Application of Cold Sintering Process for Stabilizing Heavy Metals in Municipal Solid Waste Incineration Fly Ash
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. MSWI Fly Ash
2.2. CSP Pre-Treatment
2.3. Cold Sintering Process
2.4. Taguchi Method Parameter Optimization
3. Results and Discussion
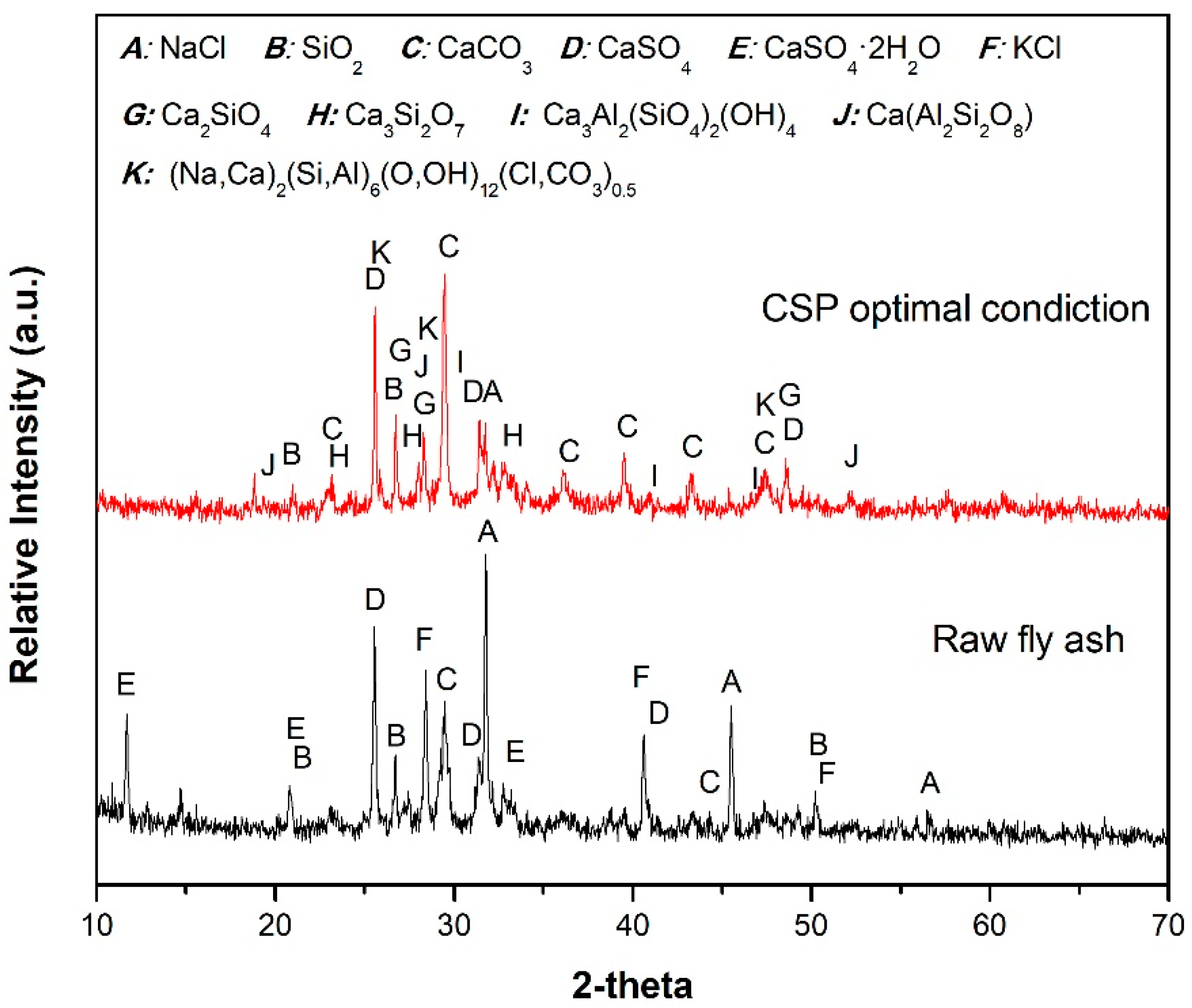
3.1. Characteristics of Fly Ashes
3.2. Cold Sintering Process Pre-Treatment
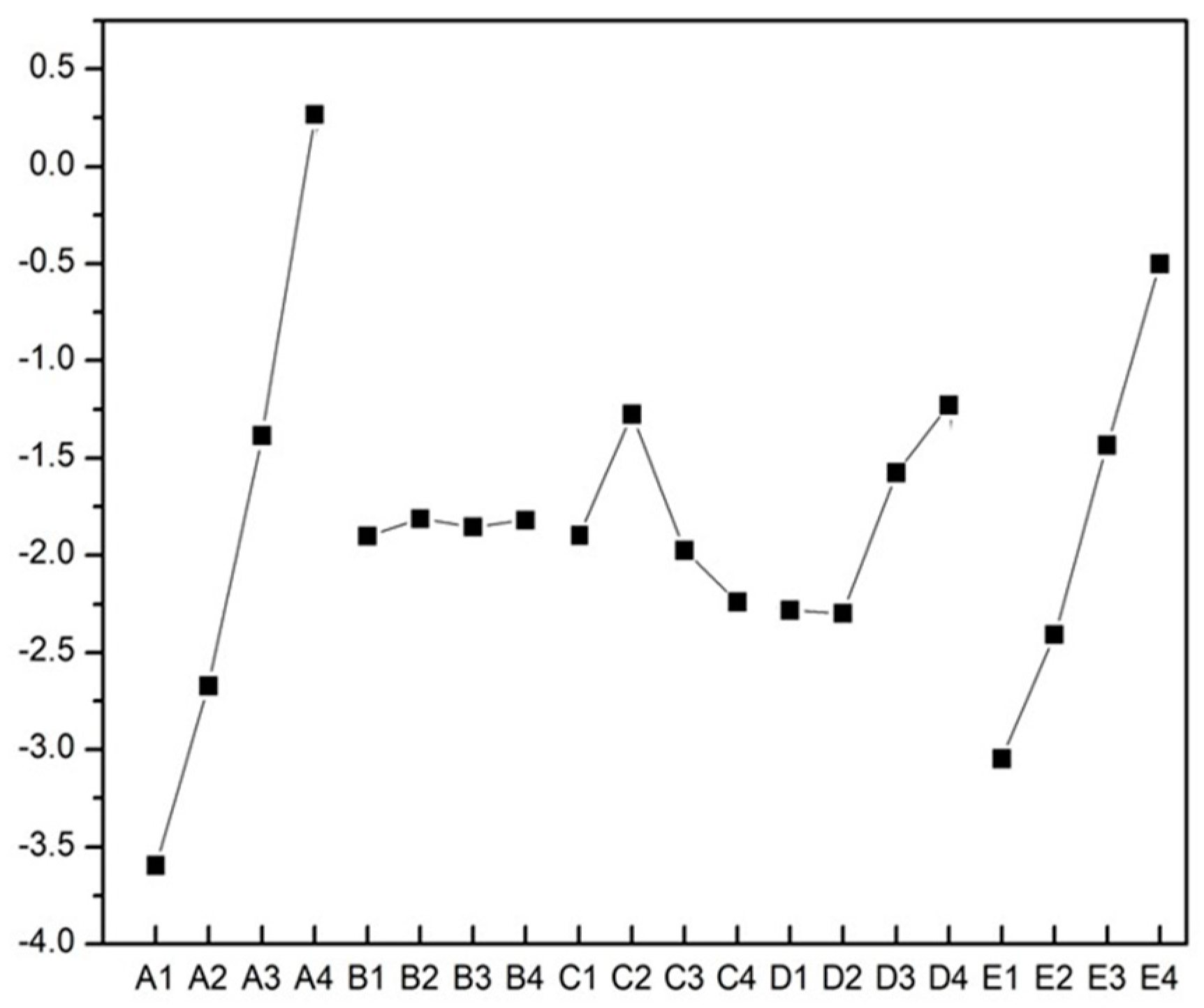
3.3. Taguchi Experiment and Optimization of Cold Sintering Process
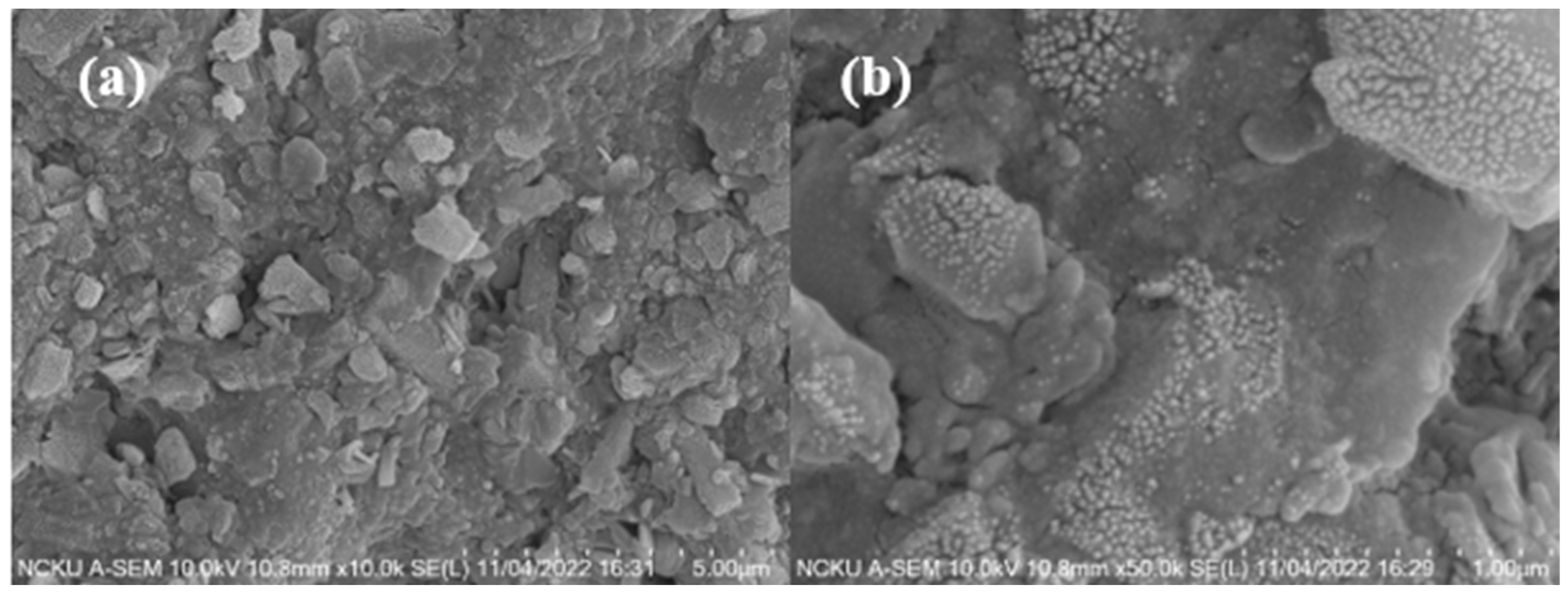
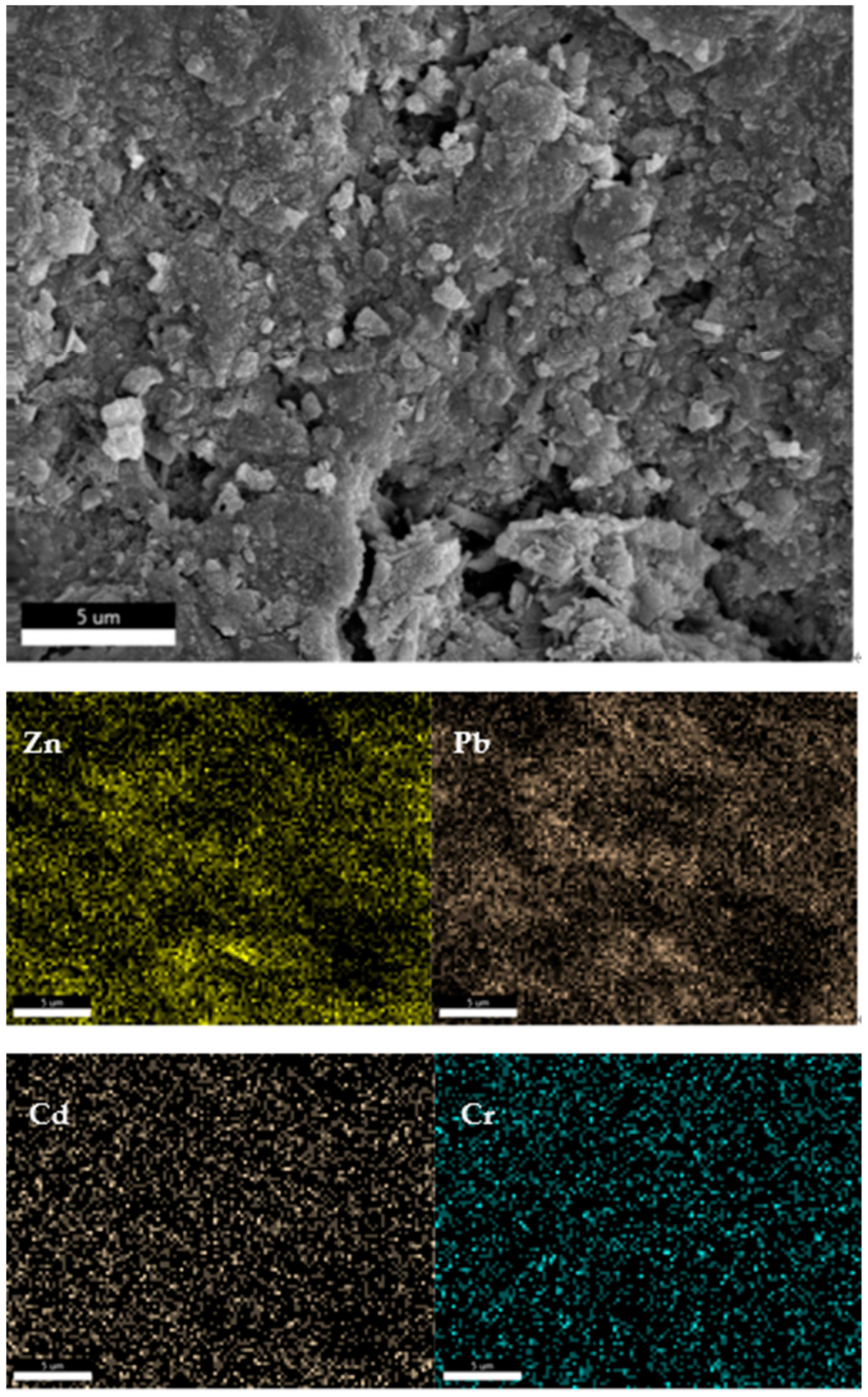
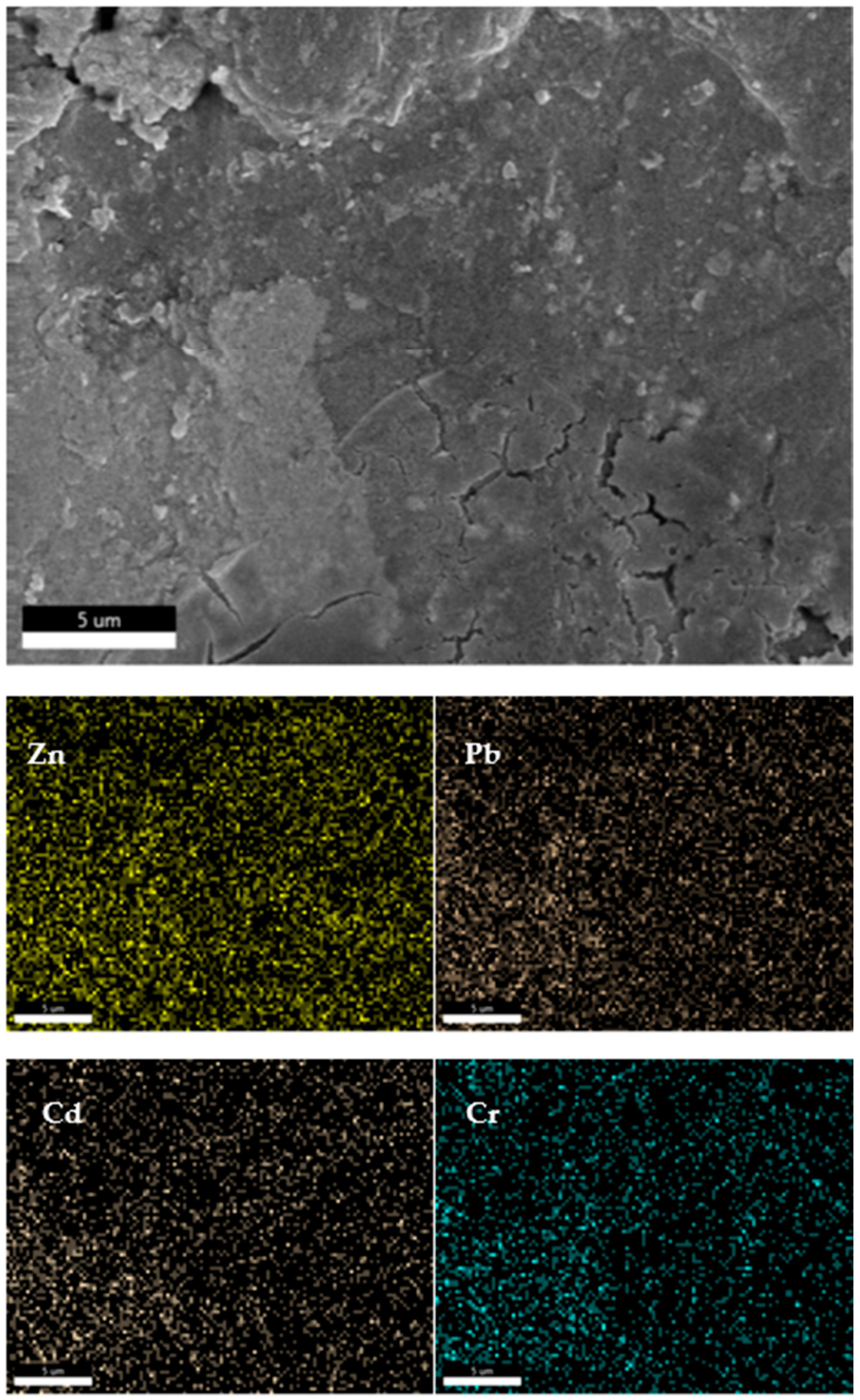
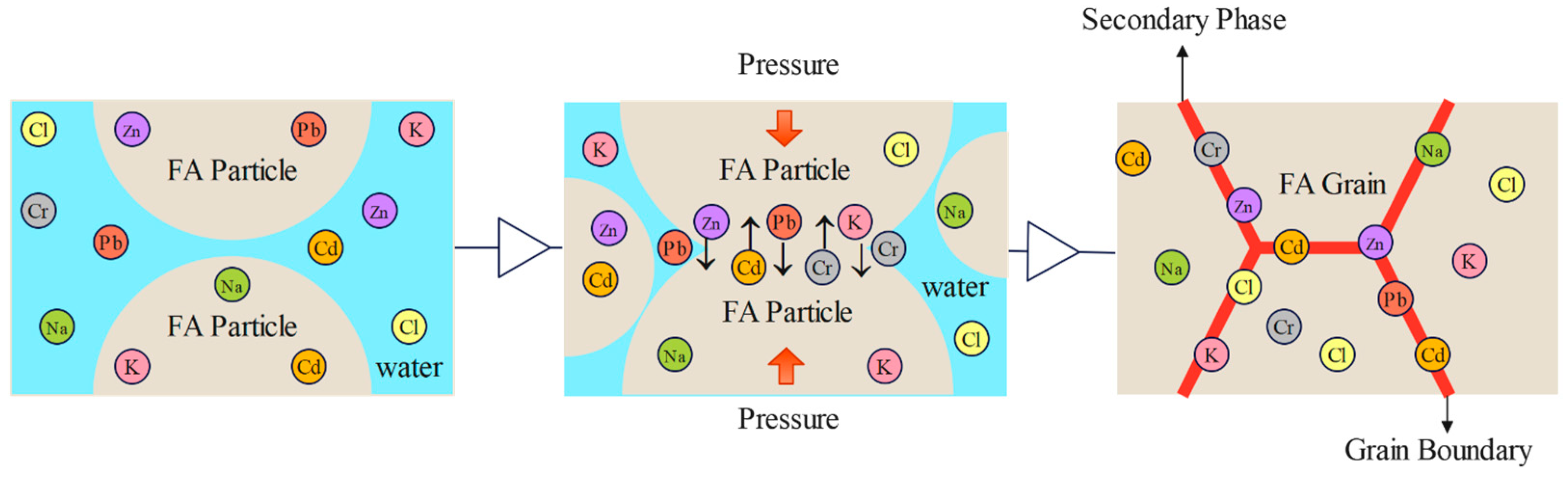
3.4. Analysis of Properties and Solidification Mechanism of Fly Ash CSP Blocks
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Giro-Paloma, J.; Formosa, J.; Chimenos, J.M. Granular material development applied in an experimental section for civil engineering purposes. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 6782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Boom, A.; Degrez, M. Belgian MSWI fly ashes and APC residues: A characterisation study. Waste Manag. 2012, 32, 1163–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, B.; Gan, M.; Ji, Z.; Fan, X.; Zhang, D.; Chen, X.; Sun, Z.; Huang, X.; Fan, Y. Recent progress on the thermal treatment and resource utilization technologies of municipal waste incineration fly ash: A review. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2022, 159, 547–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Sun, Q.; Zhang, J.; Yan, J.; Wu, K.; Pan, F.; Sheng, J. Status and Development Trend of Harmless and Resourceful Disposal of Municipal Solid Waste Incineration Fly Ash. Adv. Environ. Prot. 2017, 7, 414–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangialardi, T. Disposal of MSWI fly ash through a combined washing-immobilisation process. J. Hazard. Mater. 2003, 98, 225–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, L.; Cao, Y.; Fan, G.; Li, C.; Peng, W. A review of the applications of ion floatation: Wastewater treatment, mineral beneficiation and hydrometallurgy. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 20226–20239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, J.; Xiang, H.; Yang, X.; Hu, W.; Liang, F.; Mi, B. Ash fusion characteristics of bamboo, wood and coal. Energy 2018, 161, 517–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharifikolouei, E.; Baino, F.; Salvo, M.; Tommasi, T.; Pirone, R.; Fino, D.; Ferraris, M. Vitrification of municipal solid waste incineration fly ash: An approach to find the successful batch compositions. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 7738–7744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, A.; Wang, X.; Zhang, L. Stabilization/solidification of municipal solid waste incineration fly ash via co-sintering with waste-derived vitrified amorphous slag. Waste Manag. 2016, 56, 238–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quina, M.J.; Bordado, J.C.; Quinta-Ferreira, R.M. Treatment and use of air pollution control residues from MSW incineration: An overview. Waste Manag. 2008, 28, 2097–2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quina, M.J.; Bordado, J.C.; Quinta-Ferreira, R.M. Chemical stabilization of air pollution control residues from municipal solid waste incineration. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 179, 382–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Bi, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wang, J. Chlorides removal and control through water-washing process on MSWI fly ash. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2016, 31, 560–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.-S.; Chang, F.-C.; Shen, Y.-H.; Tsai, M.-S.; Ko, C.-H. Removal of chloride from MSWI fly ash. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 237–238, 116–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, K.; Inoue, K.; Harada, H.; Kawakita, H.; Keisuke, O. Leaching behavior of heavy metals with hydrochloric acid from fly ash generated in municipal waste incineration plants. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2011, 21, 1422–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Yu, G.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X. Fate of heavy metals during co-disposal of municipal solid waste incineration fly ash and sewage sludge by hydrothermal coupling pyrolysis process. Waste Manag. 2020, 109, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagib, S.; Inoue, K. Recovery of lead and zinc from fly ash generated from municipal incineration plants by means of acid and/or alkaline leaching. Hydrometallurgy 2000, 56, 269–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, L.; Tang, Y.; Wang, F.; Hu, B.; Shi, P.; Hu, Q. Investigation of controlling factors on toxic metal leaching behavior in municipal solid wastes incineration fly ash. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 29316–29326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, D.; Son, J.; Yoo, Y.; Park, S.; Huh, I.-S.; Park, J. Heavy-metal reduction and solidification in municipal solid waste incineration (MSWI) fly ash using water, NaOH, KOH, and NH4OH in combination with CO2 uptake procedure. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 380, 122534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Baker, A.; Guo, J.; Randall, C.A. Cold sintering process: A novel technique for low-temperature ceramic processing of ferroelectrics. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2016, 99, 3489–3507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funahashi, S.; Guo, H.; Guo, J.; Baker, A.L.; Wang, K.; Shiratsuyu, K.; Randall, C.A. Cold sintering and co-firing of a multilayer device with thermoelectric materials. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2017, 100, 3488–3496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Baker, A.L.; Guo, H.; Lanagan, M.; Randall, C.A. Cold sintering process: A new era for ceramic packaging and microwave device development. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2017, 100, 669–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randall, C.A.; Guo, J.; Baker, A.; Lanagan, M.; Guo, H. Cold Sintering Ceramics and Composites. U.S. Patent 2017/0088471A1, 30 March 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, X.; Floyd, R.; Lowum, S.; Long, D.; Dickey, E.; Maria, J.-P. Cold sintering with dimethyl sulfoxide solutions for metal oxides. J. Mater. Sci. 2019, 54, 7438–7446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grasso, S.; Biesuz, M.; Zoli, L.; Taveri, G.; Duff, A.I.; Ke, D.; Jiang, A.; Reece, M.J. A review of cold sintering processes. Adv. Appl. Ceram. 2020, 119, 115–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vakifahmetoglu, C.; Karacasulu, L. Cold sintering of ceramics and glasses: A review. Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci. 2020, 24, 100807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galotta, A.; Sglavo, V.M. The cold sintering process: A review on processing features, densification mechanisms and perspectives. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2021, 41, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toraya, H.; Yoshimura, M.; Somiya, S. Hydrothermal Reaction-Sintering of Monoclinic HfO2. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1982, 65, c159–c160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somiya, S. Hydrothermal Reactions for Materials Science and Engineering: An Overview of Research in Japan; Springer Science & Business Media: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Gutmanas, E.Y.; Rabinkin, A.; Roitberg, M. Cold sintering under high pressure. Scr. Metall. 1979, 13, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutmanas, E.; Goldman, D.; Clark, J.; Hart, S. Cold Sintered Stainless Steel—Chromium Oxide Composites. Prog. Powder Metall. 1985, 41, 631–640. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, P.; Wu, H.-C. Splitting tensile strength of fly ash activated by hydrothermal hot-pressing process. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2009, 21, 356–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vakifahmetoglu, C.; Anger, J.F.; Atakan, V.; Quinn, S.; Gupta, S.; Li, Q.; Tang, L.; Riman, R.E. Reactive Hydrothermal Liquid-Phase Densification (rHLPD) of Ceramics—A Study of the BaTiO3[TiO2] Composite System. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2016, 99, 3893–3901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.H. Taguchi Methods: Principles and Pratices of Quality Design; Gau Lih Book Co. Ltd.: Taipei City, Taiwan, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Induja, I.J.; Sebastian, M.T. Microwave dielectric properties of cold sintered Al2O3-NaCl composite. Mater. Lett. 2018, 211, 55–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sibi, N.; Rajan, A.; Subodh, G. Garnet mineral based composites through cold sintering process: Microstructure and dielectric properties. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2020, 40, 371–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suleiman, B.; Yu, Q.; Ding, Y.; Li, Y. Fabrication of form stable NaCl-Al2O3 composite for thermal energy storage by cold sintering process. Front. Chem. Sci. Eng. 2019, 13, 727–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouville, F.; Studart, A.R. Geologically-inspired strong bulk ceramics made with water at room temperature. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haug, M.; Bouville, F.; Ruiz-Agudo, C.; Avaro, J.; Gebauer, D.; Studart, A.R. Cold densification and sintering of nanovaterite by pressing with water. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2020, 40, 893–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndayishimiye, A.; Tsuji, K.; Wang, K.; Bang, S.H.; Randall, C.A. Sintering mechanisms and dielectric properties of cold sintered (1 − x) SiO2-X PTFE composites. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2019, 39, 4743–4751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Q.; Jiang, X.; Chen, Z.; Lu, S.; Ni, M. Leaching of heavy metals from MSWI fly ash: Experiments vs. simulation. Arch. Environ. Prot. 2018, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.-S.; Kan, L.-L. Leaching behavior of heavy metals from municipal solid wastes incineration (MSWI) fly ash used in concrete. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 164, 750–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, B.; Liu, B.; Yang, J.; Zhang, S. The mechanisms of heavy metal immobilization by cementitious material treatments and thermal treatments: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 193, 410–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Zhang, S.; Lin, X.; Li, X. Decomposition and reformation pathways of PCDD/Fs during thermal treatment of municipal solid waste incineration fly ash. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 394, 122526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zacco, A.; Borgese, L.; Gianoncelli, A.; Struis, R.P.W.J.; Depero, L.E.; Bontempi, E. Review of fly ash inertisation treatments and recycling. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2014, 12, 153–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Wang, L.; Yang, T.; Raninger, B. Investigation of MSWI fly ash melting characteristic by DSC–DTA. Waste Manag. 2007, 27, 1383–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Yue, Y.; Lu, M.; Zhang, J.; Sun, F.; Huang, X.; Zhou, J.; Qian, G. Comprehension of heavy metal stability in municipal solid waste incineration fly ash with its compositional variety: A quick prediction case of leaching potential. Waste Manag. 2019, 84, 329–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Ma, Z.; Fang, Z.; Qian, Y.; Zhong, P.; Yan, J. Review of harmless treatment of municipal solid waste incineration fly ash. Waste Dispos. Sustain. Energy 2020, 2, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nzihou, A.; Stanmore, B. The fate of heavy metals during combustion and gasification of contaminated biomass—A brief review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 256–257, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, C.; Liu, J.; Wu, S.; Jia, Y.; Du, B.; Yu, S. Novel method for comprehensive utilization of MSWI fly ash through co-reduction with red mud to prepare crude alloy and cleaned slag. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 384, 121315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
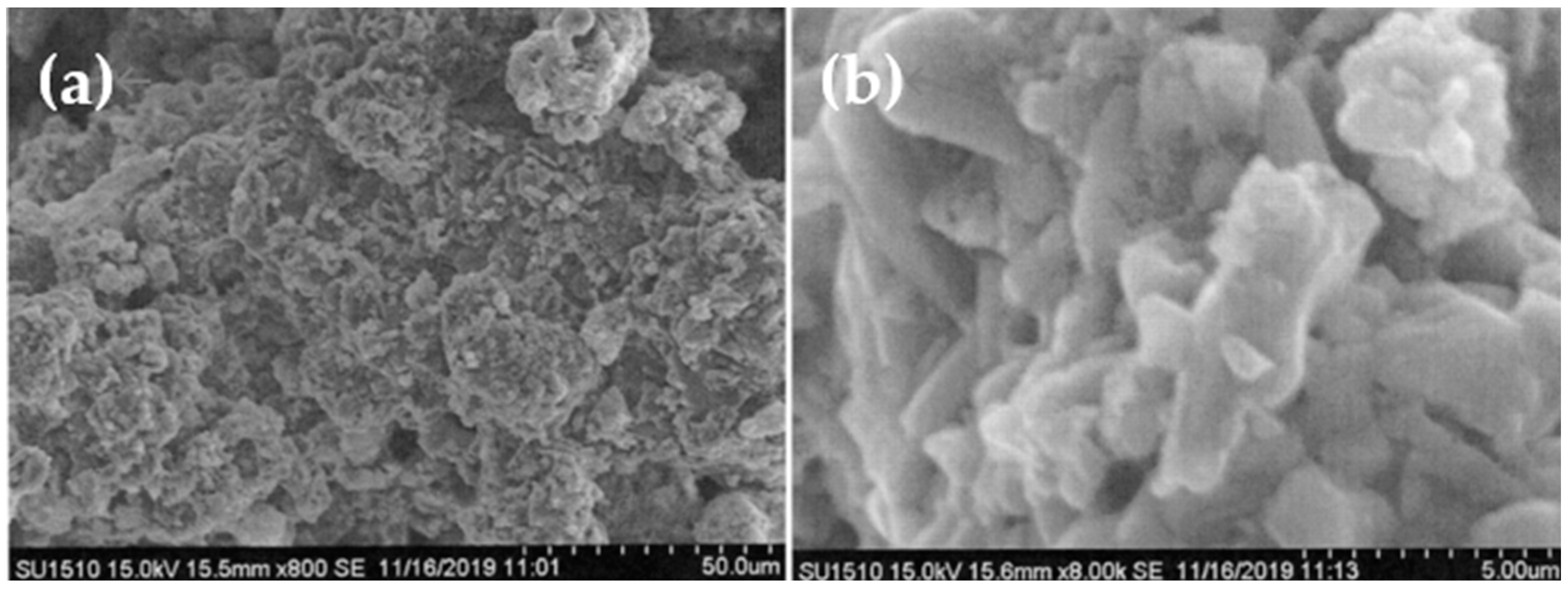
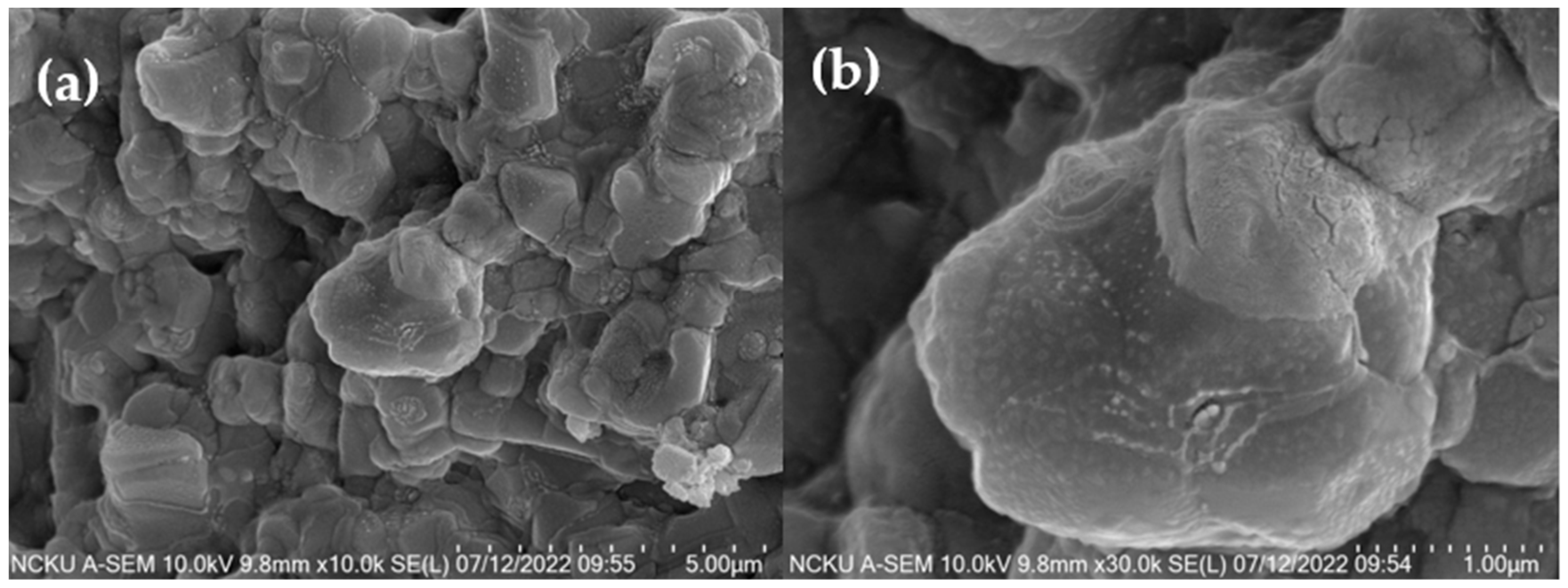
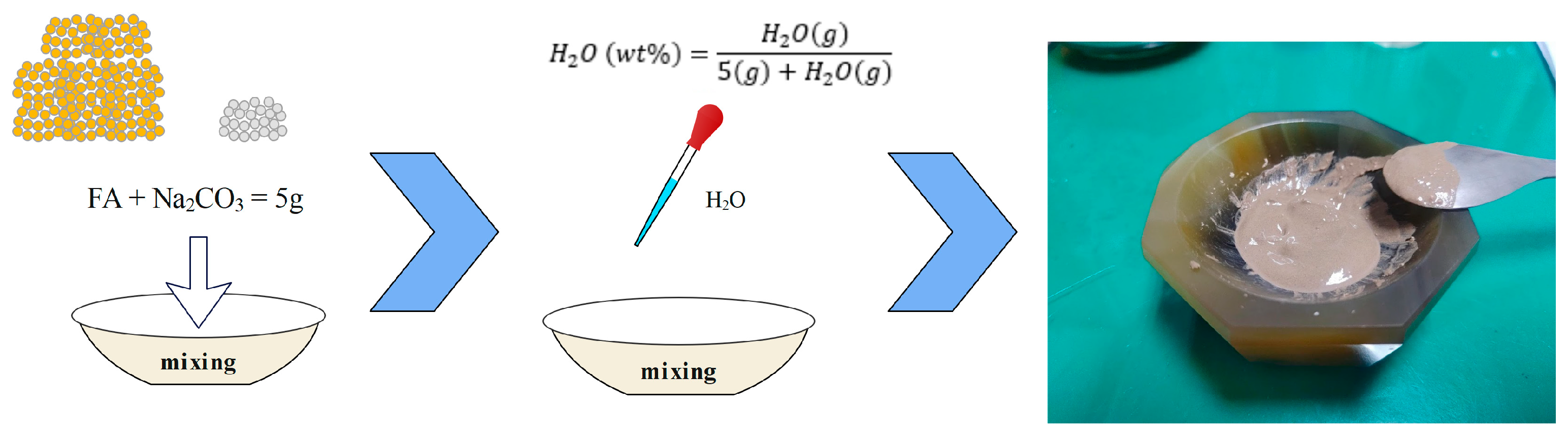

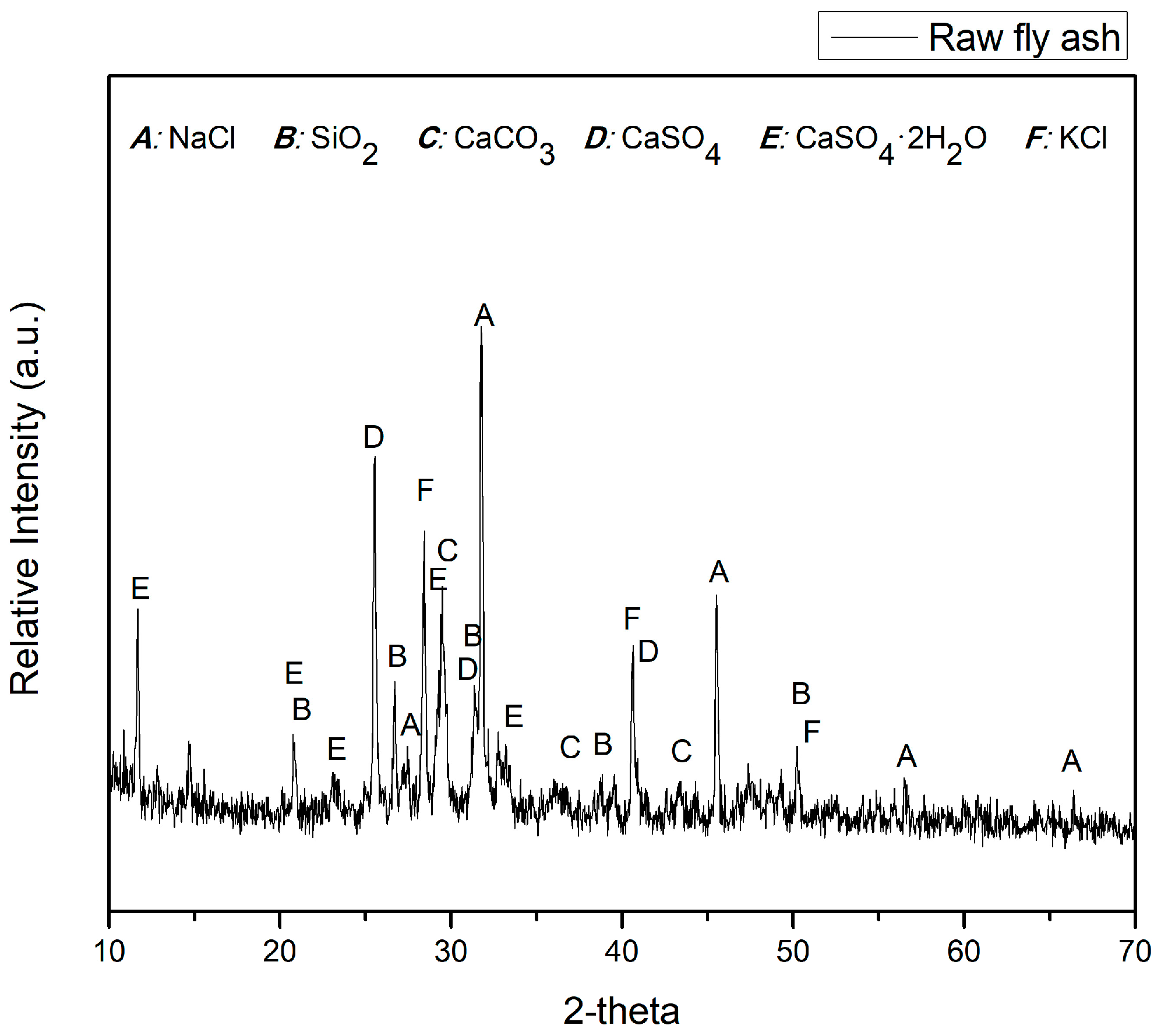

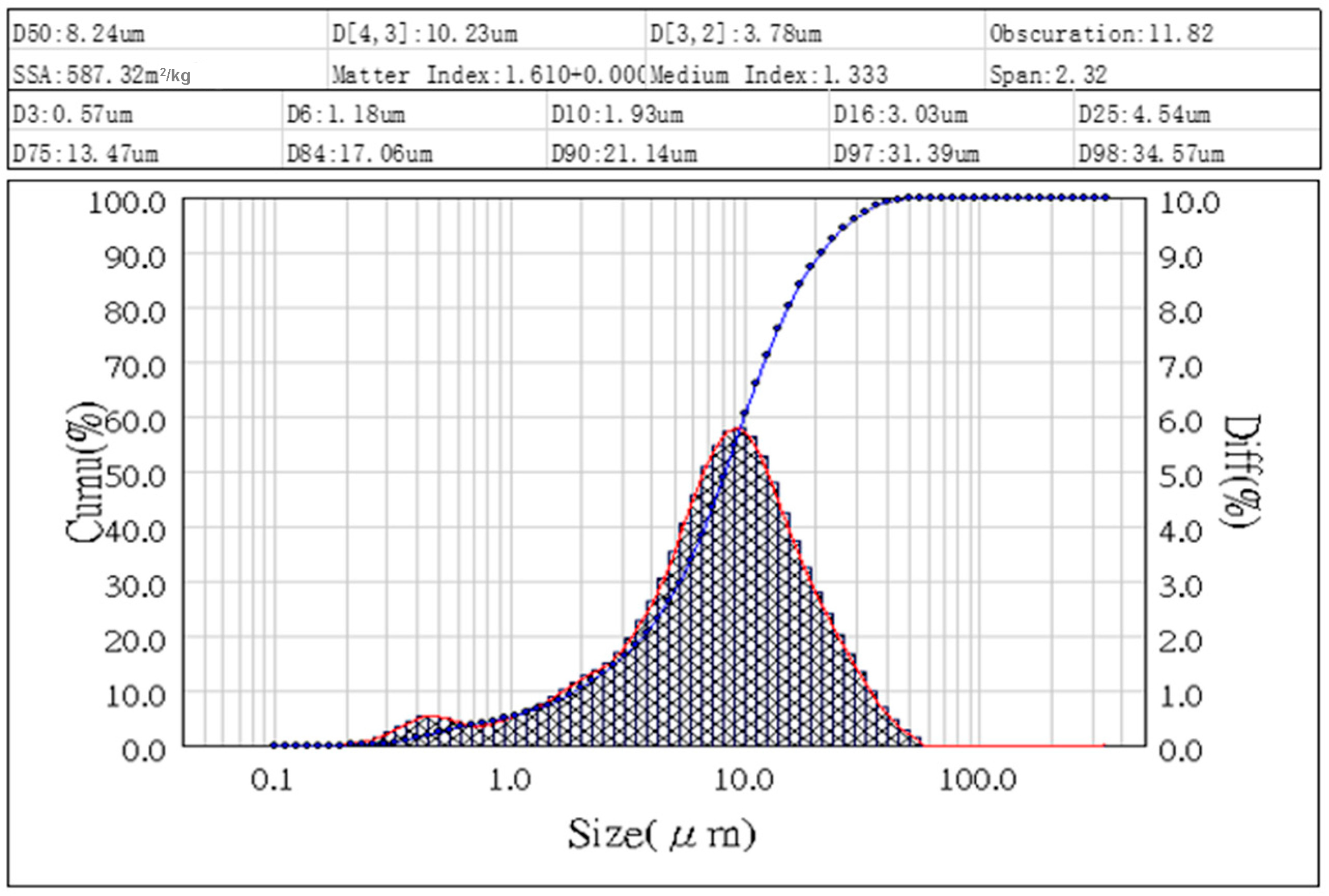

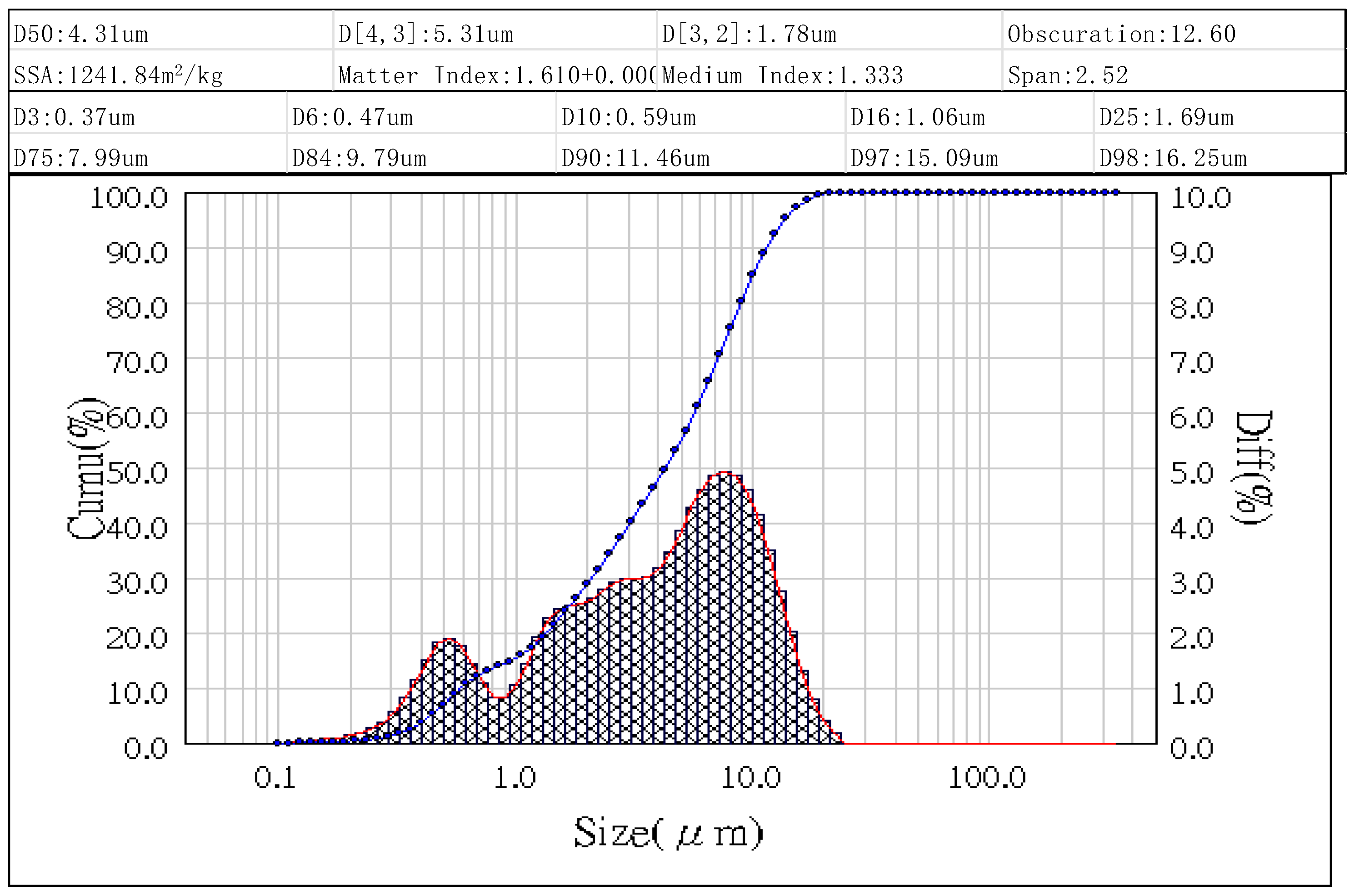

| A | B | C | D | E | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EXP. | Sintering Temperature | Uniaxial Pressure | Sintering Time | Water Additives | Na2CO3 Additives |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| 3 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| 4 | 1 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 |
| 5 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| 6 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 4 | 3 |
| 7 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 2 |
| 8 | 2 | 4 | 4 | 2 | 1 |
| 9 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 4 | 2 |
| 10 | 3 | 2 | 4 | 3 | 1 |
| 11 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 4 |
| 12 | 3 | 4 | 2 | 1 | 3 |
| 13 | 4 | 1 | 4 | 2 | 3 |
| 14 | 4 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 4 |
| 15 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 4 | 1 |
| 16 | 4 | 4 | 1 | 3 | 2 |
| Sintering Temperature | Uniaxial Pressure | Sintering Time | Water Additives | Na2CO3 Additives | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Level 1 | 150 °C | 7.5 T (234 MPa) | 30 min | 10 wt% | 3 wt% |
| Level 2 | 200 °C | 10 T (312 MPa) | 60 min | 15 wt% | 5 wt% |
| Level 3 | 250 °C | 12.5 T (390 MPa) | 90 min | 20 wt% | 7 wt% |
| Level 4 | 300 °C | 15 T (468 MPa) | 120 min | 25 wt% | 9 wt% |
| Elements | Ca | Na | K | Zn | Pb | Cu | Cr | Cd |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| wt% | 58.39 | 21.35 | 10.71 | 6.23 | 2.59 | 0.51 | 0.15 | 0.06 |
| Elements | Ca | Na | K | Zn | Pb | Cu | Cr | Cd |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AAS value (mg/L) | 2925.958 | 1052.503 | 539.745 | 275.27 | 101.952 | 20.075 | 9.614 | 3.597 |
| Ratio between elements (wt%) | 59.37% | 21.35% | 10.95% | 5.59% | 2.07% | 0.41% | 0.20% | 0.07% |
| EXP. | Cd(1) | Cd(2) | Cd(3) | Cd AVE. | Sn | S/N Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1.793 | 1.859 | 1.892 | 1.848 | 0.050 | −5.337 |
| 2 | 1.595 | 1.617 | 1.54 | 1.584 | 0.040 | −3.998 |
| 3 | 1.595 | 1.364 | 1.375 | 1.444 | 0.130 | −3.231 |
| 4 | 1.276 | 1.254 | 1.166 | 1.232 | 0.058 | −1.822 |
| 5 | 1.056 | 1.078 | 1.056 | 1.063 | 0.013 | −0.534 |
| 6 | 1.199 | 1.188 | 1.243 | 1.21 | 0.029 | −1.658 |
| 7 | 1.54 | 1.683 | 1.463 | 1.562 | 0.112 | −3.896 |
| 8 | 1.551 | 1.639 | 1.881 | 1.690 | 0.171 | −4.604 |
| 9 | 1.232 | 1.1 | 1.298 | 1.21 | 0.101 | −1.686 |
| 10 | 1.298 | 1.397 | 1.298 | 1.331 | 0.057 | −2.492 |
| 11 | 1.056 | 1.012 | 1.122 | 1.063 | 0.055 | −0.545 |
| 12 | 1.078 | 1.155 | 1.056 | 1.096 | 0.052 | −0.809 |
| 13 | 1.023 | 1.078 | 0.902 | 1.001 | 0.090 | −0.044 |
| 14 | 0.814 | 1.045 | 0.814 | 0.891 | 0.133 | 0.906 |
| 15 | 1.045 | 1.045 | 0.792 | 0.961 | 0.146 | 0.249 |
| 16 | 1.078 | 1.023 | 0.902 | 1.001 | 0.090 | −0.044 |
| AVE. | 1.262 | 0.083 | −1.846 | |||
| Cd | Sintering Temperature | Uniaxial Pressure | Sintering Time | Water Additives | Na2CO3 Additives |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Level 1 | −3.597 | −1.900 | −1.896 | −2.284 | −3.046 |
| Level 2 | −2.673 | −1.810 | −1.273 | −2.298 | −2.406 |
| Level 3 | −1.383 | −1.856 | −1.976 | −1.575 | −1.435 |
| Level 4 | 0.267 | −1.819 | −2.240 | −1.229 | −0.499 |
| Range | 3.864 | 0.090 | 0.967 | 1.069 | 2.547 |
| Rank | 1 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 |
| FACTOR | SS | DOF | Var | F | Probability | Confidence Level | Rank/Significant *? |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| sintering temperature | 2.175 | 3 | 0.725 | 8.538 | 0.152% | 99.85% | 1/Y |
| uniaxial pressure | 0.006 | 3 | 0.002 | 0.023 | 99.522% | 0.48% | 5/N |
| sintering time | 0.127 | 3 | 0.042 | 0.500 | 68.807% | 31.19% | 4/N |
| water additives | 0.329 | 3 | 0.110 | 1.293 | 31.305% | 68.70% | 3/N |
| Na2CO3 additives | 1.074 | 3 | 0.358 | 4.215 | 2.383% | 97.62% | 2/Y |
| Error | 0.283 | 32 | 0.0089 | * At least 97% confidence | |||
| TOTAL | 3.992 | 47 | 0.085 | S = 0.094 | |||
| Cd | Additive Model Calculation Value | Experimental Values |
|---|---|---|
| quality characteristic (mg/L) | 0.687 | 0.772 |
| S/N ratio (dB) | 2.842 | 2.227 |
| Cd | Pb | Zn | Cr | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FA sample | 3.239 | 2.663 | 31.915 | 0.589 |
| CSP optimal condition | 0.772 | 2.100 | 18.392 | 0.000 |
| Percentage Increase/Decrease | −77.71% | −21.14% | −42.37% | −99.99% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liao, S.-K.; Wu, Z.-E.; Shen, Y.-H. Application of Cold Sintering Process for Stabilizing Heavy Metals in Municipal Solid Waste Incineration Fly Ash. Sustainability 2023, 15, 14110. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151914110
Liao S-K, Wu Z-E, Shen Y-H. Application of Cold Sintering Process for Stabilizing Heavy Metals in Municipal Solid Waste Incineration Fly Ash. Sustainability. 2023; 15(19):14110. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151914110
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiao, Shih-Kai, Zhong-En Wu, and Yun-Hwei Shen. 2023. "Application of Cold Sintering Process for Stabilizing Heavy Metals in Municipal Solid Waste Incineration Fly Ash" Sustainability 15, no. 19: 14110. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151914110
APA StyleLiao, S.-K., Wu, Z.-E., & Shen, Y.-H. (2023). Application of Cold Sintering Process for Stabilizing Heavy Metals in Municipal Solid Waste Incineration Fly Ash. Sustainability, 15(19), 14110. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151914110






