Object Detection of UAV Images from Orthographic Perspective Based on Improved YOLOv5s
Abstract
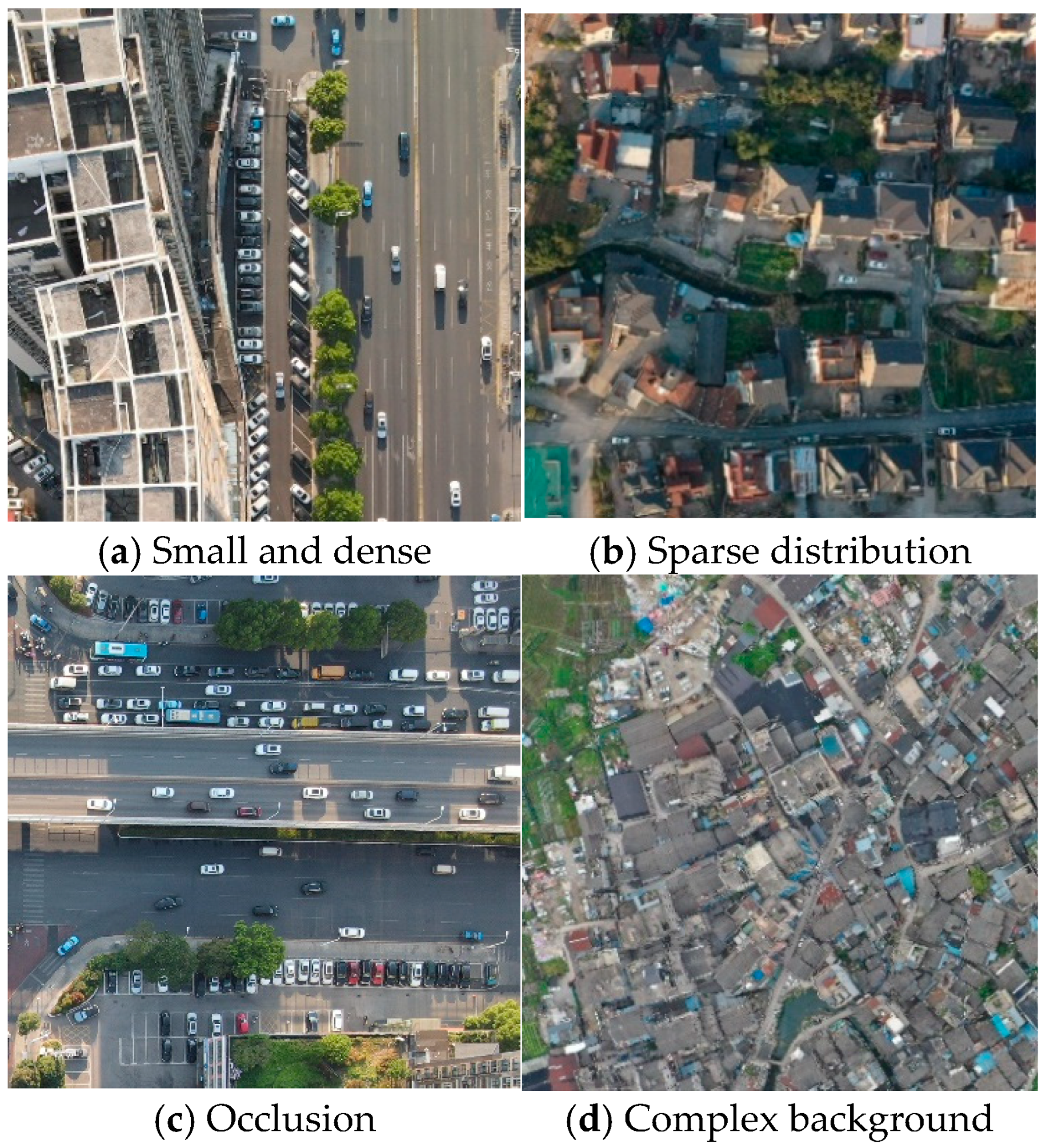
:1. Introduction
- (1)
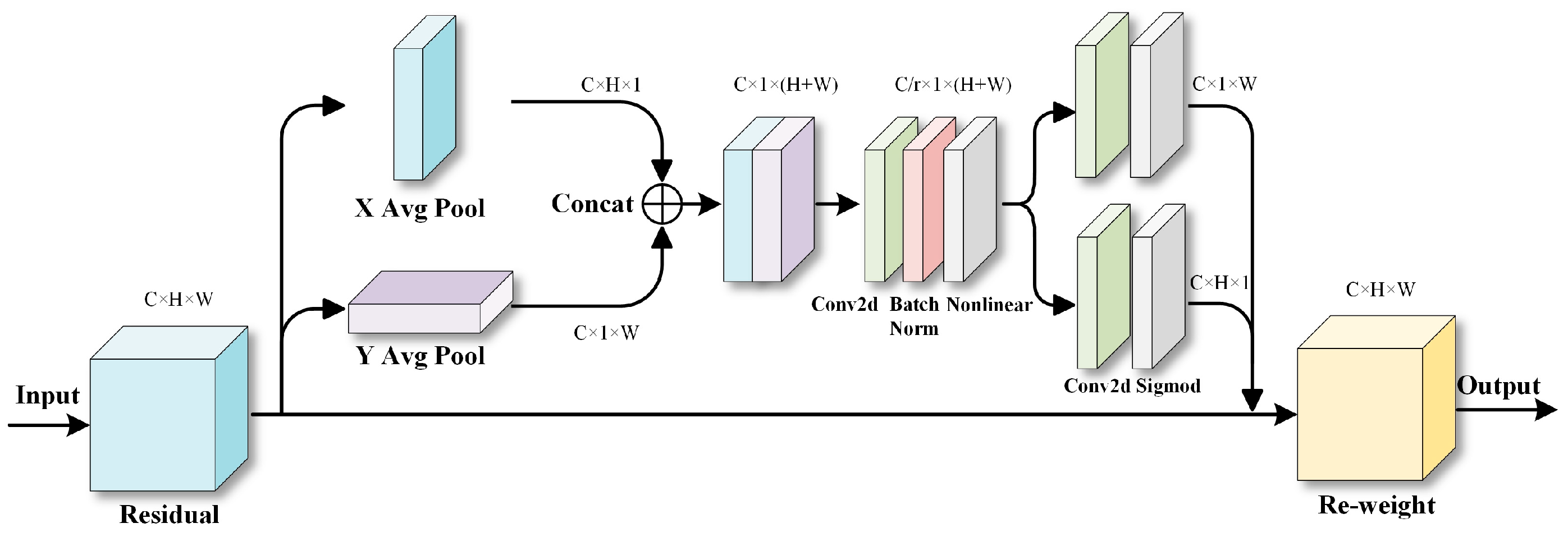
- CA (Coordinate Attention) was introduced into the neck of YOLOv5s to enable the network to pay more attention to the features from various positions, allowing the network to better comprehend the spatial information of objects and thereby enhancing the model’s perception of positional information.
- (2)
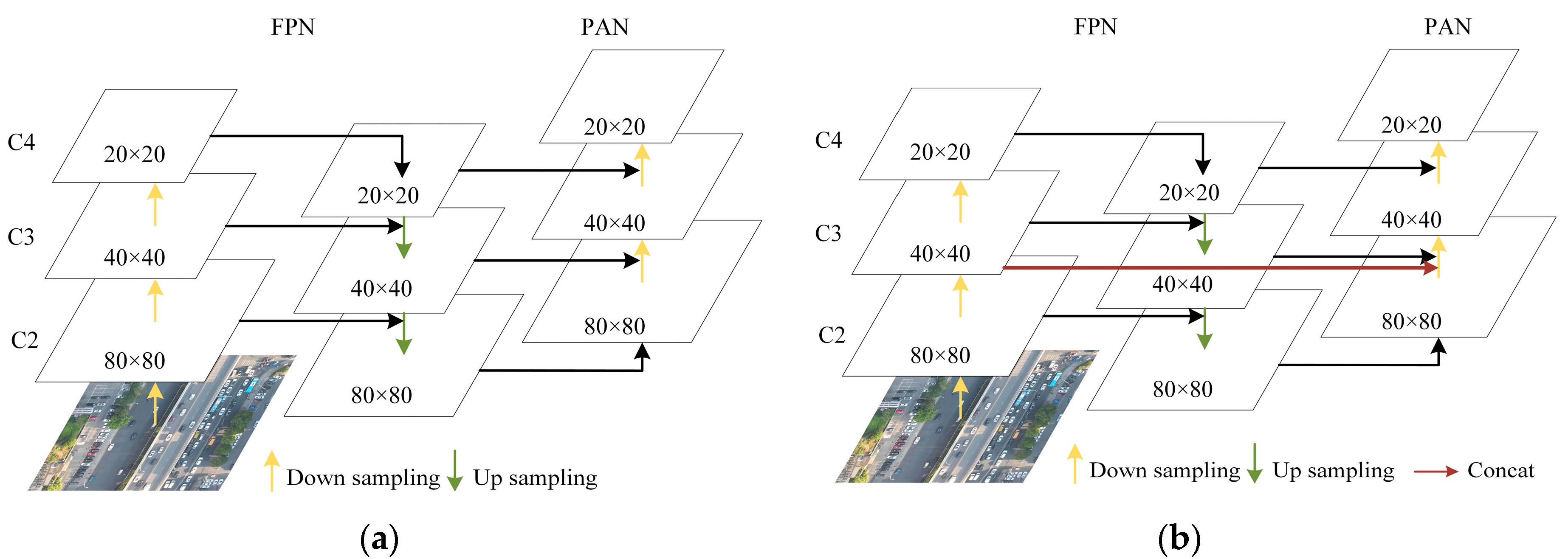
- An improved PAFPN was proposed to strengthen the features yield by different levels in a cascading way so that the lower feature can communicate with the higher feature more directly through a short path, thus enhancing the localization information of the whole feature hierarchy.
- (3)
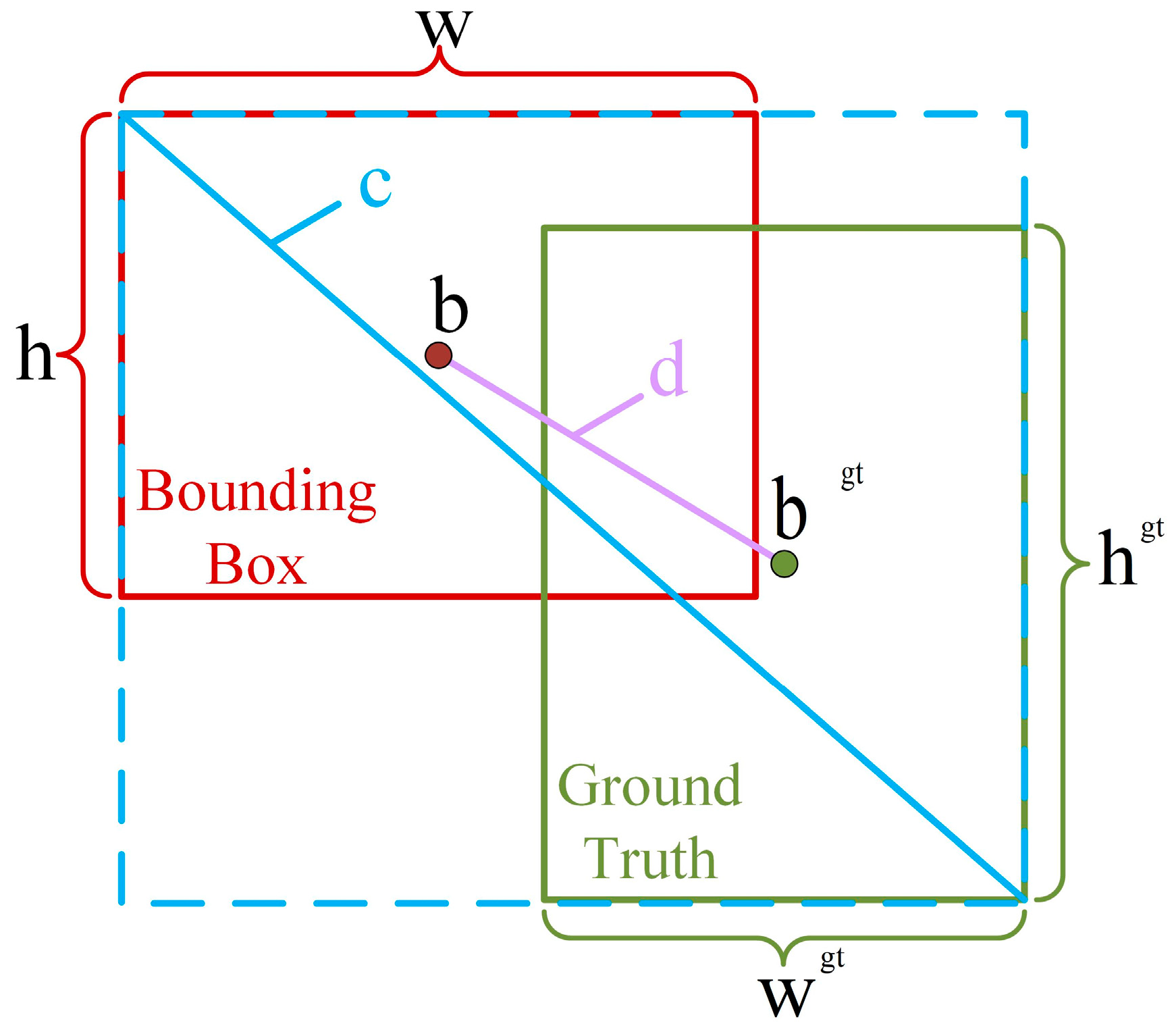
- CIoU loss is applied for the network to better adapt to vehicles with different shapes while alleviating the issues caused by category imbalances. Simultaneously, it accelerates model convergence and leads to a more precise predicted bounding box.
- (4)
- A self-built UAV-OP (Unmanned Aerial Vehicle from Orthographic Perspective) dataset, which has more than 3500 valid high-resolution UAV images labeled with five categories with 20,461 vehicle objects, was built to conduct experiments to validate the model’s performance, including detection accuracy, parameters, and GFlops.
2. Materials and Methods
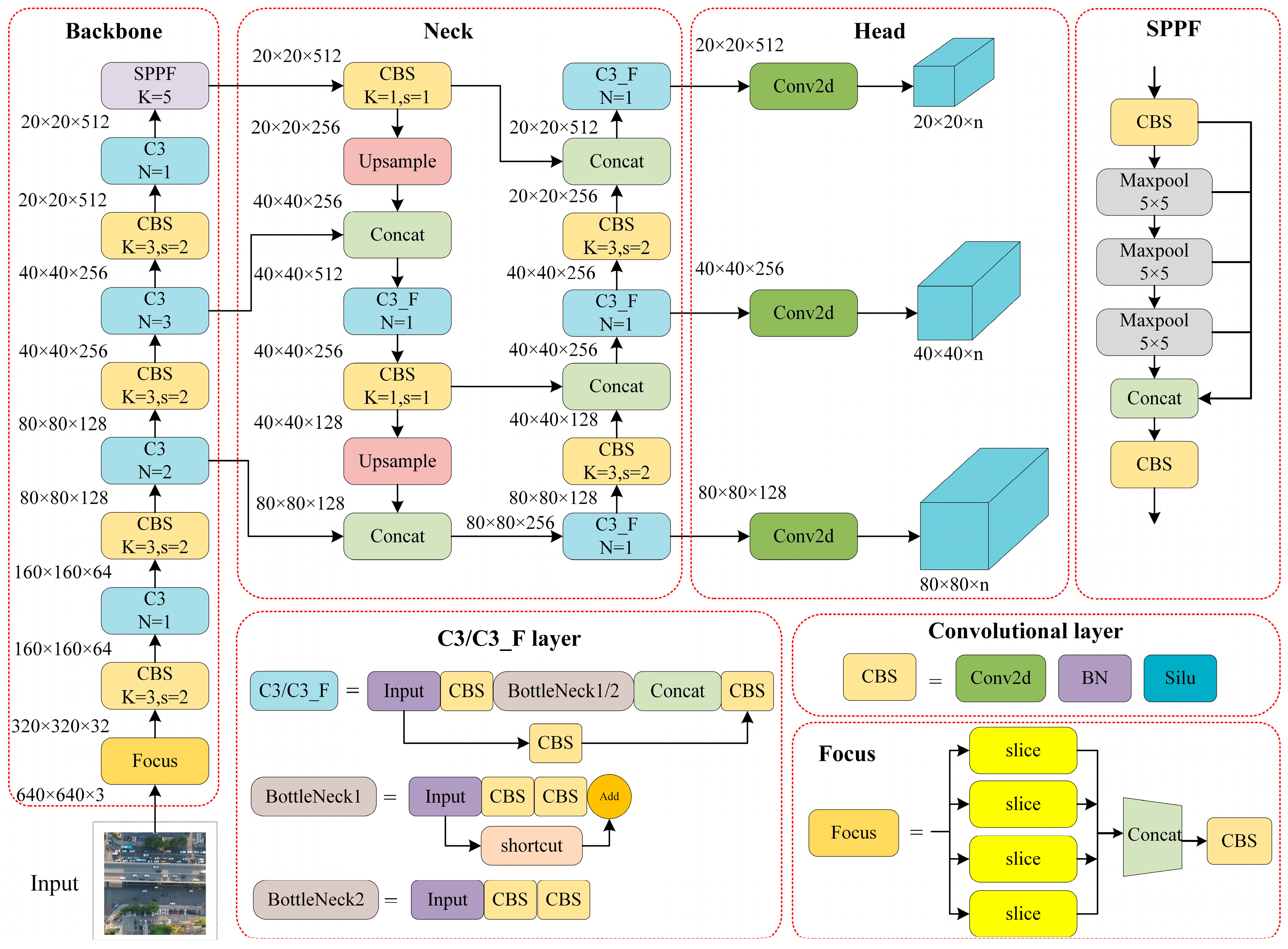
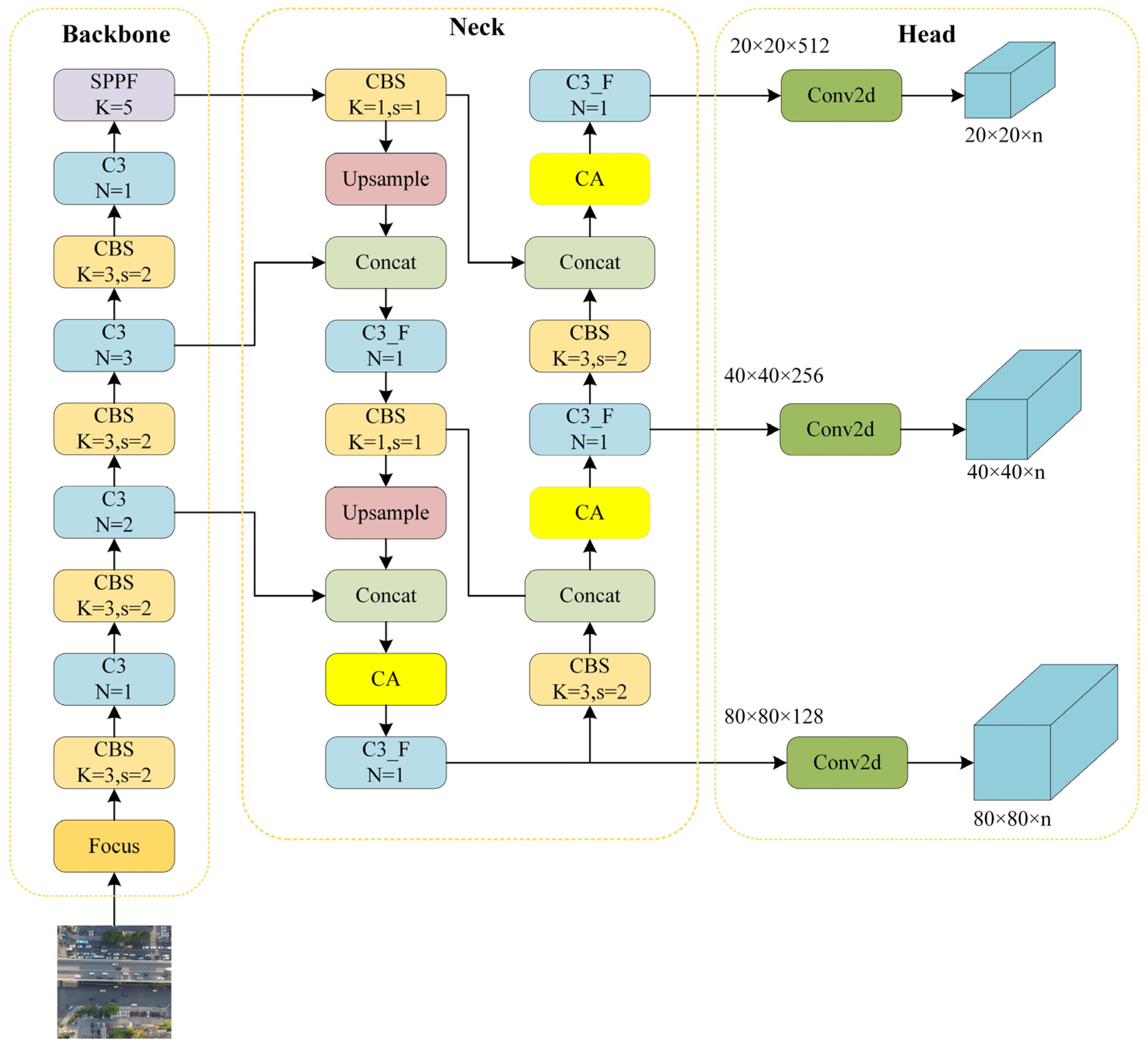
2.1. The Overview of YOLOv5
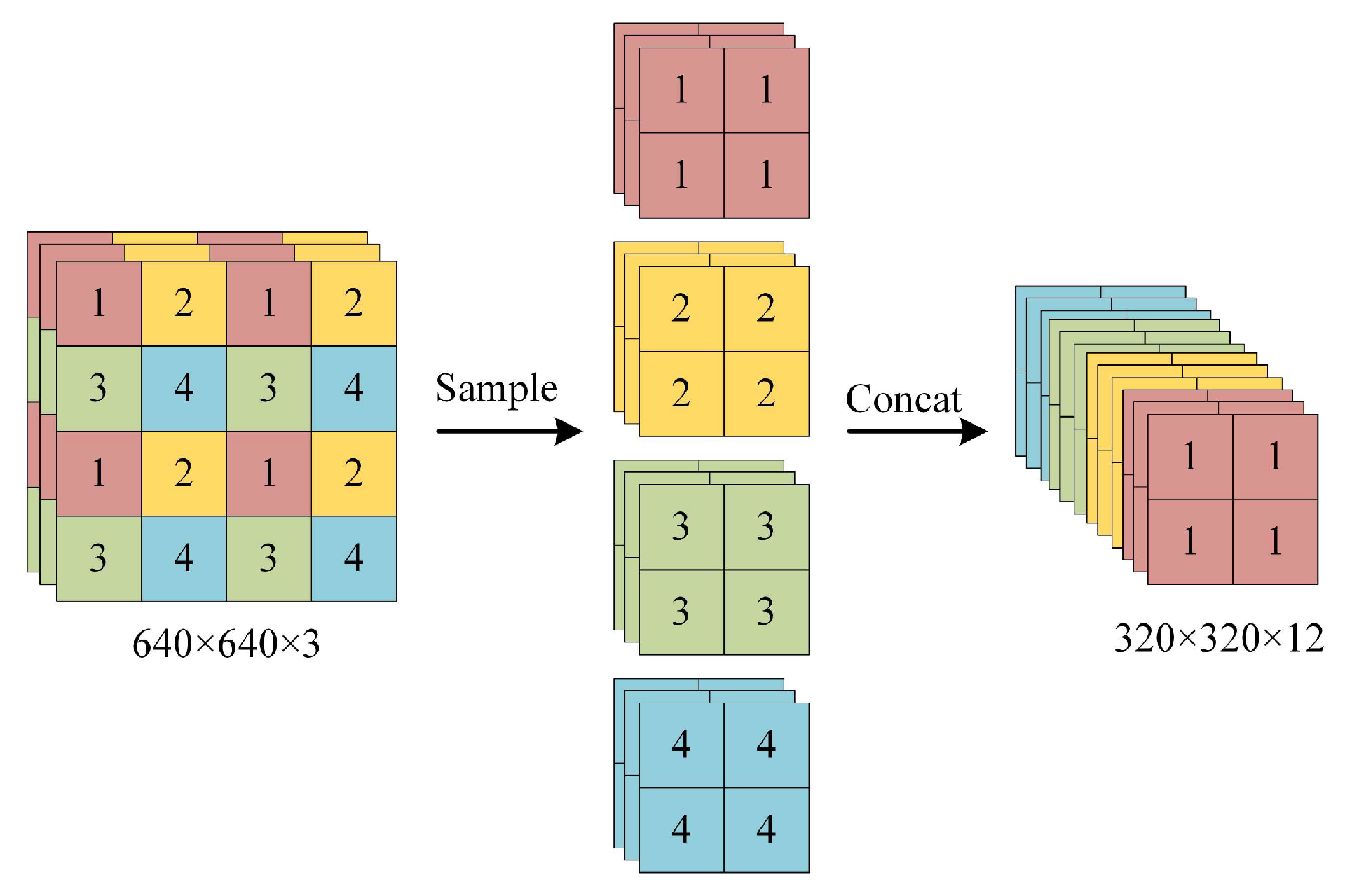
2.1.1. Input
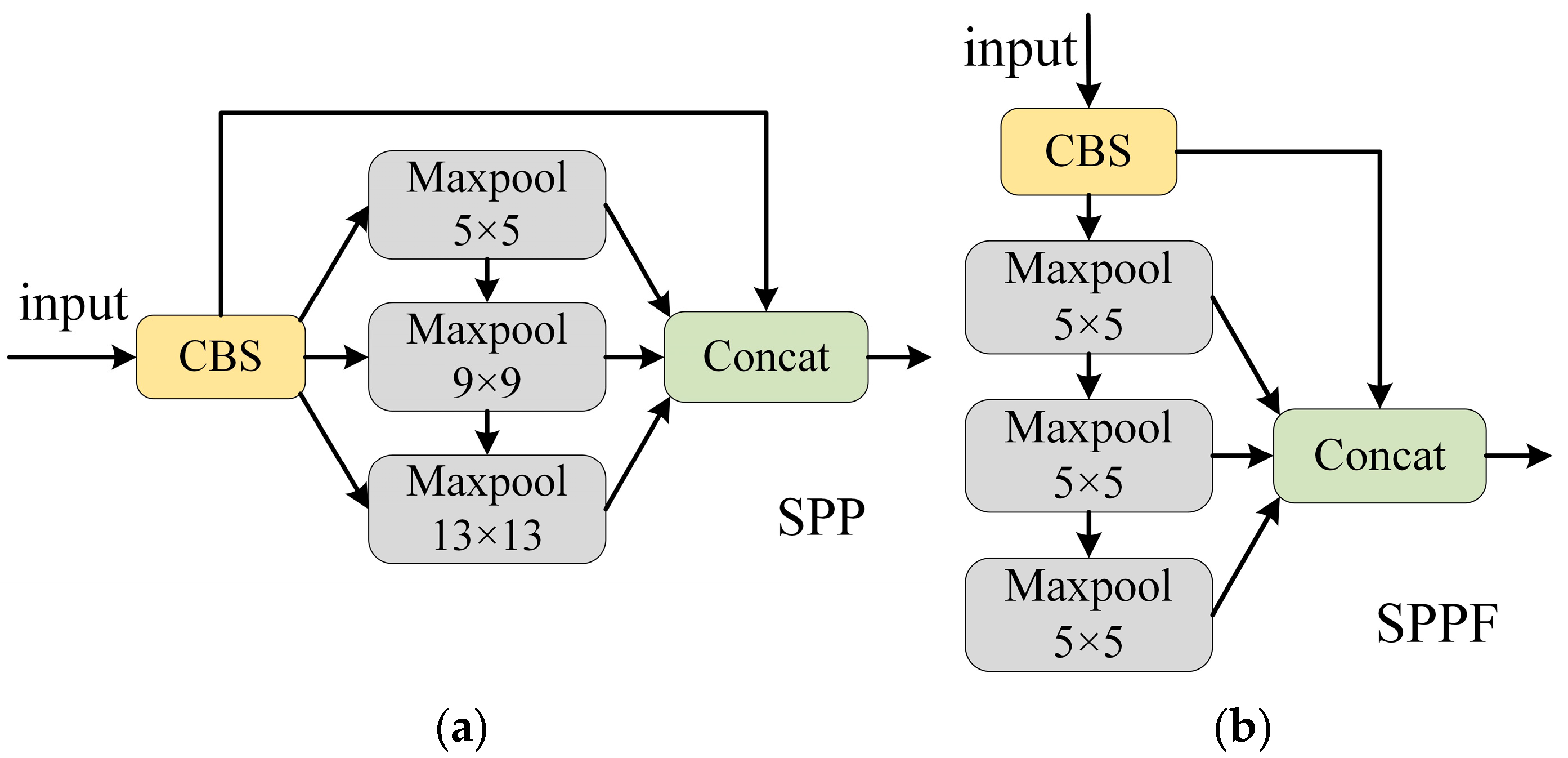
2.1.2. Backbone
2.1.3. Neck
2.1.4. Head
2.2. Improved YOLOv5s
2.2.1. Coordinate Attention
2.2.2. Improved PAFPN
2.2.3. Losses
3. Experiments and Results
3.1. Experimental Environment
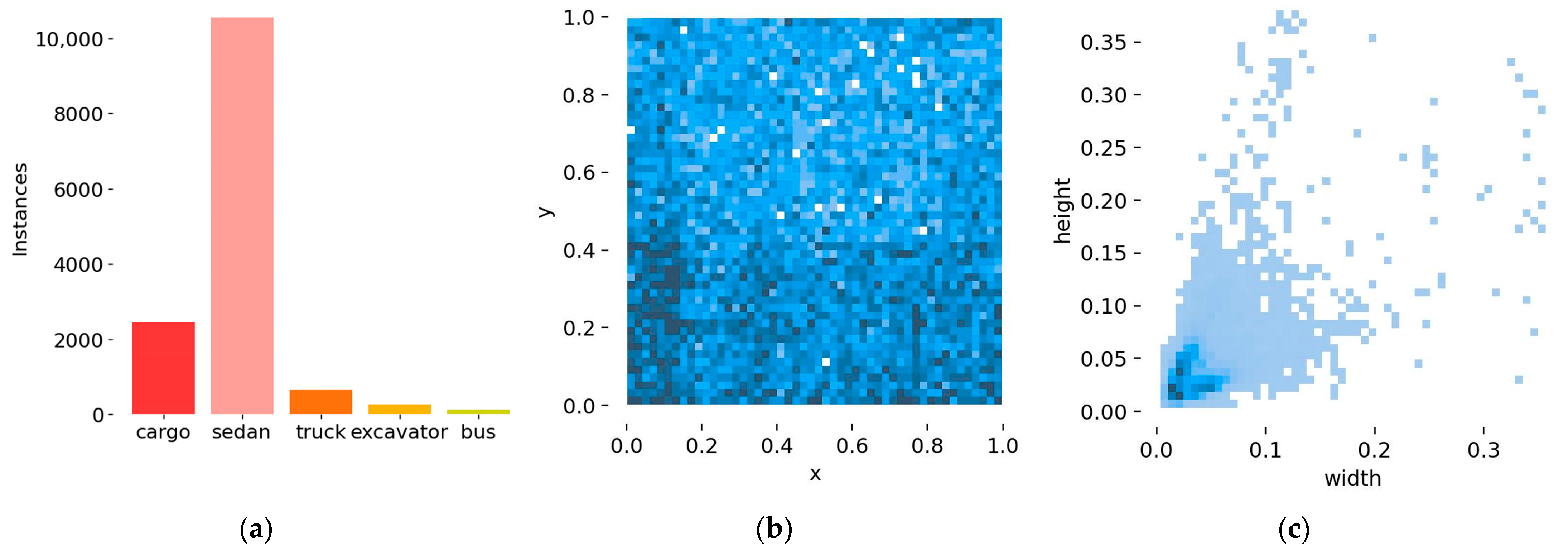
3.2. Dataset
3.3. Evaluation Indicators
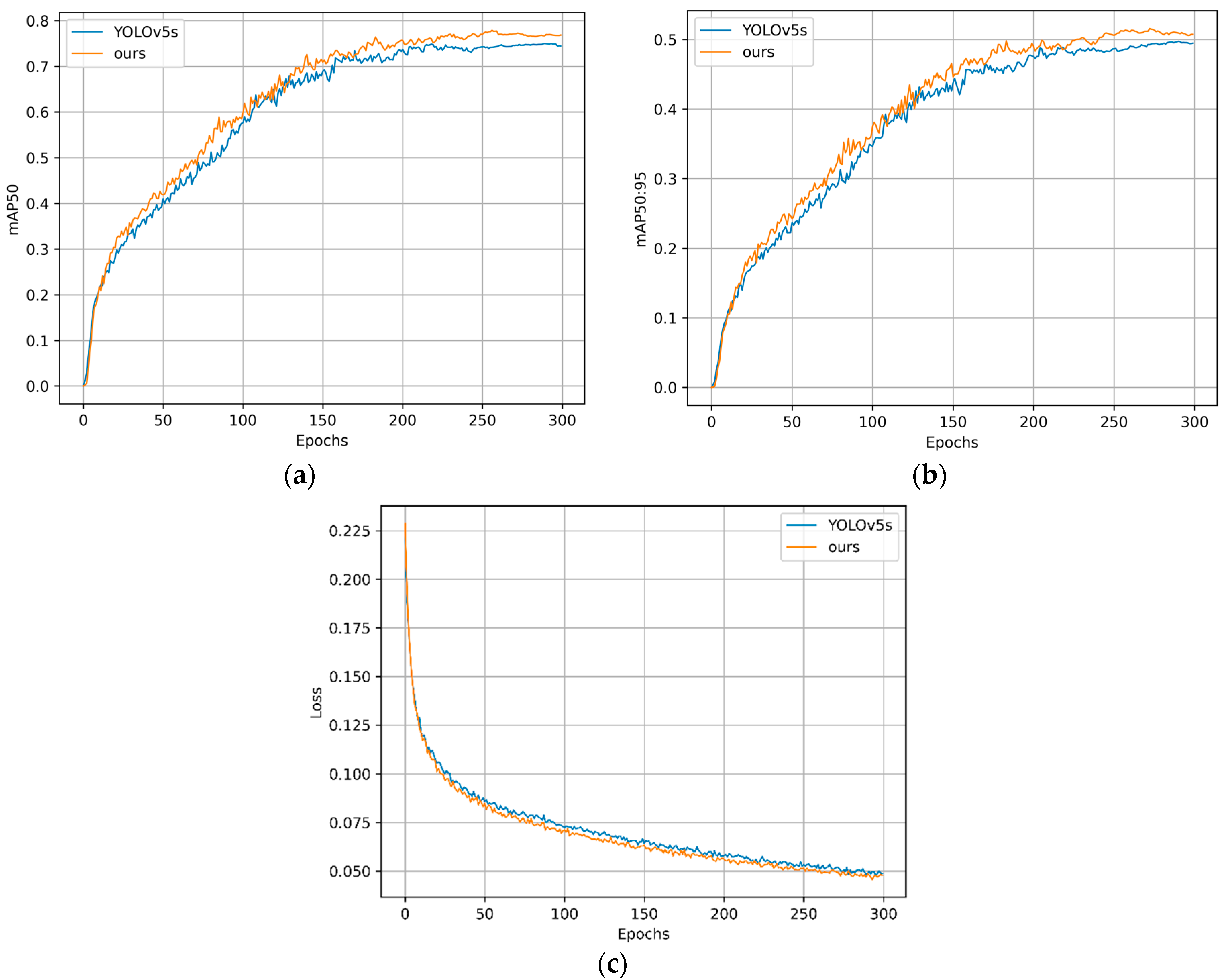
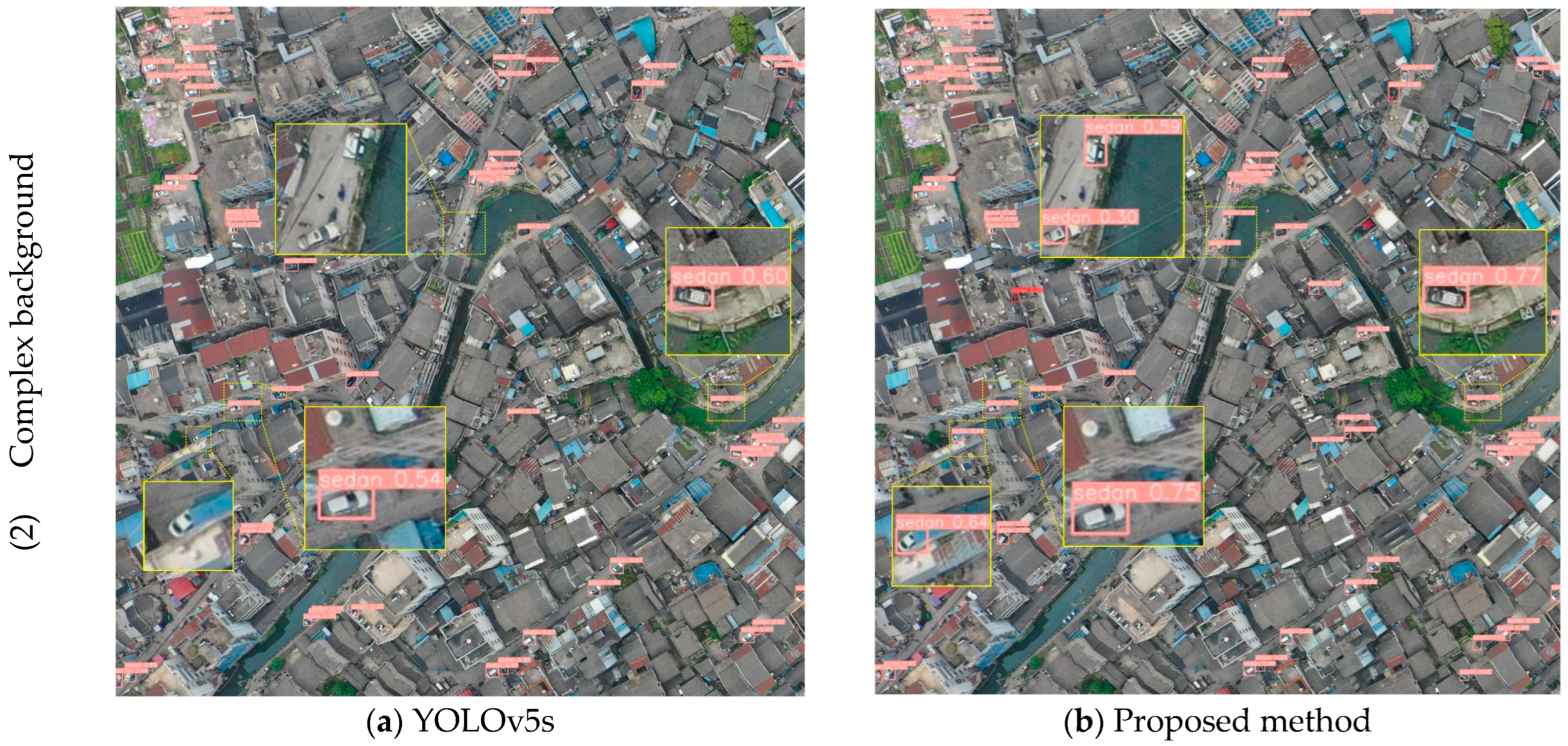
3.4. Experiments and Results
3.4.1. Study of Input Resolution
3.4.2. Evaluation of Attention Mechanisms
3.4.3. Evaluation of Feature Pyramid Networks
3.4.4. Evaluation of IoU Losses
3.4.5. Ablation Experiments
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ganesan, R.; Raajini, X.M.; Nayyar, A.; Sanjeevikumar, P.; Hossain, E.; Ertas, A.H. Bold: Bio-inspired optimized leader election for multiple drones. Sensors 2020, 20, 3134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yayli, U.C.; Kimet, C.; Duru, A.; Cetir, O.; Torun, U.; Aydogan, A.C.; Padmanaban, S.; Ertas, A.H. Design optimization of a fixed wing aircraft. Adv. Aircr. Spacecr. Sci. 2017, 4, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsouros, D.C.; Bibi, S.; Sarigiannidis, P.G. A review on UAV-based applications for precision agriculture. Information 2019, 10, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radoglou-Grammatikis, P.; Sarigiannidis, P.; Lagkas, T.; Moscholios, I. A compilation of UAV applications for precision agriculture. Comput. Netw. 2020, 172, 107148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torresan, C.; Berton, A.; Carotenuto, F.; Di Gennaro, S.F.; Gioli, B.; Matese, A.; Miglietta, F.; Vagnoli, C.; Zaldei, A.; Wallace, L. Forestry applications of UAVs in Europe: A review. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2017, 38, 2427–2447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hildmann, H.; Kovacs, E. Review: Using unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) as mobile sensing platforms (MSPs) for disaster response, civil security and public safety. Drones 2019, 3, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Afrin, T.; Scully, E.; Yodo, N. Advances of UAVs toward future transportation: The state-of-the-art, challenges, and opportunities. Future Transp. 2021, 1, 326–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, S.; Narayan, S.; Mittal, S. A survey of deep learning techniques for vehicle detection from UAV images. J. Syst. Archit. 2021, 117, 102152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girshick, R.; Donahue, J.; Darrell, T.; Malik, J. Rich feature hierarchies for accurate object detection and semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, OH, USA, 23–28 June 2014; pp. 580–587. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Spatial pyramid pooling in deep convolutional networks for visual recognition. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2015, 37, 1904–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girshick, R. Fast r-cnn. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; pp. 1440–1448. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, S.; He, K.; Girshick, R.; Sun, J. Faster r-cnn: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 39, 1137–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.; Vasconcelos, N. Cascade r-cnn: Delving into high quality object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 6154–6162. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Gkioxari, G.; Dollár, P.; Girshick, R. Mask r-cnn. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2961–2969. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, J.; Li, Y.; He, K.; Sun, J. R-fcn: Object detection via region-based fully convolutional networks. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2016, 29, 379–387. [Google Scholar]
- Redmon, J.; Divvala, S.; Girshick, R.; Farhadi, A. You only look once: Unified, real-time object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 779–788. [Google Scholar]
- Redmon, J.; Farhadi, A. YOLO9000: Better, faster, stronger. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 7263–7271. [Google Scholar]
- Redmon, J.; Farhadi, A. Yolov3: An incremental improvement. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1804.02767. [Google Scholar]
- Bochkovskiy, A.; Wang, C.Y.; Liao, H.Y.M. Yolov4: Optimal speed and accuracy of object detection. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2004.10934. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Anguelov, D.; Erhan, D.; Szegedy, C.; Reed, S.; Fu, C.Y.; Berg, A.C. Ssd: Single shot multibox detector. In Computer Vision–ECCV 2016: 14th European Conference, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 11–14 October 2016; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; Volume 14, pp. 21–37. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, T.Y.; Goyal, P.; Girshick, R.; He, K.; Dollár, P. Focal loss for dense object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2980–2988. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Liao, J.; Xu, C. Vehicle detection based on drone images with the improved faster R-CNN. In Proceedings of the 2019 11th International Conference on Machine Learning and Computing, Zhuhai, China, 22–24 February 2019; pp. 466–471. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, Z.; Yan, J.; Yang, B.; Ding, Z. A Novel UAV Aerial Vehicle Detection Method Based on Attention Mechanism and Multi-scale Feature Cross Fusion. In Proceedings of the 2021 2nd International Conference on Artificial Intelligence in Electronics Engineering, Phuket, Thailand, 15–17 January 2021; pp. 51–59. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.; Yu, G.; Wang, Y.; Wu, X.; Ma, Y. Car detection from low-altitude UAV imagery with the faster R-CNN. J. Adv. Transp. 2017, 2017, 2823617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, H.; Gao, Z.; Mei, T.; Li, Y. Improved faster R-CNN with multiscale feature fusion and homography augmentation for vehicle detection in remote sensing images. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2019, 16, 1761–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ammar, A.; Koubaa, A.; Ahmed, M.; Saad, A.; Benjdira, B. Vehicle detection from aerial images using deep learning: A comparative study. Electronics 2021, 10, 820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Tian, X.; Zhang, H.; Hou, W.; Leng, G.; Xu, W.; Jia, H.; He, X.; Wang, M.; Zhang, J. Fast automatic vehicle detection in uav images using convolutional neural networks. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, L. YOLOD: A target detection method for UAV aerial imagery. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Yi, C. Lightweight detection network for arbitrary-oriented vehicles in UAV imagery via global attentive relation and multi-path fusion. Drones 2022, 6, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; He, D. Channel pruned YOLO V5s-based deep learning approach for rapid and accurate apple fruitlet detection before fruit thinning. Biosyst. Eng. 2021, 210, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jawaharlalnehru, A.; Sambandham, T.; Sekar, V.; Ravikumar, D.; Loganathan, V.; Kannadasan, R.; Khan, A.A.; Wechtaisong, C.; Haq, M.A.; Alhussen, A.; et al. Target object detection from Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) images based on improved YOLO algorithm. Electronics 2022, 11, 2343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Shao, F.; He, X.; Zhang, Z.; Cai, Y.; Bi, S. Research on Object Detection and Recognition Method for UAV Aerial Images Based on Improved YOLOv5. Drones 2023, 7, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Qi, L.; Qin, H.; Shi, J.; Jia, J. Path aggregation network for instance segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 8759–8768. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.; Shen, L.; Sun, G. Squeeze-and-excitation networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 7132–7141. [Google Scholar]
- Woo, S.; Park, J.; Lee, J.Y.; Kweon, I.S. Cbam: Convottional block attention module. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 3–19. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, Q.; Zhou, D.; Feng, J. Coordinate attention for efficient mobile network design. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 13713–13722. [Google Scholar]
- Rezatofighi, H.; Tsoi, N.; Gwak, J.; Sadeghian, A.; Reid, I.; Savarese, S. Generalized intersection over union: A metric and a loss for bounding box regression. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 658–666. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Z.; Wang, P.; Liu, W.; Li, J.; Ye, R.; Ren, D. Distance-IoU loss: Faster and better learning for bounding box regression. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New York, NY, USA, 7–12 February 2020; Volume 34, pp. 12993–13000. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.F.; Ren, W.; Zhang, Z.; Jia, Z.; Wang, L.; Tan, T. Focal and efficient IOU loss for accurate bounding box regression. Neurocomputing 2022, 506, 146–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gevorgyan, Z. SIoU loss: More powerful learning for bounding box regression. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2205.12740. [Google Scholar]



| Environment | Versions |
|---|---|
| CPU | CoreI7-12700K@3.61 GHz CPU |
| GPU | Nvidia GeForce RTX 2080Ti GPU |
| Memory | 11 GB |
| Operating System | Windows 10 |
| Python | 3.7.0 |
| PyTorch | 1.7.1 |
| Torchvision | 0.7.2 |
| Epoch | Batch Size | Learning Rate | Weight Decay | Momentum |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 300 | 8 | 0.01 | 0.0005 | 0.937 |
| Category | Cargo | Sedan | Truck | Excavator | Bus | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Train | 2457 | 10,542 | 654 | 278 | 130 | 14,061 |
| Test | 1131 | 4868 | 253 | 101 | 47 | 6400 |
| Total | 3588 | 15,410 | 907 | 379 | 177 | 20,461 |
| Input Resolution | mAP50 | AP50 of Each Category | mAP50:95 | Params | GFlops | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cargo | Sedan | Truck | Excavator | Bus | |||||
| 640 × 640 | 0.609 | 0.666 | 0.853 | 0.503 | 0.638 | 0.384 | 0.369 | 7,023,610 | 15.8 |
| 960 × 960 | 0.730 | 0.739 | 0.925 | 0.629 | 0.699 | 0.659 | 0.468 | ||
| 1280 × 1280 | 0.749 | 0.755 | 0.940 | 0.669 | 0.727 | 0.656 | 0.497 | ||
| Method | mAP50 | AP50 of Each Category | mAP50:95 | Params | GFlops | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cargo | Sedan | Truck | Excavator | Bus | |||||
| YOLOv5s | 0.749 | 0.755 | 0.940 | 0.669 | 0.727 | 0.656 | 0.497 | 7,023,610 | 15.8 |
| YOLOv5s + SE | 0.750 | 0.751 | 0.940 | 0.632 | 0.755 | 0.672 | 0.495 | 7,025,658 | 15.8 |
| YOLOv5s + CBAM | 0.749 | 0.757 | 0.939 | 0.649 | 0.735 | 0.664 | 0.497 | 7,040,067 | 15.9 |
| YOLOv5s + CA | 0.766 | 0.760 | 0.939 | 0.676 | 0.772 | 0.683 | 0.510 | 7,062,618 | 15.9 |
| Method | mAP50 | AP50 of Each Category | mAP50:95 | Parmas | GFlops | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cargo | Sedan | Truck | Excavator | Bus | |||||
| YOLOv5s + CA | 0.766 | 0.760 | 0.939 | 0.676 | 0.772 | 0.683 | 0.510 | 7,062,618 | 15.9 |
| YOLOv5s + CA + BiFPN_Add | 0.742 | 0.770 | 0.942 | 0.631 | 0.725 | 0.645 | 0.500 | 7,188,811 | 16.5 |
| YOLOv5s + CA + BiFPN_Concat | 0.764 | 0.751 | 0.943 | 0.646 | 0.747 | 0.734 | 0.499 | 7,147,131 | 16.1 |
| YOLOv5s + CA + improved_PAFPN | 0.779 | 0.752 | 0.941 | 0.66 | 0.771 | 0.773 | 0.514 | 7,147,122 | 16.1 |
| Method | mAP50 | AP50 of Each Category | mAP50:95 | Parmas | GFlops | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cargo | Sedan | Truck | Excavator | Bus | |||||
| GIoU_Loss | 0.761 | 0.764 | 0.939 | 0.654 | 0.764 | 0.685 | 0.500 | 7,147,122 | 16.1 |
| DIoU_Loss | 0.739 | 0.755 | 0.941 | 0.647 | 0.760 | 0.593 | 0.485 | ||
| CIoU_Loss | 0.779 | 0.752 | 0.941 | 0.660 | 0.771 | 0.773 | 0.514 | ||
| EIoU_Loss | 0.758 | 0.761 | 0.941 | 0.684 | 0.724 | 0.682 | 0.505 | ||
| SIoU_Loss | 0.742 | 0.758 | 0.938 | 0.643 | 0.753 | 0.619 | 0.488 | ||
| Method | mAP50 | AP50 of Each Category | mAP50:95 | Parmas | Gflops | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cargo | Sedan | Truck | Excavator | Bus | |||||
| YOLOv5s | 0.749 | 0.755 | 0.940 | 0.669 | 0.727 | 0.656 | 0.497 | 7,023,610 | 15.8 |
| YOLOv5s + CA | 0.766 | 0.760 | 0.939 | 0.676 | 0.772 | 0.683 | 0.510 | 7,062,618 | 15.9 |
| YOLOv5s + improved_PAFPN | 0.754 | 0.773 | 0.944 | 0.667 | 0.768 | 0.619 | 0.500 | 7,089,146 | 16.0 |
| YOLOv5s + CA + improved_PAFPN | 0.779 | 0.752 | 0.941 | 0.66 | 0.771 | 0.773 | 0.514 | 7,147,122 | 16.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lu, F.; Li, K.; Nie, Y.; Tao, Y.; Yu, Y.; Huang, L.; Wang, X. Object Detection of UAV Images from Orthographic Perspective Based on Improved YOLOv5s. Sustainability 2023, 15, 14564. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151914564
Lu F, Li K, Nie Y, Tao Y, Yu Y, Huang L, Wang X. Object Detection of UAV Images from Orthographic Perspective Based on Improved YOLOv5s. Sustainability. 2023; 15(19):14564. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151914564
Chicago/Turabian StyleLu, Feng, Kewei Li, Yunfeng Nie, Yejia Tao, Yihao Yu, Linbo Huang, and Xing Wang. 2023. "Object Detection of UAV Images from Orthographic Perspective Based on Improved YOLOv5s" Sustainability 15, no. 19: 14564. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151914564
APA StyleLu, F., Li, K., Nie, Y., Tao, Y., Yu, Y., Huang, L., & Wang, X. (2023). Object Detection of UAV Images from Orthographic Perspective Based on Improved YOLOv5s. Sustainability, 15(19), 14564. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151914564






