Location of Mountain Photovoltaic Power Station Based on Fuzzy Analytic Hierarchy Process—Taking Longyang District, Baoshan City, Yunnan Province as an Example
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
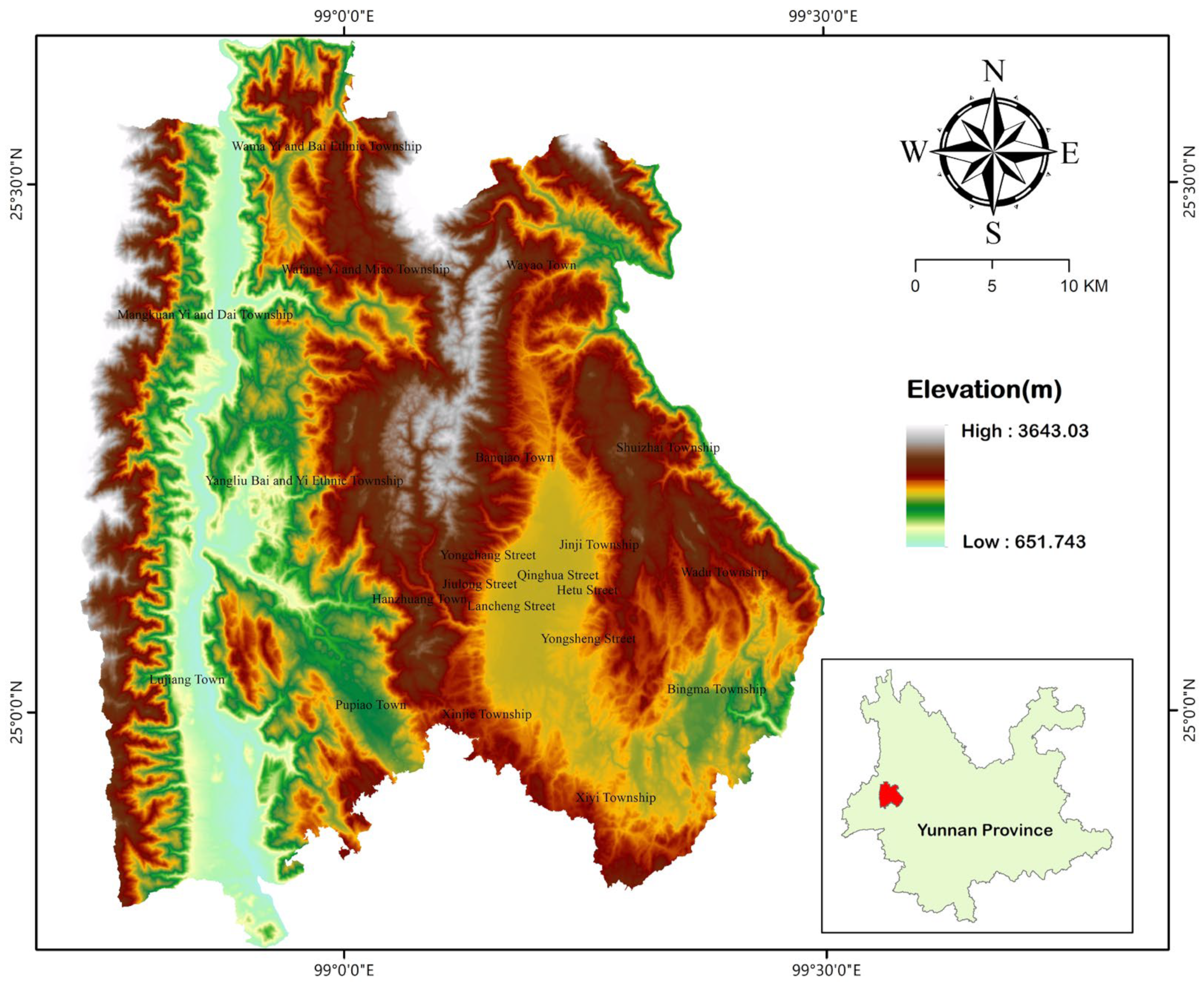
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Preparation
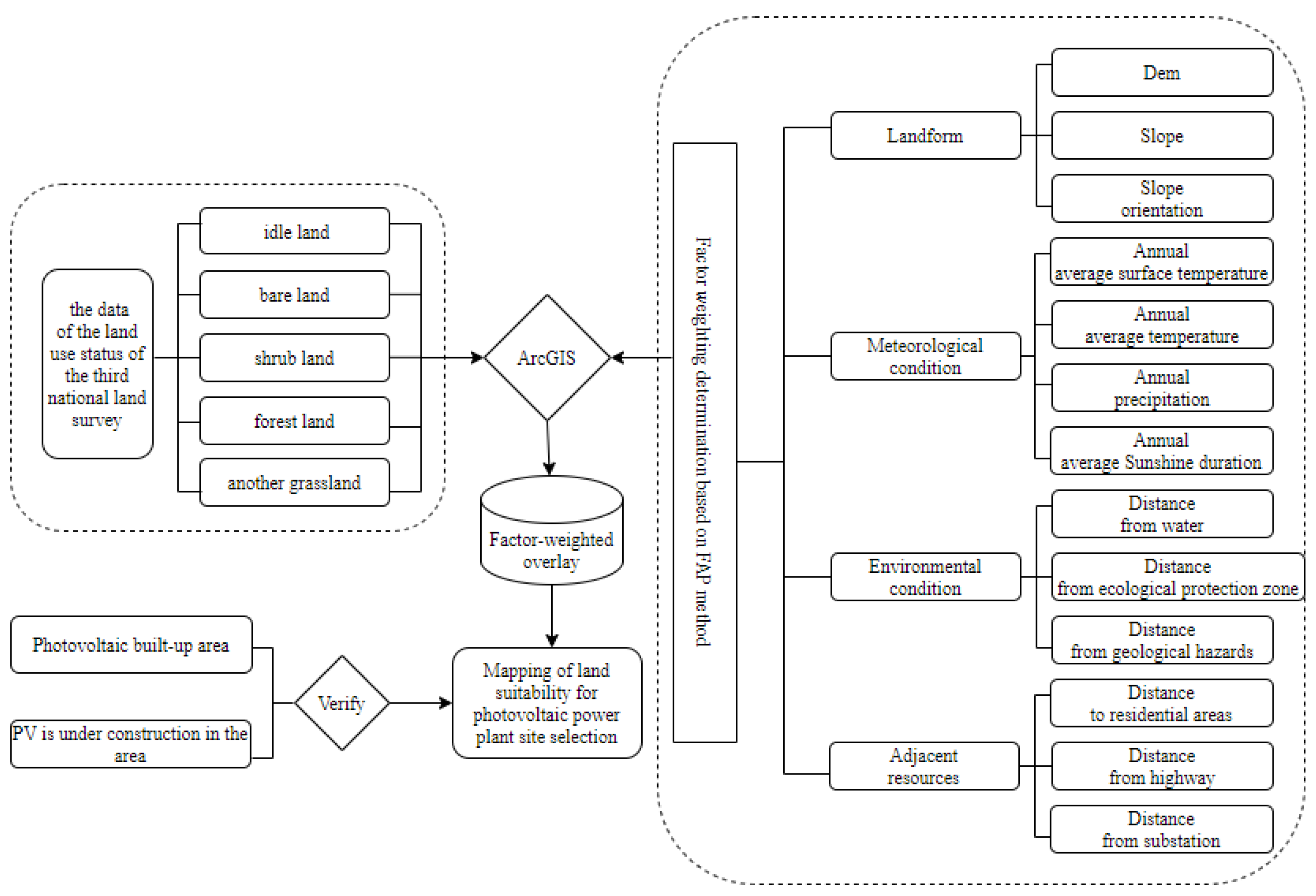
2.3. Construction of PV Location Constraints and Evaluation Index System
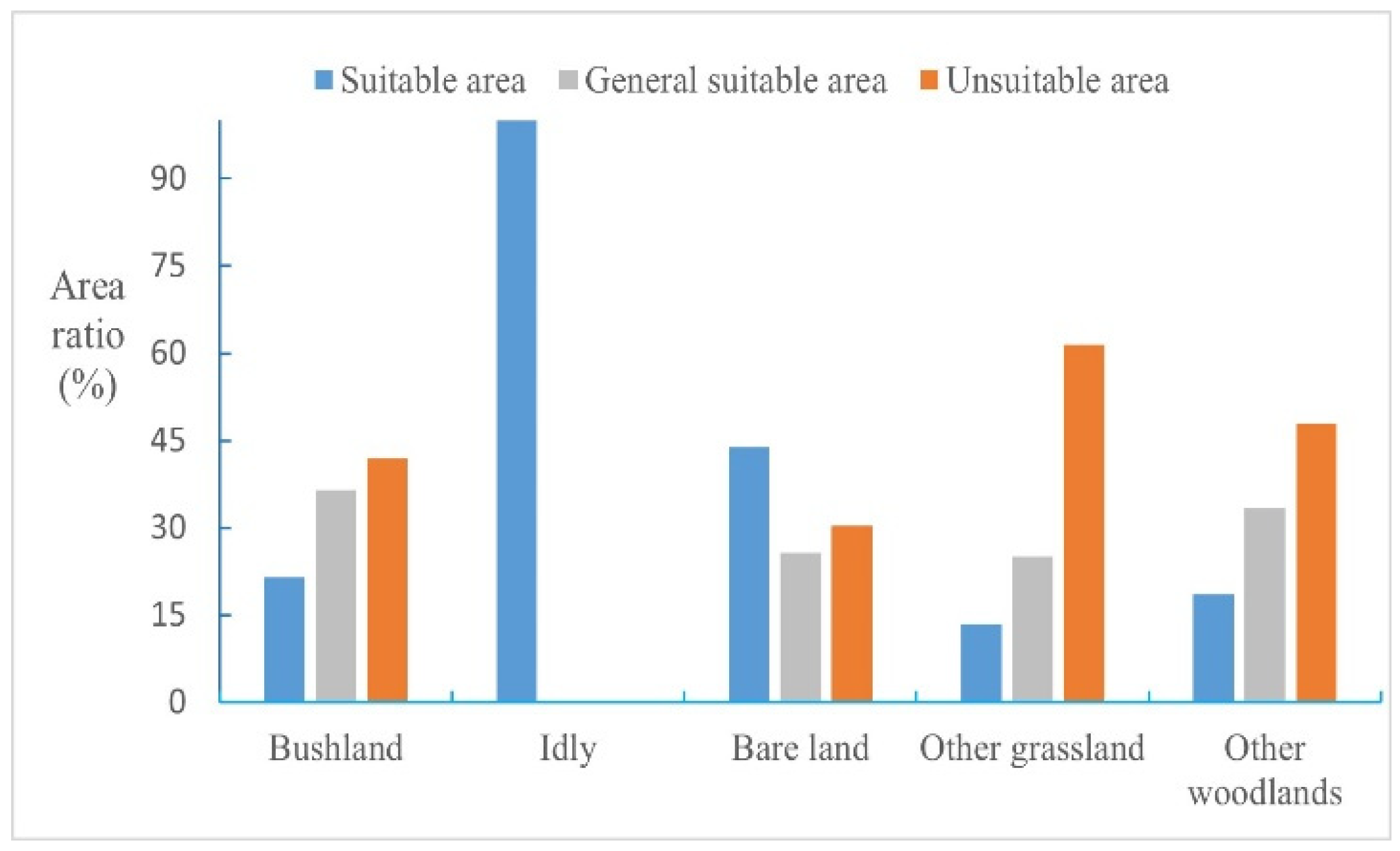
2.3.1. Constraints of Land Use Type
2.3.2. Topography and Geomorphology Constraints
2.3.3. Environmental Constraints
2.3.4. Constraints on Natural Conditions
2.4. The Suitability Assessment Index System for Photovoltaic Site Selection
2.5. Materials and Methods
2.5.1. Fuzzy Analytic Hierarchy Process
- (1)
- The fuzzy complementary matrix is obtained as follows:
- (2)
- The value of the index weight vector W in the first-level criterion layer is obtained by solving the fuzzy matrix R through row normalization. Consider n first-level criterion layer factors. Then, the index weight W is expressed as follows:
- (3)
- Various verification methods have been proposed for fuzzy matrix consistency judgment. This paper performs the matrix consistency test according to Theorems of sufficient and necessary conditions for the fuzzy matrix consistency judgment proposed in the literature [34]. This test method is more accurate, scientific, and simple than obtaining the maximum eigenvalue of a matrix and its corresponding eigenvector.
- (4)
- Determine the weight vector
2.5.2. Determining the Weight Factor Based on the Fuzzy Analytic Hierarchy Process
3. Result Analysis and Verification
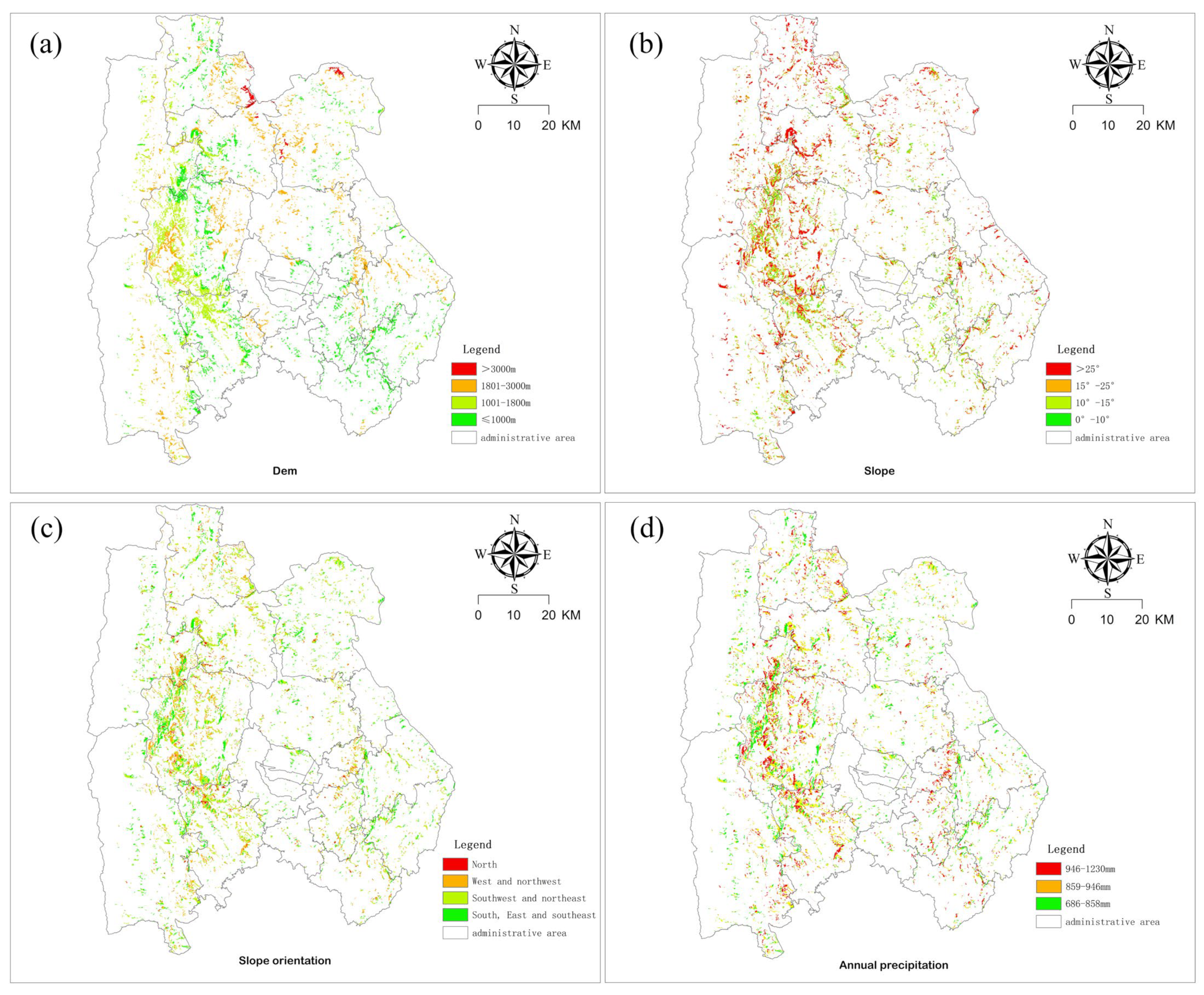
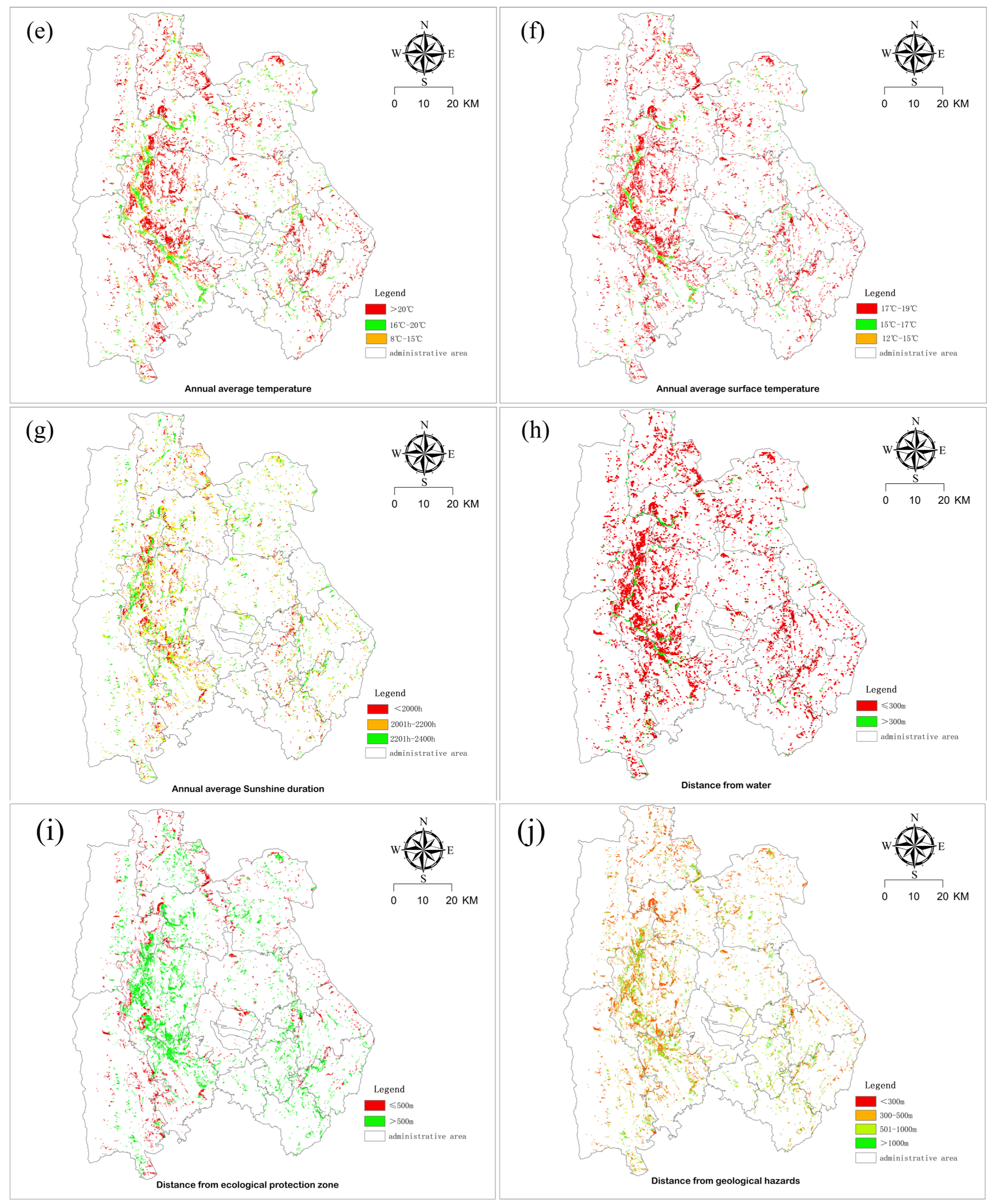
3.1. Data Processing Results
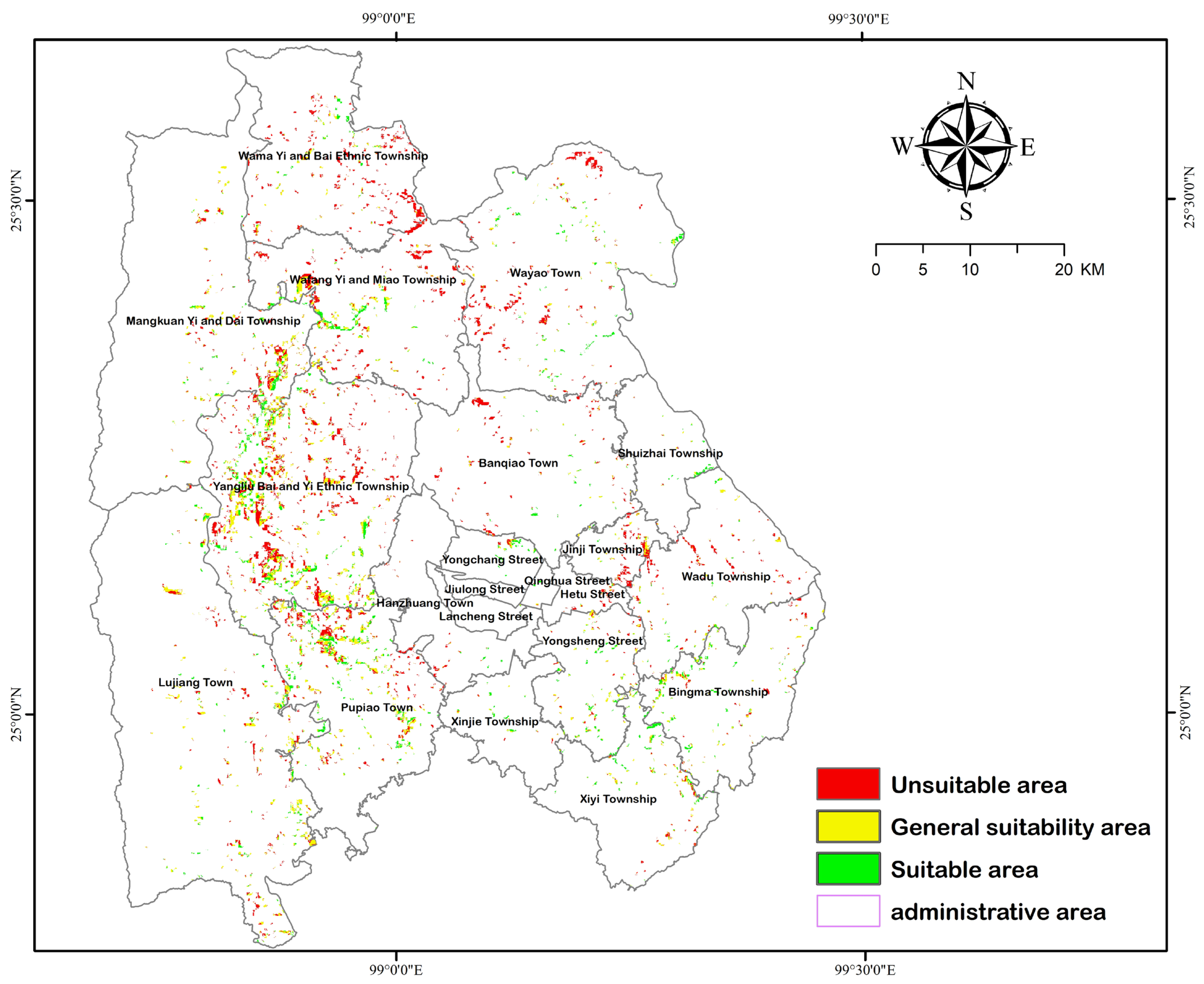
3.2. Result Analysis
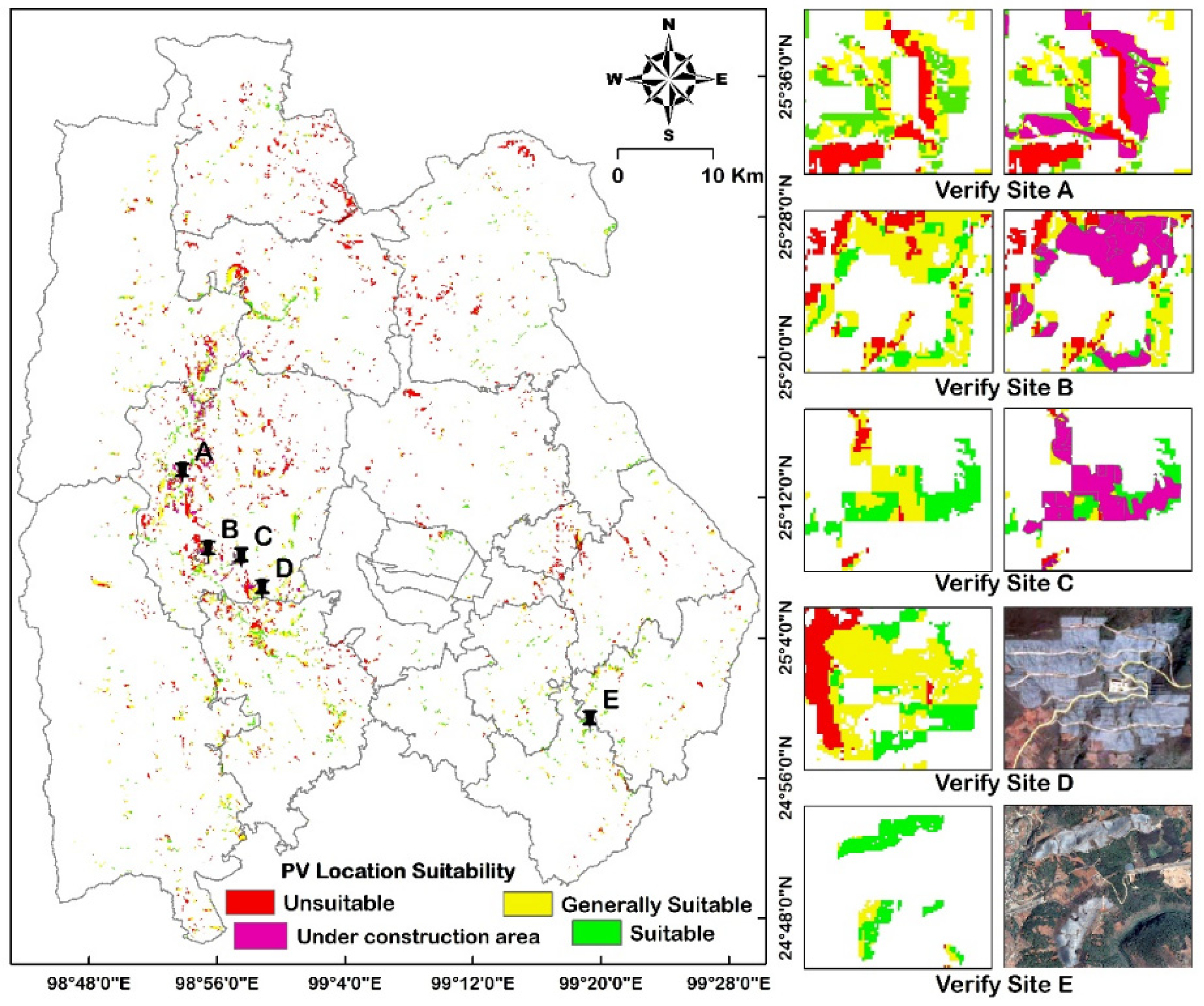
3.3. Verification of the Suitability of Longyang District Photovoltaic Site Selection
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, T.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.-G.; Li, Z.-Y. Analysis on the evolution of the compactness of the highland cities in Yunnan Province. Hubei Agric. Sci. 2022, 61, 61–67. [Google Scholar]
- Miao, B.; Cheng, M.; Sun, Y. Study on Green Energy Generation Efficiency Measurement and Countermeasures in Yunnan Province: Based on the Aggressive Cross-Evaluation DEA Model. Ecol. Econ. 2022, 72, 78–84. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, L.; Jiang, Y.; Guo, Q.; Ji, L.; Xie, Y.; Qiao, Q.; Huang, G.; Xiao, K. A GIS-based multi-criteria decision making method for the potential assessment and suitable sites selection of PV and CSP plants. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2020, 168, 105306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solangi, Y.A.; Shah, S.A.A.; Zameer, H.; Ikram, M.; Saracoglu, B.O. Assessing the solar PV power project site selection in Pakistan: Based on AHP-fuzzy VIKOR approach. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 30286–30302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y. Research and Application of Location Selection Method of Solarphotovoltaic Power Station Based on GIS. Ph.D. Thesis, Northern University for Nationalities, Yinchuan, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Doljak, D.; Stanojević, G. Evaluation of natural conditions for site selection of ground-mounted photovoltaic power plants in Serbia. Energy 2017, 127, 291–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lurwan, S.M.; Mohammed, O.I.; Goma, B.A.; Usman, S.L.; Norman, B.M. GIS-Based Optimal Site Selection for Installation of Large-Scale Smart Grid-Connected Photovoltaic PV) Power Plants in Selangor, Malaysia. Am. J. Appl. Sci. 2017, 14, 174–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Rediske, G.; Siluk, J.C.M.; Michels, L.; Rigo, P.D.; Rosa, C.B.; Cugler, G. Multi-criteria decision-making model for assessment of large photovoltaic farms in Brazil. Energy 2020, 197, 117167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majumdar, D.; Pasqualetti, M.J. Analysis of land availability for utility-scale power plants and assessment of solar photovoltaic development in the state of Arizona, USA. Renew. Energy 2019, 134, 1213–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elboshy, B.; Alwetaishi, M.; Aly, R.M.H.; Zalhaf, A.S. A suitability mapping for the PV solar farms in Egypt based on GIS-AHP to optimize multi-criteria feasibility. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2021, 13, 101618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C. Study on Distribution Law of Geological Hazards and Prevention Planning in Longyang District, Baoshan City, Yunnan Province. Ph.D. Thesis, China University of Geosciences, Beijing, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Uyan, M. GIS-based solar farms site selection using analytic hierarchy process (AHP) in Karapinar region, Konya/Turkey. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2013, 28, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habib, S.M.; Suliman, A.E.R.E.; Al Nahry, A.H.; Abd El Rahman, E.N. Spatial modeling for the optimum site selection of solar photovoltaics power plant in the northwest coast of Egypt. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2020, 18, 100313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Zhang, S.; Ge, X. Construction of Regional Large-scale PhotovoltaicPower Station Site Selection Indicator System Based on Geographic Information Technology and Fuzzy Analytic Hierarchy Process-Fuzzy Decision Making Trial and Evaluation Laboratory Methods AHP-DEMATEL, A Case Study of Inner Mongolia. Sci. Technol. Manag. Res. 2023, 43, 78–87. [Google Scholar]
- Aslam, B.; Maqsoom, A.; Alaloul, W.S.; Musarat, M.A.; Jabbar, T.; Zafar, A. Soil erosion susceptibility mapping using a GIS-based multi-criteria decision approach: Case of district Chitral, Pakistan. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2020, 12, 1637–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, F.; Xie, Q.; Dai, J. Research and application of GIS-based multiple-criteria decision making method for dual objectives. J. Chongqing Univ. 2021, 44, 161–170. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Pang, X. Selection of Antarctic Research Stations Based on GIS and Fuzzy AHP. Geomat. Inf. Sci. Wuhan Univ. 2015, 40, 249–252+257. [Google Scholar]
- Zalhaf, A.S.; Elboshy, B.; Kotb, K.M.; Han, Y.; Almaliki, A.H.; Aly, R.M.H.; Elkadeem, M.R. A High-Resolution Wind Farms Suitability Mapping Using GIS and Fuzzy AHP Approach: A National-Level Case Study in Sudan. Sustainability 2021, 14, 358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahraman, C.; Kaya, I.; Cebi, S. A comparative analysis for multiattribute selection among renewable energy alternatives using fuzzy axiomatic design and fuzzy analytic hierarchy process. Energy 2009, 34, 1603–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elagouz, M.; Abou-Shleel, S.; Belal, A.; El-Mohandes, M. El-mohandes. Detection of land use/cover change in Egyptian Nile Delta using remote sensing. Egypt. J. Remote Sens. Space Sci. 2020, 23, 57–62. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.; Su, C.; Fu, W. Study on the Site Selection of Large Ground PV Power Plant. Dongfang Turbine 2012, 126, 58–62. [Google Scholar]
- Aly, A.; Jensen, S.S.; Pedersen, A.B. Solar power potential of Tanzania: Identifying CSP and PV hot spots through a GIS multicriteria decision making analysis. Renew. Energy 2017, 113, 159–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benalcazar, P.; Komorowska, A.; Kamiński, J. A GIS-based method for assessing the economics of utility scale photovoltaic systems. Appl. Energy 2024, 353, 122044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y. Discussion on the Design and Research of Agricultural Photovoltaic Complementary Power Station. Intell. City 2018, 4, 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- IIslam, M.R.; Aziz, M.T.; Alauddin, M.; Kader, Z.; Islam, M.R. Sites suitability assessment for solar power plants in Bangladesh: A GIS-based analytical hierarchy process (AHP) and multi-criteria decision analysis MCDA) approach. Renew. Energy 2023, 119595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Garni, H.Z.; Awasthi, A. Solar PV power plant site selection using a GIS-AHP based approach with application in Saudi Arabia. Appl. Energy 2017, 206, 1225–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merrouni, A.A.; Elalaoui, F.E.; Ghennioui, A.; Mezrhab, A.; Mezrhab, A. A GIS-AHP combination for the sites assessment of large-scale CSP plants with dry and wet cooling systems. Case study: Eastern Morocco. Sol. Energy 2018, 166, 2–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Jing, R.; Yanru, P.; Peng, W. Solar energy potential assessment: A framework to integrate geographic, technological, and economic indices for a potential analysis. Renew. Energy 2020, 149, 577–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemi, G.; Noorollahi, Y.; Alavi, H.S.; Marzband, M.; Shahbazi, M. Theoretical and technical potential evaluation of solar power generation in Iran. Renew. Energy 2019, 138, 1250–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gherboudj, I.; Ghedira, H. Assessment of solar energy potential over the United Arab Emirates using remote sensing and weather forecast data. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 55, 1210–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehmet, A.G. A comprehensive framework based on GIS-AHP for the installation of solar PV farms in Kahramanmaraş, Turkey. Renew. Energy 2021, 178, 212–225. [Google Scholar]
- Doorga, J.R.S.; Rughooputh, S.D.; Boojhawon, R. High resolution spatio-temporal modelling of solar photovoltaic potential for tropical islands: Case of Mauritius. Energy 2019, 169, 972–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, J.J.; Hudson, M.D. Regional scale wind farm and solar farm suitability assessment using GIS-assisted multi-criteria evaluation. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2015, 138, 20–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J. Fuzzy Analytical Hierarchy Process. Fuzzy Syst. Math. 2000, 80–88. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=hqt_j-uEELFHEpBeeB_Y4KJ1SGIXZFk6TPQUdy_W9KG1yohl1WFQA4xISxu4qlu3rgM1Y2axIEvbT92IjsxI-r-rEVlF102bhGay1maz__lX-J3YqarG1UV-CfQE4ixk&uniplatform=NZKPT&language=CHS (accessed on 18 October 2023).
- Guo, F.; Gao, J.; Men, H.; Fan, Y.; Liu, H. Large-scale group decision-making framework for the site selection of integrated floating photovoltaic-p umped storage power system. J. Energy Storage 2021, 43, 103125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villacreses, G.; Martinez-Gomez, J.; Jijon, D.; Cordovez, M. Geolocation of photovoltaic farms using Geographic Information Systems (GIS) with Multiple-criteria decision-making (MCDM) methods: Case of the Ecuadorian energy regulation. Energy Rep. 2022, 8, 3526–3548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasti, F.; Mamkhezri, J.; McFerrin, R.; Pezhooli, N. Optimal solar photovoltaic site selection using geographic information system–based modeling techniques and assessing environmental and economic impacts: The case of Kurdistan. Sol. Energy 2023, 262, 111807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, R.; Li, X.; Li, C.; Xu, C. A MCDM framework for site selection of island photovoltaic charging station based on new criteria identification and a hybrid fuzzy approach. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 74, 103230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bocca, A.; Chiavazzo, E.; Macii, A.; Asinari, P. Solar energy potential assessment: An overview and a fast modeling approach with application to Italy. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 49, 291–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, S.; Pradip, K.S.; Nitai, P. New Location Selection Criterions for Solar PV Power Plant. Int. J. Renew. Energy Res. 2014, 4, 1020–1030. [Google Scholar]

| Data Name | Data Source |
|---|---|
| DEM date | Geospatial data cloud platform (http://www.gscloud.cn/, 20 May 2023) |
| Slope, slope direction | Generated by DEM data |
| Administrative division data | DIVA-GIS website (http://data.diva-gis.org/, 22 May 2023) |
| Meteorological, disaster, and hydrological data | Resource Environmental Science and Data Center (https://www.resdc.cn/, 21 May 2023) |
| Residential data, road data | National geographic information resources directory service system (https://www.webmap.cn/, 23 May 2023) |
| Land use data, ecological protection area data | Data of the third National Land Survey |
| Goal | Primary Index Layer | Secondary Index Layer |
|---|---|---|
| Evaluation of PV location suitability in Longyang District, Baoshan City | Landform | Dem |
| Slope | ||
| Slope orientation | ||
| Meteorological condition | Annual average surface temperature | |
| Annual average temperature | ||
| Annual precipitation | ||
| Annual average sunshine duration | ||
| Environmental condition | Distance from water | |
| Distance from ecological protection zone | ||
| Distance from geological hazards | ||
| Adjacent resources | Distance to residential areas | |
| Distance from highway | ||
| Distance from substation |
| Index | Suitable (4) | Generally Suitable (3) | Unsuitable (2) | Very Unsuitable (1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dem | ≤1000 m | 1001–1800 m | 1801–3000 m | >3000 m |
| Slope | 0°–10° | 10°–15° | 15°–25° | >25° |
| Slope orientation | South, east, southeast | Southwest and northeast | West and northwest | North |
| Annual precipitation | 686–858 mm | 859–946 mm | 946–1230 mm | |
| Annual average temperature | 16–20 °C | 8–15 °C | >20 °C | |
| Annual average surface temperature | 17–19 °C | 15–17 °C | 12–15 °C | |
| Annual average sunshine duration | 2201 h–2400 h | 2001 h–2200 h | <2000 h | |
| Distance from water | >300 m | ≤300 m | ||
| Distance from ecological protection zone | >500 m | ≤500 m | ||
| Distance from geological hazards | >1000 m | 501–1000 m | 300–500 m | <300 m |
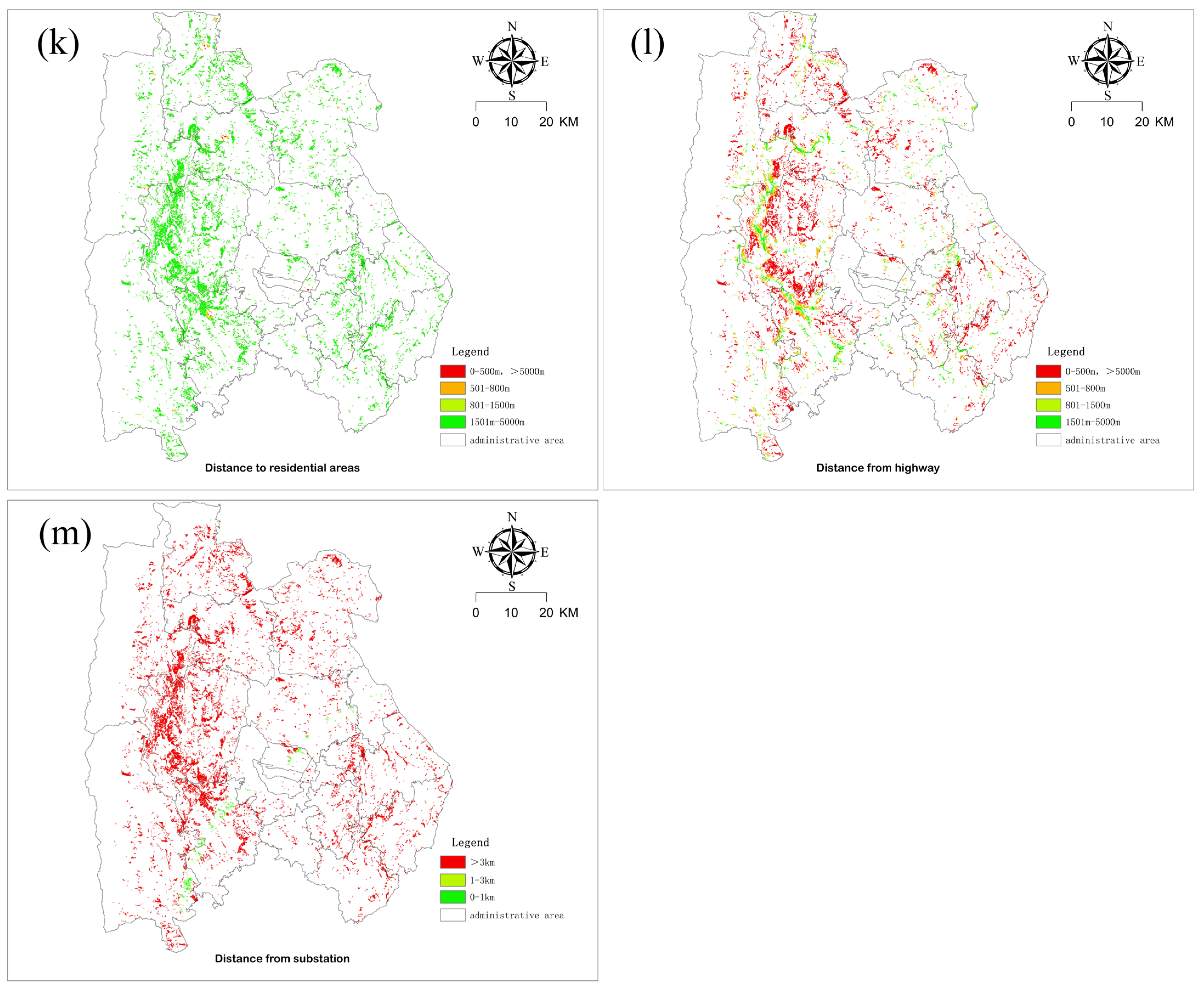
| Distance to residential areas | 1501 m–5000 m | 801–1500 m | 501–800 m | 0–500 m, >5000 m |
| Distance from highway | 1501 m–5000 m | 801–1500 m | 501–800 m | 0–500 m, >5000 m |
| Distance from substation | 0–1 km | 1–3 km | >3 km |
| Scale | Definition | Implication |
|---|---|---|
| 0.5 | Equally important | Both elements are equally important when compared |
| 0.6 | Slightly important | Comparing two elements, one element is slightly more important than the other |
| 0.7 | Obvious importance | One element is significantly more important than the other |
| 0.8 | More important | Comparing the two elements, one element is much more important than the other |
| 0.9 | Extremely important | Comparing two elements, one element is extremely important than the other |
| 0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4 | Inverse comparison | If the judgment is obtained by comparing element ai with element aj,, then the judgment obtained by comparing element aj with element ai is |
| Evaluation Indicators | Landform | Meteorological Condition | Environmental Condition | Adjacent Resources |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Landform | Equally important | Obvious importance | Inverse comparison | Slightly important |
| Meteorological condition | Inverse comparison | Equally important | Inverse comparison | Inverse comparison |
| Environmental condition | Slightly important | More important | Equally important | Obvious importance |
| Adjacent resources | Inverse comparison | Slightly important | Inverse comparison | Equally important |
| Evaluation indicators | Dem | Slope | Slope orientation | |
| Dem | Equally important | Obvious importance | Inverse comparison | |
| Slope | Inverse comparison | Equally important | Inverse comparison | |
| Slope orientation | Slightly important | More important | Equally important | |
| Evaluation indicators | Annual average surface temperature | Annual average temperature | Annual precipitation | Annual average Sunshine duration |
| Annual average surface temperature | Equally important | Inverse comparison | Inverse comparison | Inverse comparison |
| Annual average temperature | More important | Equally important | Slightly important | Obvious importance |
| Annual precipitation | Obvious importance | Inverse comparison | Equally important | Slightly important |
| Annual average Sunshine duration | Slightly important | Inverse comparison | Inverse comparison | Equally important |
| Evaluation indicators | Distance from water | Distance from ecological protection zone | Distance from geological hazards | |
| Distance from water | Equally important | Slightly important | More important | |
| Distance from ecological protection zone | Inverse comparison | Equally important | Obvious importance | |
| Distance from geological hazards | Inverse comparison | Inverse comparison | Equally important | |
| Evaluation indicators | Distance to residential areas | Distance from highway | Distance from substation | |
| Distance to residential areas | Equally important | Slightly important | Inverse comparison | |
| Distance from highway | Inverse comparison | Equally important | Inverse comparison | |
| Distance from substation | Slightly important | Obvious importance | Equally important |
| Goal | Primary Index | First-Order Index Weight | Secondary Index | Secondary Index Weight | Comprehensive Weight |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Evaluation of PV location suitability in Longyang District, Baoshan City | Landform | 0.283 | Elevation | 0.367 | 0.104 |
| Slope | 0.167 | 0.047 | |||
| Slope orientation | 0.467 | 0.132 | |||
| Meteorological condition | 0.150 | Annual average Surface temperature | 0.150 | 0.023 | |
| Annual average temperature | 0.350 | 0.053 | |||
| Annual precipitation | 0.283 | 0.043 | |||
| Annual average Sunshine duration | 0.217 | 0.033 | |||
| Environmental condition | 0.350 | Distance from water | 0.167 | 0.058 | |
| Distance from ecological protection zone | 0.366 | 0.128 | |||
| Distance from geological hazards | 0.467 | 0.163 | |||
| Adjacent resources | 0.217 | Distance to residential areas | 0.333 | 0.072 | |
| Distance from highway | 0.233 | 0.051 | |||
| Distance from substation | 0.433 | 0.094 |
| Location Suitability Analysis | Suitable | Generally Suitable | Unsuitable |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of pixels | 35,201 | 59,782 | 80,179 |
| Area (ha) | 3168.09 | 5380.38 | 7216.11 |
| Proportion (%) | 20.09 | 34.14 | 45.77 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Y.; Zhou, J.; Feng, Z. Location of Mountain Photovoltaic Power Station Based on Fuzzy Analytic Hierarchy Process—Taking Longyang District, Baoshan City, Yunnan Province as an Example. Sustainability 2023, 15, 16955. https://doi.org/10.3390/su152416955
Li Y, Zhou J, Feng Z. Location of Mountain Photovoltaic Power Station Based on Fuzzy Analytic Hierarchy Process—Taking Longyang District, Baoshan City, Yunnan Province as an Example. Sustainability. 2023; 15(24):16955. https://doi.org/10.3390/su152416955
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Yiping, Jingchun Zhou, and Zhanyong Feng. 2023. "Location of Mountain Photovoltaic Power Station Based on Fuzzy Analytic Hierarchy Process—Taking Longyang District, Baoshan City, Yunnan Province as an Example" Sustainability 15, no. 24: 16955. https://doi.org/10.3390/su152416955
APA StyleLi, Y., Zhou, J., & Feng, Z. (2023). Location of Mountain Photovoltaic Power Station Based on Fuzzy Analytic Hierarchy Process—Taking Longyang District, Baoshan City, Yunnan Province as an Example. Sustainability, 15(24), 16955. https://doi.org/10.3390/su152416955





