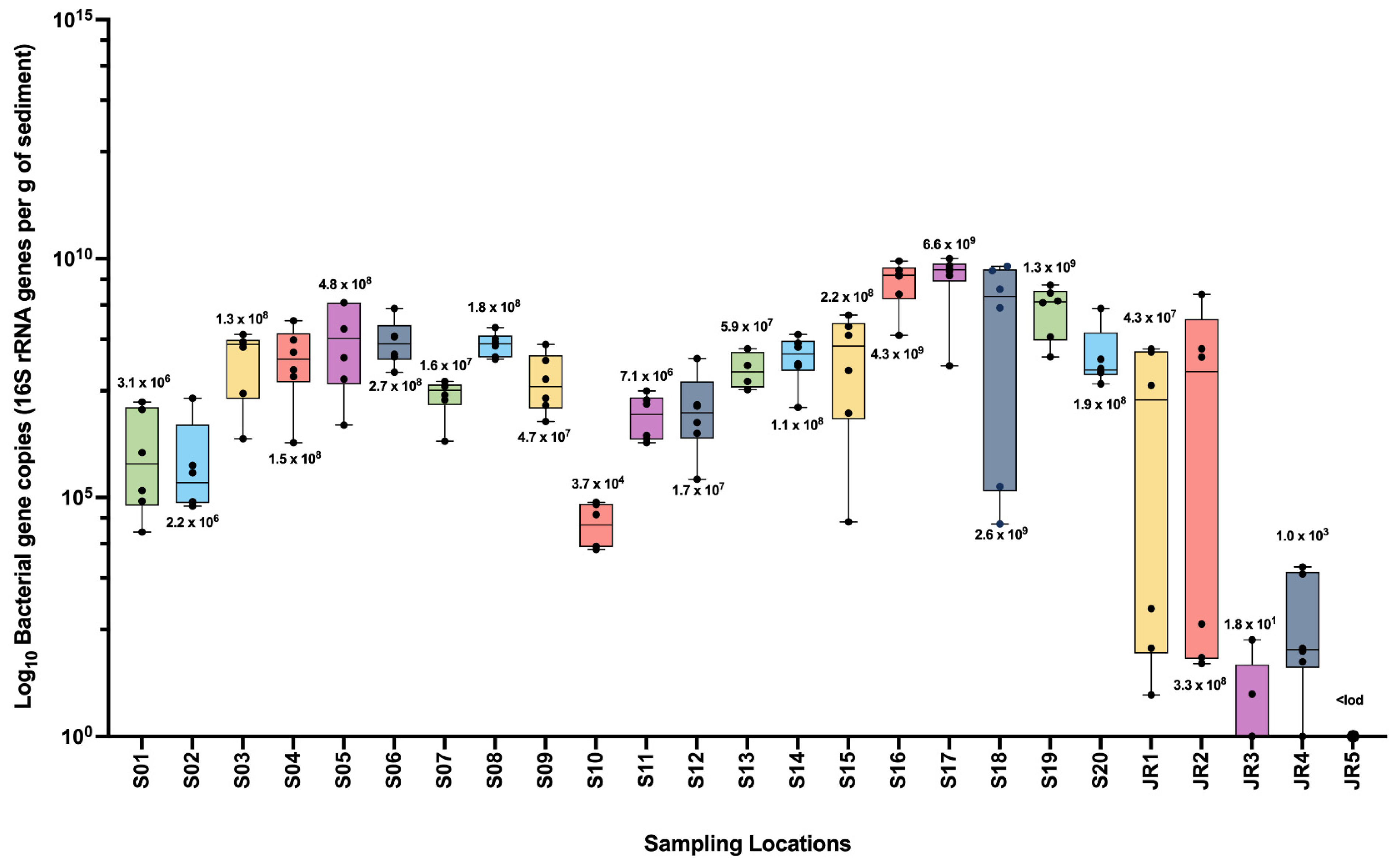
4. Bacterial Gene Counts
5. Sequencing Statistics
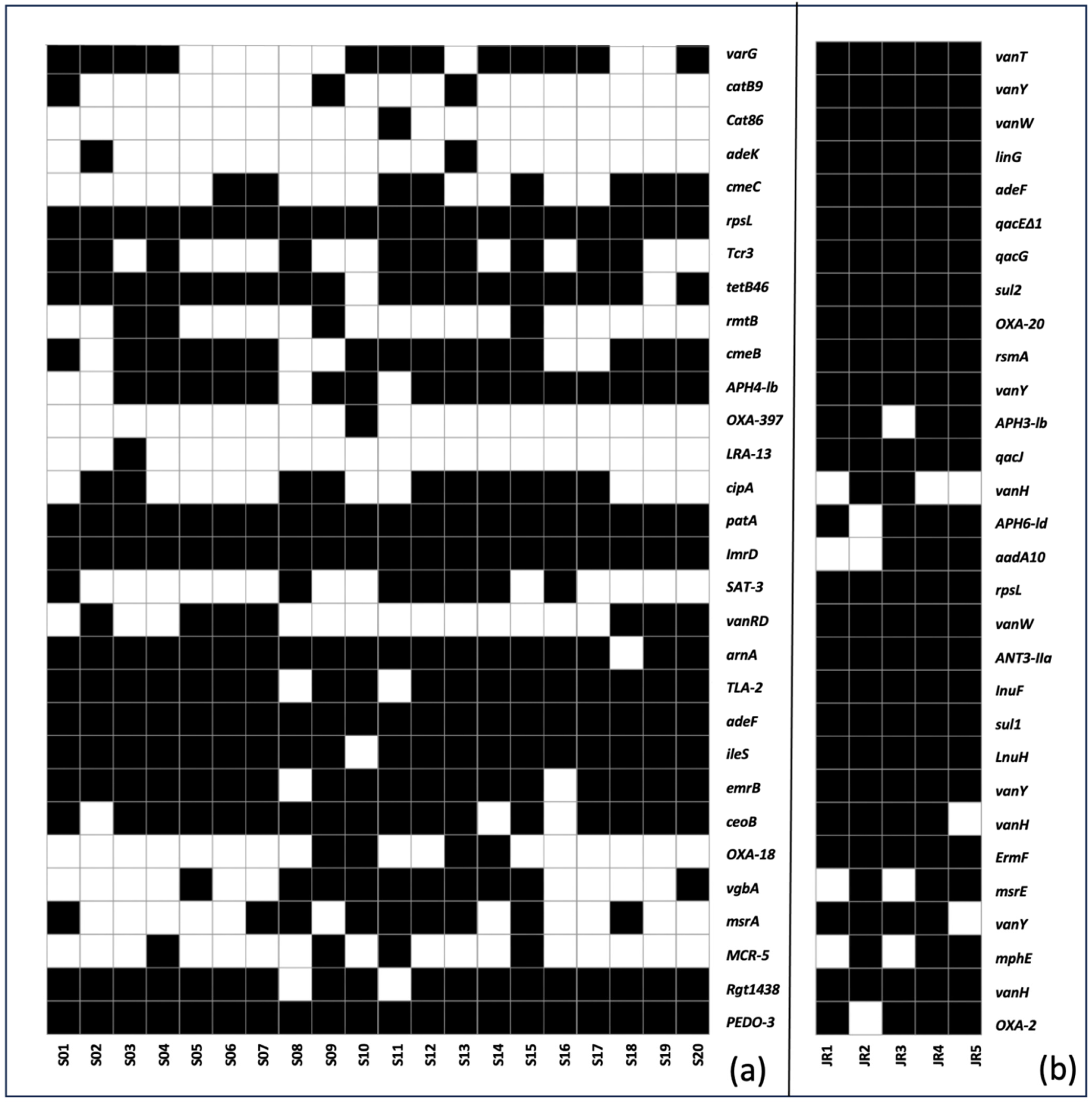
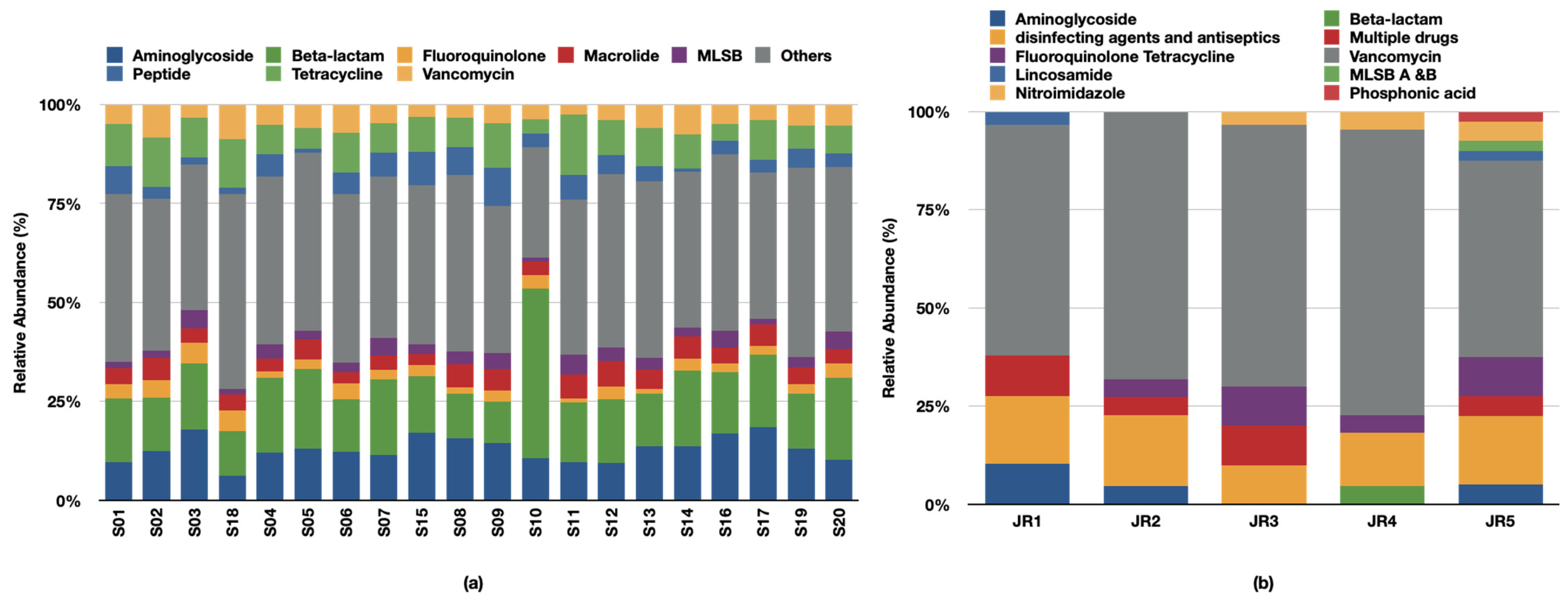
6. Prevalence and Abundance of ARGs
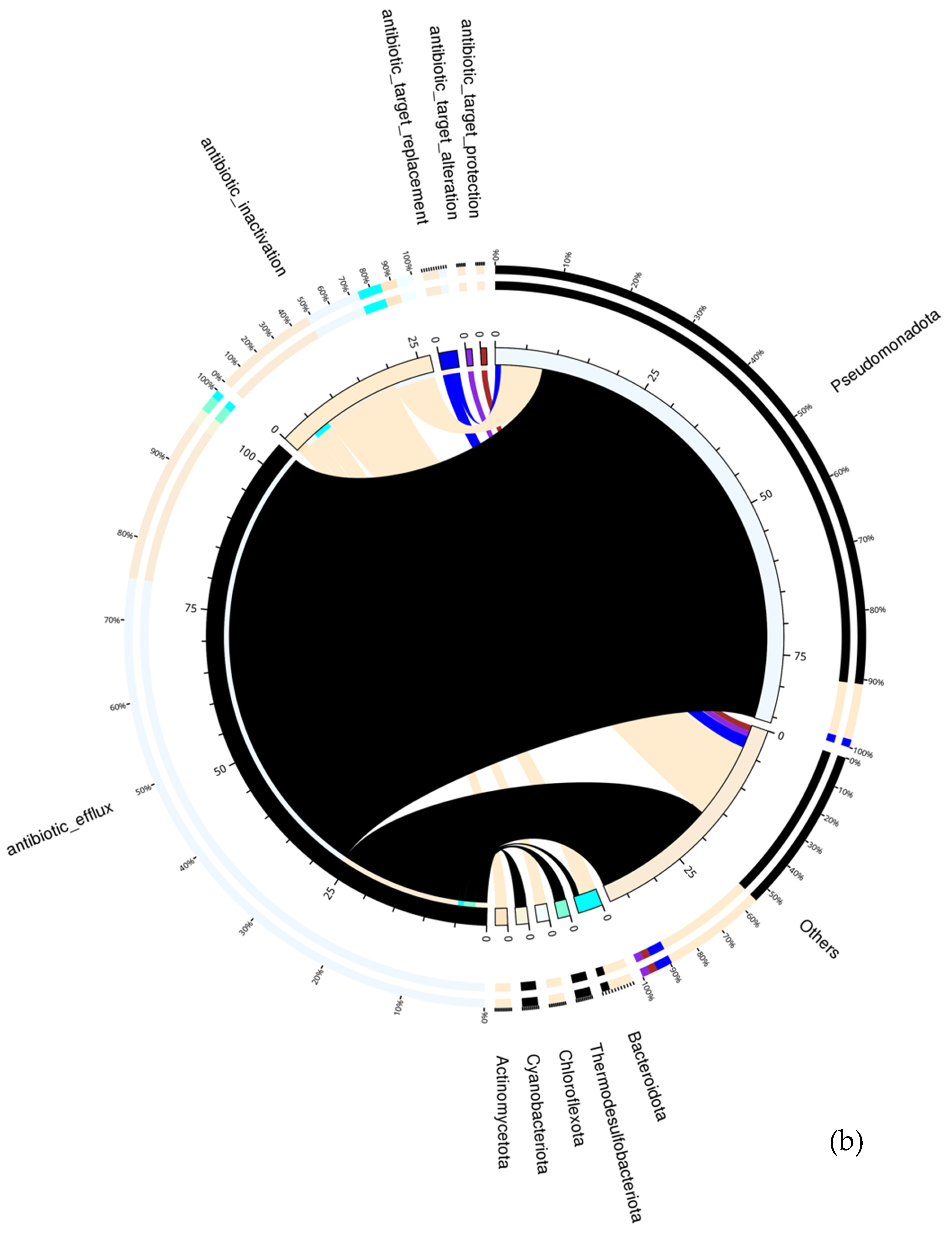
7. Mechanism of Action and Microbial Hosts
8. Discussions
9. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Honsel, L.E.; Reimann, L.; Vafeidis, A.T. Population development as a driver of coastal risk: Current trends and future pathways. Camb. Prism. Coast. Futures 2023, 1, e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, M.L.; Intralawan, A.; Vázquez, G.; Pérez-Maqueo, O.; Sutton, P.; Landgrave, R. The coasts of our world: Ecological, economic and social importance. Ecol. Econ. 2007, 63, 254–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ram-Bidesi, V.; Lal, P.N.; Conner, N. Economics of Coastal Zone Management in the Pacific; IUCN: Gland, Switzerland; Suva, Fiji, 2011; xiv + 88. [Google Scholar]
- Mehvar, S.; Filatova, T.; Dastgheib, A.; De Ruyter van Steveninck, E.; Ranasinghe, R. Quantifying Economic Value of Coastal Ecosystem Services: A Review. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2018, 6, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, Y.L.; Osleeb, J.P.; Viola, M.R. Tourism-Generated Earnings in the Coastal Zone: A Regional Analysis. J. Coast. Res. 2004, 20, 1080–1088. [Google Scholar]
- Bateman, I.J.; Mace, G.M.; Fezzi, C.; Atkinson, G.; Turner, K. Economic Analysis for Ecosystem Service Assessments. Environ. Resour. Econ. 2011, 48, 177–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jupp, B.P.; Uddin, S.; Fowler, S.W.; Faizuddin, M. Trace metal and TBT pollution in the Gulf and Oman: Spatial variation and hot spots. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 76351–76371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gevao, B.; Alegria, H.; Jaward, F.; Beg, M. Persistent Organic Pollutants in the Developing World; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2009; pp. 137–169. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B.; Matchinski, E.J.; Chen, B.; Ye, X.; Jing, L.; Lee, K. Chapter 21—Marine Oil Spills—Oil Pollution, Sources and Effects. In World Seas: An Environmental Evaluation, 2nd ed.; Sheppard, C., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; pp. 391–406. [Google Scholar]
- Nicolaus, E.E.M.; Wright, S.R.; Barry, J.; Bolam, T.P.C.; Ghareeb, K.; Ghaloom, M.; Al-Kanderi, N.; Harley, B.F.M.; Le Quesne, W.J.F.; Devlin, M.J.; et al. Spatial and temporal analysis of the risks posed by total petroleum hydrocarbon and trace element contaminants in coastal waters of Kuwait. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 120, 422–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gevao, B.; Uddin, S.; Krishnan, D.; Rajagopalan, S.; Habibi, N. Antibiotics in Wastewater: Baseline of the Influent and Effluent Streams in Kuwait. Toxics 2022, 10, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alder, A.C.; Schaffner, C.; Majewsky, M.; Klasmeier, J.; Fenner, K. Fate of beta-blocker human pharmaceuticals in surface water: Comparison of measured and simulated concentrations in the Glatt Valley Watershed, Switzerland. Water Res. 2010, 44, 936–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeilinger, J.; Steger-Hartmann, T.; Maser, E.; Goller, S.; Vonk, R.; Länge, R. Effects of synthetic gestagens on fish reproduction. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2009, 28, 2663–2670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weston, A.; Caminada, D.; Galicia, H.; Fent, K. Effects of lipid-lowering pharmaceuticals bezafibrate and clofibric acid on lipid metabolism in fathead minnow (Pimephales promelas). Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2009, 28, 2648–2655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Branchet, P.; Arpin-Pont, L.; Piram, A.; Boissery, P.; Wong-Wah-Chung, P.; Doumenq, P. Pharmaceuticals in the marine environment: What are the present challenges in their monitoring? Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 766, 142644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boxall, A.B.; Rudd, M.A.; Brooks, B.W.; Caldwell, D.J.; Choi, K.; Hickmann, S.; Innes, E.; Ostapyk, K.; Staveley, J.P.; Verslycke, T.; et al. Pharmaceuticals and personal care products in the environment: What are the big questions? Environ. Health Perspect 2012, 120, 1221–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Quesne, W.; Baker-Austin, C.; Verner-Jeffreys, D.W.; Al-Sarawi, H.A.; Balkhy, H.H.; Lyons, B.P. Antimicrobial Resistance in the Gulf Cooperation Council Region: A proposed framework to assess threats, impacts and mitigation measures associated with AMR in the marine and aquatic environment. Environ. Int. 2018, 121, 1003–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grimalt, J.O.; Fernandez, P.; Bayona, J.M.; Albaiges, J. Assessment of fecal sterols and ketones as indicators of urban sewage inputs to coastal waters. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1990, 24, 357–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florini, S.; Shahsavari, E.; Aburto-Medina, A.; Khudur, L.S.; Mudge, S.M.; Smith, D.J.; Ball, A.S. Are Sterols Useful for the Identification of Sources of Faecal Contamination in Shellfish? A Case Study. Water 2020, 12, 3076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesan, M.I.; Ruth, E.; Kaplan, I.R. Coprostanols in Antarctic marine sediments: A biomarker for marine mammals and not human pollution. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 1986, 17, 554–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolm, H.E.; Gomes, K.V.; Ishii, F.K.; Martins, C.C. An integrated appraisement of multiple faecal indicator bacteria and sterols in the detection of sewage contamination in subtropical tidal creeks. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2018, 221, 1032–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venkatesan, M.I.; Kaplan, I.R. Sedimentary coprostanol as an index of sewage addition in Santa Monica basin, southern California. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1990, 24, 208–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frena, M.; Souza, M.R.R.; Damasceno, F.C.; Madureira, L.A.S.; Alexandre, M.R. Evaluation of anthropogenic contamination using sterol markers in a tropical estuarine system of northeast Brazil. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 109, 619–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bull, I.D.; Lockheart, M.J.; Elhmmali, M.M.; Roberts, D.J.; Evershed, R.P. The origin of faeces by means of biomarker detection. Environ. Int. 2002, 27, 647–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bethell, P.H.; Goad, L.J.; Evershed, R.P.; Ottaway, J. The Study of Molecular Markers of Human Activity: The Use of Coprostanol in the Soil as an Indicator of Human Faecal Material. J. Archaeol. Sci. 1994, 21, 619–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilpin, B.J.; Gregor, J.E.; Savill, M.G. Identification of the source of faecal pollution in contaminated rivers. Water Sci. Technol. 2002, 46, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, D.; Zhang, K.; Tang, J.; Cui, X.; Sun, Y. Using fecal sterols to assess dynamics of sewage input in sediments along a human-impacted river-estuary system in eastern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 636, 787–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marvin, C.; Coakley, J.; Mayer, T.; Brown, M.; Thiessen, L. Application of Faecal Sterol Ratios in Sediments and Effluents as Source Tracers. Water Qual. Res. J. 2001, 36, 781–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Y.-J.; Kampbell, D.H.; Peter Breidenbach, G. Escherichia coli and total coliforms in water and sediments at lake marinas. Environ. Pollut. 2002, 120, 771–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rovirosa, N.; Sánchez, E.; Cruz, M.; Veiga, M.C.; Borja, R. Coliform concentration reduction and related performance evaluation of a down-flow anaerobic fixed bed reactor treating low-strength saline wastewater. Bioresour. Technol. 2004, 94, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carreira, R.; Wagener, A.; Readman, J. Sterols as markers of sewage contamination in a tropical urban estuary (Guanabara Bay, Brazil): Space-time variations. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2004, 60, 587–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratt, C.; Warnken, J.; Leeming, R.; Arthur, J.M.; Grice, D.I. Detection of Intermittent Sewage Pollution in a Subtropical, Oligotrophic, Semi-enclosed Embayment System Using Sterol Signatures in Sediments. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 792–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reeves, A.D.; Patton, D. Faecal sterols as indicators of sewage contamination in estuarine sediments of the Tay Estuary, Scotland: An extended baseline survey. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2005, 9, 81–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, F.P.; Villeneuve, J.P.; Cattini, C. Determination of organochlorine compounds, petroleum hydrocarbons, and sterols in a sediment sample, IAEA-383. Results of an intercomparison exercise. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 1999, 75, 315–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Sarawi, H.A.; Najem, A.B.; Lyons, B.P.; Uddin, S.; Al-Sarawi, M.A. Antimicrobial Resistance in Escherichia coli Isolated from Marine Sediment Samples from Kuwait Bay. Sustainability 2022, 14, 11325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habibi, N.; Uddin, S.; Lyons, B.; Al-Sarawi, H.A.; Behbehani, M.; Shajan, A.; Razzack, N.A.; Zakir, F.; Alam, F. Antibiotic Resistance Genes Associated with Marine Surface Sediments: A Baseline from the Shores of Kuwait. Sustainability 2022, 14, 8029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klindworth, A.; Pruesse, E.; Schweer, T.; Peplies, J.; Quast, C.; Horn, M.; Glöckner, F.O. Evaluation of general 16S ribosomal RNA gene PCR primers for classical and next-generation sequencing-based diversity studies. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habibi, N.; Uddin, S.; Behbehani, M.; Kishk, M.; Abdul Razzack, N.; Zakir, F.; Shajan, A. Antibiotic Resistance Genes in Aerosols: Baseline from Kuwait. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 6756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habibi, N.; Uddin, S.; Al-Sarawi, H.; Aldhameer, A.; Shajan, A.; Zakir, F.; Abdul Razzack, N.; Alam, F. Metagenomes from Coastal Sediments of Kuwait: Insights into the Microbiome, Metabolic Functions and Resistome. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Meltzer, P.; Davis, S. RCircos: An R package for Circos 2D track plots. BMC Bioinform. 2013, 14, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barter, R.L.; Yu, B. Superheat: An R package for creating beautiful and extendable heatmaps for visualizing complex data. J. Comput. Graph. Stat. 2018, 27, 910–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Readman, J.W.; Fillmann, G.; Tolosa, I.; Bartocci, J.; Mee, L.D. The use of steroid markers to assess sewage contamination of the Black Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2005, 50, 310–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tolosa, I.; Mesa, M.; Alonso-Hernandez, C.M. Steroid markers to assess sewage and other sources of organic contaminants in surface sediments of Cienfuegos Bay, Cuba. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 86, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anceski Bataglion, G.; Koolen, H.; Weber, R.; Eberlin, M. Quantification of Sterol and Triterpenol Biomarkers in Sediments of the Cananéia-Iguape Estuarine-Lagoonal System (Brazil) by UHPLC-MS/MS. Int. J. Anal. Chem. 2016, 2016, 8361375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Resende, M.F.; Santos, M.D.R.; Matos, R.C.; Matos, M.A.C. The analysis of faecal sterols in sediment samples by HPLC-UV using ultrasound-assisted treatment. Anal. Methods 2014, 6, 9581–9587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, H.; Xiao, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.; Jian, H.; Luo, Y.; Han, Z. Composition and ecological roles of the core microbiome along the Abyssal-Hadal transition zone sediments of the Mariana Trench. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e01988-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyons, B.P.; Devlin, M.J.; Abdul Hamid, S.A.; Al-Otiabi, A.F.; Al-Enezi, M.; Massoud, M.S.; Al-Zaidan, A.S.; Smith, A.J.; Morris, S.; Bersuder, P.; et al. Microbial water quality and sedimentary faecal sterols as markers of sewage contamination in Kuwait. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 100, 689–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saeed, T.; Al-Shimmari, F.; Al-Mutairi, A.; Abdullah, H. Spatial assessment of the sewage contamination of Kuwait’s marine areas. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 94, 307–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hogarth, C.; Arnold, K.; McLauchlin, A.; Rannard, S.P.; Siccardi, M.; McDonald, T.O. Evaluating the impact of systematic hydrophobic modification of model drugs on the control, stability and loading of lipid-based nanoparticles. J. Mater. Chem. B 2021, 9, 9874–9884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baena-Nogueras, R.M.; Hobman, J.L.; Gomes, R.L. Chapter 4—Occurrence and distribution of antibiotics and antibiotic resistance determinants in coastal environments. In Pharmaceuticals in Marine and Coastal Environments; Durán-Álvarez, J.C., Jiménez-Cisneros, B., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; Volume 1, pp. 121–167. [Google Scholar]
- Beiras, R. Chapter 6—Environmental risk assessment of pharmaceutical and personal care products in estuarine and coastal waters. In Pharmaceuticals in Marine and Coastal Environments; Durán-Álvarez, J.C., Jiménez-Cisneros, B., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; Volume 1, pp. 195–252. [Google Scholar]
- Biel-Maeso, M.; Lara-Martín, P.A. Chapter 1—Point and diffuse sources of pharmaceuticals in coastal zones. In Pharmaceuticals in Marine and Coastal Environments; Durán-Álvarez, J.C., Jiménez-Cisneros, B., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; Volume 1, pp. 1–25. [Google Scholar]
- Durán-Álvarez, J.C.; Mejia-Almaguer, D.; del Campo, M.N. Chapter 2—Occurrence, spatiotemporal distribution and environmental fate of pharmaceutical residues in urban estuaries. In Pharmaceuticals in Marine and Coastal Environments; Durán-Álvarez, J.C., Jiménez-Cisneros, B., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; Volume 1, pp. 27–89. [Google Scholar]
- Mahjoub, O.; Chmengui, W. Chapter 3—Pharmaceutical active compounds in marine and coastal environments of arid and semi-arid countries of the Arab region. In Pharmaceuticals in Marine and Coastal Environments; Durán-Álvarez, J.C., Jiménez-Cisneros, B., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; Volume 1, pp. 91–119. [Google Scholar]
- Prado, B.; Rodríguez-Varela, M.; Castro-Gutiérrez, J.A. Chapter 11—Occurrence of pharmaceutical residues in marine sediments. In Pharmaceuticals in Marine and Coastal Environments; Durán-Álvarez, J.C., Jiménez-Cisneros, B., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; Volume 1, pp. 351–377. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; McIlroy, S.E.; Archana, A.; Baker, D.M.; Panagiotou, G. A pollution gradient contributes to the taxonomic, functional, and resistome diversity of microbial communities in marine sediments. Microbiome 2019, 7, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Yang, Y.; Liang, X.; Yu, K.; Zhang, T.; Li, X. Metagenomic profiles of antibiotic resistance genes (ARGs) between human impacted estuary and deep ocean sediments. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 12753–12760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.; Wu, C.; Han, P.; Liu, Z.; Liang, M.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Guo, G.; He, X.; Pang, J. The microbiome and its association with antibiotic resistance genes in the hadal biosphere at the Yap Trench. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 439, 129543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tooke, C.L.; Hinchliffe, P.; Bragginton, E.C.; Colenso, C.K.; Hirvonen, V.H.; Takebayashi, Y.; Spencer, J. β-Lactamases and β-Lactamase Inhibitors in the 21st Century. J. Mol. Biol. 2019, 431, 3472–3500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanwar, J.; Das, S.; Fatima, Z.; Hameed, S. Multidrug resistance: An emerging crisis. Interdiscip. Perspect. Infect. Dis. 2014, 2014, 541340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, T. The staggering death toll of drug-resistant bacteria. Nature 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.-J.; Yuan, Y.; Tan, W.-B.; Xi, B.-D.; Wang, H.; Hui, K.-L.; Chen, J.-B.; Zhang, Y.-F.; Wang, L.-F.; Li, R.-F. Antibiotic resistance genes and heavy metals in landfill: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 464, 132395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayandele, A.A.; Adewoyin, A.G.; Olatunde, S.K. Detection of antibiotic resistant bacteria and sterol concentration in hand dug wells cited near pit latrine in Southwestern Nigeria. J. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 2018, 11, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, C.D.; Montone, R.C.; Gamba, R.C.; Pellizari, V.H. Sterols and fecal indicator microorganisms in sediments from Admiralty Bay, Antarctica. Braz. J. Oceanogr. 2005, 53, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sarawi, H.A.A.; Habibi, N.; Uddin, S.; Jha, A.N.; Al-Sarawi, M.A.; Lyons, B.P. Antibiotic Resistance Mediated by Escherichia coli in Kuwait Marine Environment as Revealed through Genomic Analysis. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 1366. [Google Scholar]
- Powers, N.C.; Wallgren, H.R.; Marbach, S.; Turner, J.W. Relationship between rainfall, fecal pollution, antimicrobial resistance, and microbial diversity in an urbanized subtropical bay. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 86, e01229-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Sample ID | Location | Latitude | Longitude | Site Description | Dates of Sample Collection |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Khadmah Bay | 29°23′10′′ N | 47°44′43′′ E | A distal end of Kuwait Bay | 15 January 2023 |
| 2 | Near MPA | 29°21′12′′ N | 47°53′15′′ E | Near Doha Multi-stage flash Power and Desalination Plant outfall | 15 January 2023 |
| 3 | Shuwaikh Outfall | 29°21′51′′ N | 47°56′59′′ E | Distant to outfall receiving emergency waste near Shuwaikh Beach | 15 January 2023 |
| 4 | Sharq | 29°23′49′′ N | 47°59′02′′ E | Distant to outfall receiving emergency waste near Kuwait City | 15 January 2023 |
| 5 | Kuwait Tower | 29°23′46′′ N | 48°00′12′′ E | Distant to outfall receiving emergency waste | 15 January 2023 |
| 6 | Marina Food Court | 29°20′55′′ N | 48°04′52′′ E | Distant to outfall receiving emergency waste | 15 January 2023 |
| 7 | Al Bida | 29°18′54′′ N | 48°05′41′′ E | Distant to outfall receiving emergency waste | 15 January 2023 |
| 8 | Khairan | 28°39′18′′ N | 48°23′50′′ E | Wastes from recreational resorts | 16 January 2023 |
| 9 | Ras Zour | 28°44′59′′ N | 48°24′17′′ E | Proximity to Al-Zour refinery | 16 January 2023 |
| 10 | Bnaider | 28°53′27′′ N | 48°16′45′′ E | Recreational beach | 16 January 2023 |
| 11 | CFP Mina Abdulla | 28°58′44′′ N | 48°10′53′′ E | The area receiving refinery waste | 16 January 2023 |
| 12 | Fahaheel | 29°05′09′′ N | 48°08′36′′ E | Distant to outfall receiving emergency waste | 16 January 2023 |
| 13 | Mahboula | 29°08′19′′ N | 48°08′12′′ E | Distant to outfall receiving emergency waste | 16 January 2023 |
| 14 | Eagila | 29°11′01′′ N | 48°07′24′′ E | Distant to outfall receiving emergency waste | 16 January 2023 |
| 15 | Messila | 29°15′29′′ N | 48°05′48′′ E | Distant to outfall receiving sewage discharge | 16 January 2023 |
| 16 | Al Qaruh | 28°48′52′′ N | 48°46′45′′ E | A remote island with oil contamination | 5 February 2023 |
| 17 | Umm Ul Maradim | 28°41′70′′ N | 48°39′30′′ E | Remote island | 5 February 2023 |
| 18 | Subiya outfall | 29°28′54′′ N | 48°07′10′′ E | Waste of Subiya power plant | 6 February 2023 |
| 19 | Failaka | 29°25′57′′ N | 48°15′54′′ E | Wastes from resorts on the island | 6 February 2023 |
| 20 | Auha | 29°23′10′′ N | 48°17′40′′ E | Remote uninhabited island | 6 February 2023 |
| JR1 | Jahra Reserve † | 29°21′32′′ N | 47°41′37′′ E | Lake in Jahra Pool Reserve | 11 May 2023 |
| JR2 | Jahra Reserve † | 29°21′41′′ N | 47°42′22′′ E | Lake in Jahra Pool Reserve | 11 May 2023 |
| JR3 | Jahra Reserve † | 29°21′42′′ N | 47°41′25′′ E | Outflow to Sea | 11 May 2023 |
| JR4 | Jahra Reserve † | 29°21′52′′ N | 47°41′33′′ E | Lake in Jahra Pool Reserve | 11 May 2023 |
| JR5 | Jahra Reserve † | 29°21′32′′ N | 47°41′27′′ E | Lake in Jahra Pool Reserve | 11 May 2023 |
| Samples ID | Coprostanol | Epicoprostanol | Cholesterol | Cholestanol | Cop/Cholesterol | Epicop/Cop | Cop/(Cop + Cholestanol) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 778.39 | 565.10 | 2889.20 | 2227.15 | 0.269 | 0.726 | 0.259 |
| 2 | <dl | <dl | <dl | <dl | - | - | - |
| 3 | <dl | <dl | <dl | <dl | - | - | - |
| 4 | 279.14 | 257.67 | 604.29 | 388.04 | 0.462 | 0.923 | 0.418 |
| 5 | 303.80 | 230.98 | 1315.22 | 480.71 | 0.231 | 0.760 | 0.387 |
| 6 | 403.85 | 399.04 | 873.08 | 658.65 | 0.463 | 0.988 | 0.380 |
| 7 | 261.28 | 237.33 | 795.54 | 428.97 | 0.328 | 0.908 | 0.379 |
| 8 | 194.17 | 203.88 | 427.18 | 257.28 | 0.455 | 1.050 | 0.430 |
| 9 | 196.32 | 202.94 | 963.24 | 311.27 | 0.204 | 1.034 | 0.387 |
| 10 | 268.37 | 274.76 | 2635.78 | 472.84 | 0.102 | 1.024 | 0.362 |
| 11 | 238.23 | 227.15 | 5531.58 | 396.12 | 0.043 | 0.953 | 0.376 |
| 12 | 206.11 | 206.11 | 531.81 | 282.44 | 0.388 | 1.000 | 0.422 |
| 13 | 265.85 | 200.00 | 485.37 | 275.61 | 0.548 | 0.752 | 0.491 |
| 14 | 253.59 | 207.69 | 425.64 | 292.31 | 0.596 | 0.819 | 0.465 |
| 15 | 215.54 | 0.00 | 729.32 | 300.75 | 0.296 | 0.000 | 0.417 |
| 16 | 243.77 | 227.15 | 1016.62 | 324.10 | 0.240 | 0.932 | 0.429 |
| 17 | <dl | 215.43 | 436.17 | 281.91 | - | - | - |
| 18 | 459.77 | 244.25 | 681.03 | 445.40 | 0.675 | 0.531 | 0.508 |
| 19 | 290.78 | 297.87 | 645.39 | 586.88 | 0.451 | 1.024 | 0.331 |
| 20 | <dl | 207.69 | 384.62 | 256.41 | - | - | - |
| JR1 | 428.92 | 16,401.96 | 5017.16 | 1345.59 | 0.085 | 38.240 | 0.242 |
| JR2 | 5021.46 | 4727.47 | 3849.79 | 2493.56 | 1.304 | 0.941 | 0.668 |
| JR3 | 888.13 | 271.69 | 2093.61 | 863.01 | 0.424 | 0.306 | 0.507 |
| JR4 | 18,713.13 | 4885.45 | 9858.59 | 405.66 | 1.898 | 0.261 | 0.979 |
| JR5 | 2800.00 | 5828.57 | 29,800.00 | 22,971.43 | 0.094 | 2.082 | 0.109 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Uddin, S.; Habibi, N.; Saeed, T.; Al-Sarawi, H.A.; Behbehani, M.; Faizuddin, M. Antibiotic Resistance Genes and Faecal Sterols in Marine Sediments: An Evidence of Their Presence away from Point Sources–Kuwait’s Example. Sustainability 2024, 16, 4320. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16104320
Uddin S, Habibi N, Saeed T, Al-Sarawi HA, Behbehani M, Faizuddin M. Antibiotic Resistance Genes and Faecal Sterols in Marine Sediments: An Evidence of Their Presence away from Point Sources–Kuwait’s Example. Sustainability. 2024; 16(10):4320. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16104320
Chicago/Turabian StyleUddin, Saif, Nazima Habibi, Talat Saeed, Hanan A. Al-Sarawi, Montaha Behbehani, and Mohammad Faizuddin. 2024. "Antibiotic Resistance Genes and Faecal Sterols in Marine Sediments: An Evidence of Their Presence away from Point Sources–Kuwait’s Example" Sustainability 16, no. 10: 4320. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16104320
APA StyleUddin, S., Habibi, N., Saeed, T., Al-Sarawi, H. A., Behbehani, M., & Faizuddin, M. (2024). Antibiotic Resistance Genes and Faecal Sterols in Marine Sediments: An Evidence of Their Presence away from Point Sources–Kuwait’s Example. Sustainability, 16(10), 4320. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16104320








