1. Introduction
People are moving from information technology to data technology, from being able to connect with each other only through computers to mobile Internet connections, to the interconnection between everything. From cloud computing technology to the age of BD, this technological revolution has accelerated human society into a new stage of development in the age of data information, and data information has become the most important resource for enterprise development. This text proposes a sustainable analysis of enterprise performance management based on the IoT and BD. It introduces the concepts of BD technology, IoT technology, and performance management, respectively, and then discusses and analyzes the mechanism of IoT technology and BD technology for enterprise performance management, which would be of great importance for enterprise development.
The research on enterprise performance management has always been the research field of many experts and scholars, which is of great significance to the development of enterprises. At present, Haryanto Aris Tri has conducted an empirical study on the relationship between market orientation, innovative learning orientation, and enterprise performance within the scope of SMEs. He also explained the importance of corporate innovation as an intermediary relationship to improve corporate performance. Hypothesis test results show that market orientation has a positive impact on the company’s operating performance and innovation. Directional learning has a positive impact on the company’s business performance and innovation. The company’s innovation has affected its business performance. His research results provide a basis for the study of the relationship between market orientation, innovative learning orientation, and enterprise performance in enterprise performance management [
1]. Subramanian Nachiappan empirically tested the impact of the new product development process with circular economy considerations on the time-to-market and profit performance of Chinese private enterprises. In addition, he also studied the role of Chinese traditional Confucian and Taoist philosophy in influencing the process of new product development with circular economy considerations—performance linkage. This provided insights for enterprises to apply Chinese philosophy to maximize benefits in the process of new product development with circular economy considerations [
2]. Khan Rizwan Ullah examined the impact of entrepreneurial orientation on the financial and non-FP of SMEs, as well as the regulatory role of financing channels. The results show that entrepreneurial orientation has significantly improved the financial and non-FP of SMEs in emerging economies. On the other hand, access to financing significantly regulates the relationship between entrepreneurial orientation and SME FP, but not between entrepreneurial orientation and non-FP [
3]. Xia Lei studied the relationship between entrepreneurial passion and new enterprise performance by introducing entrepreneurial perseverance and entrepreneurial ability as the intermediary mechanism. The empirical analysis shows that entrepreneurial passion has a positive impact on the performance of new enterprises, and entrepreneurial perseverance mediates this relationship. In addition, entrepreneurial ability has a positive mediating effect on the relationship between entrepreneurial perseverance and new enterprise performance and has a partial mediating effect on the relationship between entrepreneurial passion and new enterprise performance [
4]. These studies can help enterprises to conduct better performance management, but they are slightly insufficient in the interconnection of everything and data processing.
Performance management based on the IoT and BD can effectively solve the above problems. At present, Tang Chia-Pei discussed the impact of the implementation of the IoT on enterprise performance. He used three methods to evaluate the performance of the implementation of the IoT relative to FP, productivity, and market value. He collected secondary data and conducted a quantitative analysis with three dummy variables, including IoT adopters, pioneers, and better performers. He provided a complete reference for enterprises through different indicators, which would help evaluate the implementation of the IoT by enterprises [
5]. Liu Lixin revealed the supporting role and impact of IoT-based technology in the decision-making process of insurance companies—risk assessment and pricing, business process performance—claim accuracy and efficiency, and the role of IoT system functions in improving driver attitudes and behaviors. This provided practitioners with an overview of the value of the IoT in organizational knowledge management and demonstrated the role of IoT technology in improving enterprise performance and bringing broader social benefits [
6]. Dubey Rameshwar developed and tested a model based on the enterprise’s resource view, institutional theory, and organizational culture. The model describes the importance of resources for building capacity, skills, and BD culture and subsequently improving costs and operational performance. He provided insights on the role of external pressure in resource selection under the regulatory role of BD culture and its use in capacity building, as well as how this ability affects enterprise costs and operational performance [
7]. Niebel Thomas analyzed the relationship between BD analysis and enterprise innovation performance from the perspective of product innovation. He found suggestive evidence that BD analysis is a relevant determinant of the possibility for enterprises to become product innovators and the success of product innovation markets. These results apply to manufacturing and service industries but depend on enterprises’ investment in Internet technology-specific skills. In general, the research results support the view that BD analysis is conducive to innovation [
8]. These studies can promote the development of enterprises to varying degrees. If they can be applied in practice, they would help enterprises step into a new stage.
Society has entered a new era, and the traditional data era has already become the BD era. With the continuous development of the market economy system, the competition between enterprises is increasingly fierce. How to better realize the continuous progress of enterprises is of significance to enterprise performance management. Enterprise performance management is beneficial to the improvement of enterprise management ability. According to the FP management, it can find the shortcomings of the enterprise, find out the problems, quickly develop the corresponding solutions, and clearly put forward efficient rectification suggestions. Therefore, scientific and efficient FP management is very important for enterprises.
In order to improve the effect of enterprise performance management, this paper analyzes the application of BD and the Internet of Things in enterprise performance management systems (PMS) and the sustainability of the application. Compared with other studies, the innovation of this paper is that this paper uses the Internet of Things technology and BD technology to transform the enterprise family planning management system. Secondly, this paper proposes the sustainability analysis of enterprise performance management driven by BD and the Internet of Things.
2. Enterprise Performance Management Method
- (1)
Concepts related to IoT technology
IoT technology is an extension of the Internet. It can connect more electronic devices and devices to the network system software, breaking the old mode that data information can be collected and transmitted only through devices, so that it can directly collect information and transmit it to the application system, without complicated control in the intermediate process. The IoT is an updated way of connecting things to each other [
9,
10]. It needs to use various information sensor equipment to combine it with the Internet to complete the data sharing among people, computers, and things. The IoT only relies on the Internet to complete the data sharing between things but also cannot do without the strong support of other technologies, such as information sensors, wireless communication technology, infrared probes, and their satellite navigation systems. The enterprise performance management system uses KPI, balanced scorecard, OKR, etc.
- (2)
Concepts related to BD technology
Big data technology is simply the technology used to analyze the large-scale data generated by enterprises. The definition of BD is also popular with the rapid development of the network information age. With the rapid development of mobile Internet technology, the data that people have been exposed to are different from the previously restricted state. At present, in the face of a large number of data network resources, the definition of BD is gradually accepted and trusted by the public, and the technology for analyzing and processing BD would also become popular, and show great impact on production activities [
11,
12].
The significance of BD capability lies in that BD can help enterprises optimize their own work processes and strategic decisions, respond to the changing living environment of the outside world with flexible disposal measures, and continuously create and maintain the core competitiveness of enterprises. Under the BD environment, the company can complete the prediction analysis and regulatory decision analysis of the event development trend. The interpretation and exploration of the BD of the project life cycle can help enterprises to build insight into investment decisions and maintain core competitiveness. In addition, in the BD environment, it can conduct in-depth research on competitors based on BD capabilities, complete the real-time insight and prediction of BD on the external competitive situation of enterprises, and help enterprises improve their competitiveness in key markets [
13,
14].
- (3)
Performance-management-related concepts
Performance includes organizational performance and individual performance. It not only pays attention to the economic benefits but also the overall benefits. It should not only attach importance to economic benefits but also attach importance to the overall goal of thrift, stability, and quality. In order to ensure the work performance appraisal of the enterprise, enterprise managers would carry out accurate performance appraisals of departments and individuals on time, which is a must for all companies. The management of performance evaluation not only exists in the review stage but also can clearly propose efficient corrective measures to the company based on the results of performance evaluation. Performance evaluation is not only a link between enterprise operation and management but should be reconsidered from the perspective of the long-term development of the company [
15,
16].
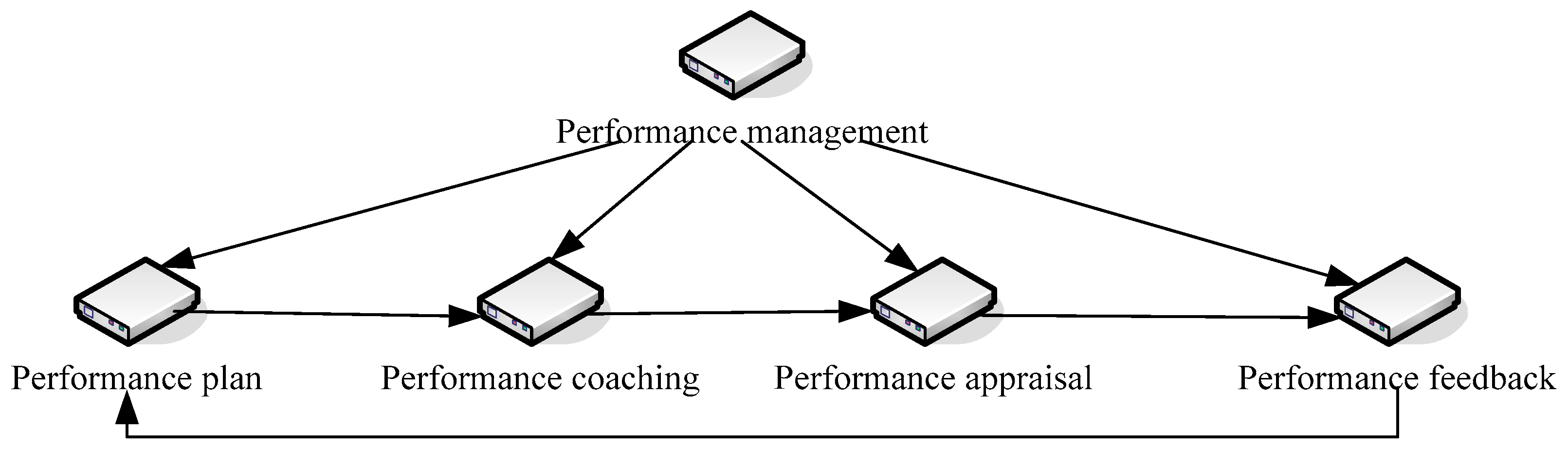
In order to ensure that BD can better participate in the construction of the PMS of equipment enterprises, this text considers the system construction required for BD to participate in the basic construction of the PMS. According to the enterprise PMS of BD technology, it would be divided into five parts: performance management business process, performance plan, performance coaching, performance evaluation, and performance feedback. Among them, the performance management business process includes an infrastructure construction system, a performance management rules and regulations system, a performance management organizational structure system, and a performance management corporate culture system. The infrastructure construction system has brought the necessary conditions for the application of BD technology in enterprise performance management. Performance management corporate culture system, rules and regulations system, and organizational structure system are important means for PMS to operate well. The corporate culture system of performance management focuses on combining the corporate culture atmosphere of BD technology in the traditional PMS to create a performance appraisal data culture. The rules and regulations system establishes the implementation steps of the management system and standard system required for the operation of the PMS in the whole process. The organizational structure system focuses on adjusting the enterprise’s organizational structure so that it can be integrated into BD to ensure the operation of BD equipment. The whole process system of performance management is a key part of the BD PMS. According to the orderly implementation of the four links of performance planning, coaching, evaluation and feedback, and the efficient application of BD technology, the organizational performance is improved, so that the enterprise’s development strategy can be realized.
Figure 1 shows the performance management process.
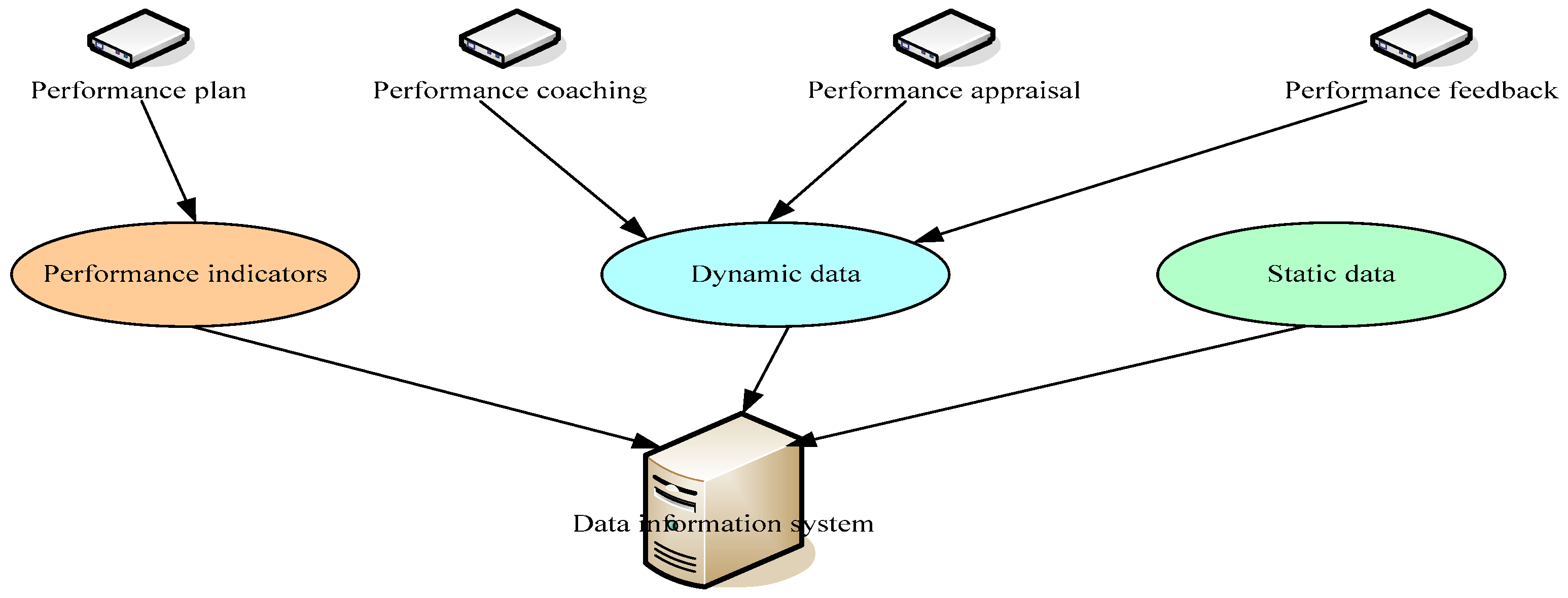
The whole process system of performance management based on BD is a relatively complete performance management infrastructure construction system, corporate culture system, and organizational structure system in the company. Under the premise of the rules and regulations system, it operates according to the BD service platform. The BD platform mining data information management system for text, photos, audio, video, and other types of performance management BD, as shown in
Figure 2, are in the enterprise performance management data information system diagram. It includes the original records composed of employees’ inherent attributes, as well as behavioral data composed of various data information generated by employees’ participation in performance management. Employees can query the real-time platform data on the intelligent terminal at any time. The performance management carried out by the BD service platform has the characteristics of diversified information sources, open and shared information content, synchronous updating and real-time, profiling data visualization, and fully automatic early warning informatization.
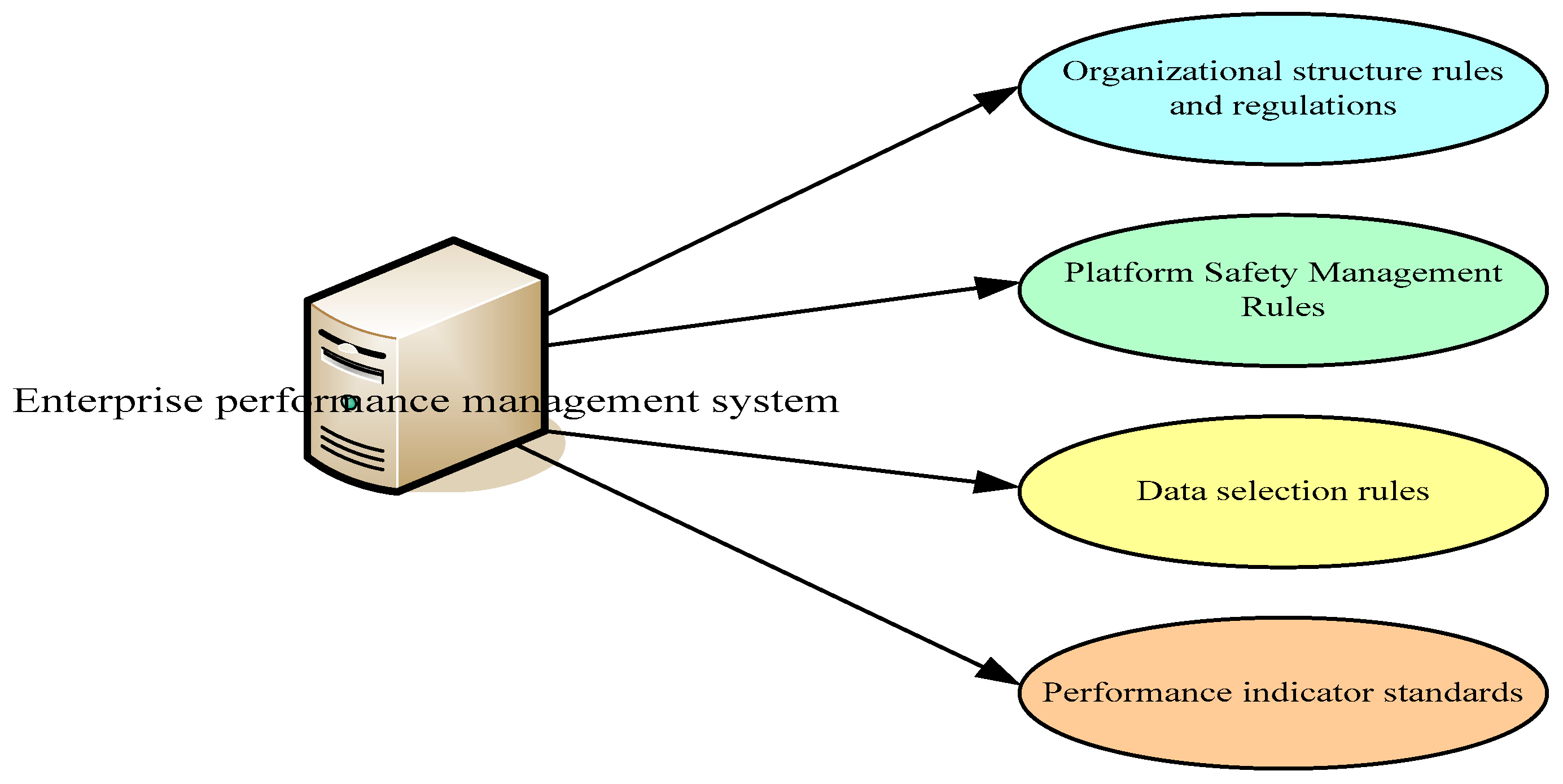
The enterprise development strategy cannot be completed without all-around institutional constraints. The enterprise infrastructure PMS driven by BD technology should infiltrate the BD technology idea into the whole process of enterprise performance management, and produce a management model with BD technology characteristics. This text subdivides the system management system of performance management driven by BD technology, as shown in
Figure 3.
Organizational structure rules and regulations: Performance management in the environment driven by BD and the IoT has a distinctive departmental architecture design. An enterprise must establish a management system for the organizational structure of performance management, self-positioning of posts, formulation of management methods, processes, and plans, etc. Platform security management rules: the enterprise shall be responsible for the maintenance of employee information when carrying out performance management according to the BD service platform. In the process of data information circulation, it is necessary to strengthen the standardization of the personal behavior of the relevant responsible person, establish the relevant permission procedures for data application, and implement the supervision and management mechanism. Data selection rules: “data” have played a leading role in the implementation of BD performance management. All kinds of data keyed in, stored, and solved in the BD platform must be true, accurate, consistent, and timely. Enterprises must create data selection rules to filter and standardize data to avoid data changes and destruction. Performance indicator standard: the whole process of performance management comes from the design of performance indicators. The enterprise must formulate the most appropriate selection method of performance indicators and the evaluation principle of each indicator value to ensure that the performance assessment and other related work can play a full role in the future.
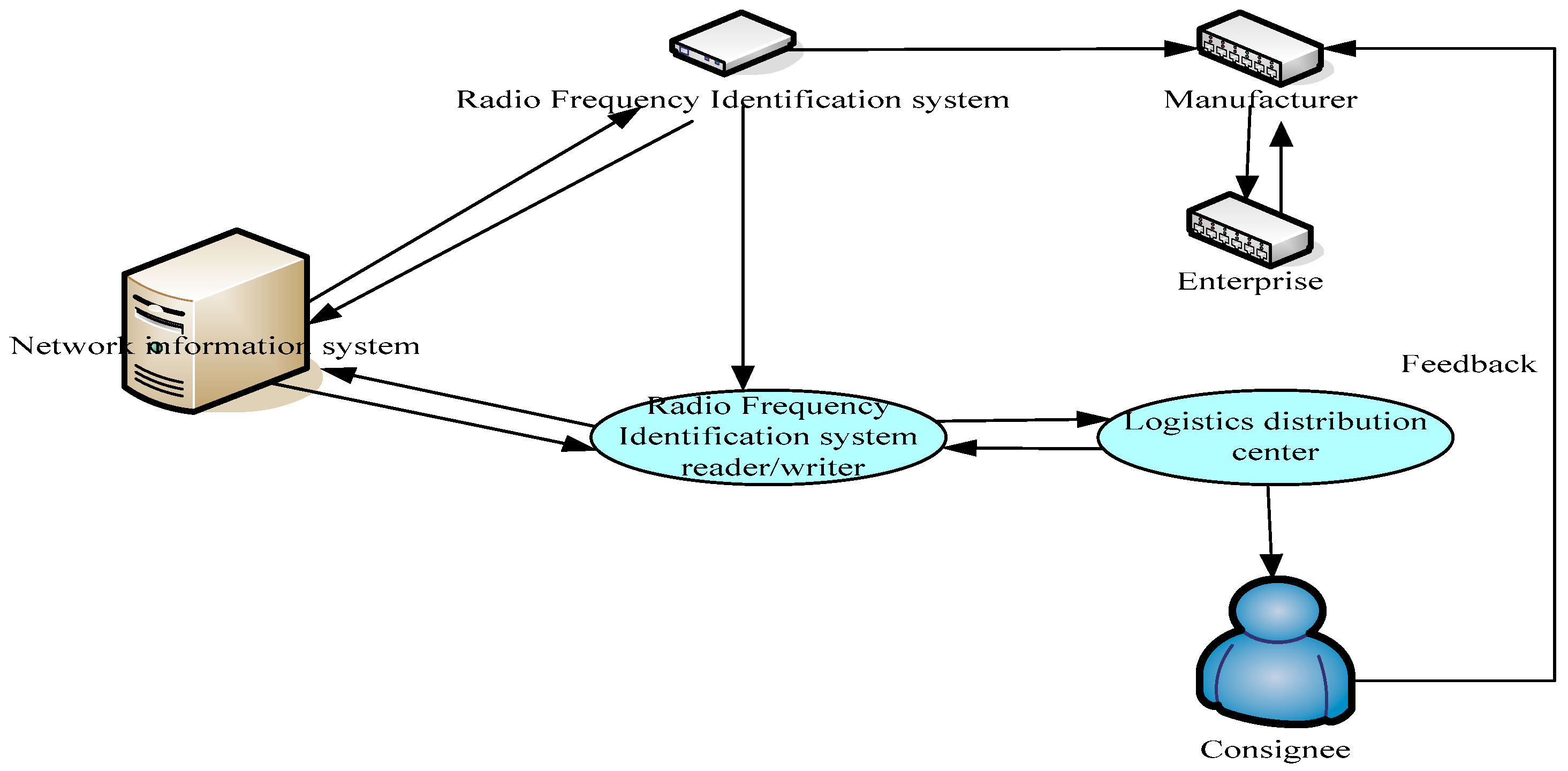
Application of IoT technology in enterprise operation: This text takes the logistics industry as an example. The logistics industry is the first field to touch and apply IoT technology in China. With the natural advantages of IoT application, it is a more common field in which IoT technology is used in rapid development and improvement. Now, in the daily operation of logistics enterprises, the application of the IoT has been gradually put into all aspects of freight logistics business services. The IoT technology is used in order to receive information, accurate positioning of goods identification, storage logistics space management, freight logistics information tracking, and other business links, based on the company’s information Internet platform. It can also efficiently circulate information among dealers, logistics enterprises, and recipients.
Figure 4 shows the business processing flow diagram of logistics enterprises using IoT technology. In the traditional business operation of logistics enterprises, information communication, and feedback are sometimes sluggish, and many of them rely on human resources collection. The cost of obtaining information is relatively high and inaccurate, and the expression of customer needs is relatively backward. The advantage of IoT technology is that it can upload freight logistics information to the Internet-sharing service platform in a timely manner. The integration of information flows can reduce the lag effect of information and improve the consistency and accuracy of information. According to the application of IoT technology, logistics enterprises can timely accept order information orders from suppliers and respond quickly to customer needs. By integrating the dynamics of commodities and improving the transportation mode, it can achieve more efficient resource allocation. This saves logistics costs and provides high-quality warehousing, logistics, transportation, and other work.
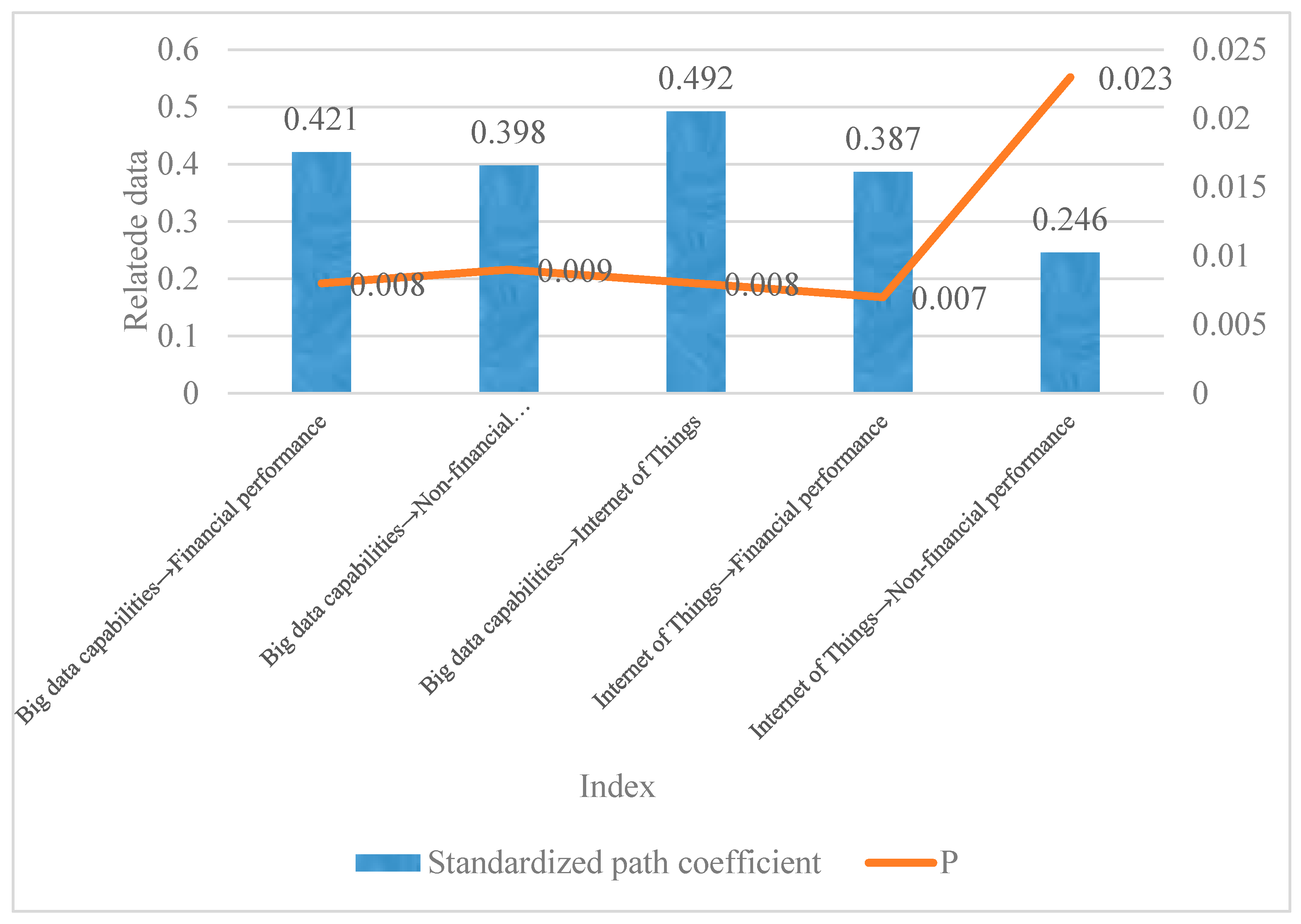
This text proposes a sustainability analysis of enterprise performance management driven by BD and the IoT, which involves the following formula:
—the difference between the profit margin of enterprises before and after using BD and IoT technology for one year, a—enterprises, u—enterprises’ time of using BD and IoT
—Probability of enterprises adopting BD and new technologies of the IoT,
—probability density function,
—financial laxity
—Inverse Mills ratio
K—Enterprises adopting BD and new technologies of the IoT
L—Enterprises without BD and new technologies of the IoT
4. Conclusions
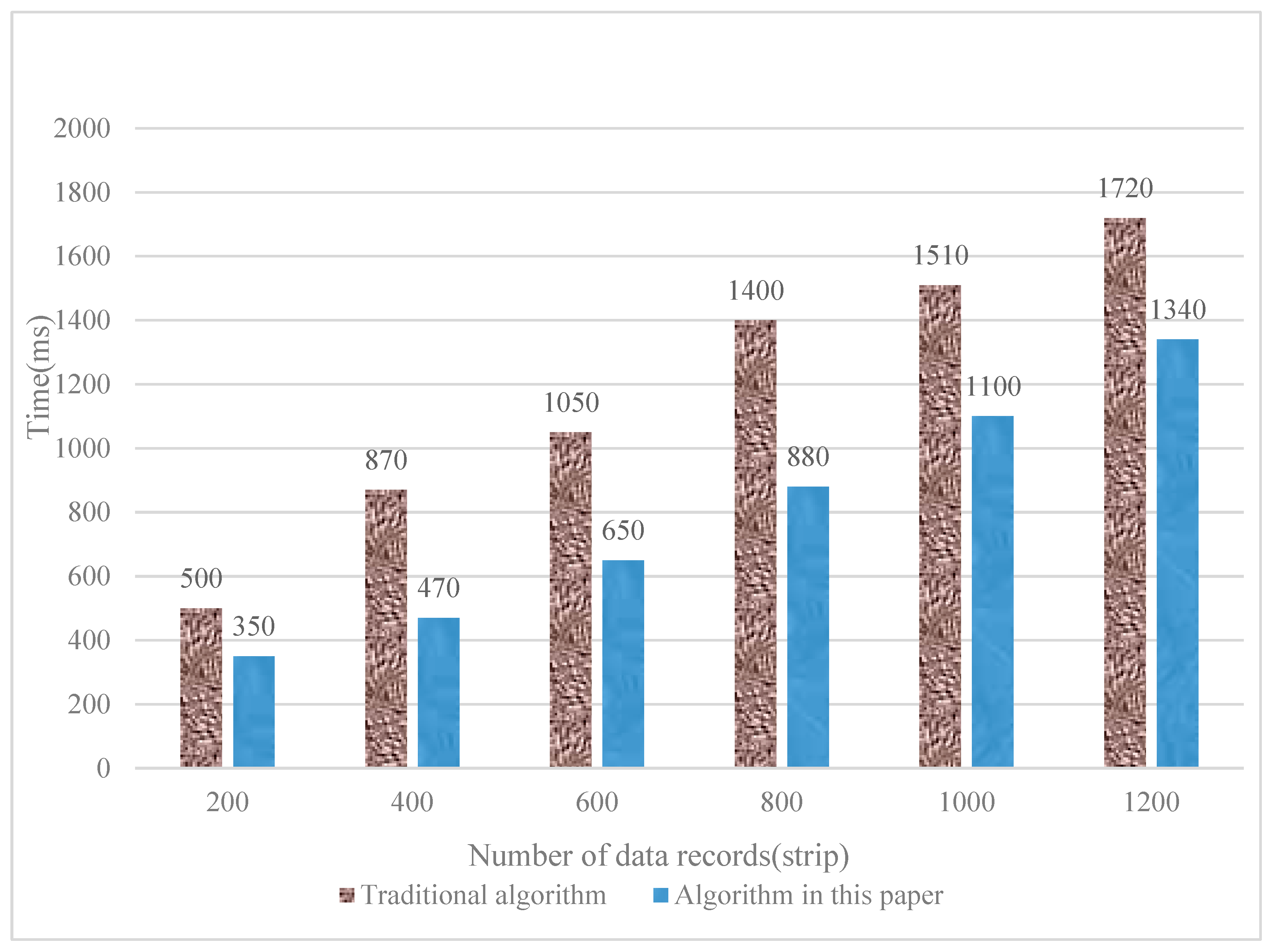
IoT technology and BD technology are both new products of the scientific and technological era, which make it possible to make a major transformation in the development of various industries. The application of IoT technology and BD technology in enterprises makes it possible for enterprises to develop intelligently. In the future, different enterprises would be able to provide users with more accurate, efficient, and considerate services. Financial performance is one of the important contents of the enterprise’s operating efficiency, which can reflect the company’s operating efficiency and the operator’s sales performance in a specific operating period. At the same time, this algorithm can improve the accuracy of FP data and achieve faster data processing. This paper finds that the processing time of enterprise financial data based on BD and the Internet of Things enterprise performance management algorithm is significantly faster than the traditional algorithm. Although the research in this paper can provide some references for relevant research, it also has certain limitations. However, there are still shortcomings in this paper. First of all, the participants of the performance appraisal are single, and this paper only compares the effectiveness study (CER). This paper takes a logistics enterprise as an example to analyze its online public information and annual report data in recent years, but it is difficult to ensure the objectivity and effectiveness of the assessment process and results. Secondly, the application method of performance appraisal results is single. This paper uses the data survey method for experimental analysis. In the future, this paper will consider the systematic, targeted, and reliable characteristics of performance management in enterprise management, establish a sound performance evaluation system, improve the corresponding management system, and find appropriate evaluation methods for experimental analysis.