Abstract
Vermicomposting emerges as an eco-friendly solution to manage a blend of agricultural residues and digested biogas slurry (DBS). This research probes the influence of two specific earthworm species, Eisenia fetida and Eugilius euganiae, on the composting dynamics of agro-residues and DBS. Moreover, it gauges their consequential impact on the growth of chili and brinjal plants. The research was conducted at the Sharda Vihar Campus in Bhopal. Several process variables, such as pH, salinity, moisture levels, temperature, carbon-to-nitrogen (C/N) ratio, nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), potassium (K), presence of pathogens, and monoculture trends, were assessed for their influence on vermicompost yield and its effect on chili and brinjal growth. Intriguingly, reactors employing E. fetida exhibited a vermicast recovery rate of 89.7%, whereas those utilizing E. eugeniae achieved 68.2% recovery, especially with an earthworm density of 125 individuals per liter. Notably, the derived NPK values from various composted and vermicomposted materials ranged from 1.5 to 1.7% for N, 0.98 to 1.19% for P, and 1.1 to 1.49% for K. This suggests its viability as both a fertilizer and soil enhancer. The E. fetida vermicompost-enriched soil notably boosted the yield of chili and brinjal. Overall, these insights highlight vermicomposting’s dual utility in waste management and augmenting bioresources.
1. Introduction
Population growth, urbanization, and intensive agricultural practices are the greatest obstacles in developing environmentally friendly and cost-effective solid organic waste (SOW) disposal processes. Therefore, investing in innovative waste management technologies and regulations that promote SOW reduction, reuse, and recycling is essential for environmental sustainability, human health, and food security. The world produces 38 billion tons of SOW annually [1]. Waste management methodologies such as composting, landfilling, incineration, and anaerobic digestion are helpful in utilizing SOW. Gupta et al. [2] and Katiyar et al. [3] examined Indian solid wastes. Cattle dung is usually applied as an organic fertilizer to agricultural land or utilized as a plant nursery medium after stabilization [4]. Yuvaraj et al. [5] examined the role of cattle solid waste feed in vermicomposting and its environmental impact. Using earthworm Eudrilus eugeniae, composting and vermicomposting recovered nutrients from solid waste [6]. To enhance feed moisture and C/N ratio, bulking agents, including waste wood chips and shavings and cereal straws, are added during stabilization [7].
Various wastes, including cow dung, sewage sludge, urban debris, fish pond waste, paper remnants, textile mill sludge, guar gum industry by-products, sugar industry leftovers, distillery residues, leather industry waste, and remnants from the beverage industry, have been processed through vermicomposting to yield nutrient-dense manure. As such, both composting and vermicomposting are leading methods for the biological stabilization of solid organic waste (SOW). Managing municipal solid waste (MSW), leaf debris, and separating biowaste at the source, followed by treatment using composting-vermicomposting or anaerobic digestion, are the most sustainable strategies [8,9] for enhancing the soil’s physicochemical properties. Industrial-scale composting of MSW has been devised and scrutinized both technically and environmentally [10]. However, composting has many drawbacks. At first, the process can be lengthy. To guarantee sufficient surface area, the material must be frequently spun and reduced in size. The final product may be diverse and lose nutrients due to prolonged composting [11].
A Goshala is located at Sharda Vihar residential higher secondary school in Mindori village near Kerwan Dam, Bhopal, Madhya Pradesh, India (Figure S1a,b). Approximately 200 cows, 60 calves, and several bullocks live in this Goshala. Milk output of Goshala averages 300 L/day. By contrast, Goshala produces tons of cow manure as SOW. This cow manure feeds biogas plants developed with MNRE, New Delhi funding under M.P. Urja Vikas Nigam Ltd. (Figure S1c). Two biogas-filled cylinders are utilized daily to cook for students and employees. The extra biogas is used to drive a 9.5 kVA dual-fuel (diesel + biogas) generator set during load shedding to reduce biogas wasting (from morning to kitchen meal preparation) (Figure S1d). However, the digested biogas slurry (DBS) is thrown in pits. The DBS can be used to make biofertilizers through engineered vermicomposting.
Vermicomposting is widely used to turn SOW materials into hygienic and valuable products due to its efficiency, sustainability, and eco-friendliness [12,13]. Vermicomposting has shown tremendous impacts on crop development in the field [7]. Earthworms provide nutrient-rich vermicompost to boost plant growth [14]. In addition, during the vermicomposting, the vermireactor feed’s pathogenic content is reduced [14]. Chili and brinjal are the two typical study plants since they grow quickly and fructify early.
To bridge existing knowledge gaps, we embarked on a series of experiments aimed at producing vermicompost from a variety of materials and subsequently assessing its influence on plant development. While numerous earthworm species can be employed for treating MSW, Eisenia andrei and Eisenia fetida are the most commonly chosen [15]. Their popularity stems from their impressive fecundity, rapid growth rate, and optimal functioning at temperatures of approximately 30 ± 2 °C. We delved into the enhancement of vermicast yields across various vermireactors. These reactors, though of the same volume, had surface area to height ratios ranging from 4 to 250. Our analysis centered on the performance of E. fetida and E. eugeniae [16]. Furthermore, we evaluated the influence of areal loading [17], variations in earthworm populations, and feeding rates [18] on vermicast output within reactors with a consistent dimension and surface area, specifically those with a diameter of 0.84 m.
Composting and vermicomposting have advanced, but many limiting factors, such as process parameters, pH, salt content, moisture content, temperature, carbon/nitrogen (C/N) ratio, nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), potassium (K), pathogen content, and culture fashion, are still unknown [18]. Thus, this study sought to identify and optimize these elements to improve composting/vermicomposting as a sustainable SOW management approach. Considering the aforementioned, this study investigated the influence of earthworms (Eisenia fetida and Eugilius euganiae) processed mixed with agriculture residues-digested biogas slurry (DBS) (vermicompost) on chili and brinjal growth, productivity, and chemical features. In contrast to other studies on vermicomposting agricultural residues, this study examines worm density effects on zoomass increase in the Sharda Vihar campus agro-residues. Combined with a rigorous assessment of NPK values across composted–vermicomposted wastes, this research pioneers a methodological approach that highlights vermicompost’s potential as a waste management solution and a commercial fertilizer-cum-soil conditioner [19]. Our work in sustainable agriculture stands out because we emphasize both the ecological and economic elements of vermicomposting.
2. Experimental Design and Procedures
2.1. Digested Biogas Slurry and Agricultural Residues
The digested biogas slurry (DBS) used in this study was procured from a storage tank of an active biogas plant at the Sharda Vihar campus in Bhopal, Madhya Pradesh, India, as illustrated in Figure S2a. This plant is nestled within the Saraswati Vidya Mandir grounds at Sharda Vihar, Bhopal, Madhya Pradesh, India. The specific geographic coordinates for this site are latitude 23°15′35.7588″ N and longitude 77°24′45.4068″ E. After retrieval, the DBS was left undisturbed on the ground for approximately a week. From this accumulation, a sample weighing close to 25 kg was taken. This selected sample was then preserved in two airtight 25 L plastic containers and conveyed to the lab, where it was stored under room conditions. Concurrently, agricultural byproducts pertinent to the research were gathered from the Sharda Vihar campus.
2.2. Initial Preparation of Varied Fresh Solid Wastes
For composting, mixtures of DBS and agricultural by-products were employed to achieve C:N ratios of 30 and 45 as both play a crucial role in plant growth [20]. This experiment utilized three distinct approaches: (i) control, (ii) traditional composting, and (iii) worm-based composting. The collected materials were structured into heaps measuring 1.5 × 1.5 × 1.5 m, alternating between 10 cm thick layers of waste residues and 5 cm layers of desiccated DBS. A 1 cm overlay of garden soil was then spread, followed by adequate hydration to attain a mean moisture content of 60% suitable for composting, as visualized in Figure S2b. To maintain an insulating environment, the heap was shielded with robust black plastic and cardboard. Temperature variations were tracked with precision, using digital sensors accurate to ±0.1 °C. After setting up, the heap was left untouched, permitting aerobic decomposition. This process naturally elevated the internal temperature of the heap from an initial 31 °C to a range of 55–60 °C. Once the temperature began to recede, the protective layers were removed, and the contents were thoroughly mixed. After replacing the covers, the reactor was left to compost again. This technique was repeated 4–5 times to turn agricultural leftovers and/or DBS into compost in 24 days. The composted trash was vermicomposted after three days at room temperature.
2.3. Experimental Design for Vermicomposting
The vermicomposting reactors made for hardwood have the dimensions 12.5 cm in length, 30 cm in height, and 10 cm in width, boasting a surface-to-volume ratio of 0.42 m2/m3, as depicted in Figure S3. In these worm reactors, mature earthworms were introduced at densities of 62.5, 125, 250, and 350 creatures per liter. These worms were provided a diet of DBS combined with agricultural residue, maintaining C:N ratios of either 30 or 45, for a duration of eight weeks. To ensure an optimal 80% moisture content, distilled water was periodically added. Post the eight-week period, the earthworms were carefully extracted from the vermicompost.
To ensure ideal conditions, the top of the reactor was shielded with a fabric cover, facilitating a consistent internal environment of approximately 30 ± 2 °C during daytime and approximately 28 ± 2 °C during nighttime. This fabric enclosure serves a dual purpose: preventing the earthworms from exiting while ensuring a degree of aeration for the internal contents. After a period of 24 days, the vermicast harvested from these worm reactors underwent testing to evaluate its physical and chemical attributes. During this study, vermi-bed substrates were consistently moistened with distilled water to ensure a 75–80% moisture level. Earthworm well-being was observed daily for the first three weeks, and any mortalities were noted. Substrate samples from each reactor were taken periodically over 24 days, dried, ground, and stored in sealed containers. Weekly, for eight weeks, earthworm weight and cocoon production were recorded.
The earthworms, primarily E. fetida and E. eugeniae, were sourced from Advanced Research Laboratory in MANIT-Bhopal, India. These mature, 6-week-old worms, shown in Figure S4, weighed approximately 0.25–0.4 g and were 2.5–5.0 cm long. Their weight was determined by rinsing, drying, and using a balance. In addition, in vermicomposting reactors, DBS and other garbage were prepared with C: N proportions of 30 and 45. These combinations were left to grow for 7–8 weeks with no addition of earthworms after the moisture content was adjusted to 80 percent.
2.4. Physico-Chemical Analysis
Using established techniques, the characteristics of the materials and compost/vermicompost, including the amount of moisture (MC), the pH level, conductivity of electricity (EC), temperature (T), C:N ratio, and concentrations of the nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), potassium (K), and pathogens, were evaluated. The amount of organic carbon was gauged using the partial-oxidation technique [21], while total N was measured in accordance with APHA guidelines [22]. These data helped to determine the C:N ratio. The Bray method [22] was employed to extract plant-acessible P content, and its concentration was subsequently evaluated colorimetrically using the molybdate blue technique at a wavelength of 712 nm with a UV–Vis spectrophotometer (HACH 6000, Loveland, CO, USA). Potassium levels were ascertained using a flame photometer (Shimadzu Model AA-7000, Kyoto, Japan), while grain sizes were inspected using sieving techniques. For microbial evaluations, one gram of compost was mixed with 9 mL of distilled water, agitated, and blended at 5000 rpm for 10 min. A milliliter of this solution was further diluted in 10 mL of distilled water and mixed similarly. To ensure purity, all samples were gathered and preserved in plastic containers. E. coli and E. faecalis concentration and prevalence were determined using the MPN method. Following the instructions in, the biochemical characterization of E. coli and E. faecalis was completed [23]. The daily vermicast production, denoted as vermicast output (V, mg/L·d) for each liter of the reactor’s volume, was calculated in the following manner:
2.5. Plant Growth
In a structured experiment involving chili and brinjal plants, three distinct pots were designated. One pot was allocated for chili saplings, another for brinjal saplings, and the third served as a control. Saplings, aged ten days, were planted in their respective pots. Among these, one pot was left undisturbed, while the other two were enriched with Palash compost and vermicompost. Concurrently, when one experimental pot was fortified with Palash vermicompost, the unaltered control pot received a similar treatment but only after a delay of two months. Each pot was consistently irrigated with an equal volume of water daily. We meticulously recorded daily metrics such as plant height, root length, the span until initial flowering, number of flowers, fruit yield, and fruit length. On the 80th and 160th days, five plants were chosen at random from each category for an in-depth analysis encompassing total plant biomass, crop biomass, the ratio of root to shoot, fecundity coefficient, and harvest index. This systematic approach was consistently employed across experiments with various waste types. The harvest index (hi) and the fertility coefficient (fc) were, respectively, calculated as follows [23]:
2.6. Tests of Significance
For each treatment, three control sets were established (n = 3). Treatment differences were evaluated using multiple regression and standard mean tests in Microsoft Excel, with a confidence level set at 95% (p < 0.05). Graphs and charts were generated using the same software. To assess the significant influence on the growth of chili and brinjal plants in compost and vermicompost-treated pots compared to controls, Student’s t-test was employed. The significance of performance metrics was ascertained by gauging the associated confidence level percentage. Standard t-test procedures were followed in the analyses, as referenced in [23,24].
3. Results and Discussion
Table 1 details the physicochemical attributes of various wastes and bulking agents, including digested biogas slurry (DBS). Specific metrics such as EC (dS/m), pH, MC (%), C:N ratio, N (%), P (%), and K (%) are presented. The moisture content (MC) for DBS was noted at 76.3 ± 6.21%, while for agricultural residues, it stood at 15.1 ± 4.21%. The observed C:N ratios were 16.3 ± 0.02 for DBS and 27.3 ± 0.03 for agricultural residues. EC values were recorded at 0.94 ± 0.03 and 2.4 ± 0.02 for DBS and agricultural residues, respectively. Pigatin et al. [23] have previously documented the chemical composition of vermicomposted agro-industrial wastes. One of the critical prerequisites for successful composting is maintaining the right moisture content. During vermicomposting, earthworms ideally thrive in an environment with an MC ranging from 60 to 70% [23]. It is crucial to ensure that the feedstock is not excessively moist, as overly wet conditions can lead to anaerobic environments detrimental to earthworms. In our study, the feed mixtures utilized maintained an MC within this optimal range. Hussain et al. [25] have also emphasized the importance of appropriate moisture levels for healthy earthworm growth.

Table 1.
Physicochemical properties of the agricultural residues and DBS from Sharda Vihar Campus waste by composting and vermicomposting treatment method and control (incubation under field for 48 days) by different treatments (n = 3.21).
pH and EC were found to be 7.5 ± 0.7, 2.71 ± 0.08, respectively, for composting and 7.2 ± 0.5, 1.62 ± 0.07, respectively, for vermicomposting when E. fetida as a earthworm and 8.0 ± 0.03, 2.01 ± 0.03, respectively, for vermicomposting when E. eugeniae as a earthworm. A control experiment was also carried out to check the feasibility study for 48 days. Ananthavalli et al. [26] reported that the total NPK contents showed a significant increment (26.72–78.17%) in vermicompost over worm-unworked composts. The vermicompost digested by E. fetida exhibited the largest reduction in C:N ratio, with both products having a lower ratio than the compost products. Figure S4d showed a bio manure image prepared by earthworms from Sharda Vihar campus agro-residue wastes. Deka et al. [27] and Ramnarain et al. [28] reported recycling of waste biomass or materials through Perionyx excavates and E. foetida beds under the reported temperature of 0–35 °C, humidity 80–100%, pH 5.5–7.0 and stabilized to near neutral on the 60th day.
pH variation in compost and vermicompost of agro-residues with DBS over experiment period is shown in Figure 1. The compost and vermicompost from agro-residues showed a change in pH that falls in the range of 8.82 ± 0.06, 8.68 ± 0.03 and 7.2 ± 0.05, 6.94 ± 0.03, respectively, which is within the optimal range for plant growth [29]. This shows a shift of pH towards neutral condition (Figure 1). The decrease in pH value is greater in the case of vermicomposting compared to the composting process. Several researchers have reported analogous findings during the vermicomposting process. They propose that the mineralization of nitrogen (N) and phosphorus (P) into nitrites/nitrates and orthophosphates, combined with the bioconversion of intricate materials into intermediary organic acid species and the subsequent release of CO2, could be the factors responsible for the observed pH reduction [30]. Khatua et al. [31] proposed that the decomposition of organic matter during vermicomposting of banana stem waste having high K, Mg, and Fe using E. fetida had high nutrient levels. Rastogi et al. [32] demonstrated that microbes become additives for the reduction in solid waste in the composting process.
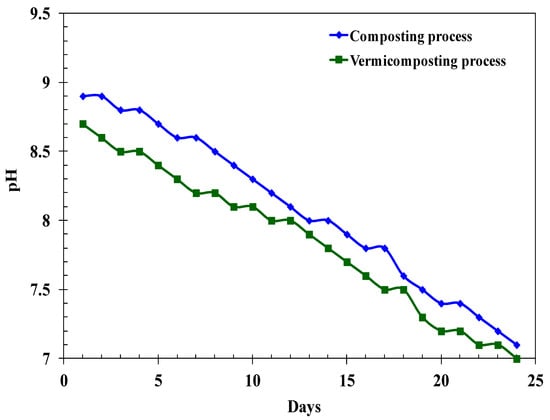
Figure 1.
Changes in the pH of the substrate in compost/vermicompost (E. fetida) of the agricultural residues over experiment period (125 animals/L).
Here, Figure 2 illustrates the temperature trends observed during the composting and vermicomposting of agricultural residues combined with DBS over a 48-day span. Within this period, the temperature in the composting reactor peaked at 49 °C on day 15, while the vermicomposting reactor reached a high of 38 °C on day 31. Subsequently, both stabilized at approximately 30 °C. Interestingly, the internal reactor temperatures displayed no apparent correlation with external atmospheric conditions, as shown in Figure 2. Wu and Smith [33] note that for effective composting-vermicomposting and the reduction in pathogens, a consistent temperature of 55 °C should be maintained for a consecutive 21 days. It has been posited that when food waste is amalgamated with DBS, effective composting can be achieved in just 14 days, after which the compost requires a curing phase [34]. In our study, the temperature soared past 49.6 °C for 15 days, dipped below 40 °C the following day, and then re-entered the thermophilic phase for another three days post day 6. Large-scale operations tend to sustain thermophilic conditions for more extended periods compared to smaller reactors, which are prone to more frequent temperature variations. The latter’s vulnerability can likely be attributed to their reduced waste volume and greater surface area leading to heat loss. Deepthi et al. [35] highlighted the vermi-transformation through the Eudrilus eugeniae bed, emphasizing the importance of optimal organic temperature and exposure zones for the worms.
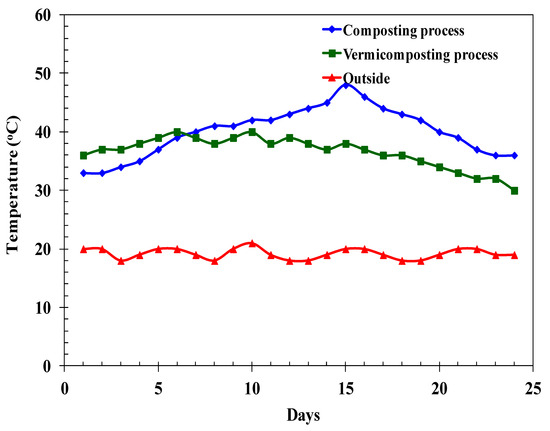
Figure 2.
Temperature of the reactor over the period of composting and vermicomposting. (E. fetida) (125 animals/L).
For composting to be effective, the ideal moisture content (MC) typically ranges between 55% and 66%. However, agricultural residues often possess a moisture content below this range. To address this, the introduction of bulking agents, such as DBS, can elevate the moisture content and foster the desired thermophilic conditions. The heat produced during the decomposition process subsequently decreases the MC. Figure 3 depicts the variations in MC throughout both composting and vermicomposting processes using E. fetida. At the outset, the MC for composting and vermicomposting were recorded at 69.2 ± 0.35% and 78.5 ± 0.25%, respectively. Over a 48-day period, the MC for both processes declined to 55 ± 3.5% for composting and 63 ± 2.1% for vermicomposting. A notable limitation of composting is the need for sufficient bulking agents, which might not always be readily accessible.
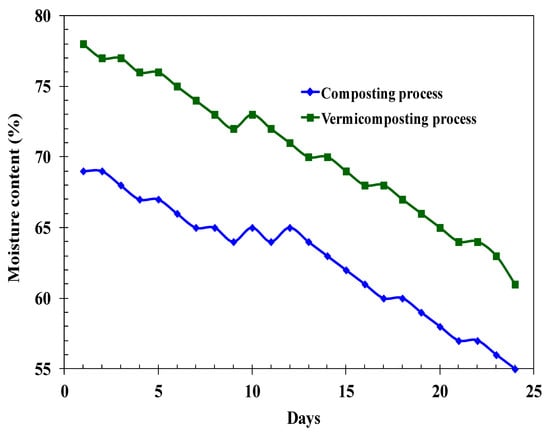
Figure 3.
The moisture content of the substrate during the period of composting and vermicomposting (E. fetida) (125 animals/L).
The numerical calculation of vermicast output allows comparison of vermireactors with different earthworm densities. The vermicast output approximation error was always 10% or less. This suggests a uniform outcome among vermireactors due to their heterogeneous solid composition and biologically volatile feed. The effect of worm number on vermicast generation was examined (Figure 4a,b). E. fetida earthworms yielded 64.4% vermicast in the reactor with 62.5 worms per liter. However, E. eugeniae worms yielded 45.6%. At 125 worms per liter, E. fetida and E. eugeniae had 89.7% and 68.2% vermicast yields, respectively. This finding aligns with prior research on the relationship between worm density and vermicast yield [36]. Based on these observations, subsequent research focused on fine-tuning process parameters while maintaining a constant worm density (specifically, 125 worms per liter for E. fetida).
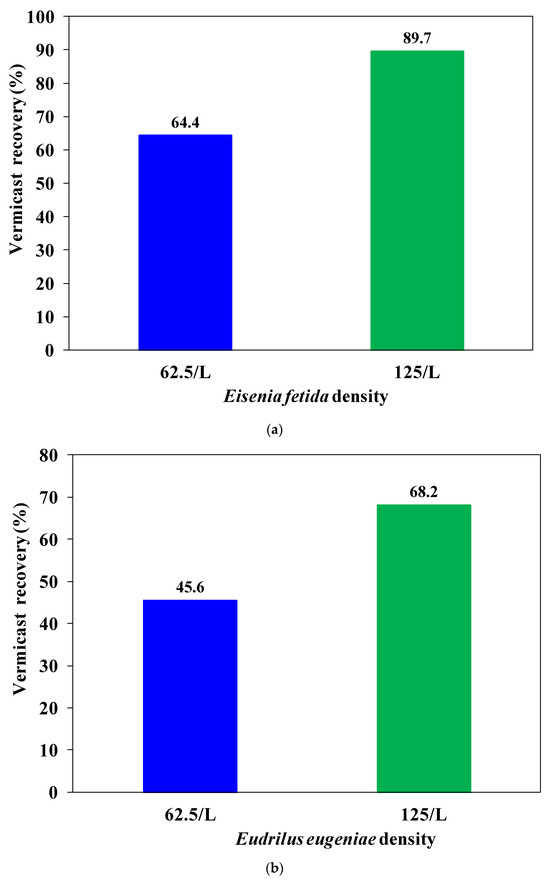
Figure 4.
Vermicast yield is examined based on earthworm densities of 62.5/L and 125/L, taking the average from nine trials conducted in the reactors based on (a) E. eugeniae, and (b) E. fetida.
The fluctuation in vermicast recovery over time is illustrated in Figure 5. Peak recovery was attained in 20 days, registering at approximately 90% for E. fetida and 84% for E. eugeniae. Subsequent to this peak, a slight decline in recovery was noted. Comparable observations were made by Ganesh et al. [16]. A couple of factors are believed to influence the rate of vermicomposting recovery. Firstly, there’s an acceleration factor: as worms become more familiar with their feed, they tend to consume larger amounts of the composted matter. Secondly, as worms grow in size, their consumption rate increases, leading them to feed more aggressively. The culmination of these factors propels vermicast production to its zenith. Following this peak, however, there was a noticeable drop in vermicast recovery. This decline can be attributed to the natural life cycle where older worms die off and younger ones are still in the process of maturing. In a separate study, Pathma and Sakthivel [37] delved into the microbial diversity of vermicompost bacteria in relation to agricultural characteristics. Drawing from the findings of Ananthavalli et al. [26], it is evident that the worm species Perionyx excavatus is adept at transforming a blend of seaweed and cow dung into nutrient-dense vermicompost.
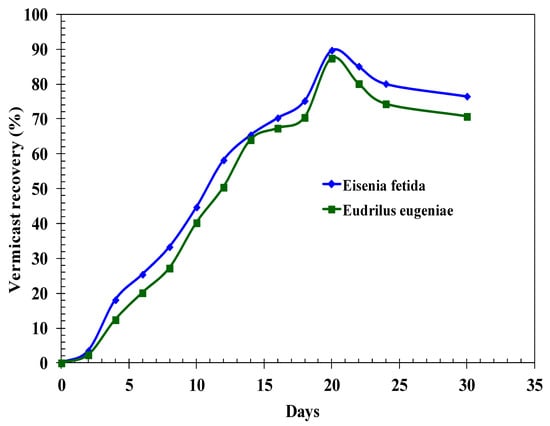
Figure 5.
Vermicast recovery of the reactor over the period of composting and vermicomposting (E. fetida) (125 animals/L) (agricultural residues).
The final product (compost and vermicast) was tested for pathogen content as outlined in the standard method [38]. All the values in mean ± SD, n = 3, are reported here. The E. coli and E. facecalis populations observed a distinct decrease from 84 MPN/g to 70 MPN/g during composting. The average number of E. coli and E. facecalis population were high at the end of composting, indicating further maturation. Lower in-term MPN/g of E. coli and E. facecalis (84 to 4.5, 84 to 5.0, and 70 to 4.8, 70 to 5.5) were observed after vermicomposting with E. fetida and E. eugeniae, respectively. The result indicated that vermicomposting yields hygienic composts after the maturation of primary stabilized composts from the composting method. The result shows E. fetida was a better worm for reducing the pathogen content in vermicast. Huang et al. [14] reported the reduction in pathogenic bacteria through the vermicomposting process.
The experimental results regarding the growth of chili and brinjal plants with the use of compost and vermicompost are presented here. In the initial three months, when the control pot received no compost–vermicompost treatment, pots that were supplemented with these organic materials exhibited enhanced growth. This was evident in both chili and brinjal plants, as they displayed marked improvements in height, root length, biomass accumulation rate, earlier flowering, and increased fruit yield. Figure 6, Figure 7, Figure 8, Figure 9, Figure 10 and Figure 11 illustrate the growth study of chili and brinjal plants when treated with compost–vermicompost derived from agricultural residues. Vermicompost, when compared to traditional compost, fostered superior growth in chili and brinjal plants, especially in metrics such as plant height and leaf count. When comparing the effects of two different worm species, E. fetida emerged as the more beneficial species. Aynehband et al. [39] found that vermicompost sourced from crop residues presented a more favorable biological environment than those produced from manure or the direct application of crop residues. Ewulo et al. [40] observed analogous results when studying cow dung manure’s impact on soil, leaf nutrients, and pepper yield. Beyond just plant growth, Suthar [41] showcased the enhancement of product value via bioconversion of crop residues and cattle shed manure using the earthworm Eudrilus eugeniae. Ananthavalli et al. [26] examined the growth and reproduction of Perionyx excavatus in a mix of seaweed and cow dung through the vermicomposting process. Their findings highlighted a significant conversion rate or growth acceleration of Perionyx excavates.
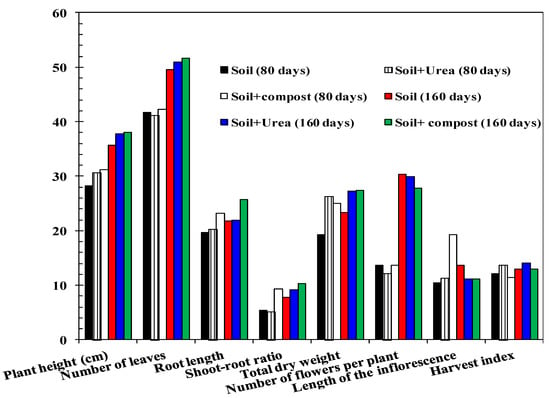
Figure 6.
Effect of the application of compost on the growth of chili plant as agricultural residue (all height and length are in centimeters and weight is in gram). SEM = 1.28; p-value of composting X Control Interaction = 0.05. Least squares mean lacking a common letter differ (p < 0.05).
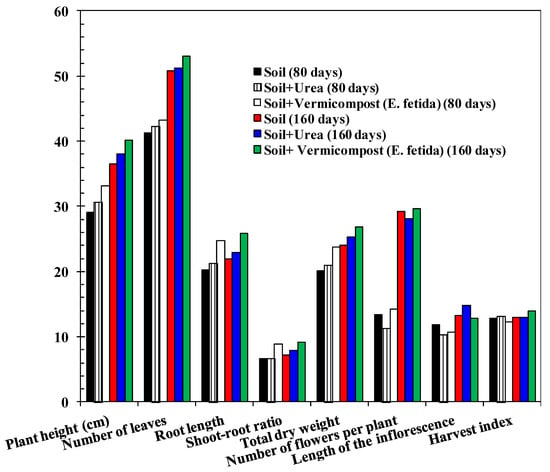
Figure 7.
Effect of the application of vermicompost (E. fetida) on the growth of chili plant as composted agricultural residue (all height and length are in centimeters and weight is in gram). SEM = 1.23; p-value of vermicompost (E. fetida) X Control Interaction = 0.03. Least squares mean lacking a common letter differ (p < 0.05).
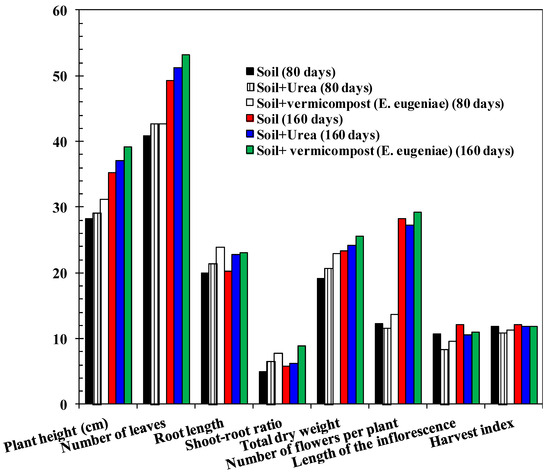
Figure 8.
Effect of the application of vermicompost (E. eugeniae) on the growth of chili plant as composted agricultural residue (all height and length are in centimeters and weight is in gram). SEM = 1.57; p-value of vermicompost (E. eugeniae) X Control Interaction = 0.12. Least squares mean lacking a common letter differ (p < 0.05).
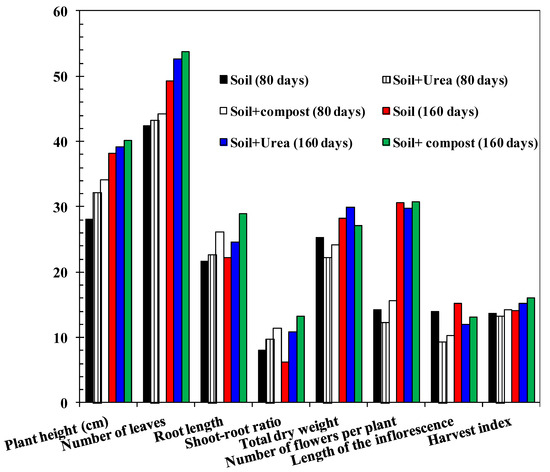
Figure 9.
Effect of the application of compost on the growth of brinjal plant as composted agricultural residue (all height and length are in centimeters and weight is in gram). SEM = 1.23; p-value of compost X Control Interaction = 0.22. Least squares mean lacking a common letter differ (p < 0.05).
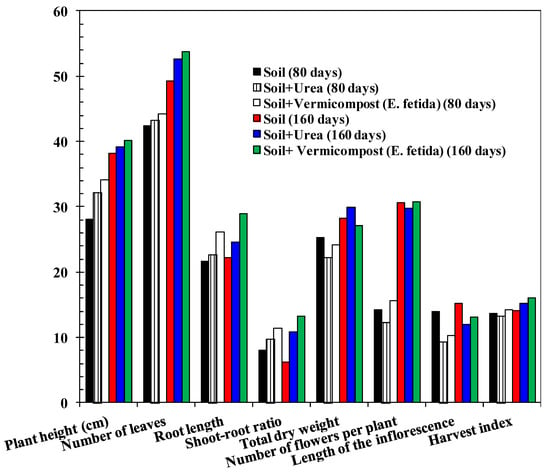
Figure 10.
Effect of the application of vermicompost (E. fetida) on the growth of brinjal plant (all height and length are in centimeters and weight is in gram). SEM = 1.12; p-value of vermicompost (E. fetida) X Control Interaction = 0.09. Least squares mean lacking a common letter differ (p < 0.05).
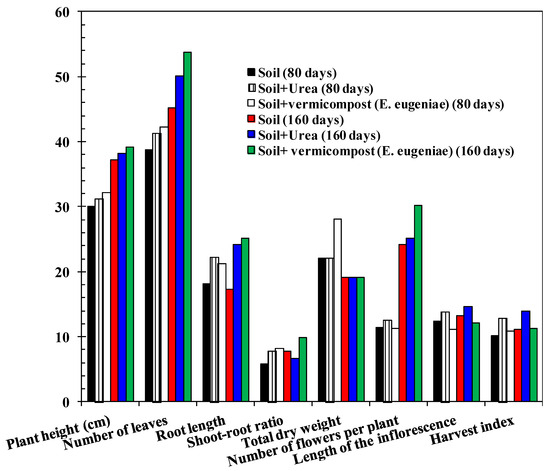
Figure 11.
Effect of the application of vermicompost (E. eugeniae) on the growth of brinjal plant (all height and length are in centimeters and weight is in gram). SEM = 1.61; p-value of vermicompost (E. eugeniae) X Control Interaction = 0.41. Least squares mean lacking a common letter differ (p < 0.05).
Figure 12 illustrates the waste and bioresource management strategy implemented at Sharda Vihar, Bhopal, aimed at producing biofertilizer via a structured vermicomposting process. The research indicates that earthworms are not only able to survive but also thrive and reproduce in vermireactors that utilize composted waste from the Sharda Vihar campus. Nuntawut et al. [42] have posited that vermicomposting is an invaluable technique for transforming agro-industrial waste, thereby promoting sustainable agriculture. This affinity towards vermicomposting may be linked to the organisms’ inclination for organic fertilizers, DBS in particular.

Figure 12.
Waste-cum-bioresource management at Sharda Vihar, Bhopal for biofertilizer through engineered vermicomposting.
4. Conclusions
In this study, we devised a method for composting and vermicomposting of agro-residues sourced from the Sharda Vihar campus.
- One notable observation was the marked influence of worm density on the increase in zoomass. The most substantial growth occurred at a worm density of 125 animals/L, which outperformed densities of 62.5, 250, and 350 animals/L.
- The resultant NPK values ranged between 1.5 and 1.7% (N), 0.98 and 1.19% (P), and 1.1 and 1.49% (K) across various composted–vermicomposted wastes, underscoring the potential of the final vermicompost product as a marketable soil fertility enhancer.
- Exploring the effects of worm loading, a recovery of 64.4% was noted with E. fetida at 62.5 animals per liter, whereas E. eugeniae achieved 45.6%. Increasing the density to 125 animals per liter resulted in recoveries of 89.7% and 68.2% for E. fetida and E. eugeniae reactors, respectively on vermicast production.
While vermicomposting presents numerous advantages, including producing nutrient-rich compost, enhancing soil fertility, and environmentally friendly waste management, it is essential to consider its challenges. Scaling up vermicomposting for broader waste disposal necessitates significant land and infrastructure, and the logistics involved in handling and processing large volumes of waste can be daunting. Ensuring consistent quality and safety standards in the produced vermicompost is also imperative. In conclusion, while vermicomposting offers a sustainable and eco-friendly solution for waste management and soil enrichment, its large-scale implementation requires careful planning and consideration of associated challenges.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/su152014701/s1, Figure S1: Photographic images of Sharda Vihar campus (a), Cows in open yard (b), Bio-gas plants of 10 and 45 m3 capacities (c), and 9.5 kVA dual fuel (diesel + bio-gas) generator-set (d). Figure S2: Photographic image of biogas slurry from pilot scale biogas plant (a), and composting reactors adopted for the study (b). Figure S3: Different laboratory-scale vermireactor adopted for the study. Figure S4: Bio-manure preparation by Earthworms. (a) vermicompost pits (b) Earthworm Eisenia fetida (c) Earthworm Eudrilus eugeniae (d) biomanure.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.S. and M.A.K.; methodology, R.B.K. and S.S.; software, A.K.S.; validation, A.K.S. and S.A.; formal analysis, A.P.-S.; investigation, R.B.K. and S.M.; resources, S.S. and A.K.S.; data curation, R.B.K., S.S. and A.K.S.; writing—original draft preparation, R.B.K. and S.S.; writing—review and editing, B.-H.J. and R.A.; visualization, M.A.K.; supervision, S.S.; project administration, S.S. and S.M.; funding acquisition, M.A.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded through Researchers Supporting Project number (RSP2023R345), King Saud University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia.
Data Availability Statement
Data are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Acknowledgments
Authors are thankful to Sharda Vihar Management and special thanks to Hukum Patidar and Vishnu Patidar for sample handling and others. Moonis Ali Khan acknowledges the financial support through Researchers Supporting Project number (RSP2023R345), King Saud University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia. Byong-Hun Jeon acknowledges National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) for funding through the Korea government (MSIT) (No. RS-2023-00219983).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Rehman, Z.U.; Ijaz, N.; Ye, W.; Ijaz, Z. Design optimization and statistical modeling of recycled waste-based additive for a variety of construction scenarios on heaving ground. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 39783–39802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, N.; Yadav, K.K.; Kumar, V. A review on current status of municipal solid waste management in India. J. Environ. Sci. 2015, 37, 206–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katiyar, R.B.; Suresh, S.; Sharma, A.K. Solid waste management in Bhopal (India): Present and future challenges. Ultra Chem. 2013, 9, 197–214. [Google Scholar]
- Benitez, E.; Nogales, R.; Elvira, C.; Masciandaro, G.; Ceccanti, B. Enzyme activities as indicators of the stabilization of sewage sludge composting with Eisenia foetida. Biores. Technol. 1999, 67, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuvaraj, A.; Thangaraj, R.; Ravindran, B.; Chang, S.W.; Karmegam, N. Centrality of cattle solid wastes in vermicomposting technology—A cleaner resource recovery and biowaste recycling option for agricultural and environmental sustainability. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 268, 1156882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soobhany, N.; Mohee, R.; Garg, V.K. Recovery of nutrient from municipal solid waste by composting and vermicomposting using earthworm Eudrilus eugeniae. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2015, 3, 2931–2942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulcu, R.; Yaldiz, O. Composting of goat manure and wheat straw using pine cones as a bulking agent. Bioresour. Technol. 2007, 98, 2700–2704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.; Suresh, S.; Chauhan, M.S.; Subbaramaiah, V.; Gosu, V. Recent Progress in Carbonaceous Materials for the NitrateAdsorption. J. Hazardous Toxic. Radioact. Waste 2022, 26, 04022013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, K.; Suresh, S.; Arisutha, S.; Sudhakar, K. Anaerobic Co-digestion of different wastes in a UASB. Waste Manag. 2018, 77, 545–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colon, J.; Cadena, E.; Pognani, M.; Barrena, R.; Sanchez, A.; Font, X.; Artola, A. Determination of the energy and environmental burdens associated with the biological treatment of source-separated Municipal Solid Wastes. Energy Environ. Sci. 2012, 5, 5731–5741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndegwa, P.M.; Thompson, S.A. Integrating composting and Vermicomposting in the treatment and bioconversion of biosolids. Bioresour. Technol. 2001, 76, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.; Jain, A.; Sarma, B.K.; Abhilash, P.C.; Singh, H.B. Solid waste management of temple floral offerings by vermicomposting using Eisenia fetida. Waste Manag. 2013, 33, 1113–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gajalakshmi, S.; Abbasi, S.A. Effect of the application of water hyacinth compost/vermicompost on the growth and flowering of Crossandra undulaefolia, and on several vegetables. Bioresour. Technol. 2002, 85, 197–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, K.; Xia, H.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Cui, G.; Li, F.; Bai, W.; Jiang, Y.; Wu, N. Elimination of antibiotic resistance genes and human pathogenic bacteria by earthworms during vermicomposting of dewatered sludge by metagenomicanalysis. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 297, 122451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khwairakpam, M.; Bhargava, R. Vermitechnology for sewage sludge recycling. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 161, 948–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganesh, P.S.; Gajalakshmi, S.; Abbasi, S.A. Vermicomposting of the leaf litter of acacia (Acacia auriculiformis): Possible roles of reactor geometry, polyphenols, and lignin. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 1819–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, W.P.; Taylor, M.; Cossins, R. Evaluation of respirometry of the loading capacity of a high rate vermicompost bed for treating sewage sludge. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 98, 2611–2618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndegwa, P.M.; Thompson, S.A.; Das, K.C. Effects of stocking density and feeding rate on vermicomposting of biosolids. Bioresour. Technol. 2000, 71, 512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suresh, S.; Keshav, A. Textbook of Separation Processes; Studium Press (India) Pvt. Ltd.: Delhi, India, 2012; pp. 1–459. ISBN 978-93-80012-32-2. [Google Scholar]
- Mishra, S.; Chauhan, M.S.; Sundaramurthy, S. Assessment of Groundwater Trends in Bhopal, Madhya Pradesh: A Statistical Approach. Sustainability 2023, 15, 11971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walkley, A.; Black, I.A. An examination of the Degtjareff method for determining soil organic matter and a proposed modification of the chromic acid titration method. Soil Sci. 1934, 37, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clesceri, L.S.; Greenberg, A.E.; Eaton, A.D. (Eds.) Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 20th ed.; American Public Health Association; American Water Works Association; Water Environment Federation: Washington, DC, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Pigatin, L.B.F.; Atoloye, I.A.; Obikoya, O.A.; Borsato, A.V.; Rezende, M.O.O. Chemical study of vermicomposted agro industrial wastes. Int. J. Recycl. Org. Waste Agric. 2016, 5, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domínguez, J.; Edwards, C.A. Effects of stocking rate and moisture content on the growth and maturation of Eisenia andrei (Oligochaeta) in pig manure. Soil. Biol. Biochem. 1997, 29, 743–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, N.; Das, S.; Goswami, L.; Das, P.; Sahariah, B.; Bhattacharya, S.S. Intensification of vermitechnology for kitchen vegetable waste and paddy straw employing earthworm consortium: Assessment of maturity time, microbial community structure, and economic benefit. J. Clean. Produc. 2018, 182, 414–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ananthavalli, R.; Ramadas, V.; Paula, J.A.J.; Selvi, B.K.; Karmegam, N. Seaweeds as bioresources for vermicompost production using the earthworm, Perionyx excavatus (Perrier). Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 275, 394–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deka, H.; Deka, S.; Baruah, C.K.; Das, J.; Hoque, S.; Sarma, H.; Sarma, N.S. Vermicomposting potentiality of Perionyx excavatus for recycling of waste biomass of java citronella—An aromatic oil yielding plant. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 11212–11217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramnarain, Y.I.; Ansari, A.A.; Ori, L. Vermicomposting of different organic materials using the epigeic earthworm Eisenia foetida. Int. J. Recycl. Org. Waste Agric. 2018, 8, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goh, K.M.; Haynes, R.J. Evaluation of potting media for commercial nursery production of container grown plants. N. Z. J. Agric. Res. 1977, 20, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndegwa, P.M.; Thompson, S.A. Effects of C-to-N ratio on vermicomposting of biosolids. Bioresour. Technol. 2000, 75, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatua, C.; Sengupta, S.; Krishna Balla, V.; Kundu, B.; Chakraborti, A.; Tripathi, S. Dynamics of organic matter decomposition during vermicomposting of banana stem waste using Eisenia fetida. Waste Manag. 2018, 79, 287–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastogi, M.; Nandal, M.; Khosla, B. Microbes as vital additives for solid waste composting. Heliyon 2020, 6, e03343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, N.; Smith, J.E. Reducing pathogen and vector attraction for biosolids. Biocycle 1999, 40, 59–61. [Google Scholar]
- Donahue, D.W.; Chalmers, J.A.; Storey, J.A. Evaluation of in-vessel composting of university postconsumer food wastes. Comp. Sci. Util. 1998, 6, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deepthi, M.P.; Kathireswari, P.; Rini, J.; Saminathan, K.; Karmegam, N. Vermitransformation of monogastric Elephas maximus and ruminant Bos taurus excrements into vermicompost using Eudrilus eugeniae. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 320 Pt A, 124302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhiday, M.R. Earthworms in agriculture. Indian Farm. 1994, 43, 31–34. [Google Scholar]
- Pathma, J.; Sakthivel, N. Microbial diversity of vermicompost bacteria that exhibit useful agricultural traits and waste management potential. Springer Plus 2012, 1, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuorinen, A.H.; Saharinen, M.H. Evolution of microbiological and chemical parameters during manure and straw co-composting in a drum com- posting system. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 1997, 66, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aynehband, A.; Gorooei, A.; Moezzi, A.A. Management in Organic Agriculture Vermicompost: An Eco-Friendly Technology for Crop Residue Management in Organic Agriculture. Energy Procedia 2017, 141, 667–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ewulo, B.S.; Hassan, K.O.; Ojeniyi, S.O. Comparative effect of cowdung manure on soil and leaf nutrient and yield of pepper. Int. J. Agri. Res. 2007, 2, 1043–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Suthar, S. Bioconversion of post-harvest crop residues and cattle shed manure into value-added products using earthworm Eudrilus eugeniae Kinberg. Ecol. Eng. 2008, 32, 206–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuntawut, C.-N.; Chuleemas, B.I.; Mongkon, T.-O. Vermicompost: Tool for agro-industrial waste management and sustainable agriculture. Int. J. Environ. Rural. Develop. 2010, 1, 38–43. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).