Analysis of the Impact of Industrial Structure Upgrading and Energy Structure Optimization on Carbon Emission Reduction
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review and Research Hypotheses
2.1. Literature Review
2.2. Research Hypothesis
2.2.1. Impact Mechanism of Industrial Structure on Carbon Emissions
2.2.2. Impact Mechanism of Industrial Structure on Energy Structure
2.2.3. Impact Mechanism of Energy Structure on Carbon Emissions
3. Model and Data
3.1. Model
3.1.1. Quantile Regression Model
3.1.2. Mediation Effect Model
3.2. Variable Selection and Measurement
3.2.1. Interpreted Variables
3.2.2. Core Explanatory Variables
3.2.3. Mediator Variable
3.2.4. Control Variables
3.3. Data Sources and Statistical Characteristics
4. Empirical Test
4.1. Regional Division
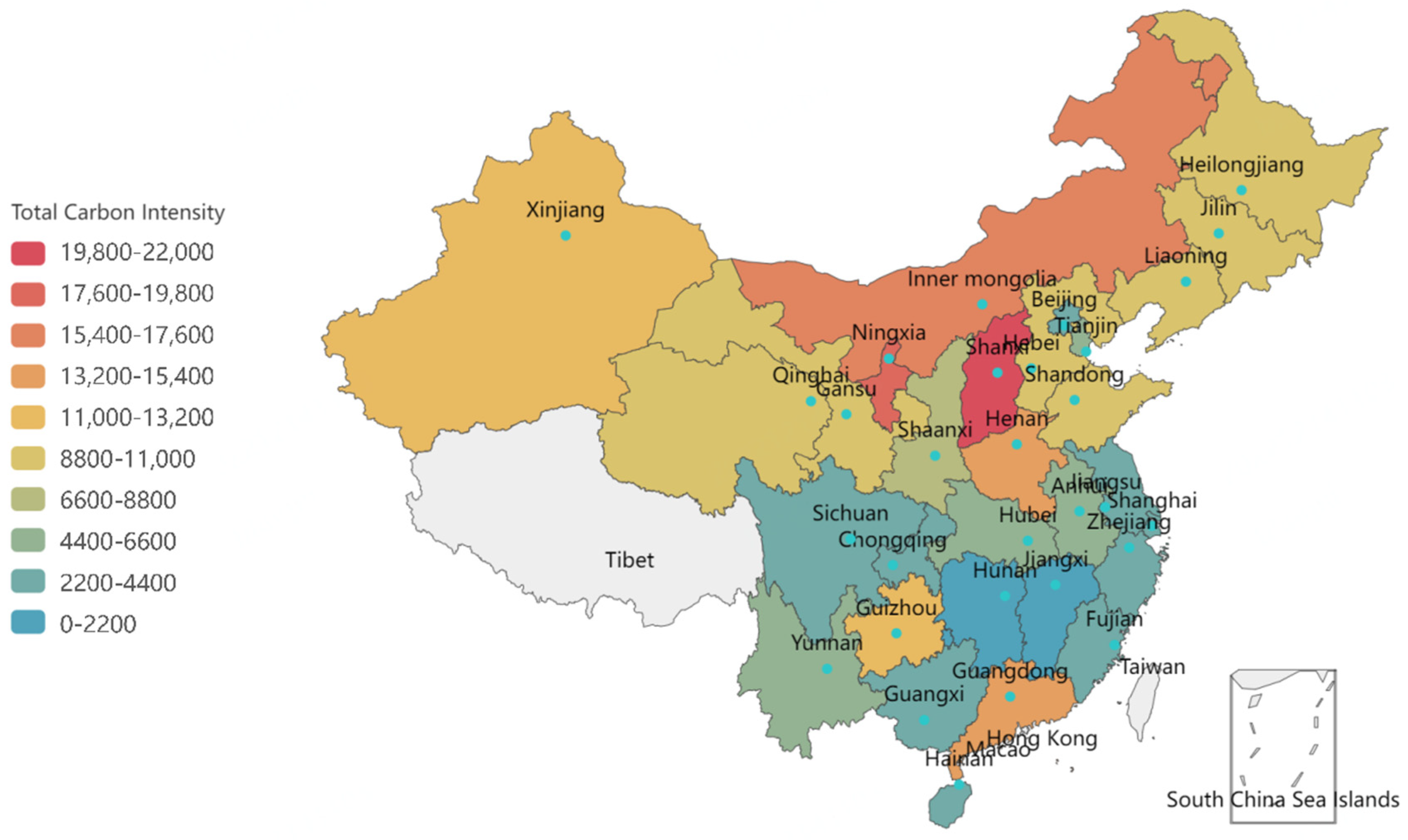
4.1.1. Current Status of Carbon Emissions in China
4.1.2. Regional Grouping
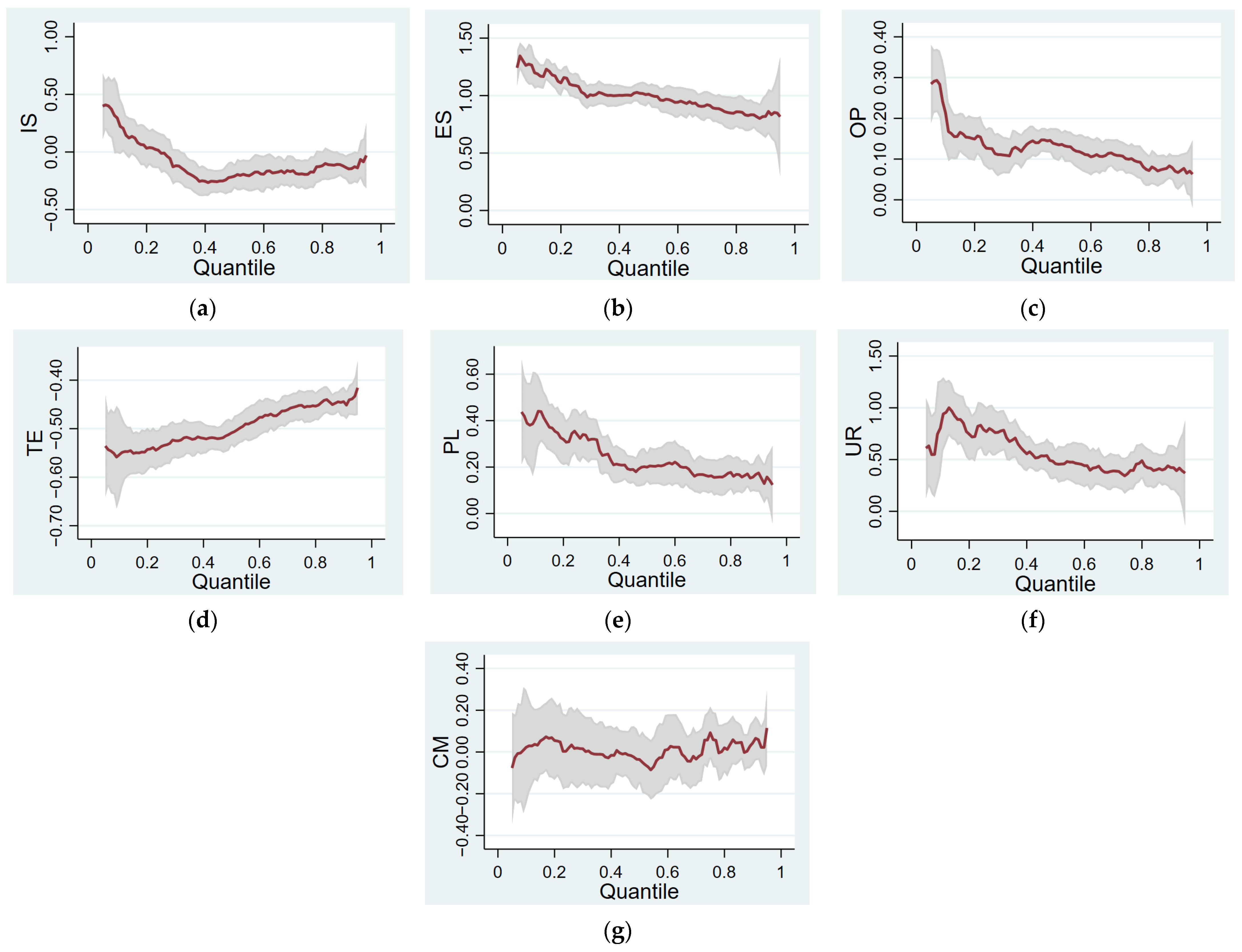
4.2. Quantile Regression Analysis
4.2.1. Panel Unit Root Test and Cointegration Test
4.2.2. Model Form
4.2.3. Analysis of Regression Results
4.2.4. Robustness Test
4.3. Mediating Effect Analysis
4.3.1. Stepwise Regression Test
4.3.2. Bootstrap Mediation Effect Test
5. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, C.; Hao, Y.; Irfan, M. Energy consumption structural adjustment and carbon neutrality in the post-COVID-19 era. Struct. Chang. Econ. Dyn. 2021, 59, 442–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Li, H.; Zhang, Q.; Tian, X.; Shi, F. Uncovering the impacts of industrial transformation on low-carbon development in the Yangtze River Delta. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2019, 150, 104442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Zhang, J.; Li, J. Industrial structural transformation and carbon dioxide emissions in China. Energy Policy 2013, 57, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Song, X.; Chen, K. Which Influencing Factors Cause CO2 Emissions Differences in China’s Provincial Construction Industry: Empirical Analysis from a Quantile Regression Model. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2020, 29, 331–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.M. The relationship between carbon dioxide emissions and economic growth: Quantile panel-type analysis. Qual. Quant. 2013, 47, 1337–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharif, A.; Raza, S.A.; Ozturk, I.; Afshan, S. The dynamic relationship of renewable and nonrenewable energy consumption with carbon emission: A global study with the application of heterogeneous panel estimations. Renew. Energy 2019, 133, 685–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossman, G.M.; Krueger, A.B. Environmental Impacts of a North American Free Trade Agreement; National Bureau of Economic Research: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panayotou, T. Empirical Tests and Policy Analysis of Environmental Degradation at Different Stages of Economic Development; International Labour Office: Geneva, Switzerland, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, J.; Dou, Y.; Jiang, Q.; Zhao, J. How Does Industrial Structure Upgrading Affect the Global Greenhouse Effect? Evidence From RCEP and Non-RCEP Countries. Front. Energy Res. 2021, 9, 683166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chang, X.; Huang, C. Research and Analysis on the Influencing Factors of China’s Carbon Emissions Based on a Panel Quantile Model. Sustainability 2022, 14, 7791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Xi, Y. Threshold Effects of Urban Population Size and Industrial Structure on CO2 Emissions in China. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, R.; Li, C.; Li, D.; Yang, Y.; Gu, S. The impact of rationalization and upgrading of industrial structure on carbon emissions in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei urban agglomeration. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 7997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Zhang, J.; Yuan, M. Carbon emissions and economic growth in the Yellow River Basin: Decoupling and driving factors. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 2466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, C.; Yu, S.; Li, M.; Cheng, Y. Coupling coordination and spatiotemporal evolution between carbon emissions, industrial structure, and regional innovation of counties in Shandong province. Sustainability 2022, 14, 7484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, P.; Wang, Y.; Zou, Y.; Su, X.; Che, X.; Yang, X. Green technology innovation and carbon emissions nexus in China: Does industrial structure upgrading matter? Front. Psychol. 2022, 13, 951172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, K.; Deng, H.; Lyu, K.; Yang, S.; Cao, Y. Market Integration, Industrial Structure, and Carbon Emissions: Evidence from China. Energies 2022, 15, 9371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brannlund, R.; Persson, L. To tax, or not to tax: Preferences for climate policy attributes. Clim. Policy 2012, 12, 704–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torvanger, A. Manufacturing sector carbon dioxide emissions in nine OECD countries, 1973–1987: A Divisia index decomposition to changes in fuel mix, emission coefficients, industry structure, energy intensities and international structure. Energy Econ. 1991, 13, 168–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Xie, S.; Pan, C. The impact of planting industry structural changes on carbon emissions in the three northeast provinces of China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, B.; Xu, Y.; Fan, X. How to achieve a win-win situation between economic growth and carbon emission reduction: Empirical evidence from the perspective of industrial structure upgrading. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 43829–43844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Peng, J.; Xiao, J.; Su, P.; Li, S. Industrial structure transformation and provincial heterogeneity characteristics evolution of air pollution: Evidence of a threshold effect from China. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2020, 11, 598–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Deng, X.; Phillips, F.; Fang, C.; Wang, C. Impacts of industrial structure and technical progress on carbon emission intensity: Evidence from 281 cities in China. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2020, 154, 119949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, L.; Lu, H.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Hu, H. Analysis of regional differences and influencing factors on China’s carbon emission efficiency in 2005–2015. Energies 2019, 12, 3081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kambara, T. The energy situation in China. China Q. 1992, 131, 608–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, L.; Li, H.; Xu, C.; Zhao, X.; Zheng, Z.; Li, Y.; Liu, W. Impacts of industrial structure adjustment, upgrade and coordination on energy efficiency: Empirical research based on the extended STIRPAT model. Energy Strategy Rev. 2022, 43, 100911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, L.; Huang, L. Analysis of influencing factors of Chinese provincial carbon emissions based on projection pursuit model and Markov transfer matrix. Int. J. Clim. Chang. Strateg. Manag. 2018, 11, 406–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borghetti Soares, J.; Tiomno Tolmasquim, M. Energy efficiency and reduction of CO2 emissions through 2015: The Brazilian cement industry. Mitig. Adapt. Strateg. Glob. Chang. 2000, 5, 297–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siitonen, S.; Tuomaala, M.; Ahtila, P. Variables affecting energy efficiency and CO2 emissions in the steel industry. Energy Policy 2010, 38, 2477–2485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yu, Z.; Zhang, J. Analysis of carbon emission performance and regional differences in China’s eight economic regions: Based on the super-efficiency SBM model and the Theil index. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0250994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, S.C.; He, Z.X.; Long, R.Y.; Chen, H. Factors that influence carbon emissions due to energy consumption based on different stages and sectors in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 115, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.; Can, P.; Xiaona, Y.; Ruixue, L. Does change of industrial structure affect energy consumption structure: A study based on the perspective of energy grade calculation. Energy Explor. Exploit. 2019, 37, 579–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Ding, C.; Wu, Z.; Guo, B.; Xue, Y.; Li, D. The impact of digital economy and industrial structure distortion on Xinjiang’s energy intensity under the goal of “double carbon”. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 1036740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koenker, R.; Bassett, G., Jr. Regression quantiles. Econom. J. Econom. Soc. 1978, 46, 33–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrlich, P.R.; Ehrlich, A.H. Population, Resources, Environment: Issues in Human Ecology; Freeman: San Francisco, CA, USA, 1970; Volume 15, pp. 7–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tursun, H.; Li, Z.; Liu, R.; Li, Y.; Wang, X. Contribution weight of engineering technology on pollutant emission reduction based on IPAT and LMDI methods. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2015, 17, 225–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, J.; Yang, D.; Zhang, W.; Wang, F.; Wang, G.; Fu, Q. Analysis of influencing factors of CO2 emissions in Xinjiang under the context of different policies. Environ. Sci. Policy 2015, 45, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- York, R.; Rosa, E.A.; Dietz, T. STIRPAT, IPAT and ImPACT: Analytic tools for unpacking the driving forces of environmental impacts. Ecol. Econ. 2003, 46, 351–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baron, R.M.; Kenny, D.A. The moderator–mediator variable distinction in social psychological research: Conceptual, strategic, and statistical considerations. J. Personal. Soc. Psychol. 1986, 51, 1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Wang, S.; Jiang, X. Preventing a rebound in carbon intensity post-COVID-19–lessons learned from the change in carbon intensity before and after the 2008 financial crisis. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2021, 27, 1841–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Chen, Y.E.; Chang, C.P. The effects of environmental regulation and industrial structure on carbon dioxide emission: A non-linear investigation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 30252–30267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, C.; Wei, J.; Liu, C. Empirical analysis of the influence of green credit on the industrial structure: A case study of China. Sustainability 2021, 13, 5997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Shang, Y.; Song, M. Industrial structure distortion and urban ecological efficiency from the perspective of green entrepreneurial ecosystems. Socio-Econ. Plan. Sci. 2020, 72, 100757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, C.H.; Zheng, R.G.; Yu, D.F. An empirical study on the effects of industrial structure on economic growth and fluctuations in China. Econ. Res. J. 2011, 5, 4–16. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Y.; Jiang, H.; Zhong, Z. Impact of green credit on industrial structure in China: Theoretical mechanism and empirical analysis. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 10506–10519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, S.; Hao, Y.; Xu, L.; Wu, H.; Ba, N. Digitalization and energy: How does internet development affect China’s energy consumption? Energy Econ. 2021, 98, 105220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yang, X.; Ran, Q.; Wu, H.; Irfan, M.; Ahmad, M. Energy structure, digital economy, and carbon emissions: Evidence from China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 64606–64629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, L.; Liu, Z.; Mohsin, M.; Zhang, C. Renewable energy, industrial upgradation, and import-export quality: Green finance and CO2 emission reduction nexus. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 13, 13327–13341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, T.; Nathwani, J.; Yang, F.; Shao, Q. Environmental regulation, technology innovation, and low carbon development: Revisiting the EKC Hypothesis, Porter Hypothesis, and Jevons’ Paradox in China’s iron & steel industry. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2022, 176, 121471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Jia, X.; Gao, L.; Zhou, Y. Effects of population flow on regional carbon emissions: Evidence from China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 62628–62639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, X.; Li, X.; Tan, W.; Xiao, R. Decoupling relationship analysis between urbanization and carbon emissions in 33 African countries. Heliyon 2022, 8, e10423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Li, J.; Li, G.; Guo, S. Emission reduction effect and carbon market efficiency of carbon emissions trading policy in China. Energy 2020, 196, 117117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, Y.; Huang, Q.; Guan, D.; Hubacek, K. China CO2 emission accounts 2016–2017. Sci. Data 2020, 7, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, Y.; Liu, J.; Liu, Z.; Xu, X.; Shao, S.; Wang, P.; Guan, D. New provincial CO2 emission inventories in China based on apparent energy consumption data and updated emission factors. Appl. Energy 2016, 184, 742–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Y.; Shan, Y.; Huang, Q.; Chen, H.; Wang, D.; Hubacek, K. Assessment to China’s recent emission pattern shifts. Earths Future 2021, 9, e2021EF002241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P.; Liu, L.; Qayyum, M. Energy efficiency comparison amongst service industry in Chinese provinces from the perspective of heterogeneous resource endowment: Analysis using undesirable super efficiency SBM-ML model. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 328, 129535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Liu, X.; Ji, J.; Ma, X. Role of economic structural change in the peaking of China’s CO2 emissions: An input–output optimization model. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 761, 143306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, Z.M.; Shen, X.; Guo, L. Technological innovation on economic growth from the perspective of investment-oriented environmental regulations: Considering the threshold effect of China human capital. Appl. Econ. 2021, 53, 4632–4645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, G.; Yu, D.; Ke, L. An empirical study on dynamic evolution of industrial structure and green economic growth—Based on data from China’s underdeveloped areas. Sustainability 2021, 13, 8154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Variable Name | Economic Meaning | Metrics | AVG | Std. | Min | Max |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CG | Carbon Intensity: the amount of carbon dioxide emitted per unit of gross national product | Carbon emissions/Gross national product (million tons/billion yuan) | 342.9253 | 270.0545 | 15.7056 | 1564.8340 |
| IS | Industrial Structure | The added value of the tertiary industry/the added value of the second industry | 1.1374 | 0.5521 | 0.5271 | 5.2340 |
| ES | Energy Consumption Structure | Regional coal consumption/regional total energy consumption (%) | 0.6853 | 0.2701 | 0.0177 | 1.7578 |
| OP | Level of Opening-up | Total import and export volume of domestic destinations and sources of goods (100 million yuan) | 7920.0000 | 17,500.0000 | 15.2940 | 128,000.0000 |
| TE | Technological Innovation | Number of patent authorizations (pieces) | 24,627.4300 | 53,679.7700 | 56.0000 | 527,390.0000 |
| PL | Population | Total population (10,000 people) | 4387.5790 | 2683.5330 | 495.6000 | 12,489.0000 |
| UR | Urbanization level | Urban population/total population (%) | 0.2707 | 0.1798 | 0.0197 | 0.8028 |
| CM | Carbon Trading Pilot Policy | 0~1 dummy variable | 0 | 1 | ||
| Group | Area |
|---|---|
| ≤0.10 quantile group | Jiangxi, Hunan, Guangxi |
| 0.10~0.25 quantile group | Beijing, Fujian, Shanghai, Hainan |
| 0.25~0.50 quantile group | Zhejiang, Jiangsu, Sichuan, Chongqing, Hubei, Yunnan, Tianjin, Anhui |
| 0.50~0.75 quantile group | Shaanxi, Hebei, Qinghai, Jilin, Liaoning, Heilongjiang, Shandong |
| 0.75~0.90 quantile group | Gansu, Xinjiang, Guizhou, Guangdong, Henan |
| ≥0.90 quantile group | Inner Mongolia, Ningxia, Shanxi |
| Variable | LLC | IPS | ADF-Fisher Chi-Square | PP-Fisher Chi-Square | Conclusion |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D_lnCG | −18.4329 *** | −16.4297 *** | 213.9499 *** | 538.7272 *** | smooth |
| (0.0000) | (0.0000) | (0.0000) | (0.0000) | ||
| D_lnIS | −13.4503 *** | −11.4533 *** | 198.5181 *** | 246.8631 *** | smooth |
| (0.0000) | (0.0000) | (0.0000) | (0.0000) | ||
| D_lnES | −19.0036 *** | −16.7741 *** | 250.4381 *** | 529.6426 *** | smooth |
| (0.0000) | (0.0000) | (0.0000) | (0.0000) | ||
| D_lnOP | −16.0971 *** | −14.7765 *** | 263.9364 *** | 452.4454 *** | smooth |
| (0.0000) | (0.0000) | (0.0000) | (0.0000) | ||
| D_lnTE | −16.8806 *** | −14.6179 *** | 161.3194 *** | 410.4722 *** | smooth |
| (0.0000) | (0.0000) | (0.0000) | (0.0000) | ||
| D_lnPL | −14.8879 *** | −12.1741 *** | 223.7696 *** | 327.3083 *** | smooth |
| (0.0000) | (0.0000) | (0.0000) | (0.0000) | ||
| D_lnUR | −17.8013 *** | −18.5908 *** | 320.9167 *** | 631.6294 *** | smooth |
| (0.0000) | (0.0000) | (0.0000) | (0.0000) | ||
| D_lnCM | −19.0570 *** | −15.3160 *** | 147.0966 *** | 407.6537 *** | smooth |
| (0.0000) | (0.0000) | (0.0000) | (0.0000) |
| Testing Method | INSPECTION FORM | Statistics | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Kao | Modified Dickey–Fuller t | −5.4478 | 0.0000 |
| Dickey–Fuller t | −4.7316 | 0.0000 | |
| Augmented Dickey–Fuller t | −5.2597 | 0.0000 | |
| Pedroni | Modified Phillips–Perron t | 8.1915 | 0.0000 |
| Phillips–Perron t | −2.9919 | 0.0014 | |
| Augmented Dickey–Fuller t | −4.4612 | 0.0000 | |
| Westerlund | −2.3487 | 0.0094 |
| Variable | lnIS | lnES | lnOP | lnTE | lnPL | lnUR | lnCM | _cons |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10% | 0.2950 *** | 1.2656 *** | 0.2134 *** | −0.5537 *** | 0.4081 *** | 0.8036 *** | 0.0228 | −3.528 *** |
| (0.0077) | (0.0000) | (0.0000) | (0.0000) | (0.0000) | (0.0000) | (0.9010) | (0.0040) | |
| 25% | −0.0114 *** | 1.0875 *** | 0.126 *** | −0.5365 *** | 0.3393 *** | 0.7888 *** | 0.0192 * | −1.3342 * |
| (0.0091) | (0.0000) | (0.0000) | (0.0000) | (0.0000) | (0.0000) | (0.0850) | (0.0530) | |
| 50% | −0.2105 *** | 1.0122 *** | 0.136 *** | −0.5087 *** | 0.1996 *** | 0.4597 *** | 0.0358 * | 1.3491 ** |
| (0.0040) | (0.0000) | (0.0000) | (0.0000) | (0.0000) | (0.0000) | (0.0656) | (0.0110) | |
| 75% | −0.1938 *** | 0.8755 *** | 0.0961 *** | −0.4518 *** | 0.1566 *** | 0.3627 *** | 0.0923 ** | 2.6937 *** |
| (0.0090) | (0.0000) | (0.0000) | (0.0000) | (0.0000) | (0.0000) | (0.0258) | (0.0000) | |
| 90% | −0.1442 *** | 0.8192 *** | 0.0671 *** | −0.4442 *** | 0.1749 *** | 0.4226 *** | 0.0434 | 2.8686 *** |
| (0.0015) | (0.0000) | (0.0000) | (0.0000) | (0.0000) | (0.0000) | (0.5040) | (0.0000) |
| Replace the Explained Variable | Replace Explanatory Variables | |
|---|---|---|
| (1) | (2) | |
| lnPC | lnCG | |
| lnIS | −0.2668 *** | |
| lnIR | −0.0261 *** | |
| lnES | 0.7018 *** | 0.6332 *** |
| lnOP | 0.2329 *** | 0.0858 * |
| lnTE | −0.1707 *** | −0.2168 *** |
| lnPL | 0.5678 *** | 0.8548 *** |
| lnUR | 0.4206 *** | 0.2920 *** |
| lnCM | −0.0603 | −0.2925 *** |
| _cons | 3.0882 *** | −2.0662 |
| adjust R2 | 0.8984 | 0.7372 |
| Model 1 | Model 2 | Model 3 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| lnCG | lnES | lnCG | |
| IS | −0.3670 *** | −0.1219 *** | −0.2943 *** |
| (0.0082) | (0.0000) | (0.0055) | |
| ES | 0.5971 *** | ||
| (0.0040) | |||
| OP | −0.0975 | −0.0096 | −0.1032 |
| (0.2920) | (0.9060) | (0.1630) | |
| TE | −0.2808 *** | −0.0677 ** | −0.2404 *** |
| (0.0020) | (0.0450) | (0.0070) | |
| PL | 0.6057 | −0.6529 | 0.9955 * |
| (0.3220) | (0.1910) | (0.0700) | |
| UR | 0.3087 * | 0.0783 | 0.2620 |
| (0.0970) | (0.4020) | (0.1470) | |
| CM | −0.4407 *** | −0.2915 ** | −0.2666 *** |
| (0.0010) | (0.0190) | (0.0090) | |
| _cons | 2.5707 | 4.7036 *** | −3.1802 |
| (0.5960) | (0.0100) | (0.5130) | |
| R2 | 0.8858 | 0.8286 | 0.9002 |
| Mediator Variable | Path | Effect | Effect Coefficient | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| energy structure | lnIS-lnES-lnCG | indirect | −0.0728 | 0.0000 |
| lnIS-lnES-lnCG | direct | −0.2943 | 0.0000 | |
| lnIS-lnCG | total effect | −0.3670 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fan, G.; Zhu, A.; Xu, H. Analysis of the Impact of Industrial Structure Upgrading and Energy Structure Optimization on Carbon Emission Reduction. Sustainability 2023, 15, 3489. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15043489
Fan G, Zhu A, Xu H. Analysis of the Impact of Industrial Structure Upgrading and Energy Structure Optimization on Carbon Emission Reduction. Sustainability. 2023; 15(4):3489. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15043489
Chicago/Turabian StyleFan, Guoliang, Anni Zhu, and Hongxia Xu. 2023. "Analysis of the Impact of Industrial Structure Upgrading and Energy Structure Optimization on Carbon Emission Reduction" Sustainability 15, no. 4: 3489. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15043489
APA StyleFan, G., Zhu, A., & Xu, H. (2023). Analysis of the Impact of Industrial Structure Upgrading and Energy Structure Optimization on Carbon Emission Reduction. Sustainability, 15(4), 3489. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15043489





