Approaching Extracurricular Activities for Teaching and Learning on Sustainable Rehabilitation of Mass Housing: Reporting from the Arena of Architectural Higher Education
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. General Background
1.2. Importance of the Workshop within the Arena of Architectural Higher Education
1.3. Paper Outline and Objectives
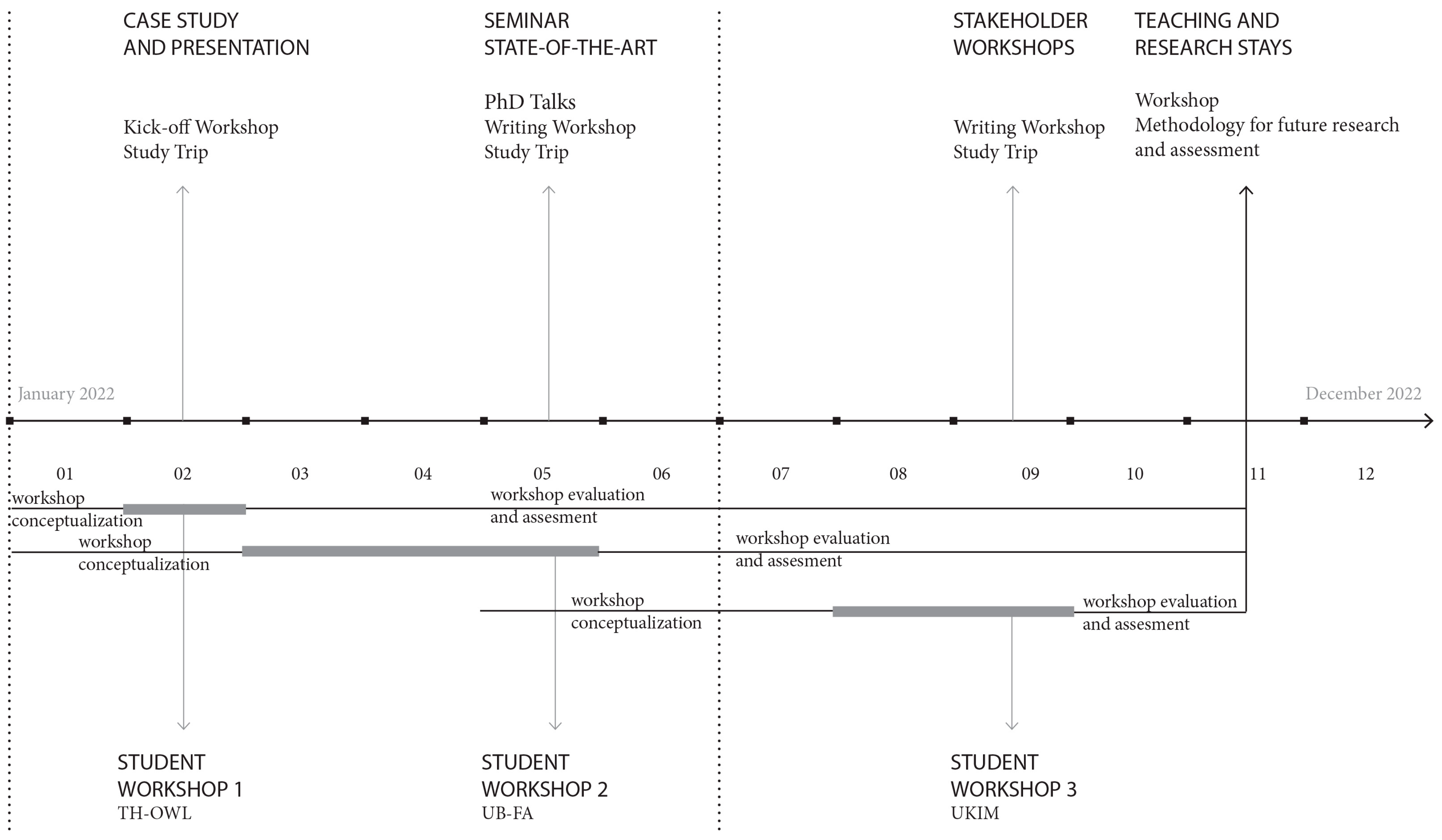
2. Research Context: RE-MHN Project-DAAD Higher Education Dialogue
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Research Conceptualisation
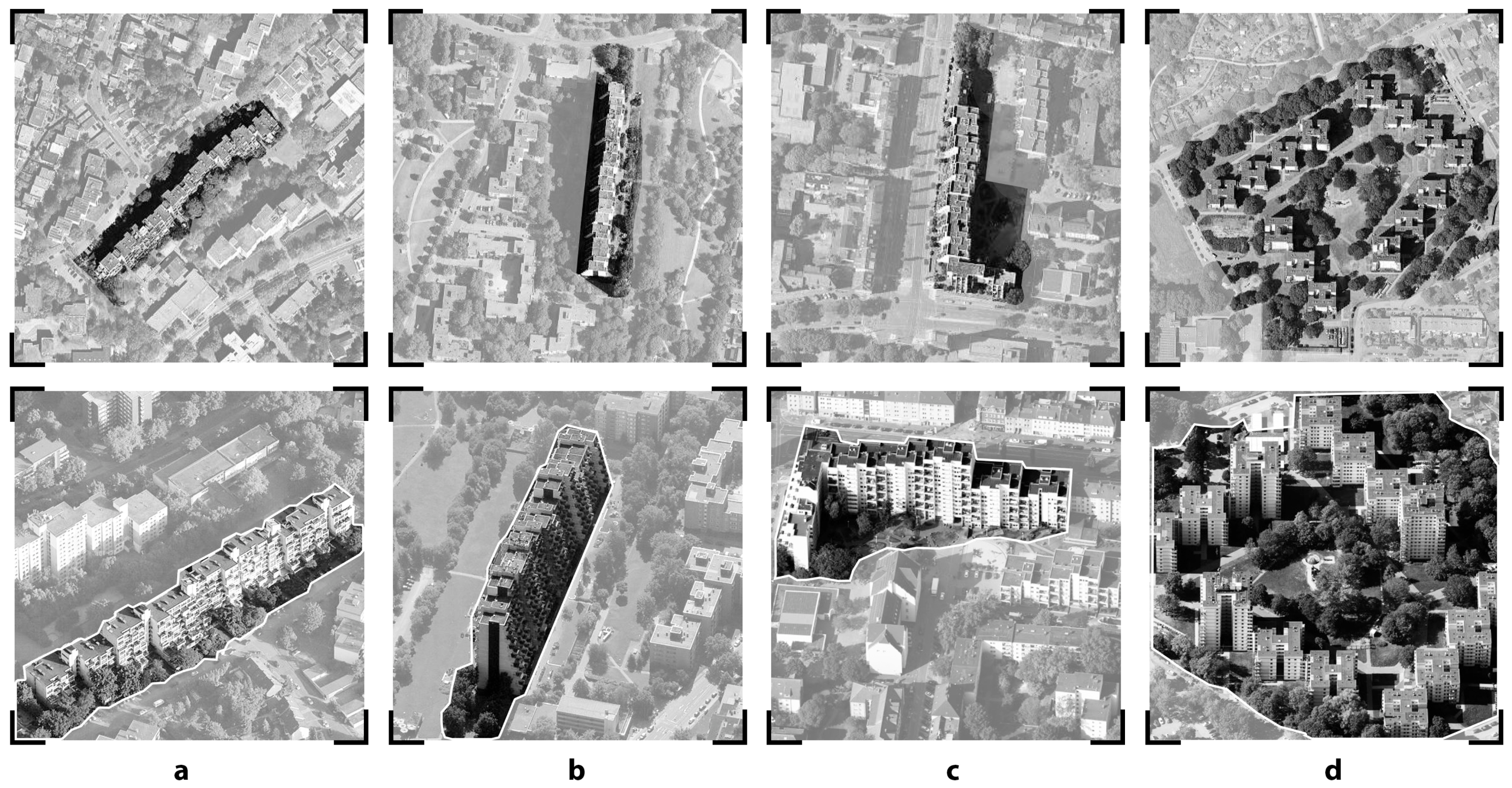
3.2. Analysis of Capabilities
3.3. General Background of Workshops
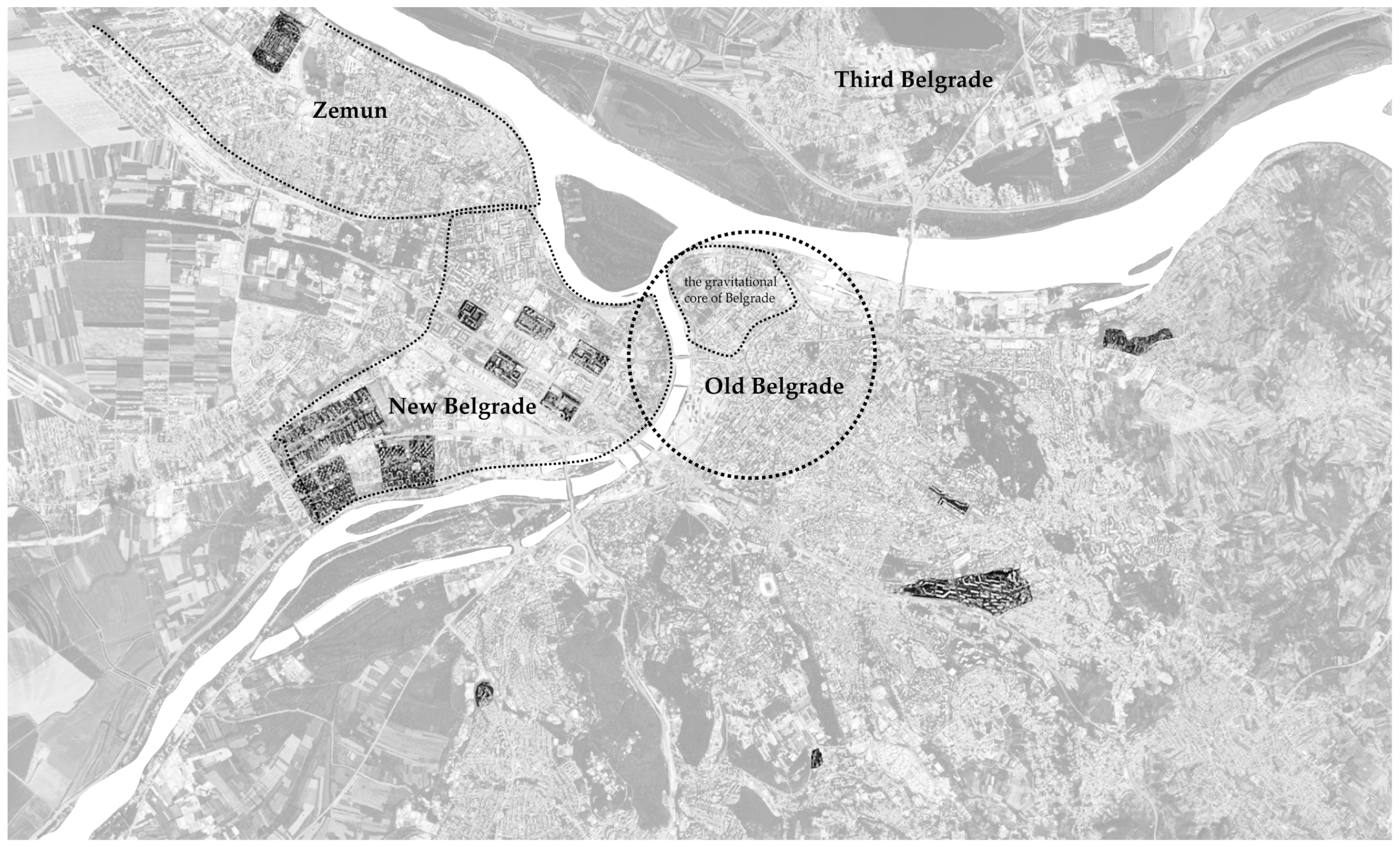
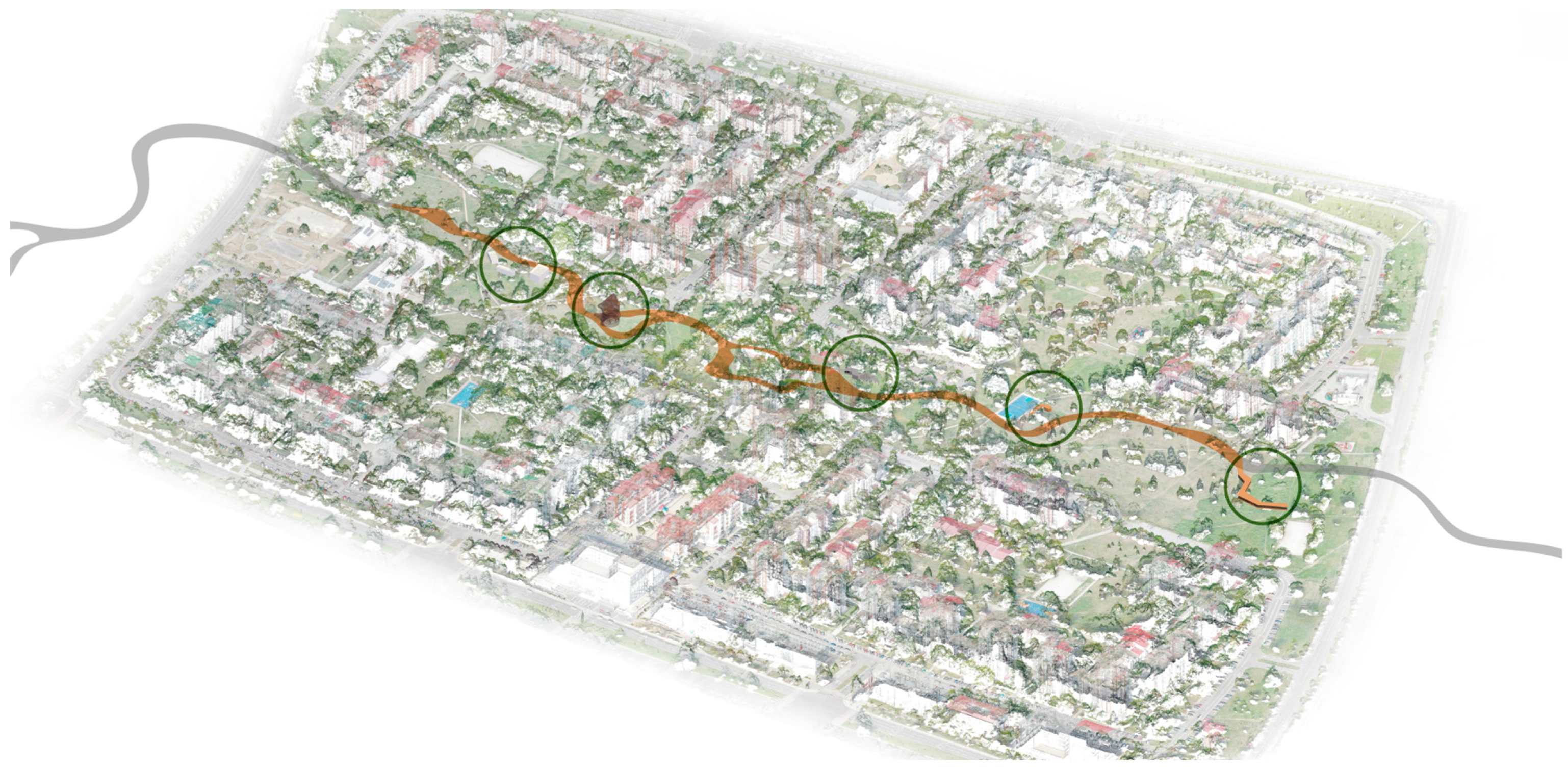
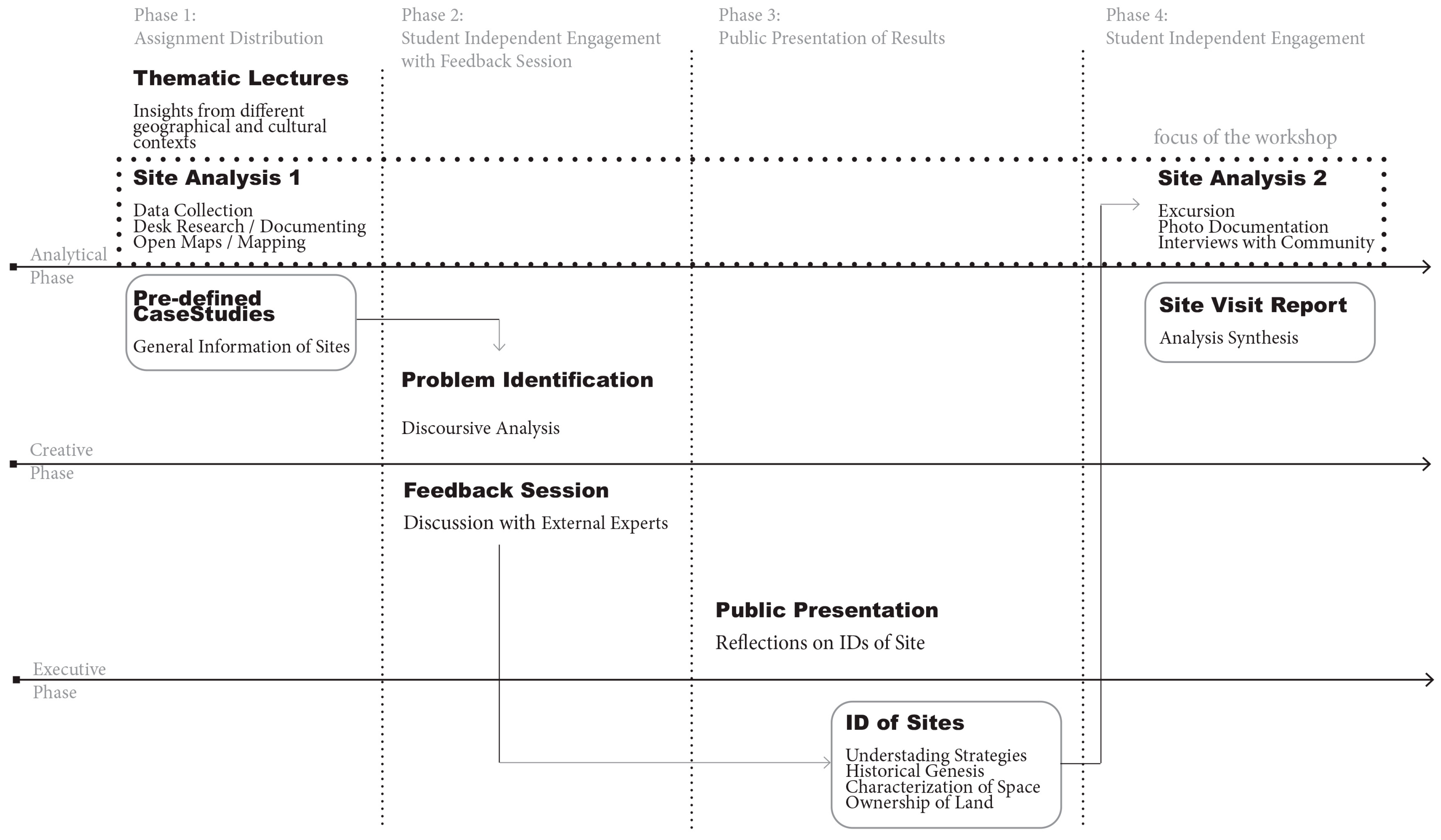
3.3.1. Workshop 1: TH OWL
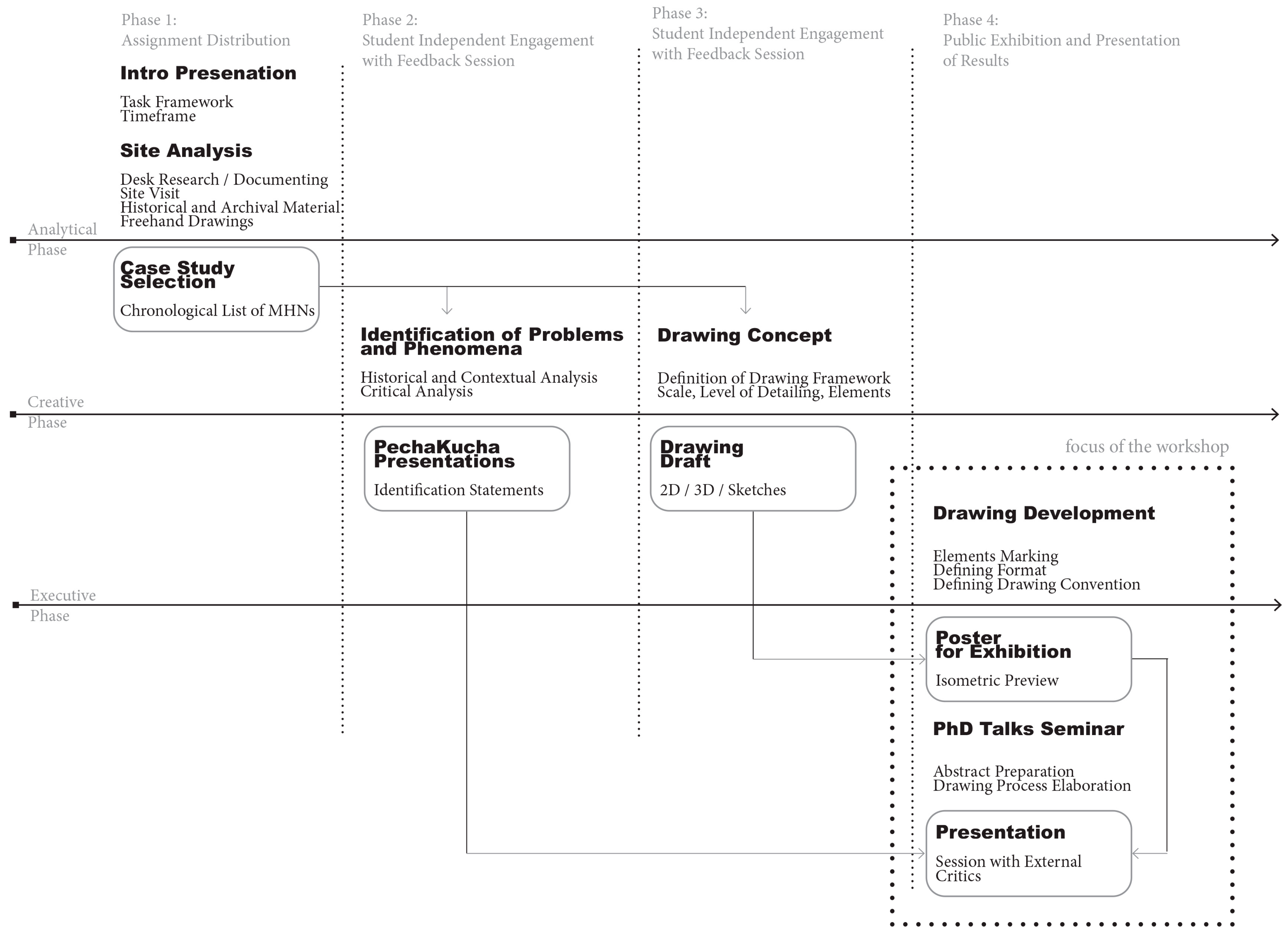
3.3.2. Workshop 2: UB-FA
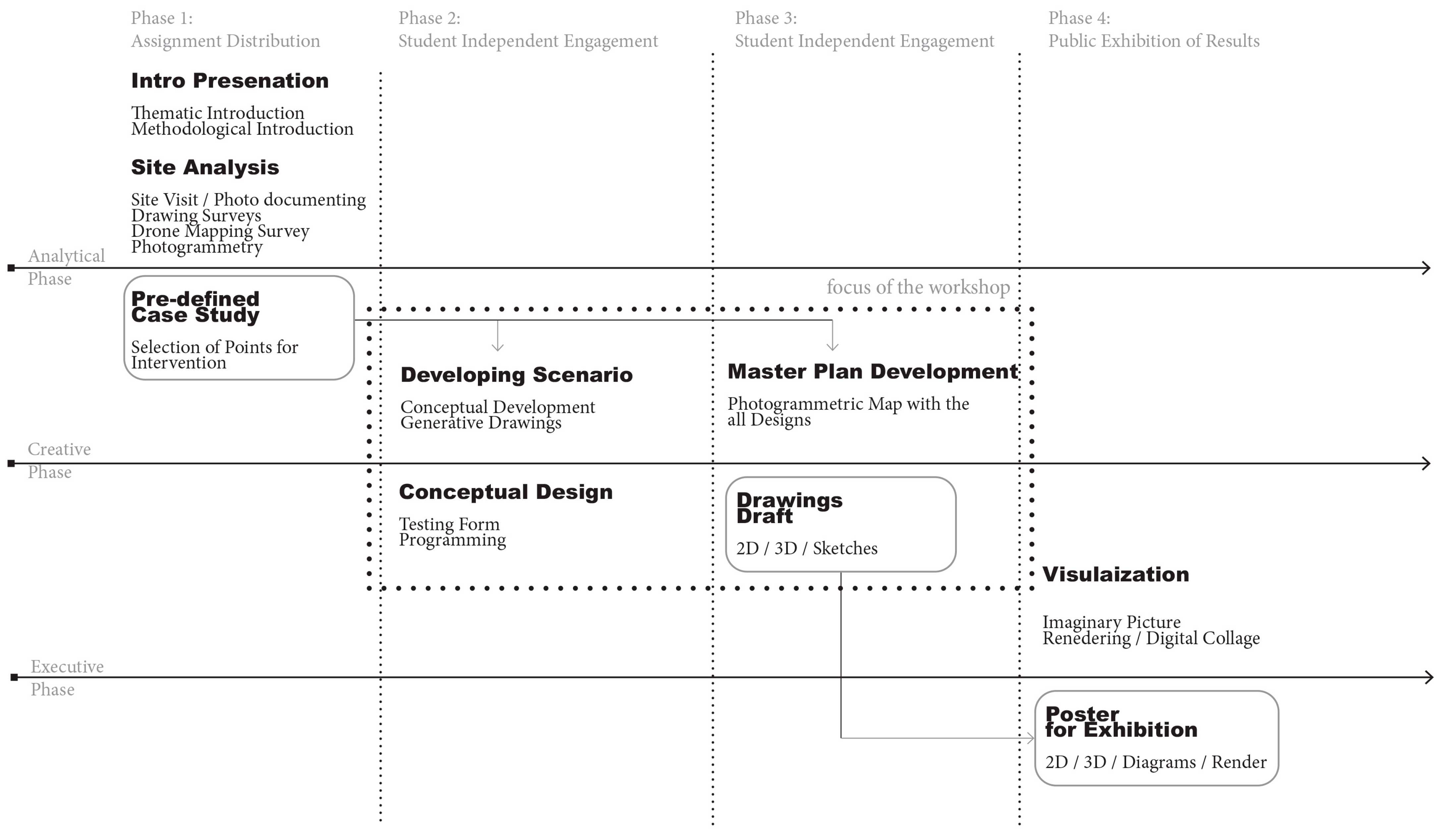
3.3.3. Workshop 3: UKIM
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Comparative Analysis of Workshops
4.2. Definition of Workshop Models
4.2.1. Workshop Model 1: Evidence Based/State-of-the-Art Directed
4.2.2. Workshop Model 2: Representation Based/Problem Directed
4.2.3. Workshop Model 3: Problem Based/Design Directed
5. Concluding Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- UN General Assembly. Transforming Our World: The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- The NEB High-Level Round Table. New European Bauhaus Concept Paper. Available online: https://new-european-bauhaus.europa.eu/system/files/2021-07/2021-06-30_New_European_Bauhaus_Concept_Paper_HLRT_FINAL.pdf (accessed on 14 December 2022).
- UIA Commission on the UN Sustainable Development Goals. UIA SDG Dhaka Declaration; International Union of Architects: Dhaka, Bangladesh, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Architects’ Council of Europe (ACE). Statement from the Architects’ Council of Europe—Designing Buildings for Circular Economy; ACE: Helsinki, Finland, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- European Ministers of Culture. Davos Declaration: Towards a HIGH-Quality ‘Baukultur‘ for Europe; Federal Department of Home Affairs, Federal Office of Culture: Davos, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Architects’ Council of Europe (ACE). Statement from the Architects’ Council of Europe—For Affordable & Quality Housing; ACE: Madrid, Spain, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- European Association for Architectural Education. Charter on Architectural Research; EAAE: Chania, Greece, 2012; Available online: https://www.eaae.be/about/statutes-and-policypapers/eaae-charter-architectural-research/ (accessed on 14 December 2022).
- Anthony, K.H. Designing for diversity: Implications for architectural education in the twenty-first century. J. Archit. Educ. 2002, 55, 257–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ‘Architects’ Council of Europe. Leeuwarden Declaration—Adaptive Re-Use of the Built Heritage: Preserving and Enhancing the Values of Our Built Heritage for Future Generations. 2018. Available online: https://www.ace-cae.eu/uploads/tx_jidocumentsview/LEEUWARDEN_STATEMENT_FINAL_EN-NEW.pdf (accessed on 9 December 2022).
- DOCOMOMO International. Manifesto on Education; DOCOMOMO: Valencia, Spain, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Mutman, D.; Yorgancioğlu, D.; Saner, M. Alternative Approaches to Architectural Design: Pedagogical Perspective of Extracurricular Activities. In Proceedings of the V. International Architectural Design Conference, Dubrovnik, Croatia, 13–14 April 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Schön, D.A. The Architectural Studio as an Exemplar of Education for Reflection-in-Action. J. Archit. Educ. 1984, 38, 2–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, D.; Hedley, P.; Molloy, M. Design learning: A reflective model. Des. Stud. 2009, 30, 13–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Casakin, H.; Kreitler, S. Correspondences and divergences between teachers and students in the evaluation of design creativity in the design studio. Environ. Plan. B Plan. Des. 2008, 35, 666–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casakin, H.; Kreitler, S. Motivation for creativity in architectural design and engineering design students: Implications for design education. Int. J. Technol. Des. Educ. 2010, 20, 477–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowaltowski, D.C.; Bianchi, G.; De Paiva, V.T. Methods that may stimulate creativity and their use in architectural design education. Int. J. Technol. Des. Educ. 2010, 20, 453–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirbaş, O.O.; Demirkan, H. Focus on architectural design process through learning styles. Des. Stud. 2003, 24, 437–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kvan, T.; Jia, Y. Students’ learning styles and their correlation with performance in architectural design studio. Des. Stud. 2005, 26, 19–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, R.; Shannon, S.J. Engaging with blended learning to improve students’ learning outcomes. Eur. J. Eng. Educ. 2013, 38, 359–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masdéu, M.; Fuses, J. Reconceptualizing the design studio in architectural education: Distance learning and blended learning as transformation factors. Archnet-IJAR Int. J. Archit. Res. 2017, 11, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldschmidt, G.; Hochman, H.; Dafni, I. The design studio “crit”: Teacher–student communication. AI Edam 2010, 24, 285–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, D.L.; Zimring, C. Supporting collaborative design groups as design communities. Des. Stud. 2000, 21, 187–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milovanović, A.; Dragutinovic, A.; Nikezić, A.; Pottgiesser, U.; Stojanovski, M.; Ivanovska Deskova, A.; Ivanovski, J.; Damjanovska, T. Rehabilitation of Mass Housing as a Contribution to Social Equality: Insights from the East-West European Academic Dialogue. Sustainability 2022, 14, 8106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNESCO-UIA Validation Council for Architectural Education. Charter UNESCO/UIA for Architectural Education; International Union of Architects: Paris, France, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Cross, N. Engineering Design Methods: Strategies for Product Design, 4th ed.; John Wiley & Sons.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Lerner, J. Urban Acupuncture; Island Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]


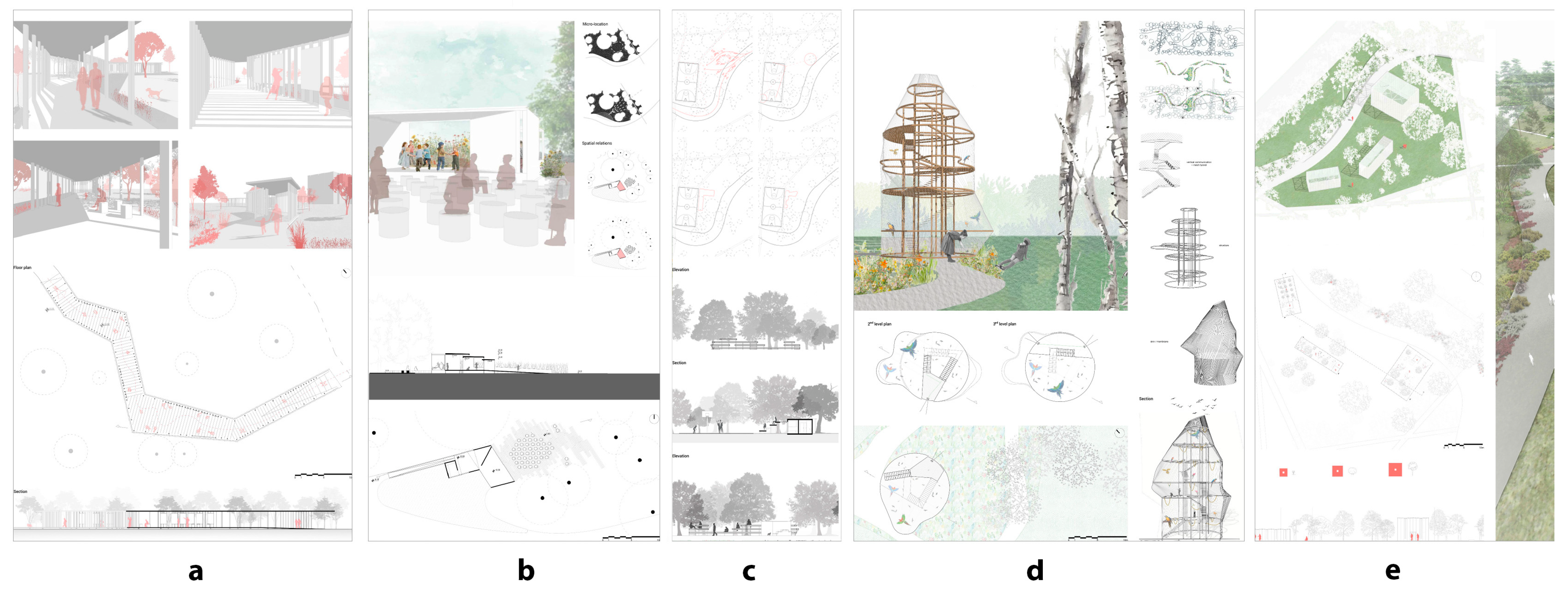
| Design | |
| D.1. | creative and innovate thinking |
| D.2. | documentation and systematisation of data |
| D.3. | problem-based and critical thinking |
| D.4. | three-dimensional thinking |
| D.5. | integrating knowledge and divergent factors |
| D.6. | formulating strategies for action and design solutions |
| Knowledge | |
| Cultural and Artistic Studies | |
| CAS.1. | considering historical and cultural precedents |
| CAS.2. | engaging fine arts in architectural design |
| CAS.3. | understanding of heritage issues |
| CAS.4. | rising awareness of other creative disciplines |
| Social Studies | |
| SS.1. | designing for and with society and users’ needs |
| SS.2 | considering contextual, spatial, and functional requirements |
| SS.3 | applying the relevant codes, regulations, and standards |
| SS.4. | considering philosophy, politics, and ethics |
| Environmental Studies | |
| ES.1. | appreciating natural systems and built environments |
| ES.2. | understanding ecological sustainability and environmental impact |
| ES.3. | planning and design in relation to glocal demography and resources |
| ES.4. | taking into account disaster risks and natural systems management |
| Technical Studies | |
| TS.1. | acquiring knowledge of structure, materials, and construction |
| TS.2. | applying and innovating building techniques |
| TS.3. | applying integrated technical design |
| TS.4. | understanding of services systems and activities |
| TS.5. | understanding the technical procedures from conception to realisation |
| Design Studies | |
| DS.1. | acquiring knowledge of design theory and methods |
| DS.2. | understanding of design procedures and processes |
| DS.3. | acquiring knowledge of design precedents and architectural criticism |
| Professional Studies | |
| PS.1. | understanding procurement of architectural services |
| PS.2. | understanding finance, real estate investment and facilities management |
| PS.3. | understanding (in) conventional roles of architects in an international context |
| PS.4. | understanding of business principles |
| PS.5. | understanding of professional ethics and codes of conduct |
| SKILLS | |
| S.1. | acting in collaborative and interdisciplinary environment |
| S.2. | utilising manual, electronic, graphic, and model-making capabilities in research and exploration |
| S.3. | utilising manual, electronic, graphic, and model-making capabilities in design and development |
| S.4. | communicating ideas through oral and written presentation |
| S.5. | communicating ideas through drawing and modelling |
| S.6. | applying systems of evaluation and performance assessments |
| Workshop 1 | Workshop 2 | Workshop 3 | |||||||
| List of Capabilities | A | C | E | A | C | E | A | C | E |
| Design | |||||||||
| D.1. | x | x | x | • | x | • | o | • | • |
| D.2. | • | • | • | o | • | o | x | x | x |
| D.3. | • | o | o | • | o | o | • | o | o |
| D.4. | x | x | x | x | x | • | x | o | • |
| D.5. | • | x | / | • | x | / | o | o | / |
| D.6. | / | x | x | / | x | x | / | • | • |
| Knowledge | |||||||||
| Cultural and Artistic Studies | |||||||||
| CAS.1. | • | o | o | • | o | x | o | o | x |
| CAS.2. | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | o |
| CAS.3. | • | o | • | • | o | o | o | o | x |
| CAS.4. | o | x | o | x | x | x | o | o | o |
| Social Studies | |||||||||
| SS.1. | • | x | x | x | x | x | • | • | o |
| SS.2 | • | o | • | • | o | o | • | • | o |
| SS.3 | x | x | x | x | x | x | o | • | o |
| SS.4. | • | o | x | o | o | x | o | o | o |
| Environmental Studies | |||||||||
| ES.1. | o | x | x | o | o | o | • | • | • |
| ES.2. | o | x | x | o | o | o | • | • | • |
| ES.3. | • | o | x | • | o | x | o | o | x |
| ES.4. | x | x | x | x | x | x | o | • | o |
| Technical Studies | |||||||||
| TS.1. | • | o | x | o | x | o | o | • | o |
| TS.2. | x | x | x | x | x | x | o | o | o |
| TS.3. | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | o | x |
| TS.4. | o | x | x | x | x | x | x | o | x |
| TS.5. | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | o | x |
| Design Studies | |||||||||
| DS.1. | x | x | x | • | o | x | o | • | o |
| DS.2. | x | x | x | x | x | x | • | • | • |
| DS.3. | o | x | x | • | o | • | o | o | o |
| Professional Studies | |||||||||
| PS.1. | o | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x |
| PS.2. | • | x | x | x | x | x | x | o | x |
| PS.3. | o | x | x | o | x | x | o | • | o |
| PS.4. | o | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x |
| PS.5. | • | x | x | x | x | x | o | o | x |
| Skills | |||||||||
| S.1. | • | • | • | • | • | • | • | • | • |
| S.2. | • | o | / | • | • | / | • | • | / |
| S.3. | / | x | / | / | o | / | / | • | / |
| S.4. | / | o | o | / | o | • | / | • | • |
| S.5. | / | x | x | / | • | • | / | • | • |
| S.6. | x | / | x | o | / | x | o | / | x |
| Workshop | Content Based | Outcome Directed | Focal Design Phase | Focal Capabilities |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Workshop Model 1 | Evidence based | State-of-the-Art directed | Analytical phase | Knowledge |
| Workshop Model 2 | Representation based | Problem directed | Executive phase | Skills |
| Workshop Model 3 | Problem based | Design directed | Creative phase | Design |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dragutinovic, A.; Milovanovic, A.; Stojanovski, M.; Damjanovska, T.; Đorđevic, A.; Nikezic, A.; Pottgiesser, U.; Ivanovska Deskova, A.; Ivanovski, J. Approaching Extracurricular Activities for Teaching and Learning on Sustainable Rehabilitation of Mass Housing: Reporting from the Arena of Architectural Higher Education. Sustainability 2023, 15, 2476. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15032476
Dragutinovic A, Milovanovic A, Stojanovski M, Damjanovska T, Đorđevic A, Nikezic A, Pottgiesser U, Ivanovska Deskova A, Ivanovski J. Approaching Extracurricular Activities for Teaching and Learning on Sustainable Rehabilitation of Mass Housing: Reporting from the Arena of Architectural Higher Education. Sustainability. 2023; 15(3):2476. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15032476
Chicago/Turabian StyleDragutinovic, Anica, Aleksandra Milovanovic, Mihajlo Stojanovski, Tea Damjanovska, Aleksandra Đorđevic, Ana Nikezic, Uta Pottgiesser, Ana Ivanovska Deskova, and Jovan Ivanovski. 2023. "Approaching Extracurricular Activities for Teaching and Learning on Sustainable Rehabilitation of Mass Housing: Reporting from the Arena of Architectural Higher Education" Sustainability 15, no. 3: 2476. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15032476
APA StyleDragutinovic, A., Milovanovic, A., Stojanovski, M., Damjanovska, T., Đorđevic, A., Nikezic, A., Pottgiesser, U., Ivanovska Deskova, A., & Ivanovski, J. (2023). Approaching Extracurricular Activities for Teaching and Learning on Sustainable Rehabilitation of Mass Housing: Reporting from the Arena of Architectural Higher Education. Sustainability, 15(3), 2476. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15032476








