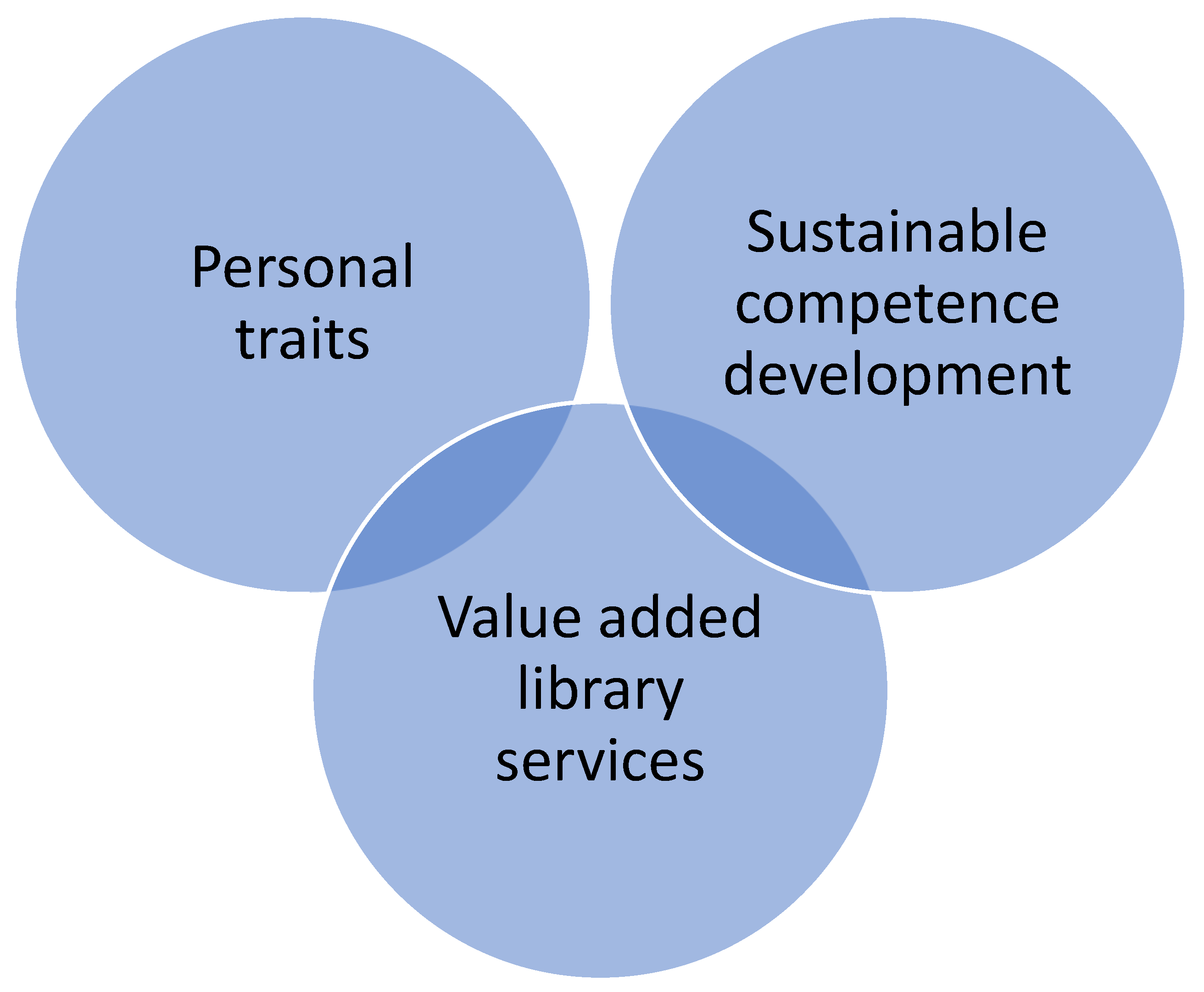
Relationship between Personal Traits and Sustainable Competence Development among Librarians in Relation to Value-Added Library Services in a Networked World: A Systematic Literature Review from 2002 to 2022
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Statement of Problem and Rationale
3. Objectives
- To identify the relationship between the personal traits and sustainable competence development of librarians;
- To explore trending practices for the development of the personal and professional competencies of librarians related to offering value-added library services in the networked world;
- To identify the challenges affecting the development of modern skills among librarians.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Part One: Planning
4.1.1. Research Objectives
4.1.2. Search Strategy
- Formulation of keywords/variables from article title;
- Construction of the study objectives;
- Employability of the key terms used by other researchers in their published articles;
- List of relevant terms, synonyms, and similar themes;
- Usage of Boolean operators “OR”, “AND”, and “NOT” and stop words, phrase searching, proximity search, truncation, and wildcards.
4.2. Part Two: Selection
4.2.1. Search Process
4.2.2. Scrutiny and Filtering
4.3. Part Three: Extraction
4.4. Part Four: Execution
5. An Overview of the Selection of Studies and Data Extraction
6. Results
7. Trending Practices for the Development of Personal and Professional Competencies
7.1. Expert Use of IT
7.2. Continuous Training Sessions
7.3. Teamwork
7.4. Usage of Social Media Forums
7.5. Customer-Oriented Approach
8. Relationship between Personal Traits and Professional Growth
9. Challenges Related to the Development of Modern Skills in Librarians
9.1. Old Curricula
9.2. Leadership Problem
9.3. Economy Issues
9.4. Lack of Personal Interest
10. Discussion and Conclusions
11. Implications
12. Limitations
- We acknowledge that some of the relevant research articles published worldwide may not have been covered in the current study;
- We also realize that more study objectives could be developed regarding the best practices that could be adopted to create the required set of skills among library professionals;
- Thirteen databases were explored to retrieve studies related to personal traits and sustainable competence development among librarians. Specific databases related to medical librarianship were not included.
13. Future Research Directions
- Future researchers could empirically test the relationship between personal traits and sustainable competence development related to the provision of value-added services in libraries in the networked world;
- Future studies could also be conducted on the impact of digital learning on the continued professional development of library professionals through the mediating role of motivational factors;
- Future investigators could conduct a systematic literature review on the relationship between personal traits and sustainable competence development among librarians by including other sources of knowledge, including books, conference proceedings, and dissertations;
- Future researchers could explore the literature on the personal and professional competencies of librarians using other databases, including PubMed, to offer a broader spectrum.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shah, S.R.U. Sustainable Competence Development of Librarians in Pakistan; Högskolan i Borås: Borås, Sweden, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Eshet-Alkalai, Y. Digital literacy: A conceptual framework for survival skills in the digital era. J. Educ. Multimed. Hypermedia 2004, 13, 93–106. [Google Scholar]
- Meyers, E.M.; Erickson, I.; Small, R.V. Digital literacy and informal learning environments: An introduction. Learn. Media Technol. 2013, 38, 355–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lester, J.; Van Fleet, C. Use of professional competencies and standards documents for curriculum planning in schools of li-brary and information studies education. J. Educ. Libr. Inf. Sci. 2008, 49, 43–69. [Google Scholar]
- Jordan, M.W. Developing leadership competencies in librarians. IFLA J. 2012, 38, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerolimos, M.; Malliari, A.; Iakovidis, P. Skills in the market: An analysis of skills and qualifications for American librarians. Libr. Rev. 2015, 64, 21–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooq, M.U.; Ullah, A.; Iqbal, M.; Hussain, A. Current and required competencies of university librarians in Pakistan. Libr. Manag. 2016, 37, 410–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narang, A.; Kumar, J. Leadership competencies for librarians. Int. J. Libr. Sci. 2016, 14, 30–40. [Google Scholar]
- Sarasvathy, P.; Namratha, G.R.; Giddaiah, D. Changing roles of the librarians in the virtual/digital era. SRELS J. Inf. Manag. 2012, 49, 495–500. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, D.K. Librarians’ Changing Role in Distance Education. J. Libr. Adm. 2001, 32, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashim, B.L.; Mokhtar, W.N.H.W. Preparing new era librarians and information professionals: Trends and issues. Int. J. Humanit. Soc. Sci. 2012, 2, 151–155. [Google Scholar]
- Bell, S.J.; Shank, J. The blended librarian: A blueprint for redefining the teaching and learning role of academic librarians. Coll. Res. Libr. News 2004, 65, 372–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherinet, Y.M. Blended skills and future roles of librarians. Libr. Manag. 2018, 39, 93–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okoye, M.O. Assessment of competencies of professional librarians in Nigeria. Libr. Philos. Pract. 2013, 1, 979. [Google Scholar]
- Bamigboye, O.B.; Agboola, I.O.; Okorie, C.N. Competency of academic librarians in using information and communication technology in service delivery: A study of university libraries in Nigeria. J. Libr. Inf. Sci. 2013, 37, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Jain, P. A paradigm shift in the 21st century academic libraries and librarians: Prospectus and opportunities. Eur. J. Acad. Res. 2013, 1, 133–147. [Google Scholar]
- Hampe, N.; Lewis, S. E-portfolios support continuing professional development for librarians. Aust. Libr. J. 2013, 62, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asogwa, B.E. Libraries in the information age. Electron. Libr. 2014, 32, 603–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jena, S.; Sahoo, C.K.; Tripathy, S.K. Impact of social, intellectual and personal competencies on managerial performance: An empirical investigation. Int. J. Indian Cult. Bus. Manag. 2015, 11, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashcroft, L. Developing competencies, critical analysis and personal transferable skills in future information professionals. Libr. Rev. 2004, 53, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Partridge, H.; Lee, J.; Munro, C. Becoming librarian 2.0: The skills, knowledge, and attributes required by library and information science professionals in a Web 2.0 world and beyond. Libr. Trends 2010, 59, 315–335. [Google Scholar]
- Osa, J.O. Managing the 21st Century Reference Department. Ref. Libr. 2003, 39, 35–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van, W.L. How do we know what we don’t know? Competencies and staff development in special libraries. Color. Libr. 2004, 30, 10–14. [Google Scholar]
- Bhatti, R.; Nadeem, M. Assessing training needs of LIS professionals: A prerequisite for developing training programs in uni-versity libraries of Pakistan. Chin. Libr. Int. Electron. J. 2014, 37, 47–62. [Google Scholar]
- Grgic, I.H.; Zivkovic, D. Core competencies for academic reference librarians in Croatia. Qual. Quant. Methods Libr. 2017, 1, 247–256. [Google Scholar]
- Mackenzie, M.L.; Smith, J.P. Management education for library directors: Are graduate library programs providing future library directors with the skills and knowledge they will need? J. Educ. Libr. Inf. Sci. 2009, 50, 129–142. [Google Scholar]
- Brill, J.M.; Bishop, M.J.; Walker, A.E. The Competencies and Characteristics Required of an Effective Project Manager: A Web-Based Delphi Study. Educ. Technol. Res. Dev. 2006, 54, 115–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chase, Z.; Laufenberg, D. Embracing the Squishiness of Digital Literacy. J. Adolesc. Adult Lit. 2011, 54, 535–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kattimani, S.F.; Naik, R.R. Evaluation of librarianship and ICT skills of library and information professionals working in the engineering college libraries in Karnataka, India: A survey. Program 2013, 47, 345–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayoku, O.A.; Okafor, V.N. ICT skills acquisition and competencies of librarians. Electron. Libr. 2015, 33, 502–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drummond, C. Embracing diversity: When is a librarian not a librarian? Aust. Libr. J. 2016, 65, 274–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gwyer, R. Identifying and Exploring Future Trends Impacting on Academic Libraries: A Mixed Methodology Using Journal Content Analysis, Focus Groups, and Trend Reports. New Rev. Acad. Libr. 2015, 21, 269–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decker, E.N. The X-factor in academic libraries: The demand for soft skills in library employees. Coll. Undergrad. Libr. 2020, 27, 17–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emanuel, J. Digital Native Academic Librarians, Technology Skills, and Their Relationship with Technology. Inf. Technol. Libr. 2013, 32, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robati, A.P.; Singh, D. Competencies required by special librarians: An analysis by educational levels. J. Libr. Inf. Sci. 2013, 45, 113–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, F.; Santos, J.N.; Nascimento, L.; Andrade, R.S.; Barros, S. Information professionals in Brazil: Core competencies and professional development. Inf. Res. 2007, 12, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Cullen, J. Catalyzing innovation and knowledge sharing. Bus. Inf. Rev. 2008, 25, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agbo, A.D. Staff training and development programs in Nigerian university libraries. The case of Michael Okpare University of Agriculture. Int. J. Multidiscip. Res. Dev. 2015, 2, 553–557. [Google Scholar]
- Harris-Keith, C.S. What Academic Library Leadership Lacks: Leadership Skills Directors Are Least Likely to Develop, and Which Positions Offer Development Opportunity. J. Acad. Libr. 2016, 42, 313–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owusu-Acheaw, M.; Akussah, H. Professional development of library staff in Ghana’s polytechnics: How proactive are the staff and how committed are the management? J. Inf. Sci. Syst. Technol. 2018, 2, 40–50. [Google Scholar]
- Samah, N.A.; Mohd Tahir, L.; Wan Mamat, W.A.W.Y.; Talib, R.; Abdul Latif, A. Malaysian research-support librarians’ self-directed learning traits: Examining demographic differences and their relationship with competencies. J. Libr. Inf. Sci. 2021, 53, 630–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamali, Z. Analysis of librarians’ personal knowledge management. Sci. Tech. Inf. Manag. 2021, 7, 243–276. [Google Scholar]
- Keshavarz, H. Personality factors and knowledge sharing behavior in information services: The mediating role of information literacy competencies. VINE J. Inf. Knowl. Manag. Syst. 2022, 52, 186–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamad, F.; Al-Fadel, M.; Fakhouri, H. The effect of librarians’ digital skills on technology acceptance in academic libraries in Jordan. J. Libr. Inf. Sci. 2021, 53, 589–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alenzuela, R. Cultural Competency of Ni-Vanuatu Librarians: Vanuatu Libraries Contribution to the Nation’s Vibrant Cultural Identity. J. Aust. Libr. Inf. Assoc. 2021, 70, 405–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamseer, L.; Moher, D.; Clarke, M.; Ghersi, D.; Liberati, A.; Petticrew, M.; Shekelle, P.; Stewart, L.A.; PRISMA-P Group. Preferred reporting items for systematic review and meta-analysis protocols (PRISMA-P) 2015: Elaboration and explanation. BMJ 2015, 350, g7647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood, K. Competencies needed for future academic librarians in Pakistan. Educ. Inf. 2002, 20, 27–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrall, S. Educating the academic librarian as a blended professional: A review and case study. Libr. Manag. 2010, 31, 567–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K. Academic libraries in the age of MOOCs. Ref. Serv. Rev. 2013, 41, 576–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oza, N.; Mehta, M. A study of ICT skills and competencies essential for corporate LIS professionals. Int. J. Res. Anal. Rev. 2018, 5, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Boamah, E. A Reflection on the Development of an Erasmus Mundus Digital Library Learning (DILL) Programme. Int. Inf. Libr. Rev. 2019, 51, 151–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alawadhi, S. Continuing Professional Development in Kuwaiti Academic Libraries. Int. Inf. Libr. Rev. 2015, 47, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, S.; Brunner, M.; Ferguson, J.; Felix, E. Assessing Library Competencies for the Future: The LibGOAL Toolkit for Success. Against Grain 2021, 31, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idhalama, O.U.; Aiyebelehin, A.J.; Okobo, O. Competencies of Librarians as a Factor Affecting Information, Service Delivery in Selected University Libraries in Delta State, Nigeria. Int. J. Integr. Educ. 2020, 3, 92–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edewor, N. Capacity Building Efforts to Develop Digital Innovation Competencies among Librarians in Nigeria. J. Libr. Adm. 2020, 60, 316–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Inclusion Criteria | Exclusion Criteria | |
|---|---|---|
| A | Articles published in the English language | Papers published in other languages |
| B | Papers covering the study’s objectives | Papers not covering the study’s objectives |
| C | Articles published from 2002 to 2022 | Articles published before 2002 |
| D | Papers covering the variables of the study; i.e., personal development, professional development, sustainable competence development, professional development methods, value-added library services, etc. | Papers not covering the variables of the study |
| E | Peer-reviewed articles in electronic databases | Books, conference proceedings, dissertations, magazines, newspaper articles, institutional newsletters, etc. |
| S. N. | Author | Year | Country | Journal | Trending Practices for the Development of Personal and Professional Competencies | Relationship between Personal Traits and Professional Growth | Challenges Related to Developing Modern Skills |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Khalid | 2002 | Pakistan | Education for Information |
|
| |
| 2. | Ashcroft | 2004 | United Kingdom | Library Review |
| ||
| 3. | Corrall | 2010 | United Kingdom | Library Management |
| ||
| 4. | Patridge et al. | 2010 | USA | Library Trends |
| ||
| 5. | Jordan | 2012 | USA | IFLA Journal |
|
|
|
| 6. | Hashim and Mokhtar | 2012 | Malaysia | International Journal of Humanities and Social Science |
|
| |
| 7. | Grgic and Zivkovic | 2012 | Croatia | Qualitative and Quantitative Methods in Libraries |
| ||
| 8. | Wu | 2013 | USA | Reference Services Review |
| ||
| 9. | Meyers et al. | 2013 | USA | Learning Media and Technology |
| ||
| 10. | Okoye | 2013 | Nigeria | Library Philosophy and Practice |
|
|
|
| 11. | Ayoku and Okafor | 2015 | Nigeria | The Electronic Library |
|
|
|
| 12. | Jain | 2013 | Botswana | European Journal of Academic Research |
|
|
|
| 13. | Hampe and Lewis | 2013 | Australia | The Australian Library Journal |
|
| |
| 14. | Robati and Singh | 2013 | Iran | Journal of Librarianship and Information Science |
| ||
| 15. | Emanuel | 2013 | USA | Information Technology and Libraries |
| ||
| 16. | Jena et al. | 2015 | India | International Journal of Indian Culture and Business Management |
| ||
| 17. | Alawadhi | 2015 | Kuwait | International Information and Library Review |
| ||
| 18. | Agbo | 2015 | Nigeria | International Journal of Multidisciplinary Research and Development |
|
| |
| 19. | Farooq et al. | 2016 | Pakistan | Library Management |
|
|
|
| 20. | Narang and Kumar | 2016 | India | International Journal of Library Science |
|
| |
| 21. | Drummond | 2016 | Australia | The Australian Library Journal |
|
| |
| 22. | Keith | 2016 | USA | The Journal of Academic Librarianship |
| ||
| 23. | Cherinet | 2017 | Ethiopia | Library Management |
|
| |
| 24. | Oza and Mehta | 2018 | India | International Journal of Research and Analytical Reviews |
| ||
| 25. | Acheaw and Akussah | 2018 | Ghana | Journal of Information Science, Systemsand Technology |
|
| |
| 26. | Bell et al. | 2019 | USA | Against the Grain |
| ||
| 27. | Boamah | 2019 | Italy | International Information and Library Review |
|
| |
| 28. | Idhalama et al. | 2020 | Nigeria | International Journal of Integrated Education |
| ||
| 29. | Edewor | 2020 | Nigeria | Journal of Library Administration |
| ||
| 30. | Decker | 2020 | USA | College and Undergraduate Libraries |
|
| |
| 31. | Samah et al. | 2021 | Malaysia | Journal of Librarianship and Information Science |
|
|
|
| 32. | Jamali | 2021 | Iran | Sciences and Techniques of Information Management |
|
| |
| 33. | Hamad et al. | 2021 | Jordan | Journal of Librarianship and Information Science |
|
| |
| 34. | Alenzuela | 2021 | Philippines | Journal of the Australian Library and InformationAssociation |
| ||
| 35. | Keshavarz | 2022 | Iran | VINE Journal of Information and Knowledge Management Systems |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shahzad, K.; Khan, S.A.; Latif, M.; Iqbal, A. Relationship between Personal Traits and Sustainable Competence Development among Librarians in Relation to Value-Added Library Services in a Networked World: A Systematic Literature Review from 2002 to 2022. Sustainability 2023, 15, 2359. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15032359
Shahzad K, Khan SA, Latif M, Iqbal A. Relationship between Personal Traits and Sustainable Competence Development among Librarians in Relation to Value-Added Library Services in a Networked World: A Systematic Literature Review from 2002 to 2022. Sustainability. 2023; 15(3):2359. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15032359
Chicago/Turabian StyleShahzad, Khurram, Shakeel Ahmad Khan, Mujahid Latif, and Abid Iqbal. 2023. "Relationship between Personal Traits and Sustainable Competence Development among Librarians in Relation to Value-Added Library Services in a Networked World: A Systematic Literature Review from 2002 to 2022" Sustainability 15, no. 3: 2359. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15032359
APA StyleShahzad, K., Khan, S. A., Latif, M., & Iqbal, A. (2023). Relationship between Personal Traits and Sustainable Competence Development among Librarians in Relation to Value-Added Library Services in a Networked World: A Systematic Literature Review from 2002 to 2022. Sustainability, 15(3), 2359. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15032359







