Combined Impacts of Climate Change and Water Withdrawals on the Water Balance at the Watershed Scale—The Case of the Allier Alluvial Hydrosystem (France)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
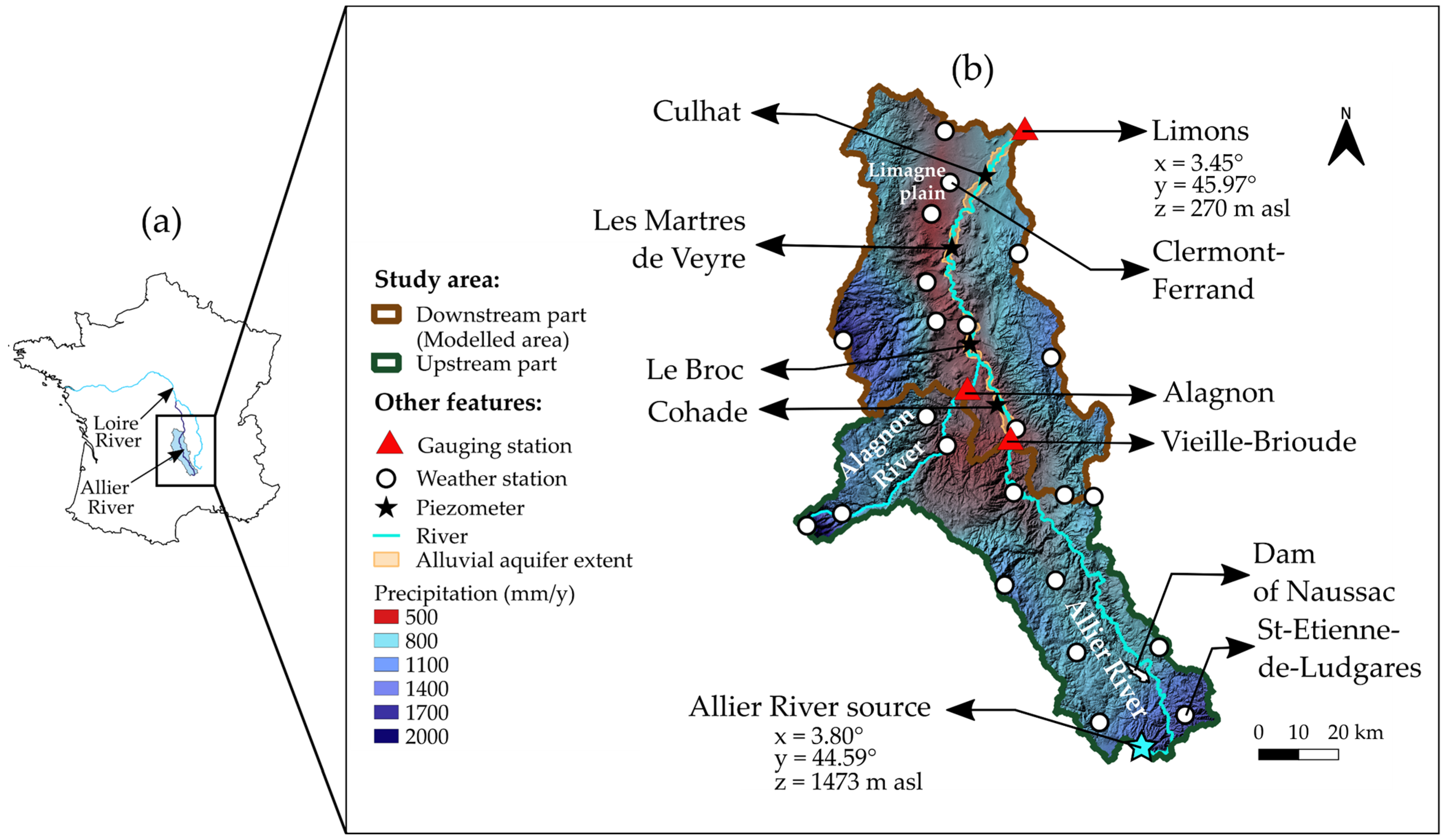
2.1. Description of the Study Area
2.2. Available Data on the Study Area
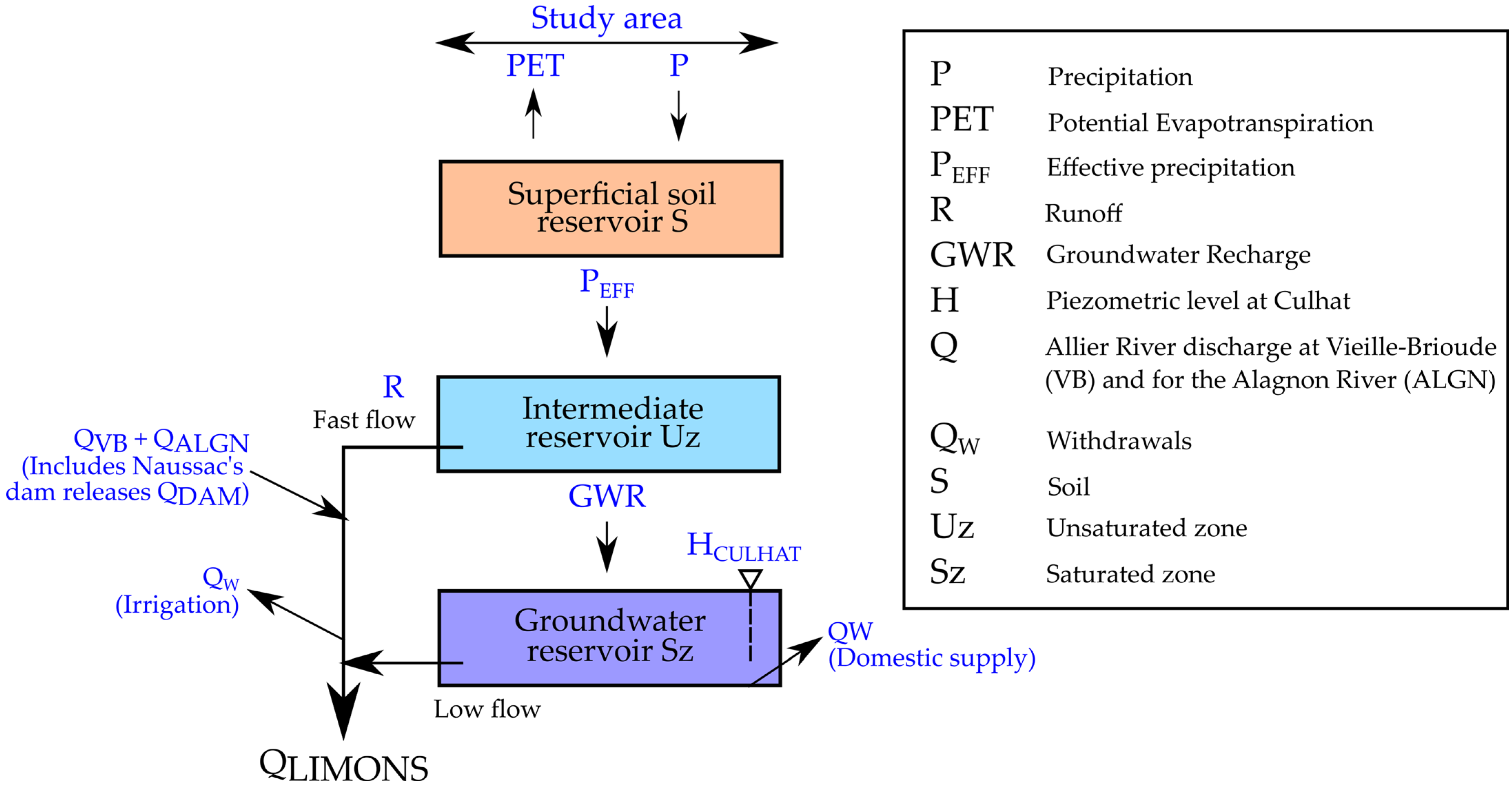
2.3. Description of the Hydrological Model Gardenia
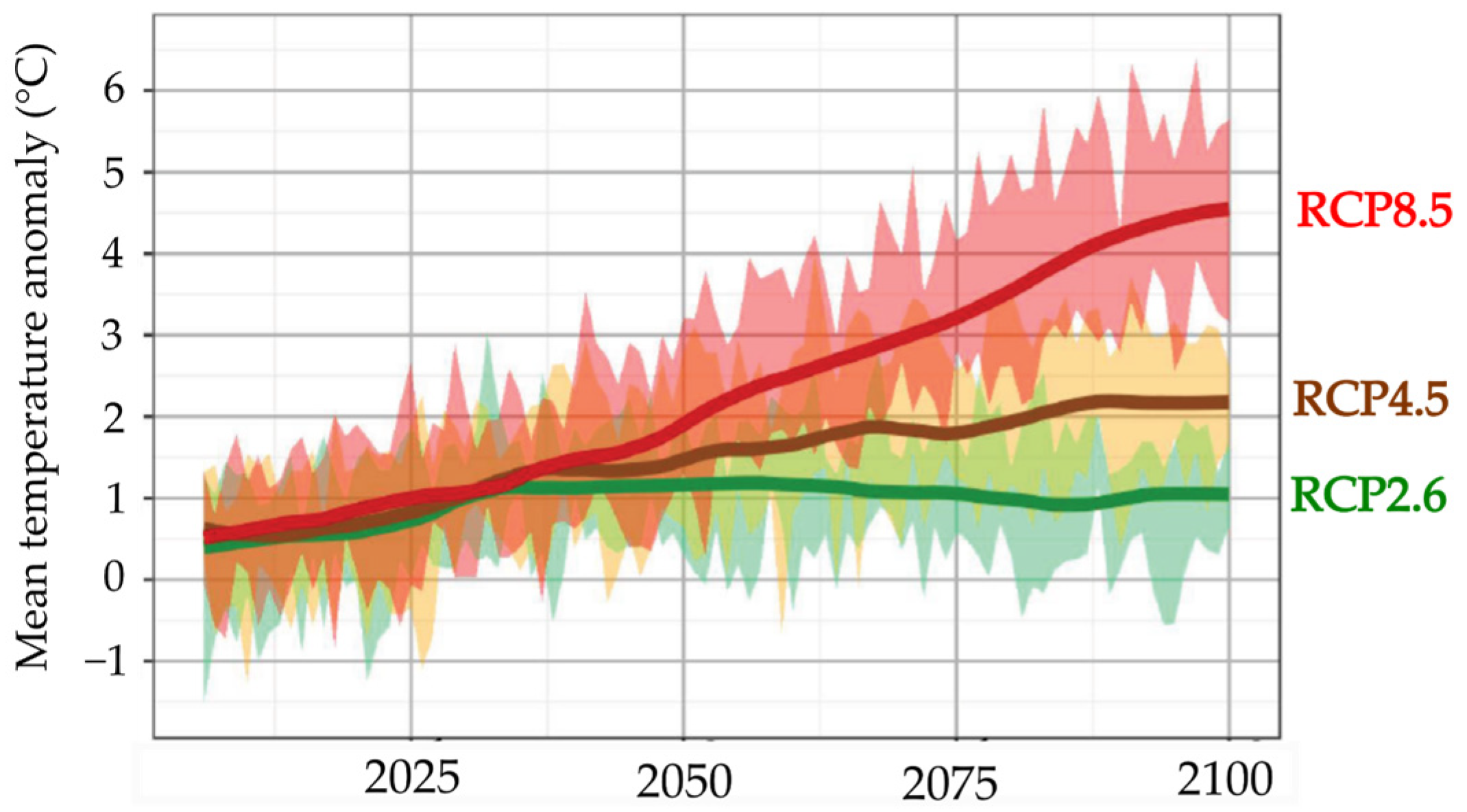
2.4. Regional Climate Model (RCM) and Representative Concentration Pathway (RCP) Scenarios for Forecasting the River Discharge and Groundwater Levels
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Identification of the Driving Factors using the Observation Data
3.1.1. Trends in 1974–2020
3.1.2. Observed Trends during the Modelling Period: 2000–2020
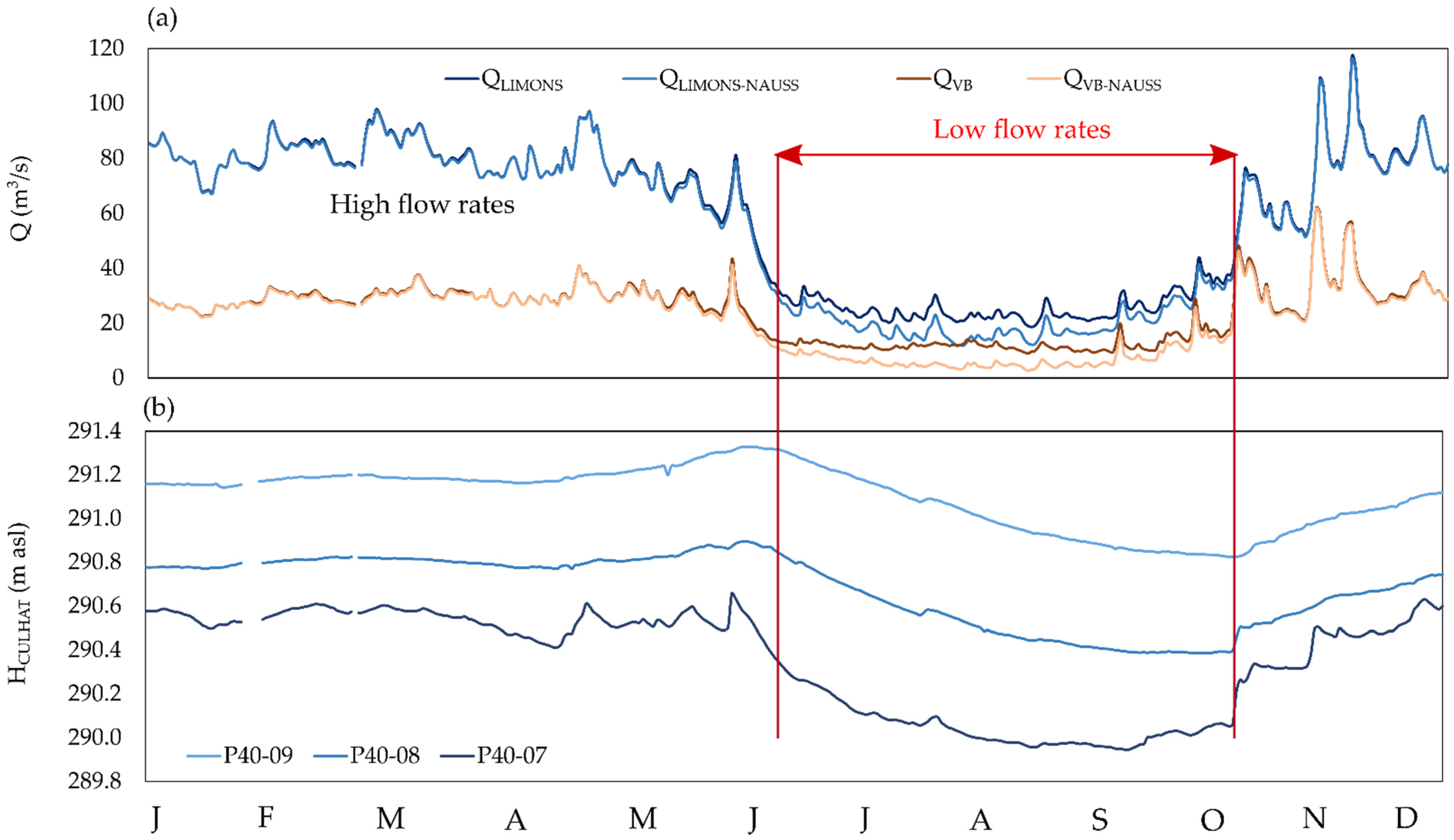
3.1.3. Subannual Variations
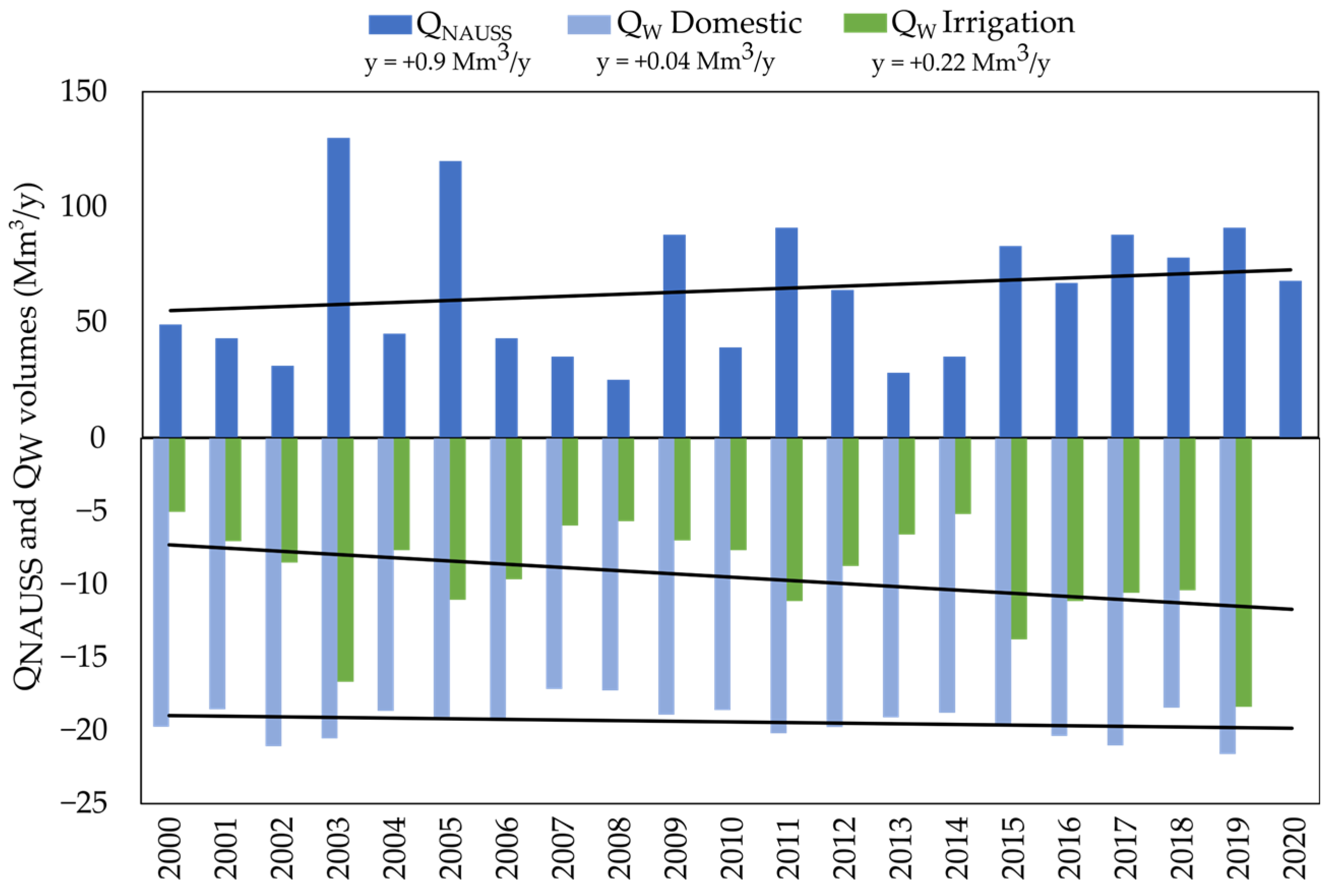
3.2. Quantification of the Driving Factors of the Water Balance from 2000 to 2020
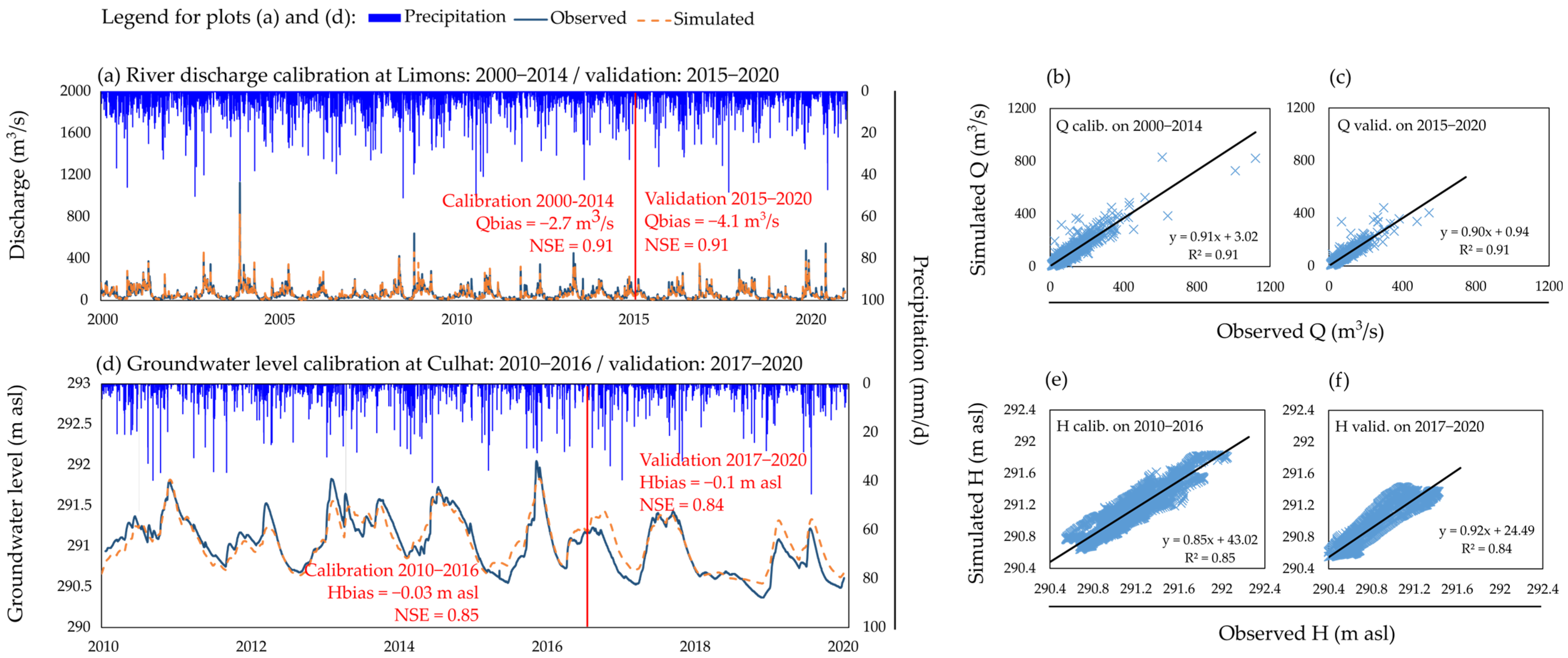
3.2.1. Calibrated Model and Parameters
3.2.2. Water Balance in the Downstream Part from 2000 to 2020
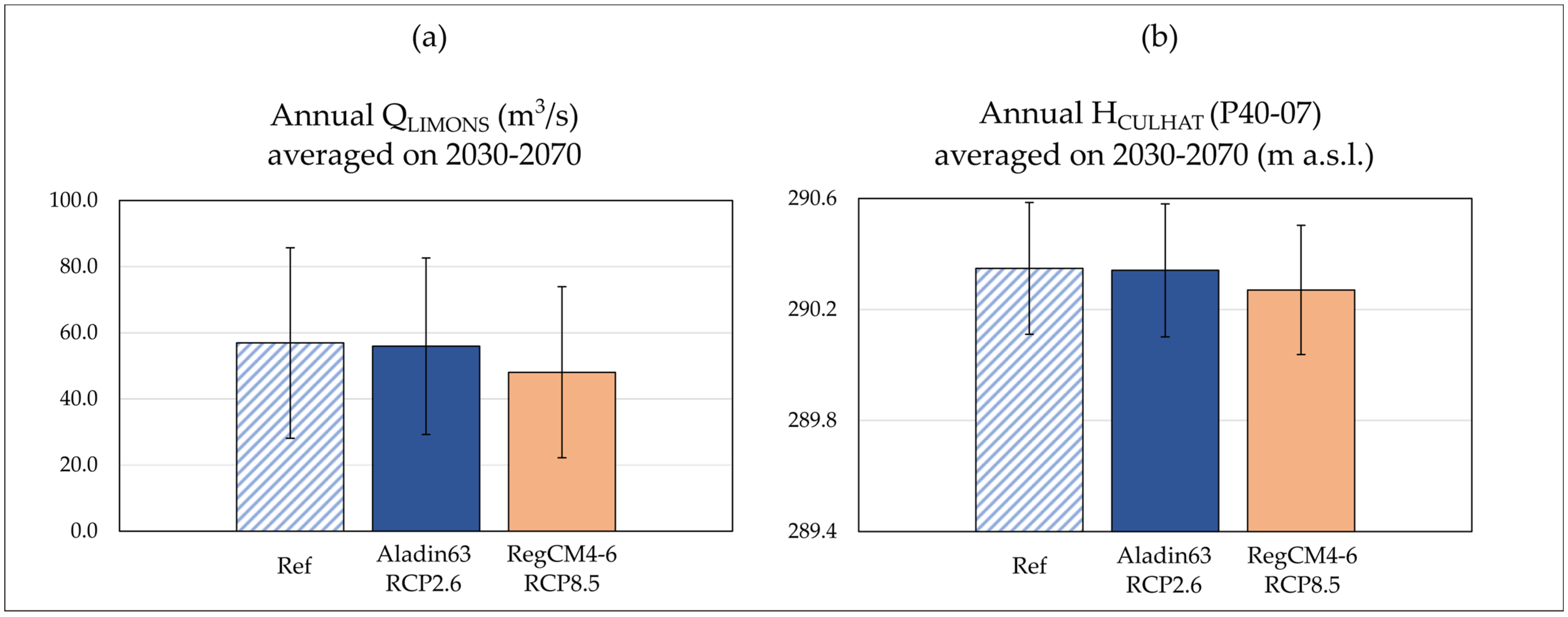
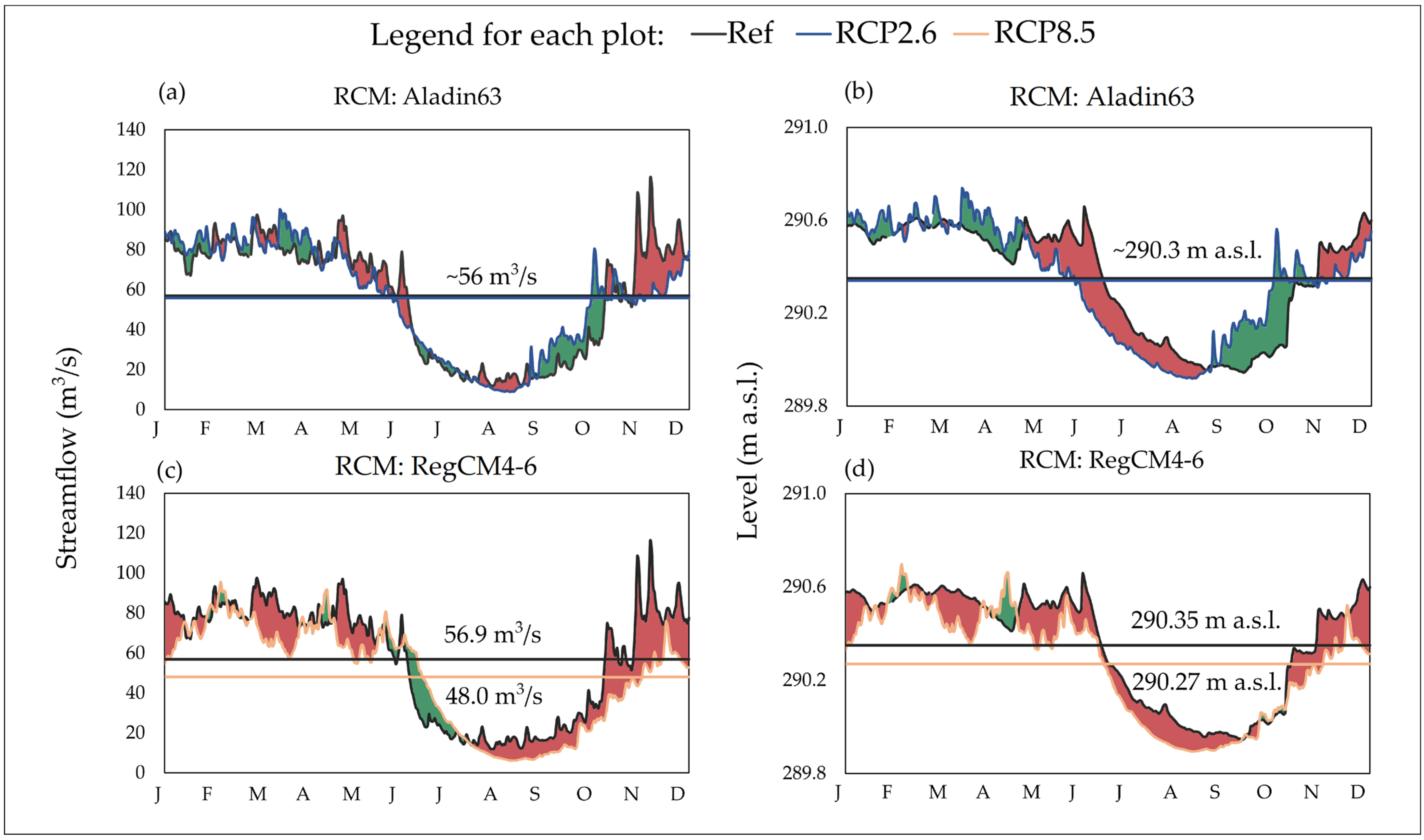
3.2.3. River Flow and Groundwater Level Variations from 2030 to 2070
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Abbreviation | Significance |
|---|---|
| CF | Clermont–Ferrand weather station (Figure 1b) |
| SEDL | St-Etienne-de-Ludgares weather station (Figure 1b) |
| VB | Vieille-Brioude (Figure 1b) |
| P | Precipitation |
| Ta | Air temperature |
| PET | Potential Evapotranspiration |
| ETa | Actual Evapotranspiration |
| PEFF | Effective precipitation |
| GWR | Groundwater recharge |
| Q | River flow/discharge |
| QW | Water withdrawal |
| QLIMONS | River flow in Limons |
| QVB | River flow in Vieille-Brioude |
| QALGN | River flow for the Alagnon River |
| QNAUSS | Water releases of the Naussac Dam |
| NSE | Nash–Sutcliffe efficiency criterium |
References
- Wang, S.; McKenney, D.W.; Shang, J.; Li, J. A National-Scale Assessment of Long-Term Water Budget Closures for Canada’s Watersheds. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119, 8712–8725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thornthwaite, C.W.; Mather, J.R. Instructions and Tables for Computing Potential Evapotranspiration and the Water Balance; Drexel Institute of Technology Laboratory of Climatology: Centerton, NJ, USA, 1957; Volume 10. [Google Scholar]
- Milly, P.C.D. Climate, Soil Water Storage, and the Average Annual Water Balance. Water Resour. Res. 1994, 30, 2143–2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasenmueller, E.A.; Criss, R.E. Water Balance Estimates of Evapotranspiration Rates in Areas with Varying Land Use. In Evapotranspiration—An Overview; Alexandris, S., Ed.; InTech: London, UK, 2013; ISBN 978-953-51-1115-3. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, C.-Y.; Singh, V.P. A Review on Monthly Water Balance Models for Water Resources Investigations. Water Resour. Manag. 1998, 12, 31–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vries, J.J.; Simmers, I. Groundwater Recharge: An Overview of Processes and Challenges. Hydrogeol. J. 2002, 10, 5–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubois, E.; Larocque, M.; Gagné, S.; Meyzonnat, G. Simulation of Long-Term Spatiotemporal Variations in Regional-Scale Groundwater Recharge: Contributions of a Water Budget Approach in Cold and Humid Climates. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2021, 25, 6567–6589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pointet, T. The United Nations World Water Development Report 2022 on Groundwater, a Synthesis. LHB 2022, 108, 2090867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations. The United Nations World Water Development Report 2022: Groundwater: Making the Invisible Visible; UNESCO: Paris, France, 2022; p. 246. [Google Scholar]
- Foster, S.S.D.; Chilton, P.J. Groundwater: The Processes and Global Significance of Aquifer Degradation. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B 2003, 358, 1957–1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maréchal, J.-C.; Rouillard, J. Groundwater in France: Resources, Use and Management Issues. In Sustainable Groundwater Management; Rinaudo, J.-D., Holley, C., Barnett, S., Montginoul, M., Eds.; Global Issues in Water Policy; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; Volume 24, pp. 17–45. ISBN 978-3-030-32765-1. [Google Scholar]
- Yasarer, L.M.W.; Taylor, J.M.; Rigby, J.R.; Locke, M.A. Trends in Land Use, Irrigation, and Streamflow Alteration in the Mississippi River Alluvial Plain. Front. Environ. Sci. 2020, 8, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dafny, E.; Silburn, D.M. The Hydrogeology of the Condamine River Alluvial Aquifer, Australia: A Critical Assessment. Hydrogeol. J. 2014, 22, 705–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rêgo, J.C.; Albuquerque, J.P.; Filho, J.D.P.; Tsuyuguchi, B.B.; Souza, T.J.; Galvao, C.O. Sustainable and Resilient Exploitation of Small Alluvial Aquifers in the Brazilian Semi-Arid Region. In Groundwater for Sustainable Livelihoods and Equitable Growth; CRC Press: London, UK, 2022; pp. 101–121. ISBN 978-1-00-302410-1. [Google Scholar]
- Ferrara, V.; Pappalardo, G. Intensive Exploitation Effects on Alluvial Aquifer of the Catania Plain, Eastern Sicily, Italy. Geofis. Int. 2004, 43, 671–681. [Google Scholar]
- Henao Casas, J.D.; Fernández Escalante, E.; Ayuga, F. Alleviating Drought and Water Scarcity in the Mediterranean Region through Managed Aquifer Recharge. Hydrogeol. J. 2022, 30, 1685–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, M.; Zavattero, E.; Ma, Q.; Delestre, O.; Gourbesville, P.; Fouché, O. 3D Hydraulic Modeling of a Complex Alluvial Aquifer for Groundwater Resource Management. Procedia Eng. 2016, 154, 340–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotterman, K.A.; Kendall, A.D.; Basso, B.; Hyndman, D.W. Groundwater Depletion and Climate Change: Future Prospects of Crop Production in the Central High Plains Aquifer. Clim. Change 2018, 146, 187–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, A.; Rai, S.C.; Rai, S.P. Impact of Anthropogenic Activities on the Alluvial Aquifers of North-East Punjab, India. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2020, 192, 527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, G.; Rojas, R.; Gonzalez, D. Trends in Groundwater Levels in Alluvial Aquifers of the Murray–Darling Basin and Their Attributions. Water 2022, 14, 1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, Y.; Villholth, K.G.; Jensen, K.H.; Stisen, S.; Lei, Y. Integrated Hydrological Modeling of the North China Plain: Options for Sustainable Groundwater Use in the Alluvial Plain of Mt. Taihang. J. Hydrol. 2012, 464–465, 79–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godwin, I.A.; Reba, M.L.; Leslie, D.L.; Adams, R.F.; Rigby, J.R. Feasibility of Farm-Scale Infiltration Galleries for Managed Aquifer Recharge in an Agricultural Alluvial Aquifer of Northeast Arkansas. Agric. Water Manag. 2022, 264, 107531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrone, K.C.; Hughes, J.D.; Van Niel, T.G.; Silberstein, R.P. Streamflow Decline in Southwestern Australia, 1950–2008: Streamflow Decline. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2010, 37, L11401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, R.; Wang, T.; Yang, D.; Yang, Y. Streamflow Decline Threatens Water Security in the Upper Yangtze River. J. Hydrol. 2022, 606, 127448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luce, C.H.; Holden, Z.A. Declining Annual Streamflow Distributions in the Pacific Northwest United States, 1948–2006. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2009, 36, L16401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Sangode, S.J.; Kandekar, A.M. Recent Decline in Streamflow and Sediment Discharge in the Godavari Basin, India (1965–2015). Catena 2021, 206, 105537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mair, A.; Fares, A. Influence of Groundwater Pumping and Rainfall Spatio-Temporal Variation on Streamflow. J. Hydrol. 2010, 393, 287–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, B.; Kam, J.; Elliott, E.; Tootle, G.; Therrell, M.; Lakshmi, V. The Recent Decline of Apalachicola–Chattahoochee–Flint (ACF) River Basin Streamflow. Hydrology 2022, 9, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, P.; Mishra, A. Separating the Impacts of Climate Change and Human Activities on Streamflow: A Review of Methodologies and Critical Assumptions. J. Hydrol. 2017, 548, 278–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabus, P. River Flow Prediction through Rainfall–Runoff Modelling with a Probability-Distributed Model (PDM) in Flanders, Belgium. Agric. Water Manag. 2008, 95, 859–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thierion, C.; Longuevergne, L.; Habets, F.; Ledoux, E.; Ackerer, P.; Majdalani, S.; Leblois, E.; Lecluse, S.; Martin, E.; Queguiner, S.; et al. Assessing the Water Balance of the Upper Rhine Graben Hydrosystem. J. Hydrol. 2012, 424–425, 68–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pumo, D.; Arnone, E.; Francipane, A.; Caracciolo, D.; Noto, L.V. Potential Implications of Climate Change and Urbanization on Watershed Hydrology. J. Hydrol. 2017, 554, 80–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; McIntyre, N.; Wheater, H.; Young, A. Selection of Conceptual Models for Regionalisation of the Rainfall-Runoff Relationship. J. Hydrol. 2005, 312, 125–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khakbaz, B.; Imam, B.; Hsu, K.; Sorooshian, S. From Lumped to Distributed via Semi-Distributed: Calibration Strategies for Semi-Distributed Hydrologic Models. J. Hydrol. 2012, 418–419, 61–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Refsgaard, J.C.; Knudsen, J. Operational Validation and Intercomparison of Different Types of Hydrological Models. Water Resour. Res. 1996, 32, 2189–2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMichael, C.E.; Hope, A.S.; Loaiciga, H.A. Distributed Hydrological Modelling in California Semi-Arid Shrublands: MIKE SHE Model Calibration and Uncertainty Estimation. J. Hydrol. 2006, 317, 307–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goderniaux, P.; Brouyère, S.; Fowler, H.J.; Blenkinsop, S.; Therrien, R.; Orban, P.; Dassargues, A. Large Scale Surface–Subsurface Hydrological Model to Assess Climate Change Impacts on Groundwater Reserves. J. Hydrol. 2009, 373, 122–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunner, P.; Simmons, C.T. HydroGeoSphere: A Fully Integrated, Physically Based Hydrological Model. Ground Water 2012, 50, 170–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santhi, C.; Arnold, J.G.; Williams, J.R.; Dugas, W.A.; Srinivasan, R.; Hauck, L.M. Validation of the swat model on a large rwer basin with point and nonpoint sources. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2001, 37, 1169–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guug, S.S.; Abdul-Ganiyu, S.; Kasei, R.A. Application of SWAT Hydrological Model for Assessing Water Availability at the Sherigu Catchment of Ghana and Southern Burkina Faso. HydroResearch 2020, 3, 124–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Q.; Sorooshian, S.; Gupta, V. Effective and Efficient Global Optimization for Conceptual Rainfall-Runoff Models. Water Resour. Res. 1992, 28, 1015–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastola, S.; Ishidaira, H.; Takeuchi, K. Regionalisation of Hydrological Model Parameters under Parameter Uncertainty: A Case Study Involving TOPMODEL and Basins across the Globe. J. Hydrol. 2008, 357, 188–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Naliaka, A.; Zhu, Z.; Ogden, F.L.; McMillan, H.K. Experimental Coupling of TOPMODEL with the National Water Model: Effects of Coupling Interface Complexity on Model Performance. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2022, 58, 50–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merz, R.; Parajka, J.; Blöschl, G. Scale Effects in Conceptual Hydrological Modeling: Scale effects in conceptual hydrological modeling. Water Resour. Res. 2009, 45, W09405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seibert, J.; Bergström, S. A Retrospective on Hydrological Catchment Modelling Based on Half a Century with the HBV Model. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2022, 26, 1371–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrin, C.; Michel, C.; Andréassian, V. Improvement of a Parsimonious Model for Streamflow Simulation. J. Hydrol. 2003, 279, 275–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sezen, C.; Bezak, N.; Bai, Y.; Šraj, M. Hydrological Modelling of Karst Catchment Using Lumped Conceptual and Data Mining Models. J. Hydrol. 2019, 576, 98–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiery, D. Forecast of Changes in Piezometric Levels by a Lumped Hydrological Model. J. Hydrol. 1988, 97, 129–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiéry, D. Logiciel Gardenia. version v8.2. Guide d’utilisation; BRGM: Orléans, France, 2014; p. 140. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammed, N.; Celle-Jeanton, H.; Huneau, F.; Le Coustumer, P.; Lavastre, V.; Bertrand, G.; Charrier, G.; Clauzet, M.L. Isotopic and Geochemical Identification of Main Groundwater Supply Sources to an Alluvial Aquifer, the Allier River Valley (France). J. Hydrol. 2014, 508, 181–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Arcy, D.; Livet, M. Massif Central. In Aquifères et Eaux Souterraines en France; BRGM Editions: Orléans, France, 2006; Volume 2, p. 944. ISBN 2-7159-0980-2. [Google Scholar]
- Korobova, E.M.; Veldkamp, A.; Ketner, P.; Kroonenberg, S.B. Element Partitioning in Sediment, Soil and Vegetation in an Alluvial Terrace Chronosequence, Limagne Rift Valley, France: A Landscape Geochemical Study. Catena 1997, 31, 91–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastre, J.-F. Les nappes alluviales de l’Allier en Limagne (Massif Central, France): Stratigraphie et corrélations avec le volcanisme régional. Quaternaire 2005, 16, 153–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiéry, D.; Diluca, C.; Diagana, B. Modelling the Aquifer Recovery after a Long Duration Drought in Burkina Faso. In Extreme Hydrological Events: Precipitation, Floods and Droughts-Yokohama (Japon); IAHS Press: Yokohama, Japan, 1993; pp. 43–50. [Google Scholar]
- Pointet, T.; Amraoui, N.; Golaz, C.; Mardhel, V.; Negrel, P.; Pennequin, D.; Pinault, J.-L. La contribution des eaux souterraines aux crues exceptionnelles de la Somme en 2001 Observations, hypothèses, modélisation. La Houille Blanche 2003, 89, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habets, F.; Boé, J.; Déqué, M.; Ducharne, A.; Gascoin, S.; Hachour, A.; Martin, E.; Pagé, C.; Sauquet, E.; Terray, L.; et al. Impact of Climate Change on the Hydrogeology of Two Basins in Northern France. Clim. Change 2013, 121, 771–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeannin, P.-Y.; Artigue, G.; Butscher, C.; Chang, Y.; Charlier, J.-B.; Duran, L.; Gill, L.; Hartmann, A.; Johannet, A.; Jourde, H.; et al. Karst Modelling Challenge 1: Results of Hydrological Modelling. J. Hydrol. 2021, 600, 126508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ly, S.; Charles, C.; Degré, A. Different Methods for Spatial Interpolation of Rainfall Data for Operational Hydrology and Hydrological Modeling at Watershed Scale. A Review. Biotechnol. Agron. Soc. Environ. 2013, 17, 392–406. [Google Scholar]
- Buytaert, W.; Celleri, R.; Willems, P.; Bièvre, B.D.; Wyseure, G. Spatial and Temporal Rainfall Variability in Mountainous Areas: A Case Study from the South Ecuadorian Andes. J. Hydrol. 2006, 329, 413–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruelland, D.; Ardoin-Bardin, S.; Billen, G.; Servat, E. Sensitivity of a Lumped and Semi-Distributed Hydrological Model to Several Methods of Rainfall Interpolation on a Large Basin in West Africa. J. Hydrol. 2008, 361, 96–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oudin, L.; Hervieu, F.; Michel, C.; Perrin, C.; Andréassian, V.; Anctil, F.; Loumagne, C. Which Potential Evapotranspiration Input for a Lumped Rainfall–Runoff Model? J. Hydrol. 2005, 303, 290–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nash, J.E.; Sutcliffe, J.V. River Flow Forecasting through Conceptual Models Part I—A Discussion of Principles. J. Hydrol. 1970, 10, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, M.P.; Woessner, W.W.; Hunt, R.J. Applied Groundwater Modeling: Simulation of Flow and Advective Transport, 2nd ed.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2015; ISBN 978-0-12-058103-0. [Google Scholar]
- Valérian, F.; Comby, G.; Kappelmann, A.; Gimon, M.; Michaux, M. Adaptation Au Changement Climatique. In Annales des Mines—Responsabilité et Environnement; Les Echos Le Parisien Médias: Paris, France, 2022; p. 116. [Google Scholar]
- Soubeyroux, J.-M.; Bernus, S.; Corre, L.; Drouin, A.; Dubuisson, B.; Etchevers, P.; Gouget, V.; Josse, P.; Kerdoncuff, M.; Samacoits, R.; et al. Les Nouvelles Projections Climatiques de Réference DRIAS 2020 Pour la Métropole; Météo-France: Paris, France, 2020; p. 98. [Google Scholar]
- Brulebois, E.; Castel, T.; Richard, Y.; Chateau-Smith, C.; Amiotte-Suchet, P. Hydrological Response to an Abrupt Shift in Surface Air Temperature over France in 1987/88. J. Hydrol. 2015, 531, 892–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renard, B.; Lang, M.; Bois, P.; Dupeyrat, A.; Mestre, O.; Niel, H.; Sauquet, E.; Prudhomme, C.; Parey, S.; Paquet, E.; et al. Regional Methods for Trend Detection: Assessing Field Significance and Regional Consistency: Regional methods for trend detection. Water Resour. Res. 2008, 44, W08419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tena, A.; Ville, F.; Reñe, A.; Yarnell, S.M.; Batalla, R.J.; Vericat, D. Hydrological Characterization of Hydropeaks in Mountain Rivers (Examples from Southern Pyrenees). River Res. Appl. 2022, rra.4058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Healy, R.W.; Winter, T.C.; LaBaugh, J.W.; Franke, O.L. Water Budgets: Foundations for Effective Water-Resources and Environmental Management; USGA: Reston, VA, USA, 2007; p. 90. [Google Scholar]
- Brutsaert, W. Catchment-Scale Evaporation and the Atmospheric Boundary Layer. Water Resour. Res. 1986, 22, 39S–45S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oki, T.; Kanae, S. Global Hydrological Cycles and World Water Resources. Science 2006, 313, 1068–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daum, J.R.; Desprats, J.F.; Durand, F. Précipitations Efficaces Moyennes Annuelles en France (1965–1994); BRGM: Orléans, France, 1996; p. 17. [Google Scholar]
- Tabarmayeh, M.; Zarei, M.; Batelaan, O. A New Approach to Quantification of Groundwater Resource Stress. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2022, 42, 101161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Ning, L.; Dai, D.; Chen, L.; Wang, Y.; Ma, Z.; Yang, Z.-L.; Zhan, C. Water Budget Variation, Groundwater Depletion, and Water Resource Vulnerability in the Haihe River Basin during the New Millennium. Phys. Chem. Earth Parts A/B/C 2022, 126, 103141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlović, I.; Marković, T.; Vujnović, T.; Larva, O. Development of a Hydrogeological Conceptual Model of the Varaždin Alluvial Aquifer. Hydrology 2021, 8, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, A.C.; Raiber, M.; Cox, M.E.; Cendón, D.I. Comparison of Groundwater Recharge Estimation Techniques in an Alluvial Aquifer System with an Intermittent/Ephemeral Stream (Queensland, Australia). Hydrogeol. J. 2017, 25, 1759–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-ahmadi, M.E.; El-Fiky, A.A. Hydrogeochemical Evaluation of Shallow Alluvial Aquifer of Wadi Marwani, Western Saudi Arabia. J. King Saud Univ.-Sci. 2009, 21, 179–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coelho, V.H.R.; Montenegro, S.; Almeida, C.N.; Silva, B.B.; Oliveira, L.M.; Gusmão, A.C.V.; Freitas, E.S.; Montenegro, A.A.A. Alluvial Groundwater Recharge Estimation in Semi-Arid Environment Using Remotely Sensed Data. J. Hydrol. 2017, 548, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Zeng, S.; Xia, J.; Wang, Y.; Huang, R.; Chen, M. Effects of the Three Gorges Dam on the Downstream Streamflow Based on a Large-Scale Hydrological and Hydrodynamics Coupled Model. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2022, 40, 101039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.; Kumar, H.; Ruhi, A.; Sankarasubramanian, A.; Devineni, N. Quantifying Dam-Induced Fluctuations in Streamflow Frequencies Across the Colorado River Basin. Water Resour. Res. 2021, 57, e2021WR029753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assani, A.A.; Gravel, É.; Buffin-Bélanger, T.; Roy, A.G. Impacts Des Barrages Sur Les Débits Annuels Minimums En Fonction Des Régimes Hydrologiques Artificialisés Au Québec (Canada). Rev. Des Sci. De L’eau 2005, 18, 103–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constantz, J.; Essaid, H. Influence of Groundwater Pumping on Streamflow Restoration Following Upstream Dam Removal. Hydrol. Processes 2007, 21, 2823–2834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatti, A.Z.; Farooque, A.A.; Krouglicof, N.; Li, Q.; Peters, W.; Abbas, F.; Acharya, B. An Overview of Climate Change Induced Hydrological Variations in Canada for Irrigation Strategies. Sustainability 2021, 13, 4833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achugbu, I.C.; Olufayo, A.A.; Balogun, I.A.; Dudhia, J.; McAllister, M.; Adefisan, E.A.; Naabil, E. Potential Effects of Land Use Land Cover Change on Streamflow over the Sokoto Rima River Basin. Heliyon 2022, 8, e09779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicente-Serrano, S.M.; Peña-Gallardo, M.; Hannaford, J.; Murphy, C.; Lorenzo-Lacruz, J.; Dominguez-Castro, F.; López-Moreno, J.I.; Beguería, S.; Noguera, I.; Harrigan, S.; et al. Climate, Irrigation, and Land Cover Change Explain Streamflow Trends in Countries Bordering the Northeast Atlantic. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2019, 46, 10821–10833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzo-Lacruz, J.; Morán-Tejeda, E.; Vicente-Serrano, S.M.; Hannaford, J.; García, C.; Peña-Angulo, D.; Murphy, C. Streamflow Frequency Changes across Western Europe and Interactions with North Atlantic Atmospheric Circulation Patterns. Glob. Planet. Change 2022, 212, 103797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mas-Pla, J.; Menció, A.; Marsiñach, A. Basement Groundwater as a Complementary Resource for Overexploited Stream-Connected Alluvial Aquifers. Water Resour. Manag. 2013, 27, 293–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, C.P.; Ahmed, S.; Gurunadha Rao, V.V.S. Conjunctive Utilization of Surface Water and Groundwater to Arrest the Water-Level Decline in an Alluvial Aquifer. J. Hydrol. 1985, 76, 351–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambast, S.K.; Tyagi, N.K.; Raul, S.K. Management of Declining Groundwater in the Trans Indo-Gangetic Plain (India): Some Options. Agric. Water Manag. 2006, 82, 279–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reba, M.L.; Massey, J.H.; Adviento-Borbe, M.A.; Leslie, D.; Yaeger, M.A.; Anders, M.; Farris, J. Aquifer Depletion in the Lower Mississippi River Basin: Challenges and Solutions. J. Contemp. Water Res. Educ. 2017, 162, 128–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tribouillois, H.; Constantin, J.; Casal, L.; Villerd, J.; Therond, O. Introducing and Expanding Cover Crops at the Watershed Scale: Impact on Water Flows. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2022, 337, 108050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, E.; Gascoin, S.; Grusson, Y.; Murgue, C.; Bardeau, M.; Anctil, F.; Ferrant, S.; Lardy, R.; Le Moigne, P.; Leenhardt, D.; et al. On the Use of Hydrological Models and Satellite Data to Study the Water Budget of River Basins Affected by Human Activities: Examples from the Garonne Basin of France. Surv. Geophys. 2016, 37, 223–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thirel, G.; Gerlinger, K.; Perrin, C.; Drogue, G.; Renard, B.; Wagner, J.-P. Quels futurs possibles pour les débits des affluents français du Rhin (Moselle, Sarre, Ill)? La Houille Blanche 2019, 105, 140–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauveau, M.; Chazot, S.; Perrin, C.; Bourgin, P.-Y.; Sauquet, E.; Vidal, J.-P.; Rouchy, N.; Martin, E.; David, J.; Norotte, T.; et al. Quels impacts des changements climatiques sur les eaux de surface en France à l’horizon 2070 ? La Houille Blanche 2013, 99, 5–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BRGM/ARMINES. Hydrologie Souterraine—Explore 2070 Eau et Changement Climatique; BRGM: Orléans, France, 2012; p. 54. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.; Choi, J.; Choi, C.; Park, S. Impacts of Changes in Climate and Land Use/Land Cover under IPCC RCP Scenarios on Streamflow in the Hoeya River Basin, Korea. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 452–453, 181–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eisner, S.; Flörke, M.; Chamorro, A.; Daggupati, P.; Donnelly, C.; Huang, J.; Hundecha, Y.; Koch, H.; Kalugin, A.; Krylenko, I.; et al. An Ensemble Analysis of Climate Change Impacts on Streamflow Seasonality across 11 Large River Basins. Clim. Change 2017, 141, 401–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Parameters | Units | Timestep | Source | Time Period |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Precipitation (P) | mm | Daily | Météo-France | 2000–2020 |
| Air temperature (Ta) | °C | Daily | Météo-France | 2000–2020 |
| River flow rate (Q) | m3/s | Daily | Hydroportail | 2000–2020 |
| Piezometric level (H) | m asl | Daily | ADES | 2007–2020 |
| Abstraction (QW) | Mm3/y | Yearly | EPLoire | 2000–2019 |
| Dam discharge (QNAUSS) | m3/s | Daily | BNPE/AELB | 2000–2020 |
| Parameters | Units | Description |
|---|---|---|
| SRES | mm | Water capacity of the soil layer. |
| HR-I | mm | Water height that leads to an equal distribution of the fast flow (R) and of the low flow (GWR). |
| FEXCH | % | The model is allowed to export/import flow to/from reservoir Sz. |
| FD | days | Delay between the emptying of Uz and Sz until it reaches the outlet. |
| Infiltr1/2 | month | Time between a PEFF reaction and an increase in the low flow component of the groundwater reservoir. |
| Dry1/2 | month | Time upon which, when no GWR occurs, the groundwater flow is divided by two. |
| GBF | m asl | Level that would be reached after an infinite time with no GWR. |
| SCOEFF | % | Storage coefficient of the aquifer. |
| Parameter | Ref | RCM Aladin63 RCP2.6 | RCM RegCM4-6 RCP8.5 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Air temperature (°C) | 11.50 | 11.30 | 12.55 |
| Precipitation (mm/y) | 770 | 909 | 886 |
| Parameter | Unit | Initial Value | Min | Max | Calibrated Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SRES | mm | 250 | 0 | 650 | 131.5 |
| HR-I | mm | 70 | 1 | 9999 | 48.6 |
| FEXCH | % | 0 | −70 | 80 | −31.0 |
| FD | day | 0 | 0 | 10 | 2.2 |
| Infilt1/2 | month | 0.5 | 0.05 | 10 | 0.05 |
| Dry1/2 | month | 2 | 0.05 | 15 | 0.36 |
| GBF | m asl | 0 | - | - | 290.5 |
| SCOEFF | (%) | 10 | 1 | 30 | 1.6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Labbe, J.; Celle, H.; Devidal, J.-L.; Albaric, J.; Mailhot, G. Combined Impacts of Climate Change and Water Withdrawals on the Water Balance at the Watershed Scale—The Case of the Allier Alluvial Hydrosystem (France). Sustainability 2023, 15, 3275. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15043275
Labbe J, Celle H, Devidal J-L, Albaric J, Mailhot G. Combined Impacts of Climate Change and Water Withdrawals on the Water Balance at the Watershed Scale—The Case of the Allier Alluvial Hydrosystem (France). Sustainability. 2023; 15(4):3275. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15043275
Chicago/Turabian StyleLabbe, Jordan, Hélène Celle, Jean-Luc Devidal, Julie Albaric, and Gilles Mailhot. 2023. "Combined Impacts of Climate Change and Water Withdrawals on the Water Balance at the Watershed Scale—The Case of the Allier Alluvial Hydrosystem (France)" Sustainability 15, no. 4: 3275. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15043275
APA StyleLabbe, J., Celle, H., Devidal, J.-L., Albaric, J., & Mailhot, G. (2023). Combined Impacts of Climate Change and Water Withdrawals on the Water Balance at the Watershed Scale—The Case of the Allier Alluvial Hydrosystem (France). Sustainability, 15(4), 3275. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15043275









