Spatial Distribution and Influencing Factors of High-Level Tourist Attractions in China: A Case Study of 9296 A-Level Tourist Attractions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Study Data
2.3. Study Method
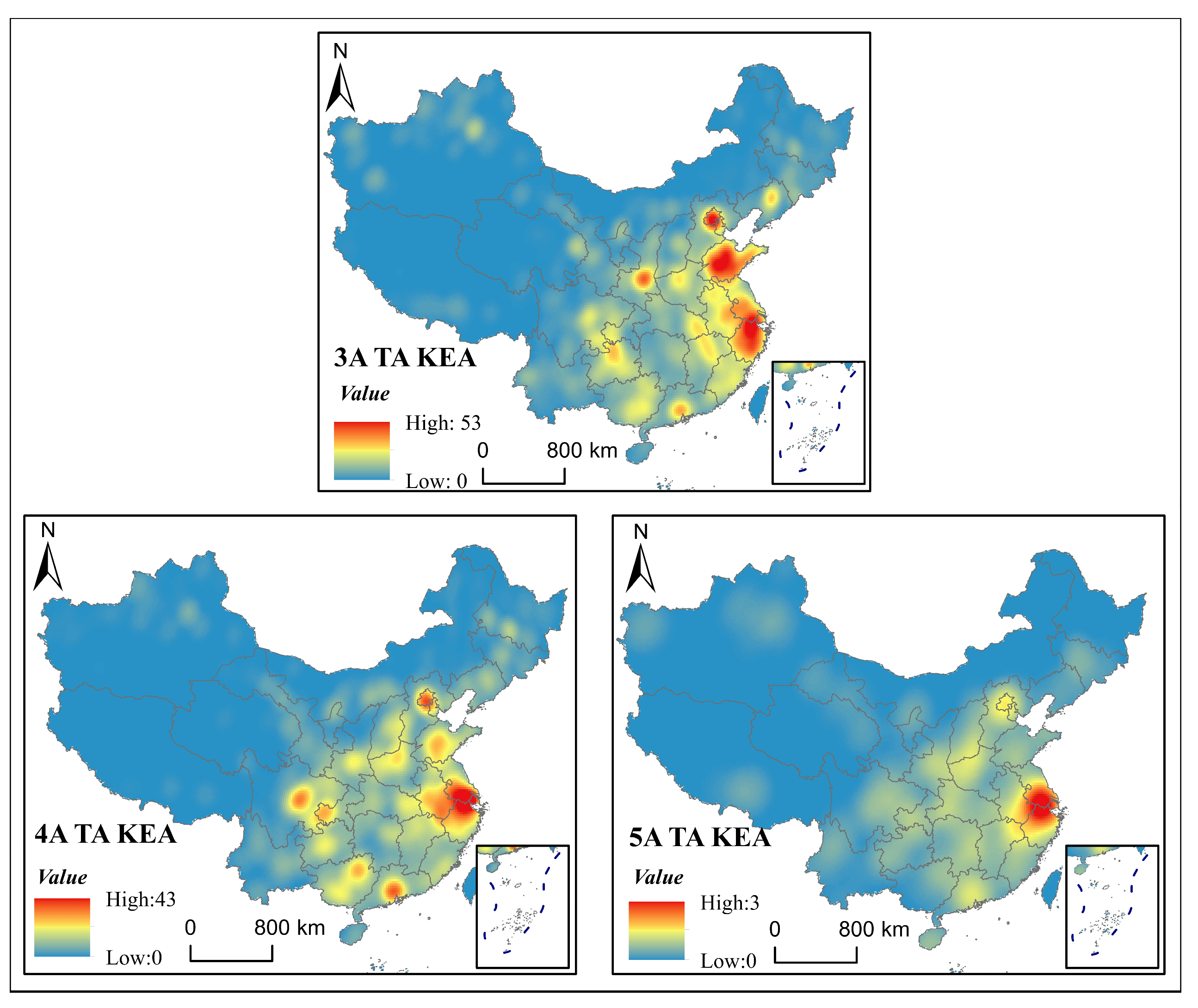
2.3.1. Kernel Density Analysis
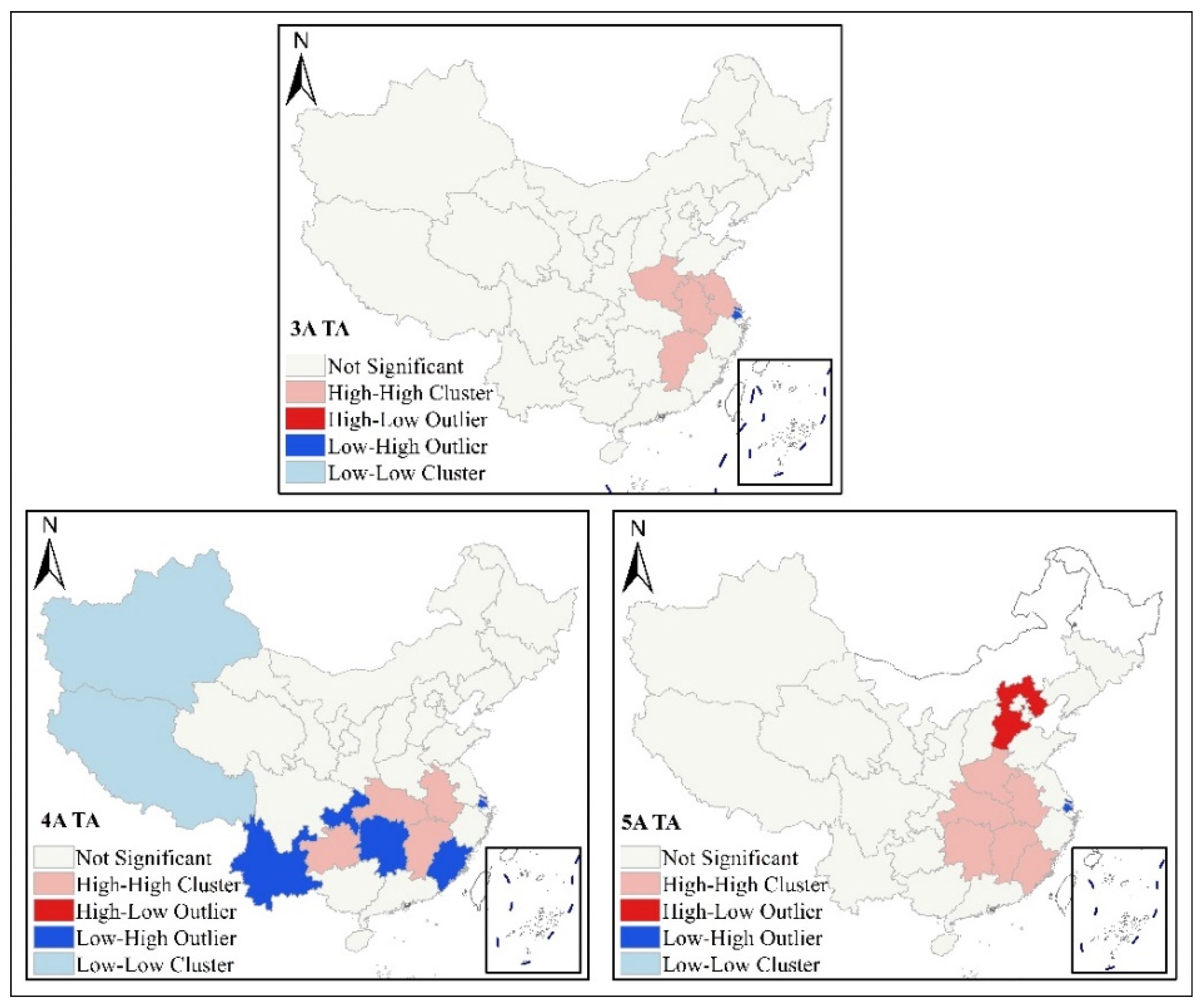
2.3.2. Local Spatial Autocorrelation
2.3.3. Geographical Detector
3. Results
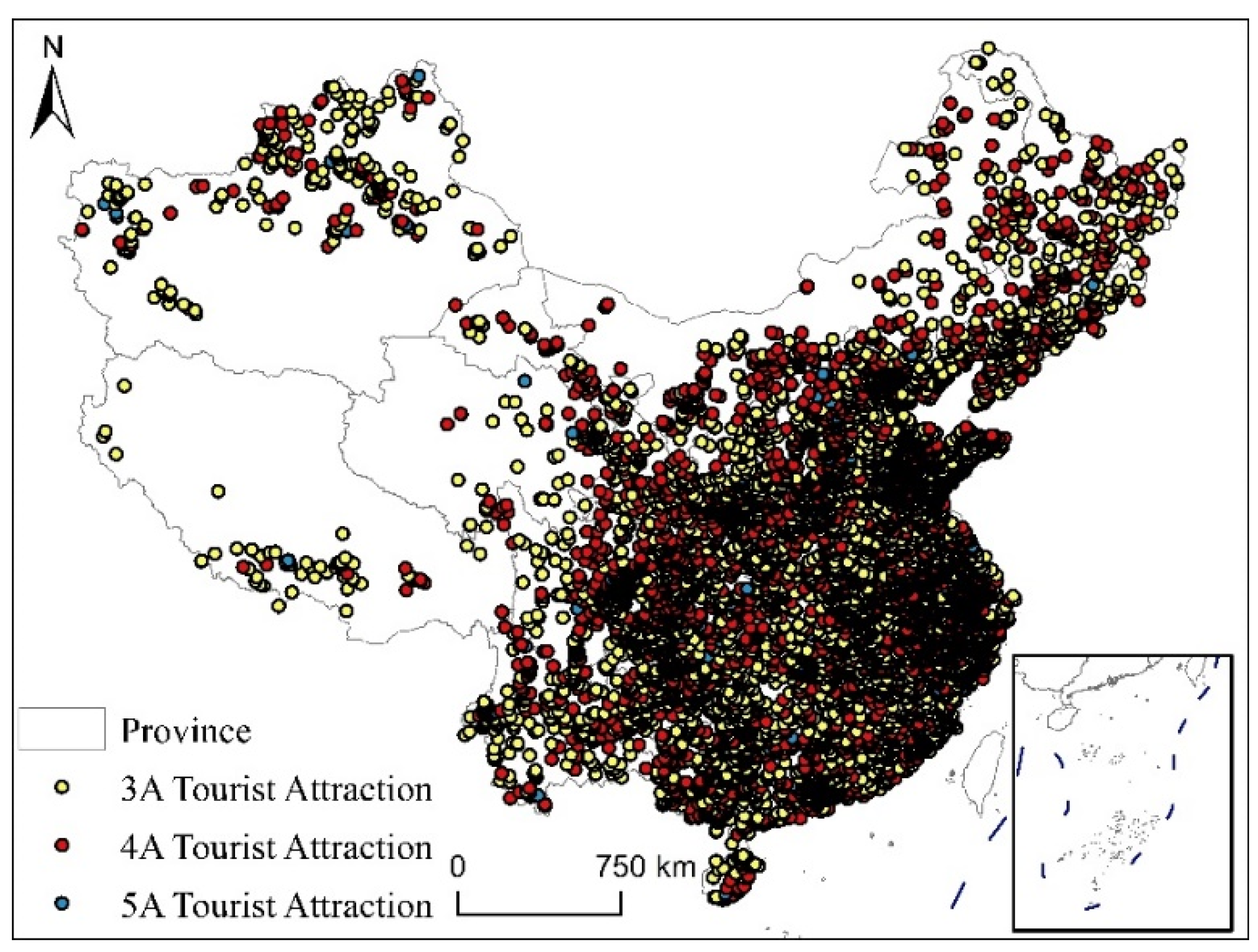
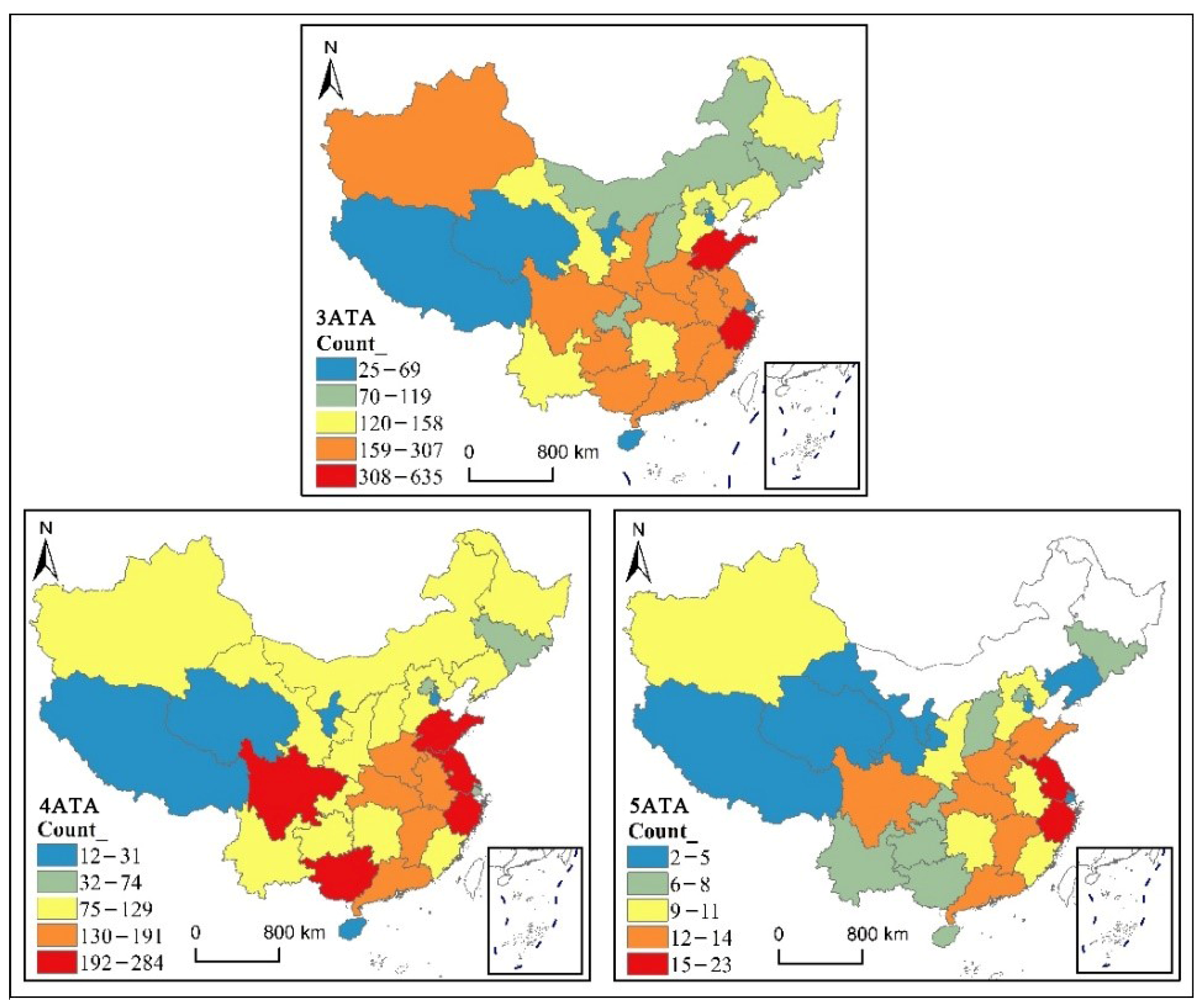
3.1. Spatial Distribution Differences of High-Level Tourist Attractions
3.2. Factors Influencing the Spatial Differentiation of High-Level Tourist Attractions
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Masiero, L.; Hrankai, R. Modeling tourist accessibility to peripheral attractions. Ann. Tour. Res. 2022, 92, 103343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Chen, Z. Destination attraction clustering: Segmenting tourist movement patterns with geotagged information. Tour. Geogr. 2023, 25, 797–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becken, S.; Simmons, D.G. Understanding energy consumption patterns of tourist attractions and activities in New Zealand. Tour. Manag. 2002, 23, 343–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, S.; Sotiriadis, M.; Zhang, Y. The influence of smart technologies on customer journey in tourist attractions within the smart tourism management framework. Sustainability 2020, 12, 4157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biraglia, A.; Gerrath, M.H.; Usrey, B. Examining how companies’ support of tourist attractions affects visiting intentions: The mediating role of perceived authenticity. J. Travel Res. 2018, 57, 811–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molinillo, S.; Japutra, A. Factors influencing domestic tourist attendance at cultural attractions in Andalusia, Spain. J. Destin. Mark. Manag. 2017, 6, 456–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlKahtani, S.J.H.; Xia, J.C.; Veenendaaland, B.; Caulfield, C.; Hughes, M. Building a conceptual framework for determining individual differences of accessibility to tourist attractions. Tour. Manag. Perspect. 2015, 16, 28–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Wu, P.; Ge, Q.; Ning, Z. Ticket prices and revenue levels of tourist attractions in China: Spatial differentiation between prefectural units. Tour. Manag. 2021, 83, 104214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montanari, A.; Staniscia, B. Culinary tourism as a tool for regional re-equilibrium. Eur. Plan. Stud. 2009, 17, 1463–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Qi, L.; Yang, A.; Shi, L.; Xu, L. Investigating spatial distribution of tourist attractions’ inlinks: A case study of three mountains. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 2010, 53, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, H.; Zheng, W.; Zhuang, X.; Lin, Z. Explore for a day? Generating personalized itineraries that fit spatial heterogeneity of tourist attractions. Inf. Manag. 2021, 58, 103557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.; Lee, G.; Kim, J.; Park, D. Identifying the spatial structure of the tourist attraction system in South Korea using GIS and network analysis: An application of anchor-point theory. J. Destin. Mark. Manag. 2018, 9, 358–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotus, J.; Rzeszewski, M.; Ewertowski, W. Tourists in the spatial structures of a big Polish city: Development of an uncontrolled patchwork or concentric spheres? Tour. Manag. 2015, 50, 98–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Z.W.; Yu, S.; Ji, T. Modeling the Trip Distributions of Tourists Based on Trip Chain and Entropy-Maximizing Theory. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 10058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Zhou, X.; Wang, M. Analyzing and visualizing the spatial interactions between tourists and locals: A Flickr study in ten US cities. Cities 2018, 74, 249–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Kim, I. Change and stability in shopping tourist destination networks: The case of Seoul in Korea. J. Destin. Mark. Manag. 2018, 9, 267–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wu, X.; Liu, Z.; Chen, H.; Zhao, Y. Spatial Patterns of Tourist Attractions in the Yangtze River Delta Region. Land 2022, 11, 1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, Y.P.; Sun, J.; Yu, B. The sightseeing bus schedule optimization under park and ride system in tourist attractions. Ann. Oper. Res. 2019, 273, 587–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mou, N.; Zheng, Y.; Makkonen, T.; Yang, T.; Tang, J.J.; Song, Y. Tourists’ digital footprint: The spatial patterns of tourist flows in Qingdao, China. Tour. Manag. 2020, 81, 104151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Wang, P. Study on distribution characteristic of tourism attractions in international cultural tourism demonstration region in South Anhui in China. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0269948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Liu, Z.; Shang, S.; Qin, Y.; Wu, B. Vitality continuation or over-commercialization? Spatial structure characteristics of commercial services and population agglomeration in historic and cultural areas. Tour. Econ. 2019, 25, 1302–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Xiao, X.; Zhang, J.; Wu, R.; Zhang, H. Spatial configuration and online attention: A space syntax perspective. Sustainability 2018, 10, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Z.; Newing, A.; Clarke, G. Understanding Chinese tourist mobility and consumption-related behaviours in London using Sina Weibo check-ins. Environ. Plan. B Urban Anal. City Sci. 2021, 48, 2436–2452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makkonen, T.; Hokkanen, T.J. ICT innovation and local economy: Mobile game as a tourist attraction. Scand. J. Hosp. Tour. 2013, 13, 257–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Han, Y.; Wang, P.; Guan, H. Invulnerability analysis of traffic network in tourist attraction under unexpected emergency events based on cascading failure. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 147383–147398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, X.R.; Zhen, F.; Zhang, J. How smart is your tourist attraction?: Measuring tourist preferences of smart tourism attractions via a FCEM-AHP and IPA approach. Tour. Manag. 2016, 54, 309–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.X.; Lin, B.S.; Chen, M.H.; Su, C.H. 5A Tourist attractions and China’s regional tourism growth. Asia Pac. J. Tour. Res. 2020, 25, 524–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Wang, L.; Ning, Z.Z. Spatial pattern of tourist attractions and its influencing factors in China. J. Spat. Sci. 2020, 65, 327–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, G.; Li, H.; Li, Y. The temporal and spatial distribution characteristics and influencing factors of tourist attractions in Chengdu-Chongqing economic circle. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2023, 25, 8677–8698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oriade, A.; Schofield, P. An examination of the role of service quality and perceived value in visitor attraction experience. J. Destin. Mark. Manag. 2019, 11, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byun, J.; Jang, S.S. Effective promotions for membership subscriptions and renewals to tourist attractions: Discount vs. bonus. Tour. Manag. 2015, 50, 194–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Peng, X.; Qin, Y.; Wang, C. What can the news tell us about the environmental performance of tourist areas? A text mining approach to China’s National 5A Tourist Areas. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2020, 52, 101818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, G.; Liu, S.; Ren, L.; Gong, D. Forecasting hourly attraction tourist volume with search engine and social media data for decision support. Inf. Process. Manag. 2023, 60, 103399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Wang, S.; Wang, F. Isolated or integrated? Planning and management of urban renewal for historic areas in Old Beijing city, based on the association network system. Habitat Int. 2019, 93, 102049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, L.; Li, M.; Rong, P.; Qin, Y. Understanding the impact of the built environment on ride-hailing from a spatio-temporal perspective: A fine-scale empirical study from China. Cities 2022, 126, 103706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Sun, J. Meta-understanding of environmental perception in tourism: Implications for China’s tourist attractions. Sustainability 2020, 12, 1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Lian, T.; Geng, H.; Li, S. Analyzing the structure of tourism destination network based on digital footprints: Taking Guilin, China as a case. Data Technol. Appl. 2023, 57, 56–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T17775-2003; Standard of Rating for Quality of Tourist Attractions. General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2003.
- Wang, Y.; Lu, C.; Chen, H.; Zhao, Y. Evaluation and Spatial Characteristics of Cooperation among Tourist Attractions Based on a Geographic Information System: A Case Study of The Yangtze River Delta Region, China. Sustainability 2022, 14, 13041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.H.; Chen, J.Y.; Hsu, S.S.; Chung, Y.H. Automatic tourist attraction and representative icon determination for tourist map generation. Inf. Vis. 2014, 13, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKercher, B.; Koh, E. Do attractions “attract” tourists? The case of Singapore. Int. J. Tour. Res. 2017, 19, 661–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueroa, V.; Herrero, L.C.; Baez, A.; Gomez, M. Analysing how cultural factors influence the efficiency of tourist destinations in Chile. Int. J. Tour. Res. 2018, 20, 11–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y. Understanding tourist attraction cooperation: An application of network analysis to the case of Shanghai, China. J. Destin. Mark. Manag. 2018, 8, 396–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T18972-2003; Classification, Investigation, and Evaluation of Tourism Resources in China. General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2003.
- He, X.; Cao, Y.; Zhou, C. Evaluation of polycentric spatial structure in the urban agglomeration of the pearl river delta (PRD) based on multi-source big data fusion. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; He, X.; Zikirya, B. Boba Shop, Coffee Shop, and Urban Vitality and Development—A Spatial Association and Temporal Analysis of Major Cities in China from the Standpoint of Nighttime Light. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Zhang, R.; Yuan, X.; Cao, Y.; Zhou, C. The role of planning policy in the evolution of the spatial structure of the Guangzhou metropolitan area in China. Cities 2023, 137, 104284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Zhou, C.; Wang, Y.; Yuan, X. Risk assessment and prediction of COVID-19 based on epidemiological data from spatiotemporal geography. Front. Environ. Sci. 2021, 9, 634156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Mei, K.; Qu, L.; Zhang, C.; Chen, H.; Wang, S.; Di, D.; Huang, H.; Wang, Z.; Xia, F.; et al. Assessment of the Geographical Detector Method for investigating heavy metal source apportionment in an urban watershed of Eastern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 653, 714–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Weng, S.; Bao, J. The changes in the geographical patterns of China’s tourism in 1978–2018: Characteristics and underlying factors. J. Geogr. Sci. 2020, 30, 487–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsson, A.K. A tourist attraction’s members: Their motivations, relations and roles. Scand. J. Hosp. Tour. 2010, 10, 411–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Huang, S.S.; Fu, H. An application of network analysis on tourist attractions: The case of Xinjiang, China. Tour. Manag. 2017, 58, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutinda, R.; Mayaka, M. Application of destination choice model: Factors influencing domestic tourists destination choice among residents of Nairobi, Kenya. Tour. Manag. 2012, 33, 1593–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Vega, M.; Herrero-Prieto, L.C. Achieving tourist destination competitiveness: Evidence from Latin-American and Caribbean countries. Int. J. Tour. Res. 2018, 20, 782–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, P.; Liu, Y. Indicator System and Construction Level of Online Service Functions on New Media Platforms of Tourist Attractions: A Case Study of Yangzhou City, China. Sustainability 2023, 15, 7441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Kang, Y. Automatic classification of photos by tourist attractions using deep learning model and image feature vector clustering. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2022, 11, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oviedo-García, M.Á.; Vega-Vázquez, M.; Castellanos-Verdugo, M.; Reyes-Guizar, L.A. Tourist satisfaction and the souvenir shopping of domestic tourists: Extended weekends in Spain. Curr. Issues Tour. 2016, 19, 845–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| 5A TA | 4A TA | 3A TA | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | Mean Value | Variable | Mean Value | Variable | Mean Value |
| Population distribution | 4.361 | Population distribution | 5.014 | Population distribution | 4.715 |
| Topography | 2.354 | Topography | 0.758 | Topography | 0.968 |
| Distribution of river systems | −1.047 | Distribution of river systems | −1.217 | Distribution of river systems | −2.113 |
| Economic foundation | 3.142 | Economic foundation | 4.109 | Economic foundation | 5.221 |
| Transportation facilities | 2.001 | Transportation facilities | 3.247 | Transportation facilities | 1.589 |
| Market demand | 0.907 | Market demand | 2.991 | Market demand | 2.674 |
| Resource allocation | 1.671 | Resource allocation | 2.178 | Resource allocation | 3.008 |
| Policy support | 0.117 | Policy support | 0.469 | Policy support | 3.447 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zikirya, B.; Zhou, C. Spatial Distribution and Influencing Factors of High-Level Tourist Attractions in China: A Case Study of 9296 A-Level Tourist Attractions. Sustainability 2023, 15, 14339. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151914339
Zikirya B, Zhou C. Spatial Distribution and Influencing Factors of High-Level Tourist Attractions in China: A Case Study of 9296 A-Level Tourist Attractions. Sustainability. 2023; 15(19):14339. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151914339
Chicago/Turabian StyleZikirya, Bahram, and Chunshan Zhou. 2023. "Spatial Distribution and Influencing Factors of High-Level Tourist Attractions in China: A Case Study of 9296 A-Level Tourist Attractions" Sustainability 15, no. 19: 14339. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151914339
APA StyleZikirya, B., & Zhou, C. (2023). Spatial Distribution and Influencing Factors of High-Level Tourist Attractions in China: A Case Study of 9296 A-Level Tourist Attractions. Sustainability, 15(19), 14339. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151914339







