Abstract
In the modern era, urban design and sustainable development are vital topics for megacities, as they are important for the wellbeing of its residents. One of the effective key performance indices (KPIs) measuring the city plan’s efficiency in quantity and quality factors is Quality of Life (QOL), an index that policymakers can use as a critical KPI to measure the quality of urbanscape design. In the traditional approach, the researchers conduct the questionnaire survey and then analyze the gathered data to acquire the QOL index. The conventional process is costly and time-consuming, but the result of the evaluation area is limited. Moreover, it is difficult to embed in an application or system; we proposed artificial intelligence (AI) approaches to solve the limitation of the traditional method in Bangkok as a case study. There are two steps for our proposed method. First, in the knowledge extraction step, we apply deep convolutional neural networks (DCNNs), including semantic segmentation and object detection, to extract helpful information images. Second, we use a linear regression model for inferring the QOL score. We conducted various state-of-the-art (SOTA) models and public datasets to evaluate the performance of our method. The experiment results show that our novel approach is practical and can be considered for use as an alternative QOL acquisition method. We also gain some understanding of drivers’ insights from the experiment result.
1. Introduction
Urban design has recently been an important issue in the sustainable development of megacities that often suffer from poor urban design due to rapid economic growth [1,2]. Many local dwellers [3] experience traffic congestion and economic loss [4] in terms of their productivity. In addition, heavy traffic leads to an increasing number of traffic accidents [5]. Many countries are also facing climate change [6], which is negatively affected by carbon dioxide (CO) emissions [2,7]. According to all the mentioned issues, policymakers must consider these problems in implementing sustainable development and eco-friendly and people-centric urban design. This improved design alleviates severe traffic congestion and mitigates CO emissions, enhancing the long-term benefits to our world [8].
Policymakers can consider the appropriate key performance index (KPI) to improve urbanscape design depending on residents’ needs. One of the sustainable KPIs [9] measuring the city plan’s efficiency in quantity and quality factors is quality of Life (QOL). The QOL concept [10] was developed to evaluate well-being and happiness, including individual needs and social interactions as a part of the city based on sustainable development [11,12,13]. Many studies employed the QOL framework to measure the quality of policies contributing to public transportation in the case of megacities, especially in emerging countries. Bangkok, in Thailand, also suffered poor city planning resulting in heavy traffic congestion due to car-oriented policies [1,2,14]. Hence, some researchers used Bangkok for the QOL evaluation case studies. Alonso [15] forecasted land-use public transportation policies depending on residents’ satisfaction. Hayashi et al. [6] and Banister [16] suggested that authorities deploy the QOL framework to improve public transport policies and decrease the problems in road use and public transport demand.
The traditional QOL evaluation method requires a large number of questionnaire surveys that is expensive and time-consuming [1,2,17]. However, the researcher can use the gathered data in QOL evaluation and socioeconomic analysis in a short period. As limiting budget and conducting time are challenging for researchers in the area, some studies have introduced alternative approaches in QOL evaluation using artificial intelligence (AI). Kantavat et al. [18] proposed using deep convolutional neural networks (DCNNs), including semantic segmentation and object detection, to extract mobility factors in transportation from images. Thitisiriwech et al. [19] presented a Bangkok Urbanscapse dataset, which is the first labeled streetscape dataset in Bangkok, Thailand, and also proposed efficient models for processing semantic segmentation.
In this work, we propose a QOL evaluation model that predicts the QOL score based on the interviewees’ satisfaction level for the driving scenes in Bangkok. Our methodology consists of two steps. Firstly, we apply two image processing techniques, semantic segmentation and object detection, to extract useful information from input images. Secondly, we use a linear regression model to learn the relationship between the extracted factors acquired in the first step and the QOL scores gathered from the questionnaire surveys. Our method can shorten the time and cost consumed by the traditional approach. We can also use the trained model to evaluate the QOL in the area outside the conducted questionnaire survey. Moreover, our model can be embedded into other IT systems, helping the QOL evaluation service to the users’ planning or the system that needs to perform a QOL simulation.
The original semantic segmentation model was trained using the Europe road dataset, Cambridge-driving Labeled Database (CamVid) [20], which might not be practical for the Bangkok road. Hence, we additionally train the model using the Bangkokscape dataset to customize it for use in Bangkok; then, we evaluate the models using the Mean square error (MSE) of the predicted QOL scores. The experiment results show that the enhanced model provides a lower MSE in QOL score prediction. The experiment also indicates that combining the information from both the semantic segmentation and object detection is superior to using semantic segmentation alone.
We also use factor correlation analysis to indicate the factor sensitivity for the QOL evaluation in the driving scenes. The result suggests the amenity factors of residents’ basic needs for transportation from place to place in Bangkok. We can conclude that the size of the road and sidewalk are essential factors for passengers. In contrast, the number of vehicles, i.e., cars and motorcycles, negatively affects the passengers.
This section provides an introduction of this work, while Section 2 will describe the literature review used as our framework. Our methodology will be provided in Section 3. Next, the experimental results and discussion will be included in Section 4 and Section 5, respectively. Finally, we provide the conclusion of this work in Section 6.
2. Literature Review
2.1. Semantic Segmentation
We provide the semantic segmentation architectures to classify every pixel of input images into the semantic classes belonging to the datasets. We provide the details of the Tiramisu approach in Section 2.1.1 and the detail of the DeepLab-v3+ approach is available in Section 2.1.2.
2.1.1. Tiramisu
The Tiramisu [21] architecture was built from the one hundred layers of Densely Connected Convolutional Networks (DenseNet) [22] image classification model. This architecture applied five dense blocks, including the blocks of transition down (TD) on the downsampling path (the encoder side). The dense blocks could extract the dominant feature maps from the input images using simple components. Each dense block contained Batch Normalization (BN) [23], 3 × 3 convolution, Rectified Linear Unit (ReLU), and randomized dropout [24] by 20.00%. The feature maps from the previous dense block would be concatenated to the previous layer of 3 × 3 convolution. Then, these concatenated kernels would be extracted on the block of transition down (TD), which contained 1 × 1 convolution, BN, ReLU, 20.00% of dropout, and 2 × 2 max-pooling layers. For the decoder side, the feature maps from the encoder side would recover information using the blocks of transition up (TU), which contained a 3 × 3 deconvolution layer with a stride value of 2. TU and the bilinear upsampling played a crucial role in enlarging the resolution of these kernels, which are predicted as segmentation masks. Tiramisu reached SOTA with a mean intersection over union (IoU) rating of 66.90% on the CamVid testing set.
2.1.2. DeepLab-v3+
DeepLab-v3+ [25] was built with a more straightforward encoder–decoder design, enhancing V3’s layers with Atrous separable convolution and retaining the advantages of its depth-wise separable convolution. This architecture was also developed with the novel version of the image classification model as Xception [26]. Those modifications could enhance the V3+ version to recognize contextual information at multiple scales by combining low-level and high-level features on its decoder side. On the encoder side of DeepLab-v3+, the image classification backbone initially generated low-level feature maps. Then, the outputs of the previous layers were sent to the Atrous Spatial Pyramid Pooling (ASPP) module, which included dilated convolutions [27] with various configurations (1 × 1, 3 × 3 rate 6, 3 × 3 rate 12, and 3 × 3 rate 18, respectively). This module was able to extract high-level features encoding rich information. In the last layer of the encoder, the 1 × 1 convolution filters were utilized to reduce the dimension of the high-level feature maps. These low-level features, which were produced from the image classification backbone, were fed to the decoder side of DeepLab-v3+ to retrieve the spatial information. Then, the 1 × 1 convolution layer was utilized to reduce the dimensions of the low-level features and the high-level features from the encoder side were upsampled by a factor of four. Next, these two adjusted feature maps were concatenated on the decoder side and the 3 × 3 dilated separable convolution layers recovered the finest details from these concatenated feature maps. Finally, these outputs were then upsampled by four to produce the predicted masks. DeepLab-v3+ performed better than its prior (DeepLab-V3 [28]) on the Pattern Analysis, Statistical Modelling, and Computational Learning Visual Object Challenge (PASCAL VOC) [29] 2012 testing set, with a mean IoU of 87.80% compared to 87.30% for DeepLab-V3 by 2.30%.
2.2. Object Detection
You Only Look Once version 3 (YOLO-v3) [30] used a variant of DarkNet [31] for 53 layers, which initially had 19 layers of DarkNet on the preliminary version of You Only Look Once version 2 (YOLO-v2) [32]. The YOLO-v3 had new features and 34 additional DCNN layers were added. The novel loss functions, such as binary cross-entropy and independent logistic classifiers, were configured to enhance the YOLO-v3 architecture’s ability to detect miniature objects. YOLO-v3 reached a mean Average Precision of 33.00% on the Common Objects In Context (COCO) testing set using an inference time of 51 milliseconds (ms). Moreover, we might use the readily accessible official repository of YOLO-v3 to implement the pre-trained weight of YOLO-v3 on the COCO dataset [33]. These factors might explain why YOLO-v3 is still the most often used off-the-shelf method.
3. Methodology
In this part, we will describe our process of predicting the QOL Score using extracted information from road objects. Our framework with a description is outlined in Section 3.1. We explain the details of the public dataset in Section 3.2. To conduct our framework, we provide our dataset in both input images and the QOL Scores as shown in Section 3.3. Next, we provide the experimental configurations for knowledge extraction methods and QOL prediction in Section 3.4 and the performance evaluation is outlined in Section 3.5. Finally, we provide the results extracted information from the source of datasets to predict the QOL score, as shown in Section 3.6.
3.1. Our Framework
We provide the overview of our framework as shown in Figure 1. We first apply the semantic segmentation architectures such as DeepLab-v3+ with a residual neural network for 101 layers (ResNet-101) [34], DeepLab-v3+ with Xception, and Tiramisu on our dataset. These models can classify every pixel on the input image regarding the classes of its training set. For example, a pre-trained segmentation model from the Bangkok Urbanscapes dataset produces the segmentation regions for each input image, where the semantic colors represent the definitions of vision objects, as shown in Figure 5. When we obtain the output image from the pre-trained model, we calculate the percentage of pixels for each semantic class from the predicted image. We then obtain the extracted attributes from the predicted images, where the percentage of pixels represents the proportion of the visual object that participates on the road. Next, we employ the pre-trained weight of the object detection model as YOLO-v3 to extract the number of vehicles on our dataset, where this number represents how much the vehicle appears on the road. These extracted attributes will be applied to the linear regression model as part of our QOL prediction model. Our first step results are shown in Section 3.6 and the further details of hyperparameter configurations for segmentation methods are shown in Section 3.4.1.
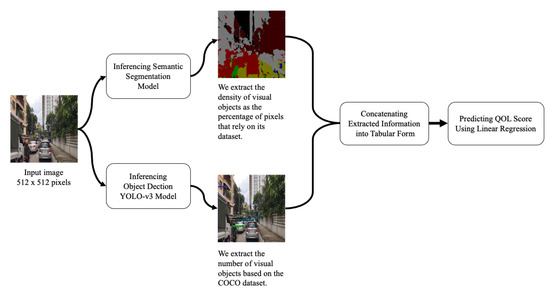
Figure 1.
Our methodology consists of two main steps: First, the knowledge extraction employs semantic segmentation and object detection methods using deep convolutional neural networks. Second, we predict the QOL score in the driving scenes using knowledge from the first step using linear regression and measure the error of predicted values in terms of Mean square error (MSE).
Second, we further study the effect of semantic labeling on the QOL scores in this paper. The percentages of pixels in both fine-tuned models using our label and the pre-trained model will be employed in the regression model to compare the performance in terms of MSE. The linear regression approach plays a vital role in learning the linear relationship between the extracted factors and the QOL score. Our experiment will be covered in three scenarios from the sources of extracted information: First, we use only the object detection model shown in Figure 7. Second, we use only the segmentation model shown in Figures 8 and 10. Third, we combine two sources of extracted information using object detection and segmentation methods shown in Figures 9 and 11. The lowest result of MSE will indicate the best combination to predict the QOL score in the driving scenes. Further details of our experimental settings of the QOL prediction model are shown in Section 3.4.2.
3.2. The Public Datasets
In this paper, we apply the segmentation methods in Section 2.1 to these public datasets [19,20] to extract information of road objects for the prediction of QOL scores. The detail of the CamVid dataset is in Section 3.2.1. We describe the Bangkok Urbanscapes dataset in Section 3.2.2.
3.2.1. The CamVid Dataset
The Cambridge-driving Labeled Database (CamVid) [20] was utilized largely for capturing diverse urban and suburban driving scenarios (including dusty and bright), especially in the United Kingdom. A Panasonic HVX200 stereo camera collected the driver’s perspective for two hours and the footage was recorded in high definition at 30 frames per second (FPS). This video has a resolution of 960 × 720 pixels, which has already calibrated every video frame using intrinsic and extrinsic techniques. All the driving sequences were reduced from 2 hours to 22 min to generate this dataset. It consisted of processed video sequences and ground truth labels. Figure 2 shows an example of input and ground truth images from the CamVid training set.

Figure 2.
The images for the CamVid training set. The input image is displayed in (a), while the ground truth is displayed in (b).
CamVid provided 701 pairs of input and annotated images at the pixel level that were annotated for visual objects as polygons. The hand-crafted labeling procedure required around from 20 to 25 min per input image and the total duration of this process required approximately 230 h. The proportions of CamVid dataset were divided into three parts: 367 for training, 101 for validation, and 233 for further testing sets. In addition, as shown in Figure 3, there are 32 distinguishable semantic classes of visual objects, such as Building, Wall, Tree, Road, Pedestrian, Car, and Sidewalk.

Figure 3.
The semantic coding colors of the CamVid dataset are encoded according to its objects on the ground truth image.
3.2.2. The Bangkok Urbanscapes Dataset
The Bangkok Urbanscapes dataset included a variety of urban landscapes along Sukhumvit Roads in Bangkok, Thailand, in 2020. The street views contained a variety of features that did not occur in the developed countries such as limited sidewalks, traffic congestion, and disorganized electric cables. The seventeen video sequences were collected by driving a Honda VEZEL equipped with a recording system, a Ladybug 5 forward-looking infrared (FLIR) twin camera system with inertial measurement unit (IMU)m and global navigation satellite system (GNSS) sensors. Consistent daylight and sunny weather were included on this dataset as environmental factors. In addition, the illumination factors were fixed during daylight and sunny conditions.
The Bangkok Urbanscapes dataset provided 701 pairs of input and annotation images with a resolution of 512 × 544 pixels. This dataset consists of 367 training, 101 validation, and 233 testing sets; the distribution of this dataset is equivalent to the CamVid dataset. The sample images of the training set of the Bangkok Urbanscapes dataset are shown in Figure 4. The corresponding semantic classes for eleven classes (Road, Building, Tree, Car, Footpath, Motorcycle, Pole, Person, Trash, Crosswalk, and Misc) are shown in Figure 5.
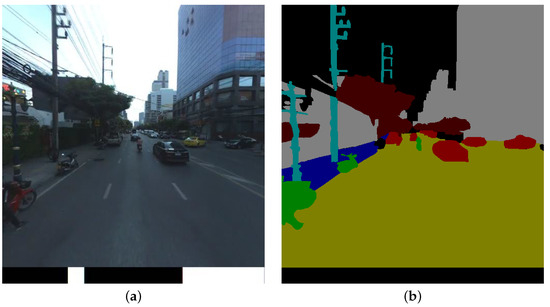
Figure 4.
Sample images for the Bangkok Urbanscapes training set. The input image is displayed in (a), while the ground truth is displayed in (b).

Figure 5.
The semantic coding colors of the Bangkok Urbanscapes dataset are encoded according to its objects on the ground truth image.
3.3. Our Dataset
We collected the Bangkok driving scenes dataset of 355 images with QOL scores [35] from one to five representing the interviewees’ satisfaction with driving in that scene. The sample images on our dataset are shown in Figure 5. Then, we select 100 images of them to craft labels for 11 segmentation classes, i.e., Road, Building, Tree, Car, Footpath, Motorcycle, Pole, Person, Trash, Crosswalk, and Miscellaneous (Misc). We used the LabelMe platform [36,37] to annotate labels on these selected images. The semantic colors with these classes are similar to the Bangkok Urbanscapes dataset, shown in Figure 6. We use these images to evaluate the semantic segmentation results in terms of mean IoU. This process took approximately 100 h to accomplish. We also conduct the peer-review process to control the quality of labels. The segmentation results are provided in Section 4.1.
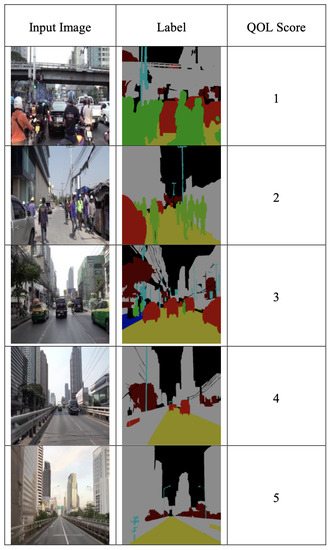
Figure 6.
The sample images of our dataset contain inputs and labels with the QOL scores.
We also include these labeled images in the Bangkok Urbanscapes dataset in the QOL-inferring step to enhance the model fine-tuning and compare the result to the pre-trained model. The inferred QOL results are provided in Section 4.2.
3.4. Experimental Configurations
We first extract the road objects from our dataset by inferring the segmentation and object detection models. The details of segmentation model settings are available in Section 3.4.1. Next, we apply this knowledge as the input data with these settings to conduct the QOL prediction in Section 3.4.2.
3.4.1. Experimental Configurations for Semantic Segmentation Models
We employ the pre-trained weights [19] from the Bangkok Urbanscapes and CamVid datasets. Three segmentation models, including Tiramisu with DenseNet-100 and the models of DeepLab-v3+ with ResNet-101 and Xception, are trained on these datasets. We used these pre-trained models to extract road data from our dataset. As indicated in Section 3.6.2, we will apply the pre-trained weights from the CamVid dataset to our dataset. In addition, we fine-tuned these models trained on the Bangkok Urbanscapes dataset on our dataset, as shown in Section 3.6.3. The hyper-parameters are the 512 × 512 random crop, Root Mean Squared propagation (RMSprop) [38] as the primary optimizer, and a learning rate of 0.0001. The seed and batch size values are fixed at 16 and 8, respectively. In addition, we have trained these models for 300 epochs and each epoch lasts approximately 2046 s. The training duration took approximately from 100 to 150 h for each dataset. The TensorFlow [39,40] framework serves as the basis for our implementation.
All the experiments were performed on computer systems with the following specification:
- Intel® XeonTM Silver 4110 Central Processing Unit (8 Cores/16 Threads, up to 2.10 GHz), 128 GB of DDR3 Memory, and two NVIDIA Tesla V100 (32 GB) graphics cards.
- Intel® CoreTM i5-4590S Central Processing Unit (with 6M Cache, up to 3.70 GHz), 32 GB of DDR4 Memory, and three SLI-connected NVIDIA GeForce GTX 1080Ti (11 GB) graphics cards.
3.4.2. Experimental Configurations for QOL Prediction Model
We employ the linear regression model to predict the QOL score in the driving scenes on our dataset as shown in Section 3.3. We reduce the observations, including our label information for 100 observations, because there is a bias in using information from our labels to fine tune the predicted segmentation masks. The new sample size is configured for the rest of the 255 observations on our dataset to predict the QOL scores. We also set this criterion to the extracted knowledge from the CamVid dataset. The sample size of the extracted attributes on the CamVid dataset also contains 255 observations. We separate these updated datasets into 60% for training, 20% for validation, 20% for the testing sets, and the random seed, which is configured at 1234. These settings are fixed for all the experiments to predict QOL scores.
We provide the source of extracted information within two sources as follows. We first select the YOLO-v3 knowledge attributes, which contain the number of road objects, including cars, persons, motorcycles, and trucks, as shown in Section 3.6.1. Second, we will select the segmentation classes with a percent more than 1% to predict the QOL scores. We obtain the percentages of segmentation classes in case of not using the labels containing Building, Car, Column_Pole, Misc_Text, Road, Sidewalk, Sky, Tree, Vegetation, Misc, and Void, as shown in Section 3.6.2. The percentages of segmentation classes using labels on our dataset include Road, Misc, Building, Tree, Car, Footpath, Motorcycle, Pole, and Person, as shown in Section 3.6.3. The experimental results will be presented to compare the effect data sources in Section 4.2.
3.5. Performance Evaluation
First, we employ the , as the mean Intersection over Union (IoU) to measure the performance of the semantic segmentation models on our dataset. It can describe how well the predicted mask overlapped with the ground truth. In addition, the mean IoU has proven to be the standard measurement on the benchmarking dataset [29]. The mean IoU is shown in Equation (1), where TP (True Positive), TN (True Negative), FP (False Positive), and FN (False Negative) are the numbers of corresponding pixels. Next, the mean square error (MSE) describes the loss function for the prediction task in this paper, as shown in Equation (2).
3.6. Knowledge Extraction Results
We employ the image recognition techniques to extract roads information on our dataset. We provide the results of the object detection model using YOLO-v3 in Section 3.6.1. Next, we provide the segmentation results using pre-trained weights from the CamVid dataset in Section 3.6.2. Finally, we provide the segmentation results using the fine-tuned models on our labels in Section 3.6.3.
3.6.1. Predicting the Number of Objects Using the YOLO-v3 Model
We employ the pre-trained weight of YOLO-v3, which is trained from the COCO dataset. This method can detect the number of road objects on our dataset. The attributes from YOLO-v3 are represented in terms of the number of road objects. These objects include cars, persons, motorcycles, and trucks. The YOLO-v3 inference result is shown in Figure 7.

Figure 7.
Inferring the pre-trained weight of YOLO-v3 on our dataset to extract number of road objects.
3.6.2. Predicting the Percentage of Pixels from the CamVid Pre-Trained Weight
We will study the effect of using annotation labels on the testing set of our dataset. First, we will use the pre-trained weights of Tiramisu and DeepLab-v3+ (ResNet-101 and Xception), which are trained on the CamVid dataset, to be the baseline methods for QOL prediction, as shown in Figure 8. Then, we infer pre-trained weights on our dataset and calculate the percentage of pixels for each corresponding class from the CamVid dataset. Finally, we use the percentage of pixels for each segmentation model and combine the number of objects from YOLO-v3 to predict the QOL scores, as shown in Figure 9.
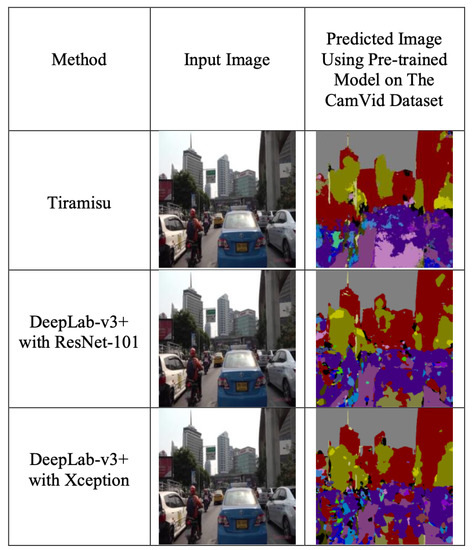

Figure 8.
Inferring the pre-trained weights from the CamVid dataset to extract the percentage of pixels on our dataset.
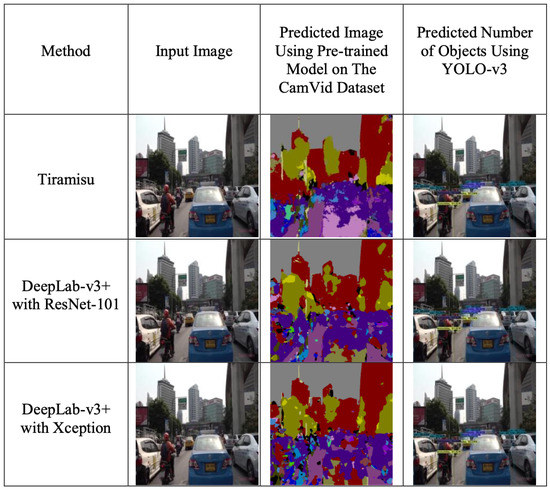
Figure 9.
Inferring the pre-trained weights from the CamVid dataset to extract the percentage of pixels on our dataset, as well as combining extracted information from object detection using YOLO-v3.
3.6.3. Predicting the Percentage of Pixels from the Training Model
We train the segmentation architectures for three models on the Bangkok Urbanscapes dataset for 300 epochs and the further details of the hyperparameter configurations are shown in Section 3.4.1. These models are trained on the Bangkok Urbanscapes dataset and then will be measured in terms of mean IoU on our testing set, as shown in Table 1. Finally, we will more precisely predict the polygon surfaces on our dataset from these architectures from the Bangkok Urbanscapes dataset. These models are trained on our labels for 100 images with 300 training epochs and, after that, the percentage of pixels is calculated from the fine-tuned segmentation architectures, as shown in Figure 10. Then, combining the number of objects with the percentages of pixels to predict the QOL scores in the driving scenes, as shown in Figure 11.

Table 1.
The semantic segmentation results that measured on our dataset in terms of mean IoU.
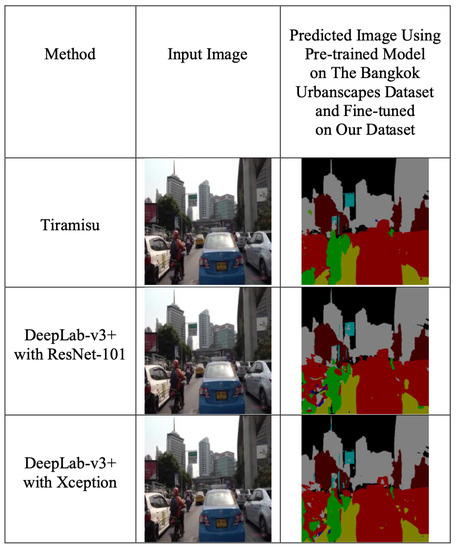

Figure 10.
Inferring the fine-tuned models on our dataset to extract the percentage of pixels on our dataset.
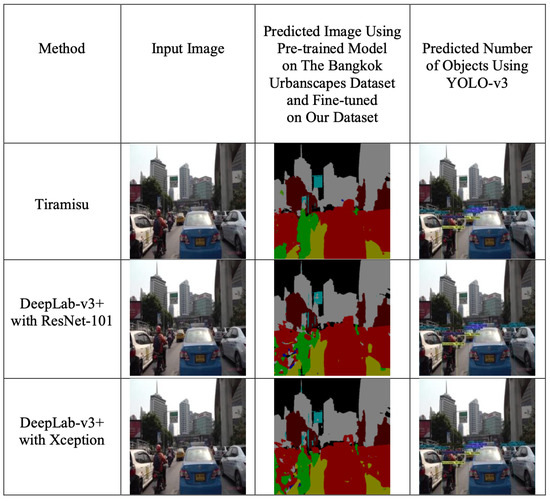
Figure 11.
Inferring the fine-tuned models on our dataset to extract the percentage of pixels on our dataset, as well as combining extracted information from object detection using YOLO-v3.
4. Experimental Results
We provide the benchmarking results for all the segmentation models on our dataset in Section 4.1. The extracted information in Section 3.6 will be utilized to predict the QOL score. Furthermore, the predicted results using linear regression will be shown in Section 4.2.
4.1. Benchmarking Results from Semantic Segmentation Models
Our experiments explore the performances of segmentation architectures on the labeled images on the Bangkok roads (including Bangkok Urbanscapes and our datasets). We make semantic segmentation inferences using the original pre-trained model trained using the CamVid dataset, including Tiramisu, DeepLab-v3+ with ResNet-101, and DeepLab-v3+ with Xception, then compare them to the results using the model fine-tuned with the Bangkok Urbanscapes dataset. The comparison of the segmentation results will be provided in Figure 12.

Figure 12.
The overall prediction results from these segmentation models regarding to the source of training data.
The benchmarking results show that the Tiramisu model, which is trained on the Bangkok Urbanscapes dataset, is the most practical method to recognize the driving scenes on our dataset. Tiramisu reached a mean IoU of 38.98% on our testing set dataset, as shown in Table 1. The effect of the semantic labelings with the different road environments shows that Tiramisu from the CamVid dataset underperformed on our testing set with a mean IoU of 15.26%. There is a huge difference between using labels and no labels with the same method, over 23.00%. We can also conclude that the semantic labeling on the target task plays a vital role in the semantic segmentation task.
4.2. QOL Prediction Results
To measure the performance of the QOL evaluation model, we deploy the knowledge-inferring data from various semantic segmentation models and also an object detection model into the linear regression model. The models’ performances inputting only semantic segmentation data or object detection data are shown in Table 2, while the models’ performance inputting both semantic segmentation data and object detection data are shown in Table 3.

Table 2.
The models’ performances inputting only semantic segmentation data or object detection data.

Table 3.
The models’ performances inputting both semantic segmentation data and object detection data.
The results show that the extracted knowledge from segmentation as the percentage of pixels on the our dataset represents the lower MSE for all methods, as shown in Table 2. We can conclude that segmentation knowledge plays a vital role in QOL prediction. The percentage of pixels can represent fine details of the road objects rather than the number of objects from the YOLO-v3 method. For example, the method using DeepLab-v3+ with ResNet-101 on our labels reaches the MSE value at almost the lowest point by 0.3958. Furthermore, the source of predicted attributes is shown in Figure 10. The significant difference in MSE between this V3+ method with ResNet-101 and YOLO-v3 is approximately four times.
We can study more sources of data that would affect the performance of the QOL prediction using the linear regression model in terms of MSE. We compare the results between Table 2 and Table 3. The results show that the combination of two data sources better performs than the single source of extracted knowledge from the computer vision techniques. The positive effect of using both percentages of pixels and the number of objects is shown in Table 3. The results of QOL prediction from DeepLab-v3+ with Xception using our labels coupled with YOLO-v3 reaches the lowest MSE for all the experiments at 0.3758, as shown in Table 3. In addition, this combination reaches a lower MSE for 0.0200 than the DeepLab-v3+ with Xception only using our labels, as shown in Table 2 and Table 3, respectively.
We can conclude that the effect of target task labeling on segmentation prediction can amplify the QOL prediction using a linear regression model. This combination represents the lowest MSE for 0.3758 in the DeepLab-v3+ with the Xception model using our labels coupled with YOLO-v3. This source of predicted attributes is shown in Figure 11. We can explain the linearity relationship for each attribute in Equation (3), which represents the coefficient of the linear regression model. This equation can also explain the QOL scores for 78.22% by inferring the adjusted R-square. The prediction results with the regression line and QOL scores on our testing set using information extracted from DeepLab-v3+ with the Xception model, which provides the lowest MSE, are shown in Figure 13.
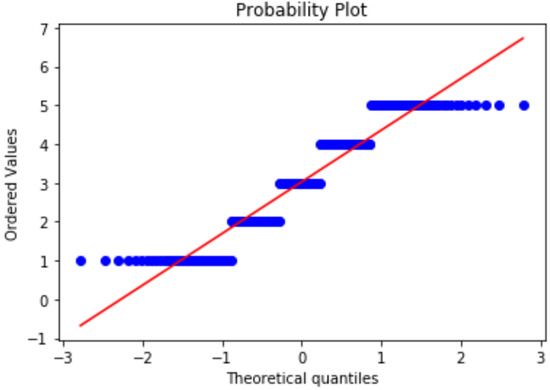
Figure 13.
The predicted regression line shows the relationship between Equation (3) and the QOL scores using information extracted from DeepLab-v3+ with the Xception model, which provides the lowest MSE.
In the regression analysis in Equation (3), we can explain the linear relationship between the extracted factors and the QOL scores using the correlation heat map shown in Figure 14. If the color of the extracted attribute is more intensive in the blue tone, the linear relationship is more positive, corresponding to the QOL scores. On the contrary, the color of the extracted attribute represents a yellow zone and the linear relationship will then be negative to the QOL scores. We consider the bottom of the horizontal axis showing the extracted factors regarding the QOL scores. The green highlighted attributes show the positively correlated segmentation attributes with a high rate to the QOL Scores as shown in Figure 14, e.g., 0.76 and 0.28, which are the percentages of roads and footpaths, respectively. However, the red highlighted attributes are negative segmentation attributes with a high rate to the QOL scores, containing 0.87 and 0.46 for the percentages of cars and motorcycles, respectively. We can conclude from the heuristic knowledge that the road and footpath areas positively affect the interviewee’s sentiment. However, traffic congestion can cause the interviewee to feel negative about the driving environment.
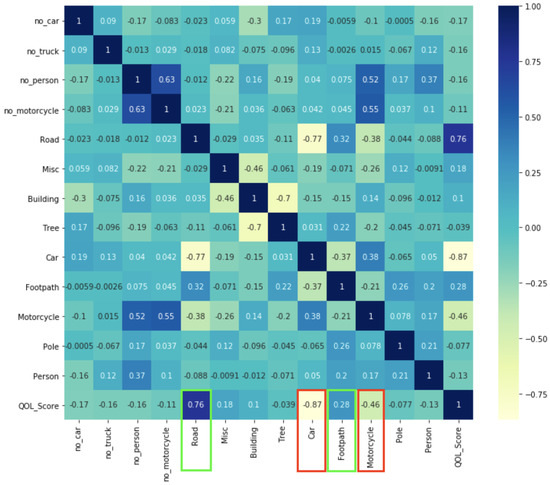
Figure 14.
The correlation heat map shows the relationship between the extracted attributes and the QOL scores. The positive attributes are Road, Misc, Building, and Footpath, while the negative attributes are no_car, no_truck, no_person, no_motorcycle, Tree, Car, Motorcycle, Pole, and Person.
We can interpret the performance of linear regression in Equation (3) using the residual analysis. The residual values are calculated using , which represent the error from the linear regression model. We then plot the histogram for all residual values to visualize how well our regression can fit our data, as shown in Figure 15. The x-axis shows the standard deviation of residual values, while the y-axis shows the frequency of residuals belonging to the interval. If the histogram plots approximate a normal curve, the error will be the normal distribution, which satisfies the assumption of the regression analysis. We can conclude that our regression in Equation (3) has the potential to apply to our use case and it does not violate the regression assumption.
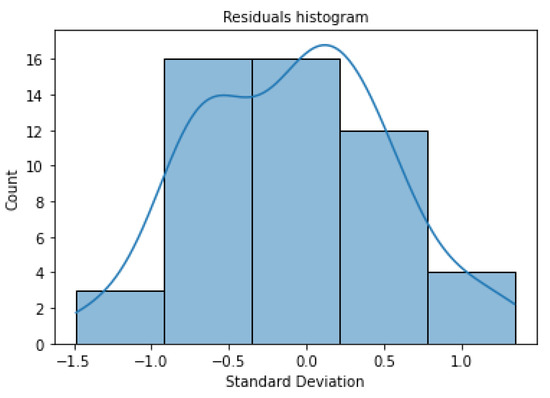
Figure 15.
The histogram of the residual plot from Equation (3) that displays the normality of the residuals calculated using , which represents the error from the linear regression model.
For inference time analysis, our framework is the end-to-end solution to predict the QOL scores from input images, as shown in Figure 1. Most running time depends on the information extraction step using semantic segmentation or object detection with DCNNs models. The models are very sophisticated with heavy computation, requiring GPUs to infer each input image. In comparison, the running time of the QOL prediction using regression is neglectable as it has a simple computation. The computer specifications are shown in Section 3.4.1. As shown in Table 4, we can explain that the inference time is equal to the segmentation time + object detection time, in which the average running time is in milliseconds (ms). The results show that the object detection method using YOLO-v3 is the fastest inference model, while the fine-tuned Tiramisu model from our dataset is the slowest model. The average inference time of YOLO-v3 is less significant than the fine-tuned Tiramisu model by about ninefold. In addition, the average inference time of the same method comparing the different datasets shows that the weight from our dataset is slower to execute in a range of from 7.13% to 10.38% in terms of ms.

Table 4.
The execution times of the segmentation and the object detection models from input images on the extracted information step in terms of the average inference time in milliseconds (ms).
5. Discussion
Urban design relying on sustainable development KPIs is the suitable approach to improve city planning. The QOL score is one of the sustainable development KPIs that can reflect the basic needs of dwellers in Bangkok. If the policymakers include this approach in their city planning to develop the urbanscapes of Bangkok city, the well-being and happiness of Bangkok residents will be increased. We propose the QOL evaluation framework using image recognition techniques and the prediction model, as shown in Figure 1, coupled with our label dataset, which can reduce the cost of a survey to collect the questionnaires compared to the traditional approach. We will discuss our findings from our experimental results and interpretations in this paper.
We employ our frameworks to predict the QOL score by extracting the information and then using the extracted attributes to indicate the QOL score by the regression. We also investigate the efficiency of the segmentation models. The results show that the segmentation model fine-tuned on the Bangkok Urbanscapes dataset outperforms the original model trained on only the CamVid dataset, which is indicated by the MSE, as shown in Table 2. The results also show that predicting the QOL score using both information from semantic segmentation and object detection models yields better accuracy than using only semantic segmentation. Equation (3) combines two sources of the extracted attributes, including the DeepLab-v3+ model fine-tuned on our labels and YOLO-v3.
Regarding the inferring time, our strategy spent less time than the Tiramisu model, approximately 2.42 times, as shown in Table 4. Moreover, our method performs at a lower MSE rate, as shown in Table 3. In conclusion, our strategy is suitable with the best prediction performance and reasonable execution time.
For the regression analysis, we obtain the insights of the regression on Equation (3) using the correlation heatmap visualization shown in Figure 14. The results indicate that people in Bangkok feel positive when they experience the wider road and footpath widths in the driving scene, which assumes that the traffic is not congested. In contrast, people in Bangkok feel negative when they experience obstacles, for example, many cars and motorcycles on the same road, representing heavy traffic congestion. In addition, we visualize the histogram of residuals of the regression model on Equation (3), as shown in Figure 15. The residuals on this plot behave nearly the normal distribution and it does not violate the regression assumption. Hence, the regression model is applicable.
6. Conclusions
Urban design is an emerging issue that aligns with the sustainable development concept. The QOL evaluation score is one of the key performance indexes used to measure city planning quality. As the traditional QOL evaluation is costly and time-consuming, we proposed AI approaches hoping to solve the limitation of the conventional method using Bangkok as a case study. Our proposed method is also beneficial in the QOL evaluation outside the survey-conducting area and can run in the application or QOL simulation systems. In the knowledge-extraction step, we apply deep convolutional neural networks (DCNNs), including semantic segmentation and object detection, to extract useful information from the driving-scene images. Then, we deploy a linear regression model to make a QOL prediction in the QOL inference step. We conducted various SOTA models and public datasets to examine the performance. We adopted the Bangkok driving scenes dataset consisting of 355 images with QOL scores from one to five, reflecting the passenger opinions of that scene. We also select 100 out of 355 images to create a craft semantic label to evaluate the models’ efficiencies in both steps.
The experiment results show that the practical strategy is deploying knowledge-extraction data from both DeepLab-v3+ with Xception fine-tuning a Bangkok labeled scene and YOLO-v3 to predict the QOL score using the linear regression model. We also analyze some passengers’ insights by interpreting data correlations, as shown in Equation (3) and Figure 14. We conclude that the Bangkokers need wider roads and walkway spaces [17], referring to positive correlation values of 0.76 for roads and 0.28 for footpaths, as it causes them to feel more delightful and secure [13] to commute from their residential place to their workplaces. In contrast, the Bangkokers feel uncomfortable when there are many vehicles on the same commuting route, referring to the negative correlations of 0.87 for cars and 0.46 for motorcycles. We can infer that heavy traffic congestion reduce drivers’ happiness.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, K.T., T.P., B.K., Y.I. and P.K.; methodology, K.T. and T.P.; software, K.T. and T.P.; validation, K.T., T.P., B.K. and P.K.; formal analysis, K.T. and T.P.; investigation, K.T., T.P., B.K., P.K. and Y.I.; resources, T.P., S.F., Y.I., Y.H. and B.K.; data curation, Y.I. and S.F.; writing—original draft preparation, K.T.; writing—review and editing, K.T., P.K. and B.K.; visualization, K.T.; supervision, K.T., T.P., B.K., P.K. and Y.I.; project administration, K.T., P.K. and Y.H.; funding acquisition, P.K., Y.I. and Y.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was mainly supported by Ratchadapiseksomphot Fund for Postdoctoral Fellowship, Chulalongkorn University. In addition, this research was funded by the Science and Technology Research Partnership for Sustainable Development (SATREPS), Japan Science and Technology Agency (JST)/Japan International Cooperation Agency (JICA) “Smart Transport Strategy for Thailand 4.0” (Chair: Yoshitsugu Hayashi, Chubu University, Japan) under Grant JPMJSA1704, and by Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS) Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (C)(20K11873) and by Chubu University Grant.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| AI | Artificial Intelligence |
| ASPP | Atrous Spatial Pyramid Pooling |
| BN | Batch Normalization |
| CamVid | Cambridge-driving Labeled Database |
| CO | Carbon dioxide |
| COCO | Common Objects In Context |
| DCNNs | Deep Convolutional Neural Networks |
| DenseNet | Densely Connected Convolutional Network |
| FLIR | Forward Looking Infrared |
| FN | False Negative |
| FP | False Positive |
| FPS | Frames Per Second |
| GNSS | Global Navigation Satellite System |
| IMU | Inertial Measurement Unit |
| IoU | Intersection over Union |
| KPI | Key Performance Index |
| KPIs | Key Performance Indices |
| Misc | Miscellaneous |
| ms | Milliseconds |
| MSE | Mean Square Error |
| PACSCAL VOC | Pattern Analysis, Statistical Modelling, and |
| Computational Learning Visual Object Challenge | |
| QOL | Quality of Life |
| ReLU | Rectified Linear Unit |
| ResNet | Residual Neural Network |
| RMSprop | Root Mean Squared propagation |
| SOTA | State-of-the-art |
| TD | Transition Down |
| TN | True Negative |
| TP | True Positive |
| TU | Transition Up |
| v | Version |
| YOLO | You Only Look Once |
References
- Nakamura, K.; Wasuntarasook, V.; Gu, F.; Vichiensan, V.; Kii, M.; Hayashi, Y. Evaluation for Low-carbon Land-use Transport Development with QOL Indexes in Asian Developing Megacities: A Case Study of Bangkok. J. East. Asia Soc. Transp. Stud. 2015, 11, 1047–1063. [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura, K.; Morita, H.; Vichiensan, V.; Togawa, T.; Hayashi, Y. Comparative analysis of QOL in station areas between cities at different development stages, Bangkok and Nagoya. Transp. Res. Procedia 2017, 25, 3188–3202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besleme, K.; Mullin, M. Community indicators and healthy communities. Natl. Civ. Rev. 1997, 86, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diener, E.; Suh, E. Measuring quality of life: Economic, social, and subjective indicators. Soc. Indic. Res. 1997, 40, 189–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kachi, N.; Kato, H.; Hayashi, Y.; BLACK, J. Making cities more compact by improving transport and amenity and reducing hazard risk. J. East. Asia Soc. Transp. Stud. 2005, 6, 3819–3834. [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi, Y.; Mai, X.; Kato, H. The role of rail transport for sustainable urban transport. In Transport Moving to Climate Intelligence; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 161–174. [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura, K.; Hayashi, Y.; Kato, H. Macroscopic design of measures to realise low-carbon land-use transport systems in Asian developing cities. Glob. Environ. Res. 2013, 17, 47–60. [Google Scholar]
- Geurs, K.; van Wee, B. Backcasting as a tool for sustainable transport policy making: The environmentally sustainable transport study in the Netherlands. Eur. J. Transp. Infrastruct. Res. 2004, 4, 47–69. [Google Scholar]
- Briassoulis, H. Sustainable development and its indicators: Through a (planner’s) glass darkly. J. Environ. Plan. Manag. 2001, 44, 409–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felce, D.; Perry, J. Quality of life: Its definition and measurement. Res. Dev. Disabil. 1995, 16, 51–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veenhoven, R. Freedom and happiness: A comparative study in forty-four nations in the early 1990s. Cult. Subj. Well-Being 2000, 257, 288. [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi, Y.; Sugiyama, I. Dual strategies for the environmental and financial goals of sustainable cities: De-suburbanization and social capitalization. Built Environ. 2003, 29, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doi, K.; Kii, M.; Nakanishi, H. An integrated evaluation method of accessibility, quality of life, and social interaction. Environ. Plan. B: Plan. Des. 2008, 35, 1098–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasuntarasook, V.; Hayashi, Y. A historic review on consequences of critical events leading revolution in Mass Rapid Transit in Bangkok. In Proceedings of the 10th International Conference of Eastern Asia Society for Transportation Studies, Taipei, Taiwan, 9–12 September 2013; pp. 9–12. [Google Scholar]
- Alonso, W. Location and Land Use; Harvard University Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1964. [Google Scholar]
- Banister, D. The sustainable mobility paradigm. Transp. Policy 2008, 15, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vichiensan, V.; Nakamura, K. Walkability perception in Asian cities: A comparative study in Bangkok and Nagoya. Sustainability 2021, 13, 6825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kantavat, P.; Kijsirikul, B.; Iwahori, Y.; Hayashi, Y.; Panboonyuen, T.; Vateekul, P.; Achariyaviriya, W. Transportation Mobility Factor Extraction Using Image Recognition Techniques. In Proceedings of the 2019 First International Conference on Smart Technology & Urban Development (STUD), Chiang Mai, Thailand, 13–14 December 2019; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Thitisiriwech, K.; Panboonyuen, T.; Kantavat, P.; Iwahori, Y.; Kijsirikul, B. The Bangkok Urbanscapes Dataset for Semantic Urban Scene Understanding Using Enhanced Encoder-Decoder with Atrous Depthwise Separable A1 Convolutional Neural Networks. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 59327–59349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brostow, G.J.; Fauqueur, J.; Cipolla, R. Semantic object classes in video: A high-definition ground truth database. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2009, 30, 88–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jegou, S.; Drozdzal, M.; Vazquez, D.; Romero, A.; Bengio, Y. The One Hundred Layers Tiramisu: Fully Convolutional DenseNets for Semantic Segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) Workshops, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, G.; Liu, Z.; Van Der Maaten, L.; Weinberger, K.Q. Densely connected convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 4700–4708. [Google Scholar]
- Ioffe, S.; Szegedy, C. Batch normalization: Accelerating deep network training by reducing internal covariate shift. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, PMLR, Hong Kong, China, 20–22 November 2015; pp. 448–456. [Google Scholar]
- Srivastava, N.; Hinton, G.; Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Salakhutdinov, R. Dropout: A simple way to prevent neural networks from overfitting. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2014, 15, 1929–1958. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.C.; Zhu, Y.; Papandreou, G.; Schroff, F.; Adam, H. Encoder-decoder with atrous separable convolution for semantic image segmentation. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 801–818. [Google Scholar]
- Chollet, F. Xception: Deep learning with depthwise separable convolutions. In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 1251–1258. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, F.; Koltun, V. Multi-scale context aggregation by dilated convolutions. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1511.07122. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.C.; Papandreou, G.; Schroff, F.; Adam, H. Rethinking atrous convolution for semantic image segmentation. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1706.05587. [Google Scholar]
- Everingham, M.; Van Gool, L.; Williams, C.K.; Winn, J.; Zisserman, A. The pascal visual object classes (voc) challenge. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2010, 88, 303–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redmon, J.; Farhadi, A. Yolov3: An incremental improvement. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1804.02767. [Google Scholar]
- Redmon, J. Darknet: Open Source Neural Networks in C. 2013–2016. Available online: http://pjreddie.com/darknet/ (accessed on 18 June 2021).
- Redmon, J.; Farhadi, A. YOLO9000: Better, faster, stronger. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 7263–7271. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, T.Y.; Maire, M.; Belongie, S.; Hays, J.; Perona, P.; Ramanan, D.; Dollár, P.; Zitnick, C.L. Microsoft coco: Common objects in context. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Zurich, Switzerland, 6–12 September 2014; pp. 740–755. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Fukui, S.; Watanabe, N.; Iwahori, Y.; Kantavat, P.; Kijsirikul, B.; Takeshita, H.; Hayashi, Y.; Okazaki, A. Deep Neural Network for Estimating Value of Quality of Life in Driving Scenes. In Proceedings of the ICPRAM, Vienna, Austria, 3–5 February 2022; pp. 616–621. [Google Scholar]
- Russell, B.C.; Torralba, A.; Murphy, K.P.; Freeman, W.T. LabelMe: A database and web-based tool for image annotation. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2008, 77, 157–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wada, K. labelme: Image Polygonal Annotation with Python. 2016. Available online: https://github.com/wkentaro/labelme (accessed on 20 March 2022).
- Tieleman, T.; Hinton, G. RMSprop Gradient Optimization. 2014. Available online: http://www.cs.toronto.edu/tijmen/csc321/slides/lecture_slides_lec6.pdf (accessed on 20 January 2022).
- Abadi, M.; Barham, P.; Chen, J.; Chen, Z.; Davis, A.; Dean, J.; Devin, M.; Ghemawat, S.; Irving, G.; Isard, M.; et al. Tensorflow: A system for large-scale machine learning. In Proceedings of the OSDI, Savannah, GA, USA, 2–4 November 2016; Volume 16, pp. 265–283. [Google Scholar]
- Abadi, M.; Agarwal, A.; Barham, P.; Brevdo, E.; Chen, Z.; Citro, C.; Corrado, G.S.; Davis, A.; Dean, J.; Devin, M.; et al. TensorFlow: Large-Scale Machine Learning on Heterogeneous Systems. 2015. Available online: tensorflow.org (accessed on 20 May 2022).
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).