Effective Load Frequency Control of Power System with Two-Degree Freedom Tilt-Integral-Derivative Based on Whale Optimization Algorithm
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- Frequency stability analysis is performed for interconnected power systems on sudden application of disturbance.
- The 2DOFTID controller is designed to achieve better stability over PID and TIDF controllers for the same system with the same disturbances. Effectiveness of the proposed 2DOFTIDF controller is verified by adding nonlinearity to the system.
- WOA is employed to find the optimum parameters.
- The WOA algorithm’s effectiveness is determined by contrasting the system outcomes with other optimization techniques.
- The proposed 2DOFTIDF controller offers better performance compared to other classical controllers in multi-area multi-source power systems.
- A practical power system model is established considering the coupling effect of excitation control and LFC loop.
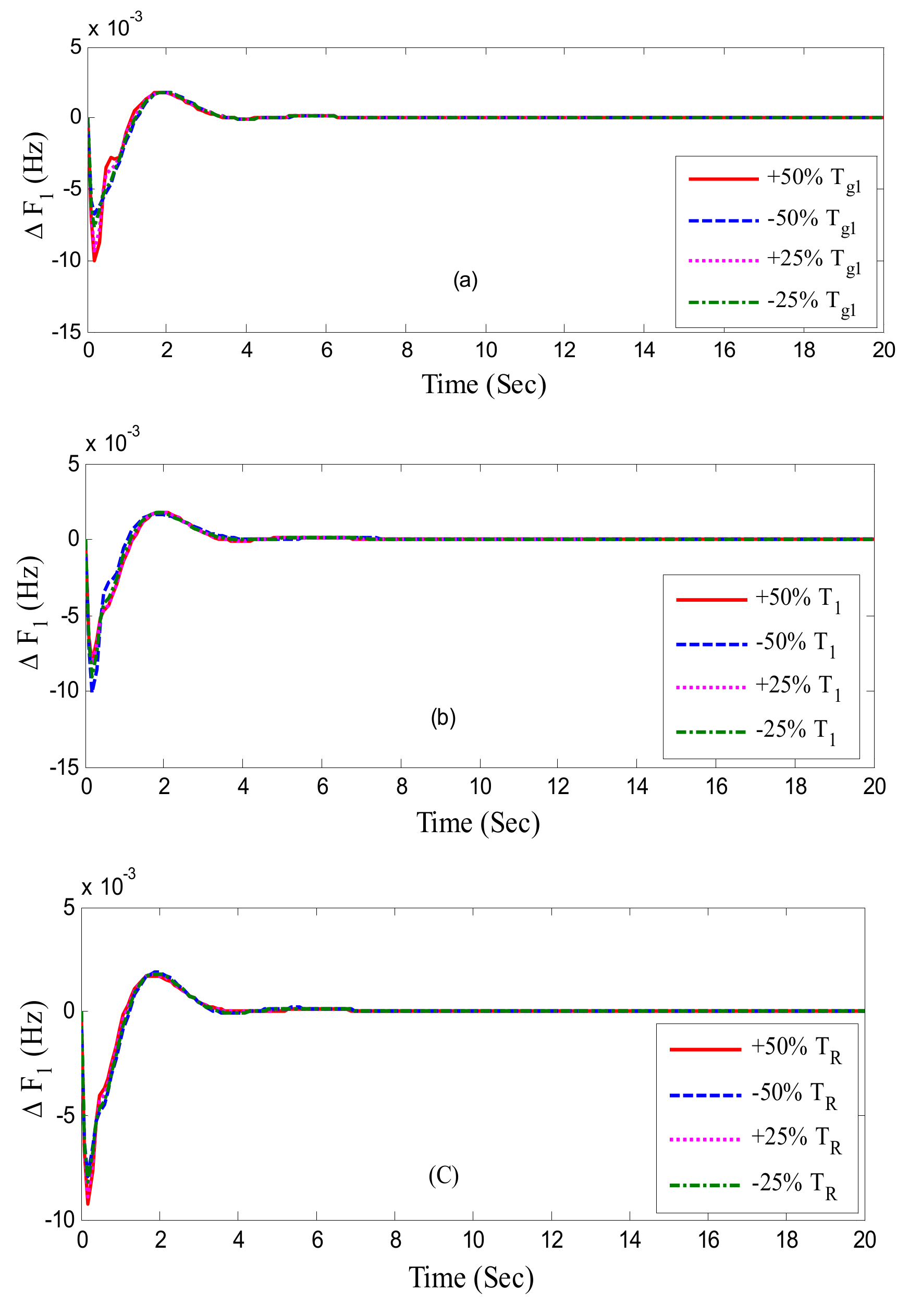
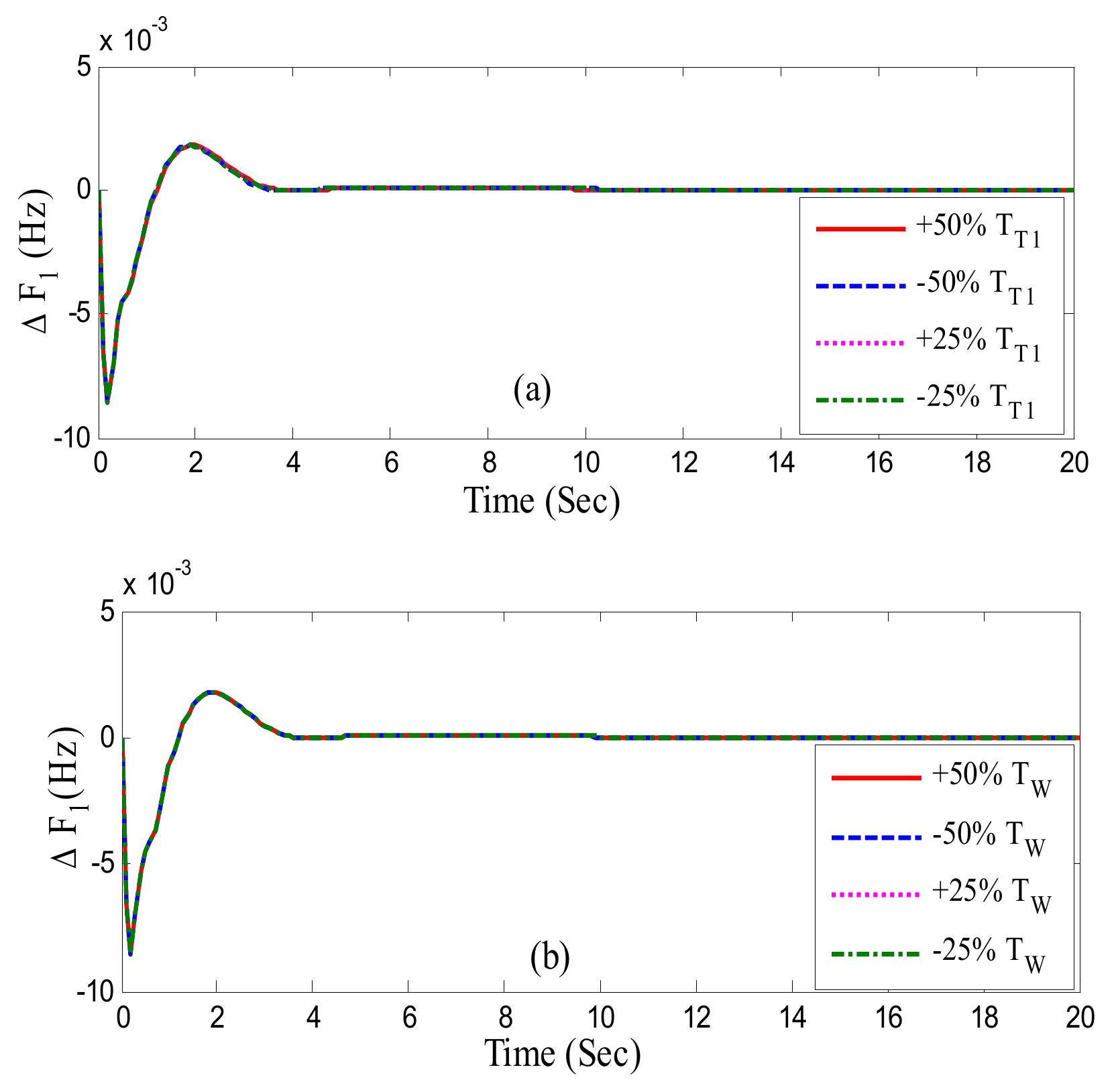
- The impact of parameter variation on the controller’s resilience is presented.
- MATLAB/Simulink results are contrasted with hardware-in-the-loop (HiL) real-time simulation data for experimental validation of the proposed method.
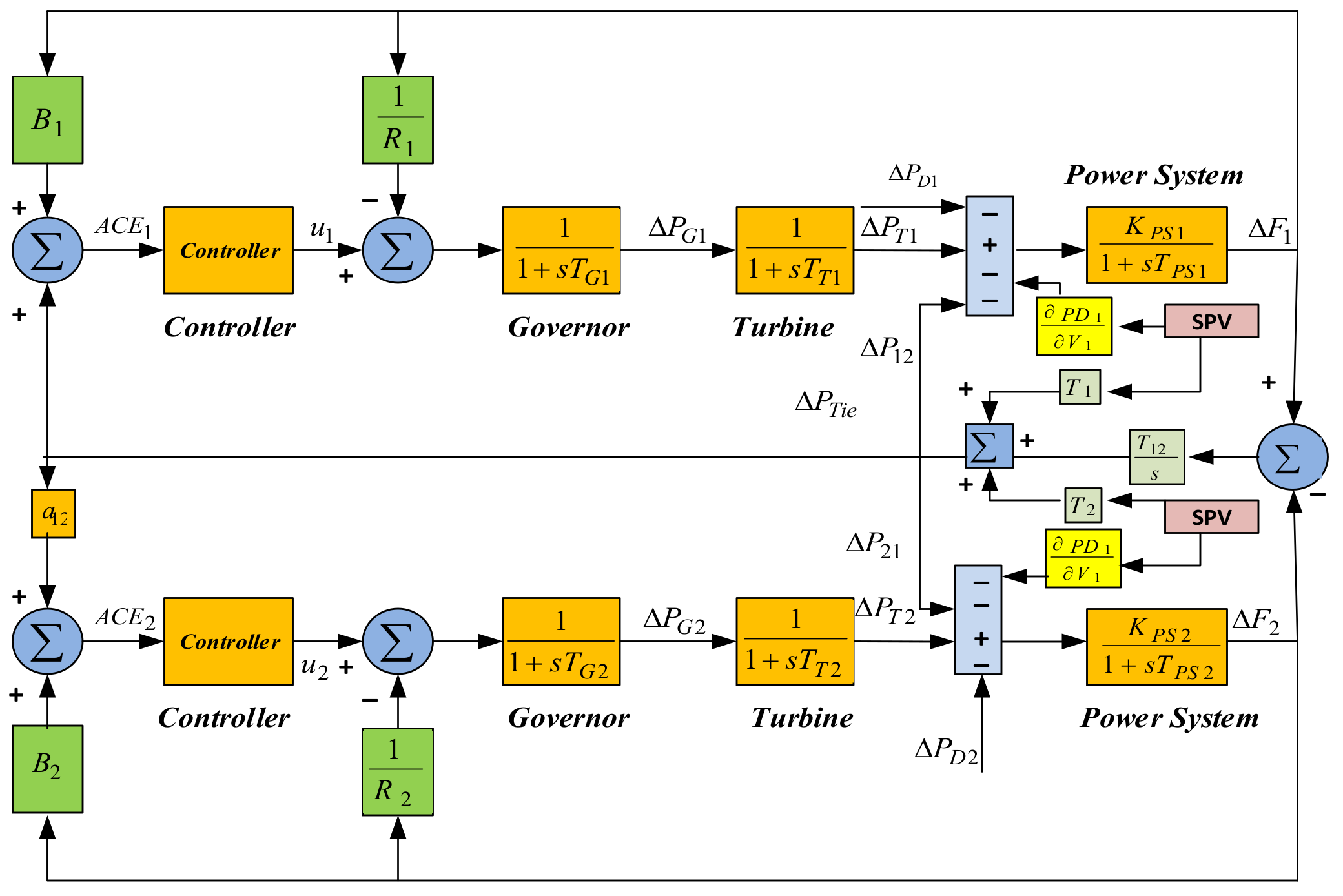
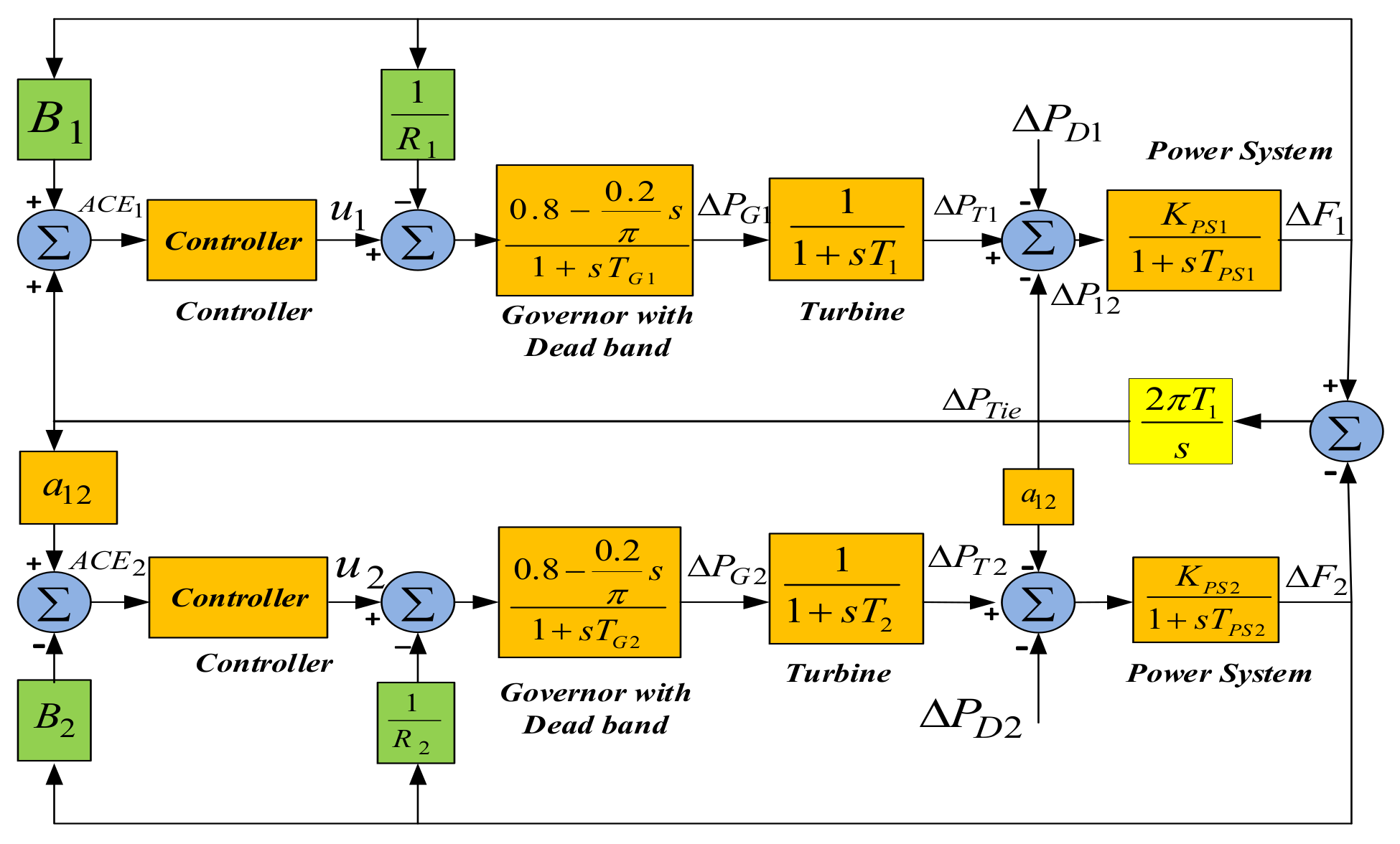
2. System Modeling
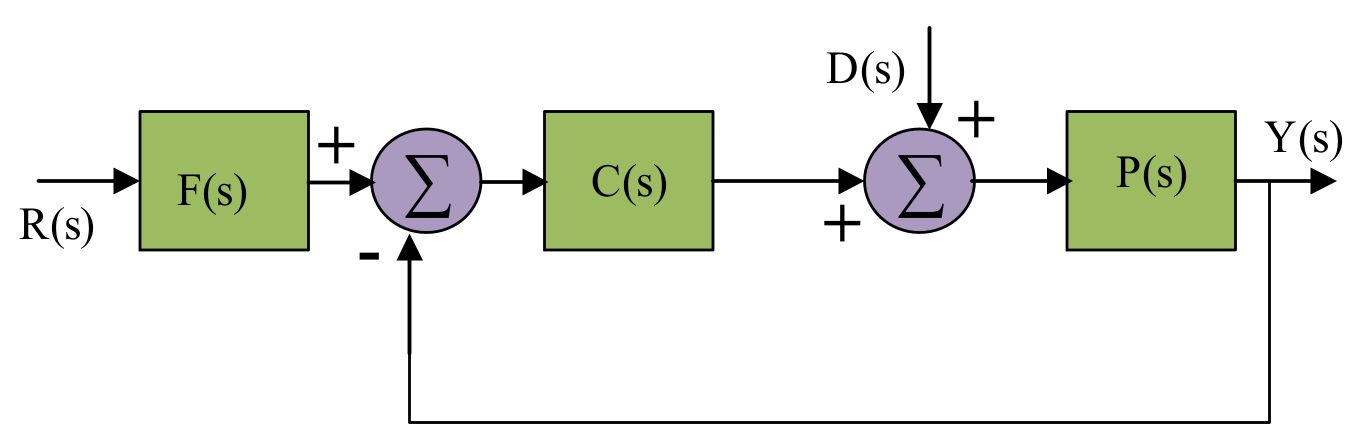
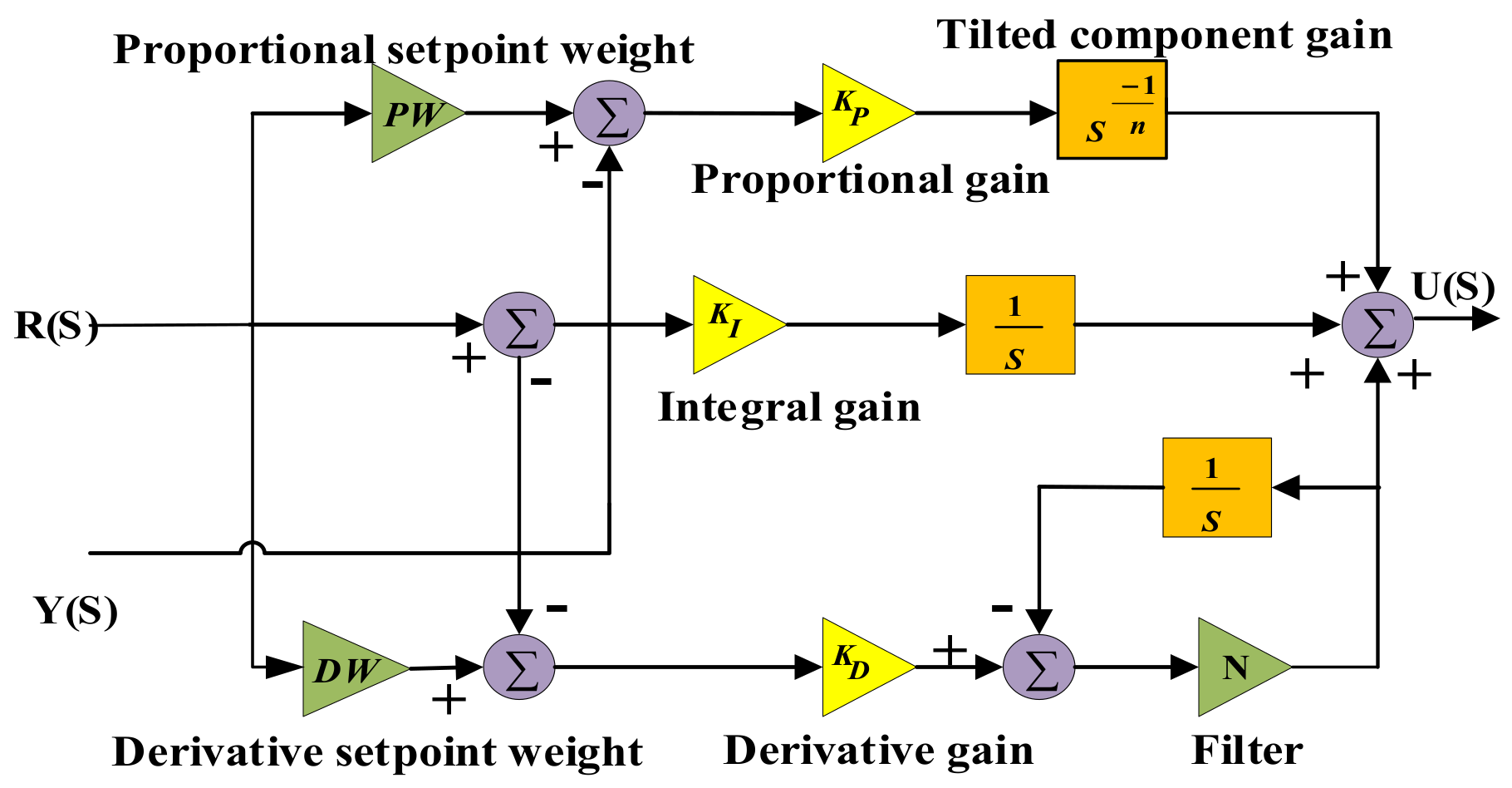
3. Control Structure
Problem Formulation
4. Whale Optimization Algorithm (WOA)
4.1. Encircling Prey
4.2. Bubble-Net Attacking Method
4.2.1. Shrinking Encircling Mechanism
4.2.2. Spiral Position Update
4.3. Search for Prey
5. Problem-Solving Scenario
5.1. Case Study Results
5.1.1. Case-1
5.1.2. Case-2 Effect of Nonlinearity
5.1.3. Case-3
5.1.4. Case-4
5.1.5. Case-5 Experimental Validation by Using OPAL RT
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
Appendix A.1
Appendix A.2
| Algorithm | Parameter | Value |
|---|---|---|
| WOA | No. of search agents | 50 |
| Number of iteration | 100 | |
| Convergence factor | [0, 2] | |
| BAT [43] | No. of search agents | 50 |
| Number of iteration | 100 | |
| Loudness | 0.5 | |
| Pulse rate | 0.5 | |
| Frequency minimum | 0 | |
| Frequency maximum | 1 | |
| GWO [44] | No. of search agents | 50 |
| Number of iteration | 100 | |
| Random Values | [0, 1] | |
| Decreasing coefficient | [0, 2] |
References
- Kundur, P. Power System Stability and Control.; Tata McGraw-Hill: New Delhi, India, 2009; 8th reprint. [Google Scholar]
- Abdelaziz, A.Y.; Ali, E.S. Static VAR Compensator Damping Controller Design Based on Flower Pollination Algorithm for a Multi-machine Power System. Electr. Power Compon. Syst. 2015, 43, 1268–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansouri, S.A.; Nematbakhsh, E.; Ahmarinejad, A.; Jordehi, A.R.; Javadi, M.S.; Marzband, M. A hierarchical scheduling framework for resilience enhancement of decentralized renewable-based microgrids considering proactive actions and mobile units. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2022, 168, 112854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansouri, S.A.; Nematbakhsh, E.; Jordehi, A.R.; Tostado-Véliz, M.; Jurado, F.; Leonowicz, Z. A risk-based bi-level bidding system to manage day-ahead electricity market and scheduling of interconnected microgrids in the presence of smart homes. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE International Conference on Environment and Electrical Engineering and 2022 IEEE Industrial and Commercial Power Systems Europe (EEEIC/I&CPS Europe), Prague, Czech Republic, 28 June 2022; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Elgerd, O.I. Electric Energy Systems Theory. An Introduction; TMH: New Delhi, India, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Bevrani, H. Robust Power System Frequency Control; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Saikia, L.C.; Nanda, J.; Mishra, S. Performance comparison of several classical controllers in AGC for multi-area interconnected thermal system. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2011, 33, 394–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabani, H.; Vahidi, B.; Ebrahimpour, M. A robust PID controller based on imperialist competitive algorithm for load-frequency control of power systems. ISA Trans. 2012, 52, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panda, S.; Mohanty, B.; Hota, P.K. Hybrid BFOA–PSO algorithm for automatic generation control of linear and nonlinear interconnected power. Appl. Soft Comput. 2013, 13, 4718–4730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madasu, S.D.; Kumar, M.S.; Singh, A.K. A flower pollination algorithm based automatic generation control of interconnected power system. Ain Shams Eng J. 2016, 9, 1215–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abdelaziz, A.Y.; Ali, E.S. Load Frequency Controller Design via Artificial Cuckoo Search. Electric Power Components and Systems. Electr. Power Compon. Syst. 2015, 44, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abo-Elyousr, F.K.; Abdelaziz, A.Y. A Novel Modified Robust Load Frequency Control for Mass-less Inertia Photovoltaics Penetrations via Hybrid PSO-WOA Approach. Electr. Power Compon. Syst. J. 2019, 47, 1744–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saikia, L.C.; Sinha, N.; Nanda, J. Maiden application of bacterial foraging based fuzzy IDD controller in AGC of a multi-area hydrothermal system. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2013, 45, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khuntia, S.R.; Panda, S. Simulation study for automatic generation control of a multi-area power system by ANFIS approach. Appl. Soft Comput. 2012, 12, 333–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, B. TLBO optimized sliding mode controller for multi-area multi-source nonlinear interconnected AGC system. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2015, 73, 872–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yesil, E. Interval type-2 fuzzy PID load frequency controller using big-bang big-crunch optimization. Appl. Soft Comput. 2014, 15, 100–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiroi, K.; Togari, Y. Two Degrees of Freedom PID Algorithm with Compound Filter. Trans. Soc. Instrum. Control. Eng. 1991, 27, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sahu, R.K.; Panda, S.; Rout, U.K. DE optimized parallel 2-DOF PID controller for load frequency control of power system with governor dead-band nonlinearity. Int. J. Electr Power Energy Syst. 2013, 49, 19–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsaied, M.M.; Hameed, W.H.A.; Hasanien, H.M. Frequency stabilization of a hybrid three-area power system equipped with energy storage units and renewable energy sources. IET Renew. Power Gener. 2022, 16, 3267–3286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daraz, A.; Malik, S.A.; Waseem, A.; Azar, A.T.; Haq, I.U.; Ullah, Z.; Aslam, S. Automatic Generation Control of Multi-Source Interconnected Power System Using FOI-TD Controller. Energies 2021, 14, 5867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debbarma, S.; Saikia, L.C.; Sinha, N. Automatic generation control using two degrees of freedom fractional order PID controller. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2014, 58, 120–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lurie, B.J. Three-Parameter Tunable Tilt-Integral Derivative (TID) Controller. US Patent US5371670, 6 December 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Sahu, R.K.; Panda, S.; Biswal, A.; Sekhar, G.C. Design and analysis of tilt integral derivative controller with filter for load frequency control of multi-area interconnected power systems. ISA Trans. 2016, 61, 251–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sain, D.; Swain, S.K.; Mishra, S.K. TID and I-TD controller design for magnetic levitation system using genetic algorithm. Perspect. Sci. 2016, 8, 370–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Asadollahi, M.; Rikhtegar ghiasi, A.; Dehghani, H. Excitation control of a synchronous generator using a novel fractional-order controller. IET Gen. Tran. Dist. 2015, 9, 2255–2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd-Elazim, S.M.; Ali, E.S. Load frequency controller design via BAT algorithm for nonlinear interconnected power system. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2016, 77, 166–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guha, D.; Roy, P.K.; Banerjee, S. Load frequency control of large scale power system using quasi-oppositional grey wolf optimization algorithm. Eng. Sci. Technol. Int. J. 2016, 19, 1693–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dash, P.; Saikia, L.C.; Sinha, N. Comparison of performance of several cuckoo search algorithm based 2DOF controllers in AGC of multi-area thermal system. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2014, 55, 429–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, R.K.; Panda, S.; Padhan, S. A hybrid firefly algorithm and pattern search technique for automatic generation control of multi area power systems. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2015, 64, 9–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, B. Performance analysis of moth flame optimization algorithm for AGC analysis. Int. J. Model. Simul. 2018, 39, 73–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirjalili, S.; Lewis, A. Whale Optimization Algorithm. Adv. Eng. Softw. 2016, 95, 51–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasanien, H.M. Whale optimization algorithm for automatic generation control of interconnected modern power system including renewable energy sources. IET Gen. Tran. Dist. 2018, 12, 607–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, C.S.; Rao, R.S.; Cherukuri, S.K.; Rayapudi, S.R. A Novel Global MPP Tracking of Photovoltaic System based on Whale Optimization Algorithm. Int. J. Renew. Energy Dev. 2016, 5, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tepljakov, A.; Petlenkov, E.; Belikov, J. FOMCON: A MATLAB Toolbox for Fractional-order System Identification and Control. Int. J. Microelectron. Comput. Sci. 2011, 2, 51–62. [Google Scholar]
- Sahu, R.K.; Panda, S.; Rout, U.K.; Sahoo, D.K. Teaching learning based optimization algorithm for automatic generation control of power system using 2-DOF PID controller. Int J Elect Power Energy Syst. 2016, 77, 287–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guha, D.; Roy, P.K.; Banerjee, S. Study of differential search algorithm based automatic generation control of an interconnected thermal-thermal system with governor dead band. Appl. Soft Comput. 2017, 52, 160–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, R.K.; Panda, S.; Padhan, S. A novel hybrid gravitational search and pattern search algorithm for load frequency control of nonlinear power system. Appl. Soft Comput. 2015, 29, 310–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, B.; Panda, S.; Hota, P.K. Differential evolution algorithm based Automatic generation control for interconnected power systems with nonlinearity. Alex. Eng. J. 2014, 53, 537–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gozde, H.; Taplamacioglu, M.C. Automatic generation control application with craziness based particle swarm optimization in a thermal power system. Int. J. Elect. Power Energy Syst. 2011, 33, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simhadri, K.S.; Mohanty, B. Performance analysis of dual-mode PI controller using quasi-oppositional whale optimization algorithm for load frequency control. Int. Trans. Elect Energy Syst. 2019, 30, e12159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simhadri, K.; Mohanty, B.; Rao, U.M. Optimized 2DOF PID for AGC of multi-area power system using dragonfly algorithm. In Applications of Artificial Intelligence Techniques in Engineering. Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing; Malik, H., Srivastava, S., Sood, Y., Ahmad, A., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2019; Volume 698, pp. 11–22. [Google Scholar]
- Chintu, J.M.R.; Sahu, R.K.; Panda, S. Design and analysis of two degree of freedom tilt integral derivative controller with filter for frequency control and real time validation. J. Electr. Eng. 2020, 71, 388–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Gao, Z.M. The bat algorithm and its parameters. In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Electronic, Communications and Networks (CECNet2014), Beijing, China, 12–15 December 2014; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2014; pp. 1323–1326. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, C.-H.; Khurshaid, T.; Wadood, A.; Farkoush, S.G.; Rhee, S.-B. Gray wolf optimizer for the optimal coordination of directional overcurrent relay. J. Electr. Eng. Technol. 2018, 13, 1043–1051. [Google Scholar]
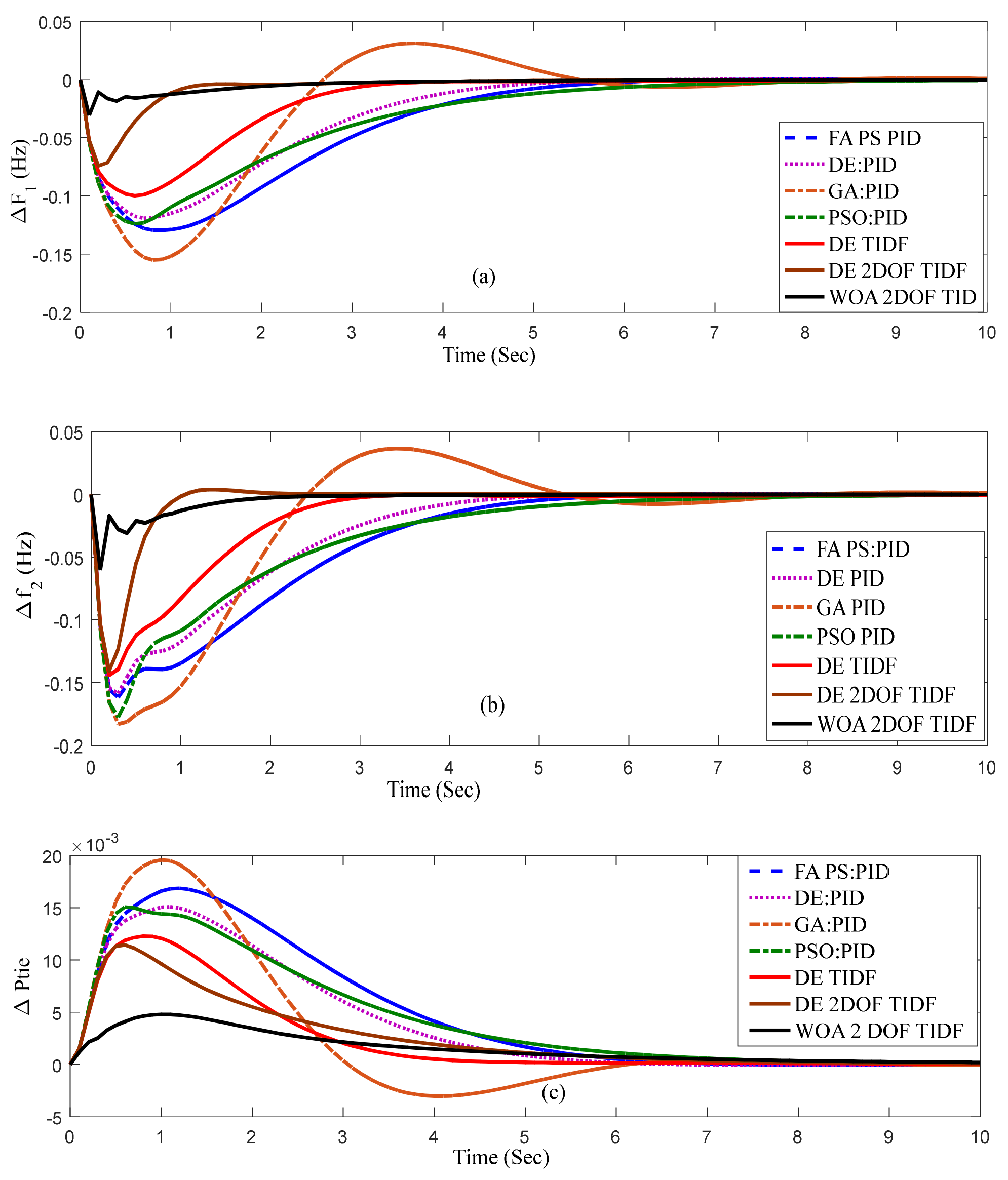
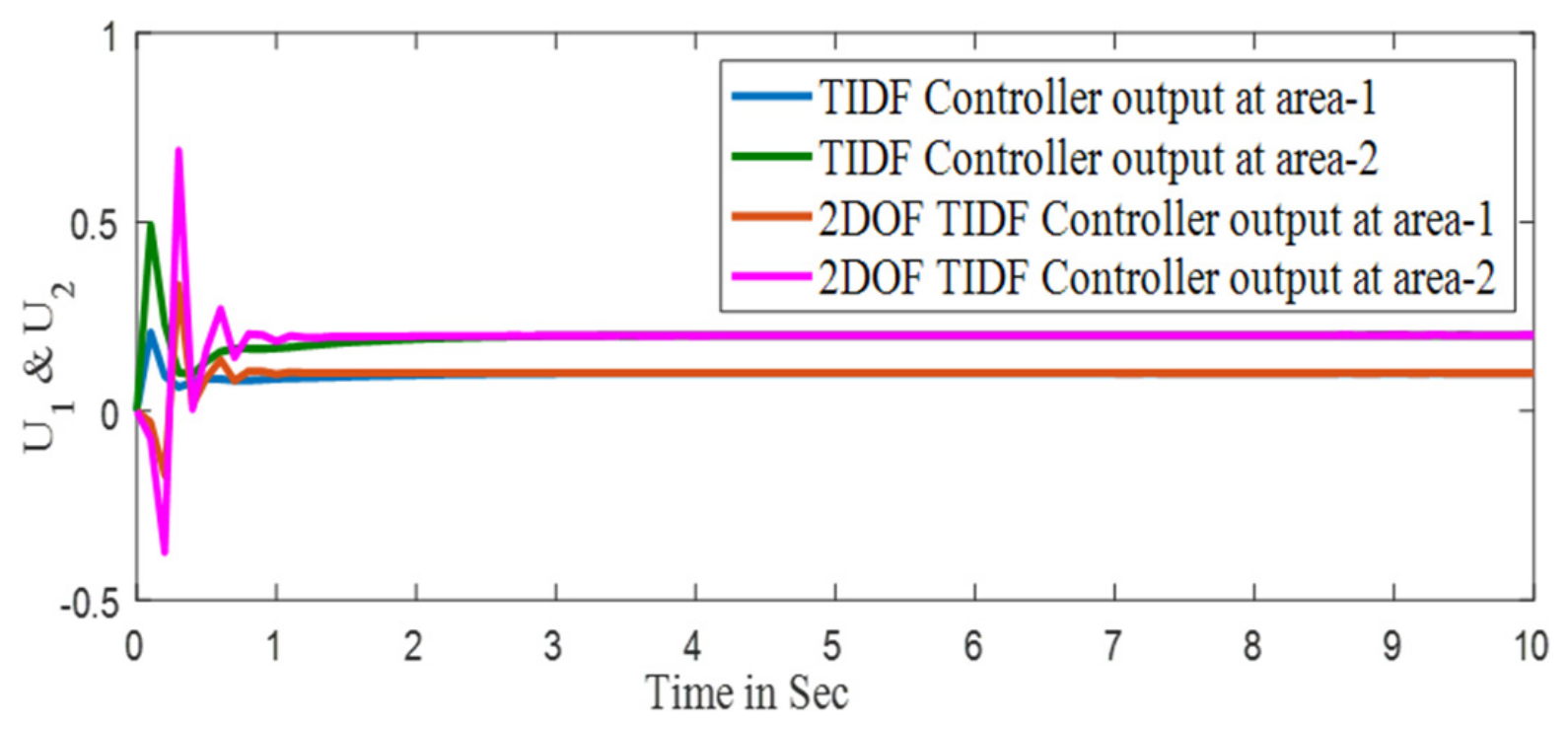
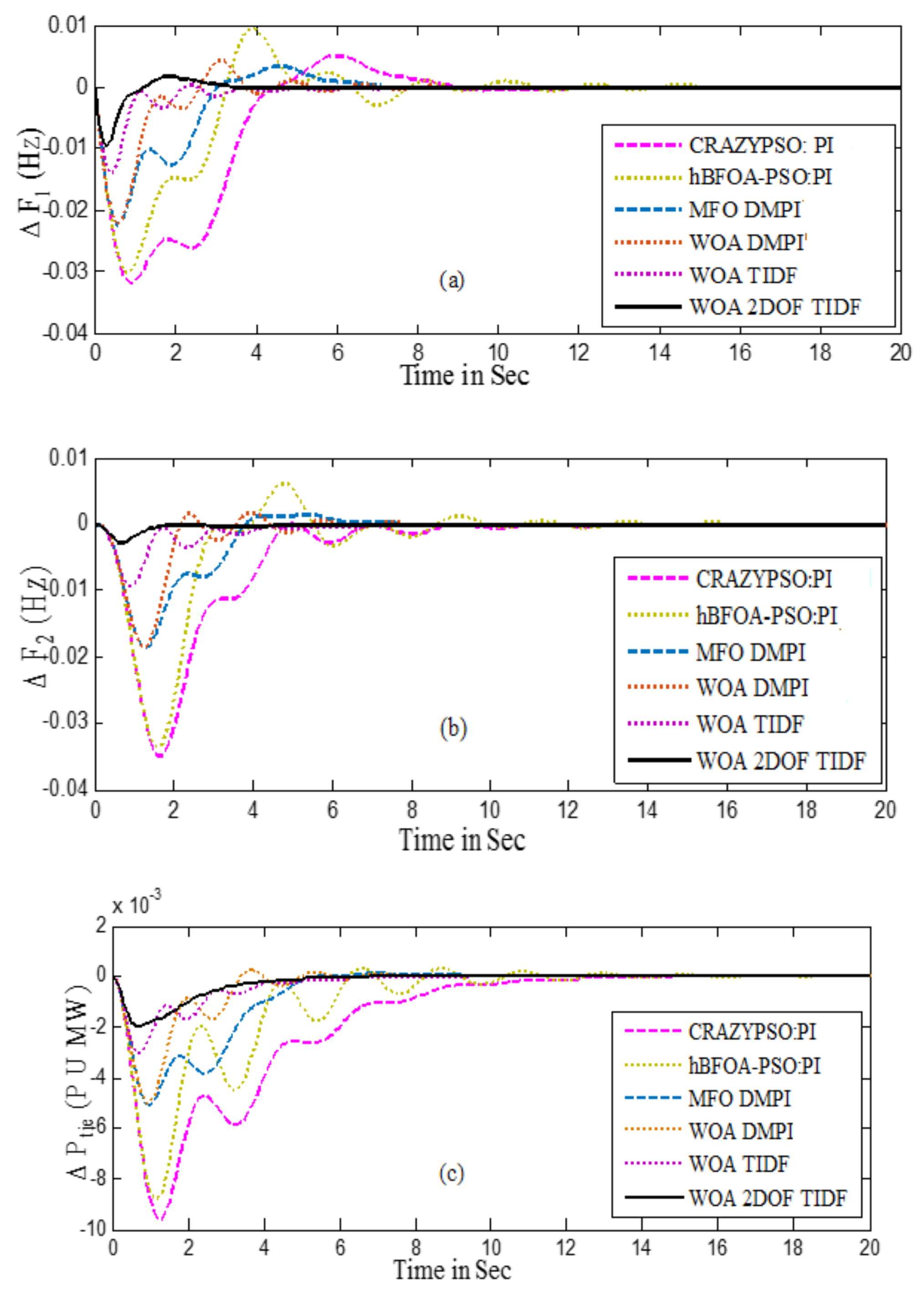
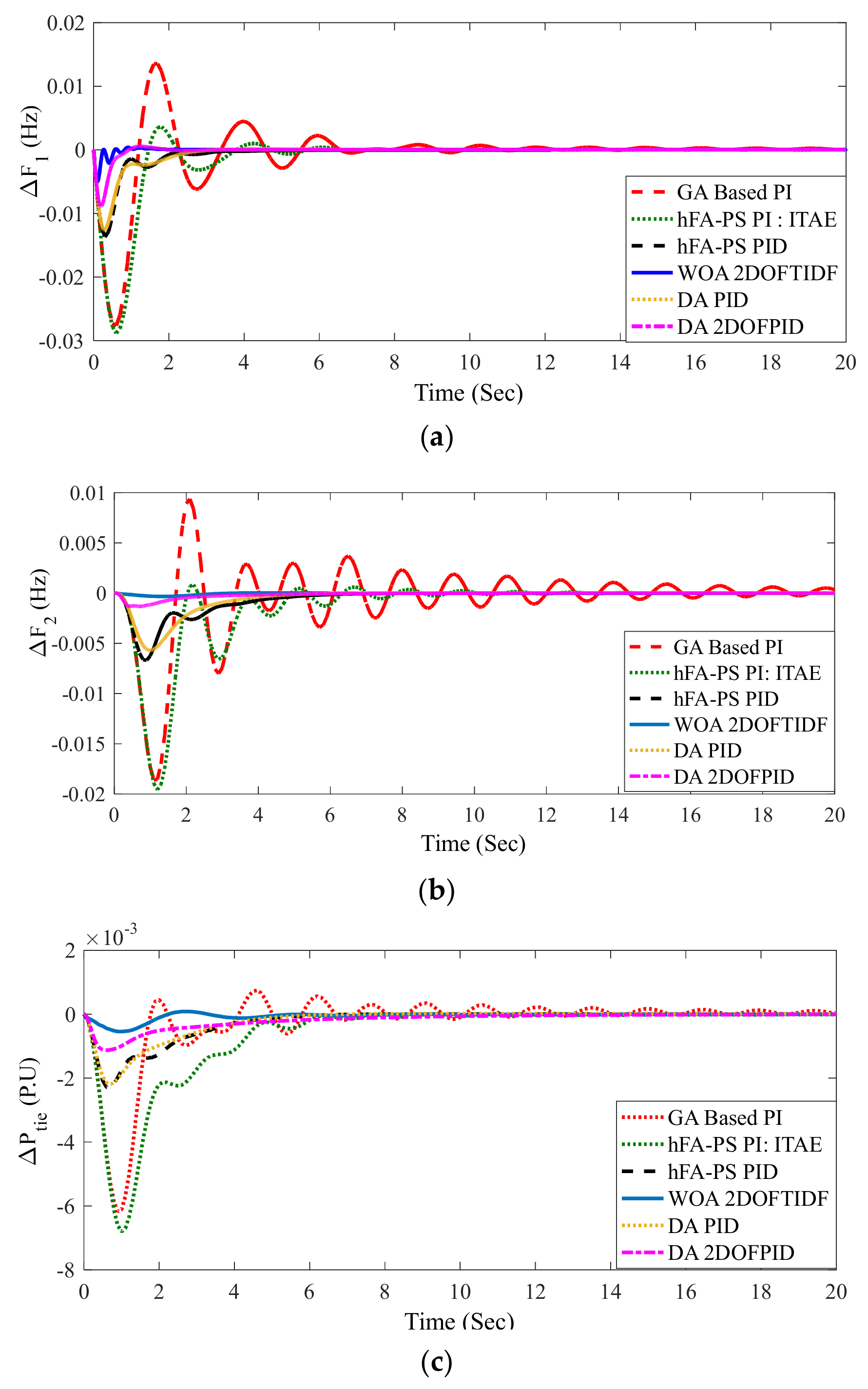
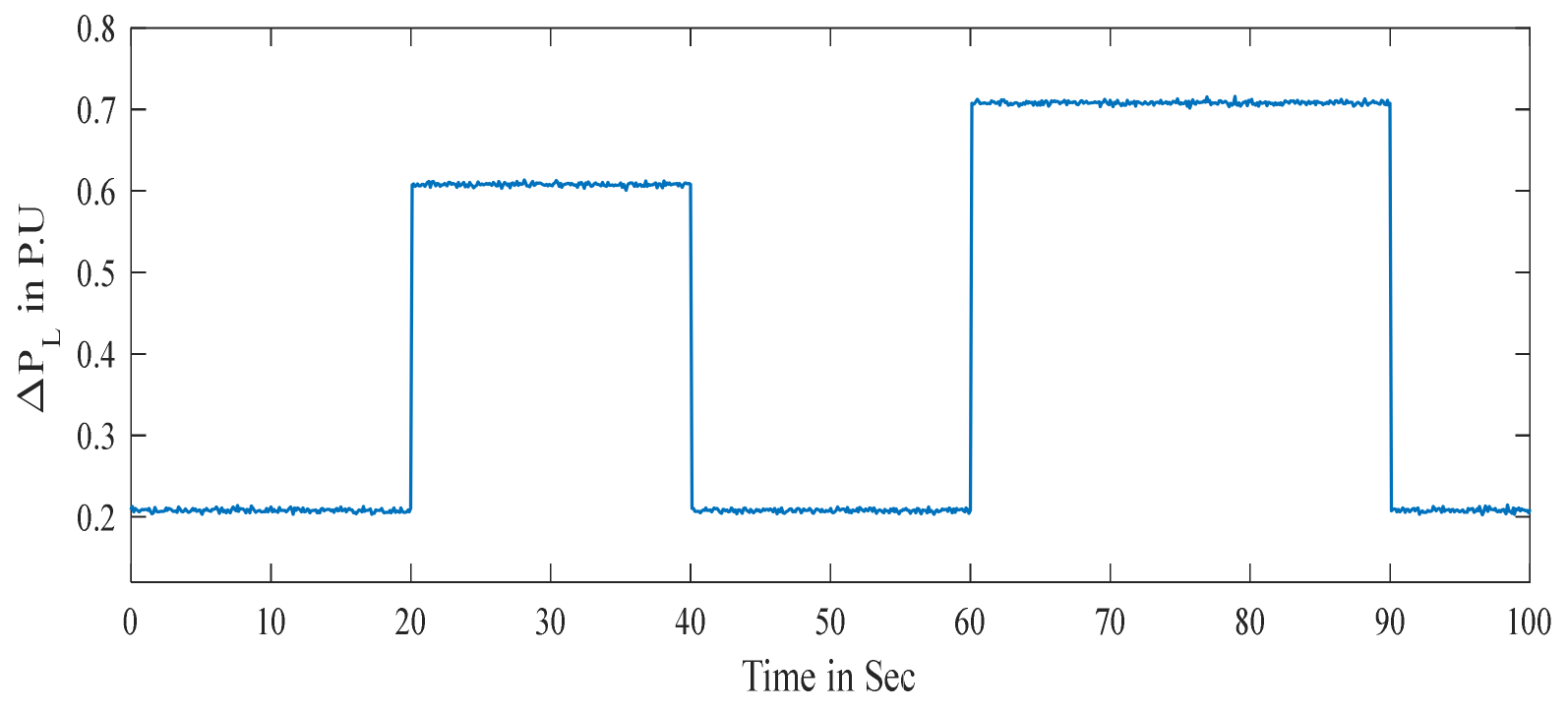
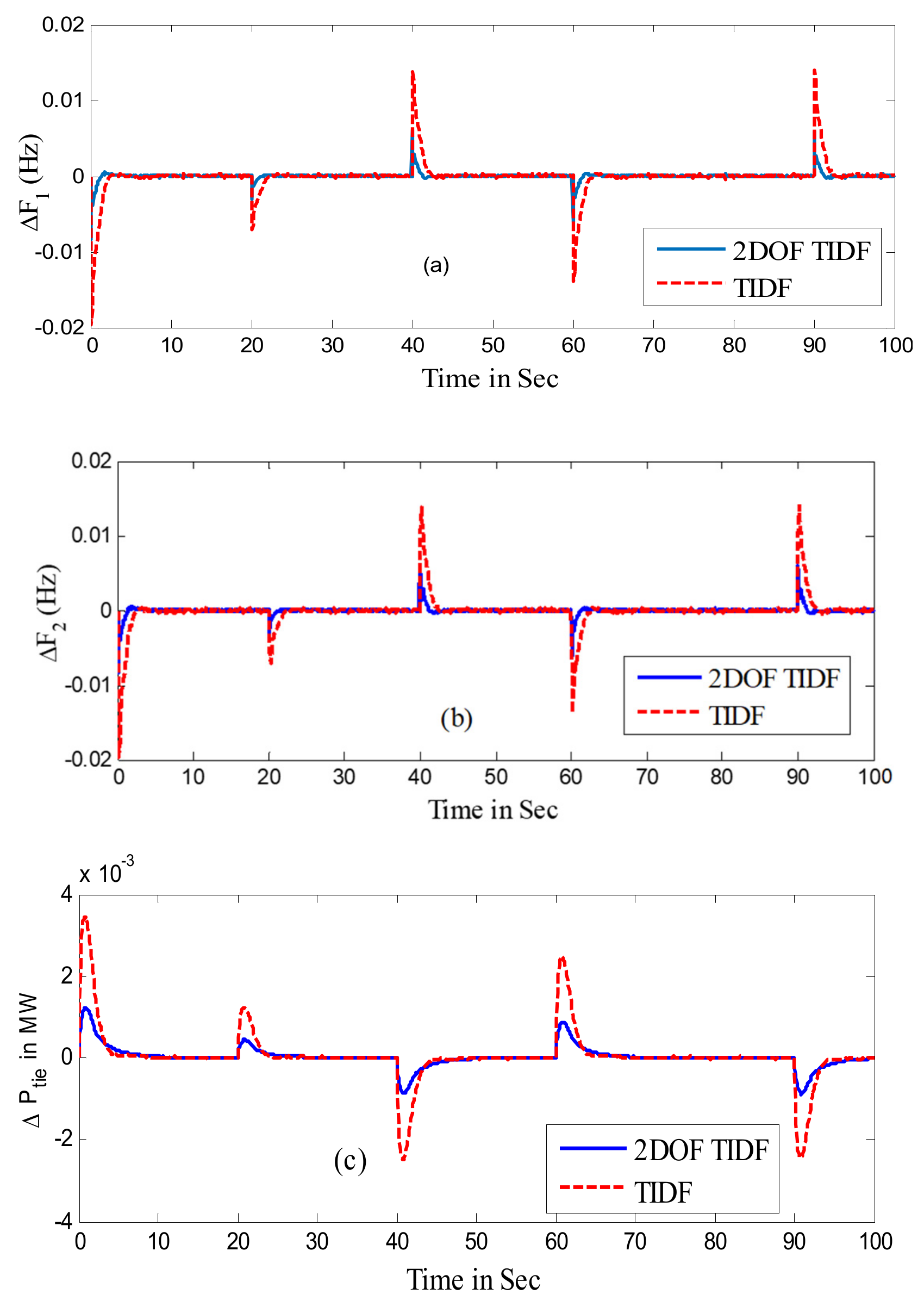
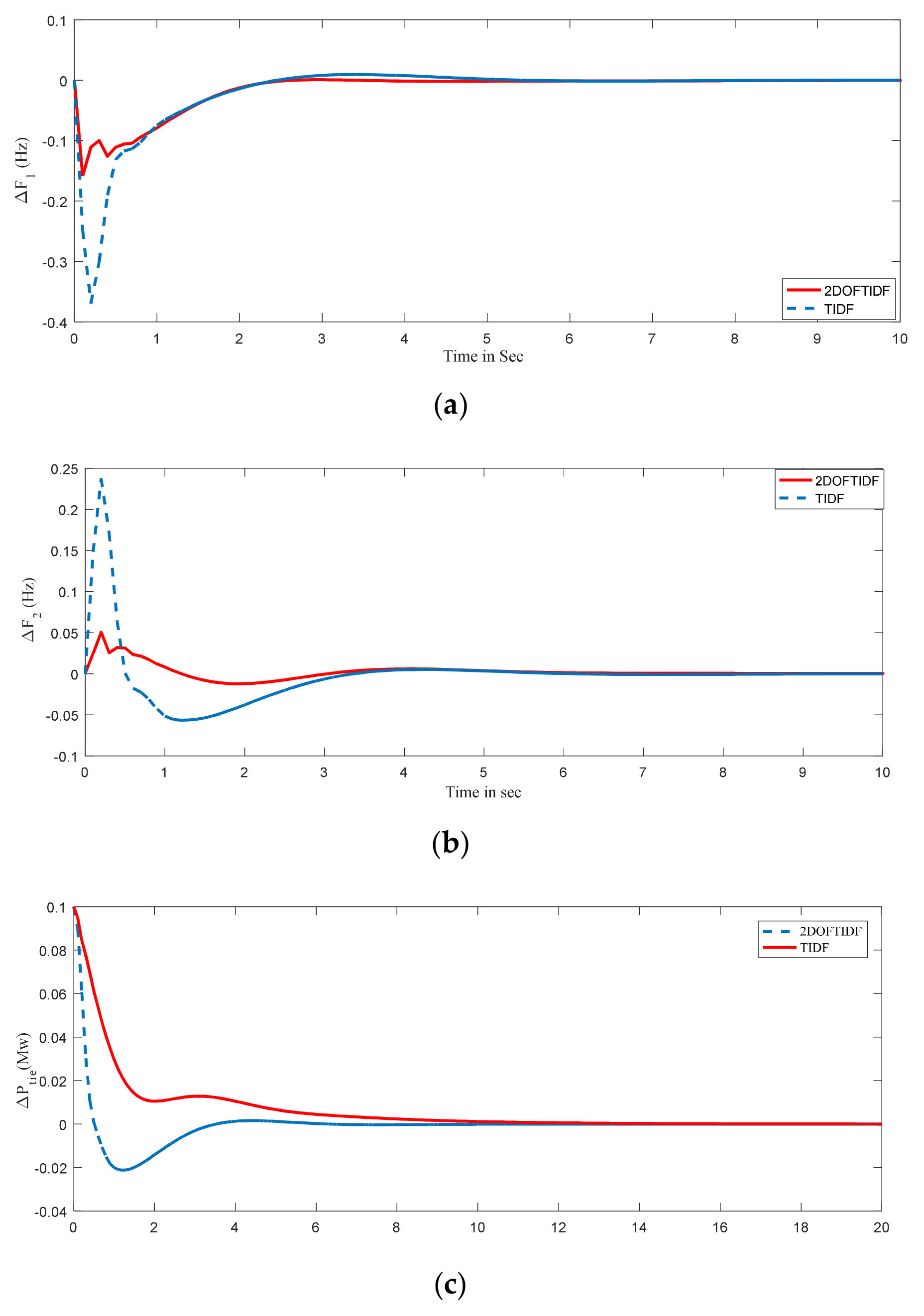
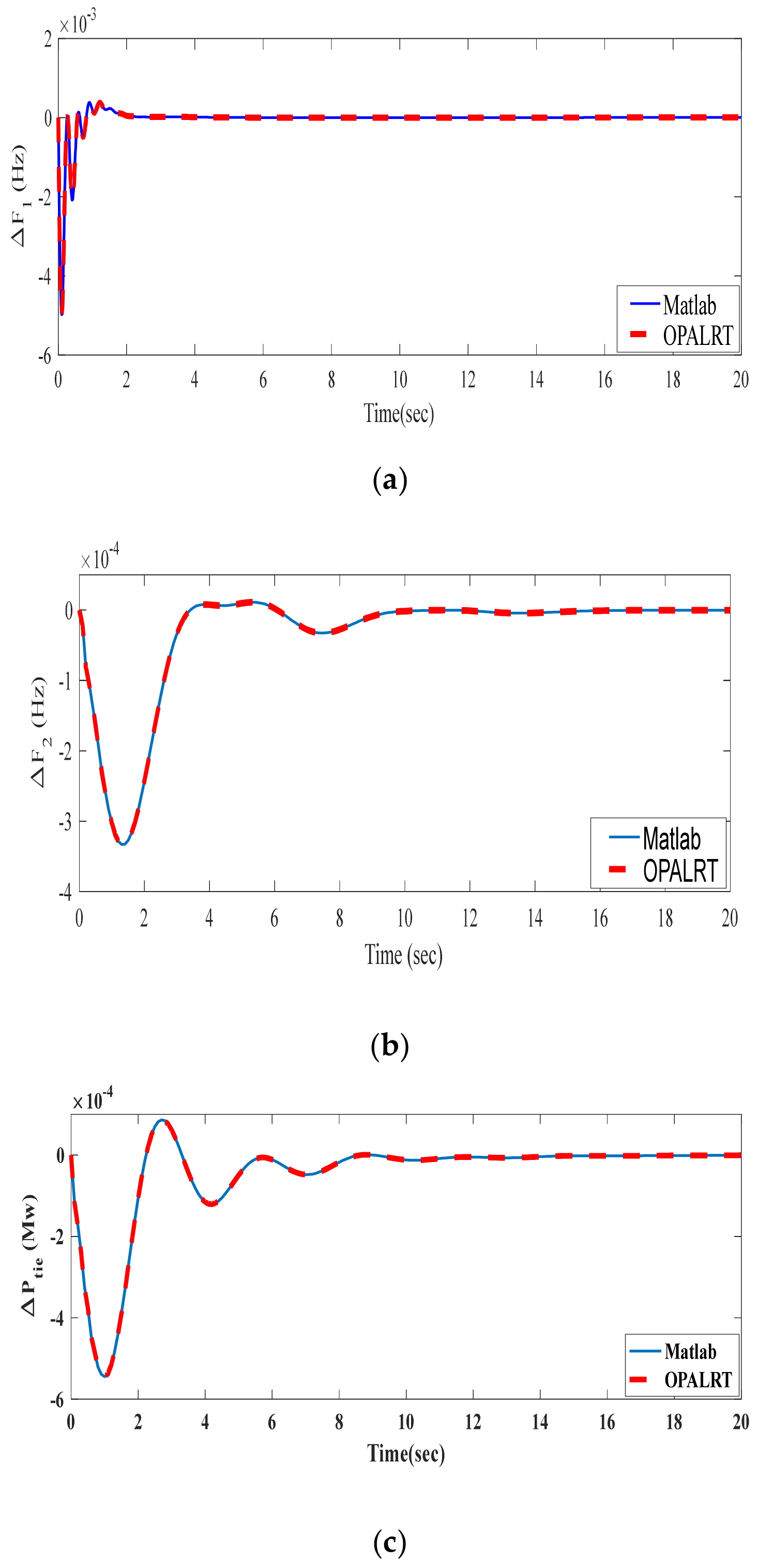
| Optimized Controller | Settling Time (Ts) in Sec | Peak Under Shoot × 10−2 | Performance Index | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ΔF1 | ΔF2 | ΔPtie | ΔF1 | ΔF2 | ΔPtie | ||
| GA-tuned PID [23] | 6.93 | 6.74 | 4.87 | −8.74 | −5.22 | −2.01 | 0.4967 |
| PSO-tuned PID [23] | 5.30 | 6.41 | 5.03 | −8.58 | −4.36 | −1.57 | 0.4854 |
| FA-tuned PID [23] | 4.25 | 5.49 | 4.78 | −7.88 | −4.28 | −1.71 | 0.4714 |
| TLBO-tuned PID [35] | 8.53 | 8.52 | 5.95 | −11.1 | 14.6 | 0.099 | 0.665 |
| DSA PIDF [36] | 7.62 | 6.3 | 6.94 | −13.3 | 15.4 | 0 | 1.09 |
| hGSA-PS PIDF [37] | 3.72 | 4.59 | 3.61 | 13.5 | 19.7 | 0 | 0.341 |
| DE-tuned PID [23] | 3.58 | 4.85 | 4.20 | −7.80 | −3.92 | −1.53 | 0.3391 |
| DE-tuned TIDF [23] | 2.20 | 3.47 | 3.01 | −6.98 | −3.18 | −1.23 | 0.2461 |
| WOA-tuned TIDF | 2 | 2.9 | 3.0 | −6.90 | −1.30 | −1.14 | 0.1167 |
| WOA-tuned 2DOF TIDF | 1.2 | 1.5 | 2.4 | −3.07 | −6.03 | 0 | 0.0734 |
| Optimization Techniques/Controller | ΔF1 | ΔF2 | ΔPtie | ITAE | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OS (×10−3) | US (×10−3) | ST | OS (×10−3) | US (×10−3) | ST | OS (×10−3) | US (×10−3) | ST | ||
| CRAZYPSO: PI [39] | 5.0 | −31.9 | 8.56 | 2.80 | −37.1 | 10.84 | 0 | −9.5 | 8.65 | 0.5693 |
| hBFOA-PSO: PI [9] | 0.536 | −33.7 | 9.97 | 4.69 | −36.2 | 10.06 | 0 | −9.1 | 7.50 | 0.5059 |
| WOA: DMPI [40] | 4.5 | −22.1 | 7.69 | 1.7 | −18.2 | 8.0 | 0.263 | −5.1 | 5.14 | 0.0959 |
| MFO: DMPI [40] | 3.3 | −23.0 | 6.99 | 1.3 | −18.5 | 7.5 | 0.128 | −5.0 | 5.21 | 0.175 |
| DE: PID [38] | 2.76 | −19.3 | 6.87 | 1.49 | −14.3 | 4.23 | 0.114 | −3.9 | 5.91 | 0.0729 |
| WOA: TIDF | 0.374 | −14.2 | 6.05 | 0 | −9.4 | 6.76 | 0 | −3.1 | 4.95 | 0.0688 |
| WOA: 2DOFTIDF | 1.6 | −9.7 | 3.2 | 0.078 | −2.7 | 4.3 | 0.00012 | −2.0 | 4 | 0.0214 |
| Optimized Controller | Settling Times (Ts) in Sec | OS × 10−3 | Performance Index | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ΔF1 | ΔF2 | ΔPtie | ΔF1 | ΔF2 | ΔPtie | ITAE × 10−3 | |
| GA: PI [29] | 16.03 | 25.72 | 9.84 | 7.8 | 5.6 | 1.2 | 625.8 |
| DA: PI [41] | 5.5 | 7.9 | 4.9 | 10.9 | 5.1 | 0.51 | 150 |
| hFA-PS: PI [29] | 6.43 | 8.60 | 5.98 | 3.6 | 0.837 | 0.0094 | 228.5 |
| hFA-PS: PID [29] | 3.29 | 5.20 | 3.92 | 0.223 | 0.012 | 0.067 | 87.0 |
| DA:PID [41] | 2.3 | 4.4 | 3.85 | 0.143 | 0.011 | 0.035 | 45.9 |
| DA: 2DOFPID [41] | 1.2 | 2.7 | 3.8 | 0.12 | 0 | 0.0022 | 19.4 |
| WOA: 2DOFSFC [32] | 1.7 | 2 | 1 | 1.8 | 0.10 | 0.105 | 24.4 |
| WOA: 2DOFTIDF | 0.97 | 1.4 | 0.6 | 0.384 | 0.004 | 0.006 | 6.4 |
| Parameter Variation | Parameter Variation | Settling Times | Overshoot × 10−3 | Obj × 10−3 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ΔF1 (Hz) | ΔF2 (Hz) | ΔPtie | ΔF1 (Hz) | ΔF2 (Hz) | ΔPtie | |||
| TH1 at area-1 | +50 | 0.97 | 1.4 | 0.6 | 0.384 | 0.004 | 0.006 | 6.4 |
| −50 | 0.98 | 1.4 | 0.6 | 0.384 | 0.003 | 0.0067 | 6.2 | |
| +25 | 0.97 | 1.3 | 0.6 | 0.384 | 0.004 | 0.006 | 6.4 | |
| −25 | 0.98 | 1.3 | 0.6 | 0.384 | 0.005 | 0.006 | 6.3 | |
| T1 at area-1 | +50 | 0.97 | 1.4 | 0.6 | 0.389 | 0.005 | 0.004 | 6.4 |
| −50 | 0.98 | 1.4 | 0.6 | 0.387 | 0.004 | 0.003 | 6.2 | |
| +25 | 0.99 | 1.3 | 0.6 | 0.384 | 0.0045 | 0.003 | 6.4 | |
| −25 | 0.98 | 1.4 | 0.6 | 0.384 | 0.004 | 0.004 | 6.4 | |
| TR at area-1 | +50 | 0.99 | 1.4 | 0.55 | 0.384 | 0.0045 | 0.004 | 6.3 |
| −50 | 0.97 | 1.3 | 0.6 | 0.384 | 0.0045 | 0.006 | 6.4 | |
| +25 | 0.97 | 1.4 | 0.59 | 0.384 | 0.0043 | 0.056 | 6.3 | |
| −25 | 0.97 | 1.4 | 0.6 | 0.384 | 0.004 | 0.006 | 6.4 | |
| TT1 at area-2 | +50 | 0.97 | 1.4 | 0.6 | 0.384 | 0.004 | 0.0063 | 6.4 |
| −50 | 0.99 | 1.3 | 0.56 | 0.384 | 0.044 | 0.0067 | 6.3 | |
| +25 | 0.99 | 1.4 | 0.6 | 0.384 | 0.004 | 0.0064 | 6.4 | |
| −25 | 0.97 | 1.4 | 0.6 | 0.384 | 0.004 | 0.0063 | 6.3 | |
| TW at area-2 | +50 | 0.97 | 1.3 | 0.58 | 0.384 | 0.045 | 0.0069 | 6.4 |
| −50 | 0.98 | 1.4 | 0.6 | 0.384 | 0.0045 | 0.0067 | 6.3 | |
| +25 | 0.97 | 1.3 | 0.6 | 0.384 | 0.004 | 0.0068 | 6.4 | |
| −25 | 0.98 | 1.3 | 0.6 | 0.384 | 0.004 | 0.0065 | 6.1 | |
| Controller | Controller Settling Time (Ts) in Sec | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| ∆F1 | ∆F2 | ∆Ptie | |
| WOA 2DOF TIDF | 1.2 | 1.5 | 2.4 |
| Adaptive Differential Evolution 2DOF TIDF | 2.54 | 3.28 | 1.05 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sahu, P.R.; Simhadri, K.; Mohanty, B.; Hota, P.K.; Abdelaziz, A.Y.; Albalawi, F.; Ghoneim, S.S.M.; Elsisi, M. Effective Load Frequency Control of Power System with Two-Degree Freedom Tilt-Integral-Derivative Based on Whale Optimization Algorithm. Sustainability 2023, 15, 1515. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15021515
Sahu PR, Simhadri K, Mohanty B, Hota PK, Abdelaziz AY, Albalawi F, Ghoneim SSM, Elsisi M. Effective Load Frequency Control of Power System with Two-Degree Freedom Tilt-Integral-Derivative Based on Whale Optimization Algorithm. Sustainability. 2023; 15(2):1515. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15021515
Chicago/Turabian StyleSahu, Preeti Ranjan, Kumaraswamy Simhadri, Banaja Mohanty, Prakash Kumar Hota, Almoataz Y. Abdelaziz, Fahad Albalawi, Sherif S. M. Ghoneim, and Mahmoud Elsisi. 2023. "Effective Load Frequency Control of Power System with Two-Degree Freedom Tilt-Integral-Derivative Based on Whale Optimization Algorithm" Sustainability 15, no. 2: 1515. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15021515
APA StyleSahu, P. R., Simhadri, K., Mohanty, B., Hota, P. K., Abdelaziz, A. Y., Albalawi, F., Ghoneim, S. S. M., & Elsisi, M. (2023). Effective Load Frequency Control of Power System with Two-Degree Freedom Tilt-Integral-Derivative Based on Whale Optimization Algorithm. Sustainability, 15(2), 1515. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15021515









