Spatio-Temporal Analysis about Resource and Environmental Carrying Capacity (RECC) of Mining Cities in Coal-Concentrated Areas: A Case Study of Huaihai Economic Zone in China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
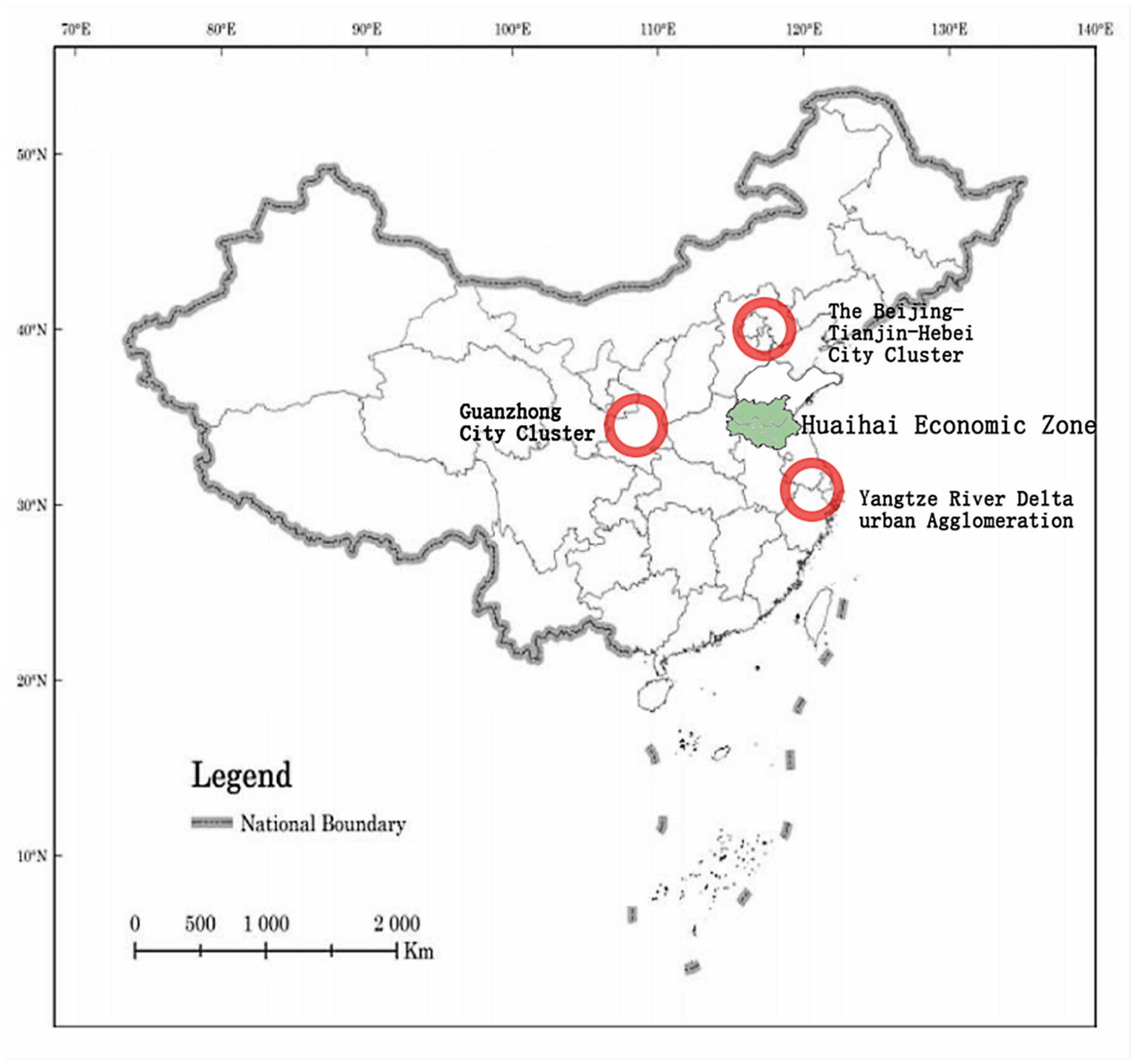
2.1. Case Study Area
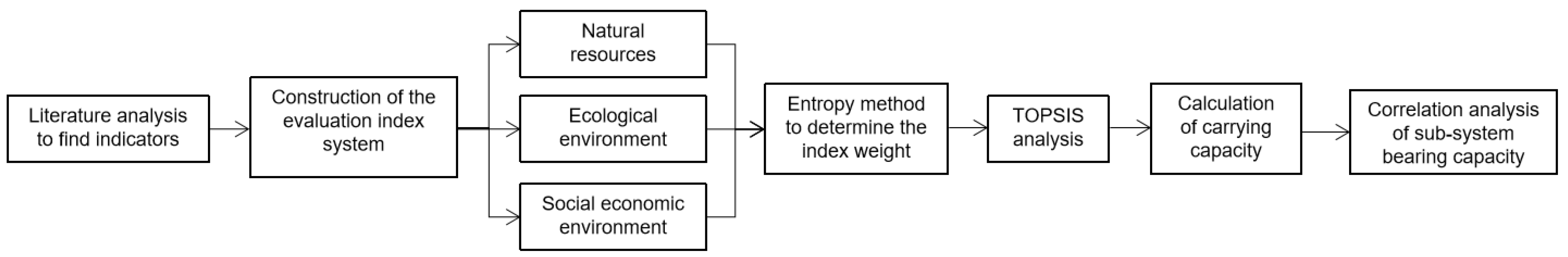
2.2. Research Methodology
2.3. Sources of the Data
2.4. Construction of Index System
2.5. Entropy Weight Method to Determine the Weight
2.5.1. Determination of Target Sequence
2.5.2. The Entropy Method Calculates the Weight
2.5.3. Construction of TOPSIS Model
2.5.4. Determine Positive and Negative Ideal Solutions
2.5.5. Distance Calculation
2.5.6. Comprehensive Calculation Results of RECC
2.6. Calculation Results of Entropy Weight and TOPSIS Model
3. Results
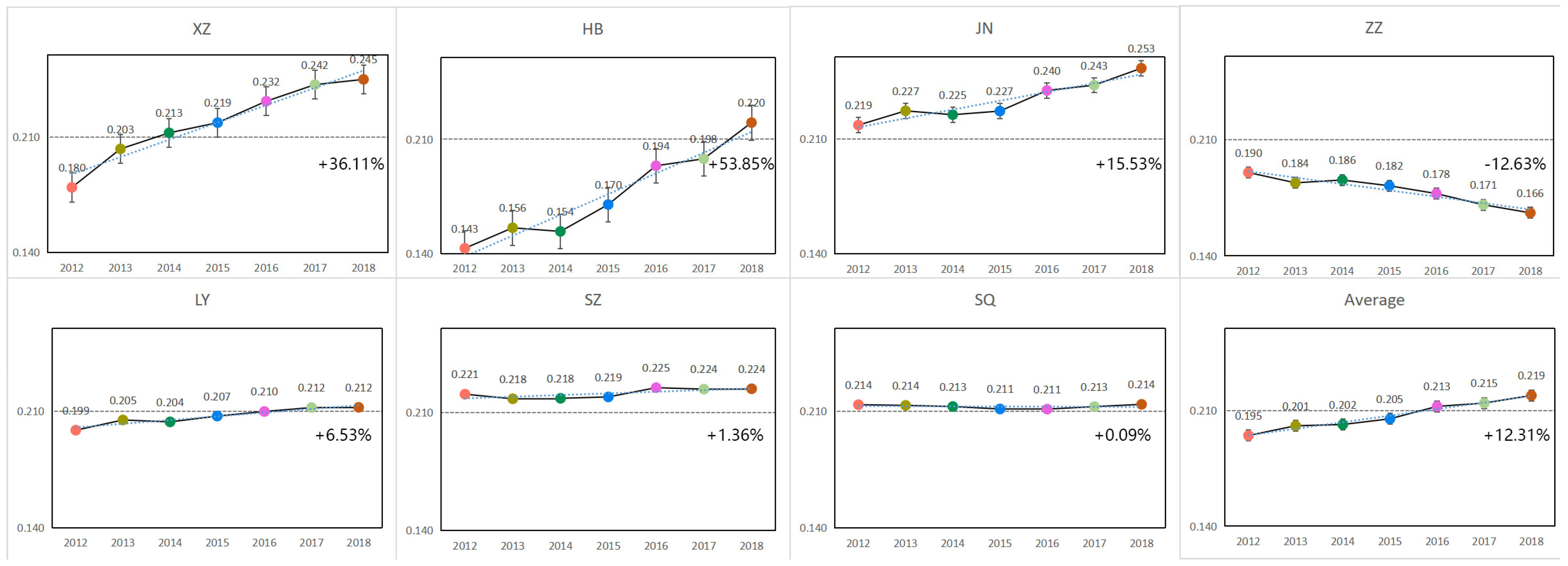
3.1. Variation Characteristics of RECC in Each City
3.2. Spatial Variation Characteristics of RECC
3.3. Variation Characteristics of RECC of Subsystem
4. Discussion
4.1. Changes about RECC of Mining Cities
4.2. The Influence of Mining City Classification on RECC
4.3. Correlation Analysis of RECC Subsystem Changes
5. Conclusions and Suggestions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, L.; Wu, D.; Liu, Y.; Teng, L.; Wu, Z.F.; Feng, Z.H. Research on “Double Assessment” of Karst Areas from the Perspective of Ecological Civilization—Taking Ningyuan County, an ecologically sensitive area, as an example. J. Nat. Resour. 2020, 35, 2385–2400. [Google Scholar]
- Li, G.; Liu, Y. Analysis on Distribution Characteristics and Development Trend of Mining Cities in China. China Min. 2014, 23, 63–70. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S. Research on Industrial Transformation of Mining Cities—Taking Ruhr District of Germany as an Example. China’s Popul. Resour. Environ. 2003, 4, 97–100. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, J. Research on the Transformation of Industrial Structure of Coal Mining Cities in China. J. Geogr. 1993, 3, 218–226. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, X.; Zhang, L.; Kong, L.; Wang, T.J. Study on the risk of dust fall, heavy metal pollution in soil and plants in Zhundong opencast coal mine in Xinjiang. Xinjiang Environ. Prot. 2020, 42, 24–32. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, F.; Zhao, H.; Song, Y.; Chen, L. Study on the effect of coal mining collapse on water environment in Shenfu Dongsheng Mining Area. J. Earth 2007, 6, 521–527. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Yu, J.; Lu, Y. Application of remote sensing monitoring of water pollution in typical western coal mining areas. J. Ecol. Rural. Environ. 2019, 35, 538–544. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q. Study on Dust Fall Mode in Undisturbed Area of Halwusu Open pit Coal Mine. Master’s Thesis, China University of Mining and Technology, Xuzhou, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, K. Environmental Effect and Ecological Restoration Technology of Coal Mining Subsidence. Master’s Thesis, Nanjing University of Science and Technology, Nanjing, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Li, D. Research on Land Use Policy in the Transformation of Resource exhausted Cities in Ruhr District, Germany. Anhui Agric. Sci. 2014, 42, 1194–1195+1210. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, P. Research on Economic Development Vulnerability and Development Strategy of Mining Cities. Master’s Thesis, Northeast Normal University, Changchun, China, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, X.; Cheng, Y.; Ren, C.; Zhou, L. Evaluation of Resources and Environment Carrying Capacity of Ordos City Based on TOPSIS Model with Entropy Weight. Ecol. Sci. 2020, 39, 95–103. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Cheng, J.; Xi, X. Evaluation and Analysis of Resources and Environment Carrying Capacity of Wuhan City Based on GRA-TOPSIS. Stat. Decis. Mak. 2014, 17, 102–105. [Google Scholar]
- Park, R.E.; Burgess, E.W. Introduction to the Science of Sociology; University of Chicago Press: Chicago, IL, USA, 1921. [Google Scholar]
- Allan, W. Studies in African Land Usage in Norther Rhodesia; Oxford University Press: Cape Town, South Africa, 1949. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, K.; Liu, J.; Wang, Y. Analysis and prediction of ecological carrying capacity of mining cities in central Liaoning. Prog. Geogr. Sci. 2009, 28, 870–876. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Y.; Yan, J.; Sha, J.; Wang, F.; Cui, W.; Ding, L.; Ma, L. Comprehensive assessment of resource and environmental carrying capacity of Tangshan City in the context of land and sea integration. China Min. 2020, 29, 23–29. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, Y.; Wang, L.; Huang, C.; Xu, M.; Liu, Y. Environmental carrying capacity assessment of a gold mine area in the northwest plateau of China. Min. Res. Dev. 2019, 39, 141–149. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, Z.; Shen, M. Research on Geological Environment Bearing Capacity of Huanggang City Based on Analytic Hierarchy Process and Variation Coefficient Method. Resour. Environ. Eng. 2019, 33, 70–74+91. [Google Scholar]
- Meadows, D.H.; Meadows, D.I.; Randers, J.; Behrens, W.W., II. The Limits to Growth: A Report to the Club of Rome; Universe Books: New York, NY, USA, 1972. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, X.; Shen, B.; Yu, J.; Liu, X.; Mo, S. Study on System Dynamics Simulation Model of Water Resources Carrying Capacity in Baoji City. J. Xi’an Univ. Archit. Technol. 2007, 1, 72–77. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Mao, Z.; Yanqing, Z. Research on optimal allocation of water resources based on bearing capacity simulation. J. Xi’an Univ. Archit. Technol. 2008, 3, 418–423. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Wei, S.; Hu, J.; Qin, D. Analysis of water resources carrying capacity based on fuzzy two-level evaluation model. People’s Yellow River 2012, 34, 63–65. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, D. Research on Dynamic Assessment of Environmental Carrying Capacity of Guizhou Province Based on Water and Gas Environment Comprehensive Index. Master’s Thesis, Chongqing Normal University, Chongqing, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Shi, P.; Zhao, W.; Feng, T.; Fu, C. Temporal and spatial characteristics of the coordinated development of urbanization and resource and environment carrying capacity in the northwest region: A case study of Lanxi urban agglomeration. J. Ecol. 2020, 39, 2337–2347. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Ning, L.; Cao, Y. Research on evaluation of marine resources and environmental carrying capacity based on entropy weight TOPSIS model—Taking Guangdong Province as an example. Ecol. Econ. 2020, 36, 162–167. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, J.H.; Tian, L. Evaluation of rural resources and environment carrying capacity based on the perspective of carrying capacity improvement: A case study of Caiyu Town, Daxing District, Beijing. J. Ecol. Rural. Environ. 2021, 37, 843–851. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Zhao, S. Spatial consistency of tourism resources and environmental carrying capacity and territorial spatial function in urban agglomeration in the middle reaches of the Yangtze River. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Basin 2021, 30, 1027–1039. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, J.; Chang, S.; Ma, W.; Wang, D. An unbalance-based evaluation framework on urban resources and environment carrying capacity. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 72, 103019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; You, Z.; Yang, Y.; Shi, H. Comprehensive assessment of resource and environmental carrying capacity in Tibet based on three-dimensional tetrahedral model. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2021, 76, 645–662. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, K.; Zhou, S. Per capita resource consumption and resource carrying capacity: Acomparison of the sustainability of 17 mainstream countries. Energy Policy 2012, 42, 603–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayoko Nakajima, E.; Ortega, E. Carrying capacity using emergy and a new calculation of the ecological footprint. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 60, 1200–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, H.; Duan, X.; Zhao, H.; Yu, Z.; Sun, R.; Meng, F. Research on Monitoring and Early Warning of Resources and Environment Carrying Capacity in Nanjing. Resour. Environ. Yangtze River Basin 2020, 29, 2727–2736. [Google Scholar]
- Arif, A.A.; Machdar, I.; Azmeri, A.; Achmad, A. Vulnerability factors in small islands and environmental carrying capacity by the AHP method. Case Study: Weh Island, Aceh, Indonesia. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 630, 012012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, R.W. The concept of carying capacity for tourism destinations: Dead or merely buried. Prog. Tour. Hosp. Res. 1996, 2, 11–21. [Google Scholar]
- Zang, H.; Xue, W.; Xu, Y.; Wu, P.; Zhang, H.; Xu, Y. Contribution of pollution emission from core area to PM2.5 of key cities in Huaihai Economic Zone. J. Environ. Sci. 2020, 40, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, G.; Lv, Z.; Cao, J.; Wu, Q. Analysis on development and utilization of large coal base in China. Energy Environ. Prot. 2020, 42, 107–110+120. [Google Scholar]
- Graymore, M.L.M.; Ricksonre, S. Sustaining human carrying capacity: A tool for regional sustainability assessment. Ecol. Econ. 2010, 69, 459–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Yang, Y.; Yan, H.; Pan, T.; Li, P. Studies on Resource and Environment Carrying Capacity in the past hundred years: From Theory to practice. Resour. Sci. 2017, 39, 379–395. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, J.; Rui, Y.; Lin, G. Evaluation of resources and environment carrying capacity in state-level new districts: A case study of GUI’an New District. J. Sichuan Univ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 32, 87–100. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, J.; Xu, X.; Duan, Y.; Zhang, G.; Wang, Z.; Wang, L.; Zheng, C. Evaluation of resource and environmental carrying capacity in rare earth mining areas in China. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 6105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, D. Evaluation of resources and environmental carrying capacity and its spatial-temporal dynamic evolution: A case study in Shandong Province, China. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2022, 82, 103916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Luo, S.; Jing, Z.; Wei, S.; Ma, Y. Evaluation and Forewarning Management of Regional Resources and Environment Carrying Capacity: A Case Study of Hefei City, Anhui Province, China. Sustainability 2020, 12, 1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, S.; Wu, Y.; Wong, S.W.; Shen, L. Provincial perspective analysis on the coordination between urbanization growth and resource environment carrying capacity (RECC) in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 730, 138964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, W.-L.; Shen, X.; Xu, H.; Zhang, C.; Liu, H.-L.; Shiau, Y.-C. Integrated evaluations of resource and environment carrying capacity of the huaihe river ecological and economic belt in china. Land 2021, 10, 1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Lu, Z.; Tan, F.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, H. Ecological carrying capacity evaluation of typical resource-based cities: A case study of Tangshan City. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2015, 35, 4852–4859. [Google Scholar]
- An, Q.; Wang, L. System dynamics simulation of resource and environmental carrying capacity in mining cities. Resour. Ind. 2016, 19, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Bao, K. Comprehensive Evaluation and Simulation Prediction of Environmental Carrying Capacity of Mature Coal Cities. Ph.D. Thesis, Anhui University of Science and Technology, Anhui, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, D.; Wang, R. Study on resource and environmental carrying capacity assessment of mining cities: A case study of Huangshi City. China Land Resour. Econ. 2015, 28, 57–61. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Hu, Y.; Liu, Q.; Liu, S. Early warning evaluation and simulation analysis of resource and environment carrying capacity in inland arid areas: Empirical analysis from Ningxia. Ecol. Econ. 2021, 37, 209–215+229. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, Y.; Tang, X.; Wang, J.; Huang, H.; Liu, L. Assessment of coordinated development between tourism development and resource environment carrying capacity: A case study of Yangtze River economic Belt in China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 141, 109125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Chen, Q. Comprehensive partitions and optimisation strategies based on tourism urbanisation and resources environment carrying capacity in the Yellow River Basin, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 23180–23193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, S.; Liu, Q.; Han, S. Spatial-temporal evolution of coupling relationship between land development intensity and resources environment carrying capacity in China. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 301, 113778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Wu, Y.; Wu, B. Comprehensive evaluation of Sustainable development of urbanization in Yangtze River Delta: Based on entropy method and quadrant diagram method. Econ. Geogr. 2015, 35, 47–53. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Z.-Q.; Chen, W.-q.; Lan, Z.-R. Study on regional green innovation capability based on entropy weight TOPSIS method. J. Enterp. Econ. 2019, 38, 20–26. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, K.; Chu, J.; Wang, Y. Spatial and temporal changes of land use and ecological carrying capacity in coal-based mining cities based on Remote Sensing. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2014, 34, 5714–5720. [Google Scholar]
- Cong, M. China’s energy structure is changing from coal to diversification. Therm. Energy Power Eng. 2018, 33, 75. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, Y.; Dai, S.-Z.; Zhao, B. The mitigation effect of small scale parks on urban heat island Effect: An empirical study based on community parks in the center of Nanjing City. J. Landsc. Archit. 2019, 8, 26–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, L.; Wang, L. Get rich building roads or getting rich working? Empirical evidence from poor areas along the Yangtze River Economic Belt. Labor Econ. Rev. 2019, 12, 56–77. [Google Scholar]




| Growth Type | Mature Type | Decay Type | Regenerative Type |
|---|---|---|---|
| Shangqiu | Jining, Suzhou | Zaozhuang, Huaibei | Xuzhou, Linyi |
| System | First Level Index | Second Level Index | Third Level Index | Efficiency (+/−) | Resources of References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Resources and environmental carrying capacity | Natural resources | Water resources | Water resources per capita (t) | + | Jingjing Bai et al. [41] |
| Annual water consumption per capita (t) | − | Yang Chen et al. [42] | |||
| Cultivated land resource | Per capita sown area (km2) | + | Guiyou zhang et al. [43] | ||
| Arable land (km2) | + | Liao Shiju et al. [44], Wei-Ling Hsu et al. [45] | |||
| Forest resources | Total forest area (km2) | + | Jin Yue [46] | ||
| Forest coverage rate (%) | + | Liao Shiju et al. [45], Jingjing Bai et al. [42] | |||
| Mineral resources | Coal production (t) | − | An Qier et al. [47], Zheng Xin et al. [12] | ||
| Raw coal consumption (t) | − | Bao Keyu [48] | |||
| Resource utilization efficiency | Coal consumption per 10,000 yuan of GDP (t) | − | Zheng Xin et al. [12], Chen Dan et al. [49] | ||
| Water consumption per 10,000 yuan of GDP (t) | − | Li Shaonan et al. [50], Zheng Xin et al. [12] | |||
| Ecological environment | Green environment | Green rate of built-up area (%) | + | Liao Shiju et al. [45], Yi Xiao et al. [51] | |
| Green area per capita (m2) | + | Chen Dan et al. [50] | |||
| Water environment | Discharge of sewage (t) | + | Yi Xiao et al. [52] | ||
| Sewage treatment rate (%) | + | Liao Shiju et al. [45], Li Shaonan et al. [51] | |||
| Atmospheric environment | Industrial SO2 emissions (t) | − | Yang Chen et al. [43], Yi Xiao et al. [52] | ||
| Industrial smoke (powder) dust treatment rate (%) | − | Bao Keyu [49] | |||
| Soil environment | Industrial solid waste production (t) | − | Zhaofeng Wang et al. [52] | ||
| Industrial solid waste disposal rate (%) | + | Tan S et al. [53] | |||
| Social economic environment | Living ability | Urban per capita housing area (m2) | + | Chen Dan et al. [50] | |
| Rural per capita housing area (m2) | + | Chen Dan et al. [50] | |||
| Traffic capacity | Road network area (m2) | + | Tan S et al. [53] | ||
| Education level | Number of students enrolled in higher education (kilo) | + | Jin Yue [47] | ||
| Income and Consumption | Engel coefficient (%) | + | Jin Yue [47] | ||
| Urban per capita disposable income (yuan) | + | Yi Xiao et al. [52], Zhaofeng Wang et al. [52] | |||
| GDP | GDP of City (billion yuan) | + | Zhaofeng Wang et al. [52], Tan S et al. [53] | ||
| GDP per capita (yuan) | + | Jingjing Bai et al. [42] | |||
| Medical and health care | Ten thousand people have the number of doctors (kilo) | + | Bao Keyu [49] | ||
| Number of health facilities | + | Zheng Xin et al. [12] |
| Third Level Index | XZ | HB | JN | ZZ | LY | SZ | SQ | Average |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water resources per capita | 0.058 | 0.070 | 0.166 | 0.239 | 0.000 | 0.182 | 0.173 | 0.127 |
| Annual water consumption per capita | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.001 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| Per capita sown area | 0.001 | 0.002 | 0.014 | 0.056 | 0.006 | 0.001 | 0.142 | 0.032 |
| Arable land | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.003 | 0.000 | 0.017 | 0.001 | 0.003 |
| Total forest area | 0.004 | 0.007 | 0.010 | 0.006 | 0.095 | 0.010 | 0.028 | 0.023 |
| Forest coverage rate | 0.004 | 0.017 | 0.003 | 0.009 | 0.097 | 0.014 | 0.024 | 0.024 |
| Coal production | 0.013 | 0.365 | 0.031 | 0.162 | 0.001 | 0.000 | 0.050 | 0.089 |
| Raw coal consumption | 0.150 | 0.017 | 0.474 | 0.020 | 0.002 | 0.001 | 0.022 | 0.098 |
| Coal consumption per 10,000 yuan of GDP | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.001 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| Water consumption per 10,000 yuan of GDP | 0.000 | 0.001 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| Green rate of built-up area | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.006 | 0.005 | 0.001 | 0.055 | 0.016 | 0.012 |
| Green area per capita | 0.017 | 0.007 | 0.074 | 0.033 | 0.014 | 0.044 | 0.084 | 0.039 |
| Discharge of sewage | 0.006 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.001 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.001 | 0.001 |
| Sewage treatment rate | 0.030 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.005 | 0.001 | 0.005 |
| Industrial SO2 emissions | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| Industrial smoke (powder) dust treatment rate | 0.000 | 0.001 | 0.000 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.001 |
| Industrial solid waste production | 0.002 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.000 | 0.005 | 0.001 | 0.000 | 0.001 |
| Industrial solid waste disposal rate | 0.002 | 0.000 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.008 | 0.013 | 0.003 | 0.004 |
| Urban per capita housing area | 0.012 | 0.018 | 0.014 | 0.019 | 0.044 | 0.032 | 0.026 | 0.024 |
| Rural per capita housing area | 0.008 | 0.007 | 0.005 | 0.024 | 0.041 | 0.031 | 0.034 | 0.021 |
| Road network area | 0.001 | 0.388 | 0.030 | 0.229 | 0.018 | 0.061 | 0.074 | 0.114 |
| Number of students enrolled in higher education | 0.002 | 0.004 | 0.056 | 0.044 | 0.114 | 0.086 | 0.012 | 0.045 |
| Engel coefficient | 0.056 | 0.013 | 0.030 | 0.021 | 0.176 | 0.122 | 0.026 | 0.063 |
| Urban per capita disposable income | 0.094 | 0.045 | 0.035 | 0.013 | 0.088 | 0.068 | 0.073 | 0.059 |
| GDP of City | 0.091 | 0.015 | 0.021 | 0.039 | 0.104 | 0.099 | 0.063 | 0.062 |
| GDP per capita | 0.098 | 0.015 | 0.015 | 0.046 | 0.101 | 0.129 | 0.115 | 0.074 |
| Ten thousand people have the number of doctors | 0.040 | 0.008 | 0.015 | 0.024 | 0.019 | 0.030 | 0.021 | 0.022 |
| Number of health facilities | 0.311 | 0.001 | 0.000 | 0.005 | 0.067 | 0.001 | 0.013 | 0.057 |
| 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| XZ | 0.180 | 0.203 | 0.213 | 0.219 | 0.232 | 0.242 | 0.245 |
| HB | 0.143 | 0.156 | 0.154 | 0.170 | 0.194 | 0.198 | 0.220 |
| JN | 0.219 | 0.227 | 0.225 | 0.227 | 0.240 | 0.243 | 0.253 |
| ZZ | 0.190 | 0.184 | 0.186 | 0.182 | 0.178 | 0.171 | 0.166 |
| LY | 0.199 | 0.205 | 0.204 | 0.207 | 0.210 | 0.212 | 0.212 |
| SZ | 0.221 | 0.218 | 0.218 | 0.219 | 0.225 | 0.224 | 0.224 |
| SQ | 0.214 | 0.214 | 0.213 | 0.211 | 0.211 | 0.213 | 0.214 |
| SUM | 1.365 | 1.406 | 1.412 | 1.436 | 1.489 | 1.503 | 1.535 |
| 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RCC | 0.623 | 0.587 | 0.524 | 0.505 | 0.493 | 0.476 | 0.412 |
| ECC | 0.309 | 0.340 | 0.401 | 0.406 | 0.439 | 0.465 | 0.521 |
| SECC | 0.434 | 0.480 | 0.487 | 0.525 | 0.557 | 0.562 | 0.602 |
| 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| XZ | 0.180 | 0.203 | 0.213 | 0.219 | 0.232 | 0.242 | 0.245 |
| RCC | 0.093 | 0.117 | 0.106 | 0.113 | 0.108 | 0.113 | 0.066 |
| ECC | 0.035 | 0.024 | 0.047 | 0.040 | 0.058 | 0.051 | 0.085 |
| SECC | 0.051 | 0.062 | 0.059 | 0.066 | 0.066 | 0.077 | 0.093 |
| HB | 0.143 | 0.156 | 0.154 | 0.170 | 0.194 | 0.198 | 0.220 |
| RCC | 0.055 | 0.044 | 0.040 | 0.040 | 0.055 | 0.044 | 0.045 |
| ECC | 0.030 | 0.055 | 0.052 | 0.061 | 0.044 | 0.074 | 0.080 |
| SECC | 0.059 | 0.057 | 0.062 | 0.069 | 0.095 | 0.081 | 0.095 |
| JN | 0.219 | 0.227 | 0.225 | 0.227 | 0.240 | 0.243 | 0.253 |
| RCC | 0.126 | 0.120 | 0.103 | 0.088 | 0.088 | 0.093 | 0.083 |
| ECC | 0.019 | 0.020 | 0.042 | 0.054 | 0.063 | 0.060 | 0.081 |
| SECC | 0.073 | 0.088 | 0.079 | 0.085 | 0.088 | 0.089 | 0.089 |
| ZZ | 0.190 | 0.184 | 0.186 | 0.182 | 0.178 | 0.171 | 0.166 |
| RCC | 0.081 | 0.075 | 0.068 | 0.067 | 0.053 | 0.043 | 0.039 |
| ECC | 0.054 | 0.049 | 0.042 | 0.038 | 0.050 | 0.056 | 0.055 |
| SECC | 0.055 | 0.061 | 0.076 | 0.078 | 0.075 | 0.072 | 0.072 |
| LY | 0.199 | 0.205 | 0.204 | 0.207 | 0.210 | 0.212 | 0.212 |
| RCC | 0.071 | 0.066 | 0.058 | 0.056 | 0.054 | 0.052 | 0.050 |
| ECC | 0.062 | 0.071 | 0.076 | 0.073 | 0.075 | 0.079 | 0.077 |
| SECC | 0.065 | 0.068 | 0.069 | 0.078 | 0.081 | 0.082 | 0.085 |
| SZ | 0.221 | 0.218 | 0.218 | 0.219 | 0.225 | 0.224 | 0.224 |
| RCC | 0.107 | 0.085 | 0.082 | 0.078 | 0.074 | 0.071 | 0.070 |
| ECC | 0.077 | 0.077 | 0.075 | 0.073 | 0.079 | 0.076 | 0.072 |
| SECC | 0.037 | 0.056 | 0.061 | 0.068 | 0.071 | 0.077 | 0.083 |
| SQ | 0.214 | 0.214 | 0.213 | 0.211 | 0.211 | 0.213 | 0.214 |
| RCC | 0.089 | 0.081 | 0.068 | 0.064 | 0.061 | 0.059 | 0.059 |
| ECC | 0.031 | 0.044 | 0.065 | 0.067 | 0.069 | 0.069 | 0.070 |
| SECC | 0.093 | 0.089 | 0.080 | 0.081 | 0.081 | 0.084 | 0.085 |
| Total | 1.365 | 1.403 | 1.412 | 1.436 | 1.489 | 1.512 | 1.534 |
| RCC | 0.623 | 0.587 | 0.524 | 0.505 | 0.493 | 0.476 | 0.412 |
| ECC | 0.309 | 0.340 | 0.401 | 0.406 | 0.439 | 0.465 | 0.521 |
| SECC | 0.434 | 0.480 | 0.487 | 0.525 | 0.557 | 0.562 | 0.602 |
| Type of Mining Cities | Growth Type | Mature Type | Decay Type | Regenerative Type | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Name | Shangqiu | Jining | Suzhou | Zaozhuang | Huaibei | Xuzhou | Linyi |
| Type of RECC | Stable | Steady growth | Stable | Decline | Rapid growth | Rapid growth | Steady growth |
| XZ | HB | JN | ZZ | LY | SZ | SQ | Total | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RCC | ECC | SECC | RCC | ECC | SECC | RCC | ECC | SECC | RCC | ECC | SECC | RCC | ECC | SECC | RCC | ECC | SECC | RCC | ECC | SECC | RCC | ECC | SECC | ||
| RCC | Pearson correlation | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||||||||||||||
| sig. (double tail) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ECC | Pearson correlation | 0.684 | 1 | −0.319 | 1 | −0.937 ** | 1 | −0.418 | 1 | −0.909 ** | 1 | 0.702 | 1 | −0.997 ** | 1 | −0.992 ** | 1 | ||||||||
| sig. (double tail) | 0.090 | 0.485 | 0.002 | 0.350 | 0.005 | 0.078 | 0.000 | 0.000 | |||||||||||||||||
| SECC | Pearson correlation | 0.797 * | 0.796 * | 1 | −0.068 | 0.923 ** | 1 | −0.950 ** | 0.985 ** | 1 | −0.560 | −0.490 | 1 | −0.933 ** | 0.735 | 1 | −0.991** | −0.740 | 1 | 0.878 ** | −0.911 ** | 1 | −0.964 ** | 0.969 ** | 1 |
| sig. (double tail) | 0.032 | 0.032 | 0.885 | 0.003 | 0.001 | 0.000 | 0.191 | 0.265 | 0.002 | 0.060 | 0.000 | 0.057 | 0.009 | 0.004 | 0.000 | 0.000 | |||||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tong, S.; Ji, X.; Chu, Y.; Liu, T.; Wang, F. Spatio-Temporal Analysis about Resource and Environmental Carrying Capacity (RECC) of Mining Cities in Coal-Concentrated Areas: A Case Study of Huaihai Economic Zone in China. Sustainability 2023, 15, 1367. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15021367
Tong S, Ji X, Chu Y, Liu T, Wang F. Spatio-Temporal Analysis about Resource and Environmental Carrying Capacity (RECC) of Mining Cities in Coal-Concentrated Areas: A Case Study of Huaihai Economic Zone in China. Sustainability. 2023; 15(2):1367. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15021367
Chicago/Turabian StyleTong, Shuai, Xiang Ji, Yun Chu, Tianlong Liu, and Fengyu Wang. 2023. "Spatio-Temporal Analysis about Resource and Environmental Carrying Capacity (RECC) of Mining Cities in Coal-Concentrated Areas: A Case Study of Huaihai Economic Zone in China" Sustainability 15, no. 2: 1367. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15021367
APA StyleTong, S., Ji, X., Chu, Y., Liu, T., & Wang, F. (2023). Spatio-Temporal Analysis about Resource and Environmental Carrying Capacity (RECC) of Mining Cities in Coal-Concentrated Areas: A Case Study of Huaihai Economic Zone in China. Sustainability, 15(2), 1367. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15021367







