Abstract
Phycoremediation of wastewater with microalgae is a viable option and is considered a process for cleaning up toxic waste using microalgae or macroalgae. Most water is modified by its use and must be treated before discharge. Given this situation, and following the example of other researchers around the world, our study focuses on the filtration method and combines it with the microalgae method to treat domestic wastewater. The aim of our work is to study the effects of using the microalgae system in combination with the decontamination and filtration system to reduce the nutrient content of domestic wastewater. The coupling of the two methods produced very significant results. However, the removal efficiencies for the filtered effluent increased to 86.34%, 100%, and 91.12% for COD, ammonia, and phosphate, respectively. The algae treatment offers an ecologically safe and less expensive system for nutrient removal and eliminates the need for tertiary treatment, which refers to the filtered treatment effluent, allowing us to conclude that the Chlorella vulgaris species has a very interesting influence on dissolved oxygen and that it had a very remarkable effect on COD, with a maximum reduction that reached 80%. The results obtained show that the phosphate content of the treated wastewater was significantly reduced during the cultivation period. In time, a decrease in solids was observed within the microalgae treatment system, influenced by the use of two different types of microalgae and the incorporation of the filtration system, which is based on the use of biosorption of methylene blue by biomass. The parameters analyzed in this study are hydrogen potential (pH), ammonia (NH3), phosphate ion (PO43−), chemical oxygen demand (COD), electrical conductivity (EC), total solids (TS), total dissolved solids (TDS), total suspended solids (TSS), nitrates, and dissolved oxygen (DO).
1. Introduction
Wastewater must be properly treated before it is discharged as it also contains organic and inorganic pathogens and polluting micro-organisms that could lead to the deterioration of the water bodies received and be detrimental in terms of safety and public health [1]. Water is considered a fundamental source of life, an essential substrate for sustaining all forms of life, including plants, animals, and humans. In order to ensure sustainable economic development, Morocco has to face a number of worrying changes and challenges: economic, social, and environmental [2,3]. In this context, there is no doubt that water scarcity is one of the major problems of the century that many countries around the world are facing [4]. Natural resources can be divided into two main types: surface water, such as freshwater ponds, rivers, and streams, and groundwater, such as springs and groundwater [5]. Only 0.5% of the planet’s water is freshwater, and its consumption is increasing with population growth and industrial activity, resulting in 380,000 billion liters of wastewater worldwide [6]. It is predicted that, by 2050, more than 50% of the world’s population will face chronic water shortages, requiring the recycling of wastewater [7]. Domestic wastewater is made up of blackwater, greywater, rainwater, and sometimes industrial wastewater [8,9]. A wide range of compounds are commonly found in domestic wastewater. These include oxygen-demanding wastes and organic and inorganic chemicals [10,11,12]. The technologies most commonly used to remove heavy metals from the environment include traditional processes such as chemical precipitation, filtration, chemical oxidation and reduction, reverse osmosis and evaporation techniques, as well as electrochemical processes [13,14,15,16,17]. There are a number of environmentally friendly techniques for treating wastewater, including those based on microalgae, which are highly promising alternatives for removing pathogens, heavy metals, nutrients, and various other contaminants from water [18]. Chlorella is a microscopic green alga. It has been used in wastewater treatment as an effective means of removing pollutants [19]. Extensive research into the biotechnological development of algae over the last few decades has led to the development of a system of wastewater treatment using algae, particularly microalgae, to reduce a range of organic nutrients, inorganic products, and highly hazardous substances [20]. According to studies currently being carried out by a number of researchers, using microalgae to treat wastewater and valorizing the resulting biomass for energy production is doubly interesting [21,22]. For wastewater treatment, the use of microalgae is known as phycoremediation, the benefit of which is the removal or biotransformation of pollutants, including nutrients, from wastewater [23]. Today, phycoremediation is widely used to reduce pollutant loads because it is recognized as not only the ideal option for pollution control but also as one of the most successful innovative technologies using biological processes to treat contamination [24,25,26]. Filtration is recognized as one of the most widely used methods for separating solids and liquids through a porous membrane. It can be classified into dead-end filtration, vacuum filtration, pressure filtration, and tangential flow filtration (such as microfiltration, ultrafiltration, macrofiltration, nanofiltration, and reverse osmosis) [27,28]. Due to their ability to collect low-density microalgae such as Chlorella species, filtration-based biomass collection techniques have proven to be the most effective [29]. A solid–liquid separation process is used to filter the microalgae cells, using a semi-permeable barrier with small pores to collect and filter the microalgae cells [30]. Biomass collection by filtration has proven to be one of the most successful techniques due to its ability to collect low-density microalgae such as Chlorella species [31,32,33,34,35].
The aim of this study is to evaluate the different physicochemical parameters of domestic wastewater with the intervention of Chlorella vulgaris by combining the method based on microalgae called phycoremediation and the method of filtration with biosorption of domestic wastewater by agricultural biomass. By this coupling of methods, we will evaluate the percentage of maximum elimination in relation to the concentration of the given microalgae, which are characterized as very important agents in the reduction in solids, as well as in the reduction in carbon dioxide. The aim is to demonstrate the efficacy of Chlorella vulgaris in assimilating nutrients and reducing contamination in order to alleviate the current problems of water degradation. In this respect, the study aims to address the following aspects:
- The evaluation of different physicochemical parameters on domestic wastewater.
- The effectiveness of Chlorella vulgaris in enhancing dissolved oxygen (DO) concentrations on domestic wastewater.
- The ability of Chlorella vulgaris to reduce chemical oxygen demand (COD), total dissolved solids (TDS), and total suspended solids (TSS) in domestic wastewater.
- Chlorella vulgaris’ performance in the uptake and removal of ammonia and phosphate (P) nutrients in domestic wastewater.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chlorella vulgaris Preparation
2.1.1. Selection of Algal Species
The alga Chlorella vulgaris was chosen for this study because it is easy to grow in the laboratory. It can produce phytochelatins in response to metals and is well known in the research world for its use in detecting trace metals. It also contains proteins and minerals, making it useful for biomass production on a commercial scale. This study focuses on two species of Chlorella vulgaris. They were obtained from a research laboratory in Marrakech and are used to treat domestic wastewater.
2.1.2. Culture Condition
The study was carried out on two beakers, the characteristics of which are summarized in Table 1 and Figure 1, and the filtration system is provided by an air-lift system. We have used two beakers of borosilicate glass with 2 L and a useful volume of 180 L. We have two beakers with an equivalent volume (30% microalgae), which explains the volume introduced of about 540 mL of microalgae, and then complete the rest of the beaker with raw domestic wastewater (remaining 1260 mL), which means that the total volume of work is 1800 mL. In the previous study, it was found that 30% of the concentrations of microalgae had a very high efficiency in elimination compared to the other concentrations [36]. For this reason, the study was carried out with a percentage of 30% of microalgae to optimize the retention time, while varying the oxygenation time by a difference of 2 h (between 2, 4, 6, ..., 24), with the following hour for each oxygenation time a decanting, respectively. Due to its ease of cultivation, rapid development, ability to withstand difficult growing conditions, high nutritional value, and numerous biologically active chemicals, the use of Chlorella vulgaris in wastewater bioremediation has been reported in the literature [37]. Chlorella vulgaris is a species of microscopic green algae, according to the classification Chlorophyta. They are characterized by their rounded, subspherical, or ellipsoidal shape, dimensions between 2 and 10 μm, immobility, and unique cup-shaped chloroplast with or without visible pyrenoids. In the chloroplasts, they store the photosynthetic compounds chlorophyll a and b. As shown in the figures below, these come in the form of single cells or columns. Chlorella vulgaris reproduces asexually by the formation of autospores. This microalgae species has been widely used in wastewater treatment due to its high growth rate and excellent nutrient uptake capacity [38,39].

Table 1.
Raw wastewater characteristics.
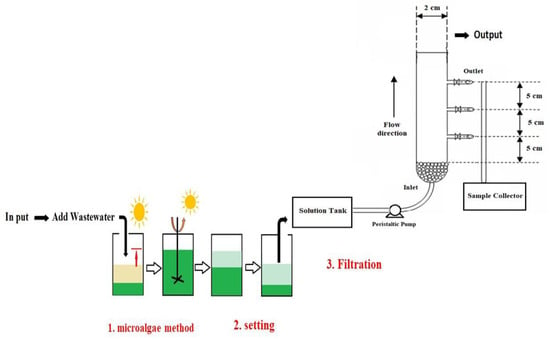
Figure 1.
Treatment system using the Microalgae method and filtration.
2.2. Analysis and Sampling of Wastewater
Fluctuations in the volume and strength of effluent are related to errors in the analysis of physicochemical water parameters or failure to meet effluent discharge standards for treatment. In this study, we used standard test procedures, as outlined in APHA 2012, to analyze parameters such as hydrogen potential (pH), such that the proposed value for wastewater required for microalgae growth is between 6.5 and 7.0, i.e., a value close to neutrality, Ammonia (NH3), Phosphate (PO43−), Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD), Electrical Conductivity (EC), where the conductivity probe is used to measure the electric current that flows between electrons and gives a conductance measurement in micro-siemens per centimeter (μS/cm) or micrometers per centimeter (μm/cm), Total Solids (TS), Total Dissolved Solids (TDS), but the TDS value must not exceed 1000 mg/L if the water is unfit for consumption, or 2000 mg/L if the filtration system has a maximum filtration capacity, Total Suspended Solids (TSS), Nitrates and Dissolved Oxygen (DO).
Domestic wastewater collected from a wastewater pumping station; the wastewater was stored in a cooler and then taken to the analysis laboratory for analysis without any pre-treatment.
2.3. Processing Methodology
Filtration System
The helical airlift photobioreactor consists of an airlift and a helical section. The airlift is divided into two sections. The ascending column is a transparent cylinder made of polymethyl methacrylate. The gas is injected at the bottom of the ascending column by means of a diffuser consisting of 24 holes of 2 mm diameter arranged in a star shape. The descending column is a second polymethyl methacrylate cylinder with a larger diameter than the ascending column, which surrounds it. It is placed at a height of 54 cm from the base of the riser, creating an annular space at the top of the airlift. The spiral section is a semi-transparent “tubclair” tube wrapped around a metal structure. The spirals are superimposed. The bottom of the helix is connected to the bottom of the ascending column, and the bottom of the descending column is connected to the top of the helix section. Experiments on wastewater biosorption by agricultural biomass from the Sahara region of Morocco were carried out in flow-through mode, using a column with an internal diameter of 20 mm and a layer of glass wool at the bottom. The wastewater liquid was removed by a peristaltic pump as shown in Figure 1.
The pigment was added to a packing bed loaded with agricultural biomass from the Moroccan Sahara after the effluent solution was discharged with an initial concentration of C0. Each time, the effluent was sampled at the column outlet and analyzed using a Shimadzu UV–Vis spectrophotometer at λ = 664 nm.
As time passes, the sorption front descends towards the saturation zone. It reaches the lower end of the conditioned bed. The effluent concentration exiting the column then becomes progressively closer to the initial concentration, representing column saturation. When the effluent concentration at the column outlet is 5% of the initial concentration, this is the breakthrough time (TB) for fixed bed adsorption. Once the effluent concentration has risen to a level between 90% and 95% of the initial concentration, the effluent exhaustion time (ET) is determined.
It can describe the optimal retention time by that which the system must work in order to have the highest possible percentage of organic load reduction and equally the nutrients in a retention time that is the shortest. It has two beakers that carry an equivalent volume (30% of microalgae), which explains the volume introduced in the order of 540 mL of microalgae, and then completing the rest of the beaker by the raw domestic wastewater (remaining 1260 mL), which implies that the total volume of work and 1800 mL to define the optimal retention time, as Figure 1 shows.
Aeration is the most energy-intensive process in wastewater treatment, accounting for 45% to 75% of total plant energy consumption.
The mixture of the two beakers was then aerated for 24 h to allow the microalgae to adapt to their host environment. The acclimatization period on the decanted supernatant is followed by a decantation of one hour. Then, the two beakers again collected the raw effluent and were aerated under a different aeration time, varying from 2 h to 24 h. Table 2 below shows the different variations in aeration time in the two beakers to evaluate the optimum retention time. An application of similar timings for a duration match occurs.

Table 2.
Time and duration of aeration for both beakers.
The microalgae were only added at the beginning of the study. The study was repeated three times to observe the effect of retention time and to understand how much time is needed for the microalgae to effectively maintain the system. The filtration method is recognized as one of the most cost-effective methods of harvesting microalgae [54]. For this reason, a large filter with a pore diameter in the range of 4.0 to 5.5 µm was used in this study to filter the effluent. A variation study of the post-treatment parameters was carried out under both pre-filtration and post-filtration conditions.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Treatment of Wastewater
Nutrient bioavailability and other physicochemical parameters, including pH, sunlight intensity, temperature, and biological variables, influence the productivity of green-growing microscopic organisms for nutrient uptake, explaining the availability of pathogens, viral aggression, predation by protozoa, and competition with microorganisms for available nutrients [55].
In this experiment, the organization of different periods of aeration followed by decantation is present for both reactors. This ensures the continuity of the system operation. In order to determine the effect of microalgae as a biological agent for the removal of substances and organic compounds, the reactors were operated in continuous mode until the end of the study. The raw domestic wastewater received after the experiment was characterized to study the removal of organic load as well as nutrients by microalgae at different retention times. The results obtained showed a wide variation. This is shown below (Table 1), showing the mean and standard deviation (SD) for all the parameters analyzed during the study.
3.2. Treatment Result
3.2.1. COD Removal
The study was carried out on filtered effluents, and the reductions in all parameters were greater than for unfiltered effluents. For COD, the shortest reduction was observed after 2 h of aeration (33.33%), with a maximum reduction of 92.5% after 10 h of aeration, as shown in Figure 2.
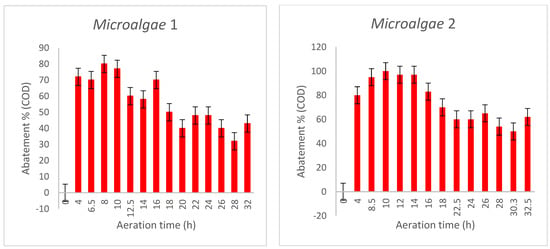
Figure 2.
COD abatement in both conditions.
The reduction in COD by Chlorella Vulgaris provides significant results. A direct fermentation of the microalgae culture could lead to a significant improvement in the economic viability of the treatment system. A yield of 14.3% of COD removal was obtained [56]. During a two-day culture period, up to 80% of COD was removed. This results in a nutrient deficiency for algal growth. It can be said that the degradation process uses organic compounds as a carbon source, hence the need for the participation of wastewater bacteria [57]. The high COD level indicates a higher amount of oxidable organic matter, which plays an essential role in the metabolism of the microalgae: photosynthesis absorbs organic carbon much faster than inorganic carbon, which is responsible for the extremely low concentration of COD in all treated wastewater samples [58]. Elimination efficiency can vary depending on the COD concentration and the type and origin of the wastewater [59].
3.2.2. Phosphate Removal
Phosphate is considered to be an intermediate in the conversion and synthesis of nucleic acids. This nutrient enters the microalgae cells by direct delivery to the plasma membrane as [22]. The phosphate removal in mg/L of the raw wastewater from both microalgae cultures is shown in Figure 3.
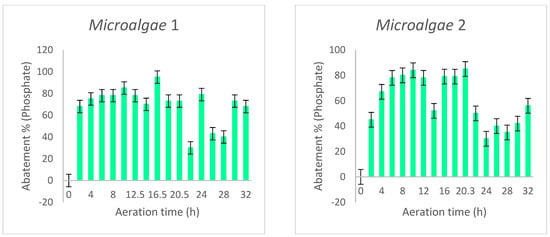
Figure 3.
Phosphate abatement in both conditions.
The results obtained show that phosphate in the treated effluent was drastically reduced during the cultivation period. The final elimination efficiency of phosphate in wastewater treated with Chlorella vulgaris has a significant percentage. During the optimum retention period of 11 h, the concentration reduction varies between 42.11% and 93.18%. An amount of phosphate concentration was found in the sequence of 0.22 mg/L. In general, the phosphate concentration in the wastewater is between 1 and 5 mg/L. However, it is possible to control lower-quality effluents, i.e., with higher phosphate levels, by collecting and sampling inappropriate agricultural practices, human and animal waste, unclean septic systems, or contaminated discharges from wastewater treatment plants.
3.2.3. Removal of Ammonia
In the case of nutrients (ammonia), a variation in the reduction in ammonia was also observed on a six-monthly basis. A maximum reduction of 100%, which concerns the concentration of ammonia in the filtered effluent below the detectable limit, is observed only after 11 h of retention. This is shown in Figure 4.
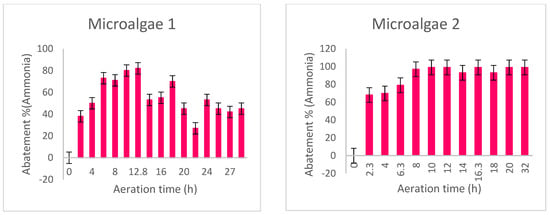
Figure 4.
Ammonia abatement in both conditions.
The removal of NH3-H was achieved by direct use of the microalgae. The undetectable levels of ammoniacal nitrogen in municipal wastewater can be attributed to the initial treatment of the wastewater by various bacteria and chemicals in the wastewater treatment plant [60]. The results obtained show that NH3-N was almost completely eliminated by Chlorella vulgaris in the processed samples due to the fact that ammoniacal nitrogen is one of the most energetically efficient nitrogen sources in algae metabolism.
Nevertheless, a study of the reduction in solids (TS, TDS, and TSS) and EC is carried out with results of 27.27%, 41.36%, 29.35%, and 24.87%, respectively, regarding the TDS, TSS, TS, and EC of the treated effluent. The pH and DO of the effluent were also tested. An increase in pH and DO was observed in the effluent for each hour of retention. After 11 h, DO and pH reached a concentration rate of around 6.90 mg/L and 8.92 mg/L, respectively.
With respect to the optimal residence time of the microalgae, Chlorella vulgaris alone performed admirably in the removal of NH3-N and phosphorus. The NH3-N removal rate was faster in the light than in the dark [61]. COD removal rates were also found to be affected under similar conditions. As a result, the reductions in COD were lower with nutrients because the formation of nitrates affected the removal of COD [36]. As the luminous flux is increased until the point of saturation of the light level is reached, the following applies [62]. In the cultivation of algae, the supply of light is considered to be an essential element of the work. The synthesis of NADPH and ATP, which bundle the carbon skeletons and display the performance of nitrifiers, also requires the use of light. Uniform disappearance of the light and reliable penetration also allow to maintain a strategic distance to the self-shadowing effect [63].
In the process of absorbing the identified supplements, light acts as an accelerating agent with mixotrophic action [64]. The efficiency of nitrogen and phosphorus removal also depends on the structure of the environment and the ecological conditions. Examples are the concentration of the underlying nutrients, the light level, the nitrogen/phosphorus ratio, the light/dark system, or the microalgae species. For microalgae-based wastewater treatment, the light/dark system is important [65]. The following study also found that extending the retention time did not increase the removal efficiency of the system. Particularly at high light intensities, the efficiency of photosynthesis can be improved by periods of darkness between short flashes of light.
One effect on the physiology of the algae cells was the change in pH, which had an effect on one form of nutrient through an increase in alkalinity [66] after photosynthesis due to an increase in the pH of the effluent [67]. Increasing the pH causes self-flocculation, which eliminates algae suspended in the effluent and reduces the phosphorus concentration thanks to the interaction between cations and phosphates, which precipitate in a complex algae–mineral structure [68]. A disinfection is conducted by Microalgal treatment of pathogens [69].
A percentage of 40 to 50% of the carbon contained in microalgae, followed by nitrogen (1 to 10%) and phosphorus (around 1.3%), with a typical structure of C106H181O45N16P Chlorella vulgaris follows the rule NH4 > NO3 > N2 under the order of use of nitrogen sources and does not use other sources of nitrogen, although ammonia is not exhausted [36]. Biomass identification, upgrading, and nitrification are the main contributors to nitrogen removal. The latter is taken up during heterotrophic growth and, to a lesser extent, is also incorporated into the biomass through cellular mixing [70].
NO3 + CO2 + microalgae + sunlight → protein
NH3 + CO2 + microalgae + sunlight → protein
In the following study, phosphorus is adsorbed to the surface of the cells, which are then digested by the biomass [71]. To obtain some of the phosphate ions, the cell membrane takes up the phosphorus through an energetic transport and assimilates it into nucleotides to form RNA and ATP [65]. It is stored in organic compounds, particularly nucleic acids, proteins, and phospholipids. For energy transfer, the cells of microalgae take up phosphate, photosynthesis, DNA, and RNA, and excess is stored in the form of polyphosphate in the algal biomass [54]. During the experiment, a predominance of the photosynthetic process of carbon oxidation and heterotrophic nitrification is shown by an increase in the dissolved oxygen concentration resulting from the increase in algae [55]. Moreover, we can add that this is due to the external ventilation.
During the submerged phase, the COD decreases due to the high degree of acclimatization of life forms in modified conditions, and, in addition, a colloidal material of carbon can exist that is gradually biodegradable [71]. The growth of micro-organisms and biomass enabled COD to be removed through the development of biomass micro-organisms. At the same time, the oxygen supplied by algal photosynthesis could be used to break down organic matter in the raw effluent [72].
In the microalgae treatment system, a reduction in solids was observed over time. Subsequently, the TDS reduction was low compared to the TS and TSS. Due to the presence of filamentous microalgae in suspension, an increase in TDS could be due to the initial phase. Decantation of microalgae over time was prevalent in the medium and in the final phase, leading to a decrease in TDS concentration. Thus, similarity between EC and TDS variation was observed.
3.3. Performance of Removing Contaminants from Wastewater Using Microalgae
The primary ways in which algae remove contaminants from wastewater are through biosorption and bioaccumulation. Biosorption is a rapid, physicochemical, reversible, metabolically independent, and passive process in which metal ions are bound to dead or inactive algal cell walls by adsorption, electrostatic interaction, ion exchange, chelation, and microprecipitation. Table 3 illustrates some efficiencies of nutrient removal using the algae process:

Table 3.
Removal efficiency of nutriments by algae.
Recent environmental contaminants in wastewater are the focus of particular attention because they exhibit a number of harmful characteristics, such as high polarity, the ability to bioaccumulate in aquatic organisms, and the ability to resist biodegradation.
4. Conclusions
The present research was carried out with the aim of solving the problems of water scarcity and water quality caused by the weak development and implementation of wastewater treatment and discharge policies. The process was carried out in photosensitive reactors, and key parameters were measured and analyzed to establish a relationship between the process and Chlorella vulgaris. The physicochemical parameters observed for domestic wastewater were variable. Untreated domestic wastewater showed the highest values for electrical conductivity, total dissolved solids, and chemical oxygen demand. The reduction in wastewater pollution is mainly achieved by the application of good practices by the users of water and aquatic environments. The many advantages of microalgae must be systematically exploited to reduce the harmful effects of nutrients in domestic wastewater. In this perspective, the species Chlorella vulgaris has been exploited to determine its efficiency in wastewater treatment. Separation by filtration of Chlorella vulgaris occurred, which is a species with excellent potential for nutrient removal. In this study, a direct combination between the filtration method and the microalgae method was used to control the raw wastewater parameters. The coupling of the two methods has produced highly significant results. The results obtained with this treatment system are evaluated in terms of a reduction in solids (TS, TDS, and TSS) and EC of 27.27%, 41.36%, 29.35%, and 24.87%, respectively, in terms of TDS, TSS, TS, and EC of the filtered treatment effluent. The results show that the filtration system provides very high removal rates of COD, ammonia, and phosphate, which are 92.5%, 100%, and 93.18%, respectively. This demonstrates the success of Chlorella vulgaris culture in removing nutrients from raw domestic wastewater. However, information and comparative studies on marine microalgae are scarce. As water resources become an increasing concern, research into the treatment of marine microalgae would be extremely useful in many parts of the world. Overall, Chlorella vulgaris has been shown to be effective in the treatment of domestic, agricultural, and industrial effluents, which may prove essential in the development and implementation of policies given the current issues of water scarcity and allocation. Several algal wastewater treatment technologies have been commercialized, but further research is needed to verify the application of these systems for nutrient removal in secondary treated wastewater in a real operating environment. In fact, this sustainable wastewater treatment process enables low-cost removal of nutrients from wastewater and the accumulation of multi-trophic biomass that can be used as feedstock for bioenergy production (biomethane). This integrated process improves the economics of the technology and contributes to climate change mitigation.
Author Contributions
Methodology, K.E.-M., H.E.B. and J.M.; Validation, K.E.-M., M.S.B. and T.L.I.; Formal analysis, D.H. and M.S.B.; Investigation, M.S.; Resources, J.M. and D.H.; Data curation, K.E.-M.; Writing—original draft, Y.F. and T.L.I.; Writing—review & editing, H.E.B. and M.S.; Visualization, Y.F., M.S., M.S.B. and T.L.I.; Supervision, J.M., Y.F. and D.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Deputyship for research and innovation, “Ministry of Education” in Saudi Arabia (IFKSUOR3-273-5).
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this article are available upon request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The authors extended their appreciation to Deputyship for research and innovation, “Ministry of Education” in Saudi Arabia for funding this research (IFKSUOR3-273-5).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Ezugbe, E.O.; Rathilal, S. Membrane Technologies in Wastewater Treatment: A Review. Membranes 2020, 10, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esmaeili, L. Bioaccumulation and Toxic Effect of Zinc on the Green Alga Chlorella Vulgaris. Master’s Thesis, University of Quebec, Montreal, QC, Canada, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- El Bakraoui, H.; Slaoui, M.; Mabrouki, J.; Hmouni, D.; Laroche, C. Recent Trends on Domestic, Agricultural and Industrial Wastewaters Treatment Using Microalgae Biorefinery System. Appl. Sci. 2022, 13, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clus, O. Condenseurs Radiatifs de la Vapeur D’eau Atmospherique (Rosee) Comme Source Alternative D’eau Douce. Ph. D. Thesis, Université Pascal Paoli, Corte, France, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Roshan, A.; Kumar, M. Water end-use estimation can support the urban water crisis management: A critical review. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 268, 110663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacob, M. Réutilisation des Eaux Usées Epurées par Association de Procédés Biologiques et Membranaires; INSA: Toulouse, France, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Benoit, G.; Dauphin, V.; Ducrocq, T.; Nougarol, S.; Salva, E. Valorisation des eaux usées épurées pour l’irrigation. Actes Sémin. Dév. Durable OIEau Engees 2011, 35, 12–13. [Google Scholar]
- Eme, C.; Boutin, C. Composition des Eaux Usées Domestiques par Source D’Émission à L’Échelle de L’Habitation. Publication Onema. 2015. Available online: https://www.assainissement-non-collectif.developpement-durable.gouv.fr/IMG/pdf/composition_eu_par_source-final_2015.pdf (accessed on 15 August 2023).
- Nassali, H.; Ben Bouih, H.; Srhiri, A.; Dhahbi, M. Influence des rejets des eaux usées sur la composition des eaux de surface et des sédiments superficiels du lac Merja Fouarate au Maroc. Afr. Sci. Rev. Int. Sci. Technol. 2005, 1, 35402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samaké, D. Traitement des Eaux Usées de Tanneries à L’aide de Matériaux à Base D’argile. Ph.D. Thesis, Université Joseph-Fourier-Grenoble I, Saint-Martin-d’Hères, France, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Aries, F.Z.; Mellit, A.; Labiad, H.; Benhamada, O.E. Adptation des Microalgues aux Métaux: Techniques de Culture et Procédés de Bioremédiation. Ph.D. Thesis, Université de Jijel, Jijel, Algeria, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Choumane, F.Z. Elimination des Métaux Lourds et Pesticides en Solution Aqueuse par des Matrices Argileuses. Ph.D. Thesis, Université de Tlemcen-Abou Bekr Belkaid, Chetouane, Algeria, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Tomgouani, K.A.O.; El Mejahed, K.; Bouzidi, A. Evaluation de la Pollution Métallique dans les sols Agricoles Irrigués par les eaux Usées de la ville de Settat (Maroc). Bull. L’Inst. Sci. Rabat 2007, 29, 89–92. [Google Scholar]
- Baize, D. Teneurs totales en métaux lourds dans les sols français. Courr. Environ. INRA 1994, 22, 37–46. [Google Scholar]
- Kehal, M.; Mennour, A.; Reinert, L.; Fuzellier, H. Heavy Metals in Water of The Skikda Bay Les Metaux Lourds dans les Eaux de la Baie De Skikda. Environ. Technol. 2004, 25, 1059–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulredha, D.S.; AlMousawi, N.J.; Azeez, N.M. Using Blue-Green Algae Hapalosiphon sp. & Green Algae Scenedesmus spp. in Reducing Organic Pollutants from Wastewater. Ann. Rom. Soc. Cell Biol. 2021, 25, 8647–8653. [Google Scholar]
- Mathew, M.M.; Khatana, K.; Vats, V.; Dhanker, R.; Kumar, R.; Dahms, H.-U.; Hwang, J.-S. Biological Approaches Integrating Algae and Bacteria for the Degradation of Wastewater Contaminants—A Review. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 801051. Available online: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmicb.2021.801051 (accessed on 15 August 2023). [CrossRef]
- Lassoui, A.; Soltani, S. Contribution a la Biorememdiation des eaux Usees par des Microalgues; Université of Eloued: El Oued, Algeria, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Rath, B. Microalgal bioremediation: Current practices and perspectives. J. Biochem. Technol. 2012, 3, 299–304. [Google Scholar]
- Bouchentouf, M.; Abdarrahmane, M.; Dehmani, S. Traitement des Eaux Usées par les Microalgues. Ph.D. Thesis, Universite Ahmed Draia-Adrar, Adrar, Algeria, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Olguín, E.J.; Sánchez-Galván, G. Heavy metal removal in phytofiltration and phycoremediation: The need to differentiate between bioadsorption and bioaccumulation. New Biotechnol. 2012, 30, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mani, D.; Kumar, C. Biotechnological advances in bioremediation of heavy metals contaminated ecosystems: An overview with special reference to phytoremediation. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 11, 843–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Yu, Z.; Jiang, L.; Hou, Q.; Xie, Z.; Liu, M.; Yu, S.; Pei, H. Alga-based dairy wastewater treatment scheme: Candidates screening, process advancement, and economic analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 390, 136105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maneechote, W.; Cheirsilp, B.; Angelidaki, I.; Suyotha, W.; Boonsawang, P. Chitosan-coated oleaginous microalgae-fungal pellets for improved bioremediation of non-sterile secondary effluent and application in carbon dioxide sequestration in bubble column photobioreactors. Bioresour. Technol. 2023, 372, 128675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.-Y.; Hong, Y. Microalgae-Based Wastewater Treatment and Recovery with Biomass and Value-Added Products: A Brief Review. Curr. Pollut. Rep. 2021, 7, 227–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantzorou, A.; Ververidis, F. Microalgal biofilms: A further step over current microalgal cultivation techniques. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 651, 3187–3201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uduman, N.; Qi, Y.; Danquah, M.K.; Forde, G.M.; Hoadley, A. Dewatering of microalgal cultures: A major bottleneck to algae-based fuels. J. Renew. Sustain. Energy 2010, 2, 012701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Japar, A.S.; Takriff, M.S.; Yasin, N.H.M. Harvesting microalgal biomass and lipid extraction for potential biofuel production: A review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 555–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Show, K.-Y.; Lee, D.-J.; Tay, J.-H.; Lee, T.-M.; Chang, J.-S. Microalgal drying and cell disruption—Recent advances. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 184, 258–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Chen, X.; Liu, T.; Yang, Z.; Xiao, Y.; Zeng, G.; Sun, X. Harvesting of Chlorella sp. using hollow fiber ultrafiltration. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2012, 19, 1416–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrusevski, B.; Bolier, G.; Van Breemen, A.; Alaerts, G. Tangential flow filtration: A method to concentrate freshwater algae. Water Res. 1995, 29, 1419–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rickman, M.; Pellegrino, J.; Davis, R. Fouling phenomena during membrane filtration of microalgae. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 423-424, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerardo, M.L.; Van Den Hende, S.; Vervaeren, H.; Coward, T.; Skill, S.C. Harvesting of microalgae within a biorefinery approach: A review of the developments and case studies from pilot-plants. Algal Res. 2015, 11, 248–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, A.; Jahanara, I.; Jolly, Y.N. Assessment of physicochemical properties of water and their seasonal variation in an urban river in Bangladesh. Water Sci. Eng. 2021, 14, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, K.; Yuan, Q.; Li, H.; Li, T.; Ma, H.; Gao, C.; Zhang, S.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, L. Chlorella pyrenoidosa Polysaccharides as a Prebiotic to Modulate Gut Microbiota: Physicochemical Properties and Fermentation Characteristics In Vitro. Foods 2022, 11, 725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Kim, J.; Lee, C. Nutrient removal and microalgal biomass production from different anaerobic digestion effluents with Chlorella species. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 6123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moondra, N.; Jariwala, N.D.; Christian, R.A. Sustainable treatment of domestic wastewater through microalgae. Int. J. Phytoremediat. 2020, 22, 1480–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.-H.; Church, J.; Lee, S.-J.; Park, J.; Lee, W.H. Use of Microalgae for Advanced Wastewater Treatment and Sustainable Bioenergy Generation. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2016, 33, 882–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgadillo-Mirquez, L.; Lopes, F.; Taidi, B.; Pareau, D. Nitrogen and phosphate removal from wastewater with a mixed microalgae and bacteria culture. Biotechnol. Rep. 2016, 11, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutayeb, M.; Bouzidi, A.; Fekhaoui, M. Etude de la qualité physico-chimique des eaux usées brutes de cinq villes de la région de la Chaouia—Ouardigha (Maroc). Bull. L’Inst. Sci. 2012, 34, 145–150. [Google Scholar]
- Valeur Limites de Rejet à Respecter—Recherche Google. Available online: https://www.google.com/search?q=valeur+limites+de+rejet+%C3%A0+respecter&oq=valeur+limites+de+rejet+%C3%A0+respecter&aqs=chrome..69i57j33i160l2.17045j0j15&sourceid=chrome&ie=UTF-8 (accessed on 13 March 2023).
- Elaouani, H.; Haffad, H.; Jaafari, K.; Elbada, N.; Mailainine, S.; Benkhouja, K. Evaluation de la qualité physico-chimique des rejets liquides industriels de la zone industrielle d’elmarsa laayoune. Rev. L’Entrep. L’Innov. 2019, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makhoukh, M.; Sbaa, M.; Berrahou, A.; Van Clooster, M. Contribution a L’etude Physico-Chimique des Eaux Superficielles de L’oued Moulouya (Maroc Oriental). LARHYSS J. 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Legros, N. La Réutilisation des eaux Usées Traitées en Irrigation comme Incubateur d’un Processus de Pérennisation et de Bonne Gouvernance des Infrastructures D’assainissement: Cas Pratique de la Station D’épuration de Tidili au Maroc. Master’s Thesis, Université de Liège, Liège, Belgium, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Hamid, C.; Elwatik, L.; Ramchoun, Y.; Fath-Allah, R.; Ayyach, A.; Fathallah, Z.; Midaoui, A.E.; Hbaiz, E.M. Étude des performances épuratoires de la technique du lagunage aéré appliquée à la station d’épuration de la ville d’Errachidia—Maroc. Afr. Sci. Rev. Int. Sci. Technol. 2014, 10. [Google Scholar]
- Dimane, F.; Haboubi, K.; Hanafi, I.; El Himri, A. Étude de la Performance du Dispositif de Traitement des Eaux UsÉes par Boues ActivÉes de la ville d’Al- Hoceima, Maroc. Eur. Sci. J. ESJ 2016, 12, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rassam, A.; Chaouch, A.; Bourkhiss, B.; Ouhssine, M.; Lakhlifi, T.; Bourkhiss, M.; El Watik, L. Caractéristiques Physico-Chimiques des Eaux Usées Brutes de la Ville D’oujda (Maroc). Technol. Lab. 2012, 7. [Google Scholar]
- Hamieh, M.T. Étude des Propriétés Physico-Chimiques et Colloïdales du Bassin de la Rivière LITANI, Liban. Ph.D. Thesis, Université de Lorraine, Lorraine, France, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- El Hammoumi, N.; Sinan, M.; Lekhlif, B.; El Mahjoub, L. Évaluation de la qualité des eaux souterraines pour l’utilisation dans l’eau potable et l’agriculture: Plaine de Tadla, Maroc. Afr. Sci. Rev. Int. Sci. Technol. 2012, 8. [Google Scholar]
- Biodiversité et Milieux. Available online: https://www.environnement.gov.ma/fr/lois-et-reglementations/textes-juridiques?id=940 (accessed on 13 March 2023).
- Valeurs Limites des Rejets. Available online: http://www.environnement.gov.ma/fr/78-cat1/1012-valeurs-limites-des-rejets (accessed on 13 March 2023).
- In BW. Available online: https://www.inbw.be/ (accessed on 13 March 2023).
- ONSSA. Code de Procédures. Available online: https://www.onssa.gov.ma/controle-des-produits-alimentaires/code-de-procedures/ (accessed on 14 March 2023).
- Benamar, A.; Mahjoubi, F.Z.; Kzaibe, F. Evaluation of water quality of Oum Er Rbia River (Morocco) using water quality index (WQI) method. J. Appl. Surf. Interfaces 2019, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, P.; Mao, B.; Lü, F.; Shao, L.; Lee, D.; Chang, J. The combined effect of bacteria and Chlorella vulgaris on the treatment of municipal wastewaters. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 146, 562–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marjakangas, J.M.; Chen, C.-Y.; Lakaniemi, A.-M.; Puhakka, J.A.; Whang, L.-M.; Chang, J.-S. Simultaneous nutrient removal and lipid production with Chlorella vulgaris on sterilized and non-sterilized anaerobically pretreated piggery wastewater. Biochem. Eng. J. 2015, 103, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-A.; Kim, M.; Kim, H.-S.; Ahn, C.-Y. Extra benefit of microalgae in raw piggery wastewater treatment: Pathogen reduction. Microbiome 2022, 10, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burns, T. How to Reduce COD in Water| bioprocessH2O. Bioprocessh2o. 2021. Available online: https://www.bioprocessh2o.com/ (accessed on 15 August 2023).
- EPA. Aquatic Life Criteria—Ammonia. 20 August 2015. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/wqc/aquatic-life-criteria-ammonia (accessed on 15 August 2023).
- Kshirsagar, A.D. Bioremediation of wastewater by using microalgae: An experimental study. Pharm. Res. 2013, 2, 339–346. [Google Scholar]
- Li, G.; Park, S.; Kang, D.W.; Krajmalnik-Brown, R.; Rittmann, B.E. 2, 4, 5-Trichlorophenol degradation using a novel TiO2-coated biofilm carrier: Roles of adsorption, photocatalysis, and biodegradation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 8359–8367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alves, A.; Sousa, R.A.; Reis, R.L. A practical perspective on ulvan extracted from green algae. J. Appl. Phycol. 2012, 25, 407–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslan, S.; Kapdan, I.K. Batch kinetics of nitrogen and phosphorus removal from synthetic wastewater by algae. Ecol. Eng. 2006, 28, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhou, W.; Hu, B.; Min, M.; Chen, P.; Ruan, R.R. Integration of algae cultivation as biodiesel production feedstock with municipal wastewater treatment: Strains screening and significance evaluation of environmental factors. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 10861–10867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kube, M.; Jefferson, B.; Fan, L.; Roddick, F. The impact of wastewater characteristics, algal species selection and immobilisation on simultaneous nitrogen and phosphorus removal. Algal Res. 2018, 31, 478–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schumacher, G.; Blume, T.; Sekoulov, I. Bacteria reduction and nutrient removal in small wastewater treatment plants by an algal biofilm. Water Sci. Technol. 2003, 47, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moondra, N.; Jariwala, N.D.; Christian, R.A. Role of phycoremediation in domestic wastewater treatment. Water Conserv. Manag. 2020, 5, 53–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, A.L.; Pires, J.C.M.; Simões, M. A review on the use of microalgal consortia for wastewater treatment. Algal Res. 2017, 24, 403–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foladori, P.; Petrini, S.; Andreottola, G. Evolution of real municipal wastewater treatment in photobioreactors and microalgae-bacteria consortia using real-time parameters. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 345, 507–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Mennerich, A.; Urban, B. Municipal wastewater treatment and biomass accumulation with a wastewater-born and settleable algal-bacterial culture. Water Res. 2011, 45, 3351–3358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, S.; Xue, G. Algal-based immobilization process to treat the effluent from a secondary wastewater treatment plant (WWTP). J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 178, 895–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, K.; Kumar, P.K.; Krishna, S.V.; Himabindu, V. Phycoremediation of Sewage-Contaminated Lake Water Using Microalgae–Bacteria Co-Culture. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2020, 231, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chawla, P.; Malik, A.; Sreekrishnan, T.R.; Dalvi, V.; Gola, D. Selection of optimum combination via comprehensive comparison of multiple algal cultures for treatment of diverse wastewaters. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2020, 18, 100758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almomani, F.; Judd, S.; Bhosale, R.R.; Shurair, M.; Aljaml, K.; Khraisheh, M. Intergraded wastewater treatment and carbon bio-fixation from flue gases using Spirulina platensis and mixed algal culture. Process. Saf. Environ. Prot. 2019, 124, 240–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldev, E.; Ali, D.M.; Pugazhendhi, A.; Thajuddin, N. Wastewater as an economical and ecofriendly green medium for microalgal biofuel production. Fuel 2021, 294, 120484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.K.; Bhattacharjya, R.; Saxena, A.; Mishra, B.; Tiwari, A. Utilization of wastewater as nutrient media and biomass valorization in marine Chrysophytes- Chaetoceros and Isochrysis. Energy Convers. Manag. X 2021, 10, 100062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheah, W.Y.; Show, P.L.; Yap, Y.J.; Zaid, H.F.M.; Lam, M.K.; Lim, J.W.; Ho, Y.-C.; Tao, Y. Enhancing microalga Chlorella sorokiniana CY-1 biomass and lipid production in palm oil mill effluent (POME) using novel-designed photobioreactor. Bioengineered 2020, 11, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).