An Assessment of the Multidimensional Drivers and Determinants of Public Risk Perception of and Behaviors Related to Exposure to Air Pollution in Serbia
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
3. Materials and Methods
- Are you interested in air quality?
- Do you think you are sufficiently informed about the impact of polluted air on health and the environment?
- To what extent do you think air pollution is dangerous to your health (from 1—no dangerous to 5—very dangerous)?
- Has a healthcare professional ever told you or anyone in your household to reduce your level of physical activity outdoors when the air quality was poor?
- A1—Spent less time outdoors;
- A2—Avoided exercise or strenuous physical activity outdoors;
- A3—Avoided opening windows and airing the rooms;
- A4—Avoided busy roads to reduce exposure to air pollution when walking, cycling, or exercising;
- A5—Thought about changing your place of residence;
- A6—Used a face mask;
- A7—Felt irritation of respiratory organs;
- A8—Have been worried about our own health or the health of family members.
4. Results
4.1. Demographic, Socioeconomic, and Health Status Features of the Respondents
4.2. Living-Environment Characteristics
4.3. Perception, Response, and Behavior Related to Air Pollution
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cohen, A.J.; Brauer, M.; Burnett, R.; Anderson, H.R.; Frostad, J.; Estep, K.; Balakrishnan, K.; Brunekreef, B.; Dandona, L.; Dandona, R.; et al. Estimates and 25-year trends of the global burden of disease attributable to ambient air pollution: An analysis of data from the Global Burden of Diseases Study 2015. Lancet 2017, 389, 1907–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Health Effects Institute. State of Global Air 2020. Special Report; Health Effects Institute: Boston, MA, USA, 2020; Available online: https://www.stateofglobalair.org/ (accessed on 1 July 2023).
- WHO. Ambient (Outdoor) Air Pollution. 2022. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/ambient-(outdoor)-air-quality-and-health (accessed on 15 July 2023).
- Fowler, D.; Pyle, J.A.; Sutton, M.A.; Williams, M.L. Global Air Quality, past present and future: An introduction. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A 2020, 378, 20190323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnett, R.; Chena, H.; Szyszkowicza, M.; Fannc, N.; Hubbelld, B.; Pope, C.A., III; Apte, J.S.; Brauer, M.; Cohen, A.; Weichenthal, S.; et al. Global estimates of mortality associated with long-term exposure to outdoor fine particulate matter. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 9592–9597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Hoek, G. Long-term exposure to PM and all-cause and cause-specific mortality: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Environ. Int. 2020, 143, 105974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maji, S.; Ahmed, S.; Kaur-Sidhu, M.; Mor, S.; Ravindra, K. Health Risks of Major Air Pollutants, their Drivers and Mitigation Strategies: A Review. Air Soil Water Res. 2023, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manisalidis, I.; Stavropoulou, E.; Stavropoulos, A.; Bezirtzoglou, E. Environmental and Health Impacts of Air Pollution: A Review. Front. Public Health 2020, 8, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, A.S.; Langrish, J.P.; Nair, H.; McAllister, D.A.; Hunter, A.L.; Donaldson, K.; Newby, D.E.; Mills, N.L. Global association of air pollution and heart failure: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet 2013, 382, 1039–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamichhane, D.K.; Kim, H.C.; Choi, C.M.; Shin, M.H.; Shim, Y.M.; Leem, J.H.; Ryu, J.S.; Nam, H.S.; Park, S.M. Lung Cancer Risk and Residential Exposure to Air Pollution: A Korean Population-Based Case-Control Study. Yonsei Med. J. 2017, 58, 1111–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guxens, M.; Lubczyńska, M.J.; Muetzel, R.L.; Dalmau-Bueno, A.; Jaddoe, V.W.V.; Hoek, G.; van der Lugt, A.; Verhulst, F.C.; White, T.; Brunekreef, B.; et al. Air Pollution Exposure During Fetal Life, Brain Morphology, and Cognitive Function in School-Age Children. Biol. Psychiatry 2018, 84, 295–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadogeorgou, G.; Kioumourtzoglou, M.A.; Braun, D.; Zanobetti, A. Low Levels of Air Pollution and Health: Effect Estimates, Methodological Challenges, and Future Directions. Curr. Environ. Health Rep. 2019, 6, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Environmental Protection Agency of the Republic of Serbia. Annual Report. Air Quality in the Republic of Serbia in 2021 (In Serbian). Belgrade, Serbia, 2022. Available online: http://www.sepa.gov.rs/download/Vazduh_2021.pdf (accessed on 20 June 2023).
- European Environment Agency. 2022; Air Quality in Europe 2022. Report no. 05/2022. Available online: https://www.eea.europa.eu/publications/air-quality-in-europe-2022 (accessed on 10 July 2023).
- Juginović, A.; Vuković, M.; Aranza, I.; Biloš, V. Health impacts of air pollution exposure from 1990 to 2019 in 43 European countries. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 22516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO Reginal Office for Europe. Health Impact of Ambient Air Pollution in Serbia. A Call to Action. 2020. Available online: https://serbia.un.org/en/22141-health-impact-ambient-air-pollution-serbia-call-action (accessed on 10 July 2023).
- Stanojević, G.; Miljanović, D.; Doljak, D.; Ćurčić, N.; Radovanović, M.; Malinović-Milićević, S.; Hauriak, E. Spatio-temporal variability of annual PM2.5 concentrations and population exposure assessment in Serbia for the period 2001–2016. J. Geogr. Inst. Jovan Cvijić SASA 2019, 69, 197–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pignocchino, G.; Di Baldassarre, G.; Mondino, E.; Raffetti, E. Public risk perception of air pollution in the general population of Italy and Sweden during the COVID-19 pandemic: Environmental and socio-demographic drivers. Prev. Med. 2023, 173, 107601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.; Yi, O.; Kim, H. The role of differences in individual and community attributes in perceived air quality. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 425, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Liu, F.; Lu, Y.; Mao, Z.; Lu, H.; Wu, Y.; Chu, Y.; Yu, L.; Liu, Y.; Ren, M.; et al. Factors Affecting Parent’s Perception on Air Quality-From the Individual to the Community Level. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13, 493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmitz, S.; Weiand, L.; Becker, S.; Niehoff, N.; Schwartzbach, F.; von Schneidemesser, E. An assessment of perceptions of air quality surrounding the implementation of a traffic-reduction measure in a local urban environment. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2018, 41, 525–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-Pizza, D.M.; Villada-Canela, M.; Reyna, M.A.; Texcalac-Sangrador, J.L.; Serrano-Lomelin, J.; Osornio-Vargas, Á. Assessing the Influence of Socioeconomic Status and Air Pollution Levels on the Public Perception of Local Air Quality in a Mexico-US Border City. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 4616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, S.J.; Cole, D.C.; Krueger, P.; Voorberg, N.; Wakefield, S. The power of perception: Health risk attributed to air pollution in an urban industrial neighbourhood. Risk Anal. Off. Publ. Soc. Risk Anal. 2019, 19, 621–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bickerstaff, K.; Walker, G. Public understandings of air pollution: The ‘localisation’ of environmental risk. Glob. Environ. Change 2001, 11, 133–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakefield, S.E.L.; Elliott, S.J.; Cole, D.C.; Eyles, J.D. Environmental risk and (re)action: Air quality, health, and civic involvement in an urban industrial neighbourhood. Health Place 2001, 7, 163–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howel, D.; Moffatt, S.; Bush, J.; Dunn, C.E.; Prince, H. Public views on the links between air pollution and health in Northeast England. Environ. Res. 2003, 91, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, F.J.; Fussell, J.C. Air pollution and public health: Emerging hazards and improved understanding of risk. Environ. Geochem. Health 2015, 37, 631–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramírez, O.; Mura, I.; Franco, J.P. How Do People Understand Urban Air Pollution? Exploring Citizens’ Perception on Air Quality, Its Causes and Impacts in Colombian Cities. Open J. Air Pollut. 2017, 6, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reames, G.T.; Bravo, A.M. People, place and pollution: Investigating relationships between air quality perceptions, health concerns, exposure, and individual- and area-level characteristics. Environ. Int. 2019, 122, 244–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bickerstaff, K.; Walker, G. The place(s) of matter: Matter out of place—Public understandings of air pollution. Prog. Hum. Geogr. 2003, 27, 45–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obolkin, V.; Molozhnikova, E.; Shikhovtsev, M.; Netsvetaeva, O.; Khodzher, T. Sulfur and Nitrogen Oxides in the Atmosphere of Lake Baikal: Sources, Automatic Monitoring, and Environmental Risks. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molozhnikova, Y.V.; Shikhovtsev, M.Y.; Netsvetaeva, O.G.; Khodzher, T.V. Ecological Zoning of the Baikal Basin Based on the Results of Chemical Analysis of the Composition of Atmospheric Precipitation Accumulated in the Snow Cover. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 8171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, H.; Wang, Y.; Xie, Y. Analysis of pollutants transport in heavy air pollution processes using a new complex-network-based model. Atmos. Environ. 2023, 292, 119395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Liu, X.; Lang, J.; Zhou, Y.; Wei, L.; Wang, X.; Guo, X. Estimating the contribution of regional transport to PM2.5 air pollution in a rural area on the North China Plain. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 583, 280–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Liu, Q.; Bian, Y.; Feng, L.; Zhao, D.; Wang, S.; Zhao, H.; Gao, K.; Xu, Z. Analysis of transport path and source distribution of winter air pollution in Shenyang. Open Geosci. 2021, 13, 1105–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, X.; Shen, X.; Li, X.; Wu, B.; Chen, W.; Yao, Z. Analysis of air pollution characteristics, transport pathways and potential source areas identification in Beijing before, during and after the COVID-19 outbreak. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 982566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossberndt, S.; Bartonova, A.; Ortiz, A.G. Public Awareness and Efforts to Improve Air Quality in Europe. Eionet Report—ETC/ATNI 2020/2. Available online: https://www.eionet.europa.eu/etcs/etc-atni/products/etc-atni-reports/etc-atni-report-2-2020-public-awareness-and-efforts-to-improve-air-quality-in-europe (accessed on 5 June 2023).
- Maione, M.; Mocca, E.; Eisfeld, K.; Kazepov, Y.; Fuzzi, S. Public perception of air pollution sources across Europe. Ambio 2020, 50, 1150–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canha, N.; Justino, A.R.; Gamelas, C.A.; Almeida, S.M. Citizens’ Perception on Air Quality in Portugal—How Concern Motivates Awareness. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 12760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lynch, K.M.; Mirabelli, M.C. Outdoor Air Quality Awareness, Perceptions, and Behaviors Among U.S. Children Aged 12–17 Years, 2015–2018. J. Adolesc. Health 2021, 68, 882–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.Y.; Kobernus, M.; Liu, H. Public Perception Survey Study on Air Quality Issues in Wuhan, China. J. Environ. Prot. 2017, 8, 1194–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhu, H.; Hu, Y.; Feng, S.; Chu, Y.; Wu, Y.; Wang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Yuan, Z.; Lu, Y. Public’s Health Risk Awareness on Urban Air Pollution in Chinese Megacities: The Cases of Shanghai, Wuhan and Nanchang. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13, 845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Commission. 2022; Special Eurobarometer 524 Report. Attitudes of European towards Air Quality. Available online: https://europa.eu/eurobarometer/surveys/detail/2660 (accessed on 5 July 2023).
- Pfleger, E.; Adrian, C.; Lutz, R.; Drexler, H. Science communication on the public health risks of air pollution: A computational scoping review from 1958 to 2022. Arch. Public Health 2023, 81, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarron, A.; Semple, S.; Braban, C.F.; Swanson, V.; Gillespie, C.; Price, H.D. Public engagement with air quality data: Using health behaviour change theory to support exposure-minimising behaviours. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2023, 33, 321–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bickerstaff, K.; Walker, G. Clearing the smog? Public responses to air-quality information. Local Environ. 1999, 4, 279–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riley, R.; de Preux, L.; Capella, P.; Mejla, C.; Kajikawa, Y.; de Nazelle, A. How do we effectively communicate air pollution to change public attitudes and behaviours? A review. Sustain. Sci. 2021, 16, 2027–2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez, A.S.; Ramondt, S.; Van Bogart, K.; Perez-Zuniga, R. Public Awareness of Air Pollution and Health Threats: Challenges and Opportunities for Communication Strategies to Improve Environmental Health Literacy. J. Health Commun. 2019, 24, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gravetter, F.J.; Wallnau, L.B. Statistics for the Behavioral Sciences, 9th ed.; Thompson Wadsworth: Belmont, CA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Statistical Office of the Republic of Serbia. Average Salaries and Wages per Employee. May 2023. Available online: https://www.stat.gov.rs/en-US/vesti/statisticalrelease/?p=13646&a=24&s=2403?s=2403 (accessed on 5 August 2023).
- Environmental Protection Agency of the Republic of Serbia. Annual Report. Air Quality in the Republic of Serbia in 2017 Belgrade, Serbia. 2018; (In Serbian). Available online: http://www.sepa.gov.rs/download/VAZDUH2017.pdf (accessed on 20 June 2023).
- WHO Global Air Quality Guidelines. Particulate Matter (PM2.5 and PM10), Ozone, Nitrogen Dioxide, Sulfur Dioxide and Carbon Monoxide. 2021. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240034228 (accessed on 28 June 2023).
- Smallbone, K. Individuals’ Interpretation of Air Quality Information. Available online: https://uk-air.defra.gov.uk/assets/documents/reports/cat14/1210261047_Individuals_interpretation_of_air_quality_information_customer_insight_&_awareness_study.pdf (accessed on 27 June 2023).
- Oltra, C.; Sala, R.A. Review of the social research on public perception and engagement practices in urban air pollution. Inf. Técnicos Ciemat 2014, 1317. Available online: https://inis.iaea.org/collection/NCLCollectionStore/_Public/45/046/45046419.pdf?r=1 (accessed on 3 July 2023).
- Mirabelli, M.C.; Boehmer, T.K.; Damon, S.A.; Sircar, K.D.; Wall, H.K.; Yip, F.Y.; Zahran, H.S.; Garbe, P.L. Air Quality Awareness Among U.S. Adults with Respiratory and Heart Disease. Am. J. Prev. Med. 2018, 54, 679–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Official Gazette of the Republic of Serbia. Strategy for Prevention and Control of Chronic Non-Communicable Diseases (In Serbian). 05 Number: 500-1597/2009-1. 2009. Available online: https://www.pravno-informacioni-sistem.rs/SlGlasnikPortal/eli/rep/sgrs/vlada/strategija/2009/22/2 (accessed on 3 August 2023).
- Simoni, M.; Baldacci, S.; Maio, S.; Cerrai, S.; Sarno, G.; Viegi, G. Adverse effects of outdoor pollution in the elderly. J. Thorac. Dis. 2015, 7, 34–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Environment Agency, Air Pollution and Children’s Health. 2023. Available online: https://www.eea.europa.eu/publications/air-pollution-and-childrens-health (accessed on 15 July 2023).
- Sekar, A.; Jasna, R.S.; Binoy, B.V.; Mohan, P.; Varghese, G.K. Air quality change and public perception during the COVID-19 lockdown in India. Gondwana Res. 2023, 114, 15–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lou, B.; Barbieri, D.M.; Passavanti, M.; Hui, C.; Gupta, A.; Hoff, I.; Lessa, D.A.; Sikka, G.; Chang, K.; Fang, K.; et al. Air pollution perception in ten countries during the COVID-19 pandemic. Ambio 2022, 51, 531–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedi, T.K.; Bhattacharya, S.P. An Investigative Study on Perceived Indoor Air Quality During COVID-19 Lockdown in India. J. Inst. Eng. India Ser. A 2021, 102, 885–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rives, R.; Elshorbany, Y.; Kaylor, S. The Relationship Between Air Quality, Health Outcomes, and Socioeconomic Impacts of the COVID-19 Pandemic in the US. GeoHealth 2023, 7, e2022GH000735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kangas, T.; Gadeyne, S.; Lefebvre, W.; Vanpoucke, C.; Rodriguez-Loureiro, L. Are air quality perception and PM2.5 exposure differently associated with cardiovascular and respiratory disease mortality in Brussels? Findings from a census-based study. Environ. Res. 2023, 219, 115180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Hao, C.; Huang, L.; Qiu, X.; Chen, X. Significant importance of negative affect and satisfaction with local governmental air control of objective air pollution, perceived air quality, and pro-environmental behavior relationships. J. Public Health 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Lu, C. Air Quality, Pollution Perception, and Residents’ Health: Evidence from China. Toxics 2023, 11, 591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
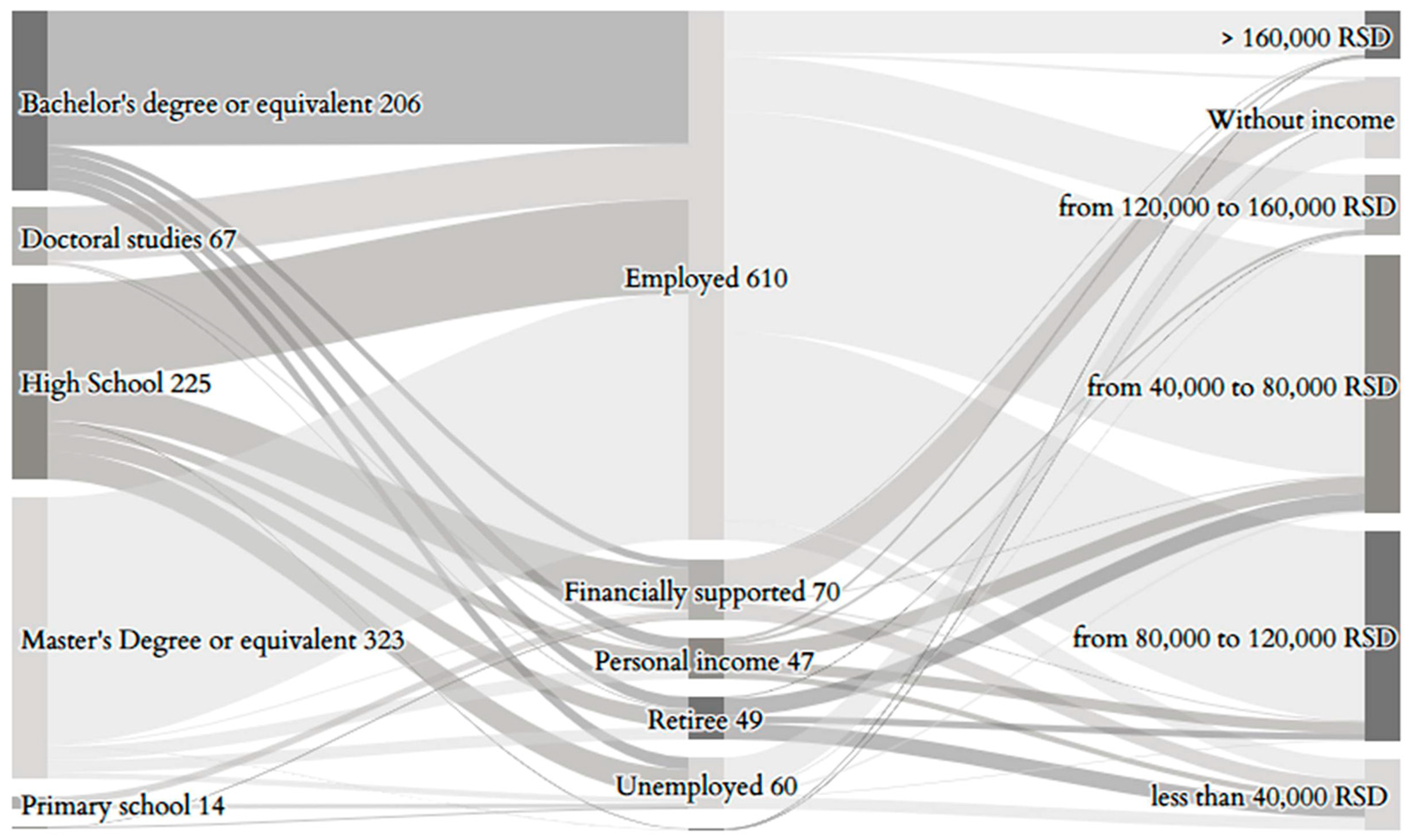
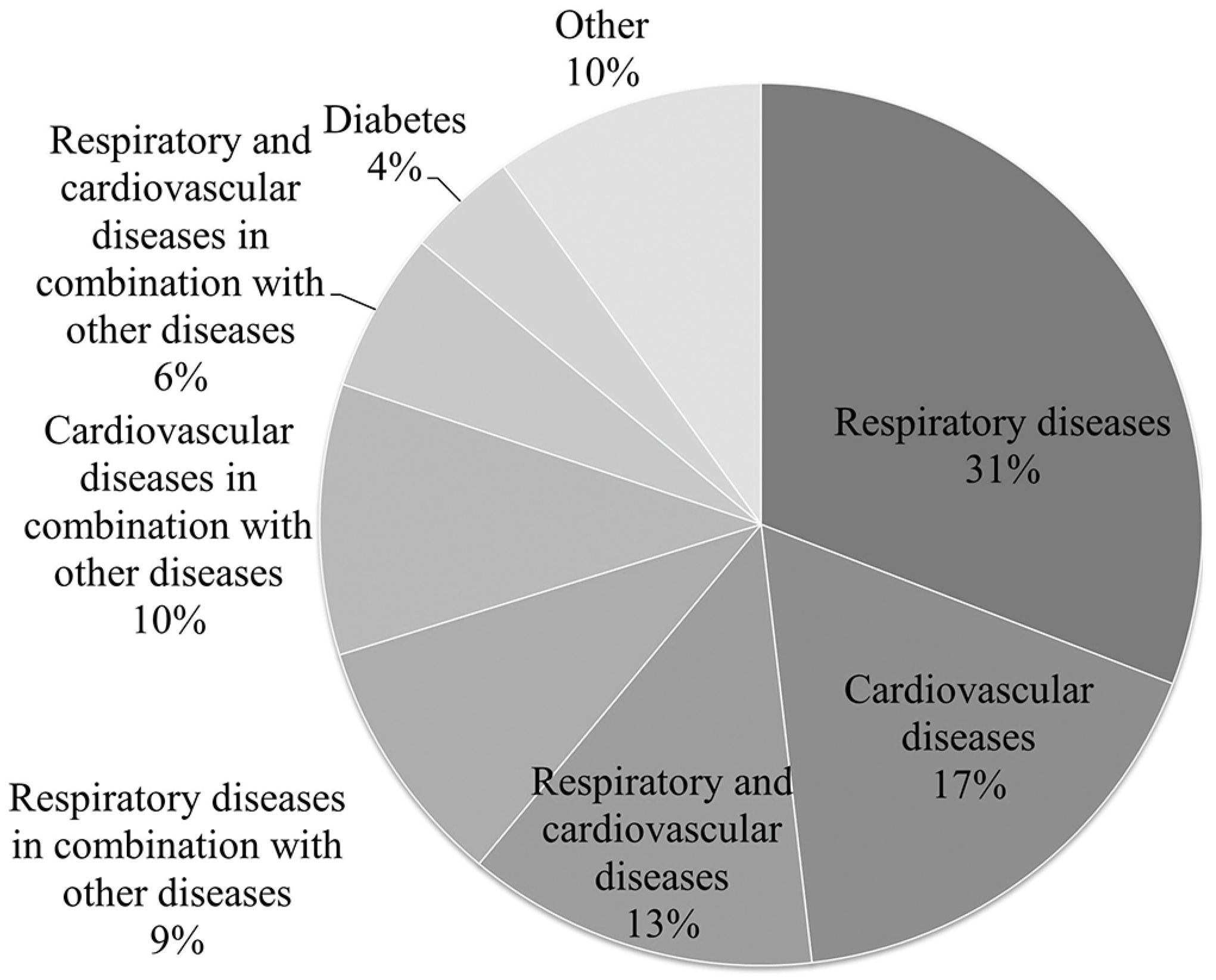

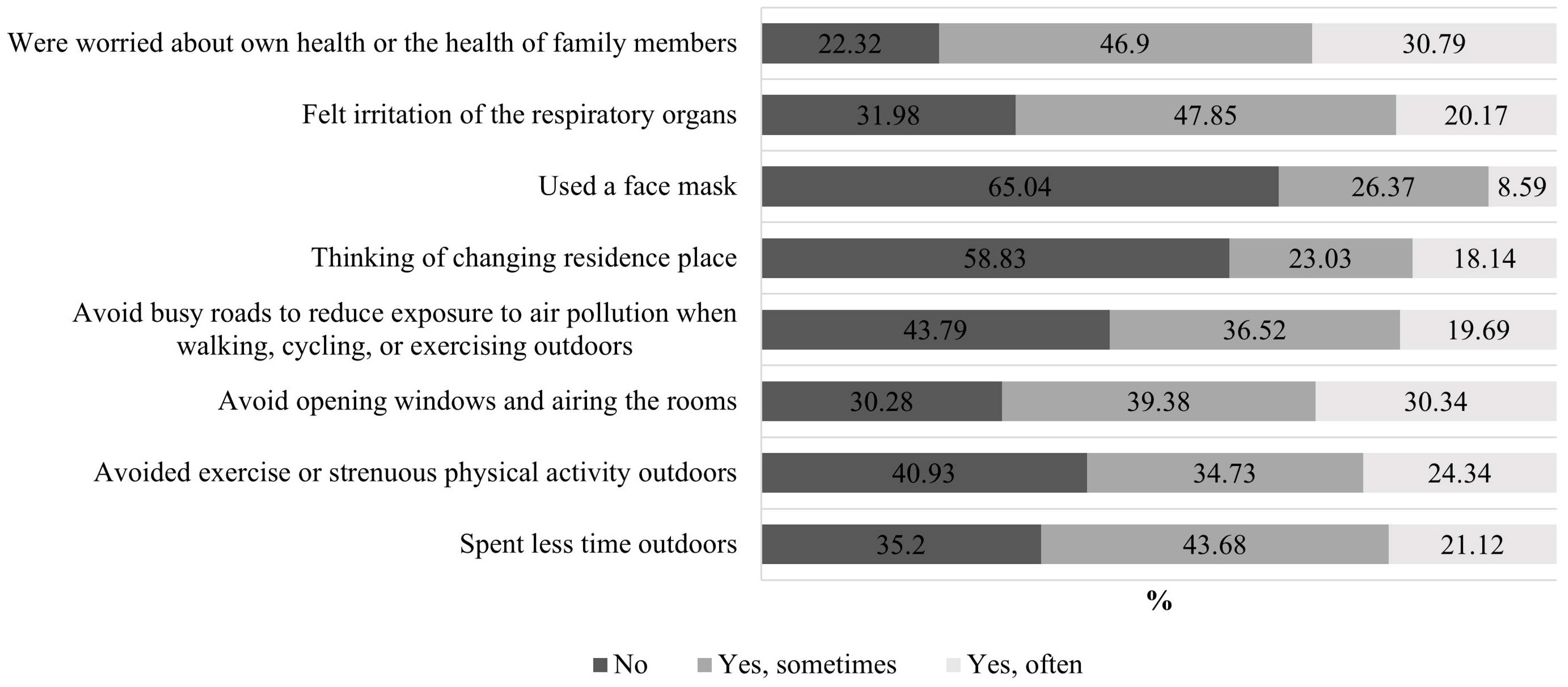
| Category | Respondents Abs. | Respondents % | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age | ≤19 | 41 | 4.89 |
| 20–39 | 358 | 42.72 | |
| 40–64 | 399 | 47.61 | |
| ≥65 | 40 | 4.77 | |
| Gender | Female | 533 | 63.60 |
| Male | 305 | 36.40 | |
| Education | Without education | 3 | 0.36 |
| Primary school | 14 | 1.69 | |
| High school | 225 | 27.17 | |
| Bachelor’s degree or equivalent | 206 | 24.88 | |
| Master’s degree or equivalent | 323 | 39.01 | |
| Doctoral studies | 67 | 8.09 | |
| Employment | Unemployed | 60 | 7.23 |
| Employed | 610 | 73.67 | |
| Retiree | 49 | 5.92 | |
| Financially dependent | 70 | 8.45 | |
| Personal income | 47 | 5.68 | |
| Other | 2 | 0.24 | |
| Monthly income | Without income | 93 | 11.23 |
| RSD < 40,000 | 81 | 9.78 | |
| RSD 40,000–80,000 | 297 | 35.87 | |
| RSD 80,000–120,000 | 241 | 29.11 | |
| RSD 120,000–160,000 | 70 | 8.45 | |
| RSD > 160,000 | 56 | 6.67 |
| Category | Respondents Abs. | Respondents % | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of household members | 1 | 93 | 11.10 |
| 2 | 175 | 20.88 | |
| 3 | 193 | 23.03 | |
| 4 | 207 | 24.70 | |
| ≥5 | 170 | 20.29 | |
| Household members ≤ 12 years | No | 480 | 57.28 |
| Yes | 358 | 42.72 | |
| Household members 13–18 years | No | 629 | 75.06 |
| Yes | 209 | 24.94 | |
| Household members ≥ 65 years | No | 613 | 73.15 |
| Yes | 225 | 26.85 |
| Do You or Someone in Your Household Suffer from a Chronic Disease? | Respondents Abs. | Respondents % |
|---|---|---|
| Yes | 272 | 32.46 |
| No | 513 | 61.22 |
| I don’t want to answer | 53 | 6.32 |
| Category | Respondents Abs. | Respondents % | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Type of housing facility | House | 366 | 43.68 |
| Flat | 472 | 56.32 | |
| Settlement type | Dominant individual housing (houses) | 308 | 36.75 |
| Dominant collective housing (buildings) | 254 | 30.31 | |
| Mixed (houses and buildings) | 276 | 32.94 | |
| Traffic intensity 1 (low intensity) to 5 (high intensity) | 1 | 17 | 2.03 |
| 2 | 72 | 8.59 | |
| 3 | 252 | 30.07 | |
| 4 | 240 | 28.64 | |
| 5 | 257 | 30.67 | |
| Type of heating | Individual—wood | 153 | 18.26 |
| Individual—gas | 94 | 11.22 | |
| Individual—electricity | 171 | 20.41 | |
| Individual—coal | 5 | 0.60 | |
| Individual—pellet | 80 | 9.67 | |
| Individual—mixed | 50 | 5.97 | |
| Remote heating systems | 275 | 32.82 | |
| Other (heating pumps, geothermal energy, fuel oil, etc.) | 10 | 1.19 | |
| Proximity to industry | Yes | 312 | 37.23 |
| No | 526 | 62.77 |
| Age | Gender | Education | Employment | Income | Household Members | Haus. Memb. ≤ 12 Years | Haus. Memb. 13–18 Years | Haus. Memb. ≥ 65 Years | Chronic Diseases | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| χ2 | 11.446 | 2.949 | 10.146 | 12.474 | 16.622 | 6.749 | 0.120 | 1.826 | 4.203 | 2.467 |
| p | 0.076 | 0.566 | 0.255 | 0.131 | 0.083 | 0.564 | 0.942 | 0.401 | 0.122 | 0.300 |
| V | 0.083 | 0.030 | 0.078 | 0.086 | 0.010 | 0.064 | 0.012 | 0.047 | 0.071 | 0.044 |
| Settlement Population Size | Type of Housing Facility | Settlement Type | Heating Type | Traffic Intensity | Industry | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| χ2 | 20.100 | 0.776 | 2.5045 | 19.281 | 12.461 | 1.623 |
| p | 0.127 | 0.685 | 0.644 | 0.037 | 0.052 | 0.443 |
| V | 0.110 | 0.030 | 0.039 | 0.108 | 0.086 | 0.044 |
| Gender | Type of Housing Facility | Industry | Chronic Diseases | Household Members ≤ 12 Years | Household Members 13–18 Years | Household Members ≥ 65 Years | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| U | 70,335 | 96,625.5 | 77,116 | 81,507 | 88,867 | 58,768.5 | 65,130.5 |
| p | <0.001 | 0.001 | 0.110 | <0.001 | 0.351 | 0.012 | 0.176 |
| z | −3.564 | 3.237 | −1.600 | 4.255 | 0.933 | 2.520 | −1.354 |
| r | 0.12 | 0.11 | 0.006 | 0.15 | 0.032 | 0.009 | 0.047 |
| Age | Population Size | Education | Employment | Income | Heating Type | Traffic Intensity | Settlement Type | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| χ2 | 28.52 | 9.83 | 44.43 | 20.90 | 24.7 | 16.15 | 27.12 | 3.49 |
| p | <0.001 | 0.198 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.008 | <0.001 | 0.174 |
| η2 | 0.031 | / | 0.004 | 0.020 | 0.024 | 0.014 | 0.029 | / |
| α | 0.008 | / | 0.005 | 0.005 | 0.003 | / | 0.008 | / |
| A1 | A2 | A3 | A4 | A5 | A6 | A7 | A8 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | χ2 | 23.239 | 25.020 | 16.839 | 32.4966 | 18.909 | 5.897 | 8.487 | 13.834 |
| p | 0.001 | 0.000 | 0.010 | <0.001 | 0.004 | 0.435 | 0.205 | 0.032 | |
| V | 0.118 | 0.122 | 0.100 | 0.139 | 0.106 | 0.059 | 0.071 | 0.091 | |
| Gender | χ2 | 6.577 | 5.757 | 6.103 | 4.721 | 0.837 | 20.261 | 18.781 | 7.911 |
| p | 0.037 | 0.056 | 0.047 | 0.094 | 0.658 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.019 | |
| V | 0.089 | 0.083 | 0.085 | 0.075 | 0.032 | 0.155 | 0.150 | 0.097 | |
| Education | χ2 | 50.884 | 46.323 | 33.634 | 40.767 | 32.736 | 10.101 | 19.065 | 27.770 |
| p | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.258 | 0.015 | 0.001 | |
| V | 0.175 | 0.167 | 0.142 | 0.156 | 0.140 | 0.0780 | 0.107 | 0.129 | |
| Employment | χ2 | 27.645 | 18.192 | 32.855 | 25.905 | 30.255 | 8.157 | 7.276 | 24.144 |
| p | 0.001 | 0.020 | <0.001 | 0.001 | <0.001 | 0.418 | 0.507 | 0.002 | |
| V | 0.129 | 0.104 | 0.1402 | 0.124 | 0.135 | 0.070 | 0.067 | 0.120 | |
| Monthly income | χ2 | 35.327 | 25.937 | 26.403 | 18.264 | 21.775 | 8.712 | 10.075 | 30.075 |
| p | <0.001 | 0.004 | 0.003 | 0.051 | 0.016 | 0.560 | 0.434 | 0.001 | |
| V | 0.145 | 0.124 | 0.126 | 0.104 | 0.114 | 0.072 | 0.078 | 0.1340 | |
| Household members | χ2 | 21.579 | 10.708 | 16.626 | 9.633 | 13.342 | 9.491 | 6.497 | 8.283 |
| p | 0.006 | 0.219 | 0.034 | 0.292 | 0.073 | 0.303 | 0.594 | 0.406 | |
| V | 0.1135 | 0.080 | 0.100 | 0.076 | 0.093 | 0.075 | 0.062 | 0.070 | |
| Household members ≤ 12 years | χ2 | 8.878 | 3.630 | 3.351 | 2.710 | 2.361 | 1.173 | 0.707 | 6.860 |
| p | 0.012 | 0.163 | 0.187 | 0.258 | 0.307 | 0.556 | 0.702 | 0.032 | |
| V | 0.103 | 0.066 | 0.063 | 0.057 | 0.053 | 0.037 | 0.029 | 0.090 | |
| Household members 13–18 years | χ2 | 20.448 | 15.714 | 4.001 | 3.896 | 10.323 | 2.602 | 8.526 | 13.179 |
| p | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.135 | 0.143 | 0.001 | 0.272 | 0.014 | 0.001 | |
| V | 0.156 | 0.137 | 0.069 | 0.068 | 0.111 | 0.056 | 0.101 | 0.125 | |
| Household members ≤ 65 years | χ2 | 1.591 | 0.629 | 13.180 | 1.354 | 7.798 | 2.467 | 1.130 | 1.952 |
| p | 0.451 | 0.730 | 0.001 | 0.508 | 0.020 | 0.291 | 0.568 | 0.377 | |
| V | 0.044 | 0.027 | 0.125 | 0.040 | 0.097 | 0.054 | 0.037 | 0.048 | |
| Chronic diseases | χ2 | 15.497 | 18.339 | 16.194 | 10.637 | 13.695 | 6.950 | 44.385 | 41.448 |
| p | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.005 | 0.001 | 0.031 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |
| V | 0.141 | 0.153 | 0.144 | 0.116 | 0.132 | 0.094 | 0.238 | 0.224 | |
| A1 | A2 | A3 | A4 | A5 | A6 | A7 | A8 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Settlement population size | χ2 | 62.245 | 38.416 | 62.453 | 19.324 | 44.465 | 21.867 | 33.058 | 50.611 |
| p | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.153 | <0.001 | 0.0814 | 0.003 | <0.001 | |
| V | 0.196 | 0.152 | 0.193 | 0.108 | 0.163 | 0.144 | 0.142 | 0.170 | |
| Type of housing facility | χ2 | 9.916 | 5.481 | 15.067 | 4.393 | 29.531 | 9.560 | 8.640 | 14.225 |
| p | 0.007 | 0.064 | 0.001 | 0.111 | <0.001 | 0.008 | 0.013 | <0.001 | |
| V | 0.109 | 0.081 | 0.1341 | 0.072 | 0.188 | 0.107 | 0.102 | 0.130 | |
| Settlement type | χ2 | 4.249 | 5.168 | 11.917 | 5.563 | 20.230 | 14.889 | 9.411 | 14.670 |
| p | 0.373 | 0.271 | 0.018 | 0.234 | <0.001 | 0.005 | 0.052 | 0.005 | |
| V | 0.050 | 0.055 | 0.084 | 0.058 | 0.110 | 0.094 | 0.075 | 0.094 | |
| Heating type | χ2 | 21.313 | 18.207 | 25.366 | 9.085 | 39.372 | 14.332 | 17.083 | 16.927 |
| p | 0.019 | 0.052 | 0.005 | 0.524 | <0.001 | 0.158 | 0.073 | 0.076 | |
| V | 0.114 | 0.105 | 0.124 | 0.074 | 0.155 | 0.093 | 0.102 | 0.101 | |
| Traffic intensity | χ2 | 17.544 | 10.869 | 24.048 | 26.176 | 35.787 | 7.783 | 23.185 | 30.427 |
| p | 0.008 | 0.092 | 0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.254 | 0.001 | <0.001 | |
| V | 0.102 | 0.081 | 0.120 | 0.125 | 0.146 | 0.068 | 0.118 | 0.135 | |
| Industry | χ2 | 0.640 | 2.105 | 0.362 | 0.962 | 4.479 | 2.501 | 2.615 | 6.180 |
| p | 0.887 | 0.349 | 0.835 | 0.618 | 0.107 | 0.286 | 0.271 | 0.047 | |
| V | 0.019 | 0.050 | 0.021 | 0.034 | 0.073 | 0.055 | 0.056 | 0.085 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stanojević, G.; Malinović-Milićević, S.; Ćurčić, N.B.; Radovanović, M.; Radivojević, A.; Popović, T.; Ćurčić, S. An Assessment of the Multidimensional Drivers and Determinants of Public Risk Perception of and Behaviors Related to Exposure to Air Pollution in Serbia. Sustainability 2023, 15, 16901. https://doi.org/10.3390/su152416901
Stanojević G, Malinović-Milićević S, Ćurčić NB, Radovanović M, Radivojević A, Popović T, Ćurčić S. An Assessment of the Multidimensional Drivers and Determinants of Public Risk Perception of and Behaviors Related to Exposure to Air Pollution in Serbia. Sustainability. 2023; 15(24):16901. https://doi.org/10.3390/su152416901
Chicago/Turabian StyleStanojević, Gorica, Slavica Malinović-Milićević, Nina B. Ćurčić, Milan Radovanović, Aleksandar Radivojević, Teodora Popović, and Srećko Ćurčić. 2023. "An Assessment of the Multidimensional Drivers and Determinants of Public Risk Perception of and Behaviors Related to Exposure to Air Pollution in Serbia" Sustainability 15, no. 24: 16901. https://doi.org/10.3390/su152416901
APA StyleStanojević, G., Malinović-Milićević, S., Ćurčić, N. B., Radovanović, M., Radivojević, A., Popović, T., & Ćurčić, S. (2023). An Assessment of the Multidimensional Drivers and Determinants of Public Risk Perception of and Behaviors Related to Exposure to Air Pollution in Serbia. Sustainability, 15(24), 16901. https://doi.org/10.3390/su152416901









