An Overview of the Implication of Climate Change on Fish Farming in Egypt
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. The Meaning of Climate Change
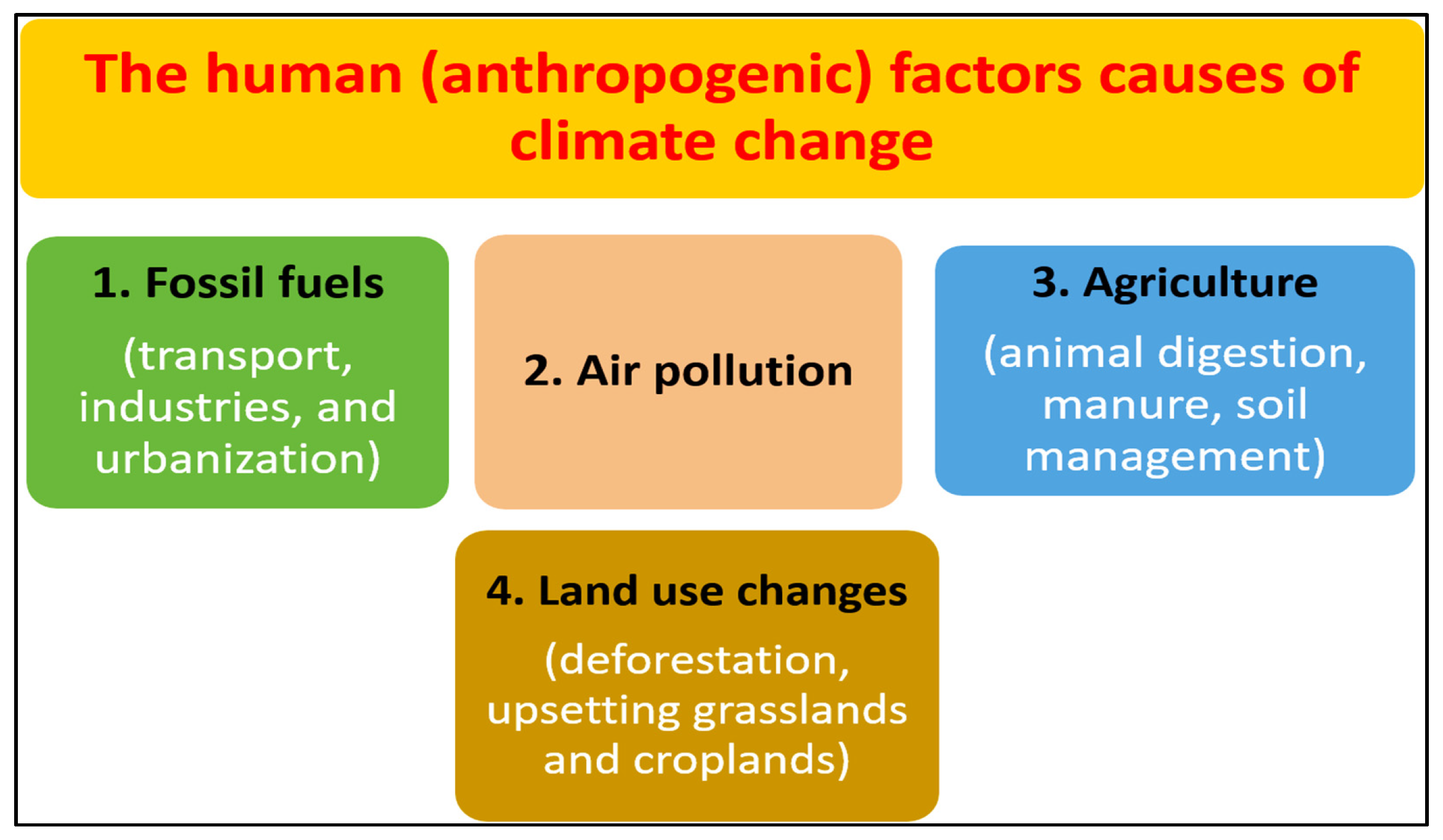
3. The Cause Factors of Climate Change
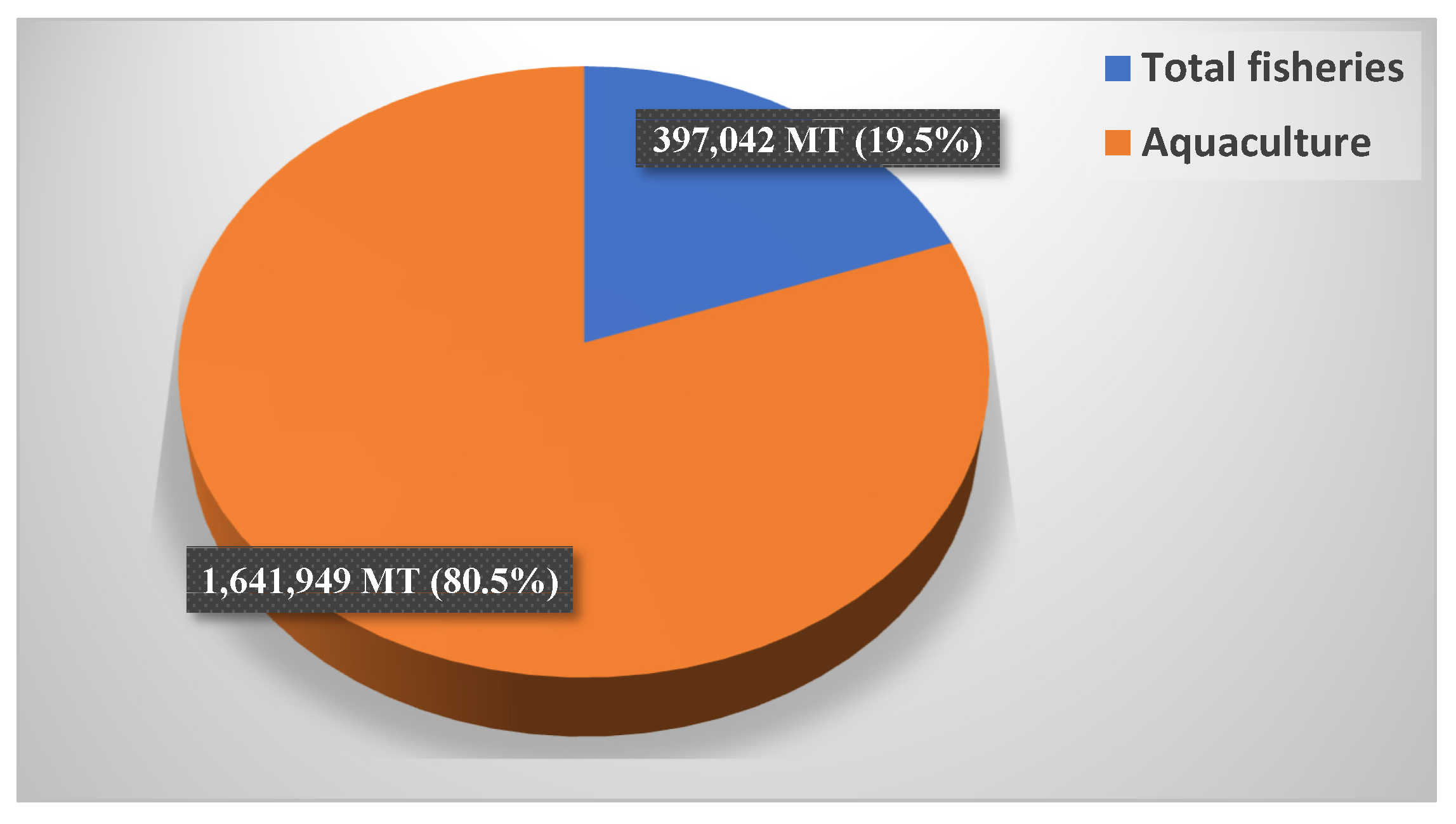
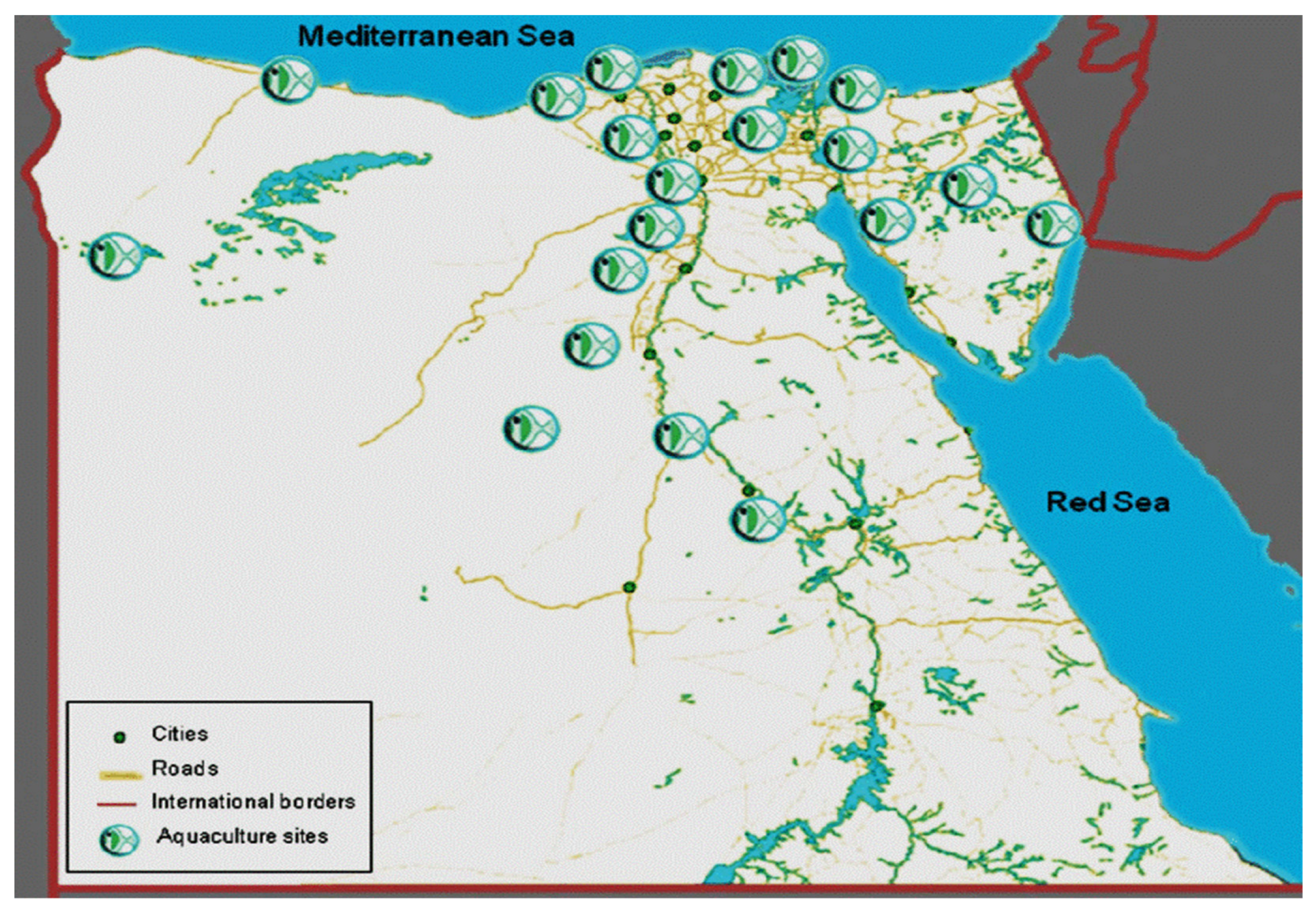
4. Effects of Climate Change on the Fish Farming Sector in Egypt
4.1. Water
4.2. Land
4.3. Feed
4.4. Seeds
5. The Threats of Climate Change on Food Security in Egypt
6. Effect of Climate Change on the Sustainability of the Fish Farm Sector in Egypt
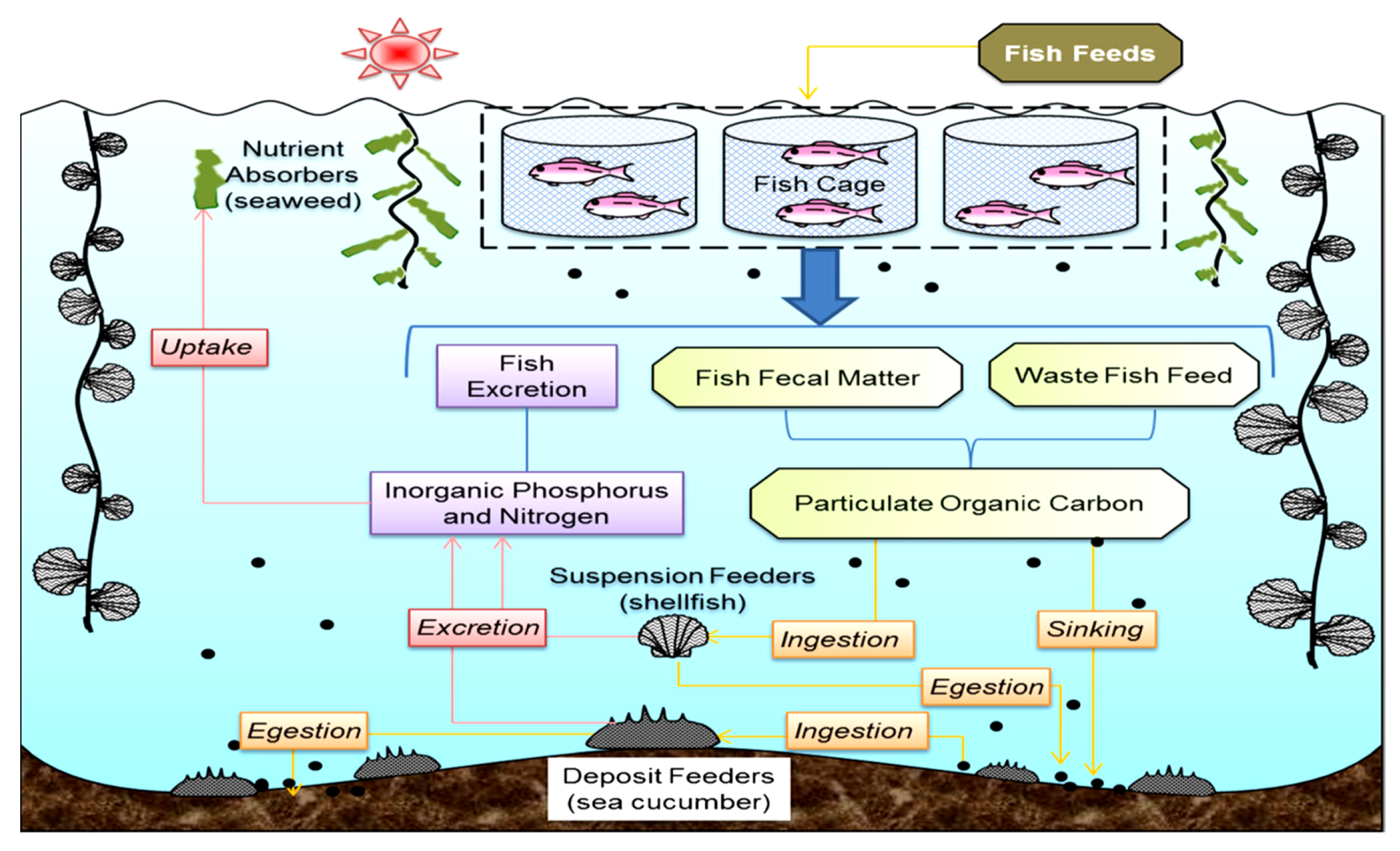
7. The Mitigation of Negative Impacts of Climate Change on Fish Culture
Role of Modern Aquaculture (Integrated) Systems to Mitigate the of Impacts of the Climate Change
- A.
- Recirculation aquaculture system (RAS)
- B.
- Aquaponics system
- C.
- Biofloc technology (BFT)
- D.
- Integrated multi-trophic aquaculture (IMTA)
8. Conclusions
- Greater public awareness, especially among all related stakeholders to the fish farming sector in Egypt, must be raised about the problems of climate change and its negative effects on the fish sector;
- Using environmentally friendly aquaculture techniques such as RAS, aquaponics, BFT, or cage farming systems;
- Using groundwater and effluent discharge in order to overcome the present and future anticipated limitations of fresh water and brackish water;
- Researchers should start to evaluate the economic feasibility and optimum usage of novel proteins as fishmeal substitutes. Furthermore, the improvement of local raw materials to be used in fish feed formulation is also highly recommended;
- The creation of new fish strains with increased salinity tolerance or increased temperature tolerance to cope with alterations by climate change;
- The easier solution is to diversify the production to a heat-tolerant fish species or gradually increase the production of fish species such as the African catfish, which is more resistant to higher temperatures, has a larger thermal window, and better responds to thermal stress;
- Increasing the production of fish seeds in hatcheries, as well as the genetic selection of seeds that adapt to new environmental conditions;
- Reducing energy use through energy conservation and introducing possible renewable energy approaches.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- FAO. The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture 2020. Sustainability in Action; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Béné, C. Small-Scale Fisheries: Assessing Their Contribution to Rural Livelihoods in Developing Countries; FAO Fisheries Circular. No. 1008; Food and Agriculture Organization: Rome, Italy, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Allison, E. Aquaculture, Fisheries, Poverty and Food Security; Working Paper 2011-65; The WorldFish Center: Penang, Malaysia, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- FAO. The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture 2016. Contributing to Food Security and Nutrition for All; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, A.; ElSayed, M.; Radwan, R.; Hefny, R. An economic study of the fish production system in Egypt. Sinai J. of Appl. Sci. 2020, 9, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GAFRD. The General Authority for Fishery Resources Development: Fisheries Statistics Yearbook 2019, 29th ed.; General Authority for Fish Resources Development, Ministry of Agriculture: Cairo, Egypt, 2019; 104p. [Google Scholar]
- El-Sayed, A.-F.M. Aquaculture Feed and Fertilizer Resource Atlas of Egypt; FAO, Regional Office of the Near East: Cairo, Egypt, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Soliman, N.F.; Yacout, D.M.M. The prospects of analysing the environmental impacts of Egyptian aquaculture using life cycle assessment. Int. J. Aquac. 2015, 5, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. Egypt—National Aquaculture Sector Overview; FAO Fisheries Department, Fisheries Information, Data and Statistics Unit: Rome, Italy, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Wally, A. The state and development of aquaculture in Egypt. Glob. Agric. Inf. Netw. 2016, 1–14. Available online: https://www.fas.usda.gov/data/egypt-state-and-development-aquaculture-egypt (accessed on 10 May 2022).
- Suloma, A.; Ogata, H.Y. Future of rice-fish culture, desert aquaculture and feed development in Africa: The case of Egypt as the leading country in Africa. Jpn. Agric. Res. Q. 2006, 40, 351–360. Available online: https://www.jircas.affrc.go.jp (accessed on 22 March 2022). [CrossRef]
- El-Gayar, O. Aquaculture in Egypt and Issue for Sustainable Development. Aquac. Econ. Manag. 2003, 7, 137–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naziri, D. Financial services for SME (small and medium-scale enterprise) aquaculture producers. Marine Policy 2003, 37, 106–114. [Google Scholar]
- Mur, R. Development of the Aquaculture Value Chain in Egypt: Report of the National Innovation Platform Workshop, 19–20 February 2014; WorldFish: Cairo, Egypt, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- FAO. The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture; FAO Fisheries Department, Fisheries Information, Data and Statistics Unit: Rome, Italy, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Mansour, E.; Moustafa, E.D.; Qabil, N.; Abdelsalam, A.; Wafa, H.A.; Kenawy, A.E.; Casas, A.M.; Igartua, E. Assessing different barley growth habits under Egyptian conditions for enhancing resilience to climate change. Field Crop. Res. 2018, 224, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPCC. Climate Change 2007: The Physical Science Basis: Contribution of Working Group to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Solomon, S., Qin, D., Manning, M., Chen, Z., Marquis, M., Averyt, K.B., Tignor, M., Miller, H.L., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- IPCC. Climate Change: Synthesis Report: Contribution of Working Groups I, II and III to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Core Writing Team, Pachauri, R.K., Meyer, L.A., Eds.; IPCC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Rutenberg, I.; Gwagwa, A.; Omino, M. Use and Impact of Artificial Intelligence on Climate Change Adaptation in Africa; Oguge, N., Ayal, D., Adeleke, L., da Silva, I., Eds.; African Handbook of Climate Change Adaptation; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maulu, S.; Hasimuna, O.J.; Haambiya, L.H.; Monde, C.; Musuka, C.G.; Makorwa, T.H.; Munganga, B.P.; Phiri, K.J.; Nsekanabo, J.D. Climate Change Effects on Aquaculture Production: Sustainability Implications, Mitigation, and Adaptations. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2021, 5, 609097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cianconi, P.; Betrò, S.; Janiri, L. The Impact of Climate Change on Mental Health: A Systematic Descriptive Review. Front. Psychiatry 2020, 11, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amoak, D.; Luginaah, I.; McBean, G. Climate Change, Food Security, and Health: Harnessing Agroecology to Build Climate Resilient Communities. Sustainability 2022, 14, 13954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, G.; Gurney-Smith, H.; Marcogliese, D.; Knowler, D.; Benfey, T.; Garber, A.; Forster, I.; Chopin, T.; Brewer-Dalton, K.; Moccia, R.; et al. Climate change and aquaculture: Considering biological response and resources. Aquacult. Environ. Interact. 2019, 11, 569–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volkoff, H.; Rønnestad, I. Effects of temperature on feeding and digestive processes in fish. Temperature 2020, 7, 307–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Ding, L.; Wang, J.; Ding, C.; Tao, J. The impacts of climate change on fish growth: A summary of conducted studies and current knowledge. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 121, 106976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magouz, F.I.; Amer, A.A.; Faisal, A.; Sewilam, H.; Aboelenine, S.M.; Dawood, M.A.O. The effects of dietary oregano essential oil on the growth performance, intestinal health, immune, and antioxidative responses of Nile tilapia under acute heat stress. Aquaculture 2022, 548, 737632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skeeles, M.R.; Winkler, A.C.; Duncan, M.I.; James, N.C.; van der Walt, K.A.; Potts, W.M. The use of internalheart rate loggers in determining cardiac breakpoints of fish. J. Therm. Biol. 2020, 89, 102524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haverinen, J.; Vornanen, M. Reduced ventricular excitability causes atrioventricular block and depression of heart rate in fish at critically high temperatures. J. Exp. Biol. 2020, 223, jeb225227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, S.; Ergün, S.; Çelik, E.Ş.; Banni, M.; Ahmadifar, E.; Dawood, M.A.O. The impact of acute cold water stress on blood parameters, mortality rate and stress-related genes in Oreochromis niloticus, Oreochromis mossambicus and their hybrids. J. Therm. Biol. 2021, 100, 103049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Kim, S.-K.; Hur, Y.B. Temperature-mediated changes in stress responses, acetylcholinesterase, and immune responses of juvenile olive flounder Paralichthys olivaceusin a biofloc environment. Aquaculture 2019, 506, 453–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbinati, E.C.; Zanuzzo, F.S.; Biller, J.D. Stress and Immune System in Fish. InBiology and Physiology of Freshwater Neotropical Fish; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 93–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feidantsis, K.; Pörtner, H.O.; Giantsis, I.A.; Michaelidis, B. Advances in understanding the impacts of globalwarming on marine fishes farmed offshore:Sparus aurataas a case study. J. Fish Biol. 2021, 98, 1509–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cejko, B.I.; Krejszeff, S.; Judycka, S.; Targońska, K.; Kucharczyk, D. Effect of different treatment agents and post-treatment latency times on spermiation stimulation of northern pike (Esox lucius) under controlled conditions. Theriogenology 2019, 142, 260–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dadras, H.; Dzyuba, V.; Golpour, A.; Xin, M.; Dzyuba, B. In vitro antioxidant enzyme activity and sperm motility at different temperatures in starlet Acipenser ruthenus and rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2019, 45, 1791–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Servili, A.; Canario, A.V.M.; Mouchel, O.; Muñoz-Cueto, J.A. Climate change impacts on fish reproduction aremediated at multiple levels of the brain-pituitary-gonad axis. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2020, 291, 113439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.L.; Zhao, L.L.; Liao, L.; Tang, X.H.; Cui, C.; Liu, Q.; Yang, S. Interactive effect of thermal and hypoxia on largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides) gill and liver: Aggravation of oxidative stress, inhibition of immunity and promotion of cell apoptosis. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2020, 98, 923–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cascarano, M.C.; Stavrakidis-Zachou, O.; Mladineo, I.; Thompson, K.D.; Papandroulakis, N.; Katharios, P. Mediterranean aquaculture in a changing climate: Temperature effects on pathogens and diseases of three farmed fish species. Pathogens 2021, 10, 1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, M.J.; Kunzmann, A.; Slater, J.M. Responses of aquaculture fish to climate change induced extreme temperatures: A review. J. World Aquac. Soc. 2022, 53, 314–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leach, K.; Zalat, S.; Gilbert, F. Egypt’s protected area network under future climate change. Biol. Conserv. 2013, 159, 490–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouda, S.; Ewise, M.; Noreldin, T. Projection of productivity of cultivated crops in rain-fed areas in Egypt under climate change. Cogent Food Agric. 2016, 2, 1136256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NRC National Research Council. Climate Change: Evidence and Causes: Update 2020; The National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPCC. Special Report on the Ocean and Cryosphere in a Changing Climate. 2019. Available online: https://www.ipcc.ch/srocc (accessed on 20 May 2022).
- IPCC (Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change). Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis; Working Group I contribution to the IPCC Sixth Assessment Report; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2021; Available online: www.ipcc.ch/assessment-report/ar6 (accessed on 9 August 2022).
- Kobiruzzaman, M.M. Cause of Climate Change-9 Natural Causes of Climate Change in 2022. Newsmoor- Educational Website For Online Learning. 2022. Available online: https://newsmoor.com/natural-causes-of-climate-change-9-natural-causes-of-climate-change/ (accessed on 15 July 2022).
- Onoja, U.S.; Dibua, U.M.E.; Enete, A.A. Climate change: Causes, effects and mitigation measures-A Review. GJPAS 2011, 17, 469–479. [Google Scholar]
- Waite, R.; Beveridge, M.; Brummet, R.; Castine, S.; Chaiyawannakarn, N.; Kaushik, S.; Mungkung, R.; Nawapakpilai, S.; Phillips, M. Improving Productivity and Environmental Performance of Aquaculture; Working Paper, Installment of Creating a Sustainable Food Future; World Resources Institute: Washington, DC, USA, 2014; Available online: http://www.worldresourcesreport.org (accessed on 23 January 2022).
- Gado, T.A.; El-Agha, D.E. Climate Change Impacts on Water Balance in Egypt and Opportunities for Adaptations; Abu-hashim, M., Khebour Allouche, F., Negm, A., Eds.; Agro-Environmental Sustainability in MENA Regions. Springer Water; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, O.; Abdelhalim, A.; Liu, Y.; Rico-Ramirez, M.; Han, D. Climate change adaptations for food security in vulnerable areas of the Egyptian Nile—Or tackling the overlooked nexus hazards of hydrological extremes and waste pollutions. Water 2021, 13, 412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soliman, N.F.; Yacout, D.M.M. Aquaculture in Egypt: Status, constraints and potentials. Aquacult. Int. 2016, 24, 1201–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Raey, M. Impacts and implications of climate change for the coastal zones of Egypt. In Coastal Zones and Climate Change; Michel, D., Pandya, A., Eds.; The Henry L. Stimson Center: Washington DC, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Hammond, M. The Grand Ethiopian Renaissance Dam and the Blue Nile: Implications for Transboundary Water Governance; Discussion Paper 1307; Global Water Forum: Canberra, Australia, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Schilling, J.; Hertig, E.; Tramblay, Y.; Scheffran, J. Climate Change Vulnerability, Water Resources and Social Implications in North Africa; Regional Environmental Change; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, J.; McCarl, B.; Kirshen, P.; Jones, R.; Deck, L.; Abdrabo, M.; Borhan, M.; El-Ganzori, A.; El-Shamy, M.; Hassan, M.; et al. Egypt’s economic vulnerability to climate change. Clim. Res. 2014, 62, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasgupta, S.; Laplante, B.; Murray, S.; Wheeler, D. Sea-Level Rise and Storm Surges: A Comparative Analysis of Impacts in Developing Countries; Policy Research working paper No. 4901; The World Bank-Development Research Group—Environment and Energy Team: Washington, DC, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- IUCN. The National Strategy for Mainstreaming Gender in Climate Change in Egypt; International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN): Grand, Swiss, 2011; Available online: https://genderandenvironment.org/resource/egypt-national-strategy-formainstreaming-gender-in-climate-change-in-egypt/ (accessed on 19 April 2021).
- Brander, K.M. Global fish production and climate change. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 19704–19714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. Climate Change Implications for Fisheries and Aquaculture; The State of Fisheries and Aquaculture 2008; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2008; pp. 87–91. [Google Scholar]
- Soliman, N.F. Aquaculture in Egypt under Changing Climate: Challenges and Opportunities; Working Paper No. (4); Alexandria Research Center for Adaptation to Climate Change (ARCA): Alexandria, Egypt, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Swaminathan, M.S. Aquaculture and sustainable nutrition security in a warming planet, Keynote Address. In Proceedings of the Global Conference on Aquaculture—Farming the Waters for People and Food, Phuket, Thailand, 22–25 September 2010; Subasinghe, R.P., Arthur, J.R., Bartley, D.M., De Silva, S.S., Halwart, M., Hishamunda, N., Mohan, C.V., Sorgeloos, P., Eds.; pp. 3–19. [Google Scholar]
- Sayed, M.A.-A. Impacts of Climate Change on the Nile Flows. Ph.D. Thesis, Faculty of Engineering, Ain Shams University, Cairo, Egypt, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Mohamed, Y.A.; van den Hurk, B.; Savenije, H.H.G.; Bastiaanssen, W.G.M. Hydroclimatology of the Nile: Results from a regional climate model. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2005, 9, 263–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elshamy, M.E. Assessing the Hydrological Performance of the Nile Forecast System in Long Term Simulations. Nile Basin Sci. Mag. 2008, 1, 22–36. [Google Scholar]
- Khordagui, H. Climate change in ESCWA region: Reasons for concern. In Proceedings of the Expert Group Meeting on Trade and Environment Priorities in the Arab Region, Cairo, Egypt, 11–13 November 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Abd Ellah, R.G. Water resources in Egypt and their challenges, Lake Nasser case study. Egypt. J. Aquat. Res. 2020, 46, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadek, S. An overview on desert aquaculture in Egypt. In Aquaculture in Desert and Arid Lands: Development Constraints and Opportunities: FAO Technical Workshop, 6–9 July 2010, Hermosillo, Mexico; Crespi, V., Lovatelli, A., Eds.; FAO Fisheries and Aquaculture Proceedings No. 20; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2011; pp. 141–158. [Google Scholar]
- El-Guindy, S. The Use of Brackishwater in Agriculture and Aquaculture; Panel Project on Water Management Workshop on brackish water use in agriculture and aquaculture. 2–5 December 2006; Ministry of Water Resources and Irrigation National Water Research Center Administration Building: Cairo, Egypt, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Mostafa, S.M.; Wahed, O.; El-Nashar, W.Y.; El-Marsafawy, S.M.; Zeleňáková, M.; Abd-Elhamid, H.F. Potential climate change impacts on water resources in Egypt. Water 2021, 13, 1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeleke, M.L.; Al-Kenawy, D.; Nasr-Allah, A.M.; Dickson, M.; Ayal, D. Impacts of Environmental Change on Fish Production in Egypt and Nigeria: Technical Characteristics and Practice. In African Handbook of Climate Change Adaptation; Oguge, N., Ayal, D., Adeleke, L., da Silva, I., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MSEA. National Environmental Action Plan (NEAP) 2002–2017; Ministry of State for Environmental Affairs (MSEA): Cairo, Egypt, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Yates, D.N.; Strzepek, K.M. An assessment of integrated climate change impacts on the agricultural economy of Egypt. Clim. Chang. 1998, 38, 261–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, W.S. The subterranean estuary—A reaction zone of ground water and seawater. Mar. Chem. 1999, 65, 111–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MAB. Fisheries and Aquaculture in a Changing Climate; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- De Silva, S.S. Climate change impacts: Challenges for aquaculture. In Proceedings of the Farming the Waters for People and Food, Proceedings of the Global Conference on Aquaculture 2010, Phuket, Thailand, 22–25 September 2010; Subasinghe, R.P., Arthur, J.R., Bartley, D.M., De Silva, S.S., Halwart, M., Hishamunda, N., Mohan, C.V., Sorgeloos, P., Eds.; FAO: Rome, Italy; NACA: Bangkok, Thailand, 2012; pp. 75–110. [Google Scholar]
- Tacon, A.D.J.; Hasan, M.R.; Subasinghe, R.P. Use of Fishery Resources as Feed Inputs for Aquaculture Development: Trends and Policy Implications; FAO Fisheries Circular No. 1018; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- El-Sayed, A.-F.M. Value chain Analysis of the Egyptian Aquaculture Feed Industry; Project Report; WorldFish: Penang, Malaysia, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Tacon, A.G.; Hasan, M.R.; Metian, M. Demand and Supply of Feed Ingredients for Farmed Fish and Crustaceans; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- FAO. FAOSTAT. 2013. Available online: http://faostat.fao.org/site/339/default.aspx (accessed on 20 May 2021).
- El-Sayed, A.-F.M.; Dickson, M.W.; El-Naggar, G.O. Value chain analysis of the aquaculture feed sector in Egypt. Aquaculture 2015, 437, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramachandran, S.; Ray, A.K. Nutritional evaluation of fermented black gram (Phaseolus mungo) seed meal in compound diets for rohu, Labeo rohita (Hamilton), fingerlings. J. Appl. Ichthyol. 2007, 23, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goda, A.M.A.-S.; Saad, A.; Wafa, M. Complete substitution of dietary wheat bran with Duckweed Lemna species supplemented with exogenous digestive enzymes for freshwater prawn, Macrobrachium rosenbergii (De Man 1879) post larvae. In Proceedings of the Oral Presentation at the International Conference and Exposition of Aquaculture Europe, San Sebastian, Spain, 14–17 October 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Tacon, A.G.J. Use of fishmeal and fish oil in aquaculture: A global perspective. Aquat. Resour. Cult. Dev. 2004, 1, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yones, A.M.M.; Metwalli, A.A. Effects of fishmeal substitution with poultry by-product meal on growth performance, nutrients utilization and blood contents of juvenile Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). J. Aquac. Res. Dev. 2015, 7, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharawya, Z.; Goda, A.M.A.; Hassaan, M.S. Partial or total replacement of fish meal by solid state fermented soybean meal with Saccharomyces cerevisiae in diets for Indian prawn shrimp, Fenneropenaeus indicus, Post larvae. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2016, 212, 90–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Asgah, N.A.; Younis, E.M.; Abdel-Warith, A.A.; Shamlol, F.S. Evaluation of red seaweed, Gracilaria arcuata as dietary ingredient in African catfish, Clarias gariepinus. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2016, 23, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Warith, A.A.; Younis, E.M.I.; Al-Asgah, N.A. Potential use of green macroalgae, Ulva lactuca as a feed supplement in diets on growth performance, feed utilization and body composition of the African catfish, Clarias gariepinus. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2016, 23, 404–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pankhurst, N.W.; Munday, P.L. Effects of climate change on fish reproduction and early life history stages. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2011, 62, 1015–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alami-Durante, H.; Olive, N.; Rouel, M. Early thermal history significantly affects the seasonal hyperplastic process occurring in the myotomal white muscle of Dicentrarchus labrax juvenile. Cell Tissue Res. 2007, 327, 553–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sneddon, L.U. Trigeminal somatosensory innervation of the head of a teleost fish with particular reference to nociception. Brain Res. 2003, 972, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashley, P.J.; Sneddon, L.U.; Mccrohan, C.R. Nociception in fish: Stimulus–response properties of receptors on the head of trout Oncorhynchus mykiss. Brain Res. 2007, 1166, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, L.A.; Chalde, T.; Elisio, M.; Strussmann, C.A. Effects of global warming on fish reproductive endocrine axis, with special emphasis in pejerrey Odontesthes bonariensis. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2013, 192, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahnsteiner, F.; Leitner, S. Effect of temperature on gametogenesis and gamete quality in brown trout, Salmo trutta. J. Exp. Zool. A Ecol. Genet. Physiol. 2013, 319, 138–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strussmann, C.A.; Patino, R. Sex determination, environmental. In Encyclopedia of Reproduction; Knobil, E., Neill, J.D., Eds.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1999; pp. 402–409. [Google Scholar]
- Piferrer, F.; Blazquez, M.; Navarro, L.; Gonzalez, A. Genetic, endocrine, and environmental components of sex determination and differentiation in the European sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax L.). Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2005, 142, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usman, I.; Auta, J.; Abdullahi, S.A. Effect of monthly variation in water temperature on artificial breeding of common carp (Cyprinus carpio L.) in Zaria, Nigeria. Int. J. Fish. Aquat. Stud. 2015, 3, 353–356. [Google Scholar]
- Khater, E.S.G.; Ali, S.A.; Mohamed, W.E. Effect of water temperature on masculinization and growth of Nile tilapia fish. J. Aquac. Res. Dev. 2017, 8, 8–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazumder, S.K.; De, M.; Mazlan, A.G.; Zaidi, C.C.; Rahim, S.M.; Simon, K.D. Impact of global climate change on fish growth, digestion and physiological status: Developing a hypothesis for cause and effect relationships. J. Water Clim. Chang. 2015, 6, 200–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Gorman, E.J.; Ólafsson, Ó.P.; Demars, B.O.L.; Friberg, N.; Guðbergsson, G.; Hannesdóttir, E.R.; Jackson, M.C.; Johansson, L.S.; McLaughlin, Ó.B.; Ólafsson, J.S.; et al. Temperature effects on fish production across a natural thermal gradient. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2016, 22, 3206–3220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikari, S.; Chaudhury, A.K.; Gangadhar, B.; Ramesh, R.; Mandal, R.N.; Sarosh, I.; Saha, G.S.; De, H.K.; Sivaraman, I.; Mahapatra, A.S.; et al. Adaptation and mitigation strategies of climate change impact in freshwater aquaculture in some states of India. J. FisheriesSciences.com 2018, 12, 16–21. [Google Scholar]
- Valeta, J.S.; Likongwe, J.S.; Kassam, D.; Maluwa, A.O. Temperature-dependent egg development rates, hatchability and fry survival rate of Lake Malawi Tilapia (Chambo), Oreochromis karongae (Pisces: Cichlidae). Int. J. Fish. Aquac. 2013, 5, 55–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okunsebor, S.; Ofojekwu, P.; Kakwi, D.; Audu, B. Effect of temperature on fertilization, hatching and survival rates of Heterobranchus bidorsalis eggs and hatchlings. Br. J. Appl. Sci. Technol. 2015, 7, 372–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marks, C.; Kaut, K.P.; Moore, F.B.; Bagatto, B. Ontogenetic oxygen changes alter zebra fish size, behavior, and blood glucose. Physiol. Biochem. Zool. 2012, 85, 635–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Rio, A.M.; Davis, B.E.; Fangue, N.A.; Todgham, A.E. Combined effects of warming and hypoxia on early life stage Chinook salmon physiology and development. Conserv. Physiol. 2019, 7, coy078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welch, M.J.; Munday, P.L. Contrasting effects of ocean acidification on reproduction in reef fishes. Coral Reefs 2016, 35, 485–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milazzo, M.; Cattano, C.; Alonzo, S.H.; Foggo, A.; Gristina, M.; Rodolfo-Metalpa, R.; Sinopoli, M.; Spatafora, D.; Stiver, K.A.; Hall-Spencer, J.M. Ocean acidification affects fish spawning but not paternity at CO2 seeps. Proc. Biol. Sci. 2016, 283, 20161021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehtonen, T.K.; Wong, B.B.; Kvarnemo, C. Effects of salinity on nest-building behaviour in a marine fish. BMC Ecol. 2016, 16, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruz Vieira, A.B.; Weber, A.A.; Ribeiro, Y.M.; Luz, R.K.; Bazzoli, N.; Rizzo, E. Influence of salinity on spermatogenesis in adult Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) testis. Theriogenology 2019, 131, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, M.A. Freshwater fish seed resources in Egypt. In Assessment of Freshwater Fish Seed Resources for Sustainable Aquac; BondadReantaso, M.G., Ed.; FAO Fisheries Technical Paper; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2007; pp. 241–255. [Google Scholar]
- GAFRD. The General Authority for Fishery Resources Development: Fisheries Statistics Yearbook 2020, 30th ed.; General Authority for Fish Resources Development, Ministry of Agriculture: Cairo, Egypt, 2020; 102p. [Google Scholar]
- Nasr-Allah, A.M.; Dickson, M.W.; Al-Kenawy, D.A.; Fathi, M.; El-Naggar, G.O.; Azazy, G.E.; Grana, Y.S.; Diab, A.M. Value chain analysis of Egyptian fish seed production. In Proceedings of the 4th Conference of Central Laboratory for Aquaculture Research, held in the International Agricultural Center, Doki, Egypt, 11–12 March 2014; pp. 351–372. [Google Scholar]
- Macfadyen, G.; Nasr-Alla, A.M.; Al-Kenawy, D.; Fathi, M.; Hebicha, H.; Diab, A.M.; Hussein, S.M.; Abou-Zeid, R.M.; El-Naggar, G. Value-chain analysis—An assessment methodology to estimate Egyptian aquaculture sector performance. Aquaculture 2012, 362, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naiel, R.A.; Aamer, M.G.; Ibrahim, A.A.; Azazy, G.E. Economics of fry production of fish hatcheries. Zagazig J. Agric. Res. 2011, 38, 1329–1341. [Google Scholar]
- Abbass, K.; Qasim, M.Z.; Song, H.; Murshed, M.; Mahmood, H.; Younis, I. A review of the global climate change impacts, adaptation, and sustainable mitigation measures. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 42539–42559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yassin, L. Climate Change and Food Security in Egypt. Master’s Thesis, The American University, Cairo, Egypt, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, Z.; Hu, Y.; Jenkins, K.; He, Y.; Forstenhäusler, N.; Warren, R.; Yang, L.; Jenkins, R.; Guan, D. Assessing the economic impacts of future fluvial flooding in six countries under climate change and socio-economic development. Clim. Chang. 2021, 166, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNDP. Adaptation to Climate Change in the Nile Delta through Integrated Coastal Zone Management. Climate Change Project Document; United Nations Development Program: New York, NY, USA, 2016; Available online: https://iwlearn.net/iw-projects/3242 (accessed on 17 December 2021).
- Conway, D.; Krol, M.; Alcamo, J.; Hulme, M. Future availability of water in Egypt: The interaction of global, regional and basin scale driving forces in the Nile Basin. Ambio 1996, 25, 336–342. [Google Scholar]
- Bizikova, L.; Robinson, J.; Cohen, S. Linking climate change and sustainable development at the local level. Clim. Policy 2007, 7, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Hu, X. Fish and its multiple human health effects in times of threats to sustainability and affordability are there alternatives. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Nutr. 2009, 18, 553–563. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shaw, D.J. World Food Summit, 1996. In World Food Security; Palgrave Macmillan: London, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omar, M.E.M.; Moussa, A.M.A.; Hinkelmann, R. Impacts of climate change on water quantity, water salinity, food security, and socioeconomy in Egypt. Water Sci. Eng. 2021, 14, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, G.C.; Rosegrant, M.W.; Palazzo, A.; Gray, I.; Ingersoll, C.; Robertson, R.D.; Tokgoz, S.; Zhu, T.; Sulser, T.B.; Ringler, C.; et al. Food Security, Farming, and Climate Change to 2050: Scenarios, Results, Policy Options; International Food Policy Research Institute (IFPRI): Washington, DC, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tielens, J.; Candel, J.J.L. Reducing Food Wastage, Improving Food Security? Food and Business Knowledge Platform. 2014. Available online: http://knowledge4food.net/wp-content/uploads/2014/07/140702_fbkp_report-foodwastage_DEF.pdf (accessed on 25 November 2021).
- Tabthipwon, P. Aquaculture Development toward the Sustainable and Current Situation of Aquaculture; Food Fertil Technol Center: Taipei, China, 2008; pp. 45–55. [Google Scholar]
- Johnston, P.; Everard, M.; Santillo, D.; Robert, K.H. Reclaiming the definition of sustainability. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2007, 14, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valenti, W.C.; Kimpara, J.M.; Preto, B.L.; Moraes-Valenti, P. Indicators of sustainability to assess aquaculture systems. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 88, 402–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogard, J.R.; Farmery, A.K.; Little, D.C.; Fulton, E.A.; Cook, M. Will fish be part of future healthy and sustainable diets? Lancet Planet. Health 2019, 3, e159–e160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaleem, O.; Singou Sabi, A.-F.B. Overview of aquaculture systems in Egypt and Nigeria, prospects, potentials, and constraints. Aquac. Fish. 2021, 6, 535–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bueno, P.B.; Soto, D. Adaptation Strategies of the Aquaculture Sector to the Impacts of Climate Change; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Barange, M.; Bahri, T.; Beveridge, M.C.M.; Cochrane, A.L.; Funge-Smith, S.; Paulain, F. Impacts of Climate Change on Fisheries and Aquaculture, Synthesis of Current Knowledge, Adaptation and Mitigation Options; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Shaalan, M.; El-Mahdy, M.; Saleh, M.; El-Matbouli, M. Aquaculture in Egypt: Insights on the current trends and future perspectives for sustainable development. Rev. Fish. Sci. Aquac. 2018, 26, 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yassien, S.A.; Abd El-Rahim, S.A.; Osman, M.F.; Hamouda, R.E.; Soliman, M.A.M.; Nageib, R.M. Factors affecting aquaculture farms’ profitability and constraints facing fish farmers in Egypt. Egypt. J. Aquat. Biol. Fish. 2022, 26, 519–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, M.T.; Fishar, M.R.; Emam, W.W.M.; Soliman, K.M.; El-Naggar, M.M. Impact of Climate Change on Aquatic Biodiversity of Egypt (A Concise Review). Egypt. J. Aquat. Biol. Fish. 2022, 26, 183–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Ramady, H.R.; El-Marsafawy, S.M.; Lewis, L.N. Sustainable agriculture and climate changes in Egypt. In Sustainable Agriculture Reviews; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 41–95. [Google Scholar]
- Kandlikar, M.; Risbey, J. Agricultural Impacts of Climate Change: If Adaptation is the Answer, What is the Question? Clim. Chang. 2000, 45, 529–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godfray, H.C.J.; Beddington, J.R.; Crute, I.R.; Haddad, L.; Lawrence, D.; Muir, J.F.; Pretty, J.; Robinson, S.; Thomas, S.M.; Toulmin, C. Food security: The challenge of feeding 9 billion people. Science 2010, 327, 812–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivera-Ferre, M.; Ortega-Cerdà, M.; Baumgärtner, J. Rethinking. Study and Management of Agricultural Systems for Policy Design. Sustainability 2013, 5, 3858–3875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velten, S.; Leventon, J.; Jager, N.; Newig, J. What Is Sustainable Agriculture: A Systematic Review. Sustainability 2015, 7, 7833–7865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sae-Lim, P.; Kause, A.; Mulder, H.A.; Olesen, I. Breeding and genetics symposium: Climate change and selective breeding in aquaculture. J. Anim. Sci. 2017, 95, 1801–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mbow, C.; Rosenzweig, C.; Barioni, L.G.; Benton, T.G.; Herrero, M.; Krishnapillai, M.; Liwenga, E.; Pradhan, P.; Rivera-Ferre, M.G.; Sapkota, T.; et al. Food Security. In Climate Change and Land: An IPCC Special Report on Climate Change, Desertification, Land Degradation, Sustainable Land Management, Food Security and Greenhouse Gas Fluxes in Terrestrial Ecosystems; IPCC: Geneva Switzerland, 2019; Available online: https://www.ipcc.ch/site/assets/uploads/sites/4/2020/02/SRCCLChapter-5.pdf (accessed on 28 December 2021).
- Ebeling, J.M.; Timmons, M.B. Recirculating Aquaculture Systems. In Aquaculture Production Systems; Tidwell, J.H., Ed.; John Willey& Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Avnimelech, Y. Biofloc Technology—A Practical Guidebook, 3rd ed.; The World Aquaculture Society: Baton Rouge, LA, USA, 2014; 285p. [Google Scholar]
- Kingler, D.; Naylor, R. Searching for Solutions in Aquaculture: Charting a Sustainable Course. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 2012, 37, 247–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyson, R.C.; Treadwell, D.D.; Simonne, E.H. Opportunities and Challenges to Sustainability in Aquaponic Systems. HorTechnology 2011, 21, 6–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farghally, H.M.; Atia, D.M.; El-madany, H.T.; Fahmy, F.H. Control methodologies based on geothermal recirculating aquaculture system. Energy 2014, 78, 826–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holan, A.B.; Good, C.; Powell, M.D. Health Management in Recirculating Aquaculture Systems (RAS). In Aquaculture Health Management; Kibenge, F.S.B., Powell, M.D., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2020; pp. 281–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bregnballe, J. A Guide to Recirculation Aquaculture: An Introduction to the New Environmentally Friendly and Highly Productive Closed Fish Farming Systems; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO): Rome, Italy; EUROFISH International Organisation: Rome, Italy, 2015; 100p. [Google Scholar]
- Ramírez-Godínez, J.; Beltrán-Hernández, R.; Coronel-Olivares, C.; Contreras-López, E.; Quezada-Cruz, M.; Vázquez-Rodríguez, G. Recirculating systems for pollution prevention in aquaculture facilities. J. Water Resour. Prot. 2013, 5, 5–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piedrahita, R.H. Reducing the potential environmental impact of tank aquaculture effluents through intensification and recirculation. Aquaculture 2003, 226, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, N.; Turchini, G.M. Recirculating aquaculture systems (RAS): Environmental solution and climate change adaptation. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 297, 126604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ako, H.; Baker, A. Small-Scale Lettuce Production with Hydroponics or Aquaponics. College of Tropical Agriculture and Human Resources, University of Hawaii at Mānoa. 2009. Available online: http://www.ctahr.hawaii.edu/oc/freepubs/pdf/SA-2.pdf (accessed on 24 December 2022).
- Somerville, C.; Cohen, M.; Pantanella, E.; Stankus, A.; Lovatelli, A. Small-scale aquaponic food production. Integrated fish and plant farming. In FAO Fisheries and Aquaculture; Technical Paper. No. 589; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2014; 262p. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.Y.; Chang, C.Y.; Chien, Y.H.; Lai, H.T. The performance of coupling membrane filtration in recirculating aquaponic system for tilapia culture. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2016, 107, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, J. Evolution of Aquaponics. Aquaponics J. 2002, 6, 14–17. [Google Scholar]
- Rakocy, J.E.; Masser, M.P.; Losordo, M. Recirculating Aquaculture Tank Production Systems: Aquaponics—Integrating Fish and Plant Culture; Southern Regional Aquaculture Center (SRAC): Stoneville, MS, USA, 2006; SRAC Publication No. 454; pp. 1–15. Available online: http://www.aces.edu/dept/fisheries/aquaculture/documents/309884-SRAC454.pdf (accessed on 22 December 2022).
- Goddek, S.; Delaide, B.; Mankasingh, U.; Ragnarsdottir, K.V.; Jijakli, H.; Thorarinsdottir, R. Challenges of sustainable and commercial aquaponics. Sustainability 2015, 7, 4199–4224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Essawy, H. Aquaponics as a Sustainable Alternative to New Land Reclamation and Conventional Agriculture in Egypt. Master’s Thesis, The American University, Cairo, Egypt, 2017. AUC Knowledge Fountain. Available online: https://fount.aucegypt.edu/etds/191 (accessed on 22 December 2022).
- El Essawy, H.; Nasr, P.; Sewilam, H. Aquaponics: A sustainable alternative to conventional agriculture in Egypt—A pilot scale investigation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 15872–15883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodman, E.R. Aquaponics: Community and Economic Development. Master’s Thesis, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, MA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, A.; Bandhana, R.S.; Sangotra, R. Comparison of water quality and composition of bioflocs reared in indoor and outdoor conditions. Int. Res. J. Biol. Sci. 2018, 7, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Avnimelech, Y. Biofloc Technology: A Practical Guidebook; World Aquaculture Society: Sorrento, FL, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Crab, R.; Defoirdt, T.; Bossier, P.; Verstraete, W. Biofloc technology in aquaculture: Beneficial effects and future challenges. Aquaculture 2012, 356–357, 351–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anjalee, D.C.A.; Kurup, B.M. Biofloc Technology: An Overview and its application in animal food industry. Int. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2015, 5, 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Hargreaves, J.A. Photosynthetic suspended-growth systems in aquaculture. Aquac. Eng. 2006, 34, 344–363–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De-Schryver, P.; Crab, R.; Defoirdt, T.; Boon, N.; Verstraete, W. The basics of bioflocs technology: The added value for aquaculture. Aquaculture 2008, 277, 125–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanjani, M.H.; Sharifinia, M. Biofloc technology as a promising tool to improve aquaculture production. Rev. Aquac. 2020, 12, 1836–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bossier, P.; Ekasari, J. Biofloc technology application in aquaculture to support sustainable development goals. Microb. Biotechnol. 2017, 10, 1012–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suneetha, K.; Kavitha, K.; Darwin, C.H. Biofloc Technology: An emerging tool for sustainable aquaculture. Int. J. Zool. Stud. 2018, 3, 87–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crab, R.; Avnimelech, Y.; Defoirdt, T.; Bossier, P.; Verstraete, W. Nitrogen removal techniques in aquaculture for a sustainable production. Aquaculture 2007, 270, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azim, M.E.; Little, D.C. The biofloc technology (BFT) in indoor tanks: Water quality, biofloc composition, and growth and welfare of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Aquaculture 2008, 283, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhn, D.D.; Boardman, G.D.; Lawrence, A.L.; Marsh, L.; Flick, J. Microbial floc meal as a replacement ingredient for fishmeal and soybean protein in shrimp feed. Aquaculture 2009, 296, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avnimelech, Y. Feeding with microbial flocs by tilapia in minimal discharge bioflocs technology ponds. Aquaculture 2007, 264, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Li, H.; Wei, H.; Zhu, X.; Han, D.; Jin, J.; Yang, Y.; Xie, S. Biofloc formation improves water quality and fish yield in a freshwater pond aquaculture system. Aquaculture 2019, 506, 256–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neori, A.; Chopin, T.; Troell, M.; Buschmann, A.H.; Kraemer, G.P.; Halling, C.; Shpigel, M.; Yarish, C. Integrated aquaculture: Rationale, evolution and state of the art emphasizing seaweed biofiltration in modern mariculture. Aquaculture 2004, 231, 361–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buschmann, A.H.; Varela, D.A.; Hernández-González, M.C.; Huovinen, P. Opportunities and challenges for the development of an integrated seaweed-based aquaculture activity in Chile: Determining the physiological capabilities of Macrocystis and Gracilaria as biofilters. J Appl. Phycol. 2008, 20, 571–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olesen, I.; Myhr, A.I.; Rosendal, G.K. Sustainable aquaculture: Are we getting there? Ethical perspectives on salmon farming. J. Agric. Environ. Ethics 2011, 24, 381–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasdravanidis, C.; Alvanou, M.V.; Lattos, A.; Papadopoulos, D.K.; Chatzigeorgiou, I.; Ravani, M.; Liantas, G.; Georgoulis, I.; Feidantsis, K.; Ntinas, G.K.; et al. Aquaponics as a promising strategy to mitigate impacts of climate change on Rainbow trout culture. Animals 2022, 12, 2523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Silva, S.S.; Soto, D. Climate Change and Aquaculture: Potential Impacts, Adaptation and Mitigation, Climate Change Implications for Fisheries and Aquaculture: Overview of Current Scientific Knowledge; FAO Fisheries and Aquaculture Technical Paper 2009, 530; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2009; pp. 151–212. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Kitazawa, D.; Yang, C. A numerical modeling approach to support decision-making on design of integrated multitrophic aquaculture for efficiently mitigating aquatic waste. Mitig. Adapt. Strateg. Glob. Chang. 2016, 21, 1247–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padilla-Rivera, A.; Russo-Garrido, S.; Merveille, N. Addressing the social aspects of a circular economy: A systematic literature review. Sustainability 2020, 12, 7912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, N.; Bunting, S.W.; Glaser, M.; Flaherty, M.S.; Diana, J.S. Can greening of aquaculture sequester blue carbon? Ambio 2017, 46, 468–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goda, A.M.A.-S.; Essa, M.A.; Hassaan, M.S.; Sharawy, Z. Bio economic features for aquaponic systems in Egypt. Turk. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2015, 15, 525–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goda, A.M.A.-S.; Essa, M.A.; Hassaan, M.S.; Sharawy, Z. Bio–Economic Study of Freshwater Integrated Multi-Trophic Aquaculture (IMTA) Systems in Egypt. World Appl. Sci. J. 2014, 32, 1367. [Google Scholar]
- OECD/Thierry Chopin. Integrated Multi-Trophic Aquaculture. In Advancing the Aquaculture Agenda: Workshop Proceedings; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.J.; Kieu, E. Tackling Regional Climate Change Impacts and Food Security Issues: A Critical Analysis across ASEAN, PIF, and SAARC. Sustainability 2020, 12, 883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elshamy, M.E.; Seierstad, I.A.; Sorteberg, A. Impacts of climate change on Blue Nile flows using bias-corrected GCM scenarios. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2009, 13, 551–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassaan, M.A.; Abdrabo, M.A. Vulnerability of the Nile Delta coastal areas to inundation by sea level rise. Environ. Monit. Assess 2013, 185, 6607–6616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mehrim, A.I.; Refaey, M.M. An Overview of the Implication of Climate Change on Fish Farming in Egypt. Sustainability 2023, 15, 1679. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15021679
Mehrim AI, Refaey MM. An Overview of the Implication of Climate Change on Fish Farming in Egypt. Sustainability. 2023; 15(2):1679. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15021679
Chicago/Turabian StyleMehrim, Ahmed I., and Mohamed M. Refaey. 2023. "An Overview of the Implication of Climate Change on Fish Farming in Egypt" Sustainability 15, no. 2: 1679. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15021679
APA StyleMehrim, A. I., & Refaey, M. M. (2023). An Overview of the Implication of Climate Change on Fish Farming in Egypt. Sustainability, 15(2), 1679. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15021679